1. Introduction
Since the Industrial Revolution, it is a well-known fact that greenhouse gas emissions have contributed to global warming and adversely affected air quality, climate, and the environment, severely deteriorating human health [
1,
2]. In response, various policies have been established worldwide, notably the adoption of the Paris Agreement in the 2015 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) meeting. Additionally, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) emphasizes the need for fossil fuel reduction, gradual phase-out, expansion of renewable energy, and improvement in energy efficiency to achieve carbon neutrality [
1]. In this context, exploration and transition from fossil fuel to carbon-neutral and renewable resources have become essential. Biomass holds tremendous potential in meeting these societal demands, with the development of biorefineries significantly contributing to solving sustainability and environmental issues.
One promising resource in biorefineries is alga, which requires no farmland or fertilizer with rapid reproduction and high yield [
3,
4]. Particularly, brown algae, due to their high consumption in Asia, account for 47.3 % of the world's cultivation at 16.4 million tons [
5]. With this increasing production, waste generated during processing poses a problem, affecting local environments through landfill and incineration [
6]. Since 2013, ocean dumping has been prohibited under the London Convention, leading to a significant increase in waste disposal costs. Therefore, exploring the utilization of such waste is necessaryet.
Undaria pinnatifida,
Saccharina japonica, and
Pyropia yezoensis account for almost 97 % of Korea's total algae production [
7].
Undaria pinnatifida(sea mustard) contains various physiologically active compounds including monosaccharides, polysaccharides (alginate, saccharin, mannans), polyphenols, polyunsaturated fatty acids, peptides, phytosterols, and vitamins, making it a useful resource [
8].
Among components of
Undaria pinnatifida, mucilaginous polysaccharide alginate is highly valued due to its biocompatibility, biodegradability, antibacterial properties, and ease of gel formation [
9]. It plays a crucial role in various fields such as food industry thickeners, wound healing agents, and drug delivery systems [
10]. However, the biorefining process of alginate typically requires low yield, high energy input, and long processing time [
11]. To overcome these limitations, microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) has been proposed. This technology demonstrates compatibility with the biorefinery concept by offering rapid hydrolysis and low energy consumption compared to traditional methods. Although MAE has been proven to be effective for various extractions, research on its suitability for rapid alkali extraction of alginate from brown algae has not been vigorously pursued [
12,
13,
14].
The goal of this study was to optimize the extraction process of sodium alginate from Undaria pinnatifida using MAE. Using Response Surface Methodology, we derived optimal conditions based on key parameters such as solid/liquid ratio, extraction temperature, and extraction solvent concentration. This approach aims to not only improve the yield of extracted alginic acid sodium, but also apply this process to biorefinery systems, promoting sustainability and economic viability. This research is expected to make a significant contribution to biorefining and sustainable material science by providing a new, efficient, and scalable method for extracting sodium alginate. Furthermore, it presents a viable and sustainable solution for commercial-scale production of alginate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Undaria pinnatifida was purchased from GreenNatural (Korea). Sodium alginate used as a standard substance was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich(USA). Sulfuric acid (95% H2SO4) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3) used for analyzing monosaccharides and sodium alginate compositions in Undaria pinnatifida were purchased from Daejung (Korea). Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) and hydrochloric acid (37% HCl) used for sodium alginate extraction of Undaria pinnatifida and pH neutralization were acquired from Daejung (Korea) and Junsei (Japan), respectively. Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) for HPLC analysis were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich(USA) HPLC Water was purchased from Honeywell(USA).
2.2. Analysis method of sugars and sodium alginate in Undaria pinnatifida
Monosaccharide compositions of
Undaria pinnatifida were analyzed according to the standard procedure of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). First, 0.025 g of sample was hydrolyzed with 250 µL of 72 % H
2SO
4 at 30 ℃ for 1 h and then further hydrolyzed with 7 mL of DW at 121 ℃ for 1h. The hydrolyzed sample was quantified using HPLC. Sodium alginate content was analyzed following the procedure of a previous study [
15]. Briefly, 0.1 g of sample was reacted with 10 mL of 0.4 M H
2SO
4 at room temperature overnight and then filtered to obtain residues. These residues were reacted with 20 mL of 3 % Na
2CO
3 at 50 ℃ overnight and diluted with 80 mL of DW. Then 1 mL of the diluted sample was reacted with 6 mL of 95 % H
2SO
4 at room temperature for 20 min. Half (3.5 mL) was used as a blank. To the other half (3.5 mL), 0.3 mL of carbazole-ethanol solution was added and reacted at room temperature for 45 min. The reacted sample was quantified using a UV-Vis spectrum.
2.3. Effect of variables on sodium alginate yield using microwave-assisted extraction
Solid/liquid ratio, extraction temperature, and extraction solvent concentration were identified as variables significantly affecting sodium alginate extraction from
Undaria pinnatifida. The impact of these variables was investigated. Sodium alginate was extracted using a microwave system (Multiwave 5000, Anton Paar, Austria). Extraction time and solvent amount were set to be 5 min and 20 mL, respectively. Ranges for solid/liquid ratio, extraction temperature, and extraction solvent concentration were set to be 20~100 g/L, 50~90 ℃, and 1~10 %, respectively. Sodium alginate yield was calculated using the following equation:
2.4. Experimental design and statistical optimization
To determine optimal extraction conditions of sodium alginate from
Undaria pinnatfida, the D-optimal design of Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was used. Independent variables affecting sodium alginate extraction, such as solid/liquid ratio (x
1), extraction temperature (x
2), and extraction solvent concentration (x
3), were selected (
Table 1), with the response being the yield (%) of sodium alginate. The relationship between variables affecting the response was estimated using the following quadratic equation:
where Y was the dependent variable (Sodium alginate yield), x
i and x
j were independent variables, β0 was the offset term, β
i was the first-order model coefficient, βii was the second-order model coefficient for variable i, and β
ij was the linear model coefficient for the interaction between variables i and j [
16].
2.5. Analytical methods
2.5.1. HPLC
Extracted samples were diluted and quantified using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) according to a previous method with slight modifications [
17]. Quantification was performed using a Shimadzu HPLC system (SPD-20A, Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with a UV detector and a C18 stationary phase column (5 μm, 4.6 x 150 mm). The mobile phase was a buffer solution (0.5 mL of phosphoric acid in 1L of deionized water). Its pH was adjusted to 7.0 using 1M NaOH. The flow rate was set to be 0.6 mL/min. The temperature was set at 25 ℃. An injection volume of 20 μL was used. Sodium alginate was analyzed at a wavelength of 200 nm.
2.5.2. FT-IR
Functional groups of precipitated and dried sodium alginate from the extract were identified using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR; FT/IR-1600, Jasco, Japan) [
18]. Measurements were recorded in the range of 4000~500 cm
-1 with a resolution of 4 cm
-1. The IR laser wavenumber, scanning speed, and aperture were set to be 15802.00 cm
-1, 2 mm/sec, and 7.1 mm, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of components in Undaria pinnatifida
To evaluate the potential of
Undaria pinnatifida as a source of sodium alginate, carbohydrate compositions of
Undaria pinnatifida were investigated (
Table 2). Quantitative analysis of monosaccharides showed the presence of 4.9 % glucose and a combined 3.0 % of xylose/mannose/galactose. However, arabinose was not detected. The content of sodium alginate was quantified at 41.11 %, consistent with previous reports showing that sodium alginate contents in
Undaria pinnatifida were 35~40 wt% [
19,
20,
21]. Research has also shown that spore leaves, which are often discarded for edible uses, contain the highest amount of sodium alginate [
22]. This analysis confirms the high potential of
Undaria pinnatifida as a biomass resource given its high sodium alginate content and the utilization of otherwise discarded parts.
3.2. Investigation of variables affecting sodium alginate microwave-assisted extraction
Previous studies have suggested that solvent type, solvent concentration, solid-to-liquid ratio, temperature, and time can affect sodium alginate extraction from brown algae [
9,
23,
24,
25]. Solvent concentration, solid-to-liquid ratio, and temperature were found to be significant variables. Their effects on sodium alginate extraction from
Undaria pinnatifida were studied. Alkaline solvents are reported to be favorable for extracting sodium alginate from algae, as alginic acid, mainly present as calcium salts in brown algae, undergoes ion exchange to form soluble sodium alginate [
26]. Acid pretreatment has been reported to enhance extraction efficiency, although the difference is minimal and non-essential [
26]. An alkaline single-step process also simplifies the procedure, offering environmental and economic benefits.
Preliminary investigations were carried out to set significant ranges for RSM. Variables were extraction temperature (50, 70, 90 ℃), extraction solvent concentration (1, 5, 10 % (w/v)), and solid/liquid ratio (20, 60, 100 g/L). Results of preliminary experiments are presented in
Table 3. The solid/liquid ratio showed a significant decrease in yield as it increased from 20 g/L to 100 g/L. The decrease in solid/liquid ratio increased the amount of alkaline solution used for a certain weight of algae, allowing more Na+ ions for ion exchange with Ca2+ ions and increasing the amount of soluble sodium alginate formed. However, very low S/L ratios could complicate industrial application. Hence, a range of 10~30 g/L was set as the optimum. The extraction temperature showed increased yields as temperature increased from 50 ℃ to 90 ℃. This was attributed to enhanced penetration of the alkaline solution into cell walls, increasing the solubility and dissociation rate of sodium alginate [
17]. Therefore, the extraction temperature range for optimization was set to be 50 ℃ to 100 ℃. The extraction solvent concentration showed a decrease in yield with increasing concentration. This was because sodium alginate decomposed into monocarboxylic and dicarboxylic acids at high alkali concentrations, particularly at pH above 10 [
27].
For sodium alginate extraction using alkali, preliminary experiments defined the following ranges for significant variables: 10~30 g/L for solid/liquid ratio, 50~100 ℃ for extraction temperature, and 1~5 % for extraction solvent concentration. There ranges were consistent with previous research [
24].
3.3. Optimization of alkali extraction conditions for Undaria pinnatifida using RSM
To determine To optimize alkali extraction conditions for sodium alginate, D-optimal designs in response surface methodology (RSM) were employed. RSM is a statistical and mathematical tool for reliable data analysis of interactions between multiple variables and their effects on the response. D-optimal designs can efficiently reduce the number of required test runs compared to other RSMs [
28]. A total of 20 experiments were designed to study effects of three independent variables (x
1= solid/liquid ratio, x
2 = extraction temperature, x
3 = extraction solvent concentration) on sodium alginate yield (Y) (
Table 4).
Regression analysis based on experimental data (
Table 4) yielded the following predictive quadratic polynomial model:
Here, factors were investigated in relation to their impact on sodium alginate yield (Y).
Table 5 presents ANOVA results for the second-order response surface model. The model and its terms were significant, as indicated by a high F value of 54.29 and a low P-value of < 0.0001. Independent variables x
1, x
2, and x
3 were significant (p < 0.05) model terms for the yield of sodium alginate. The interaction term x
2x
3 (P = 0.0002) was significant, unlike x
1x
2 (P = 0.1690) or x
1x
3 (P = 0.1677). The coefficient of determination (R
2) was very high at 0.9799, well above the significant value of 0.9 [
29]. The coefficient of variation (CV) was low at 3.0121 %, far below the 10% threshold [
29], indicating the model's accuracy and reliability. Adequate precision was high at 23.4970, significantly above the desirable value of 4 [
30], showing that the model could be effectively used to navigate the design space.
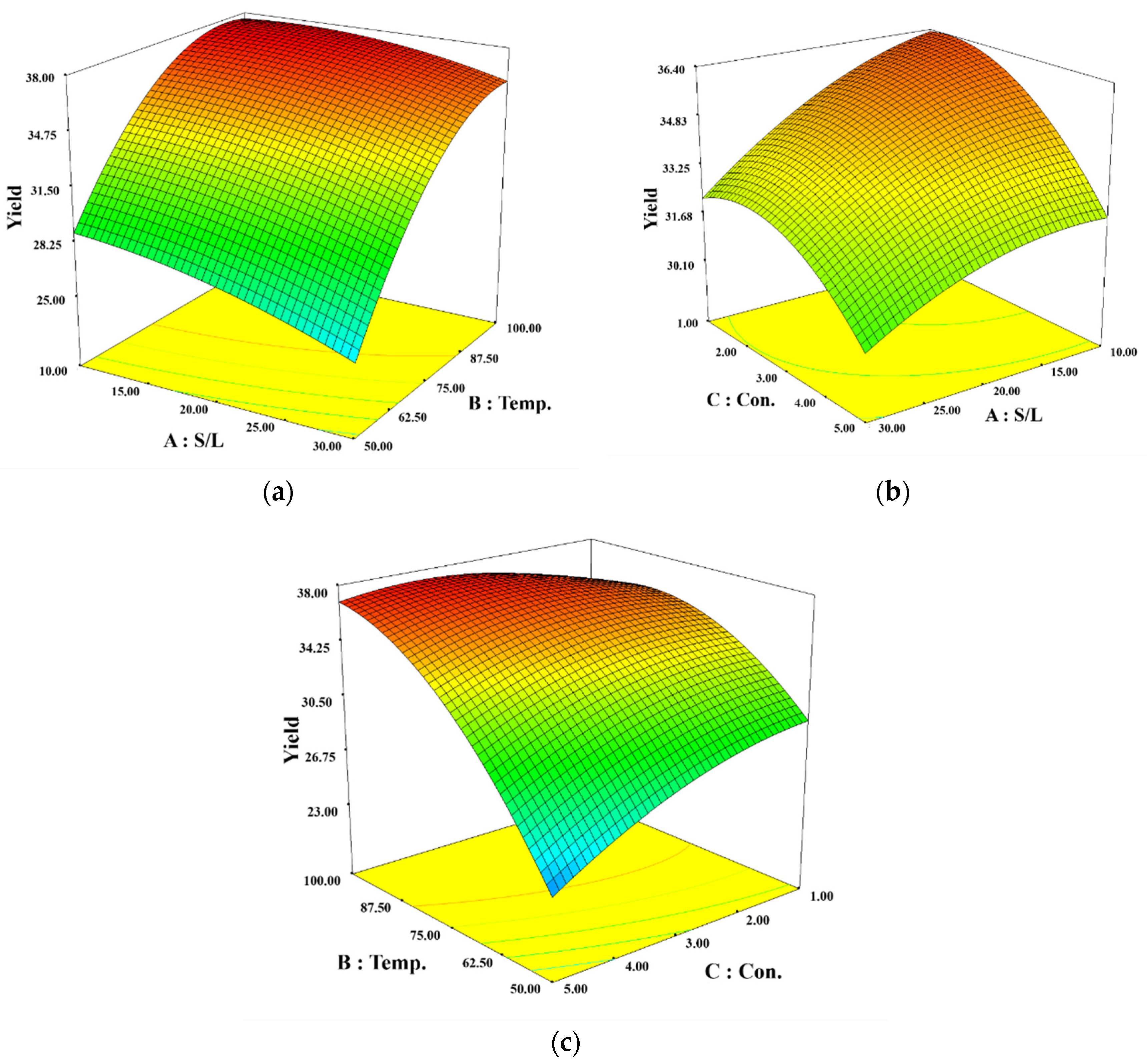
Interactions between independent variables and their effects were visualized in 3D response surface plots shown in
Figure 1.
Figure 1 (a) displays the interaction between S/L and Temp., showing an increase in sodium alginate yield with decreasing S/L and increasing Temp. The yield was particularly high (above 35 %) at temperatures above 90 ℃.
Figure 1 (b) illustrates the interaction between S/L and Con., where a decrease in both S/L and Con. increased the yield of sodium alginate, showing less variation in yield due to these variables in the specified range.
Figure 1 (c) shows interaction between Temp. and Con. Increasing Temp. enhanced sodium alginate yield. Yield also increased with decreasing Con. as Temp. increased.
Optimal conditions for the highest yield of sodium alginate using a microwave system were found to be: a solid/liquid ratio of 13.27 g/L, an extraction temperature of 91.86 ℃, and an ex-traction solvent concentration of 2.51 % (w/w). Under these optimal conditions, the model predicted a sodium alginate yield of 37.79 %, which was validated by an experimental yield of 36.21 % (
Table 6).
3.4. Effect of extraction time on yield
Optimal extraction time was investigated using RSM (
Figure 2). The extraction time was set at 5, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min, with the highest yield of 38.41 % observed at 15 min. It was also found that under the optimized high-temperature conditions, prolonged extraction time caused more sodium alginate degradation, resulting in decreased yield. The decrease in yield over time might be due to decomposition of sodium alginate into new dicarboxylic saccharinate compounds under high temperature and alkaline conditions [
31]. This aligns with previous studies using microwave and ultrasound hybrid systems, suggesting a negative impact of increased extraction time on sodium alginate yield. Therefore, the extraction time is a crucial factor affecting the yield of sodium alginate, with the optimal time being 15 min. This finding serves as an important indicator for optimizing the sodium alginate extraction process.
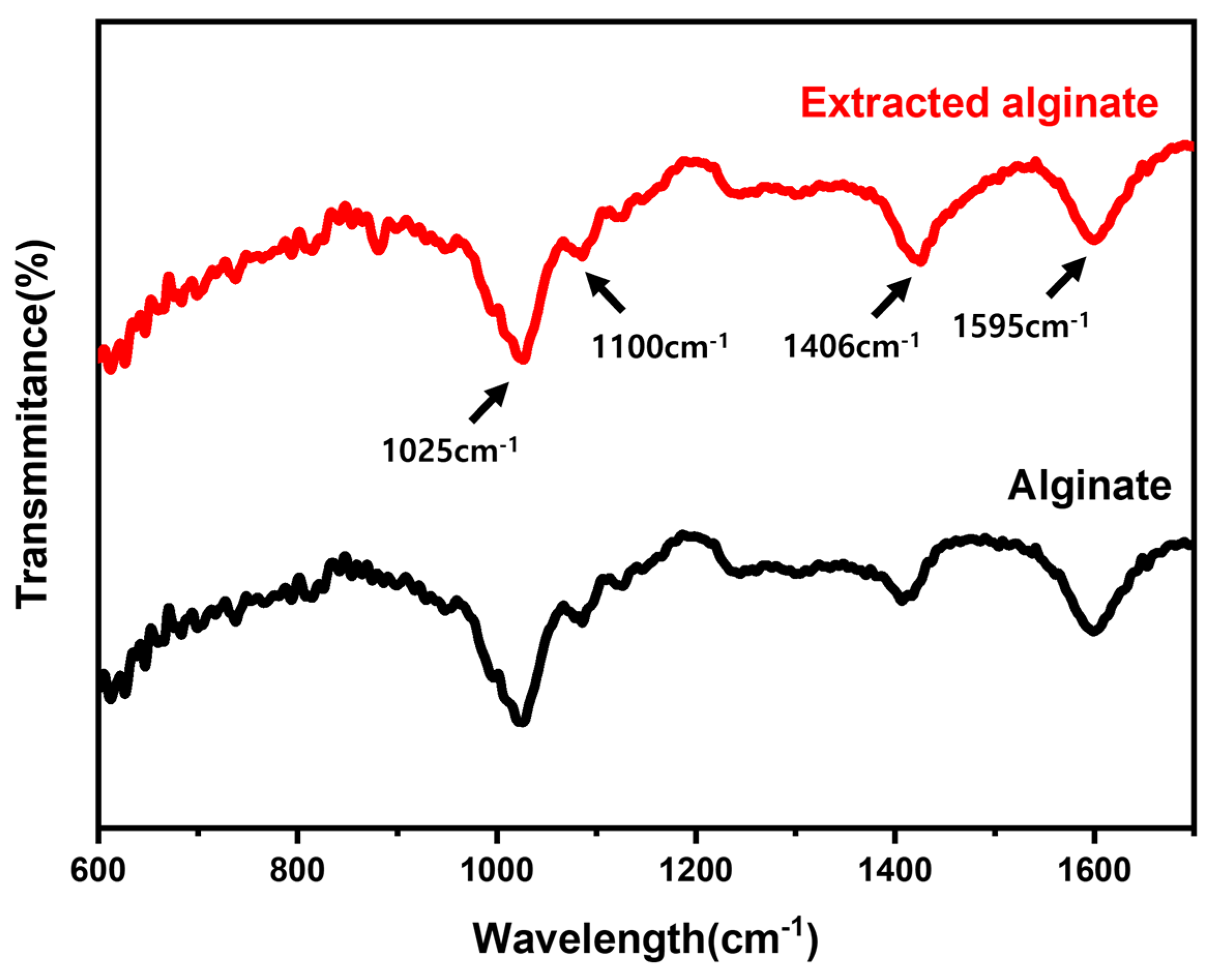
3.5. FT-IR
FT-IR spectra in
Figure 3 showed peaks representing functional groups present in the sodium alginate structure. A notable peak at 1025 cm
-1 represented C-C stretching vibrations of the pyranose ring. The peak at 1100 cm
-1 was attributed to C-O stretching vibrations of the C-O-C glycosidic bond. Previous papers have identified G-blocks at the 1025 cm
-1 band and M-blocks at the 1100 cm
-1 band [
32]. Peaks at 1595 cm
-1 and 1406 cm
-1 were attributed to asymmetric stretching vibrations of carboxylate groups (COO
-) and weak carboxylate symmetric vibrations of mannuronate and guluronate residues, respectively [
17]. The extracted sodium alginate showed similar functional groups to commercial sodium alginate, suggesting a similar structure composed of guluronic and mannuronic acid units.
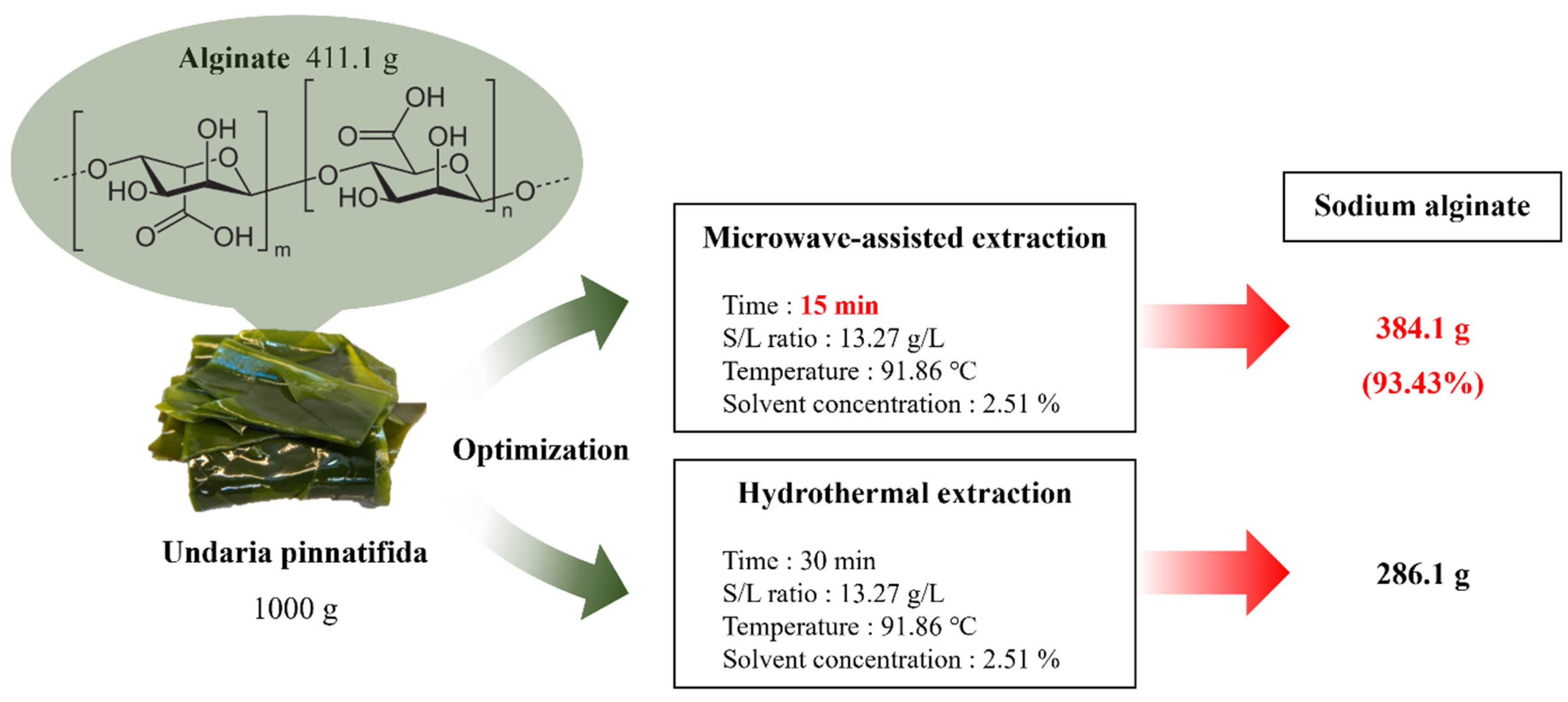
3.6. Evaluation of the sodium alginate extraction process
Mass balance for the sodium alginate extraction process according to the extraction system is presented in
Figure 4. The MAE sodium alginate extraction process was optimized at an S/L ratio of 13.27 g/L, an extraction temperature of 91.86 ℃, a solvent concentration of 2.51 %, and an extraction time of 15 min. Under these conditions, approximately 384.1 g of sodium alginate was obtained from 1000 g of
Undaria pinnatifida, equating to 93.43 % of the theoretical sodium alginate content of 411.1 g. The maximum yield achievable through hydrothermal extraction was 386.1 g even after 30 min, whereas our process achieved a 1.34 times higher yield in just 15 min. This aligned with previous research, suggesting that microwaves could accelerate the extraction process and increase the efficiency through electromagnetic effects on the cell structure [
19]. However, the potential of microwaves to disrupt polymer chains necessitates consideration when setting optimal extraction conditions [
21].
Table 7 presents studies of sodium alginate extracted from algae through various methods and conditions. Compared to traditional hydrothermal extraction, which typically features high extraction temperatures, long extraction time, and no safety hazards, microwave systems offer advantages of high extraction speed, low energy consumption, and minimal waste production [
33]. Thus, in the current context with increasing interest in sustainable development, microwave systems can be a viable eco-friendly technology in extraction processes. In this study, a process was designed to recover a high yield of 38.41 % sodium alginate in just 15 min, compared to other processes.
4. Conclusions
This study proposed a new biorefinery approach for utilizing Undaria pinnatifida as an effective source for sodium alginate extraction and identified optimal extraction conditions through statistical analysis. Optimal conditions established for sodium alginate extraction from Undaria pinnatifida were: a solid/liquid ratio of 13.27 g/L, an extraction temperature of 91.86 ℃, and an extraction solvent concentration of 2.51 % (w/v). Under these conditions, microwave-assisted extraction yielded a maximum yield of 38.61 % in just 15 min, 1.34 times higher than traditional hydrothermal extraction. This result lays an important foundation for our subsequent research in evaluating potential utilization of sodium alginate in various fields such as the food industry, medical sector, biotechnology, and 3D printing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.B.N.; methodology, K.H.L. and H.Y.Y.; software, K.H.L.; validation, J.H.L., C.P. and J.M.L.; formal analysis, H.B.N.; investigation, H.B.N.; data curation, K.H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.B.N. and K.H.L.; writing—review and editing, J.H.L., C.P. and J.M.L.; visualization, H.B.N. and K.H.L..; supervision, H.Y.Y.; project administration, J.H.L. and J.M.L.; funding acquisition, J.H.L.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Soonchunhyang University Research Fund (No. 20220461). This work was supported by a grant (NRF-2022R1F1A1071014 to Professor Lee JH) of National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korea government (MSIT).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Chen, L.; Msigwa, G.; Yang, M.; Osman, A. I.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D. W.; Yap, P. S. Strategies to achieve a carbon neutral society: a review. Environ Chem Lett 2022, 20(4), 2277–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathour, R. K.; Devi, M.; Dahiya, P.; Sharma, N.; Kaushik, N.; Kumari, D.; Kumar, P.; Baadhe, R. R.; Walia, A.; Bhatt, A. K.; Bhatia, R. K. , Recent Trends, Opportunities and Challenges in Sustainable Management of Rice Straw Waste Biomass for Green Bio-refinery. Energies 2023, 16(3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E. K.; Yotsukura, N.; Pang, S. J.; Su, L.; Shan, T. F. , Seaweed breeding programs and progress in eastern Asian countries. Phycologia 2019, 58(5), 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovich, R.; Neori, A.; Valderrama, D.; Reddy, C. R. K.; Cronin, H.; Forster, J. , Farming of seaweeds. In Seaweed Sustain-ability, 2015; pp 27-59. [CrossRef]
- Fisheries, F. , The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. 2006. 2007.
- Choi, Y.; Lee, E. C.; Na, Y.; Lee, S. R. , Effects of dietary supplementation with fermented and non-fermented brown algae by-products on laying performance, egg quality, and blood profile in laying hens. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2018, 31(10), 1654–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J. S.; Shin, S. K.; Wu, H.; Yarish, C.; Yoo, H. I.; Kim, J. K. , Evaluation of nutrient bioextraction by seaweed and shellfish aquaculture in Korea. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society 2021, 52(5), 1118–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Park, Y.-J.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Ryu, B. , Bioactivities of the edible brown seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida: A review. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 873–880 [. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, S.; Hebden, A.; Goswami, P.; Du, C. A Brief Review on the Development of Alginate Extraction Process and Its Sustain-ability. Sustainability 2022, 14(9). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothale, D.; Verma, U.; Dewangan, N.; Jana, P.; Jain, A.; Jain, D. Alginate as promising natural polymer for pharmaceutical, food, and biomedical applications. Current drug delivery 2020, 17(9), 755–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C. H.; Yusoff, R.; Ngoh, G. C.; Kung, F. W. Microwave-assisted extractions of active ingredients from plants. J Chro-matogr A 2011, 1218(37), 6213–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoore, R. V.; Butler, T. O.; Pandhal, J.; Vaidyanathan, S. , Microwave-Assisted Extraction for Microalgae: From Biofuels to Biorefinery. Biology (Basel) 2018, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, K.; Katuwal, S.; Biswas, A.; Sharma, B. K. , Effective delignification of lignocellulosic biomass by microwave assisted deep eutectic solvents. Bioresour Technol 2020, 303, 122897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattina, M. I.; Berger, W. I.; Denson, C. Microwave-assisted extraction of taxanes from Taxus biomass. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 1997, 45(12), 4691–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Lu, C.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Duan, D. Transcriptome sequencing of Saccharina japonica sporophytes during whole developmental periods reveals regulatory networks underlying alginate and mannitol biosynthesis. BMC Genomics 2019, 20(1), 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba-Abbad, M. M.; Kadhum, A. A. H.; Mohamad, A. B.; Takriff, M. S.; Sopian, K. Optimization of process parameters using D-optimal design for synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via sol–gel technique. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2013, 19(1), 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Rivers, A.; Stuckey, D. C.; Ward, K. , Alginate extraction from Sargassum seaweed in the Caribbean region: Optimization using response surface methodology. Carbohydr Polym 2020, 245, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fertah, M.; Belfkira, A.; Dahmane, E. m.; Taourirte, M.; Brouillette, F. , Extraction and characterization of sodium alginate from Moroccan Laminaria digitata brown seaweed. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2017, 10, S3707–S3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.-G. , Chemical composition and rheological properties of polysaccharides isolated from different parts of brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida. Korean Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2020, 53(5), 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skriptsova, A.; Khomenko, V.; Isakov, V. , Seasonal changes in growth rate, morphology and alginate content in Undaria pin-natifida at the northern limit in the Sea of Japan (Russia). Journal of applied phycology 2004, 16, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.-O.; Lee, S.-C.; Rhim, J.-W.; Kim, J.-M. , Comparison of alginic acid yields and viscosity by different extraction con-ditions from various seaweeds (Laminaria religiosa, Hizikia fusiforme, and Undaria pinnatifida). JOURNAL-KOREAN SOCIETY OF FOOD SCIENCE AND NUTRITION 2004, 33(4), 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J. , A study on mineral and alginic acid contents by different parts of sea mustards (Undaria pinnatifida). Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture 2004, 19(6), 691–700. [Google Scholar]
- Lorbeer, A. J.; Lahnstein, J.; Bulone, V.; Nguyen, T.; Zhang, W. , Multiple-response optimization of the acidic treatment of the brown alga Ecklonia radiata for the sequential extraction of fucoidan and alginate. Bioresour Technol 2015, 197, 302–9 [. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, A.; Holdt, S. L.; De Francisci, D.; Alvarado-Morales, M.; Mishra, H. N.; Angelidaki, I. , Extraction of alginate from Sargassum muticum: process optimization and study of its functional activities. Journal of Applied Phycology 2016, 28(6), 3625–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiono, S.; Masruri, M.; Estiasih, T.; Widjanarko, S. B. Optimization of extrusion-assisted extraction parameters and charac-terization of alginate from brown algae (Sargassum cristaefolium). J Food Sci Technol 2019, 56(8), 3687–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Carmona, G.; McHugh, D. J.; Arvizu-Higuera, D. L.; Rodríguez-Montesinos, Y. E. , Pilot plant scale extraction of alginate from Macrocystis pyrifera. 1. Effect of pre-extraction treatments on yield and quality of alginate. Journal of Applied Phycology 1998, 10, 507–513. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, M.; Cortizo, A.; Oberti, T.; Fernández, J. Characterization of commercial and algae (Undaria pinnatifida) extracted sodium alginate for future application in bone tissue engineering. In Colaob. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.-E.; Perera, R. , Damage identification by response surface based model updating using D-optimal design. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2011, 25(2), 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B. G.; Fidell, L. S. , Experimental designs using ANOVA. Thomson/Brooks/Cole Belmont, CA: 2007; Vol. 724.
- Chauhan, B.; Gupta, R. , Application of statistical experimental design for optimization of alkaline protease production from Bacillus sp. RGR-14. Process Biochemistry 2004, 39(12), 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Bissoon, R.; Bajnath, E.; Mohammed, K.; Lee, T.; Bissram, M.; John, N.; Jalsa, N. K.; Lee, K. Y.; Ward, K. , Mul-tistage extraction and purification of waste Sargassum natans to produce sodium alginate: An optimization approach. Car-bohydr Polym 2018, 198, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liudvinaviciute, D.; Rutkaite, R.; Bendoraitiene, J.; Klimaviciute, R.; Dagys, L. , Formation and characteristics of alginate and anthocyanin complexes. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 164, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, S. , Ultrasonic- and microwave-assisted extraction and modification of algal components. In Functional Ingredients from Algae for Foods and Nutraceuticals, 2013; pp 585-605.
- Faidi, A.; stumbé, J. F.; Safta, F.; Sfar, S. , Implementation of response surface methodology for the optimization of the extraction of sodium alginate from Padina pavonica brown algae. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization 2022, 16(6), 4457–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C. G.; Perez Lambrecht, M. V.; Lozano, J. E.; Rinaudo, M.; Villar, M. A. , Influence of the extraction-purification con-ditions on final properties of alginates obtained from brown algae (Macrocystis pyrifera). Int J Biol Macromol 2009, 44(4), 365–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borazjani, N. J.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.; Rezaei, M. , Effects of extraction methods on molecular characteristics, antioxidant prop-erties and immunomodulation of alginates from Sargassum angustifolium. Int J Biol Macromol 2017, 101, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez-Fernandez, N.; Dominguez, H.; Torres, M. D. , A green approach for alginate extraction from Sargassum muticum brown seaweed using ultrasound-assisted technique. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 124, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, P.; Hamdami, N.; Keramat, J. , Microwave-assisted extraction of sodium alginate from brown macroalgae Nizimuddinia zanardini, optimization and physicochemical properties. Separation Science and Technology 2021, 57(6), 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).