Adaptive Artificial Intelligence represents a dynamic approach that can help improve memorization and knowledge in the study of human anatomy. In this pilot study, which focuses on a module on embryology and the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the liver, the information and learning objectives are provided in a sequential manner, without compromising the learner's freedom of choice, creating paths that the learner can face and even repeat. The module also promotes personalized training by stimulating a process of self-assessment in the learner, through the combination of different cognitive elements (vocal, visual and textual), multiple-choice quizzes and gaming, to make the learning experience more autonomous, personalized and engaging, stimulating in the learner an independent commitment appropriate to their level of knowledge and needs. At the same time, artificial intelligence also offers an additional advantage as it can deliver quality feedback on learners' performance, with a significant impact on the results and quality of the educational offer.
The Authors confirm that neither the manuscript nor any parts of its content are currently under consideration or published in another journal.
Introduction
Anatomy education is crucial for medical students and physicians as it lays the foundation for understanding the human body and is vital for clinical practice [
1,
2,
3,
4].
However, in recent years, the decrease in anatomy teaching time, the reduced allocation of resources, a shortage of trained anatomists and of skilled teaching staff and conversely the increasing number of students are critically impacting both undergraduate anatomy curricula and medical formation, with significant implications in medico-legal claims [
5,
6,
7].
This is also particularly true for anatomical dissection programs, long considered a cornerstone in developing anatomy knowledge [
8]. High costs, ethical issues, low donation rate, the reduction of time in teaching anatomy, the difficult to enroll qualified staff, the recent technological advancements and the negative emotional experiences of students are limiting the use cadaveric dissection, despite its significant role in allowing a 3D visualization of the organization of human body including anatomical variations and in the preparatory work for the transfer of concepts from normal anatomy to pathological aspects [
9,
10].
Another critical factor in developing a profound understanding of anatomy is the substantial cognitive load associated with studying it during the preclinical years at the beginning of one's university education. This also applies to other fundamental sciences. Additionally, there is a noticeable decrease in the retention of information related to the basic sciences, especially anatomy, acquired during the first 1-2 years of medical school when students enter the clinical years. In this context, emphasizing the clinical significance, both in theory and practice, of fundamental scientific knowledge (such as promoting ongoing and focused anatomical education during medical training) could prove immensely advantageous in preserving not only anatomy knowledge but also information related to other foundational sciences [
11,
12].
Various methods have been explored in anatomy education, including radiologic imaging technologies, living anatomy, problem-based learning, digital dissection, and emerging technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR) and 3D printing [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. Specifically, the integration of AR and VR into medical school curricula remains a topic of debate, and further research is necessary to evaluate their impact on enhancing educational outcomes in the learning and understanding of anatomy [
19,
20].
These challenges underscore the need for innovative approaches to enhance anatomy learning in medical education [
21].
This article explores the potential of technological advancements, particularly artificial intelligence (AI) and adaptive learning, which combine advanced machine learning algorithms with a more responsive and flexible approach to autonomous learning, aiming to enhance the teaching and learning of anatomy. Adaptive AI has the potential to revolutionize anatomy education throughout the continuum of medical courses by providing valuable support to anatomy instructors.
We present a pilot project centered on liver anatomy as a case study conducted during the Course of Anatomy at Vialba Medical School, University of Milan.
Methods
The project involved 123 first-year medical students and used the Rhapsode platform developed by Area9 Lyceum (
https://area9lyceum.com).
Regarding the content, the module was developed in close collaboration between the Coordinator of the Course of anatomy and Area9 Medical Learning Architects and Engineers.
The topics of the module focused on different aspects of liver anatomy (microscopic and macroscopic anatomy, embryology, clinical anatomy).
Content and resources of the module were adaptable to various digital devices (i.e., smartphone, tablet, computer) and each student received by email a personal code to access to the platform.
The test was conducted anonymously.
The project design incorporated a flipped classroom approach, which combined asynchronous adaptive learning modules with interactive in-class sessions.
The adaptive learning module provided personalized learning experiences based on the students' individual needs and progress.
For every question posed to students, as well as whenever a learning resource is presented to them, before they can proceed, the system asks them to also indicate their level of confidence regarding their knowledge and answers (i.e., for question: I know - I think so - I'm not sure - I have no idea; for resources: I knew it - Now I understand - I think I understand - I don't understand).
The AI-driven system collected comprehensive data on student performance, including advancement rates and time taken to achieve mastery. Metacognitive data was also collected, assessing students' confidence levels and awareness of their knowledge gaps.
Results
The outcomes of the pilot project indicated significant improvements in learning outcomes and student engagement. The students demonstrated high levels of mastery acquisition, with an average progress rate of 98%. Among the participating students, 115 out of 123 (93.5%) achieved a 100% progress, indicating full mastery of the defined learning objectives within the adaptive learning module. The average time taken to achieve full mastery of the 34 learning objectives was 38 minutes and 25 seconds. The minimum time recorded for achieving 100% advancement was 19 minutes, while the maximum time was 58 minutes.
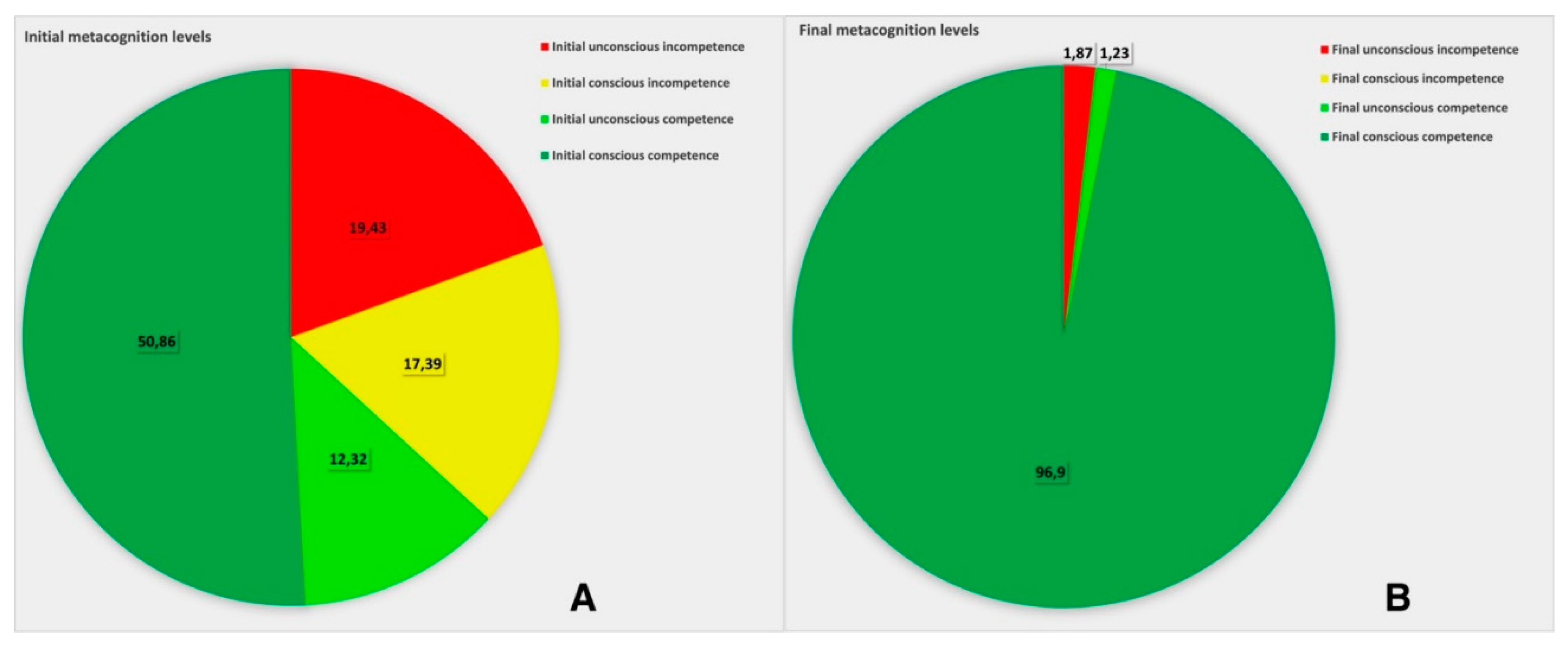
Analysis of the metacognitive data revealed that, initially, students exhibited a 19.43% level of unconscious incompetence, i.e. they answered almost every fifth question stating they believed to know the subject, but they actually didn’t (
Figure 1, A and B).
Additionally, students displayed a 18,11% level of conscious incompetence, recognizing thereby their lack of knowledge in some learning objectives. However, in 50.86% of the cases students exhibited conscious competence, indicating a strong awareness of their knowledge.
After participating in the adaptive learning module, only 1.87% of students remained in the category of unconscious incompetence.
Moreover, most of students (98.73%) demonstrated conscious mastery of the materials, with a clear understanding of their level of competence.
The interactive in-class session facilitated discussions and clarifications for topics that were identified as more challenging based on the AI system's data analysis. The students expressed increased clarity and understanding compared to traditional in-person lectures.
The Rhapsode platform's analytical tools enabled also to collect valuable data regarding to the progress of each individual student, as well as of the course as a whole together and in detail, so helping to develop the best path to reach learning goals.
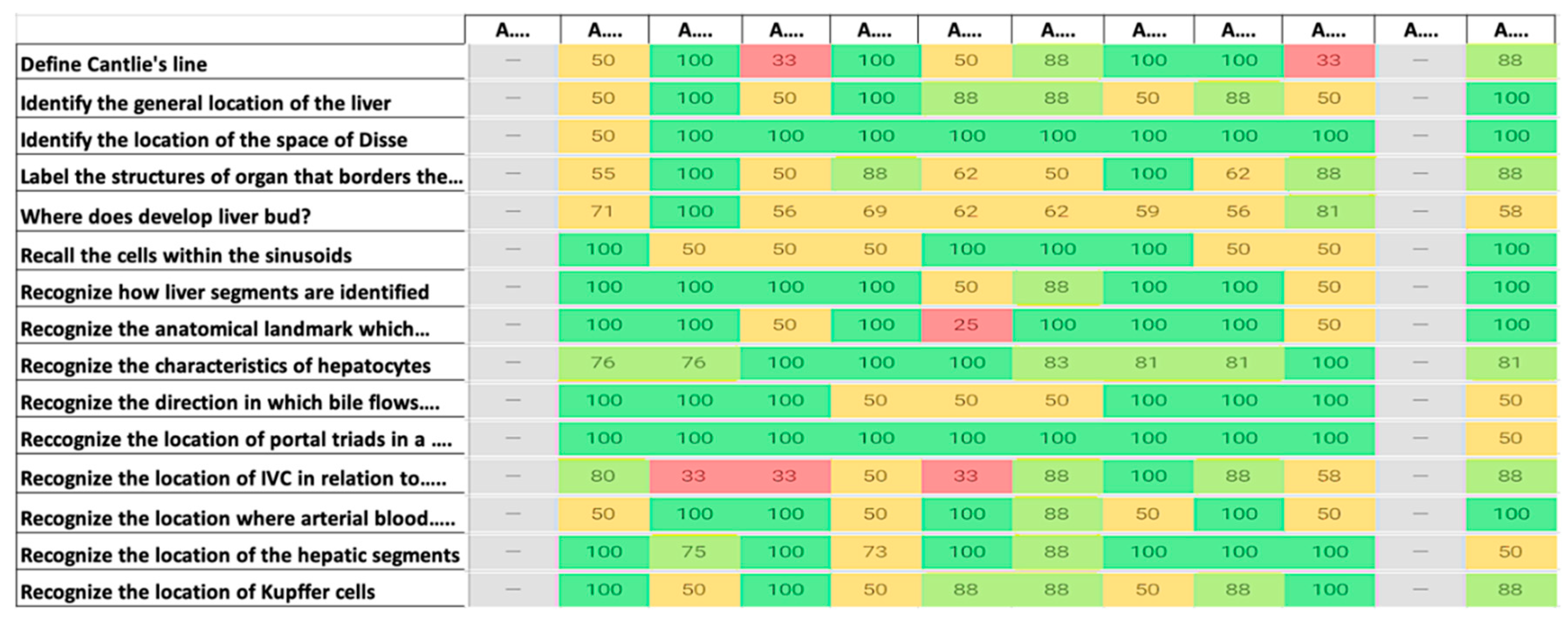
A heat map (
Figure 2: the figure provides a purely indicative snapshot) displays in a concise manner the performance of each individual student (on the x-axis) with respect to the individual learning objectives (on the y-axis).
The concrete analysis of the thermal map of the course made it possible to identify 2 learning objectives as in the case it was necessary to improve the resources imparted to the students to learn.
On the other hand, the presence of too many yellow or red rectangles in the vertical columns, allowed us to identify 11 students out of 123 who could benefit from a supplement of personal help, especially from the point of view of study method.
Discussion
The findings of the pilot project underscore the potential of flipped classroom learning and AI-based adaptive learning platforms in anatomy education, allowing monitoring of student activity based on models that could accurately predict student outcomes. The personalized learning experiences offered by the Rhapsode platform empowered students to take an active role in their learning process. The integration of AI technologies facilitated the identification of individual learning needs, promoted critical thinking skills, and optimized learning outcomes.
The preliminary pedagogical considerations highlighted the importance of high-quality learning materials, continuous assessment, and professional development of teachers to effectively implement adaptive learning systems [
22,
23].
The incorporation of adaptive learning modules in anatomy education has several benefits.
Firstly, it allows students to learn at their own pace, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. The adaptive nature of the platform ensures that students receive targeted instruction, addressing their specific areas of weakness and reinforcing their strengths. This personalized approach enhances student engagement, motivation, and knowledge retention.
Moreover, the AI-driven system provides valuable insights into student performance, enabling educators to identify areas where students commonly struggle. This information can inform instructional design and curriculum development, ensuring that teaching materials and resources are tailored to address the specific needs of learners. The platform's metacognitive assessment tools also contribute to students' self-awareness of their learning progress and areas for improvement, promoting lifelong learning skills.
The interactive in-class sessions complemented the adaptive learning modules by providing opportunities for real-time discussions, questions, and deeper exploration of complex topics. The teacher's role shifted from a traditional lecturer to a facilitator, guiding students through active learning experiences. This promoted critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaborative skills—essential competencies for future healthcare professionals.
The project's results also revealed the importance of continuous assessment and immediate meaningful feedback. The AI-driven system collected detailed data on student performance, enabling educators to identify knowledge gaps, misconceptions, and areas that require additional support. This data-driven feedback on performance allows for timely interventions, personalized remediation, and targeted teaching strategies with a significant impact on the results and quality of the educational offer [
24,
25]. Furthermore, the feedback loop encourages students to reflect on their learning progress and actively engage in self-directed strategies that could improve student's learning.
Lastly, the system also allows for a quick and efficient evaluation of resources provided to students. The analysis of issues revealed by artificial intelligence has allowed us to verify that in four questions, a significant percentage of students tended to choose a specific incorrect answer. Such an issue can be improved by adding a micro-correction to these wrong answers, which will appear immediately when the system informs students that they have made a mistake. Moreover, the system allows to modify and adjust learning materials, so enabling a more dynamic and responsive learning experience that evolves with the student and with the continually challenge of the scientific knowledge.
While the pilot project focused on liver anatomy, the success and positive outcomes indicate the potential for applying adaptive learning modules to other anatomical areas. The outcomes of this project encourage further research and the expansion of adaptive learning modules to other anatomical areas.
Conclusions
This pilot project demonstrated the effectiveness of flipped classroom learning and AI-based adaptive learning platforms in enhancing anatomy education. The study provided valuable insights into improving teaching methods, individualizing learning experiences, and fostering metacognitive awareness among medical students. By leveraging AI and adaptive learning technologies, anatomy education can be transformed to meet the demands of the digital era, ensuring that future healthcare professionals are well-equipped with comprehensive anatomical knowledge.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: M.P. and M.V.; methodology, M.V.; software, M.V.; validation, M.P, G.V. and M.V.; investigation, M.V. and M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.V.; writing—review and editing, M.V. and M.P..; supervision, G.V., M.P. and M.V.; project administration, M.P. and M.V.; funding acquisition, M.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Regione Lombardia under the Program “Call Hub Ricerca e Innovazione” (POR-FESR 2014–2020, project ID 1170989—PRINTMED-3D). Fondazione Romeo ed Enrica Invernizzi
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the participating students for their active involvement and valuable feedback in this pilot project.
Conflicts Of Interest
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Estai M, Bunt S. Best teaching practices in anatomy education: A critical review. Ann Anat. 2016; 208:151-157. [CrossRef]
- Older J. Anatomy: a must for teaching the next generation. Surgeon. 2004;2(2):79-90. [CrossRef]
- Sugand K, Abrahams P, Khurana A. The anatomy of anatomy: A review for its modernization. Anat Sci Ed. 2010;3: 83-93. [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk KA, Majewski A. Analysis of surgical errors associated with anatomical variations clinically relevant in general surgery. Review of the literature. Transl Res Anat. 2021;23. 100107. [CrossRef]
- Leveritt S, McKnight G, Edwards K, et al. What anatomy is clinically useful and when should we be teaching it? Anat Sci Educ. 2016;9(5):468-75. [CrossRef]
- McBride JM, Drake LR. National survey on anatomical sciences in medical education: Anatomical Sciences in Medical Education. Anat Sci Educ. 2018;11. [CrossRef]
- Porzionato A, Macchi V, Stecco C, et al. Clinical Anatomy and Medical Malpractice-A Narrative Review with Methodological Implications. Healthcare (Basel). 2022;30;10(10):1915. [CrossRef]
- McLachlan JC, Patten D. Anatomy teaching: ghosts of the past, present and future. Med Educ. 2006;40(3):243-53. [CrossRef]
- Dissabandara LO, Nirthanan SN, Khoo TK, et al. Role of cadaveric dissections in modern medical curricula: a study on student perceptions. Anat Cell Biol. 2015;48(3):205-12. [CrossRef]
- Burr J, Winter R, Heyerdahl-King I, et al. A qualitative study of how students learn from human cadavers. European Journal of Anatomy. 2019;23 (6). pp. 447-452. ISSN 1136-4890.
- Malau-Aduli BS, Lee AY, Cooling N, et al. Retention of knowledge and perceived relevance of basic sciences in an integrated case-based learning (CBL) curriculum. BMC Med Educ 2013;13,139. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt HG, Mamede S. How to improve the teaching of clinical reasoning: a narrative review and a proposal. Med Educ. 2015;49(10):961-73. [CrossRef]
- Hisley K. An Overview of Traditional and Advanced Visualization Techniques Applied to Anatomical Instruction Involving Cadaveric Dissection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1431:35-63. [CrossRef]
- Gloy K, Weyhe P, Nerenz E, et al. Immersive Anatomy Atlas: Learning Factual Medical Knowledge in a Virtual Reality Environment. Anat Sci Educ. 2022;15(2):360-368. [CrossRef]
- Khaki AA, Tubbs RS, Zarrintan S, et al. The First Year Medical Students' Perception of and Satisfaction from Problem-based Learning Compared to Traditional Teaching in Gross Anatomy: Introducing Problem-based Anatomy into a Traditional Curriculum in Iran. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2007;1(1):113-8. PMID: 21475460; PMCID: PMC3068663.
- Asad MR, Al Mutairi A, AlZahrani RE, et al. Role of Living Anatomy in Medical Education: A Narrative Review. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2023;15(Suppl2):S843-S845. [CrossRef]
- Sinha S, DeYoung V, Nehru A, et al. Determinants of Learning Anatomy in an Immersive Virtual Reality Environment—A Scoping Review. Med Sci Educ. 2023;33,287–297. [CrossRef]
- Ye Z, Dun A, Jiang H, et al. The role of 3D printed models in the teaching of human anatomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Educ . 2020;20,335. [CrossRef]
- Bergman EM, Verheijen IWH, Albert J J A Scherpbier AJJA, et al. Influences on anatomical knowledge: The complete arguments. Clin Anat. 2014;27(3):296-303. [CrossRef]
- Lufler RS, Zumwalt AC, Romney CA, et al. Effect of visual-spatial ability on medical students’ performance in a gross anatomy course. Anat Sci Educ. 2012; 5(1):3-9. [CrossRef]
- Sugand K, Abrahams P, Khurana A. The anatomy of anatomy: a review for its modernization. Anat Sci Educ. 2010;3(2):83-93. [CrossRef]
- Cortese A. Metacognitive resources for adaptive learning. Neurosci Res. 2022;178:10-19. [CrossRef]
- Kellman PJ, Krasne S. Accelerating expertise: Perceptual and adaptive learning technology in medical learning. Med Teach. 2018;40(8):797-802. [CrossRef]
- Eriksson E, Boistrup BL, Thornberg R. A qualitative study of primary teachers’ classroom feedback rationales Educ Res. 2018;60:2:189-205. [CrossRef]
- Mamoon-Al-Bashir, Rezaul Kabir, Ismat Rahman. The Value and Effectiveness of Feedback in Improving Students’ Learning and Professionalizing Teaching in Higher Education. J Educ Pract. 2016;7:38-41.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).