Submitted:
01 January 2024
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and methods
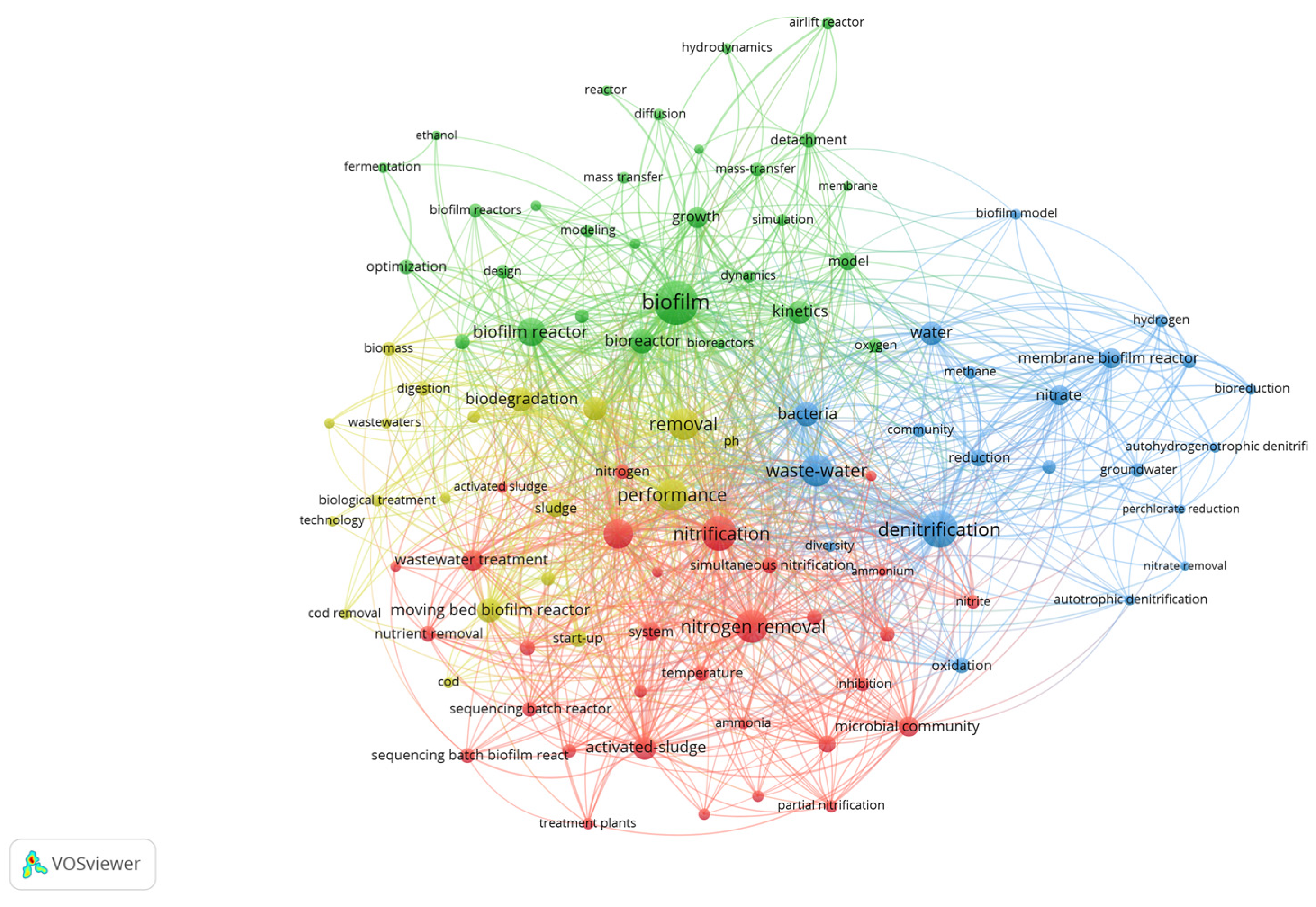
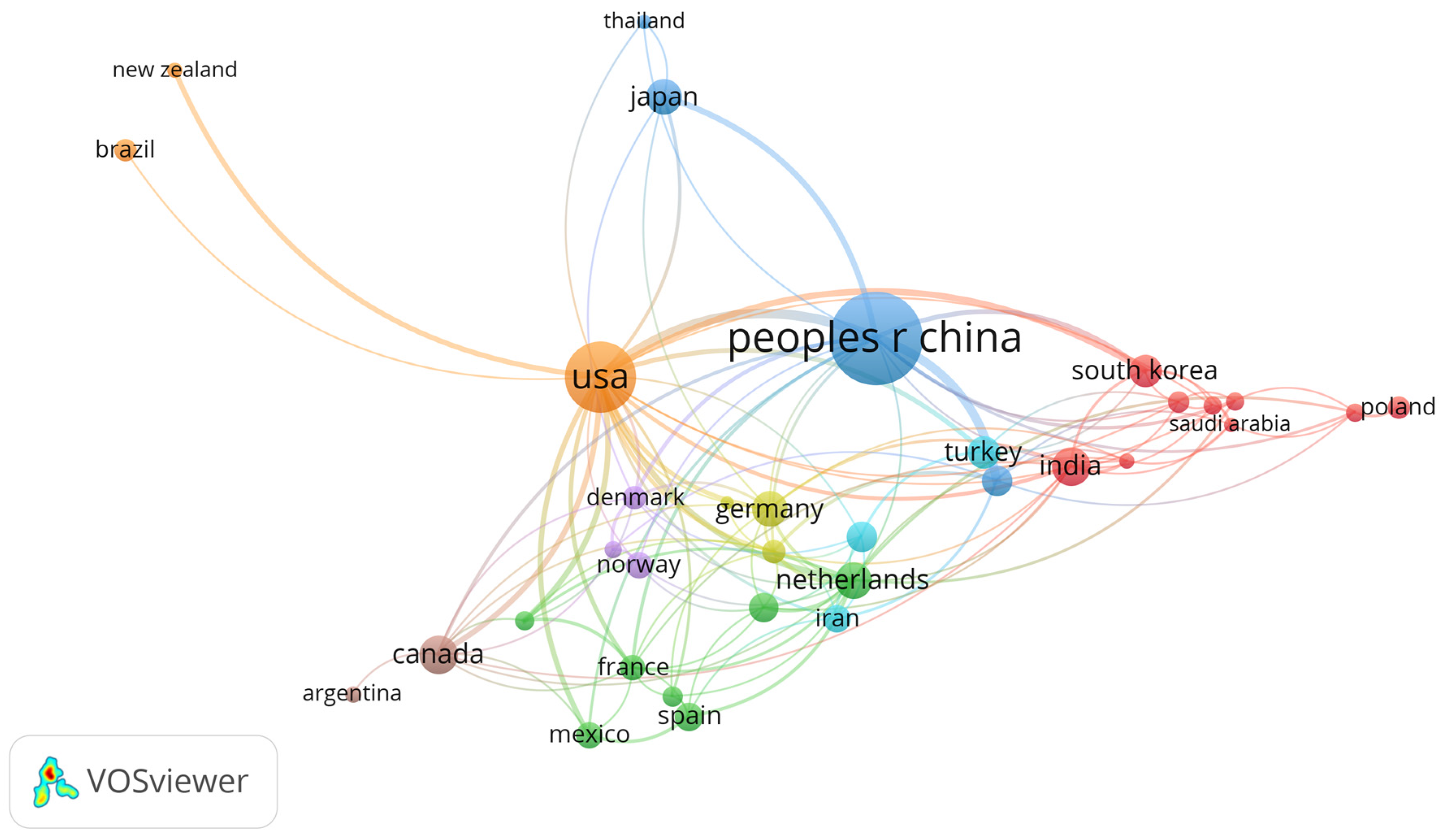
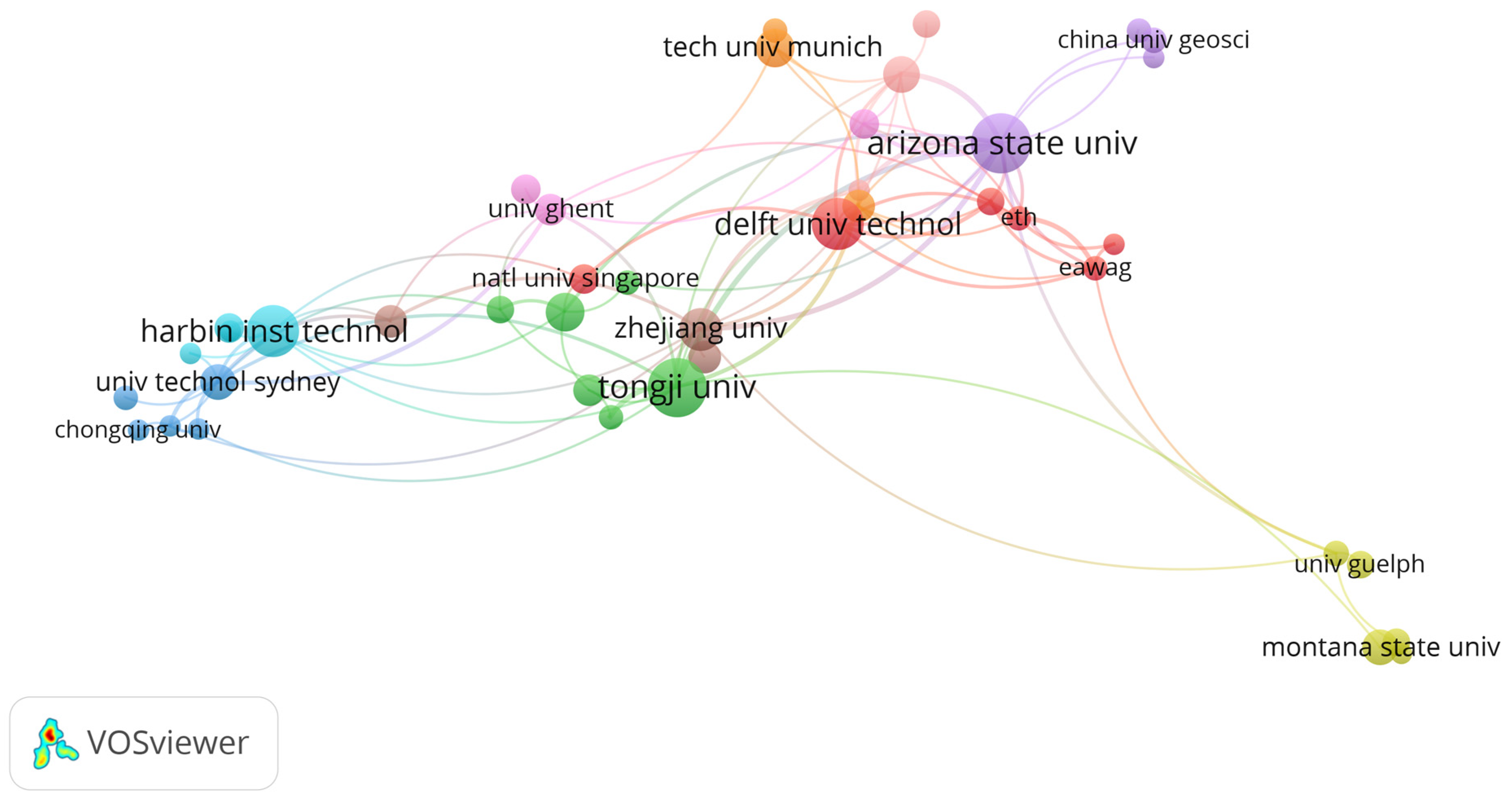
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Versatility in Action: Biofilm Reactors for a Sustainable Future
| Species | Key findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Shewanelle oneidensis | The capability of Shewanella oneidensis and its mutant biofilm for effectively removing heavy metals is notable. | [35,36,37] |
| Shewanella oneidensis | The utilization of Shewanella oneidensis biofilm-based microbial fuel cells proves to be effective in generating electricity. | [38,39,40] |
| Comamonas testosteroni | The biofilm formed by Comamonas testosteroni demonstrates efficiency in the biodegradation of 3-chloroaniline. | [41] |
| Bacillus halodurans | Bacillus halodurans biofilm serves to mend cracks in cementitious materials. | [42,43,44] |
| Escherichia coli | Oxygen availability's impact on in vitro biofilm formation by Escherichia coli K-12 and clinical strains was compared, revealing strain-dependent variations in anaerobic conditions. | [45] |
| Possible multiple species (Activated sludge) | A push-flow microalgae-bacteria biofilm reactor demonstrated efficient greywater treatment with enhanced biofilm characteristics and nitrogen metabolisms, reducing energy input for wastewater treatment. | [46] |
| Possible multiple species (Nitrifiers) | Particle-based biofilm reactors offer compact, high-rate processes with large biomass content (up to 30 g/l) and specific surface area (up to 3000 m2/m3). | [47] |
4.2. The Future Landscape: Big Data and Machine Learning in Biofilm Reactor Research
References
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nature reviews microbiology 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, Y.; Chennaoui, M.; Sylla, A.; Mountadar, M.; Rihani, M.; Assobhei, O. Characterization, structure, and function of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial biofilm in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Desalination and Water Treatment 2016, 57, 16220–16237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Neu, T.R.; Wozniak, D.J. The EPS matrix: the “house of biofilm cells”. Journal of bacteriology 2007, 189, 7945–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, S.; Antony, R.; Thamban, M. Extracellular polymeric substances in Antarctic environments: A review of their ecological roles and impact on glacier biogeochemical cycles. Polar Science 2021, 30, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Sehar, S.; Manefield, M. The roles of extracellular DNA in the structural integrity of extracellular polymeric substance and bacterial biofilm development. Environmental microbiology reports 2013, 5, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.J.; Qian, H.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y. Insights into the role of extracellular DNA and extracellular proteins in biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Frontiers in Microbiology 2020, 11, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fang, H.H.P. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. Journal of biotechnology 2002, 95, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, P.; Sauer, K.; Davies, D.G.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms as complex differentiated communities. Annual Reviews in Microbiology 2002, 56, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.J.; Chang, C.; Akiyama, T.; Bothner, B. New technologies for studying biofilms. Microbial Biofilms 2015, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.A.; Anandapandian, K.T.K.; Parthiban, K. Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides (EPS) from biofilm forming marine bacterium. Brazilian archives of biology and technology 2011, 54, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahto, K.U.; Priyadarshanee, M.; Samantaray, D.P.; Das, S. Bacterial biofilm and extracellular polymeric substances in the treatment of environmental pollutants: Beyond the protective role in survivability. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022, 134759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanowska, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I. Microbial origin of excreted DNA in particular fractions of extracellular polymers (EPS) in aerobic granules. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 2019, 230, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Di Martino, P. Extracellular polymeric substances, a key element in understanding biofilm phenotype. AIMS microbiology 2018, 4, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y. Importance of extracellular proteins in maintaining structural integrity of aerobic granules. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, B.; Chen, M.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Bacterial extracellular polysaccharides involved in biofilm formation. Molecules 2009, 14, 2535–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panlilio, H.; Rice, C.V. The role of extracellular DNA in the formation, architecture, stability, and treatment of bacterial biofilms. Biotechnology and bioengineering 2021, 118, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, R.J.L.; Manzanera, M. The effects of plant-associated bacterial exopolysaccharides on plant abiotic stress tolerance. Metabolites 2021, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Bai, H.; Kong, F.; Liss, S.N.; Liao, B. Recent advances in membrane aerated biofilm reactors. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 2021, 51, 649–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brading, M.G.; Jass, J.; Lappin-Scott, H.M. Dynamics of bacterial biofilm formation. Microbial biofilms 1995, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y. Heavy metal pollution and transboundary issues in ASEAN countries. Water Policy 2019, 21, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, P.; Mahadevan, R.; Yakunin, A.F. Heavy metal removal by bioaccumulation using genetically engineered microorganisms. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology 2018, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moga, I.C.; Ardelean, I.; Petrescu, G.; Crăciun, N.; Popa, R. The potential of biofilms from moving bed bioreactors to increase the efficiency of textile industry wastewater treatment. Industria textila 2018, 69, 412–418. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolella, C.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Heijnen, J.J. Wastewater treatment with particulate biofilm reactors. Journal of biotechnology 2000, 80, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltz, J.P.; Smets, B.F.; Rittmann, B.E.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Morgenroth, E.; Daigger, G.T. From biofilm ecology to reactors: a focused review. Water Science and Technology 2017, 75, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muffler, K.; Lakatos, M.; Schlegel, C.; Strieth, D.; Kuhne, S.; Ulber, R. Application of biofilm bioreactors in white biotechnology. Productive biofilms 2014, 123–161. [Google Scholar]
- Saidulu, D.; Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K. A systematic review of moving bed biofilm reactor, membrane bioreactor, and moving bed membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment: Comparison of research trends, removal mechanisms, and performance. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2021, 9, 106112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsek, M.R.; Fuqua, C. Biofilms 2003: emerging themes and challenges in studies of surface-associated microbial life. Journal of bacteriology 2004, 186, 4427–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, X.; Qian, C.; Li, W. Responses of biofilm microorganisms from moving bed biofilm reactor to antibiotics exposure: Protective role of extracellular polymeric substances. Bioresource technology 2018, 254, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Lee, K.W.K.; Burmølle, M.; Kjelleberg, S.; Rice, S.A. All together now: experimental multispecies biofilm model systems. Environmental Microbiology 2017, 19, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. A bibliography study of Shewanella oneidensis biofilm. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2023, 99, fiad124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. Tackling Heavy Metal Pollution: Evaluating Governance Models and Frameworks. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Zha, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhu, C.; Chen, E. A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer of publications on COVID-19. Annals of translational medicine 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D. VOSviewer. Technical Services Quarterly 2018, 35, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Peng, N.; Du, Y.; Ji, L.; Cao, B. Disruption of putrescine biosynthesis in Shewanella oneidensis enhances biofilm cohesiveness and performance in Cr (VI) immobilization. Applied and environmental microbiology 2014, 80, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.-Y. Molecular evidence of a toxic effect on a biofilm and its matrix. Analyst 2019, 144, 2498–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Szymanski, C.; Fredrickson, J.; Shi, L.; Cao, B.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.-Y. In situ molecular imaging of the biofilm and its matrix. Analytical chemistry 2016, 88, 11244–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.e.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, V.B.; Zhang, Y.; Kjelleberg, S.; Loo, J.S.C.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Q. Hybrid conducting biofilm with built-in bacteria for high-performance microbial fuel cells. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-e.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, V.B.; Bao, B.; Kjelleberg, S.; Cao, B.; Loo, S.C.J.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. Chemically functionalized conjugated oligoelectrolyte nanoparticles for enhancement of current generation in microbial fuel cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2015, 7, 14501–14505. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cao, B.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Song, H. Enhancing bidirectional electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis by a synthetic flavin pathway. ACS synthetic biology 2015, 4, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cohen, Y.; Cao, B. Elevated level of the second messenger c-di-GMP in Comamonas testosteroni enhances biofilm formation and biofilm-based biodegradation of 3-chloroaniline. Applied microbiology and biotechnology 2015, 99, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Weng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Use of genetically modified bacteria to repair cracks in concrete. Materials 2019, 12, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Influence of bacterial incorporation on mechanical properties of engineered cementitious composites (ECC). Construction and Building Materials 2019, 196, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S. Mechanical performance of strain-hardening cementitious composites (SHCC) with bacterial addition. Journal of Infrastructure Preservation and Resilience 2022, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjergbæk, L.A.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Reisner, A.; Molin, S.; Roslev, P. Effect of oxygen and growth medium on in vitro biofilm formation by Escherichia coli. Biofilms 2006, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Ran, T.; Liu, S.; Li, Q.; Cui, X.; Zhou, Y. Biofilm bioactivity affects nitrogen metabolism in a push-flow microalgae-bacteria biofilm reactor during aeration-free greywater treatment. Water Research 2023, 244, 120461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolella, C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Heijnen, S.J. Particle-based biofilm reactor technology. Trends in Biotechnology 2000, 18, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Pan, S.; Wang, J.; Vasilakos, A.V. Machine learning on big data: Opportunities and challenges. Neurocomputing 2017, 237, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’heureux, A.; Grolinger, K.; Elyamany, H.F.; Capretz, M.A.M. Machine learning with big data: Challenges and approaches. Ieee Access 2017, 5, 7776–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, K.; Chinna Rao, B.; Saikumar, K.; Lakshman Pratap, N. An optimal hybrid solution to local and global facial recognition through machine learning. A fusion of artificial intelligence and internet of things for emerging cyber systems 2022, 203–226. [Google Scholar]
- Bachute, M.R.; Subhedar, J.M. Autonomous driving architectures: insights of machine learning and deep learning algorithms. Machine Learning with Applications 2021, 6, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. Machine Learning and Its Applications in Studying the Geographical Distribution of Ants. Diversity 2022, 14, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. A Machine Learning Approach to Predicting Academic Performance in Pennsylvania’s Schools. Social Sciences 2023, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagermann, H. Change through digitization—Value creation in the age of Industry 4.0. In Management of permanent change; Springer, 2014; pp. 23–45. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Xu, G. Novel performance prediction model of a biofilm system treating domestic wastewater based on stacked denoising auto-encoders deep learning network. Chemical Engineering Journal 2018, 347, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





