Submitted:
01 January 2024
Posted:
03 January 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
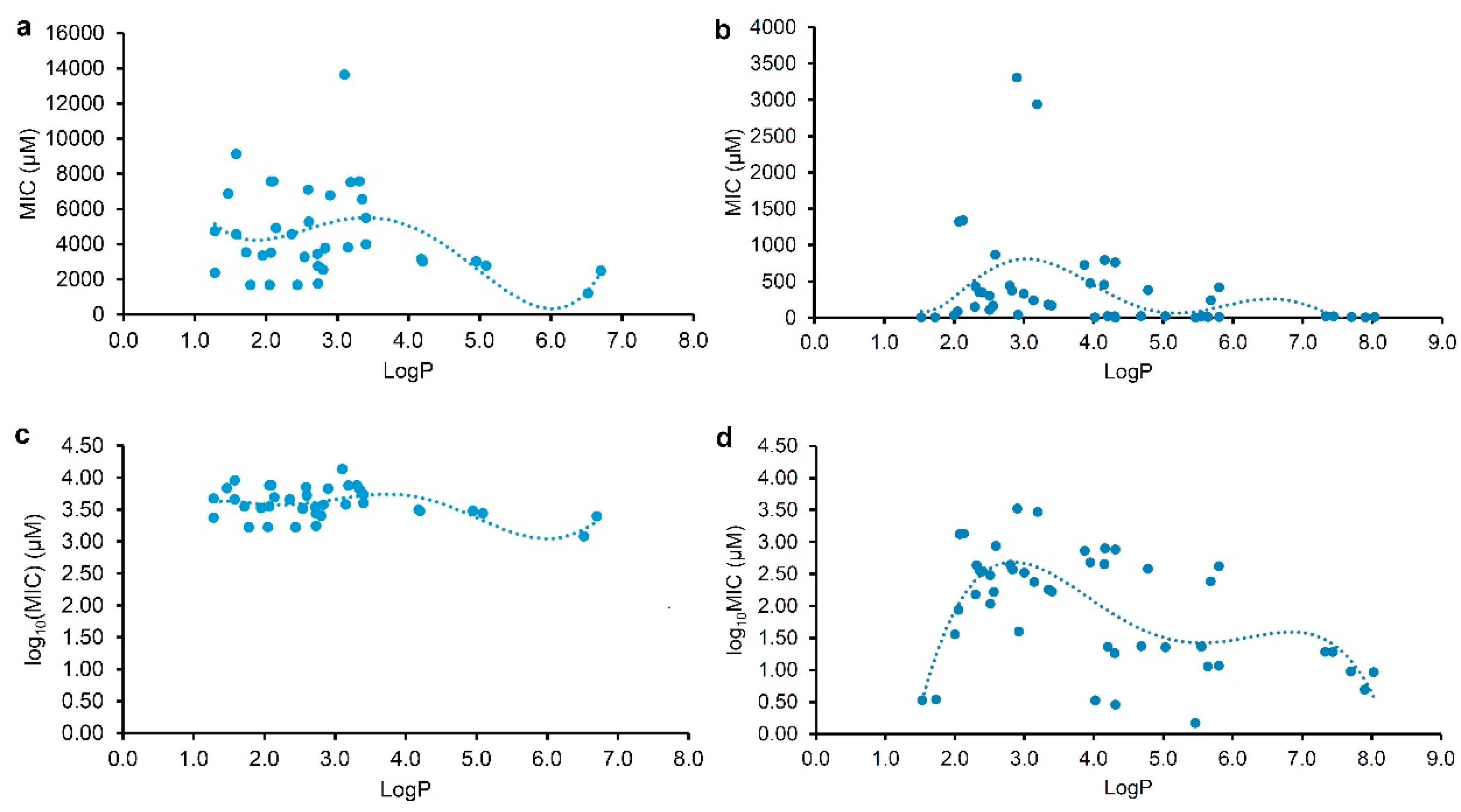
2.1. Structure, Antibacterial Activity, and Physicochemical Parameter
2.2. Correlation and Regression Analyses for the MICs and the Physicochemical Parameters
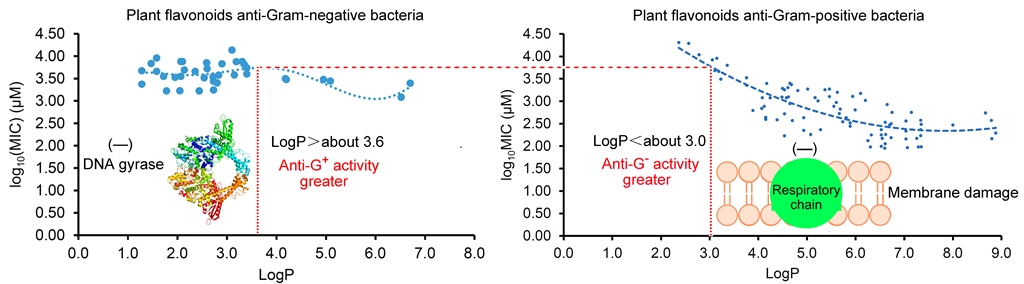
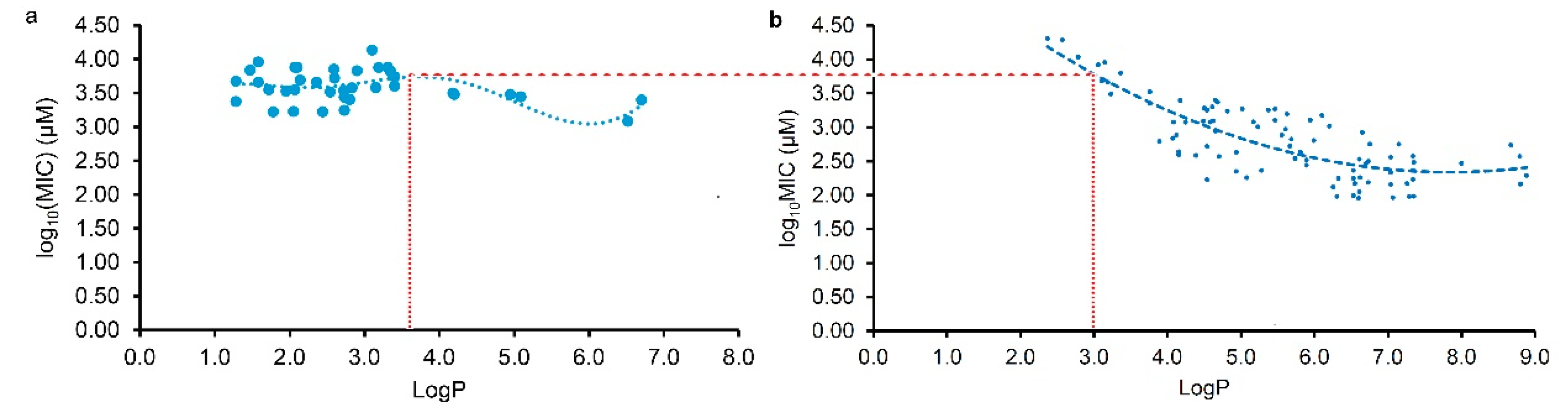
2.3. Different Actions of Plant Flavonoids to Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials, Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Bacterial Strains and Growth Condition
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Assay
4.4. Structures and MICs of plant flavonoids reported
4.5. Correlation and regression analyses
4.7. Comparision for the characters of regression curves
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Wool, P.R.E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Sridhar, D.; Blaser, M.; Wang, M.; Woolhouse, M. Achieving global targets for antimicrobial resistance. Science 2016, 353, 874–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosu, M.; Siricilla, S.; Mitachi, K. Advances in MRSA drug discovery: where are we and where do we need to be? Exp. Opin. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 1095–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Zhou, M. Synergistic combination of two antimicrobial agents closing each other's mutant selection windows to prevent antimicrobial resistance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Ge, X.; Xua, H.; Ma, K.; Zhang, W.; Zan, Y.; Efferth, T.; Xue, Z.; Hua, X. Phytochemicals with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, L.; Duarte-Sierra, A. Recent advancements in enhancing antimicrobial activity of plant-derived polyphenols by biochemical means. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yang, W.; Tang, F.; Chen, X.; Ren, L. Antibacterial activities of flavonoids: structure-activity relationship and mechanism. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Deng, J.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, Z. The antibacterial activity of natural-derived flavonoids. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Hu, X.; Ren, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Antibacterial modes of herbal flavonoids combat resistant bacteria. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 873374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Yang, Z.Q.; Liu, F.; Peng, W.J.; Qu, S.Q.; Li, Q.; Song, X.B.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J.Z. Antibacterial effect and mode of action of flavonoids from licorice against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, S.; Li, S.M. Naturally occurring prenylated chalcones from plants: structural diversity, distribution, activities and biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 2236–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górniak, I.; Bartoszewski, R.; Króliczewski, J. Comprehensive review of antimicrobial activities of plant flavonoids. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 241–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, F.; Khameneh, B.; Iranshahi, M.; Iranshahy, M. Antibacterial activity of flavonoids and their structure-activity relationship: An update review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, L.; Duarte-Sierra, A. Recent advancements in enhancing antimicrobial activity of plant-derived polyphenols by biochemical means. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, N.F.; Ahmed, Q.U.; Mahmood, S.; Ali Shah, S.A.; Khatib, A.; Mukhtar, S.; Alsharif, M.A.; Parveen, H.; Zakaria, Z.A. Antibacterial effects of flavonoids and their structure-activity relationship study: A comparative interpretation. Molecules 2022, 27, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Xia, X.; Guan, Y.; Yi, H.; Lai, S.; Sun, Y.; Cao, S. Antimicrobial quantitative relationship and mechanism of plant flavonoids to gram-positive bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Guan, Y.; Yi, H.; Lai, S.; Sun, Y.; Cao, S. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of plant flavonoids to gram-positive bacteria predicted from their lipophilicities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Yuan, G.; Li, S.; Deng, B.; Luo, X. Quinone pool, a key target of plant flavonoids inhibiting gram-positive bacteria. Molecules 2023, 28, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaveng, A.T.; Sandjo, L.P.; Tankeo, S.B.; Ndifor, A.R.; Pantaleon, A.; Nagdjui, B.T.; Kuete, V. Antibacterial activity of nineteen selected natural products against multi-drug resistant Gram-negative phenotypes. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwujekwu, J.C.; Van Heerden, F.R.; Van Staden, J. Antibacterial activity of flavonoids from the stem bark of Erythrina caffra Thunb. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalari, G.; Bennett, R.N.; Bisignano, G.; Trombetta, D.; Saija, A.; Faulds, C.B.; Gasson, M.J.; Narbad, A. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids extracted from bergamot (Citrus bergamia Risso) peel, a byproduct of the essential oil industry. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, N.D.; Katerere, D.R.; Eloff, J.N. Biological activity of five antibacterial flavonoids from Combretum erythrophyllum (Combretaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 93, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagla, V.P.; McGaw, L.J.; Elgorashi, E.E.; Eloff, J.N. Antimicrobial activity, toxicity and selectivity index of two biflavonoids and a flavone isolated from Podocarpus henkelii (Podocarpaceae) leaves. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zang, X.; He, M.; Pan, S.; Xu, X. Structure-activity relationship of flavonoids on their anti-Escherichia coli activity and inhibition of DNA gyrase. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2013, 61, 8185–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edziri, H.; Mastouri, M.; Mahjoub, M.A.; Mighri, Z.; Mahjoub, A.; Verschaeve, L. Antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic activities of two flavonoids from Retama raetam flowers. Molecules 2012, 17, 7284–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Abdelkader, K.; Gomaa, H.A.M.; Batubara, A.S.; Gamal, M.; Sayed, A.M. Mechanistic study of the antibacterial potential of the prenylated flavonoid auriculasin against Escherichia coli. Arch. Pharm. Weinheim 2022, 355, e2200360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eumkeb, G.; Siriwong, S.; Thumanu, K. Synergistic activity of luteolin and amoxicillin combination against amoxicillin-resistant Escherichia coli and mode of action. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2012, 117, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaisinghani, R.N. Antibacterial properties of quercetin. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 8, 6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzoyem, J.P.; Melong, R.; Tsamo, A.T.; Tchinda, A.T.; Kapche, D.G.; Ngadjui, B.T.; McGaw, L.J.; Eloff, J.N. Cytotoxicity, antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of eight compounds isolated from Entada abyssinica (Fabaceae). BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eumkeb, G.; Siriwong, S.; Phitaktim, S.; Rojtinnakorn, N.; Sakdarat, S. Synergistic activity and mode of action of flavonoids isolated from smaller galangal and amoxicillin combinations against amoxicillin-resistant Escherichia coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozçelik, B.; Orhan, I.; Toker, G. Antiviral and antimicrobial assessment of some selected flavonoids. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2006, 61, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuete, V.; Simo, I.K.; Ngameni, B.; Bigoga, J.D.; Watchueng, J.; Kapguep, R.N.; Etoa, F.X.; Tchaleu, B.N.; Beng, V.P. Antimicrobial activity of the methanolic extract, fractions and four flavonoids from the twigs of Dorstenia angusticornis Engl. (Moraceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, M. de los A.; Zarelli, V.E.; Pappano, N.B.; Debattista, N.B. Bacteriostatic action of synthetic polyhydroxylated chalcones against Escherichia coli. Biocell. 2004, 28, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Hao, Z.; Ding, S.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J. Plant natural flavonoids against multidrug resistant pathogens. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory and Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, Approved Standards, CLSI document M07-A10, 10th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory and Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
| Compounds (No.)a | Structure types | LogPb | LogD7.40b | E. coli ATCC 25922 | S. aureus ATCC 25923 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (μM)c | Log10(MIC)c | MIC (μM)c | Predicted MIC (μM)d | ||||
| Sophoraflavanone G (1) | Dihydroflavones | 6.52 | 6.33 | 1206.15 | 3.0814 | 9.42 | 16.37 |
| Neohesperidin (2) | Dihydroflavones | 2.44 | 1.99 | 1677.12 | 3.2246 | >1677.12 | 1816.01 |
| Naringin (3) | Dihydroflavones | 2.73 | 2.30 | 1763.88 | 3.2465 | >1763.88 | 1151.90 |
| Hesperidin (4) | Dihydroflavones | 1.78 | 1.33 | 1677.12 | 3.2246 | >1677.12 | 4440.63 |
| Methyl hesperidin (5) | Dihydroflavones | 2.54 | 2.10 | 3278.95 | 3.5157 | >3278.95 | 8410.66 |
| Eriodictyol (6) | Dihydroflavones | 2.59 | 2.34 | 7104.70 | 3.8515 | >7104.70 | 1442.76 |
| Eriocitrin (7) | Dihydroflavones | 1.47 | 1.03 | > 3433.13 | > 3.5357 | >3433.13 | 6397.02 |
| Hesperitin (8) | Dihydroflavones | 2.90 | 2.65 | 6775.18 | 3.8309 | >6775.18 | 863.94 |
| Naringenin (9) | Dihydroflavones | 3.19 | 2.96 | 7527.47 | 3.8766 | 3763.74 | 509.64 |
| didymin (10) | Dihydroflavones | 2.72 | 2.29 | 3444.51 | 3.5371 | >3444.51 | 1170.98 |
| Narirutin (11) | Dihydroflavones | 2.07 | 1.65 | 3527.75 | 3.5475 | >3527.75 | 3063.61 |
| Baicalein (12) | Flavones | 3.31 | 2.60 | > 3789.22 | > 3.5785 | >3789.22 | 404.47 |
| Licoflavone C (13) | Flavones | 4.20 | 3.77 | 3026.36 | 3.4809 | 3026.36 | 85.1 |
| Tangeritin (14) | Flavones | 2.73 | 2.73 | 2749.95 | 3.4393 | >2749.95 | 1151.9 |
| Nobiletin (15) | Flavones | 2.8 | 2.80 | 2544.73 | 3.4056 | >2544.74 | 1025.21 |
| Vitexin (16) | Flavones | 1.28 | 0.45 | 2368.29 | 3.3744 | 2368.29 | 7888.23 |
| Isovitexin (17) | Flavones | 1.28 | 0.15 | > 2368.29 | > 3.3744 | 2368.29 | 7888.23 |
| Diosmin (18) | Flavones | 2.05 | 1.23 | 1682.69 | 3.2260 | >1682.69 | 3146.25 |
| Rhoifolin (19) | Flavones | 1.72 | 0.91 | 3540.07 | 3.5490 | >3540.07 | 4777.21 |
| Apigenin (20) | Flavones | 2.10 | 1.57 | 7578.45 | 3.8796 | >7578.45 | 2942.82 |
| Diosmetin (21) | Flavones | 3.10 | 2.55 | > 6820.53 | > 3.8338 | >6820.53 | 603.30 |
| 5-Demethylnobiletin (22) | Flavones | 2.60 | 2.28 | 5273.32 | 3.7221 | >5273.32 | 1420.23 |
| 4',5,7-Trimethoxyflavone (23) | Flavones | 3.35 | 3.35 | 6557.38 | 3.8167 | >6557.38 | 373.96 |
| Sinensetin (24) | Flavones | 3.40 | 3.40 | 5499.91 | 3.7404 | >5499.91 | 338.78 |
| Orientin (25) | Flavones | 1.58 | 0.72 | > 4567.55 | > 3.6597 | >4567.55 | 5639.27 |
| Isoorientin (26) | Flavones | 1.58 | 0.41 | 4567.55 | 3.6597 | >4567.55 | 5639.27 |
| Quercetin (27) | Flavonols | 2.07 | 1.40 | > 3388.04 | > 3.5299 | 13552.14 | 3063.61 |
| Galangin (28) | Flavonols | 2.83 | 2.16 | 3789.22 | 3.5785 | >3789.22 | 974.47 |
| Icaritin (29) | Flavonols | 5.09 | 4.54 | 2779.66 | 3.4430 | 2779.66 | 75.22 |
| Rutin (30) | Flavonols | 1.95 | 1.22 | > 1677.26 | > 3.2246 | 1677.26 | 3585.77 |
| Quercitrin (31) | Flavonols | 2.36 | 1.63 | 4567.55 | 3.6597 | >4567.55 | 2043.95 |
| Isoliquiritigenin (32) | Chalcones | 3.40 | 3.26 | 3995.94 | 3.6016 | 3995.94 | 338.78 |
| Licochalcone A (33) | Chalcones | 4.95 | 4.85 | 3026.00 | 3.4809 | 11.82 | 74.44 |
| Formononetin (34) | Isoflavones | 3.15 | 2.91 | 3817.05 | 3.5817 | >3817.04 | 549.61 |
| Puerarin (35) | Isoflavones | 2.14 | 1.59 | 4918.58 | 3.6918 | 614.82 | 2787.56 |
| Glabridin (36) | Isoflavanes | 4.18 | 4.18 | 3156.79 | 3.4992 | 49.32 | 86.81 |
| α-Mangostin (37) | Xanthones | 6.70 | 6.10 | 2494.70 | 3.3970 | 4.87 | 8.17 |
| Compounds (No.)a | Structure types | LogPb | LogD7.40b | MIC (μM)c | Log10(MIC)c | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candidone (38) | Dihydroflavones | 5.64 | 5.64 | 11.35 | 1.0540 | 19 |
| Atalantoflavone (39) | Flavones | 4.31 | 3.58 | 761.13 | 2.8815 | 19 |
| 2'-hydroxyatalantoflavone (40) | Flavones | 3.87 | 3.10 | 726.57 | 2.8613 | 19 |
| Neocyclomorusin (41) | Flavones | 4.30 | 2.87 | 18.33 | 1.2632 | 19 |
| Neobavaisoflavone (42) | Isoflavones | 4.68 | 4.69 | 23.64 | 1.3736 | 19 |
| Daidzein (43) | Isoflavones | 3.14 | 2.61 | 236.83 | 2.3744 | 19 |
| Isowighteone (44) | Isoflavones | 4.78 | 4.23 | 380.57 | 2.5804 | 19 |
| Isoneorautenol (45) | Dihydroisoflavones | 4.16 | 4.16 | 794.14 | 2.8999 | 19 |
| Abyssione-V 4′-O-methyl ether (46) | Dihydroflavones | 8.03 | 7.79 | 9.23 | 0.9652 | 20 |
| 6,8-diprenylgenistein (47) | Isoflavones | 7.33 | 7.16 | 19.19 | 1.2831 | 20 |
| Alpinumisoflavone (48) | Isoflavones | 5.80 | 4.93 | 11.60 | 1.0645 | 20 |
| Eriodictyol (49) | Dihydroflavones | 2.59 | 2.34 | 867.27 | 2.9382 | 21 |
| Hesperetin (50) | Dihydroflavones | 2.90 | 2.65 | 3308.19 | 3.5196 | 21 |
| Neohesperidin (51) | Dihydroflavones | 2.44 | 1.99 | >1637.81 | >3.2143 | 21 |
| Neoeriocitrin (52) | Dihydroflavones | 2.13 | 1.68 | 1341.07 | 3.1275 | 21 |
| Naringin (53) | Dihydroflavones | 2.73 | 2.30 | >1722.53 | >3.2362 | 21 |
| Naringenin (54) | Dihydroflavones | 3.19 | 2.96 | 2938.37 | 3.4681 | 21 |
| 5-hydroxy-7,4'-dimethoxyflavone (55) | Flavones | 3.40 | 2.78 | 167.62 | 2.2243 | 22 |
| Genkwanin (56) | Flavones | 2.36 | 1.75 | 351.78 | 2.5463 | 22 |
| Quercetin-5,3'-dimethylether (57) | Flavonols | 2.30 | 1.74 | 151.38 | 2.1801 | 22 |
| Rhamnazin (58) | Flavonols | 2.51 | 1.73 | 302.76 | 2.4811 | 22 |
| Rhamnocitrin (59) | Flavonols | 2.56 | 1.82 | 166.52 | 2.2215 | 22 |
| 7,4', 7'', 4'''-tetramethoxy amentoflavone (TMA) (60) | Bioflavones | 5.80 | 4.10 | 420.47 | 2.6237 | 23 |
| Isoginkgetin (IGG) (61) | Bioflavones | 5.68 | 4.32 | 242.29 | 2.3843 | 23 |
| Podocarpusflavone A (PFA) (62) | Bioflavones | 4.15 | 2.53 | 452.5 | 2.6556 | 23 |
| Nobiletin (63) | Flavones | 2.80 | 2.80 | 439.86 | 2.6433 | 24 |
| Kaempferol (64) | Flavonols | 2.05 | 1.40 | 87.34 | 1.9412 | 24 |
| Licoflavone C (65) | Flavones | 4.20 | 3.77 | 23.08 | 1.3632 | 25 |
| Derrone (66) | Isoflavones | 5.55 | 4.82 | 23.22 | 1.3659 | 25 |
| Epimedokoreanin B (67) | Flavones | 6.59 | 6.14 | >151.49 | >2.1804 | 26 |
| Auriculasin (68) | Isoflavones | 7.70 | 6.89 | 9.51 | 0.9782 | 26 |
| Pomiferin (69) | Isoflavones | 7.44 | 7.06 | 19.03 | 1.2794 | 26 |
| Gancaonin L (70) | Isoflavones | 5.03 | 4.58 | 22.58 | 1.3537 | 26 |
| Mopanin (71) | Flavonols | 1.94 | 1.04 | >214.59 | >2.3316 | 26 |
| Luteolin (72) | Flavones | 2.40 | 1.85 | 349.36 | 2.5433 | 27 |
| Quercetin (73) | Flavonols | 2.07 | 1.40 | 1323.45 | 3.1217 | 28 |
| Quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucosyl (1→4)-α-L-rhamnoside (74) | Flavonols | 2.92 | 2.20 | 40.02 | 1.6023 | 29 |
| Quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside or quercitrin (75) | Flavonols | 2.51 | 1.78 | 108.13 | 2.0339 | 29 |
| Entadanin (76) | Flavonols | 2.00 | 0.086 | 36.31 | 1.5600 | 29 |
| Kaempferide (77) | Flavonols | 3.00 | 2.33 | 333.03 | 2.5225 | 30 |
| Kaempferide-3-O-β-D-glucoside (78) | Flavonols | 2.31 | 1.60 | 432.52 | 2.6360 | 30 |
| Galangin (79) | Flavonols | 2.83 | 2.16 | 370.04 | 2.5682 | 30 |
| Tiliroside (80) | Flavonols | 4.02 | 3.32 | 3.36 | 0.5263 | 31 |
| Quercetin-3,7-O-α-L-dirhamnoside (81) | Flavonols | 1.53 | 0.53 | 3.36 | 0.5263 | 31 |
| Kaempferol-3,7-O-α-L-dirhamnoside (82) | Flavonols | 1.73 | 0.76 | 3.46 | 0.5391 | 31 |
| Scandenone (83) | Isoflavones | 7.90 | 7.12 | 4.94 | 0.6937 | 31 |
| Angusticornin B (84) | Chalcones | 4.31 | 4.07 | 2.87 | 0.4579 | 32 |
| Bartericin A (85) | Chalcones | 5.46 | 5.77 | 1.49 | 0.1732 | 32 |
| 2',4',2-(OH)3-chalcone (86) | Chalcones | 3.95 | 3.66 | 476.08 | 2.6777 | 33 |
| 2',4',3-(OH)3-chalcone (87) | Chalcones | 3.35 | 3.05 | 179.51 | 2.2541 | 33 |
| Isobavachalcone (88) | Chalcones | 5.49 | 5.44 | >394.6 | >2.5962 | 34 |
| α-Mangostin (89) | Xanthones | 6.70 | 6.10 | >311.84 | >2.4939 | 34 |
| Equation number | Sample numbers (n) |
Parametersa(x) | Regression equation ( rb ) | Coefficient of determination (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | 37 | LogP | y = 154.74x4 - 2328.1x3 + 11774x2 - 23630x + 20574 (0.3736) c | 0.1396 |
| (2) | y = -0.0022x6 + 0.0574x5 - 0.5624x4 + 2.6776x3 - 6.4916x2 + 7.5985x + 0.2396 (0.4714) d | 0.2222 | ||
| (3) | 37 | LogD7.40 | y = 51.533x4 - 648.46x3 + 2399.6x2 - 2834x + 5407.4 (0.3412) c | 0.1164 |
| (4) | 46 | LogP | y = 3.4251x6 - 99.079x5 + 1128.5x4 - 6389x3 + 18606x2 - 25841x + 13552 (0.4108) c | 0.1688 |
| (5) | y = -0.0358x4 + 0.7264x3 - 5.2356x2 + 15.438x - 13.244 (0.6670) d | 0.4449 | ||
| (6) | y = 0.0621x3 - 0.9417x2 + 4.0824x - 2.9354 (0.5875) d | 0.3452 | ||
| (7) | 46 | LogD7.40 | / e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





