Submitted:
16 May 2023
Posted:
17 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
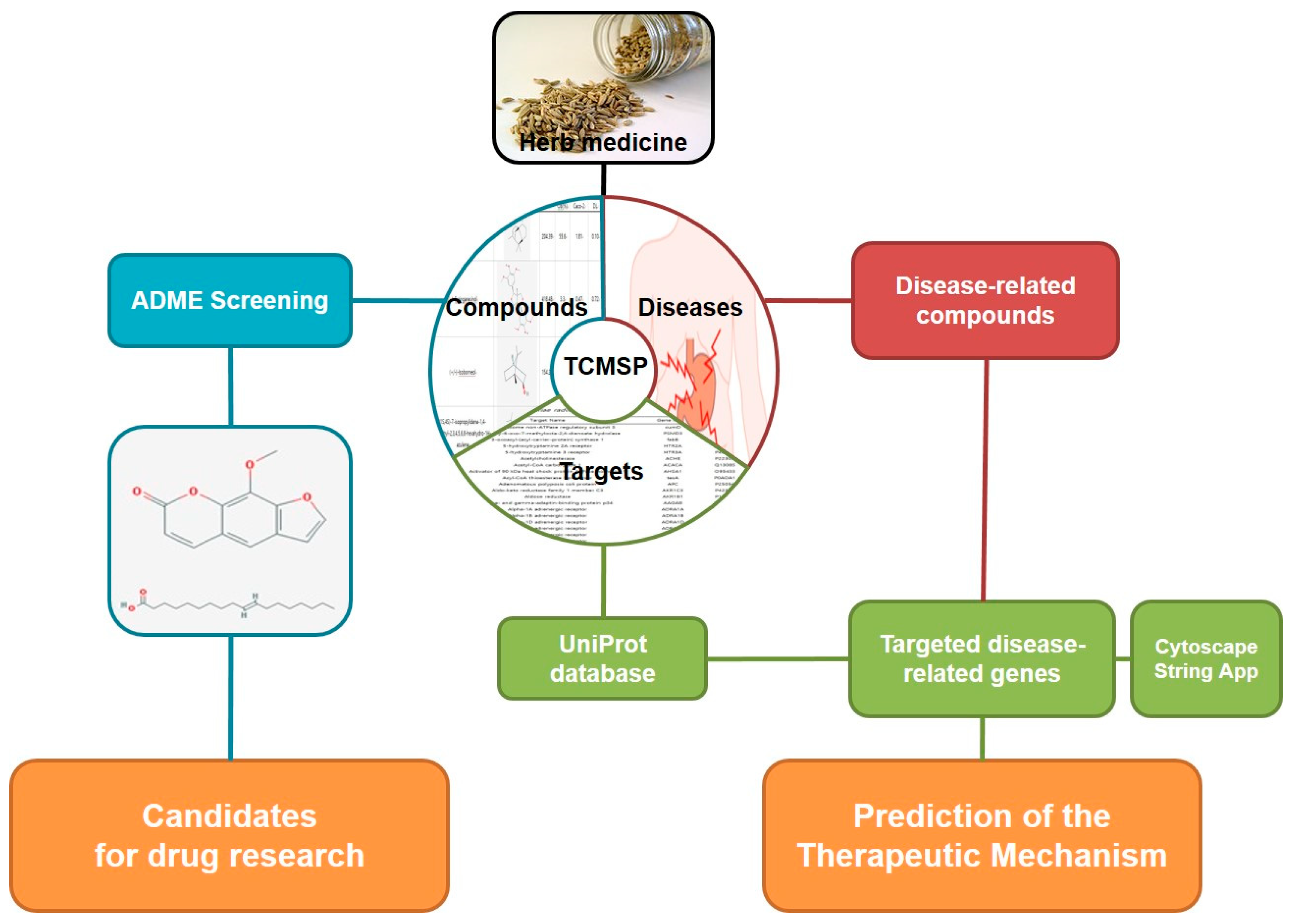
2.1. Analysis of Network pharmacology
2.1.1. Identifying compounds of F. fructus
2.1.2. Target network
2.1.3. Analysis of network
2.1.4. Screening of Active compound
2.2. Analysis of F. fructus
2.2.1. Instrument and Reagent
2.2.2. Preparation of the standard solution
2.2.3. Preparation of the test liquid for quantitative analysis
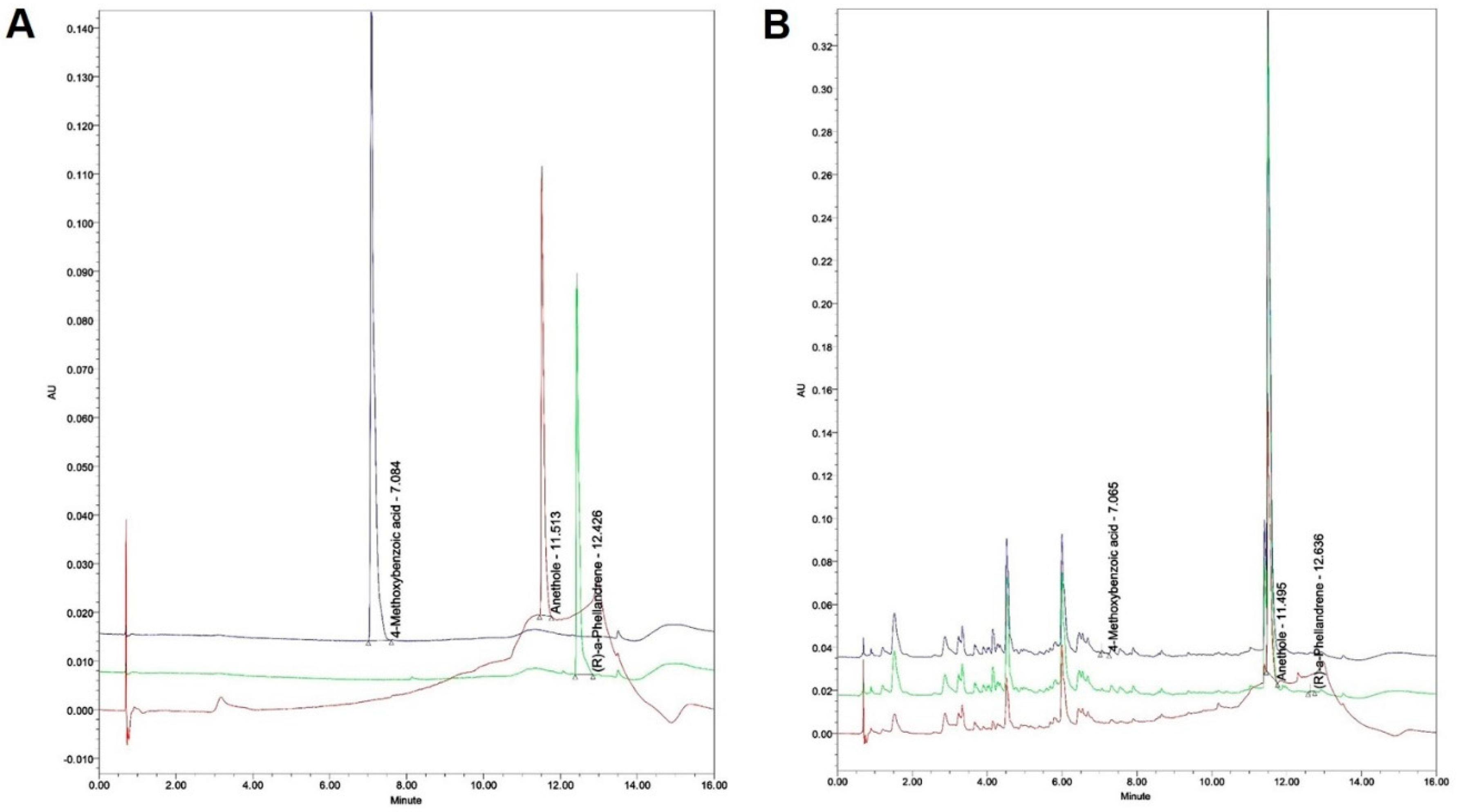
2.2.4. Quantitation of the F. fructus extract
2.3. Animal testing
2.3.1. Design of Animal experiment
2.3.2. Assessment of gastric weight and gastric emptying by phenol red
2.3.3. Assessment of intestinal transit rate by Evans blue
2.3.4. Western blot analysis for check of protein level
2.3.5. Quantitative real-time PCR to evaluate gene expression
3. Results
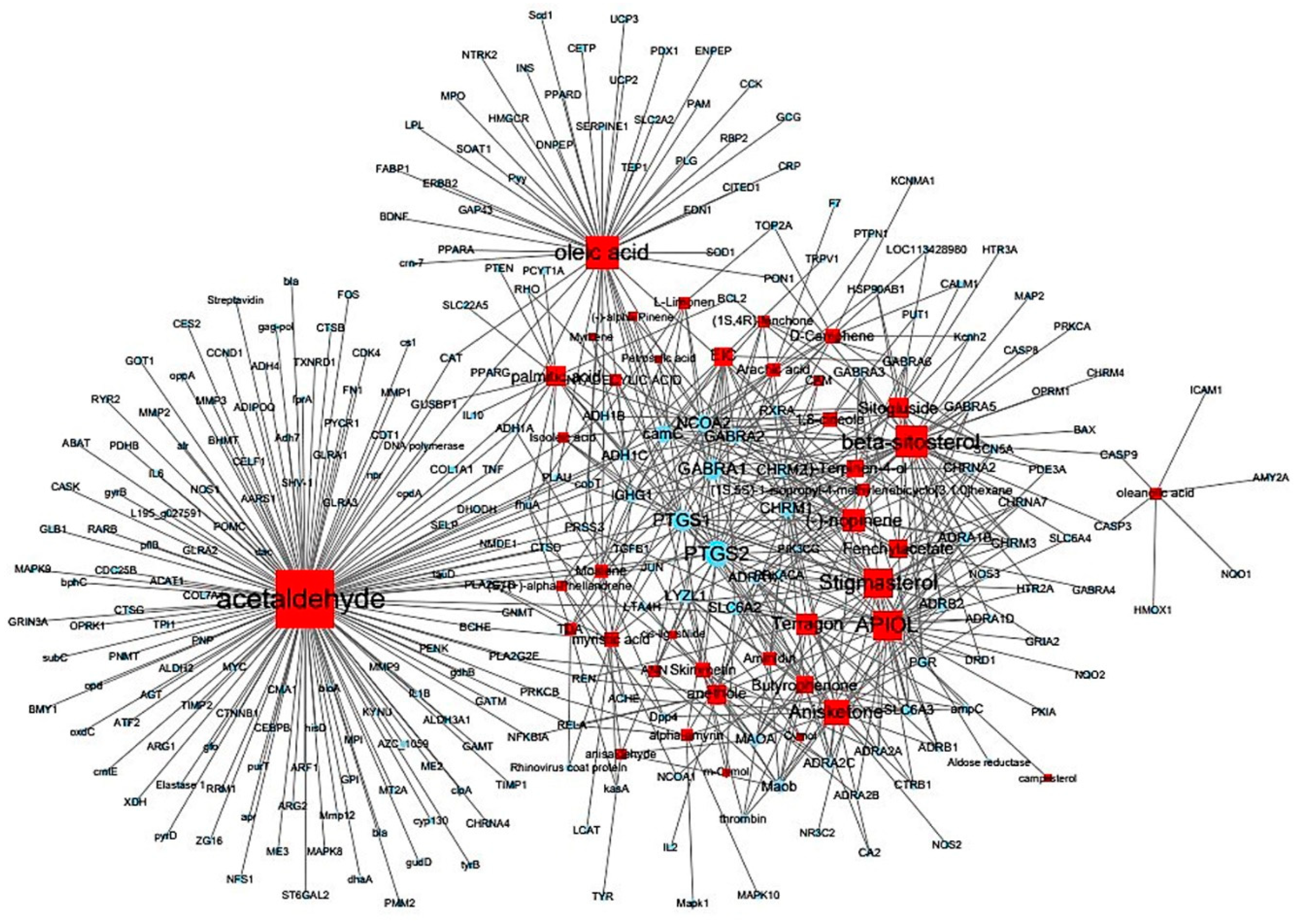
3.1. Target information derived by examining correlations between compounds and targets
3.2. Twenty active compounds achieved the criteria for the applied absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion parameters
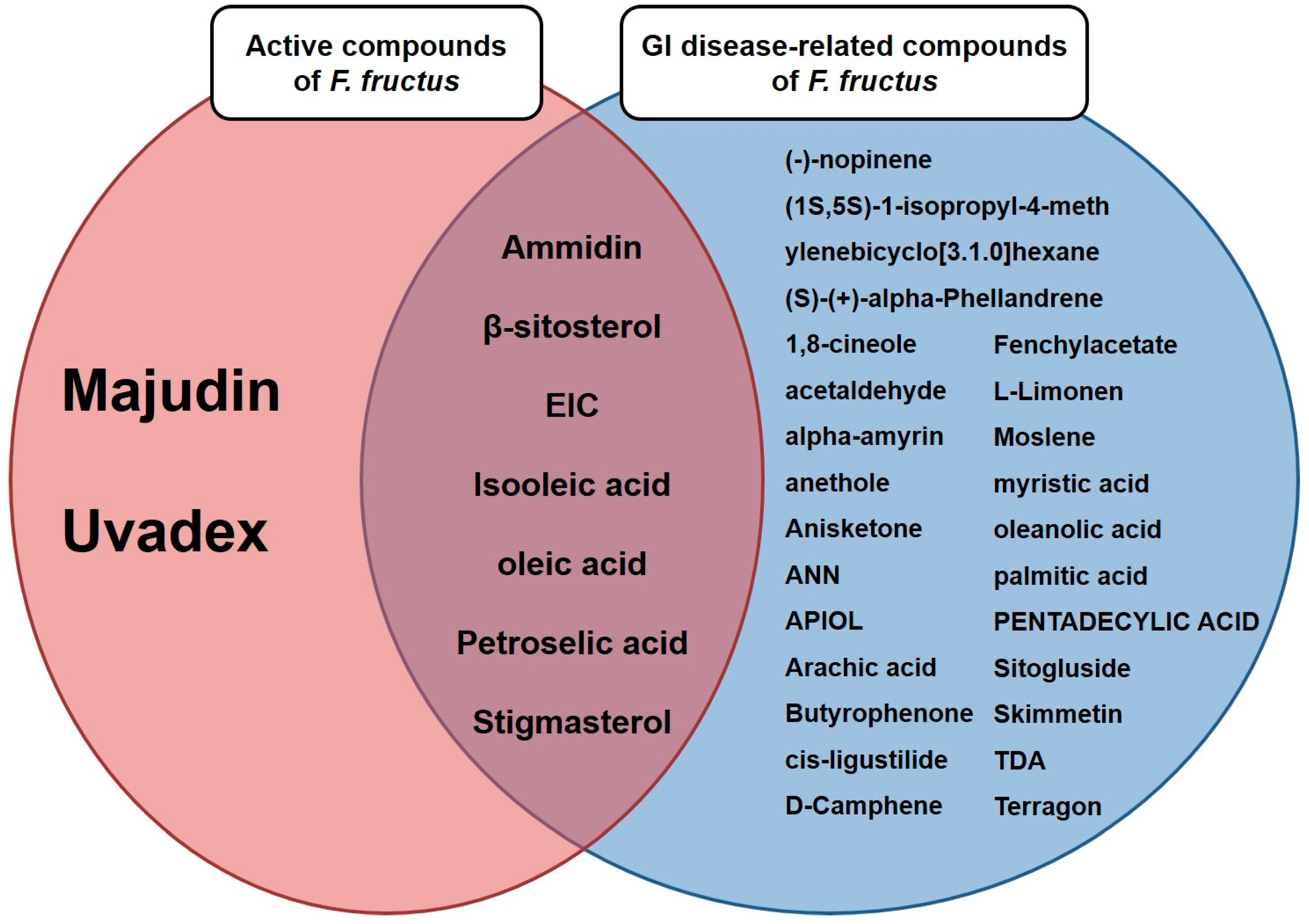
3.3. Thirty-two compounds associated with gastrointestinal (GI) diseases were identified in F. fructus
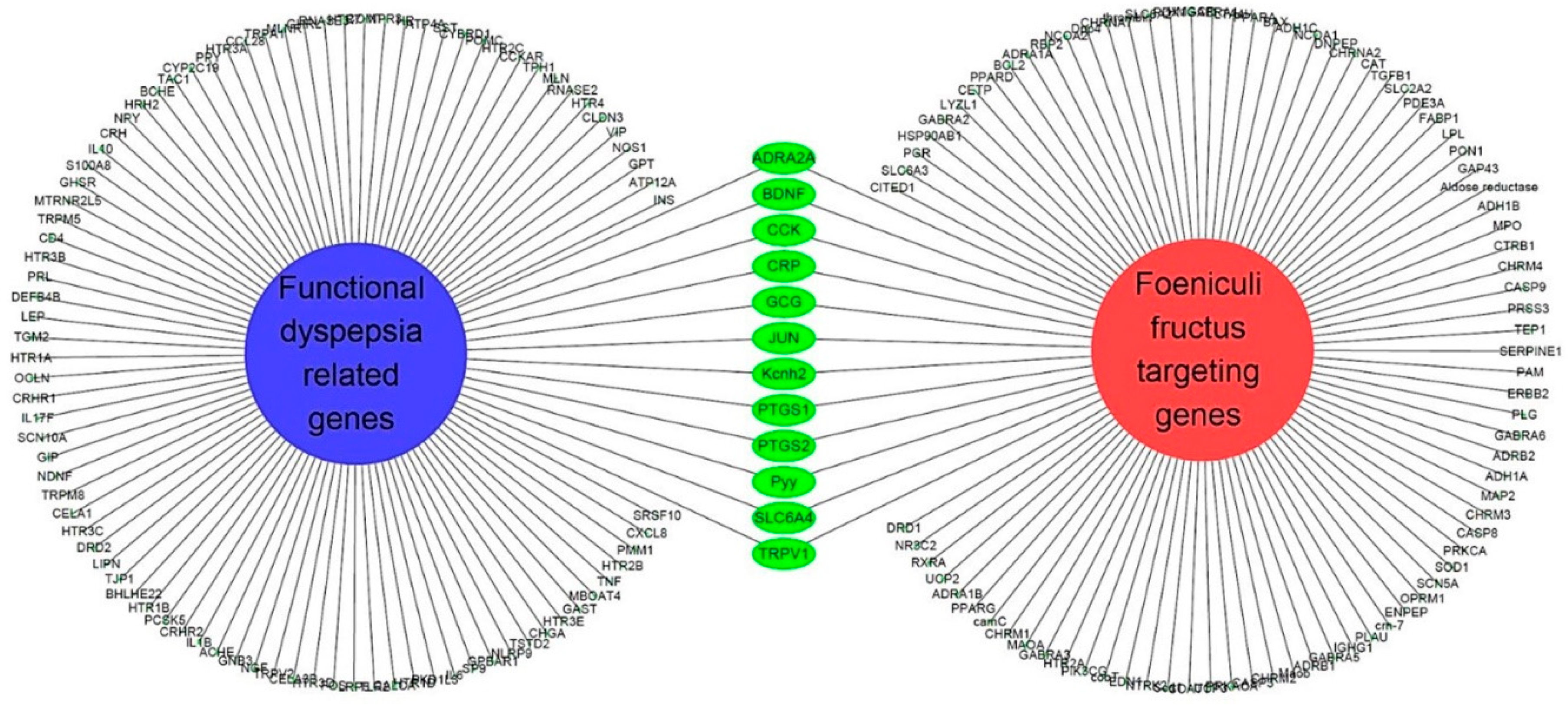
3.4. All 31 GI disease-related compounds in F. fructus except oleanolic acid were associated with functional dyspepsia
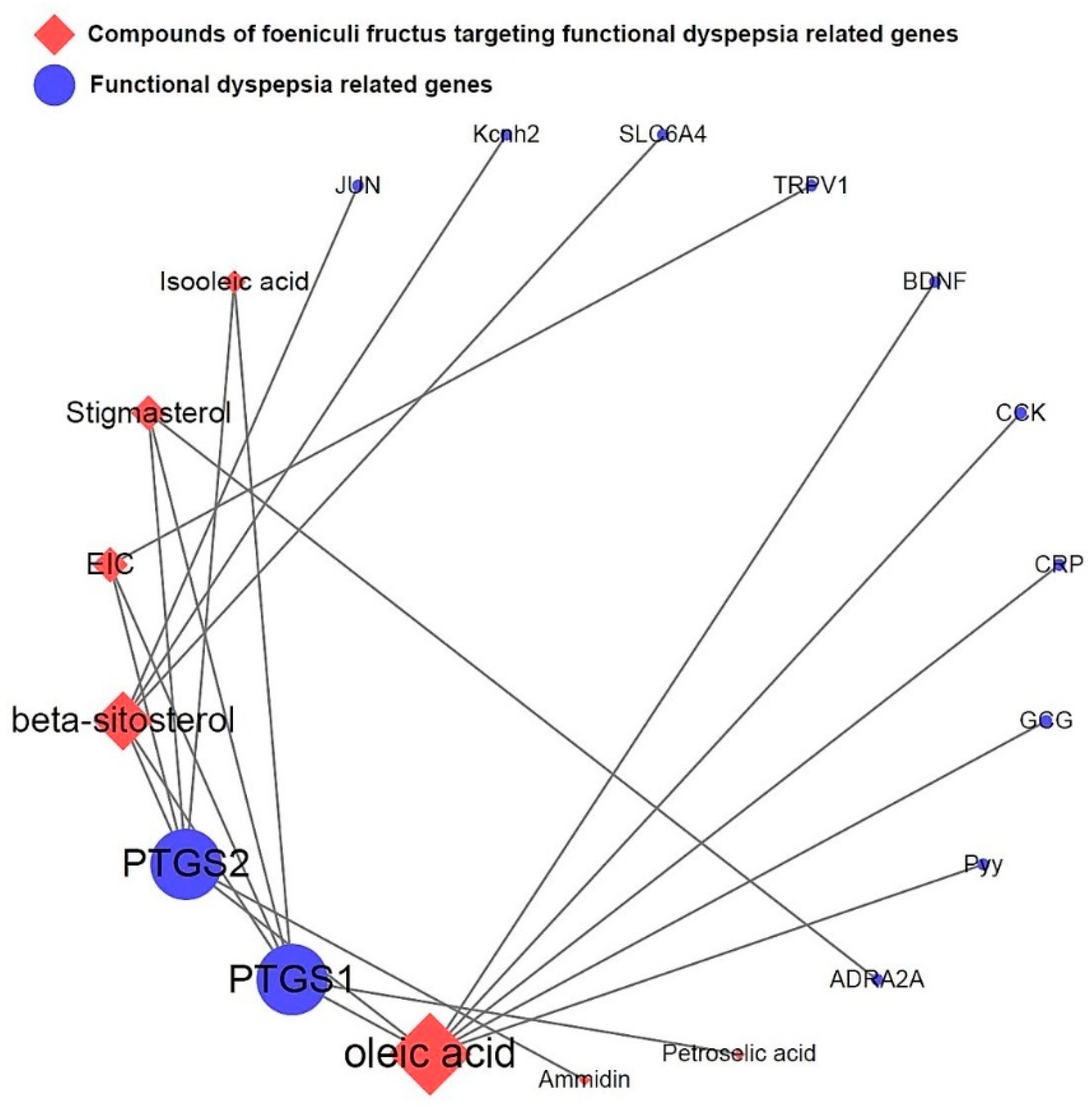
3.5. Network of functional dyspepsia-associated genes and compounds for identification of interesting molecules
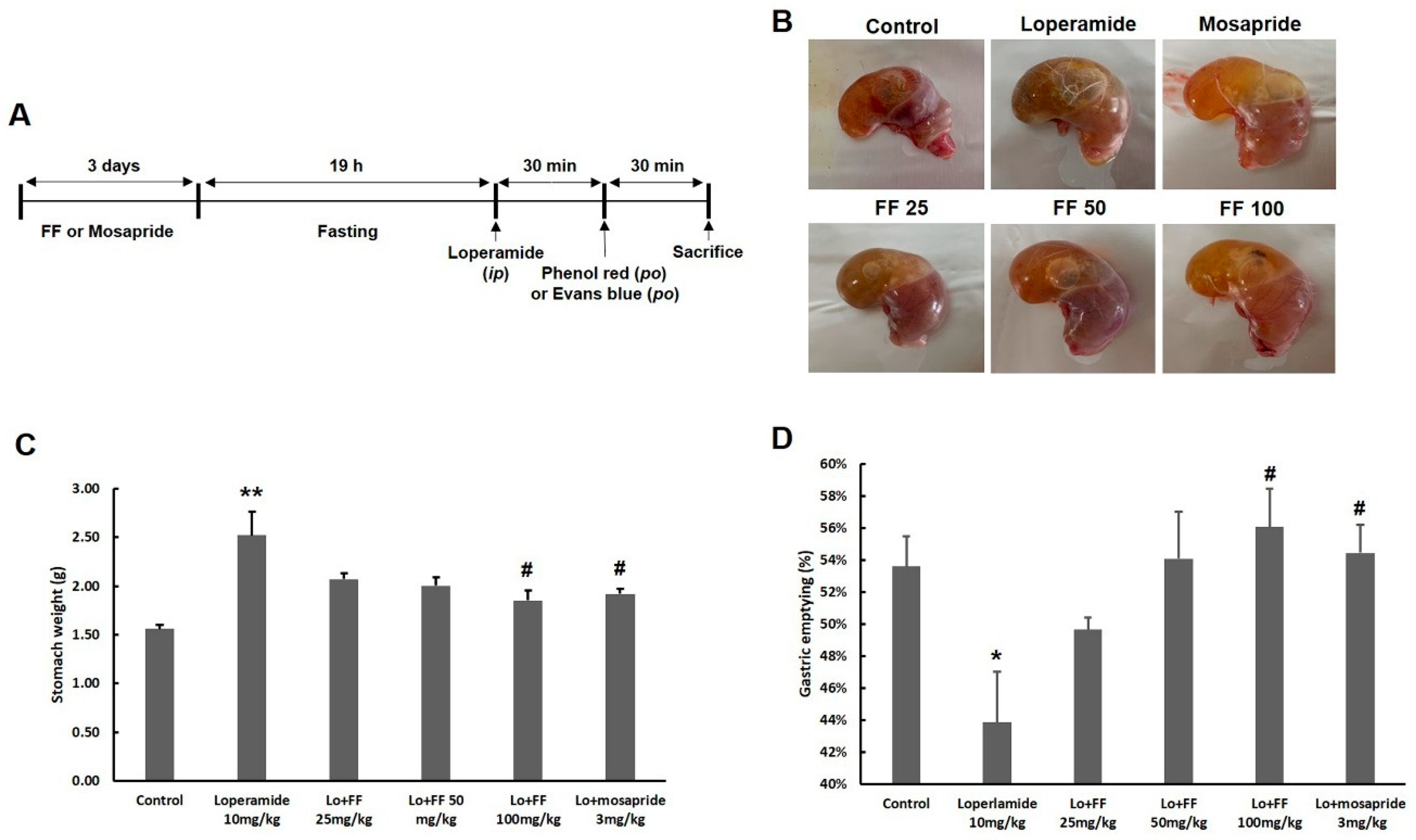
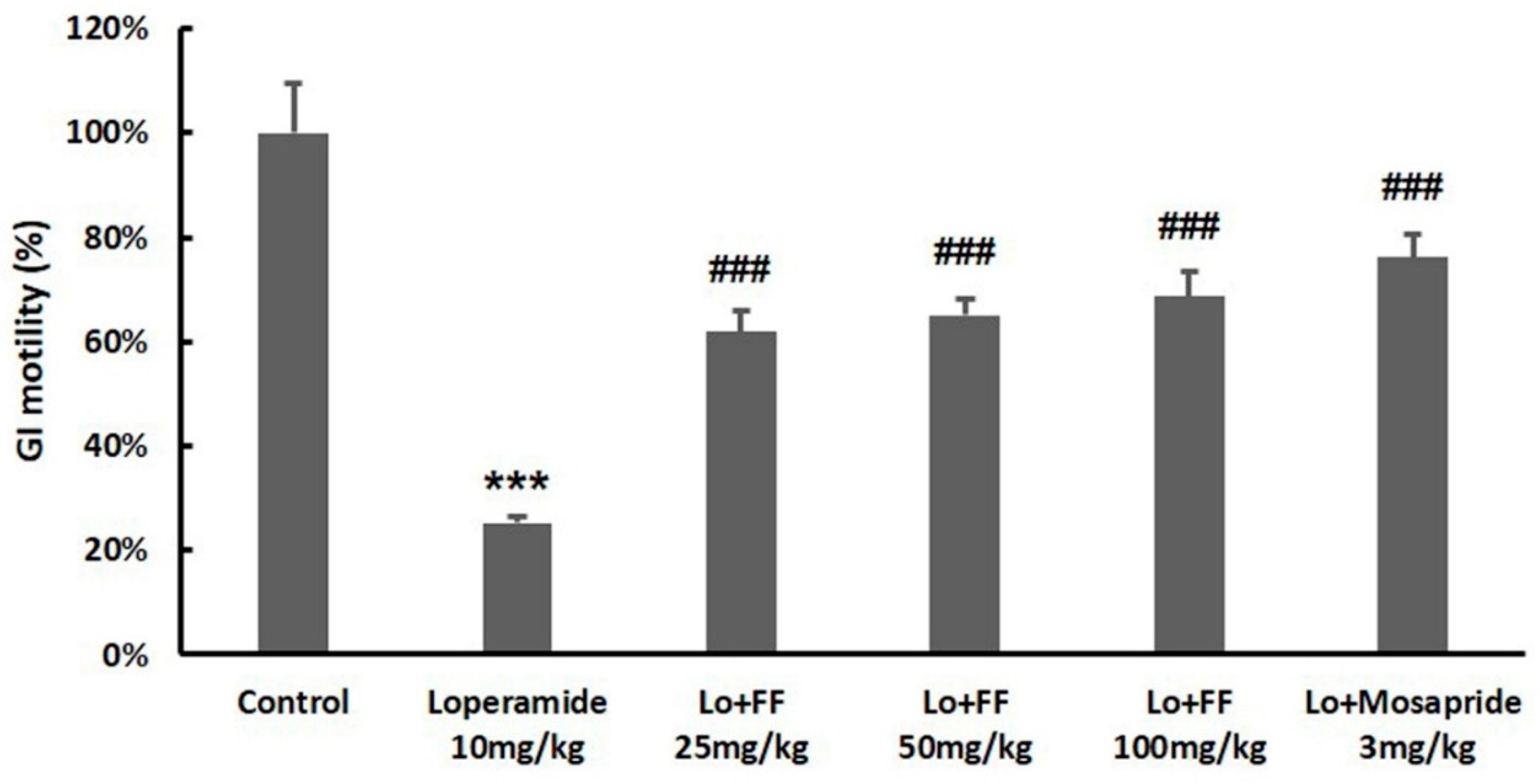
3.6. Mouse experiment on delayed gastric emptying
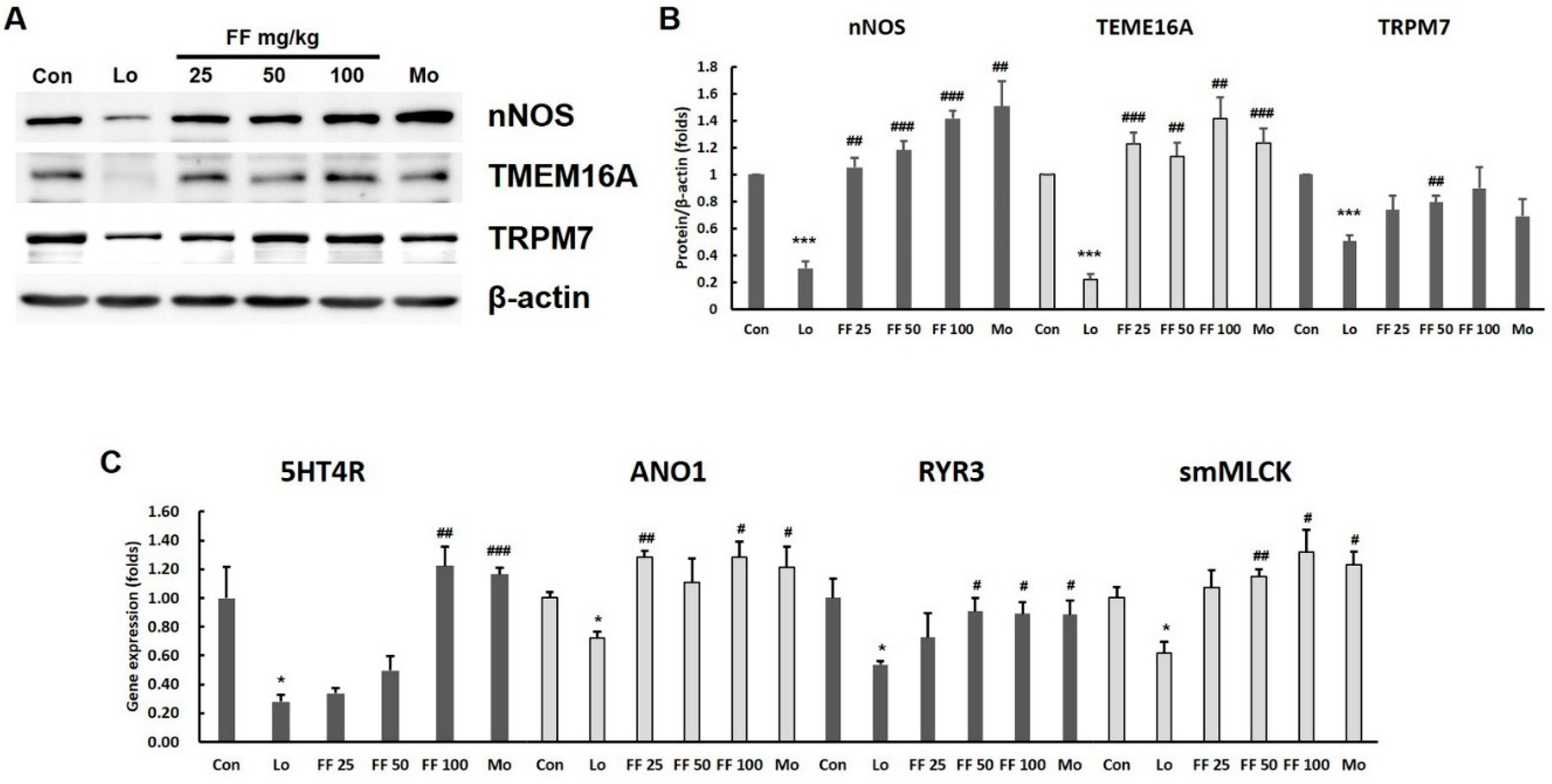
3.7. Mouse experiment on molecules involved in gastrointestinal motility
3.8. Mouse experiment on intestinal motility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clouse, R.E.; Mayer, E.A.; Aziz, Q.; Drossman, D.A.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Mönnikes, H.; Naliboff, B.D. Functional Abdominal Pain Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, N.J.; McNeil, D.; Hayden, A.; Piper, D.W. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial of cimetidine and pirenzepine in nonulcer dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 1986, 91, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayyedi, P.; Delaney, B.C.; Vakil, N.; Forman, D.; Talley, N.J. The efficacy of proton pump inhibitors in nonulcer dyspepsia: A systematic review and economic analysis. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, L.; Schoenfeld, P.; Fennerty, M.B. Therapy for Helicobacter pylori in Patients with Nonulcer Dyspepsia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.C.; Cheng, H.H. 2003. Genetic mapping of the chicken stem cell antigen 2 (SCA2) gene to chromosome 2 via PCR primer mutagenesis: Brief notes. Anim. Genet. 2003, 34, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.M.; Hwang, J.K. Antiinflammatory, analgesic and antioxidant activities of the fruit of Foeniculum vulgare. Fitoterapia 2004, 75, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, R.; Barros, L.; Carvalho, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Infusions and Decoctions of Mixed Herbs used in Folk Medicine: Synergism in Antioxidant Potential: SYNERGISM IN ANTIOXIDANT POTENTIAL OF MIXED HERBS FROM FOLK MEDICINE. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert-Puleo, M. Fennel and anise as estrogenic agents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1980, 2, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostad, S.N.; Soodi, M.; Shariffzadeh, M.; Khorshidi, N.; Marzban, H. The effect of fennel essential oil on uterine contraction as a model for dysmenorrhea, pharmacology and toxicology study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 76, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Cresi, F.; Castagno, E.; Silvestro, L.; Oggero, R. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of a standardized extract of Matricariae recutita,Foeniculum vulgare andMelissa officinalis (ColiMil®) in the treatment of breastfed colicky infants. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, H.; Uğraş, S.; Dülger, H.; Bayram, İ.; Tuncer, İ.; Öztürk, G.; Öztürk, A. Hepatoprotective effect of Foeniculum vulgare essential oil. Fitoterapia 2003, 74, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badgujar, S.B.; Patel, V.V.; Bandivdekar, A.H. Foeniculum vulgare Mill: A Review of Its Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Contemporary Application, and Toxicology. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima, P.; Kumar, J.D.; Zhao, Q.; Blunder, M.; Efferth, T. Network pharmacology of cancer: From understanding of complex interactomes to the design of multi-target specific therapeutics from nature. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.Y.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, C.E. The Methodological Trends of Traditional Herbal Medicine Employing Network Pharmacology. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Ou, S.; Chen, S.; Ding, S. Network Pharmacology-Based Study on the Molecular Biological Mechanism of Action for Compound Kushen Injection in Anti-Cancer Effect. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.L.; Liu, C.; Xu, M.; Wang, R.S. Network Pharmacology to Uncover the Molecular Mechanisms of Action of LeiGongTeng for the Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, B.; Xue, W.; Feng, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, P.; Cao, J.; Zhu, C. Anticancer Effect of Radix Astragali on Cholangiocarcinoma In Vitro and Its Mechanism via Network Pharmacology. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M. 2020. A Network Pharmacology Approach to Explore the Potential Mechanisms of Huangqin-Baishao Herb Pair in Treatment of Cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Xu, H.B.; Zhang, S.J.; Li, X.Y. Identification of the Active Compounds and Significant Pathways of Artemisia Annua in the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma based on Network Pharmacology. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, I.H.; Park, S.I.; Lee, D.Y. Network Pharmacology-Based Investigation of the System-Level Molecular Mechanisms of the Hematopoietic Activity of Samul-Tang, a Traditional Korean Herbal Formula. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, M.; Yang, L.; Xie, C.; Gao, H.; Fu, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y. Network Pharmacology-Based Identification of the Mechanisms of Shen-Qi Compound Formula in Treating Diabetes Mellitus. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhong, M.; Long, F.; Yang, R. Deciphering the Active Ingredients and Molecular Mechanisms of Tripterygium hypoglaucum (Levl.) Hutch against Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Network Pharmacology. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.H.; Su, Y.F.; Sun, C.X.; Fan, H.F.; Gao, W.J. A Network Pharmacology-Based Identification Study on the Mechanism of Xiao-Xu-Ming Decoction for Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Fan, Y.; Tian, C.; Jin, Y.; Du, S.; Zeng, P.; Wang, A. Deciphering the Molecular Targets and Mechanisms of HGWD in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis via Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, H.; Jin, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Chu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Song, Y. Study on the Multitarget Mechanism of Sanmiao Pill on Gouty Arthritis Based on Network Pharmacology. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Tan, L.; Xiong, Y.; Ji, W.; Mu, J.; Pei, Y.; Cheng, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Integrated Analysis of the Mechanisms of Da-Chai-Hu Decoction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by a Network Pharmacology Approach. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, R.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Borgatti, M. Virtual Screening Technique Used to Estimate the Mechanism of Adhatoda vasica Nees for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, K.; Li, K.; Long, S.; Kong, C.; Zhu, S. 2020. Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Chaihu-Shugan-San in Treatment of Breast Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Zeng, L.; Ge, J. Exploring the Pharmacological Mechanism of Danzhi Xiaoyao Powder on ER-Positive Breast Cancer by a Network Pharmacology Approach. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liao, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Lin, S.; Lan, J.; Mao, H.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y. A Network Pharmacology Approach to Investigate the Active Compounds and Mechanisms of Musk for Ischemic Stroke. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, Z.; Tong, Q.; Pan, J.; Wan, L.; Chen, J. Network Pharmacology Analysis of Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula Xiao Ke Yin Shui Treating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Cytoscape StringApp: Network Analysis and Visualization of Proteomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Moore, D.D. A traditional herbal medicine enhances bilirubin clearance by activating the nuclear receptor CAR. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 113, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Aida, S.; Suemasu, S.; Mizushima, T. Anethole restores delayed gastric emptying and impaired gastric accommodation in rodents. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 472, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpignato, C.; Capovilla, T.; Bertaccini, G. Action of caerulein on gastric emptying of the conscious rat. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1980, 246, 286–294. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes Marona, H.R.; Bastos Lucchesi, M.B. Protocol to refine intestinal motility test in mice. Lab Anim 2004, 38, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelstadt, S.W.; Hemenway, C.L.; Spruell, R.D. Effects of fasting on evaluation of gastrointestinal transit with charcoal meal. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2005, 52, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Soud, N.A.; El-Laithy, N.; El-Saeed, G.; Wahby, M.S.; Khalil, M.; Morsy, F.; Shaffie, N. Antidiabetic Activities of Foeniculum vulgare Mill. Essential Oil in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats 8. Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Malini, T.; Vanithakumari, G.; Megala, N.; Anusya, S.; Devi, K.; Elango, V. Effect of Foeniculum vulgare Mill. seed extract on the genital organs of male and female rats. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1985, 29, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oktay, M.; Gülçin, İ.; Küfrevioğlu, Ö.İ. Determination of in vitro antioxidant activity of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) seed extracts. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 36, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Sribhuwaneswari, S.; Karthikeyan, D.; Minz, S.; Sure, P.; Chandu, A.N.; Mishra, U.; Kamalakannan, K.; Saravanankumar, A.; Sivakumar, T. 2008. In-vitro Cytoprotection Activity of Foeniculum vulgare and Helicteres isora in Cultured Human Blood Lymphocytes and Antitumour Activity against B16F10 Melanoma Cell Line. Research J. Pharm. And Tech. 2008, 1, 450–452. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, İl. E.; Özçeli̇K, B.; Kartal, M.; Kan, Y. 2012. Antimicrobial and antiviral effects of essential oils from selected Umbelliferae and Labiatae plants and individual essential oil components. Turk. J. Biol. 2012, 36, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Thaler, K.; Kaminski, A.; Chapman, A.; Langley, T.; Gartlehner, G. Bach Flower Remedies for psychological problems and pain: a systematic review. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Carvalho, A.M.; Sánchez-Mata, M.C.; Cámara, M.; Molina, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. 2012. Tocopherol composition and antioxidant activity of Spanish wild vegetables. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2012, 59, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdane, F.M.; Cemek, M.; Birdane, Y.O.; Gülçin, I.; Büyükokuroğlu, M.E. Beneficial effects of Foeniculum vulgare on ethanol-induced acute gastric mucosal injury in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakŭrski, I.; Matev, M.; Koĭchev, A.; Angelova, I.; Stefanov, G. Treatment of chronic colitis with an herbal combination of Taraxacum officinale, Hipericum perforatum, Melissa officinaliss, Calendula officinalis and Foeniculum vulgare. Vutr. Boles 1981, 20, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.K.; To, K.F.; Ng, Y.P.; Lee, T.L.; Cheng, A.S.; Leung, W.K.; Sung, J.J. Expression and cellular localization of COX-1 and -2 in Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vane, J.R.; Bakhle, Y.S.; Botting, R.M. Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1998, 38, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.L.; Devchand, P.R. 2005. Emerging roles for cyclooxygenase-2 in gastrointestinal mucosal defense. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 145, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.C.; van Citters, G.W.; Heimer, F.; Bonorris, G. Slowing of gastrointestinal transit by oleic acid: a preliminary report of a novel, nutrient-based treatment in humans. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2001, 46, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, K.; Tan, Y.; Ding, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, X.; Fang, J.; Xu, D.; Zhang, H.; Lu, W.; Li, M.; et al. β-Sitosterol improves experimental colitis in mice with a target against pathogenic bacteria. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 5687–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Ha, W.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Jung, Y.; Kim, B.J. Effects of Lizhong Tang on gastrointestinal motility in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, M.; Hussain, F.; Salamat, A.; Khan, M.B. Gastric emptying scintigraphy in postprandial distress syndrome. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarter, A.O.; De Wit, N.J.; Lodder, A.C.; Numans, M.E.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Hoes, A.W. Disturbed Solid-Phase Gastric Emptying in Functional Dyspepsia (A Meta-Analysis). Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 2028–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futagami, S.; Yamawaki, H.; Shimpuku, M.; Izumi, N.; Wakabayashi, T.; Kodaka, Y.; Nagoya, H.; Shindo, T.; Kawagoe, T.; Sakamoto, C. Impact of Coexisting Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Non-erosive Reflux Disease on Postprandial Abdominal Fullness and Sleep Disorders in Functional Dyspepsia. J. Nippon. Med. Sch. 2013, 80, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shiba, M.; Kohata, Y.; Yamagami, H.; Tanigawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Tominaga, K.; Arakawa, T. Prevalence of overlaps between GERD, FD and IBS and impact on health-related quality of life: Overlap of FGIDs and HR-QOL. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Kim, N.; Yoon, H.; Shin, C.M.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, D.H.; Jung, H.C. Overlap between irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia including subtype analyses: Overlap of IBS and dyspepsia. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terauchi, A.; Kobayashi, D.; Mashimo, H. Distinct roles of nitric oxide synthases and interstitial cells of Cajal in rectoanal relaxation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G291–G299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Baeg, M.K.; Lim, C.H.; Cho, Y.K.; Choi, M.G. Nitric Oxide Synthase Gene Polymorphisms in Functional Dyspepsia. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Pinilla, P.J.; Gibbons, S.J.; Bardsley, M.R.; Lorincz, A.; Pozo, M.J.; Pasricha, P.J.; de Rijn, M.V.; West, R.B.; Sarr, M.G.; Kendrick, M.L.; et al. Ano1 is a selective marker of interstitial cells of Cajal in the human and mouse gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G1370–G1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, K.M.; Hwang, S.J.; Ward, S.M. Neuroeffector apparatus in gastrointestinal smooth muscle organs: Neural regulation of GI smooth muscle. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 4621–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, Y.; Torii, Y.; Ohi, Y.; Nagano, N.; Atsuki, K.; Yamamura, H.; Muraki, K.; Watanabe, M.; Bolton, T.B. Ca2+ images and K+ current during depolarization in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig vas deferens and urinary bladder. J. Physiol. 1998, 510, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.N.; Ohya, S.; Wang, J.; Imaizumi, Y.; Nakayama, S. Involvement of ryanodine receptors in pacemaker Ca2+ oscillation in murine gastric ICC. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 328, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lv, N.; Tang, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Gao, S.; Chen, H.; Zhi, G.; et al. Myosin Light Chain Kinase Is Central to Smooth Muscle Contraction and Required for Gastrointestinal Motility in Mice. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 610–620.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Feng, P. Myosin Light Chain Kinase Is Involved in the Mechanism of Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, A.; Bernard, C.E.; Strege, P.R.; Beyder, A.; Galietta, L.J.V.; Pasricha, P.J.; Rae, J.L.; Parkman, H.P.; Linden, D.R.; Szurszewski, J.H.; et al. Altered Expression of Ano1 Variants in Human Diabetic Gastroparesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 13393–13403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Time (minute) | 0.1% FA/water (%) | 0.1% FA/acetonitrile (%) | Flow rate (ml/minute) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 98 | 2 | 0.40 |
| 1.0 | 98 | 2 | 0.40 |
| 3.0 | 85 | 15 | 0.40 |
| 5.0 | 75 | 25 | 0.40 |
| 6.0 | 55 | 45 | 0.40 |
| 8.0 | 50 | 50 | 0.40 |
| 9.0 | 30 | 70 | 0.40 |
| 10.0 | 10 | 90 | 0.40 |
| 12.0 | 2 | 98 | 0.40 |
| 14.0 | 98 | 2 | 0.40 |
| 16.0 | 98 | 2 | 0.40 |
| F. fructus (Unit: mg/kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-Methoxybenzoic acid | 0.219± 0.042 | ||
| Anethole | 63.029 ± 2.076 | ||
| R-(a)-Phellandrene | 0.792 ± 0.059 | ||
| Gene | Primer | Sequence (5' to 3') | Product length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5HT4R | Forward | AGTTCCAACGAGGGTTTCAGG | 92 |
| Reverse | CAGCAGGTTGCCCAAGATG | ||
| ANO1 | Forward | GGCATTTGTCATTGTCTTCCAG | 140 |
| Reverse | TCCTCACGCATAAACAGCTC | ||
| RYR3 | Forward | GGCCAAGAACATCAGAGTGACTAA | 79 |
| Reverse | TCACTTCTGCCCTGTCAGTTTC | ||
| smMLCK | Forward | AGAAGTCAAGGAGGTAAAGAATGATGT | 76 |
| Reverse | CGGGTCGCTTTTCATTGC | ||
| GAPDH | Forward | CATGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCT | 103 |
| Reverse | CCTGCTTCACCACCTTCTTGA |
| Molecule Name | Structure | MW | OB(%) | Caco-2 | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammidin* | 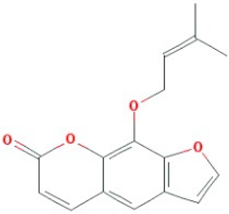 |
270.3 | 34.55 | 1.13 | 0.22 |
| beta-sitosterol | 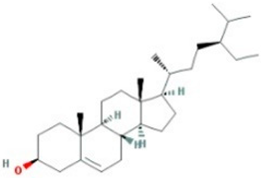 |
414.79 | 36.91 | 1.32 | 0.75 |
| EIC | 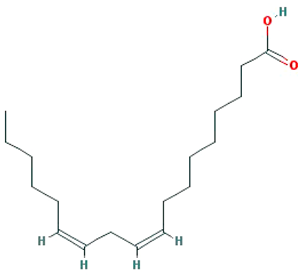 |
280.5 | 41.9 | 1.16 | 0.14 |
| Isooleic acid | 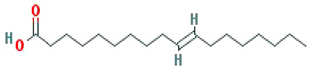 |
282.52 | 33.13 | 1.15 | 0.14 |
| Majudin | 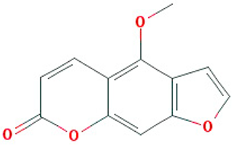 |
216.2 | 42.21 | 0.94 | 0.13 |
| oleic acid | 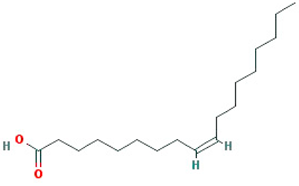 |
282.52 | 33.13 | 1.17 | 0.14 |
| Petroselic acid | 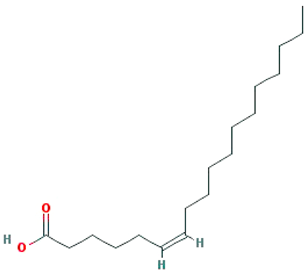 |
282.52 | 33.13 | 1.17 | 0.14 |
| Stigmasterol |  |
412.77 | 43.83 | 1.44 | 0.76 |
| Uvadex |  |
216.2 | 35.3 | 1.05 | 0.13 |
| Molecule name | Gene name | Disease name |
|---|---|---|
| (-)-nopinene | PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| (1S,5S)-1-isopropyl-4 -methylenebicyclo [3.1.0]hexane |
PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
| (S)-(+)-alpha-Phellandrene | ACHE | *Functional dyspepsia |
| 1,8-cineole | NOS3 | Colorectal cancer |
| PTGS2 | *Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| acetaldehyde |
BCHE | *Functional dyspepsia |
| CTNNB1 | Colorectal cancer | |
| FOS | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| IL1B | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| IL6 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| JUN | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| LTA4H | Oesophageal cancer | |
| MAPK8 | Crohns's Disease, unspecified | |
| MAPK9 | Crohns's Disease, unspecified | |
| MMP1 |
Kaposi's Sarcoma Pancreatic Cancer |
|
| Mmp12 |
Crohns's Disease, unspecified Gastro-intestinal ulcers Ulcerative colitis |
|
| MMP2 |
Kaposi's Sarcoma Pancreatic Cancer |
|
| MMP3 | Pancreatic Cancer | |
| NOS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| OPRK1 | Diarrhea | |
| POMC | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| RARB | Pancreatic Cancer | |
| RRM1 | Pancreatic Neoplasms | |
| TNF |
*Functional dyspepsia Crohns's Disease, unspecified |
|
| alpha-amyrin | PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
| Ammidin | PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
| anethole | JUN | *Functional dyspepsia |
| Anisketone | ACHE | *Functional dyspepsia |
| ADRA2A | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| CA2 | Pancreatic Cancer | |
| NOS3 | Colon cancer | |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| ANN | PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| APIOL | ADRA2A | *Functional dyspepsia |
| LTA4H | Oesophageal cancer | |
| NOS3 | Colon cancer | |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| SLC6A4 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| Arachic acid | HSP90AB1 | Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| beta-sitosterol | HSP90AB1 | Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) |
| JUN | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| Kcnh2 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| OPRM1 |
Diarrhea Opioid-induced bowel dysfunction |
|
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| SLC6A4 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| Butyrophenone | CA2 | Pancreatic Cancer |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| cis-ligustilide | PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
| D-Camphene | Kcnh2 | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| EIC | PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| TRPV1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| Fenchylacetate | PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
| Isooleic acid |
PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| L-Limonen | PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
| Moslene | ACHE | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| myristic acid | BCHE | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| oleanolic acid | AMY2A | Pancreatic disease |
| oleic acid | BDNF | *Functional dyspepsia |
| CCk | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| CRP | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| GCG | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 | *Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| Pyy | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| palmitic acid | IL10 | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 |
*Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| TNF | *Functional dyspepsia Crohns's Disease, unspecified |
|
| PENTADECYLIC ACID | PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS2 | *Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| Petroselic acid | PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia |
| Sitogluside | HSP90AB1 | Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) |
| HTR3A | *Functional dyspepsia Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting Diarrhea Irritable bowel syndrome Postoperative nausea and vomiting |
|
| Kcnh2 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 | *Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| Skimmetin | ADRA2A | *Functional dyspepsia |
| LTA4H | Oesophageal cancer | |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 | *Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| Stigmasterol | ADRA2A | *Functional dyspepsia |
| LTA4H | Oesophageal cancer | |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 | *Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
|
| TDA | PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia |
| Terragon | ADRA2A | *Functional dyspepsia |
| PTGS1 | *Functional dyspepsia | |
| PTGS2 | *Functional dyspepsia Colorectal cancer Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma Peutz-Jeghers syndrome |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





