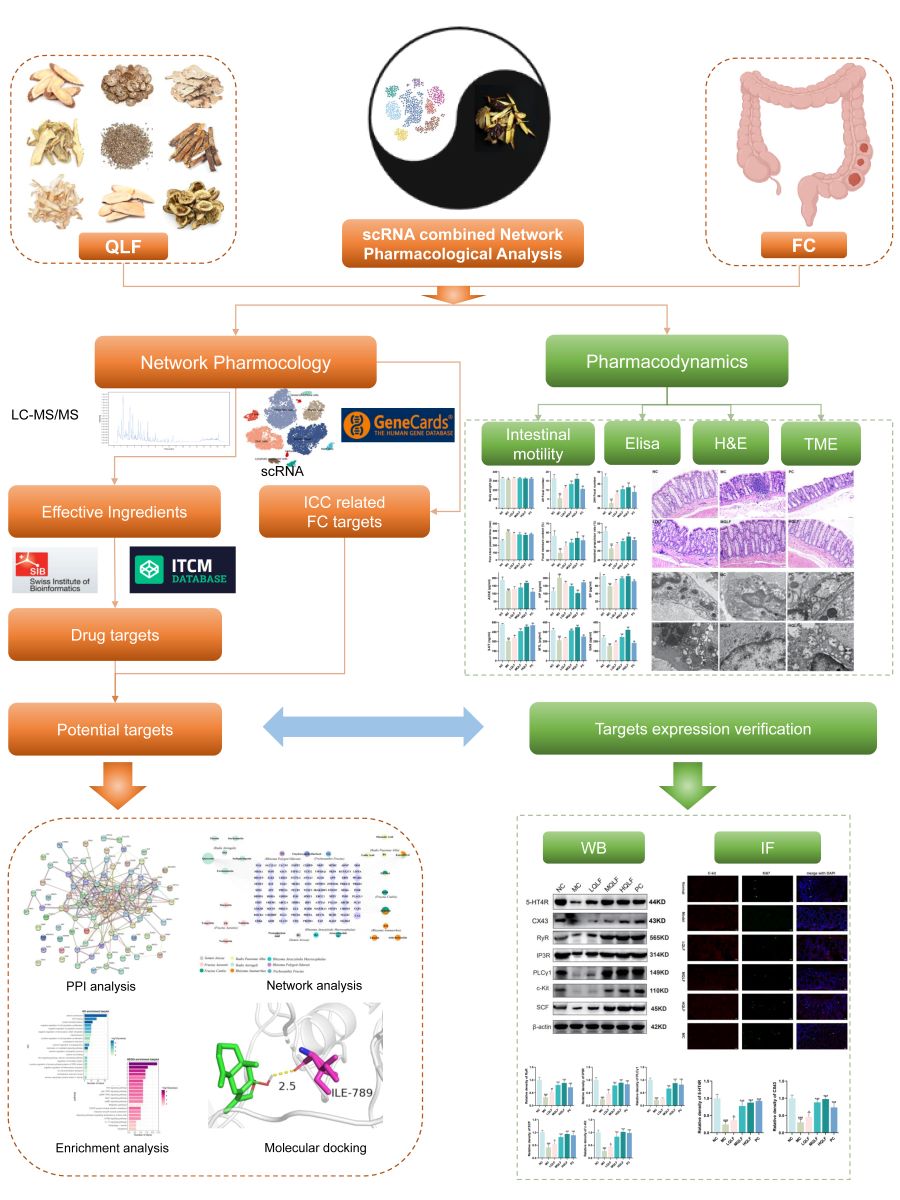
Introduction
Constipation is a gastrointestinal functional disorder characterized by infrequent bowel movements, prolonged defecation time, difficulty passing stool, dry and hard stool, abdominal pain, and other symptoms. According to Rome Ⅳ, the global average prevalence of constipation is 10.1%[
1]. In Europe and America, the incidence of constipation is as high as 14% to 30%, whereas in China, the prevalence is approximately 8.5%[
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. Presently, primary constipation management strategies encompass dietary and lifestyle adjustments, rehabilitation training, surgical interventions, laxative administration, and medications to enhance bowel motility. However, their effectiveness is constrained, frequently failing to provide a lasting solution and potentially fostering a reliance on laxatives. These approaches often fall short of desired outcomes and may result in medication dependence for individuals with constipation. Past studies suggested that traditional Chinese medicine offered potential benefits with fewer side effects[
7,
8,
9,
10]. The Qilang formula (QLF) is proved to be effective for chronic constipation in clinical practice. Researchers observed increased levels of serum motilin (MTL), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), and short-chain fatty acids in feces, along with decreased serum NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12, and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) after QLF treatment for constipation. This suggests that QLF may work by modulating these factors, but its precise pharmacological mechanism remains uncertain. To address this, our study combines data analysis and empirical validation.
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) were pacemaker cells mainly located in the muscular layer of the gastrointestinal tract[
11,
12,
13]. The number and structure of ICC were associated with gastrointestinal motility[
14,
15]. Studies showed that KIT (also known as KIT proto-oncogene, c-Kit, and CD117), a cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase, was a marker of ICC in the digestive tract[
16]. The SCF/c-Kit signaling pathway could affect the differentiation, proliferation, and phenotype maintenance of ICC. Furthermore, it was essential for the generation of slow-wave activity in the gastrointestinal muscles[
17,
18]. Studies indicated that constipated patients had fewer or less dense ICC in the colon than normal individuals, and cell morphology changes, such as the shortening of synapses, and the alteration or ablation of the colonic ICC network, could lead to colonic motility dysfunction, such as constipation[
19]. Another study found that the epidural infusion of morphine combined with low-dose naloxone could effectively inhibit rabbit gastrointestinal motility by reducing ICC in the proximal colon of rabbits[
20]. In summary, ICC was closely related to the occurrence of constipation. Therefore, this study explored the effect of QLF on ICC to investigate the mechanism of QLF in treating constipation.
In our research, we employed scRNA-seq data combined with the Genecards database to identify targets related to ICC-associated constipation. We then compared drug and disease targets to identify those QLF addresses when countering ICC-associated constipation. Through western blot (WB) experiments, we observed that QLF up-regulated the protein expression of c-Kit/SCF signaling pathways. Immunofluorescence (IF) experiments indicated that QLF promoted ICC proliferation. In summary, QLF may alleviate constipation symptoms by promoting ICC proliferation, restoring intestinal motility, and upregulating the SCF/c-Kit signaling pathways and their downstream targets. The workflow of this study is shown in
Figure 1.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
The Qilang formula is provided by Shanghai Wanshicheng Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Mosapride citrate was purchased from Chengdu Kanghong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China). Diphenoxylate was purchased from Shandong Renhetang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Linyi, China). Motile (MTL), gastrin (GAS), substance P (SP), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) ELISA kits were purchased from Shanghai Primacy Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Powdered activated carbon and gum Arabic from Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.2. Preparation and qualitative analysis of QLF
QLF consists of 9 traditional chinese herbs, including Radix Astragali, Semen Arecae, Fructus Aurantii, Rhizoma Anemarrhee, Rhizoma Polygonati Odorati, Trichosanthis Fructus, Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae, Fructus Canbis, and Radix Paeoniae Alba. The ratio of each component is as the following 15:15:15:9:15:15:30:30:30. The QLF used in our experiment is provided by Shanghai Wanshicheng Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
UPLC-MS/MS analysis was performed on an UHPLC system (Vanquish, Thermo Fisher Scientific) with a Waters UPLC BEH C18 column (100 mm*2.1mm, 1.7 μm). The mobile phase is 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution (A) and 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile solution (B). Gradient elution procedure: 0-11 min, 85-25% A; 11-12 min, 25-2% A; 12-14min, 2-2% A; 14-14.1 min, 2-85% A. The column temperature was 50℃, the flow rate was 0.5mL· min-1, and the sample volume was 5μL. An Orbitrap Exploris 120 mass spectrometer coupled with an Xcalibur software was employed to obtain the MS and MS/MS data based on the IDA acquisition mode. During each acquisition cycle, the mass range was from 100 to 1500, and the top four of every cycle were screened and the corresponding MS/MS data were further acquired. Sheath gas flow rate: 35 Arb, Aux gas flow rate: 15 Arb, Ion Transfer Tube Temp: 350 ℃, Vaporizer Temp: 350 ℃, Full MS resolution: 60000, MS/MS resolution: 15000, Collision energy: 16/38/42 in NCE mode, Spray Voltage: 5.5 kV (positive) or -4 kV (negative).
2.3. Network pharmacology
2.3.1. Drug targets of QLF
The results of UPLC-MS/MS combined with online databases such as PubMed (
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), Pubchem (
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), Herb (
http://herb.ac.cn/), ITCM (
http://itcm.biotcm.net/) and SwissADME (
http://www.swissadme.ch/) were used to collect the active ingredients and related targets of QLF. The screening criteria for this study focused on two main parameters: Lipinski rule as "YES" and high gastrointestinal (GI) permeability. Following active ingredient screening with these criteria, drug targets were identified using Herb and ITCM databases, and relevant literature was consulted. To improve prediction accuracy, we consolidated data from these databases and removed duplicate entries.
2.3.2. Dimensionality Reduction, Clustering and Annotation of scRNA-Seq Data
Download 10×scRNA-seq data from 14 colon samples from the GSE156905 series[
21]. The "Seurat" R package was utilized to convert the data into a Seurat object. The following functions are all derived from Seurat. Quality control was conducted on the raw counts by calculating the percentages of mitochondrial and erythrocyte genes and excluding cells with low quality. Subsequently, homogenization was carried out using the "NormalizeData" function. The top 3000 highly variable features were filtered using the "FindVariableFeatures" function, and normalization was performed using the "ScaleData" function. Principal component analysis (PCA), a preliminary linear dimensionality reduction method, was applied to the scaled data, with batch effects eliminated using the default settings of Harmony (v1.0). The t-SNE algorithm, a nonlinear dimensionality reduction technique, was employed for cluster identification. Biologically significant cell types were annotated using the "FindAllMarkers" function to identify representative genes for each cluster in conjunction with typical cell markers.
2.3.3. Therapeutic targets for constipation
Genecards (
https://www.genecards.org/) is a comprehensive and integrated database that utilizes a comprehensive calculation of disease-gene relevance scores to discover disease-associated genes. The target of constipation was collected with the keyword "constipation". ICC marker genes were obtained from the above scRNA-seq data. Conclusively, online Venn diagram tool “jvenn” (
https://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/static/others/jvenn/example.html) was used to identify potential targets for QLF targeting ICC for constipation treatment.
2.3.4. Network construction
The potential targets of QLF targeting ICC against constipation were uploaded to the online tool String database (
https://string-db.org/), and the minimum required interaction score was set to the highest confidence (0.4) as the threshold for screening. Subsequently, PPI and drug-ingredient-target networks were constructed using Cytoscape 3.9.1 software. The PPI network were further analyzed using the cytoHubba plugin to identify and prioritize the hub targets.
2.3.5. Enrichment analysis
The KOBAS database (
http://kobas.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) was utilized for conducting GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. The analysis results were filtered to select items with smaller p-values. R language was used to visualize the results. The top 20 significant KEGG pathways (P < 0.05) and the top 20 GO enrichments (P < 0.05) were plotted separately using bar graphs.
2.4. Molecular docking
Hub targets and active ingredients earlier filtered by network pharmacology were docking with AutoDock Vina. The structural formulas of active ingredients were obtained from the PubChem database (
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Chem3D software was utilized to generate 3D structures of these active ingredients. The 3D structures of the target proteins were downloaded from the PDB database (
http://www.rcsb.org/). PyMOL software was employed for protein-related operations, including dehydration and hydrogenation. Furthermore, AutoDockTools (v1.5.7) software was utilized to search for ligand-binding pockets. Subsequently, the Vina script was applied to calculate molecular binding energy and visualize the molecular docking results. Finally, the obtained results were imported into PyMOL for visualization.
2.5. Animals
48 healthy male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (12 weeks old) were provided by Sipeifu (Beijing) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (certificate numbers: SCXK (Jing) 2019-0010; Beijing, China). The animal experimental procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Approved on February 9, 2022; NO.202201). All rats were kept in an animal laboratory with a specific pathogen free (SPF) environment (certificate numbers: SCXK (Hu) 2020-0014; Shanghai, China). Feeding conditions: Room temperature maintained at (22±4) ℃, humidity at (52±8) %, 12 hours of daylight exposure per day, 12 hours of darkness, free access to food and water.
2.6. Establishment of rat model and drug administration
After a 7-day adaptation period, 48 rats were randomly and evenly divided into the following 6 groups: Normal control group (Normal) received ultrapure water; Model group (Model) received diphenoxylate; Low-dose QLF group (LQLF) was induced with diphenoxylate and orally administered QLF at a dosage of 8.95 g/kg per day; Medium-dose QLF group (MQLF) was induced with diphenoxylate and orally administered QLF at a dosage of 17.89 g/kg per day; High-dose QLF group (HQLF) was induced with diphenoxylate and orally administered QLF at a dosage of 35.78 g/kg per day; Mosapride Citrate group (MC) received diphenoxylate and orally administered mosapride citrate at a dosage of 1.54 mg/kg per day. The MQLF dosage used in rats was calculated from clinical dosage using the following formula: MQLF dosage = 174 g × 6.17 / 60 kg. The clinical drug dosage of QLF was 174 g/person/day, and the average body weight of normal adults was 60 kg, resulting in an equivalent dose ratio of 6.17 between rats and humans. Except for the Normal group, all other groups were orally administered diphenoxylate at a dosage of 50 mg/kg/day for 14 consecutive days to establish the constipation rat model. All animals were orally administered ultrapure water, QLF or mosapride citrate tablets according to the designated dosages for a duration of 14 days.
2.7. Measurement of laxative effect of QLF on model rats
2.7.1. Calculation of first defecation time and fecal moisture content
The rats were fasted for 24 hours prior to the final administration. Thirty minutes after the final administration, they were orally administered 1 ml of a 10% activated charcoal suspension. Normal drinking water and food intake were restored, and the rats were individually housed. The time of the first defecation was recorded. Rat feces were collected within a 4-hour period and weighed fresh and dried. The feces were placed in a 90℃ electric constant temperature oven and continuously heated until a constant weight was obtained. Fecal moisture content was measured using the following formula: Fecal moisture content (%) = (wet weight - dry weight) / wet weight × 100%.
2.7.2. Determination of intestinal propulsion rate
After a 24-hour fasting period following the last administration, the rats were orally administered 1 mL of a 10% activated charcoal suspension. Then, 30 minutes later, rats were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of 50 mg/kg of pentobarbital sodium. and killed by bloodletting via the main abdominal vein. The entire length of the small intestine from the pylorus to the cecum was carefully removed. In a tension-free state, the total length of the small intestine (L1) and the distance from the pylorus to the leading edge of the black charcoal were measured (L2). The intestinal propulsion rate was calculated using the following formula: Intestinal propulsion rate = L2/L1 × 100%.
2.8. ELISA assay
Whole blood was collected while the serum was isolated through centrifugation. The level of MTL, GAS, SP, 5-HT, AChE and VIP were assayed by ELISA kits according to their protocols.
2.9. H&E staining
Fresh colon tissue was fixed in 10% buffered formali for at least 24 hours, dehydrated, and then embedded in paraffin wax. Subsequently, 5-micron sections were cut and mounted on glass slides. One section per sample was subjected to hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining to evaluate histopathological changes.
2.10. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
We obtained about 1mm3 of proximal colon tissue, fixed it with 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 24h, then with 1% osmic acid for 2h, dehydrated it with ethanol and acetone gradient, embedded EMBed 812, and cut it into 60nm ultra-thin sections on an ultra-micro microtome. 2% uranium acetate saturated alcohol solution and 2.6% lead citrate solution were stained for 8 min, avoiding carbon dioxide. We observed mitochondria, autophagosome and Rough endoplasmic reticulum of colonic ICC under a HITACHI HT7800 transmission electron microscope.
2.11. Western blot
Proteins from colon tissue were extracted with RIPA cracking buffers containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Beyotime, Shanghai, China, Cat# P0013C). After centrifugation at 12000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C, the resulting supernatant was collected. Protein concentration was quantified using a BCA assay kit. Equal protein amounts were separated on SDS-PAGE gel, transferred onto a 0.45 μm PVDF membrane, and blocked with 5% BSA in TBST for 2 hours at room temperature. Membranes were incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies, including anti-CX43 (Cat#AB11370; Abcam, UK), anti-RyR (Cat#AB2868; Abcam, UK), anti-PLCγ1 (Cat#AB76155; Abcam, UK), anti-IP3R (Cat#AB108517; Abcam, UK), anti-5-HT4R (Cat#DF3503; Affinity Biosciences, China), anti-c-Kit (Cat#18696-1-AP; Proteintech, China) and anti-SCF (Cat#26582-1-AP; Proteintech, China), followed by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies. Enhanced chemiluminescence was used for band visualization, and Image J for band analysis and quantification.
2.12. Immunofluorescence staining
Paraffin was removed from the slide and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) at 4°C for 10 minutes. The slides were washed three times with PBS and treated with 0.1% Triton X-100 at room temperature for 20 minutes.The slides were blocked with 3%BSA solution at room temperature for 30min. Subsequently, slides were incubated overnight at 4°C with rabbit anti-rat Ki67 (Cat#AB16667; Abcam, UK) or rabbit anti-rat (Cat#18696-1-AP; Proteintech, China). After washing with PBS for three times, the slides were incubated with specific secondary antibody Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit (Cat#GB25303; Servicebio, China) or Cy3 conjugated goat anti-rabbit (Cat#GB21303; Servicebio, China) at room temperature for 50 minutes away from light. Glass slides were prepared by mounting coverslips, and the DNA was counterstained using staining reagent containing DAPI (Servicebio). Image were obtained on NIKON ECLIPSE C1 fluorescence microscope (Nikon).
2.13. Statistical analysis
All data were presented as mean ± SD and analyzed using GraphPad Prism 9.0 for statistical analysis and data visualization. For comparisons between two groups, the Student's t-test was utilized. For comparisons involving more than two groups, one-way analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA) was performed. The p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all results.
Discussion
Constipation not only takes a toll on a patient's physical and mental well-being but also places a significant financial strain on the healthcare system. Traditional Chinese Medicine approaches disease treatment with a multi-faceted strategy, encompassing various components, targets, pathways, and mechanisms[
8]. It is known for its minimal side effects, reduced chances of recurrence, and pronounced effectiveness. QLF has achieved good clinical results in the treatment of constipation. In a randomized controlled trial, the overall clinical effectiveness rate of QLF for constipation was as high as 91.1%[
25]. In addition, several herbs of QLF, such as
Fructus Aurantii, Radix Astragali, and
Rhizoma Atractylodis, have been used for centuries in the treatment of constipation[
26]. However, the mechanism of QLF in treating constipation is still largely unknown. In this study, we discovered that, in rats with constipation, QLF significantly improved intestinal motility, increased the moisture content of feces, modulated intestinal neurotransmission, and up-regulated the SCF/c-Kit pathway to restore the ICC phenotype.
Traditional techniques can only identify a few highly active compounds or components in herbal formulations, failing to systematically depict the complex efficacy network of traditional medicine. Single-cell omics technology could enhance the study of the targets of traditional Chinese medicine, providing more precise experimental data and further constructing a "drug-component-cell target" spatial regulation network. An increasing number of traditional Chinese medicine studies are utilizing single-cell technology to explore the microscopic effects of herbal formulations on cells[
27,
28]. We searched the GEO database for suitable single-cell data and combined it with network pharmacology, identifying the targets of QLF in treating constipation by targeting ICCs, and conducted subsequent research on the core targets.
Rhythmic slow waves of gastrointestinal muscle contraction are mediated by a variety of cell types, including smooth muscle cells, enteric neurons, telocytes, and ICC[
29]. ICC mediates nerve and smooth muscle cells and regulates the transmission of neuromuscular signals, thereby controlling the contraction and peristalsis of the corresponding digestive tract smooth muscle[
30]. Abnormalities in the number and structure of ICCs are associated with some gastrointestinal motility disorders[
29], such as functional dyspepsia (FD)[
31], intestinal obstruction[
32], Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) and constipation[
33,
34]. The SCF/c-Kit signaling pathway is crucial for the normal development, maturation, and survival of ICCs. It is essential for maintaining the phenotype and function of the ICC network[
35], therefore, KIT is widely used to specifically detect ICCs.
Gastrointestinal motility is regulated by gastrointestinal hormones, 5-HT is an important neurotransmitter in the enteric nervous system, and about 95% of 5-HT is produced in the gastrointestinal tract, which contributes to electrolyte secretion and absorption and intestinal peristalsis[
36]. 5-HT4R is an important 5-HT excitatory receptor that is widely present in the gastrointestinal tract. 5-HT4R is a structurally active Gs-coupled 5-HT receptor, and the distribution of 5-HT4R in intestinal smooth muscle can directly regulate the movement of smooth muscle[
37], playing a central role in gastrointestinal motility. In the intermuscular plexus, 5-HT4R promotes the release of neurotransmitters from the cholinergic system, thereby improving gastrointestinal smooth muscle contraction. In addition, 5-HT4R can increase secretion-enhancing pacing of ICCs[
38]. Endocrine disorders and neurologic deficits may lead to abnormal and inactivation of gastrointestinal hormone secretion, leading to further gastrointestinal dysfunction. Therefore, changing hormone levels will promote gastrointestinal motility. Our study found that QLF treatment not only reversed the recovery of neurotransmitters such as motilin, substance P, somatostatin, endothelin, and vasoactive intestinal peptide, but also upregulated the expression of c-Kit and SCF. In addition, the number of goblet cells and mucus layer thickness increased after QLF treatment, suggesting that improving gastrointestinal hormone secretion may be one of the key mechanisms of QLF in intestinal motility. Recent studies have revealed that a class of connexins found in colonic epithelial cells is strongly associated with gastrointestinal slow waves and gastrointestinal dyskinesia, and the expression of CX43 protein in the intestinal mucosa of patients with functional constipation is significantly reduced. ICCs are connected to other ICCs and smooth muscle cells through gap junction to form syncytia in gastrointestinal tissues[
11], CX43 is the main connexin of human slit junction, and its expression change is closely related to the occurrence of gastrointestinal diseases such as gastrointestinal tumors, Hirschsprung disease, and functional dyspepsia. Decreased expression of CX43 might lead to weakened cell-to-cell communication, suggesting that the onset of constipation may be related to the destruction of the gap junction between cells. The expression of CX43 in the model group we studied was reduced, so it can be seen that CX43 as a channel changes, so that the electrophysiological signals of the colon cannot be produced, and also affect the signal transmission to the smooth muscle of the colon, which in turn leads to colonic motility disorders, which may be one of the important mechanisms causing constipation[
39].
In this study, we observed that QLF elevated the protein levels of c-Kit, SCF, PLCγ, RyR, and IP3R in rat colon tissue. This suggested that QLF might enhance intestinal motility by promoting the expression of scf/c-Kit and its downstream pathway proteins, thereby reversing the phenotype of ICC. To comprehensively understand the effects of QLF on the SCF/c-Kit signaling pathway, we employed immunofluorescence to assess the proliferation of ICCs in different groups. Our results indicated that there was no significant ICC proliferation in the rats from the model group, but QLF seemed to augment ICC proliferation. c-Kit activation is followed by the recruitment and activation of several downstream signaling molecules including Erk 1/2, Grb2, p38 MAPK, SFK and PLCγ[
40]. There was a relationship between PLCγ activity and autophagy for the two hydrolysis products of PIP2 induced by PLC (IP3 and DAG). IP3 could activate IP3R to bidirectionally regulate autophagy[
41]. IP3R can also be combined with Beclin1 (IP3 bound domain via IP3R) and Bcl-2 (transduction domain in the middle of regulation and IP3R) to form Beclin1-IP3R-Bcl-2 complexes. This study indicated that the ICCs in the model group showed morphological mitochondrial swelling and autophagy, with a noticeable enlargement of some parts of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. This suggested that ICCs in constipated rats might have experienced excessive autophagy. However, after QLF intervention, the ICCs regained structural integrity to some extent, suggesting that QLF might inhibit excessive autophagy in ICCs of constipated rats.
However, there are some limitations to this study. First, we only verified the preliminary mechanism through molecular docking and in vivo experiments, not in vitro experiments. Second, we did not set up a target inhibitor group or agonist group for response experiments. Third, single cell transcriptome sequencing was not performed on colon tissues of constipated rats before and after drug treatment. Therefore, further in vitro and in vivo experiments as well as multi-omics experimental methods are needed to confirm the mechanism and effect of QLF against constipation by targeting ICC, so as to provide scientific basis for clinical application.
Figure 1.
Comprehensive workflow of the study.
Figure 1.
Comprehensive workflow of the study.
Figure 2.
Cell type constitution of the colon tissues. (A) t-SNE plots of cells from fourteen patients (14 samples). Colors represent cell types. Cells were clustered into 10 sub-clusters based on biological annotation. Each dot represents a single cell. (B) Violin plot of proportion of cells in the respective cluster expressing selected marker genes. Violin size represents the percentage of cells that express the gene. (C) Expression of the ANO1 at the single cell level. (D) The proportion of different cell types in sex.
Figure 2.
Cell type constitution of the colon tissues. (A) t-SNE plots of cells from fourteen patients (14 samples). Colors represent cell types. Cells were clustered into 10 sub-clusters based on biological annotation. Each dot represents a single cell. (B) Violin plot of proportion of cells in the respective cluster expressing selected marker genes. Violin size represents the percentage of cells that express the gene. (C) Expression of the ANO1 at the single cell level. (D) The proportion of different cell types in sex.
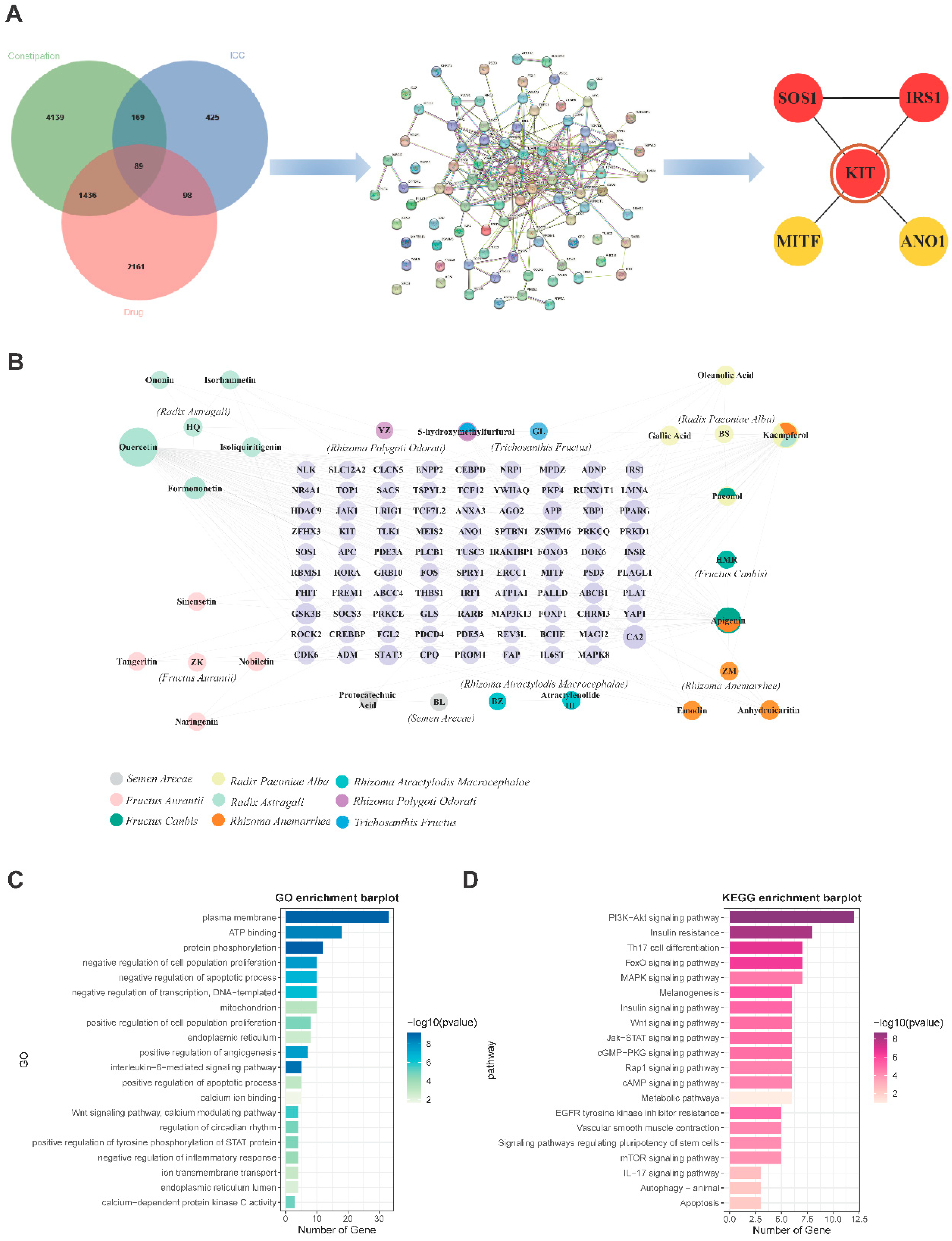
Figure 3.
The key ingredients and key targets for the treatment of constipation and functional enrichment analysis. (A) Venn diagram of 89 targets for QLF targeting ICC against constipation, PPI network and five hub targets. (B) QLF-ingredient-target network. (C) GO and KEGG enrichment analysis.
Figure 3.
The key ingredients and key targets for the treatment of constipation and functional enrichment analysis. (A) Venn diagram of 89 targets for QLF targeting ICC against constipation, PPI network and five hub targets. (B) QLF-ingredient-target network. (C) GO and KEGG enrichment analysis.
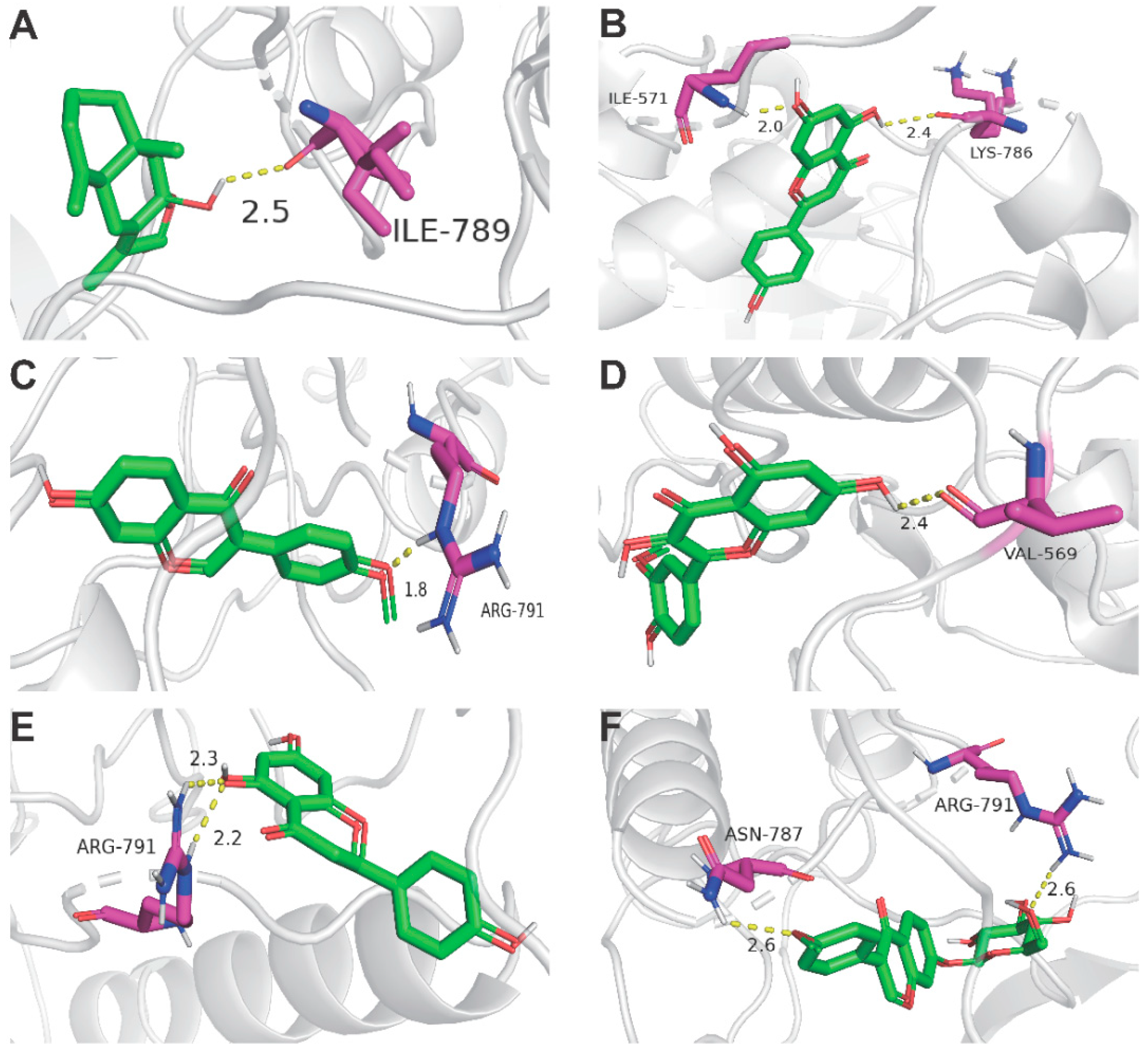
Figure 4.
Docking complexes 3D diagram of 6 key ingredients along with their strongest binding target (KIT). (A) KIT (PDB ID: 6MOB) with Atractylenolide Ⅲ; (B) KIT with Apigenin; (C) KIT with Formononetin (D); KIT with Isorhamnetin; (E) KIT with Isorhamnetin; (F) KIT with Ononin.
Figure 4.
Docking complexes 3D diagram of 6 key ingredients along with their strongest binding target (KIT). (A) KIT (PDB ID: 6MOB) with Atractylenolide Ⅲ; (B) KIT with Apigenin; (C) KIT with Formononetin (D); KIT with Isorhamnetin; (E) KIT with Isorhamnetin; (F) KIT with Ononin.
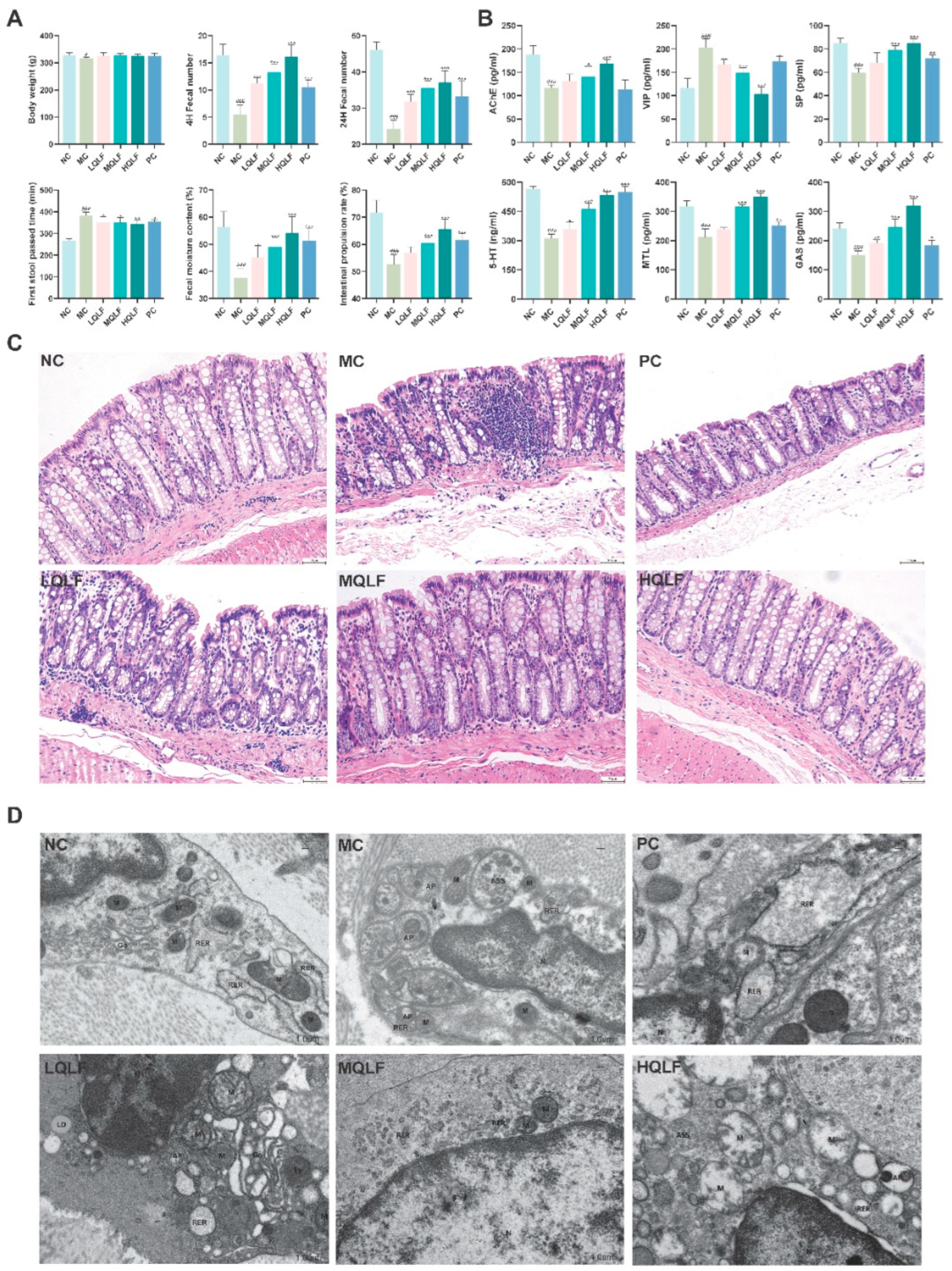
Figure 5.
Effects of QLF on defecation function, serum levels of neurotransmitters, intestinal pathology and intestinal cajal cells in rats with constipation. (A) Final body weight, fecal number, first defecation time, fecal moisture content and Intestinal propulsion rate were determined at the end of the study. (B) AChE, VIP, SP, 5-HT, MTL and GAS in serum were assayed by ELISA, n = 6. (C) Colon stained with H&E (original magnification, ×40). (D) Observation of mitochondria, autophagosome and Rough endoplasmic reticulum of colonic ICC by transmission electron microscopy. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, compared to the NC group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared to the MC group.
Figure 5.
Effects of QLF on defecation function, serum levels of neurotransmitters, intestinal pathology and intestinal cajal cells in rats with constipation. (A) Final body weight, fecal number, first defecation time, fecal moisture content and Intestinal propulsion rate were determined at the end of the study. (B) AChE, VIP, SP, 5-HT, MTL and GAS in serum were assayed by ELISA, n = 6. (C) Colon stained with H&E (original magnification, ×40). (D) Observation of mitochondria, autophagosome and Rough endoplasmic reticulum of colonic ICC by transmission electron microscopy. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, compared to the NC group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared to the MC group.
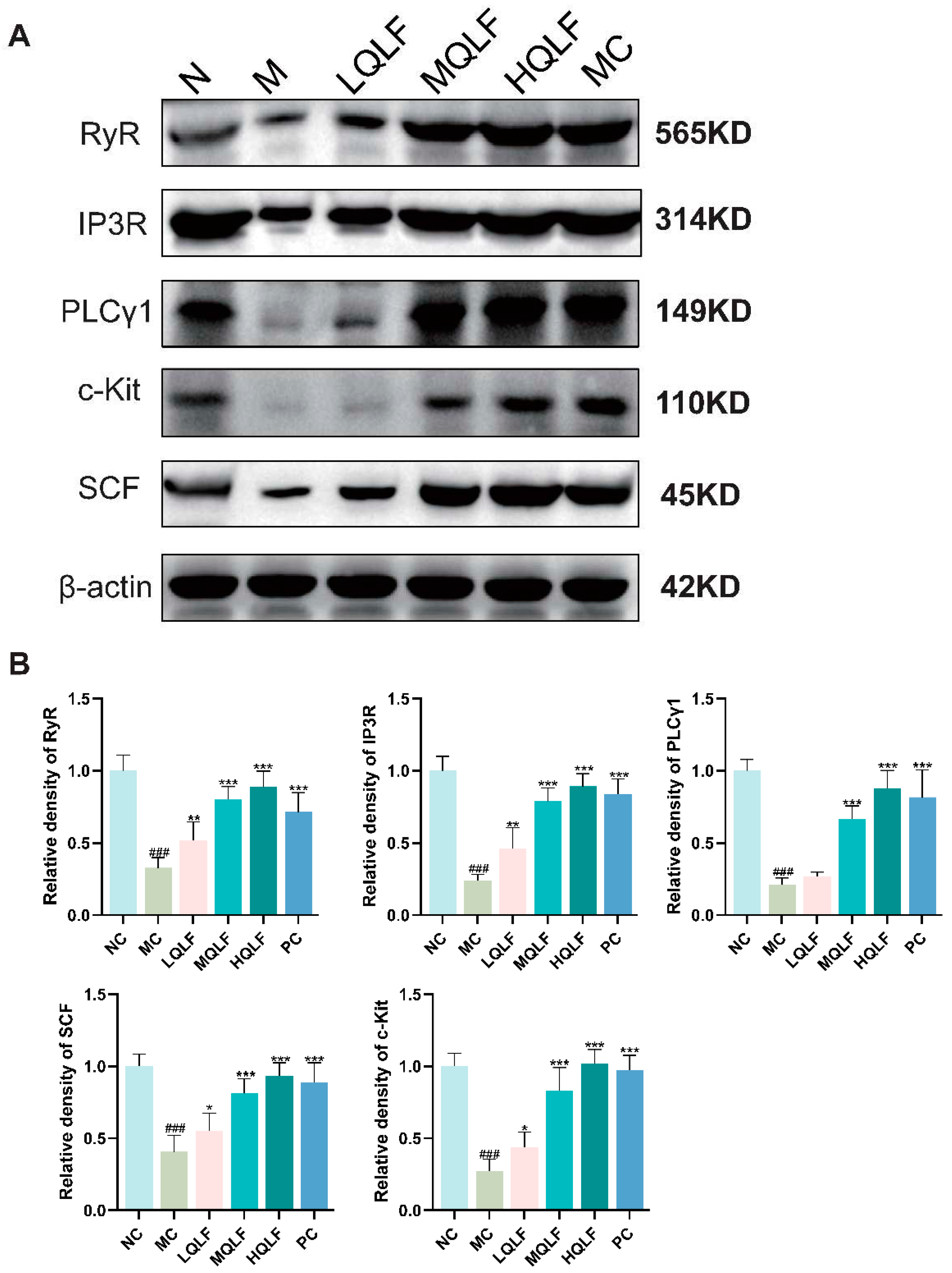
Figure 6.
Effects of QLF on SCF/C-kit and its downstream signaling pathway in rats. (A-B) the protein levels of SCF/c-kit and its downstream signaling pathway in colon tissue detected by Western blotting assay, n=6 . Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, compared to the NC group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared to the MC group.
Figure 6.
Effects of QLF on SCF/C-kit and its downstream signaling pathway in rats. (A-B) the protein levels of SCF/c-kit and its downstream signaling pathway in colon tissue detected by Western blotting assay, n=6 . Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, compared to the NC group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared to the MC group.
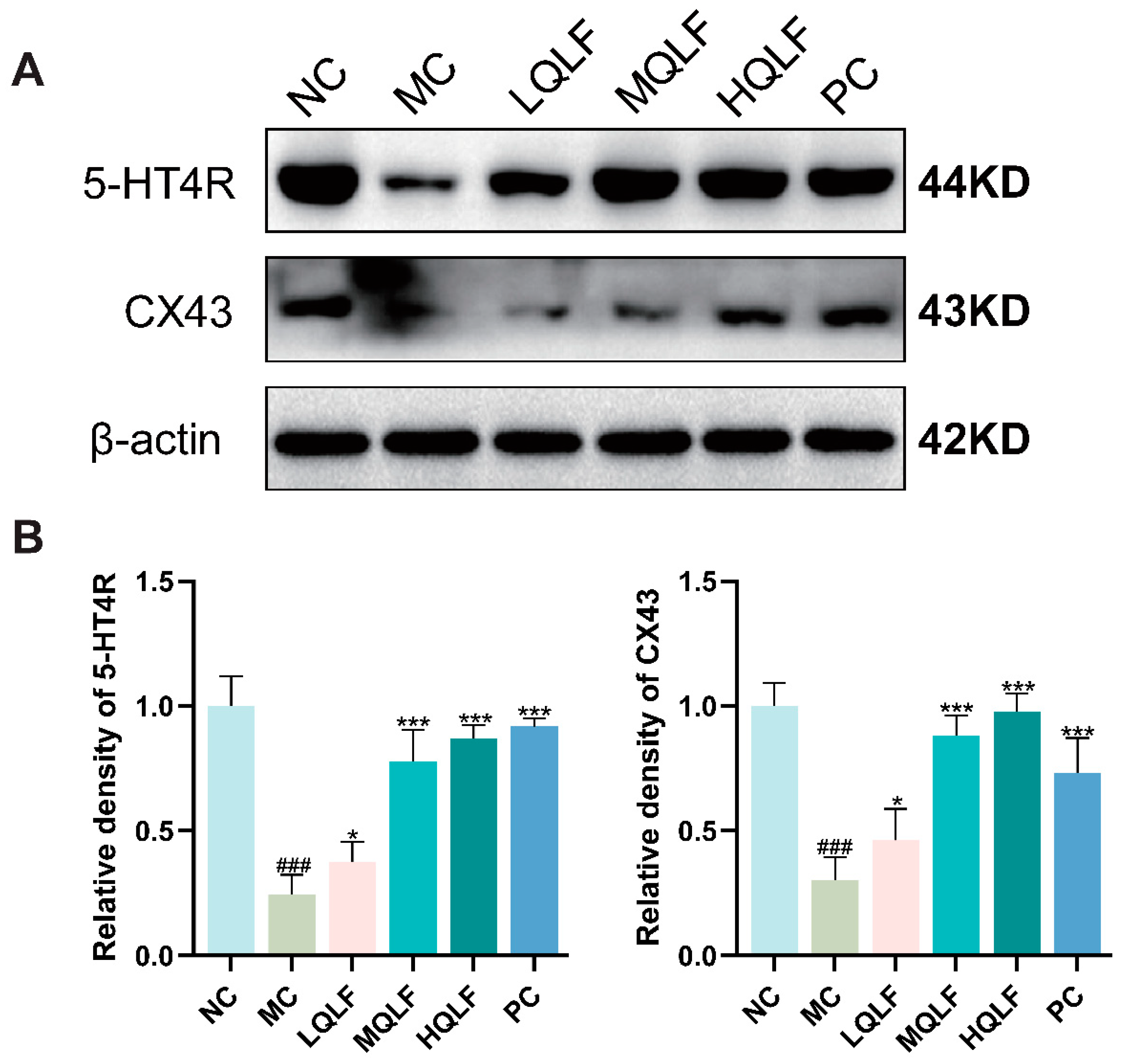
Figure 7.
Effects of QLF on CX43 and 5-HT4R protein expression in rats. (A-B) the protein levels of CX43 and 5-HT4R in colon tissue based on WB assay, n=6. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, compared to the NC group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared to the MC group.
Figure 7.
Effects of QLF on CX43 and 5-HT4R protein expression in rats. (A-B) the protein levels of CX43 and 5-HT4R in colon tissue based on WB assay, n=6. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, compared to the NC group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared to the MC group.
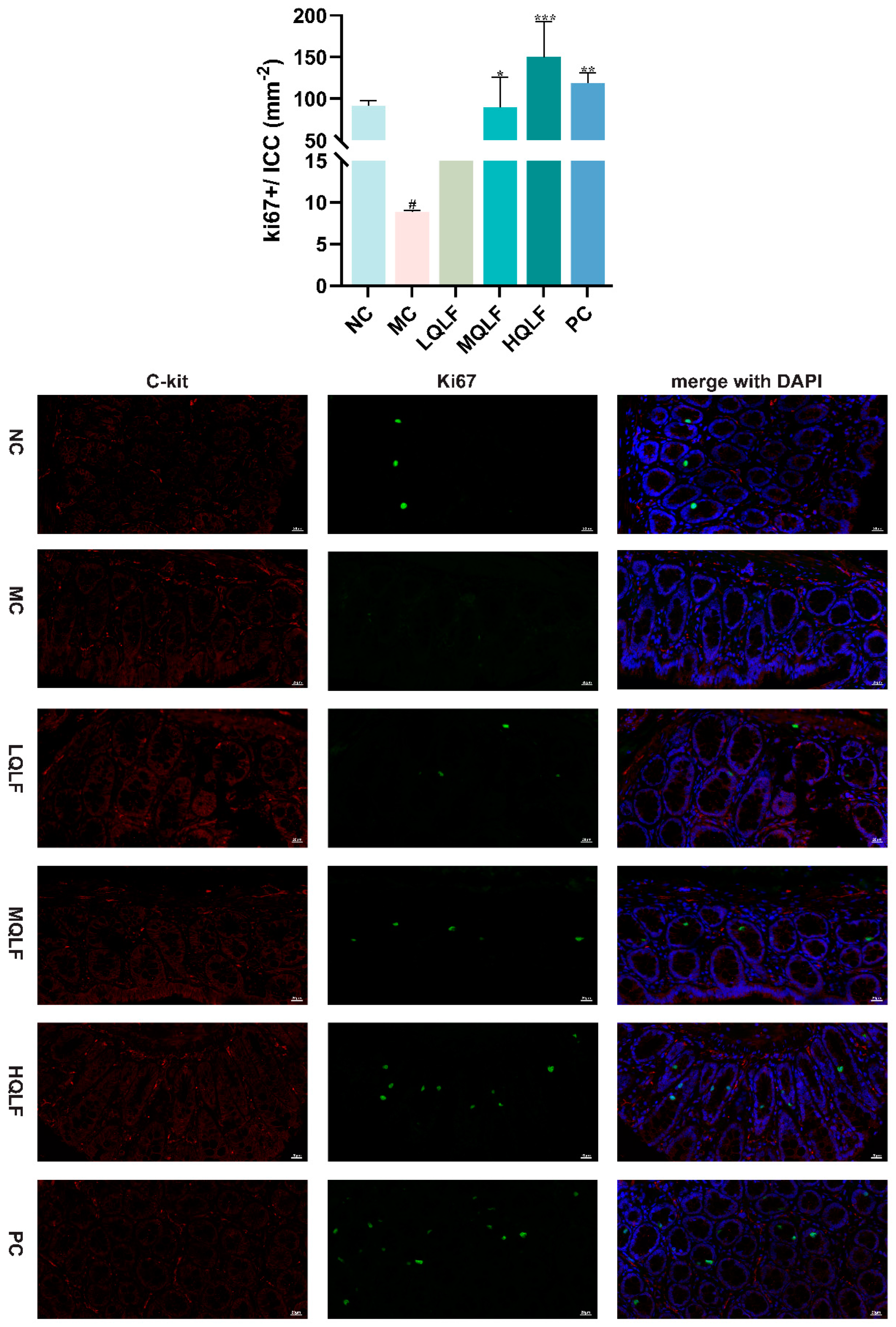
Figure 8.
The proliferation of intestinal cajal cells in each group was detected by Ki67 and c-kit double standard immunofluorescence staining, n=3. (c-kit: red; ki67: green; DAPI: blue), Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #p < 0.05, compared to the NC group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared to the MC group.
Figure 8.
The proliferation of intestinal cajal cells in each group was detected by Ki67 and c-kit double standard immunofluorescence staining, n=3. (c-kit: red; ki67: green; DAPI: blue), Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #p < 0.05, compared to the NC group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared to the MC group.