Submitted:
27 December 2023
Posted:
27 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Initial Literature Review
2.1. AI for Sustainability
2.2. Sustainability of AI
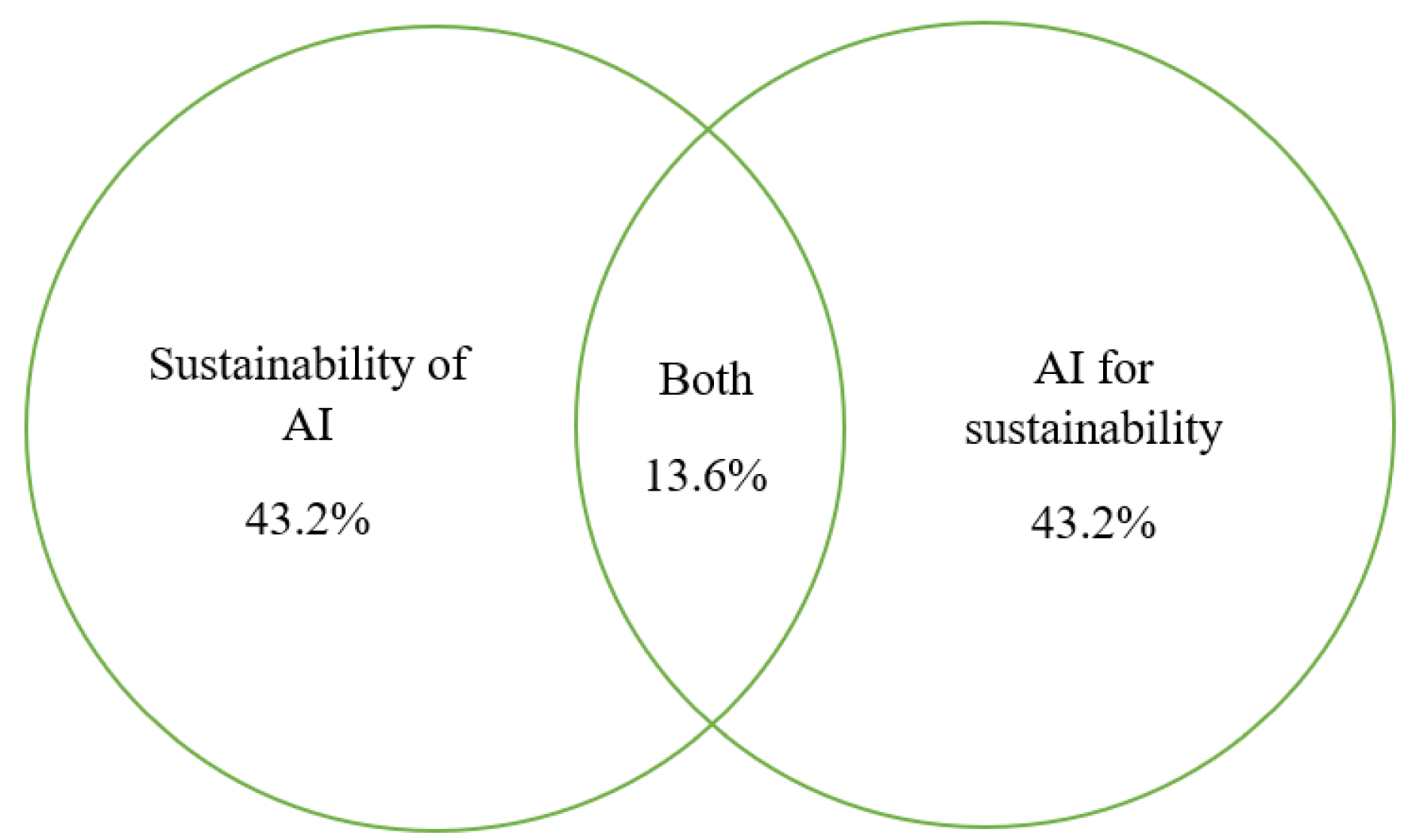
2.3. Combining AI for Sustainability and Sustainability of AI
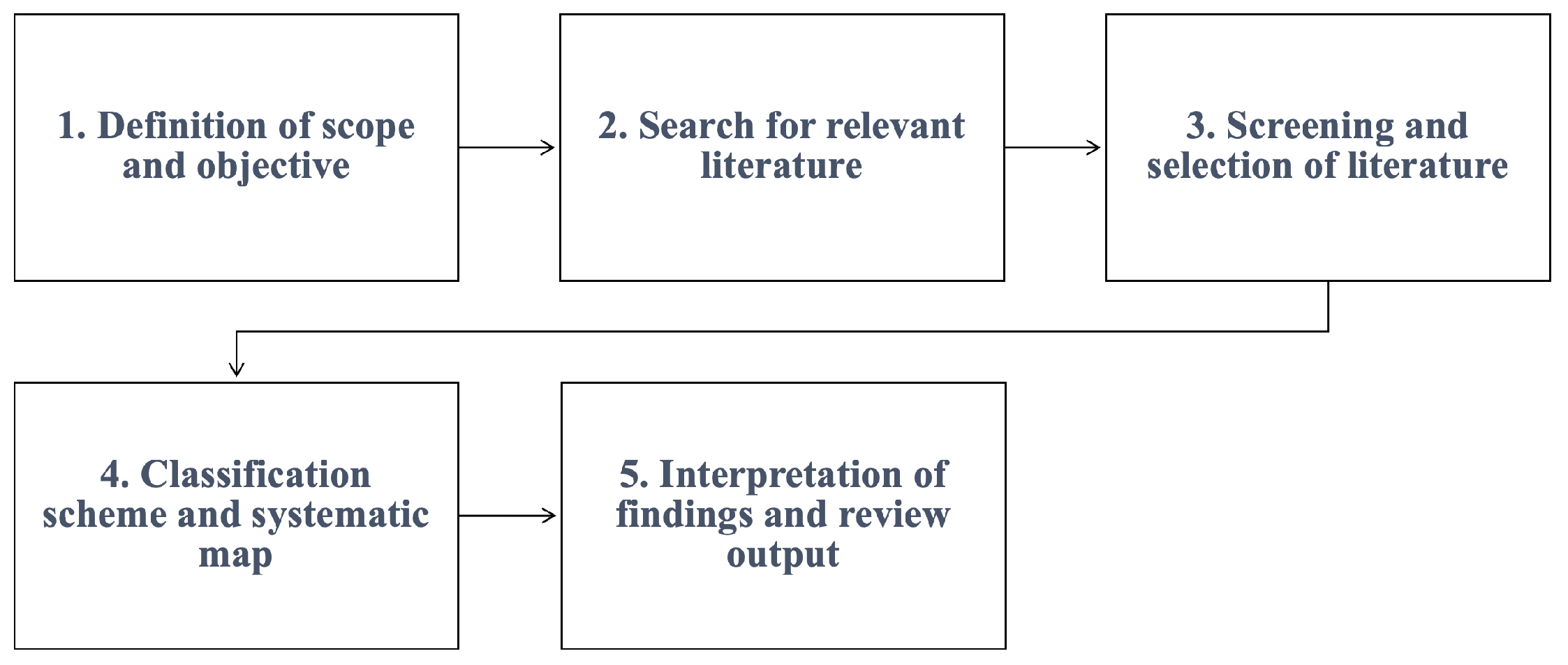
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Definition of scope and objective
3.2. Search for relevant literature
- Google Scholar
- Science Direct
- IEEE
- Springer Link
- Elicit.org
- ACM Digital Library
- AIS eLibrary
- AI Sustainability
- Artificial intelligence sustainability
- Sustainable AI
- AI environmental impact
- AI economic impact
- AI social impact
- Artificial intelligence environmental impact
- Artificial intelligence economic impact
- Artificial intelligence social impact
- AI ethics
3.3. Screening and selection of literature
3.3.1. Inclusion Criteria:
- I1: Abstract explicitly highlights the topic of AI Sustainability. This criterion helped us to only choose research papers having both components and to remove the papers talking about AI in some other context, and not explicitly stating either AI for sustainability or the impact of AI on sustainability.
- I2: The paper’s focus aligns with the chosen research focus. While going through the paper, if the research paper did not cohesively talk about AI Sustainability, then that paper was not included in our analysis.
- I3: Abstract and keywords contain key terms related to the topic. Using this, we eliminated papers that contained the keywords of AI Sustainability, but whose content was outside the scope of our research.
3.3.2. Exclusion Criteria:
- E1: Content focuses only on a specific niche sub-field of research regarding AI Sustainability. To have an overall understanding of our topic, papers corresponding to a niche-specific sub-field of research with AI Sustainability were not included.
- E2: Publication date before 2000 (or after the first half of 2023). This criterion is useful because very few papers on this topic exist in the year range 2010-2018. Further, the year range 2000-2010 did not give any significant results. Hence, keeping the threshold at 2000 helped us to make our analysis extensive and at the same time a bit more efficient. The cut-off of our search and analysis is the first half of 2023.
- E3: Abstract does not cover AI Sustainability. To ensure that the analysis is strictly within the scope of our research, we excluded those papers whose abstracts exhibited a complete absence of any reference to AI Sustainability.
- E4: Full paper not accessible. Papers that looked relevant from the title and first information, but were not accessible, were also excluded from our analysis.
- E5: Language not in English. The papers that were not available in English, were simply excluded from our analysis.
3.4. Classification scheme and systematic map
3.5. Interpretation of findings and review output
4. Results and Visualization
4.1. RQ1: How does the existing literature capture AI Sustainability?
4.2. RQ2: What is the maturity level of the research field of AI Sustainability?
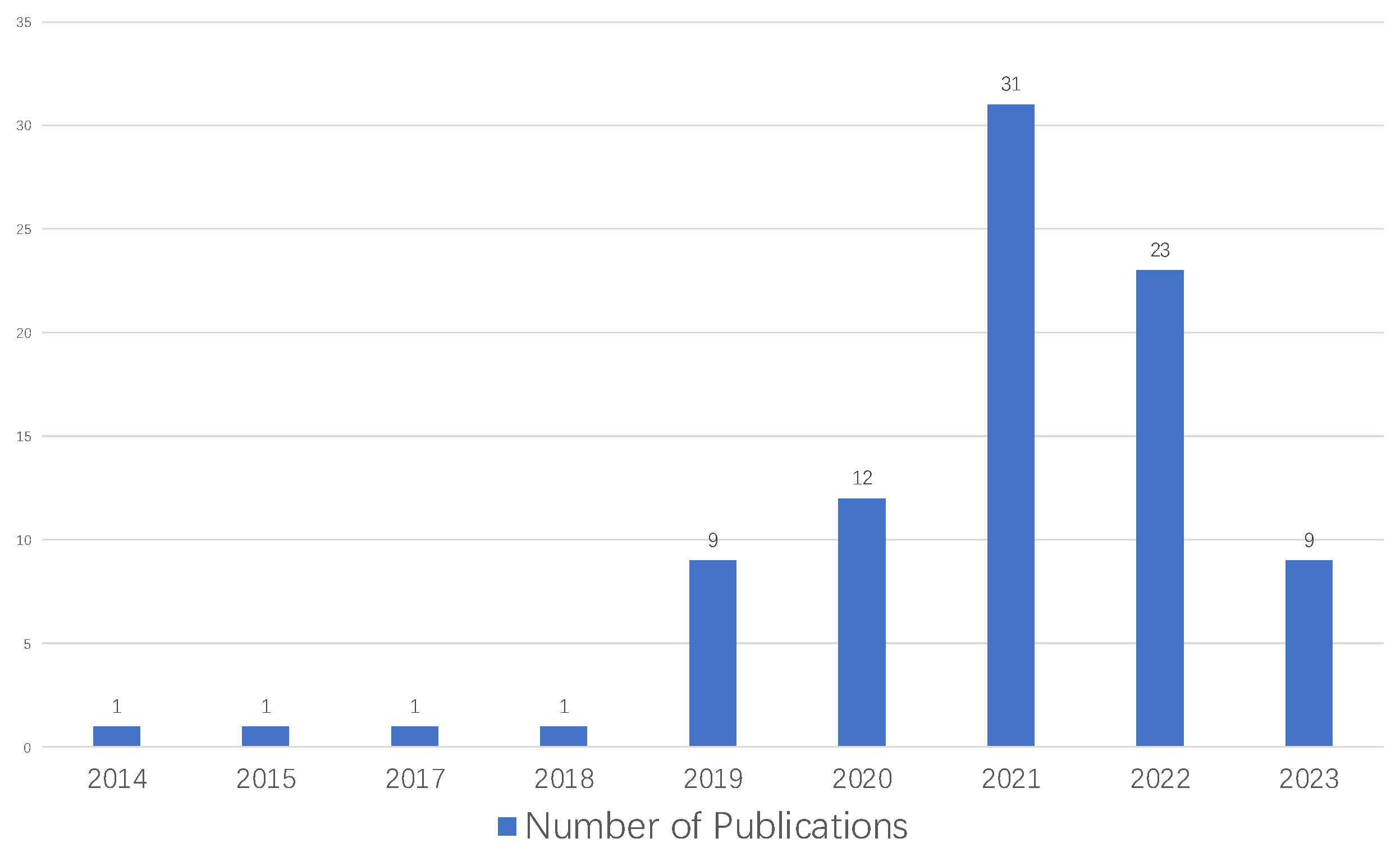
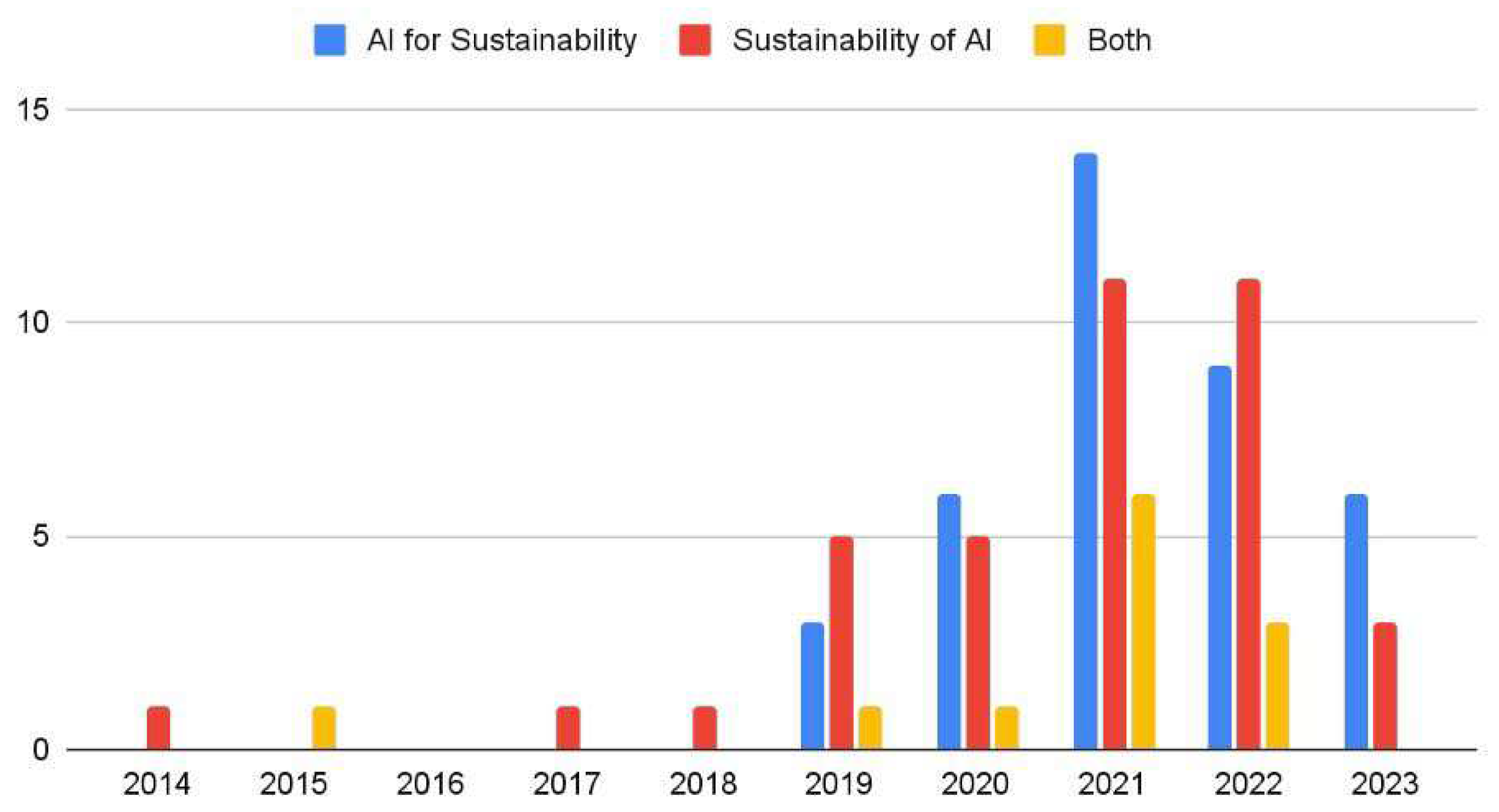
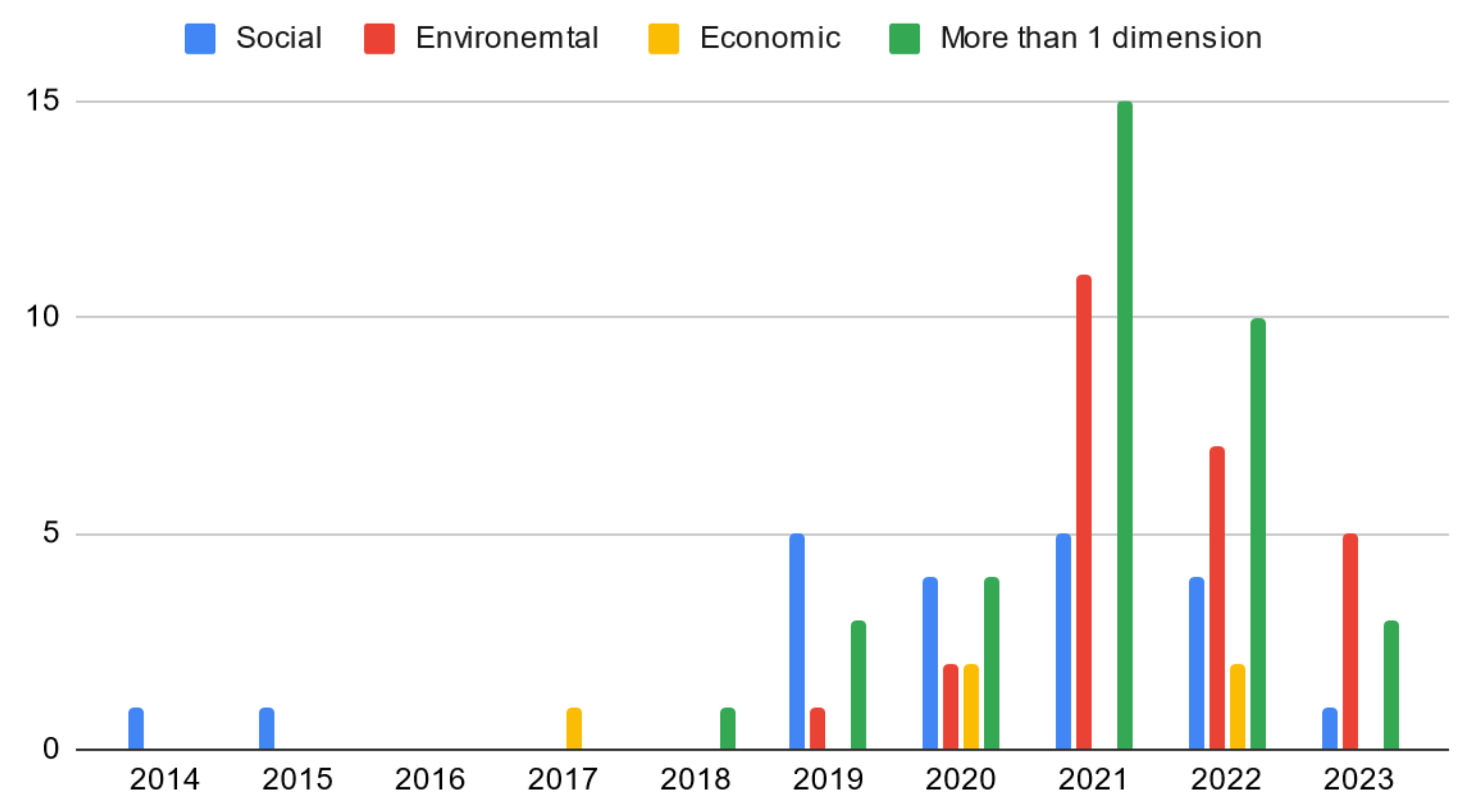
4.2.1. Publication Years
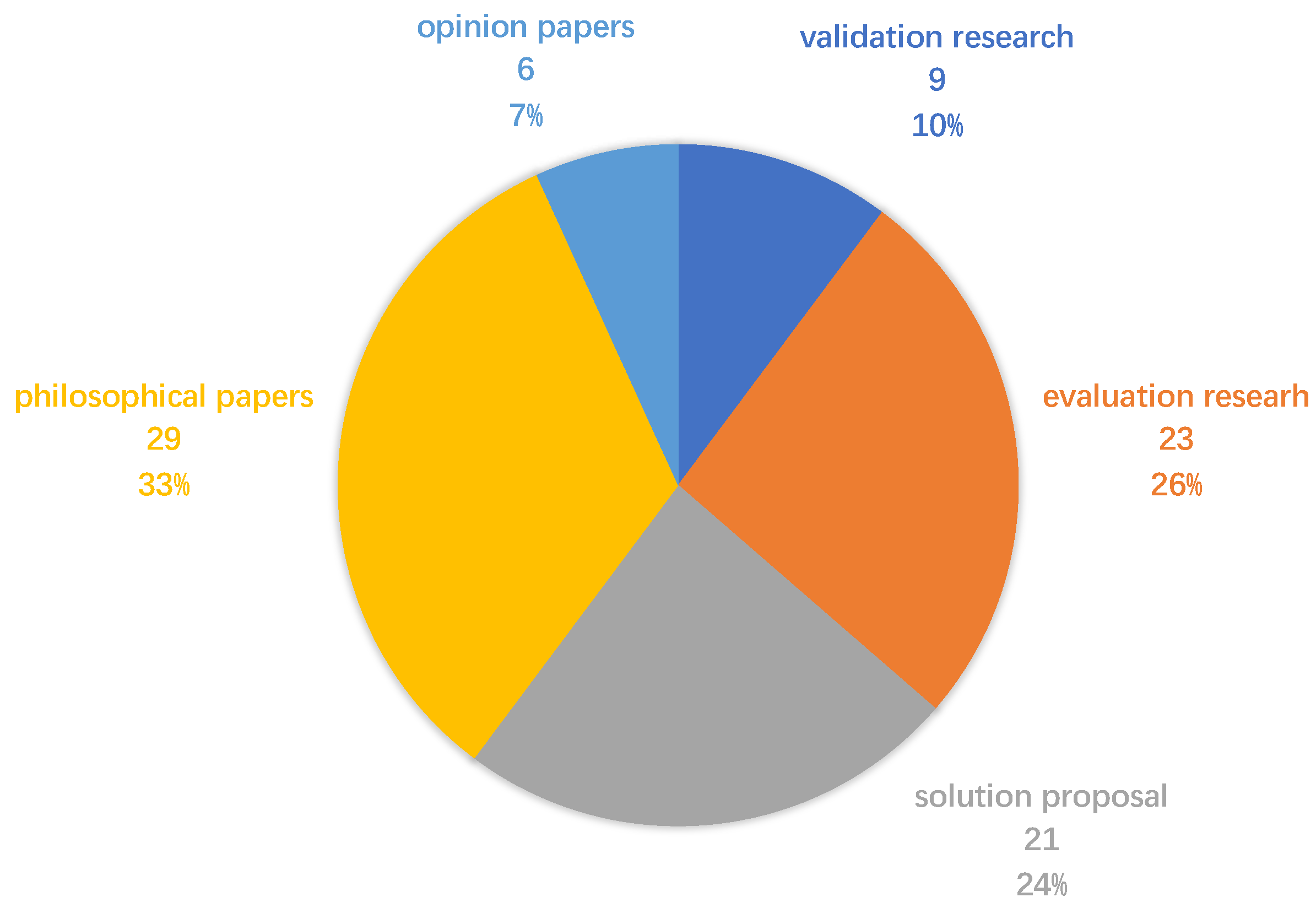
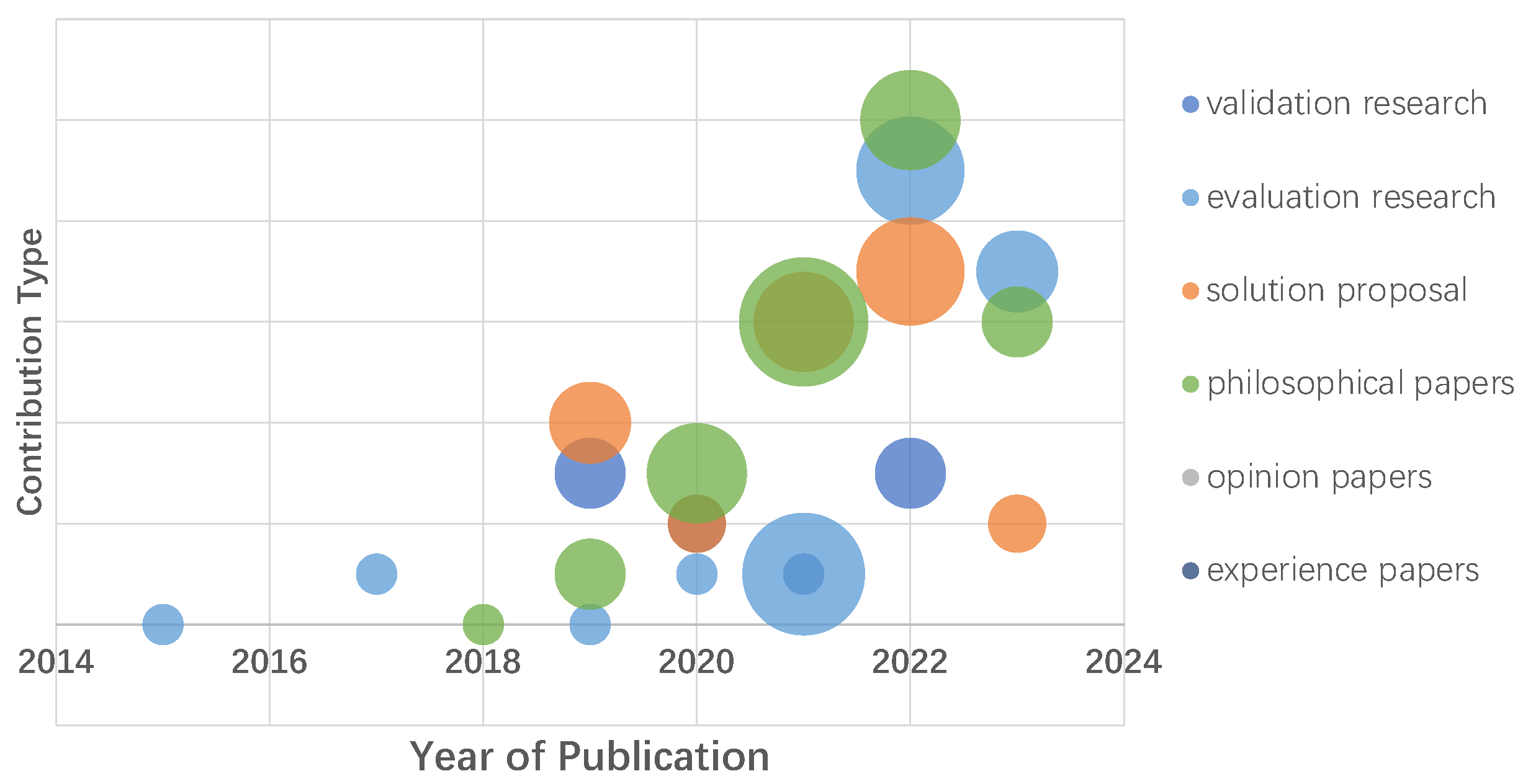
4.2.2. Contribution Types
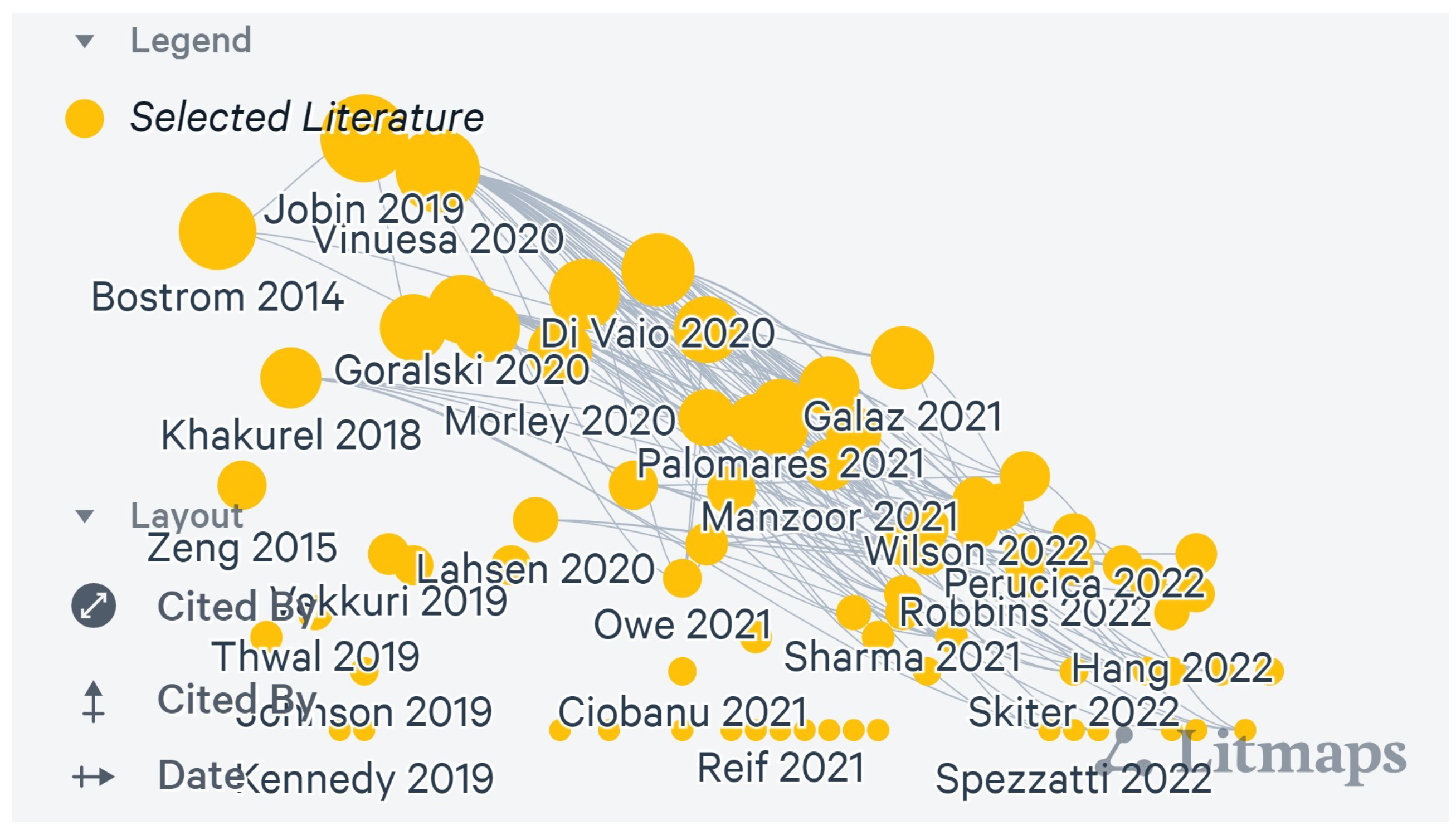
4.2.3. Citations
Procedure
Litmaps Analysis
Maturity Quotient
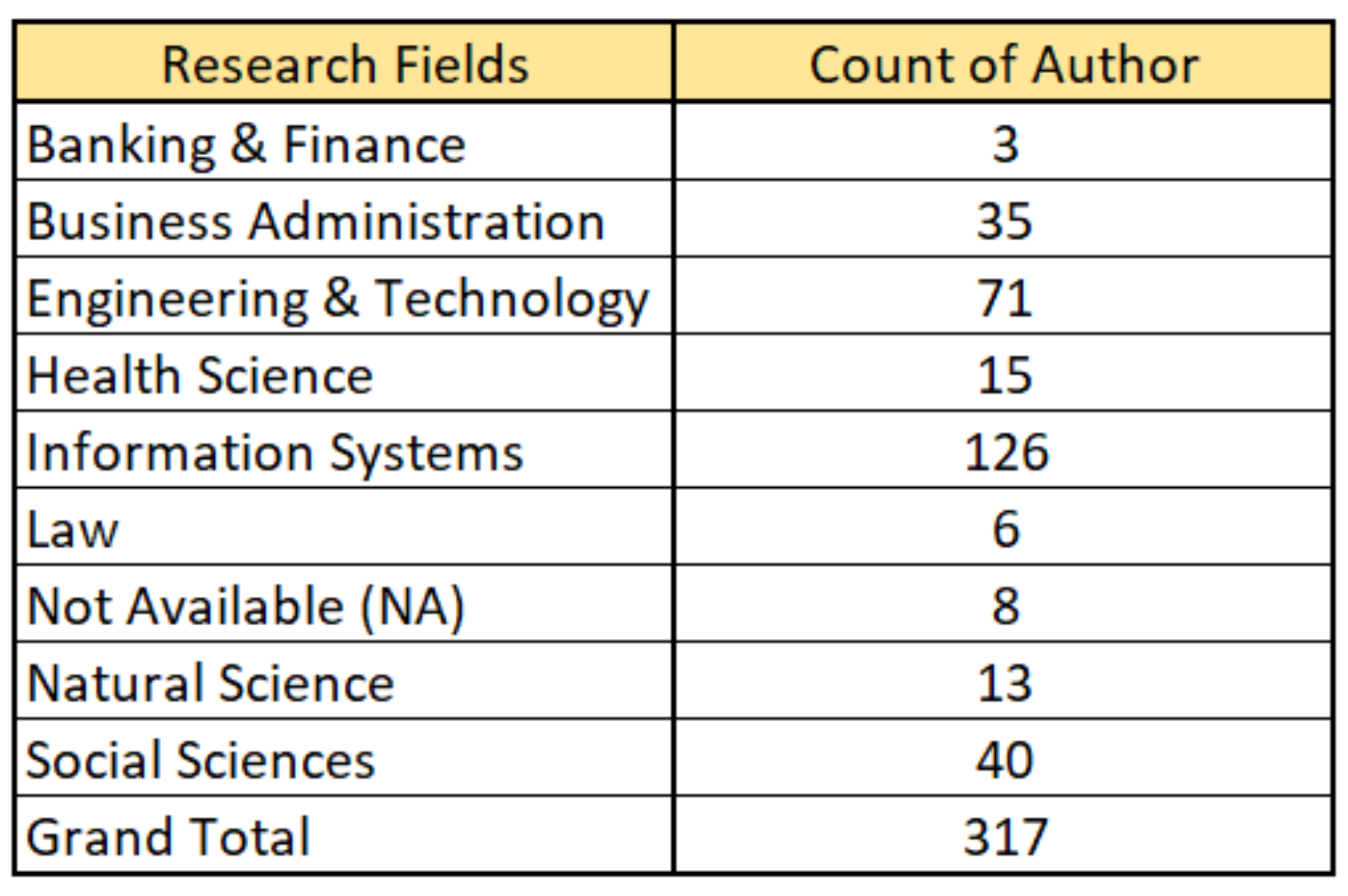
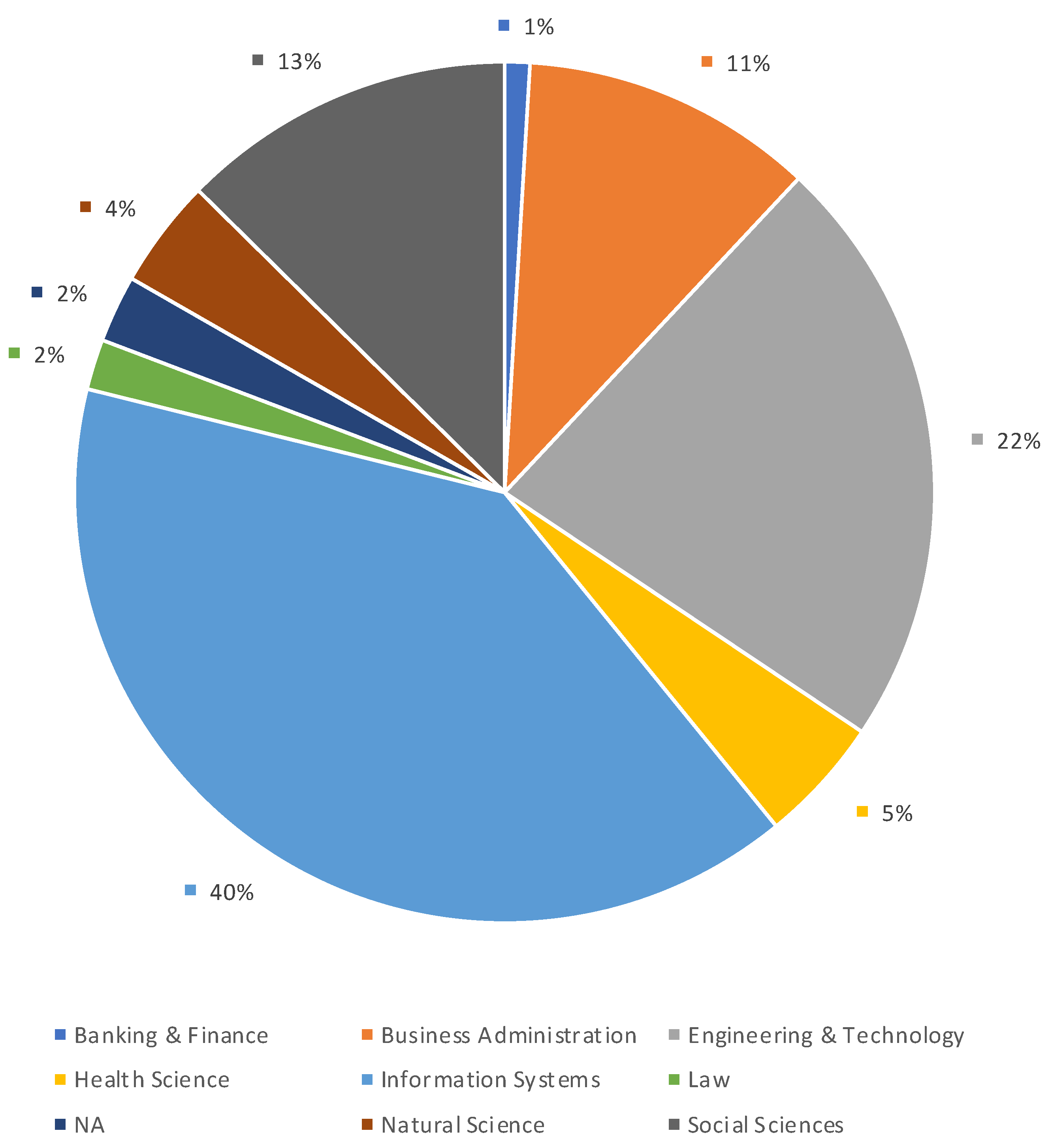
4.2.4. Authorship Analysis
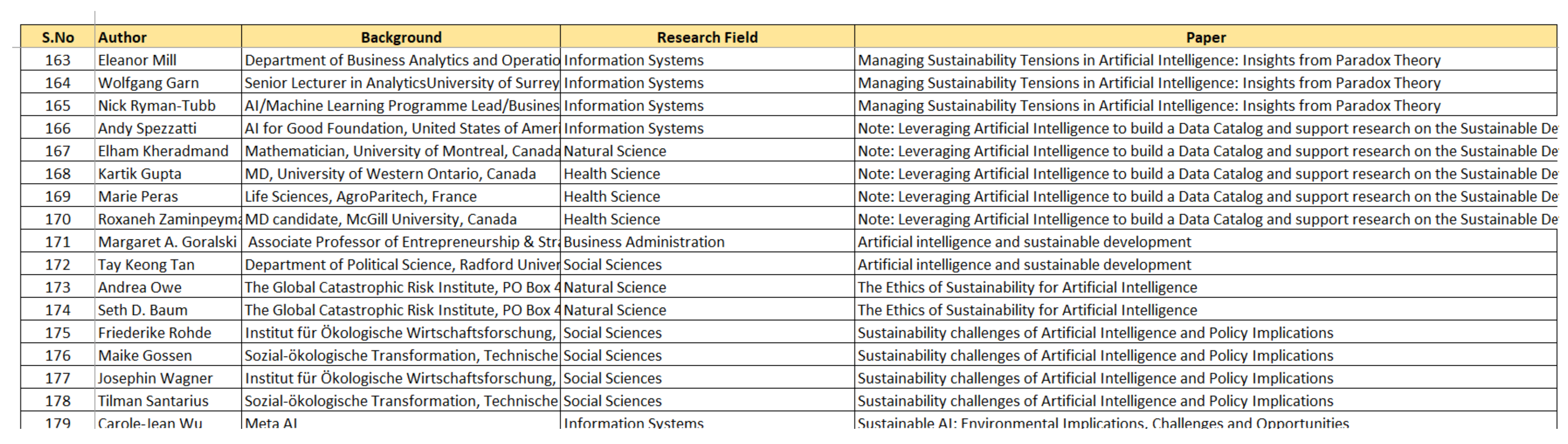
- Banking and Finance: This field consists of backgrounds like finance, accounting, working in a bank, etc.
- Business Administration: The authors in this field have backgrounds related to economics, business administration, management, entrepreneurship, etc.
- Engineering and Technology: This field comprises backgrounds such as software engineering, computer engineering, electrical engineering, industrial engineering, information technology, civil engineering, environmental engineering, biomedical engineering, etc.
- Health Science: This field consists of authors from backgrounds like health labs, medical institutes, health research centers, Doctor of Medicine candidates, life sciences, etc.
- Information Systems: The authors in this field have backgrounds related to artificial intelligence, machine learning, data science, etc. Furthermore, some authors had job titles more suited to the research field of “Engineering and Technology”, however, their work profiles were more suited to information systems. Hence, they have been placed in this field.
- Law: The authors in this research field are mostly working in departments such as the faculty of law.
- Natural Science: This field comprises backgrounds such as sustainability, freshwater ecology, energy, climate change, etc.
- Social Sciences: The authors in this field have backgrounds related to philosophy, theology, religion and culture, public affairs, social studies, internal and regional studies, etc.
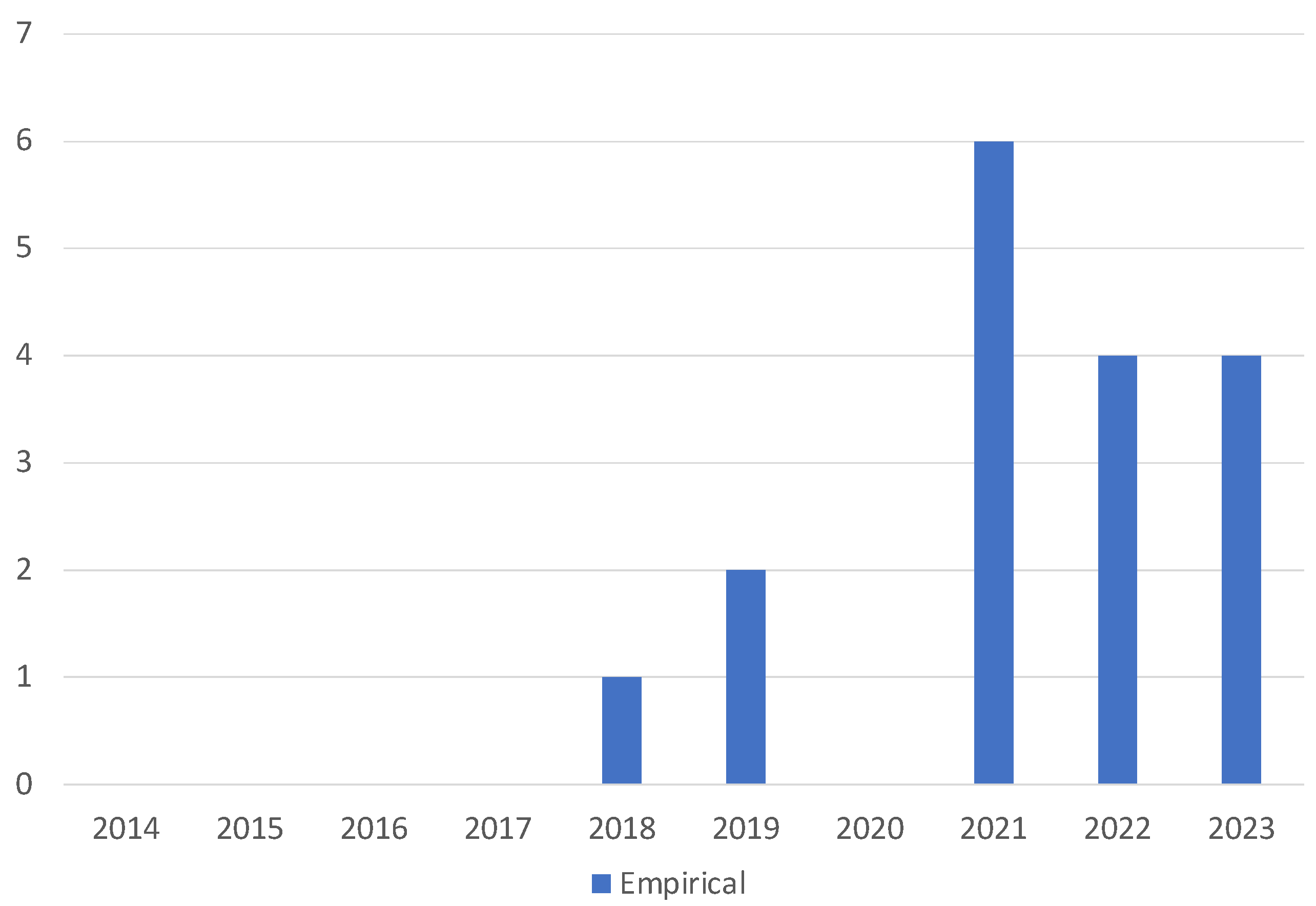
4.2.5. Breadth of Methods Analysis
4.3. RQ3: What is the future research agenda of the research field of AI Sustainability?
5. Discussion and Limitations
5.1. Construct Validity
5.2. Conclusion Validity
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CV | Computer Vision |
| FSSD | Framework for Strategic Sustainable Development |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| LLMs | Large Language Models |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| SLR | Systematic Literature Review |
| SMS | Systematic Mapping Study |
References
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, fourth ed.; Pearson Education Limited; United Kingdom, 2021.
- Davenport, T.H.; Ronanki, R.; et al. Artificial intelligence for the real world. Harvard business review 2018, 96, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Enholm, I.M.; Papagiannidis, E.; Mikalef, P.; Krogstie, J. Artificial Intelligence and Business Value: a Literature Review. Information Systems Frontiers 2022, 24, 1709–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Yoon, S.N. Application of Artificial Intelligence-Based Technologies in the Healthcare Industry: Opportunities and Challenges. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abduljabbar, R.; Dia, H.; Liyanage, S.; Bagloee, S.A. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Transport: An Overview. Sustainability 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.; Doshi, A.; Patel, P.; Shah, M. A comprehensive review on automation in agriculture using artificial intelligence. Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture 2019, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dai, N.; Song, Y.; Chen, H. Artificial intelligence in sustainable energy industry: Status Quo, challenges and opportunities. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 289, 125834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Olmsted, S.M. A Review of Artificial Intelligence Adoptions in the Media Industry. International Journal on Media Management 2019, 21, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, B.; Mao, Y.; Robinson, D. Three Pillars of Sustainability: In Search of Conceptual Origins. Sustainability Science 2019, 14, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wynsberghe, A. Sustainable AI: AI for Sustainability and the Sustainability of AI. AI and Ethics 2021, 1, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J. WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE? http://www-formal.stanford.edu/jmc/whatisai/, 2007.
- Nishant, R.; Kennedy, M.; Corbett, J. Artificial Intelligence for Sustainability: Challenges, Opportunities, and a Research Agenda. International Journal of Information Management 2020, 53, 102104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.K.; Choudhary, S.K.; Singh, V.K. How Can Artificial Intelligence Impact Sustainability: A Systematic Literature Review. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022, 376, 134120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdecchia, R.; Sallou, J.; Cruz, L. A Systematic Review of Green AI, 2023, [arxiv:cs/2301.11047].
- Natarajan, H.K.; de Paula, D.; Dremel, C.; Uebernickel, F. A Theoretical Review on AI Affordances for Sustainability. AMCIS 2022 Proceedings 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, W.; Fu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, L. A Survey on Green Deep Learning, 2021, [arxiv:cs/2111.05193].
- Mittal, S. A Survey on Optimized Implementation of Deep Learning Models on the NVIDIA Jetson Platform. Journal of Systems Architecture 2019, 97, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scells, H.; Zhuang, S.; Zuccon, G. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Green Information Retrieval Research. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Madrid Spain, 2022; pp. 2825–2837. [CrossRef]
- Tonn, B. [No Title Found]. Futures 2010, 42, 1032–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westley, F.; Olsson, P.; Folke, C.; Homer-Dixon, T.; Vredenburg, H.; Loorbach, D.; Thompson, J.; Nilsson, M.; Lambin, E.; Sendzimir, J.; et al. Tipping Toward Sustainability: Emerging Pathways of Transformation. AMBIO 2011, 40, 762–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joppa, L.N. The Case for Technology Investments in the Environment. Nature 2017, 552, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earth, F. Digital Disruptions for Sustainability (D^2S) Agenda– Cross-Cutting Actions Agenda. Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development 2020, 62, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, R.; Azizpour, H.; Leite, I.; Balaam, M.; Dignum, V.; Domisch, S.; Felländer, A.; Langhans, S.D.; Tegmark, M.; Fuso Nerini, F. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nature Communications 2020, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearn, O.R.; Freeman, R.; Jacoby, D.M.P. Responsible AI for Conservation. Nature Machine Intelligence 2019, 1, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaz, V.; Mouazen, A.M. `New Wilderness’ Requires Algorithmic Transparency: A Response to Cantrell et Al. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 2017, 32, 628–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galaz, V.; Centeno, M.A.; Callahan, P.W.; Causevic, A.; Patterson, T.; Brass, I.; Baum, S.; Farber, D.; Fischer, J.; Garcia, D.; et al. Artificial Intelligence, Systemic Risks, and Sustainability. Technology in Society 2021, 67, 101741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçales, L.J.; Farias, K.; Da Silva, B.C. Measuring the Cognitive Load of Software Developers: An Extended Systematic Mapping Study. Information and Software Technology 2021, 136, 106563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Y.; J. Ellis, T. A Systems Approach to Conduct an Effective Literature Review in Support of Information Systems Research. Informing Science: The International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 2006, 9, 181–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strubell, E.; Ganesh, A.; McCallum, A. Energy and Policy Considerations for Modern Deep Learning Research. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2020, 34, 13693–13696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilinger, J.C.; Kempt, H.; Nagel, S. Beware of Sustainable AI! Uses and Abuses of a Worthy Goal. AI and Ethics 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, N.; Yudkowsky, E. The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence. In The Cambridge Handbook of Artificial Intelligence, 1 ed.; Frankish, K.; Ramsey, W.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press, 2014; pp. 316–334. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D. AI Ethics: Science Fiction Meets Technological Reality. IEEE Intelligent Systems 2015, 30, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghion, P.; Jones, B.; Jones, C. Artificial Intelligence and Economic Growth. Technical Report w2 3928, MA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakurel, J.; Penzenstadler, B.; Porras, J.; Knutas, A.; Zhang, W. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence under the Lens of Sustainability. Technologies 2018, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobin, A.; Ienca, M.; Vayena, E. The Global Landscape of AI Ethics Guidelines. Nature Machine Intelligence 2019, 1, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelstadt, B. Principles Alone Cannot Guarantee Ethical AI. Nature Machine Intelligence 2019, 1, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakkuri, V.; Kemell, K.K.; Abrahamsson, P. AI Ethics in Industry: A Research Framework. ArXiv 2019, abs/1910.12695.
- van der Loeff, A.S.; Bassi, I.; Kapila, S.; Gamper, J. AI Ethics for Systemic Issues: A Structural Approach, 2019, [arxiv:cs/1911. 0 3216.
- Kennedy, M.L. What Do Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Ethics of AI Mean in the Context of Research Libraries? Research Library Issues 2019, pp. 3–13. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.A. Technology Innovation and AI Ethics. Research Library Issues 2019, pp. 14–27. [CrossRef]
- Thwal, C.M.; Thar, K.; Hong, C. Edge AI Based Waste Management System for Smart City 1. 2019.
- Szczepanski, M. Economic Impacts of Artificial Intelligence (AI) 2019.
- Morley, J.; Floridi, L.; Kinsey, L.; Elhalal, A. From What to How: An Initial Review of Publicly Available AI Ethics Tools, Methods and Research to Translate Principles into Practices 2019. [CrossRef]
- Siau, K.; Wang, W. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Ethics: Ethics of AI and Ethical AI. Journal of Database Management 2020, 31, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneault, F.; Laflamme, A.S. AI Ethics: How Can Information Ethics Provide a Framework to Avoid Usual Conceptual Pitfalls? An Overview. AI & SOCIETY 2021, 36, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence-Archer, A. AI Ethics: A Strategic Communications Challenge. Defence Strategic Communications 2020, 8, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.; Machado, C.C.; Burr, C.; Cowls, J.; Joshi, I.; Taddeo, M.; Floridi, L. The Ethics of AI in Health Care: A Mapping Review. Social Science & Medicine 2020, 260, 113172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.A.A.; Asadullah, A. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Waste Management and Recycling. Engineering International 2020, 8, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahsen, M. Should AI Be Designed to Save Us From Ourselves?: Artificial Intelligence for Sustainability. IEEE Technology and Society Magazine 2020, 39, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, M.; Hassan, S.; Bhaumik, A. Academic Policy Regarding Sustainability and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Sustainability 2020, 12, 9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralski, M.A.; Tan, T.K. Artificial Intelligence and Sustainable Development. The International Journal of Management Education 2020, 18, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, A.; Palladino, R.; Hassan, R.; Escobar, O. Artificial Intelligence and Business Models in the Sustainable Development Goals Perspective: A Systematic Literature Review. Journal of Business Research 2020, 121, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santor, E. The Impact of Digitalization on the Economy: A Review Article on the NBER Volume "Economics of Artificial Intelligence: An Agenda". International Productivity Monitor 2020, 39, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L. Application of Artificial Intelligence on the CO2 Capture: A Review. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 2021, 145, 1751–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Lee, K.Y. The Mutual Benefits of Renewables and Carbon Capture: Achieved by an Artificial Intelligent Scheduling Strategy. Energy Conversion and Management 2021, 233, 113856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourbakhsh, I.R. AI Ethics: A Call to Faculty. Communications of the ACM 2021, 64, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazim, E.; Koshiyama, A.S. A High-Level Overview of AI Ethics. Patterns 2021, 2, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwafor, I.E. AI Ethical Bias: A Case for AI Vigilantism (AIlantism) in Shaping the Regulation of AI. International Journal of Law and Information Technology 2021, p. eaab008. [CrossRef]
- Heo, J. Ethical Review in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. AI Ethics Journal 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, A.C.; Meșniță, G. AI ETHICS IN BUSINESS – A BIBLIOMETRIC APPROACH. Review of Economic and Business Studies 2021, 14, 169–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corea, F. Artificial Intelligence: ethical and social considerations. BioLaw Journal - Rivista di BioDiritto 2021, pp. 307–313 Paginazione. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, S.; BalaMurugan, S.; Tamizharasi, G. Artificial Intelligence Based E-Waste Management for Environmental Planning. Environmental Impact Assessment Review 2021, 87, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, S.; Herzog, B.; Hemp, J.; Schröder-Preikschat, W.; Hönig, T. AI Waste Prevention: Time and Power Estimation for Edge Tensor Processing Units: Poster. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Future Energy Systems, Virtual Event Italy, 2021; pp. 300–301. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Vaid, U. Emerging Role of Artificial Intelligence in Waste Management Practices. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2021, 889, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijos, J.C.B.F.; Queiroz, L.M.; Zanta, V.M.; Oliveira-Esquerre, K.P. Towards Artificial Intelligence in Urban Waste Management: An Early Prospect for Latin America. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2021, 1196, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, E.; Hermann, G. Artificial Intelligence in Research and Development for Sustainability: The Centrality of Explicability and Research Data Management. AI and Ethics 2022, 2, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sætra, H.S. AI in Context and the Sustainable Development Goals: Factoring in the Unsustainability of the Sociotechnical System. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Langhans, S.D.; Domisch, S.; Fuso-Nerini, F.; Felländer, A.; Battaglini, M.; Tegmark, M.; Vinuesa, R. Assessing Whether Artificial Intelligence Is an Enabler or an Inhibitor of Sustainability at Indicator Level. Transportation Engineering 2021, 4, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, A.; Baum, S. The Ethics of Sustainability for Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on AI for People: Towards Sustainable AI, CAIP 2021, 20-24 November 2021, Bologna, Italy, Bologna, Italy, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Rohde, F.; Gossen, M.; Wagner, J.; Santarius, T. Sustainability Challenges of Artificial Intelligence and Policy Implications. Ökologisches Wirtschaften - Fachzeitschrift 2021, 36, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Raghavendra, R.; Gupta, U.; Acun, B.; Ardalani, N.; Maeng, K.; Chang, G.; Behram, F.A.; Huang, J.; Bai, C.; et al. Sustainable AI: Environmental Implications, Challenges and Opportunities, 2022, [arxiv:cs/2111.00364].
- Saheb, T.; Dehghani, M. Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Energy: A Contextual Topic Modeling and Content Analysis 2021. [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T. Greening the Artificial Intelligence for a Sustainable Planet: An Editorial Commentary. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, I.; Martínez-Cámara, E.; Montes, R.; García-Moral, P.; Chiachio, M.; Chiachio, J.; Alonso, S.; Melero, F.J.; Molina, D.; Fernández, B.; et al. A Panoramic View and Swot Analysis of Artificial Intelligence for Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals by 2030: Progress and Prospects. Applied Intelligence 2021, 51, 6497–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isensee, C.; Griese, K.M.; Teuteberg, F. Sustainable Artificial Intelligence: A Corporate Culture Perspective. Sustainability Management Forum | NachhaltigkeitsManagementForum 2021, 29, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Mehmood, R.; Corchado, J.M. Green Artificial Intelligence: Towards an Efficient, Sustainable and Equitable Technology for Smart Cities and Futures. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, B.; Othman, I.; Durdyev, S.; Ismail, S.; Wahab, M. Influence of Artificial Intelligence in Civil Engineering toward Sustainable Development—A Systematic Literature Review. Applied System Innovation 2021, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigola, A.; Da Costa, P.R.; Carvalho, L.C.; Silva, L.F.D.; Kniess, C.T.; Maccari, E.A. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Digital Technologies to the Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals: A Perspective from Brazil and Portugal. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, I.; Singh, G.; Tiwar, A.; Kumar, A.; Prasad, H. Impact of AI on Environment. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT) 2021, 12, 1928–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoormann, T.; Strobel, G.; Möller, F.; Petrik, D. Achieving sustainability with artificial intelligence-a survey of information systems research. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS 2021), 2021.
- Kumar, A.; Madaan, G.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, A. Application of Disruptive Technologies on Environmental Health: An Overview of Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain and Internet of Things. Asia Pacific Journal of Health Management 2021, 16, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Badshah, S.; Liang, P.; Khan, B.; Waseem, M.; Niazi, M.; Akbar, M.A. Ethics of AI: A Systematic Literature Review of Principles and Challenges 2021. [CrossRef]
- Christoforaki, M.; Beyan, O. AI Ethics—A Bird’s Eye View. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallamaa, J.; Kalliokoski, T. AI Ethics as Applied Ethics. Frontiers in Computer Science 2022, 4, 776837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andeobu, L.; Wibowo, S.; Grandhi, S. Artificial Intelligence Applications for Sustainable Solid Waste Management Practices in Australia: A Systematic Review. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 834, 155389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalakshmi, J.; Sumangali, K.; Jayanthi, J.; Muthulakshmi, K. Artificial Intelligence with Earthworm Optimization Assisted Waste Management System for Smart Cities. Global NEST Journal 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, H.; Chen, Z. How to Realize the Full Potentials of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Digital Economy? A Literature Review. Journal of Digital Economy 2022, 1, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budennyy, S.; Lazarev, V.; Zakharenko, N.; Korovin, A.; Plosskaya, O.; Dimitrov, D.; Arkhipkin, V.; Oseledets, I.; Barsola, I.; Egorov, I.; et al. Eco2AI: Carbon Emissions Tracking of Machine Learning Models as the First Step towards Sustainable AI 2022. [CrossRef]
- Perucica, N.; Andjelkovic, K. Is the Future of AI Sustainable? A Case Study of the European Union. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy 2022, 16, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, M.; Chan, A.; Li, X.; Ong, Y.S. A Survey on AI Sustainability: Emerging Trends on Learning Algorithms and Research Challenges 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.; Van Der Velden, M. Sustainable AI: An Integrated Model to Guide Public Sector Decision-Making. Technology in Society 2022, 68, 101926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mill, E.; Garn, W.; Ryman-Tubb, N. Managing Sustainability Tensions in Artificial Intelligence: Insights from Paradox Theory. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2022 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, Oxford United Kingdom, 2022; pp. 491–498. [CrossRef]
- Spezzatti, A.; Kheradmand, E.; Gupta, K.; Peras, M.; Zaminpeyma, R. Note: Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Build a Data Catalog and Support Research on the Sustainable Development Goals. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCAS/SIGCHI Conference on Computing and Sustainable Societies (COMPASS), Seattle WA USA; 2022; pp. 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachot, A.; Patissier, C. Towards Sustainable Artificial Intelligence: An Overview of Environmental Protection Uses and Issues 2022. [CrossRef]
- Salas, J.; Patterson, G.; De Barros Vidal, F. A Systematic Mapping of Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Sustainability Challenges in Latin America and the Caribbean. IEEE Latin America Transactions 2022, 20, 2312–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, D. A Framework to Analyze the Impacts of AI with the Sustainable Development Goals. Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology 2022, 17, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, S.; Van Wynsberghe, A. Our New Artificial Intelligence Infrastructure: Becoming Locked into an Unsustainable Future. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wynsberghe, A.; Vandemeulebroucke, T.; Bolte, L.; Nachid, J. Special Issue “Towards the Sustainability of AI; Multi-Disciplinary Approaches to Investigate the Hidden Costs of AI”. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralski, M.A.; Tan, T.K. Artificial Intelligence and Poverty Alleviation: Emerging Innovations and Their Implications for Management Education and Sustainable Development. The International Journal of Management Education 2022, 20, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabelle, D.A.; Westerlund, M. A Review and Categorization of Artificial Intelligence-Based Opportunities in Wildlife, Ocean and Land Conservation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiter, N.N.; Rogachev, A.F.; Ketko, N.V.; Simonov, A.B.; Tarasova, I.A. Sustainable Development of Enterprises in Conditions of Smart Ecology: Analysis of The Main Problems and Development of Ways to Solve Them, Based on Artificial Intelligence Methods and Innovative Technologies. Frontiers in Environmental Science 2022, 10, 892222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqi, A.; Abdeldayem, M.M.; Aldulaimi, S.H. Embedding Artificial Intelligence and Green Ideology in Formulating Corporate and Marketing Strategies. In Proceedings of the 2022 ASU International Conference in Emerging Technologies for Sustainability and Intelligent Systems (ICETSIS), Manama, Bahrain; 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopka, A.; Grashof, N. Artificial Intelligence: Catalyst or Barrier on the Path to Sustainability? Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2022, 175, 121318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solos, W.K.; Leonard, J. On the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Economy. Science Insights 2022, 41, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, C.; Douglas, D.; Lu, Q.; Schleiger, E.; Whittle, J.; Lacey, J.; Newnham, G.; Hajkowicz, S.; Robinson, C.; Hansen, D. AI Ethics Principles in Practice: Perspectives of Designers and Developers. IEEE Transactions on Technology and Society 2023, 4, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, I.; Aziz Al-Talib, G.A. Waste Classification Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques:Literature Review. Technium: Romanian Journal of Applied Sciences and Technology 2023, 5, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.S.S.; Senjyu, T. Shaping the Future of Sustainable Energy through AI-enabled Circular Economy Policies. Circular Economy 2023, 2, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Yu, J.; Chen, Z.; Osman, A.I.; Farghali, M.; Ihara, I.; Hamza, E.H.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.S. Artificial Intelligence for Waste Management in Smart Cities: A Review. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2023, 21, 1959–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal Filho, W.; Yang, P.; Eustachio, J.H.P.P.; Azul, A.M.; Gellers, J.C.; Gielczyk, A.; Dinis, M.A.P.; Kozlova, V. Deploying Digitalisation and Artificial Intelligence in Sustainable Development Research. Environment, Development and Sustainability 2023, 25, 4957–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, M.S. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Social Science Issues: A Case Study on Predicting Population Change. Journal of the Knowledge Economy 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piya, S.; Lennerz, J.K. Sustainable Development Goals Applied to Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence Applications in Low- to Middle-Income Countries. Frontiers in Medicine 2023, 10, 1146075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Research on the Impact of Artificial Intelligence Technology on Green Innovation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering and Computer Communication (EIECC 2021); Zhu, Z.; Cen, F., Eds., Nanchang, China; 2022; p. 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.; Feldt, R.; Mujtaba, S.; Mattsson, M. Systematic Mapping Studies in Software Engineering. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering (EASE); 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R. Economic Growth given Machine Intelligence. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research - JAIR 2001.
- Acemoglu, D.; Restrepo, P. Automation and New Tasks: How Technology Displaces and Reinstates Labor. Technical Report w2 5684, MA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgesius, Z. Discrimination, Artificial Intelligence, and Algorithmic Decision-Making. 2018.
- Bender, E.M.; Gebru, T.; McMillan-Major, A.; Shmitchell, S. Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, New York, NY, USA, 2021; FAccT ’21, p. 610–623. [CrossRef]
- Strubell, E.; Ganesh, A.; McCallum, A. Energy and Policy Considerations for Deep Learning in NLP. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics; pp. 20193645–3650. [CrossRef]
- Tomašev, N.; Cornebise, J.; Hutter, F.; Mohamed, S.; Picciariello, A.; Connelly, B.; Belgrave, D.C.M.; Ezer, D.; Haert, F.C.V.D.; Mugisha, F.; et al. AI for Social Good: Unlocking the Opportunity for Positive Impact. Nature Communications 2020, 11, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeemering, E.S. Sustainability Management, Strategy and Reform in Local Government. Public Management Review 2018, 20, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keathley-Herring, H.; Gonzalez Aleu, F.; Orlandini, P.; Van Aken, E.; Deschamps, F.; Leite, L. Proposed Maturity Assessment Framework for a Research Field; 2013.
- Wieringa, R.; Maiden, N.; Mead, N.; Rolland, C. Requirements Engineering Paper Classification and Evaluation Criteria: A Proposal and a Discussion. Requirements Engineering 2006, 11, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloni, M.J.; Carter, C.R.; Carr, A.S. Assessing Logistics Maturation through Author Concentration. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management 2009, 39, 250–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luccioni, A.S.; Jernite, Y.; Strubell, E. Power Hungry Processing: Watts Driving the Cost of AI Deployment? ArXiv 2023, 6863. [Google Scholar]
| No. | Title | Year | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence | 2014 | Bostrom and Yudkowsky [31] |
| 2 | AI Ethics: Science Fiction Meets Technological Reality | 2015 | Zeng [32] |
| 3 | Artificial Intelligence and Economic Growth | 2017 | Aghion et al. [33] |
| 4 | The Rise of Artificial Intelligence under the Lens of Sustainability | 2018 | Khakurel et al. [34] |
| 5 | Artificial Intelligence: the Global Landscape of Ethics Guidelines | 2019 | Jobin et al. [35] |
| 6 | Principles Alone Cannot Guarantee Ethical AI | 2019 | Mittelstadt [36] |
| 7 | AI Ethics in Industry: A Research Framework | 2019 | Vakkuri et al. [37] |
| 8 | AI Ethics for Systemic Issues: A Structural Approach | 2019 | van der Loeff et al. [38] |
| 9 | What Do Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Ethics of AI Mean in the Context of Research Libraries? | 2019 | Kennedy [39] |
| 10 | Technology Innovation and AI Ethics | 2019 | Johnson [40] |
| 11 | Edge AI based Waste Management System for Smart City | 2019 | Thwal et al. [41] |
| 12 | Economic impacts of artificial intelligence | 2019 | Szczepanski [42] |
| 13 | From What to How: An Initial Review of Publicly Available AI Ethics Tools, Methods and Research to Translate Principles into Practices | 2019 | Morley et al. [43] |
| 14 | Artificial Intelligence (AI) Ethics: Ethics of AI and Ethical AI | 2020 | Siau and Wang [44] |
| 15 | AI Ethics: How Can Information Ethics Provide A Framework To Avoid Usual Conceptual Pitfalls? An Overview | 2021 | Bruneault and Laflamme [45] |
| 16 | AI Ethics: A Strategic Communications Challenge | 2020 | Lawrence-Archer [46] |
| 17 | The Ethics Of AI In Health Care: A Mapping Review. | 2020 | Morley et al. [47] |
| 18 | Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Waste Management and Recycling | 2020 | Ahmed and Asadullah [48] |
| 19 | Artificial Intelligence For Sustainability: Challenges, Opportunities, And A Research Agenda | 2020 | Nishant et al. [12] |
| 20 | The Role Of Artificial Intelligence In Achieving The Sustainable Development Goals | 2020 | Vinuesa et al. [23] |
| 21 | Should AI Be Designed To Save Us From Ourselves? | 2020 | Lahsen [49] |
| 22 | Academic Policy Regarding Sustainability and Artificial Intelligence (AI) | 2020 | Tanveer et al. [50] |
| 23 | Artificial Intelligence And Sustainable Development | 2020 | Goralski and Tan [51] |
| 24 | Artificial Intelligence And Business Models In The Sustainable Development Goals Perspective: A Systematic Literature Review | 2020 | Di Vaio et al. [52] |
| 25 | The Impact of Digitalization on the Economy: A Review Article on the NBER Volume "Economics of Artificial Intelligence: An Agenda" | 2020 | Santor [53] |
| 26 | Application Of Artificial Intelligence On The CO2 Capture: A Review | 2021 | Cao [54] |
| 27 | The Mutual Benefits Of Renewables And Carbon Capture: Achieved By An Artificial Intelligent Scheduling Strategy | 2021 | Chen et al. [55] |
| 28 | AI Ethics: A Call To Faculty | 2021 | Nourbakhsh [56] |
| 29 | A High-Level Overview of AI Ethics | 2021 | Kazim and Koshiyama [57] |
| 30 | AI Ethical Bias: A Case For AI Vigilantism (Ailantism) In Shaping The Regulation of AI | 2021 | Nwafor [58] |
| 31 | Ethical Review in The Age of Artificial Intelligence | 2021 | Heo [59] |
| 32 | AI Ethics In Business – A Bibliometric Approach | 2021 | Ciobanu and Meșniță [60] |
| 33 | Artificial Intelligence: Ethical And Social Considerations | 2021 | Corea [61] |
| 34 | Artificial Intelligence Based E-Waste Management For Environmental Planning | 2021 | Chen et al. [62] |
| 35 | AI Waste Prevention: Time and Power Estimation for Edge Tensor Processing Units | 2021 | Reif et al. [63] |
| 36 | Emerging Role Of Artificial Intelligence In Waste Management Practices | 2021 | Sharma and Vaid [64] |
| 37 | Towards Artificial Intelligence In Urban Waste Management: An Early Prospect For Latin America | 2021 | Bijos et al. [65] |
| 38 | Sustainable AI: AI for Sustainability And The Sustainability Of AI | 2021 | Van Wynsberghe [10] |
| 39 | Artificial Intelligence, Systemic Risks, And Sustainability | 2021 | Galaz et al. [26] |
| 40 | Artificial Intelligence In Research And Development For Sustainability: The Centrality Of Explicability And Research Data Management | 2022 | Hermann and Hermann [66] |
| 41 | AI in Context and the Sustainable Development Goals: Factoring in the Unsustainability of the Sociotechnical System | 2021 | Sӕtra [67] |
| 42 | Assessing Whether Artificial Intelligence Is An Enabler Or An Inhibitor Of Sustainability At Indicator Level | 2021 | Gupta et al. [68] |
| 43 | The Ethics of Sustainability for Artificial Intelligence | 2021 | Owe and Baum [69] |
| 44 | Sustainability Challenges of Artificial Intelligence and Policy Implications | 2021 | Rohde et al. [70] |
| 45 | Sustainable AI: Environmental Implications, Challenges and Opportunities | 2022 | Wu et al. [71] |
| 46 | Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Energy: A Contextual Topic Modeling and Content Analysis | 2021 | Saheb and Dehghani [72] |
| 47 | Greening the Artificial Intelligence for a Sustainable Planet: An Editorial Commentary | 2021 | Yigitcanlar [73] |
| 48 | A Panoramic View And Swot Analysis Of Artificial Intelligence For Achieving The Sustainable Development Goals By 2030: Progress And Prospects | 2021 | Palomares et al. [74] |
| 49 | Sustainable Artificial Intelligence: A Corporate Culture Perspective | 2021 | Isensee et al. [75] |
| 50 | Green Artificial Intelligence: Towards an Efficient, Sustainable and Equitable Technology for Smart Cities and Futures | 2021 | Yigitcanlar et al. [76] |
| 51 | Influence of Artificial Intelligence in Civil Engineering toward Sustainable Development—A Systematic Literature Review | 2021 | Manzoor et al. [77] |
| 52 | Artificial Intelligence-Driven Digital Technologies to the Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals: A Perspective from Brazil and Portugal | 2021 | Pigola et al. [78] |
| 53 | Impact of AI on Environment | 2021 | Verma et al. [79] |
| 54 | Achieving Sustainability with Artificial Intelligence-A Survey of Information Systems Research | 2021 | Schoormann et al. [80] |
| 55 | Application of Disruptive Technologies on Environmental Health: An overview of artificial intelligence, blockchain and internet of things | 2021 | Kumar et al. [81] |
| 56 | Ethics of AI: A Systematic Literature Review of Principles and Challenges | 2021 | Khan et al. [82] |
| 57 | AI Ethics—A Bird’s Eye View | 2022 | Christoforaki and Beyan [83] |
| 58 | AI Ethics as Applied Ethics | 2022 | Hallamaa and Kalliokoski [84] |
| 59 | Artificial Intelligence Applications For Sustainable Solid Waste Management Practices In Australia: A Systematic Review. | 2022 | Andeobu et al. [85] |
| 60 | Artificial Intelligence with Earthworm Optimization Assisted Waste Management System for Smart Cities | 2023 | Rajalakshmi et al. [86] |
| 61 | How Can Artificial Intelligence Impact Sustainability: A Systematic Literature Review | 2022 | Kar et al. [13] |
| 62 | How To Realize The Full Potentials Of Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Digital Economy? A Literature Review | 2022 | Hang and Chen [87] |
| 63 | ECO2AI: Carbon Emissions Tracking Of Machine Learning Models As The First Step Towards Sustainable AI | 2022 | Budennyy et al. [88] |
| 64 | Is the future of AI Sustainable? A Case Study of the European Union | 2022 | Perucica and Andjelkovic [89] |
| 65 | A Survey on AI Sustainability: Emerging Trends on Learning Algorithms and Research Challenges | 2022 | Chen et al. [90] |
| 66 | Sustainable AI: An Integrated Model to Guide Public Sector Decision-Making | 2022 | Wilson and Van Der Velden [91] |
| 67 | Managing Sustainability Tensions in Artificial Intelligence: Insights from Paradox Theory | 2022 | Mill et al. [92] |
| 68 | Note: Leveraging Artificial Intelligence To Build A Data Catalog And Support Research On The Sustainable Development Goals | 2022 | Spezzatti et al. [93] |
| 69 | Towards Sustainable Artificial Intelligence: An Overview of Environmental Protection Uses and Issues | 2022 | Pachot and Patissier [94] |
| 70 | A Systematic Mapping of Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Sustainability Challenges in Latin America and the Caribbean | 2022 | Salas et al. [95] |
| 71 | A Framework to Analyze the Impacts of AI with the Sustainable Development Goals | 2022 | Si [96] |
| 72 | Our New Artificial Intelligence Infrastructure: Becoming Locked into an Unsustainable Future | 2022 | Robbins and Van Wynsberghe [97] |
| 73 | Special Issue “Towards the Sustainability of AI; Multi-Disciplinary Approaches to Investigate the Hidden Costs of AI” | 2022 | Van Wynsberghe et al. [98] |
| 74 | Artificial Intelligence and Poverty Alleviation: Emerging Innovations and Their Implications for Management Education and Sustainable Development | 2022 | Goralski and Tan [99] |
| 75 | A Review and Categorization of Artificial Intelligence-Based Opportunities in Wildlife, Ocean and Land Conservation | 2022 | Isabelle and Westerlund [100] |
| 76 | Sustainable Development of Enterprises in Conditions of Smart Ecology: Analysis of The Main Problems and Development of Ways to Solve Them, Based on Artificial Intelligence Methods and Innovative Technologies | 2022 | Skiter et al. [101] |
| 77 | Embedding Artificial Intelligence and Green Ideology in Formulating Corporate and Marketing Strategies | 2022 | Baqi et al. [102] |
| 78 | Artificial intelligence: Catalyst or Barrier on the Path to Sustainability? | 2022 | Kopka and Grashof [103] |
| 79 | On the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Economy | 2022 | Solos and Leonard [104] |
| 80 | A Systematic Review of Green AI | 2023 | Verdecchia et al. [14] |
| 81 | AI Ethics Principles in Practice: Perspectives of Designers and Developers | 2023 | Sanderson et al. [105] |
| 82 | Waste Classification Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques:Literature Review | 2023 | Nasir and Aziz Al-Talib [106] |
| 83 | Shaping the Future of Sustainable Energy through AI-Enabled Circular Economy Policies | 2023 | Danish and Senjyu [107] |
| 84 | Artificial Intelligence for Waste Management in Smart Cities: a Review | 2023 | Fang et al. [108] |
| 85 | Deploying Digitalisation and Artificial Intelligence in Sustainable Development Research | 2023 | Leal Filho et al. [109] |
| 86 | Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Social Science Issues: a Case Study on Predicting Population Change | 2023 | Farahani [110] |
| 87 | Sustainable Development Goals Applied to Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence Applications in Low- to Middle-Income Countries | 2023 | Piya and Lennerz [111] |
| 88 | Research on the Impact of Artificial Intelligence Technology on Green Innovation | 2022 | Zhang [112] |
| AI for Sustainability | Sustainability of AI | Both | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
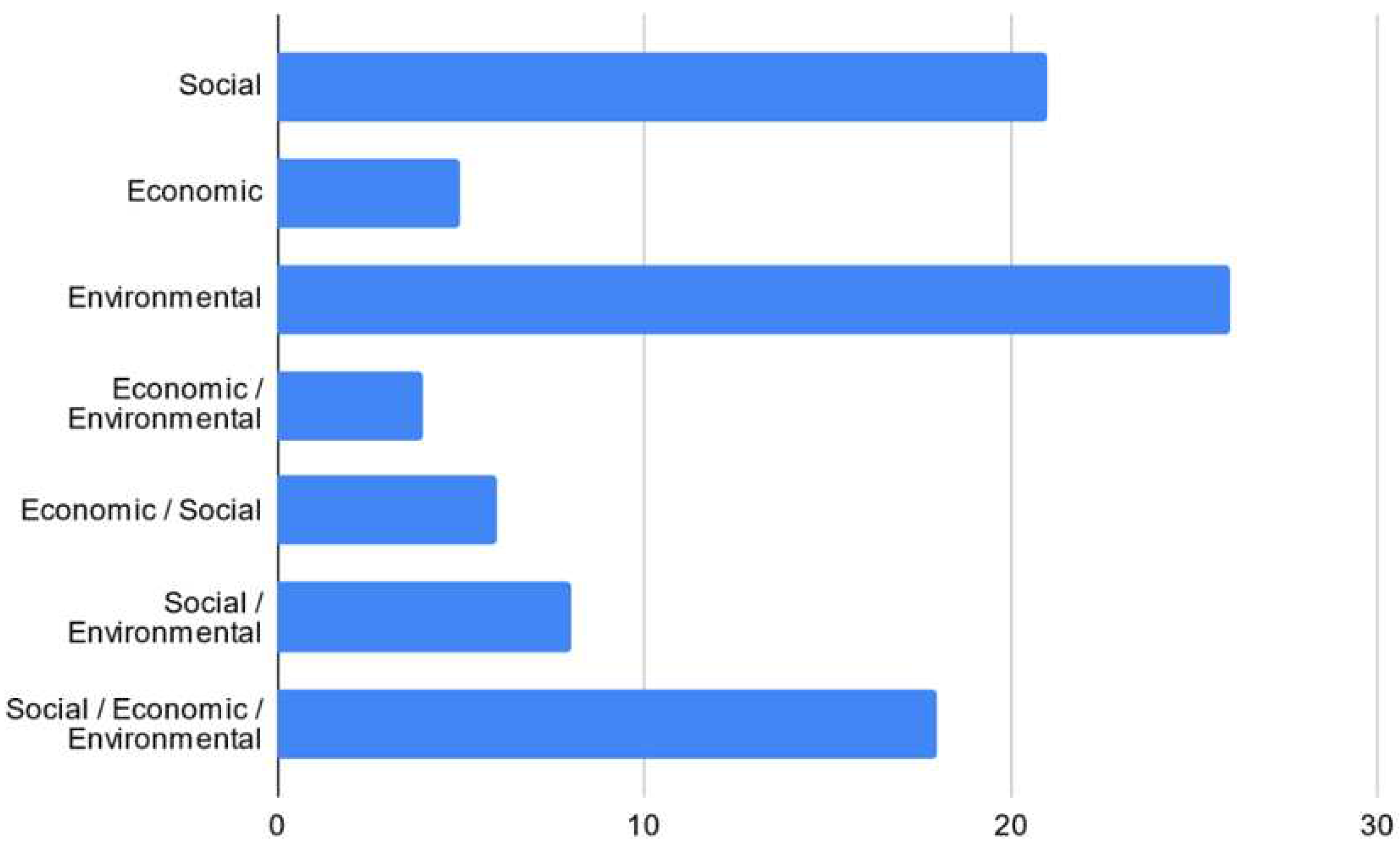
| Social | 3 | 15 | 3 | 21 |
| Economic | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| Environmental | 16 | 7 | 3 | 26 |
| Economic / Environmental | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Economic / Social | 1 | 5 | 0 | 6 |
| Social / Environmental | 4 | 4 | 0 | 8 |
| Social / Economic / Environmental | 9 | 4 | 5 | 18 |
| Total | 38 | 38 | 12 | 88 |
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Validation Research | Techniques investigated are novel and have not yet been implemented in practice. Techniques used are for example experiments, i.e., work done in the lab. |
| Evaluation Research | Techniques are implemented in practice and an evaluation of the technique is conducted. That means it is shown how the technique is implemented in practice (solution implementation) and what are the consequences of the implementation in terms of benefits and drawbacks (implementation evaluation). This also includes identifying problems in the industry. |
| Solution Proposal | A solution for a problem is proposed, the solution can be either novel or a significant extension of an existing technique. The potential benefits and the applicability of the solution are shown by a small example or a good line of argumentation. |
| Philosophical Papers | These papers sketch a new way of looking at existing things by structuring the field in the form of a taxonomy or conceptual framework. |
| Opinion Papers | These papers express the personal opinion of somebody on whether a certain technique is good or bad, or how things should be done. They do not rely on related work and research methodologies. |
| Experience Papers | Experience papers explain what and how something has been done in practice. It has to be the personal experience of the author. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





