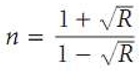1. Introduction
Methylenebis[hydroxybenzoic acid] has acquired prominence because it serves as a polyfunctional intermediate in condensation products that are appropriate for the surface coatings and plastics industries. Literature has documented just a few of synthesizes of certain methylenebis[hydroxybenzoic acid] compounds [1]. Recently, very selective extraction of Pb(II) over Ni(II), Cd(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II), from aqueous solution into chloroform was studied for methylenebis[hydroxybenzoic acid] ligands having different spacers between two hydroxybenzoic / salicylic acid unites [2]. It was reported that an ethylene spacer shows superior Pb(II) extraction selectivity compared to Cu(II). It is evident from the literature that effort had been paid to create solid 3,3’-Methylenebis[2-hydroxybenzoic acid] (MHB) complexes by traditional techniques. However, not much physico-chemical research has been done on MHB complexes. The MHB is capable of producing chelated colorful compounds when combined with copper and iron in addition Ba and Mg -MHB were prepared [3]. Noteworthy, 5, 5'-methylenedisalicylic acid that highly similar to MHB may establish solid complex with aluminum [4]. The physicochemical research on square planar CuII, NiII and CoII complexes with bis-oxime of 5, 5}–methylene(salicylaldehyde) has been discussed by Patel et al. [5]. The results indicated that the thermal stability of the complexes has the following arrangment: Co (II) > Ni (II) > Cu (II). Some enzymes or catalysts in biological reactions are built from zinc complexes [6,7]. Transition metal- polycarboxylate complexes have fascinating magnetic, biological, and structural characteristics [8–11]. The applications of transition metal complexes of methylenebis[hydroxybenzoic acid] in catalysis, bioinorganic, electrochemistry, corrosion, metallic deactivators, environmental chemistry and separation methods are noteworthy [5,12,13].
Bacterial resistance is a significant issue for public health. The World Health Organization, or WHO, has reported that bacterial natural phenomena can cause fundamental antibiotics to lose their efficacy in multiple cases [15]. The fact that many pathogenic bacteria have developed resistance makes research into novel antimicrobial drugs crucial. Chemotherapeutic agents are the names given to the chemical substances that have been created and are used to treat infectious diseases. Thousands of compounds are created annually to discover potential chemotherapeutic agent to combat harmful microbes. Since salicylic acid, which possesses antibacterial and antiseptic effects, has a structure that is quite similar to MHB, the MHB was chosen to examine its bacterial effect. Salicylic and some of its derivatives, which have structures resembles MHB and contain OH and COOH groups, have been described in the literature and revealed antibacterial effects [16–19].
The purpose of this work is to synthesize and characterize 3,3′-methylenebis[hydroxybenzoic acid], (MHB) and its Zn(II) complex. Several techniques have been used to describe the isolated materials. The optical parameters like penetration depth, optical conductivity, band gap and refractive index were also explored. The investigation also aimed to determine the biological impacts of the ligand (MHB) on bacteria and normal mammalian cells in order to provide insight into potential therapeutic applications.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and methods
The highest grade reagents from BDH were all used without further purification. Trypan blue dye and MTT were obtained from Sigma, Missouri, the United States. DMEM, Fetal Bovine serum, HEPES buffer solution, gentamycin, L-glutamine and 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA were bought from Lonza (Belgium). ATCC (The American Type Culture Collection) provided the mammalian cells: VERO (African Green Monkey Kidney) and HFB4 (Human Normal Melanocytes of Skin). The elemental analysis (C, H), metal content (wt %) and melting point were estimated as previously indicated [20]. The IR spectra were recorded using the ATR method using Thermo Scientific's iS50 FT-IR spectrometer. At room temperature, a Bruker spectrometer was used to perform a 1H-NMR (400 MHz) analysis in dimethylsulfoxide. With the help of tetramethylsilane, (TMS) as an internal reference, the chemical changes are stated in parts per million (ppm). On Thermo Scientific GCMS model ISQ, mass spectrum was carried out on Direct Inlet part to mass analyzer. The electron impact mode had been employed for the mass spectrometry. Using a Perkin-Elmer lambda 35 UV-Vis Spectrophotometer and the Nujol-mull approach, electronic spectra were captured in the range 200–1100 nm. With a Shimadzu 50 H thermal analyzer, thermal analysis (TG) was conducted under nitrogen. A drop of the solution was put to the carbon coated copper grids for TEM analysis, and the drop was allowed to dry at room temperature. The Regional Center for Mycology and Biotechnology (RCMB), in Egypt, used a JEOL GEM-1010 transmission electron microscope operating at 80 kV for collecting electron micrographs. Germany's XRD Bruker Co. D8 Discover was used to examine the crystallinity of MHB and the Zn(II) complex over 2 angles ranging from 3 to 80 degrees with Cu target K radiation (1.54 Å, 40 kV, and 40 mA). The band gap energy (Eg) of MHB and its corresponding Zn(II) complex were computed in order to elucidate the conductivity of the separated compounds [21–23]. The approximate absorption coefficient (α) was determined by applying the formula α = 1/d ln(1/T), where T is the measured transmittance and d is the cell width. With the use of Tuac's equation, αhʋ = A (hʋ-Eg)m , the optical band gap was calculated. A is an energy-independent constant, and m is equal to 1/2 and 2 for direct and indirect transitions, respectively. From the plot of (αhυ)2 vs. hυ, an indirect band gap was determined by extending the linear part of the curve to (αhυ)2 = 0. Antibacterial and cytotoxicity evaluations were conducted at RCMB, Egypt.
2.2. Sample collection (MHB and Zn-MHB)
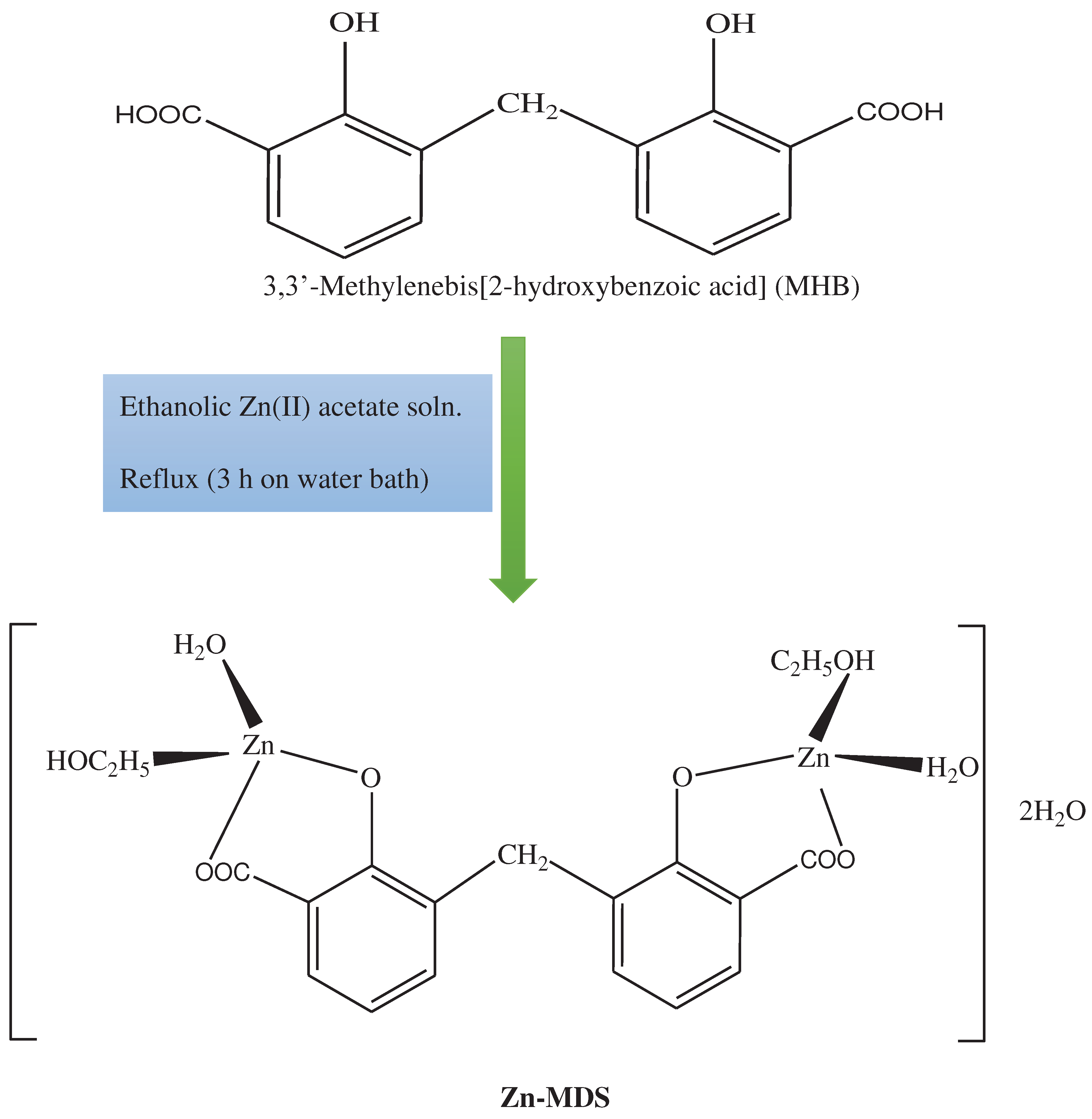
3,3’-Methylenebis[2-hydroxybenzoic acid], MHB,
Scheme 1, was obtained using the recipe outlined in the literature [2–4] as follows: 180 g of 50% sulfuric acid, 27.6 g of hydroxybenzoic acid and 9.4 g of 30% formaldehyde, were refluxed for 7 hours. To get rid of any remaining unreacted hydroxybenzoic acid, the separated powder was allowed to cool, filtered out, and then extensively cleaned with cold water and then hot water/ethanol solutions. After being separated and recrystallized from acetone, the cream powder was allowed to air dry for 48 hours [Lit./ Exp. m.p = 238 °C]. The MHB is soluble in alcohol, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, normal ether, dimethylformamide (DMF) and dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO) but insoluble in water.
By mixing ethanolic solutions of 0.01 mole MHB with 0.02 mole Zn(II) acetate, the Zn-MHB complex was created. On a water bath, the reaction mixtures were refluxed for three hours. The colored granules were heated, filtered, and thoroughly washed with hot ethanol before being dried in the air. The fact that the complex is insoluble in typical organic solvents indicates that the function of the polar groups (OH, COOH) has been lost. This can be interpreted as proof that the deprotonated hydroxyl and carboxyl groups successfully coordinated the ligand with the metal.
2.3. Pharmacological screening of MHB
2.3.1. Antibacterial activity
NCCLS (1993; National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards) guidelines were followed for doing tests for susceptibility. We used the well diffusion approach to conduct screening tests related to the inhibition zone [24].
The inoculum suspension was obtained by inoculating Mueller-Hinton broth (fungi utilizing malt broth) with colonies grown over the night on a plate of agar. The MHB compound was dissolved in DMSO at three different doses: 2.5, 5 and 10 mg/mL. To inoculate Mueller-Hinton agar plates, a sterile swab had been dipped in the suspension. An inhibition zone was determined surrounding each well after a 24-hour period at 37 oC. Correct execution of the DMSO controls was made.
2.3.2. Cytotoxic Assessment
The cells were grown in a medium called Dulbecco's modified Eagle's, which was enriched with 50µg/ml of gentamycin, 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 1% L-glutamine, and HEPES buffer. Every cell was cultivated twice a week at 37 ºC in a humidified environment with 5% CO2.
The cytotoxicity experiment [25,26] was conducted using a viability assay in which 100µL of growth medium was added to 96-well plates with a cell concentration of 1×104 per well. After 24 hours of seeding, fresh medium with varying quantities of the test sample was introduced. Confluent cell monolayers were pipetted into 96-well flat-bottomed micro-titer plates (Falcon, NJ, USA) using a multichannel pipette, and serial two-fold dilutions of the chemical component under test were added. For twenty-four hours, the micro-titer plates were kept at 37 ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. For every test sample concentration, three wells were utilized. Control cells have been incubated with or without DMSO and without the test sample. There was no impact of the small amount of DMSO (maximum 0.1%) on the experiment. The MTT test was used in a colorimetric technique to measure the viable cell yield following incubation of the cells. The 96-well plate's medium was taken out and 100 µl of fresh culture RPMI 1640 medium without phenol red was added instead. Thereafter, 10 µL of the 12 mM MTT stock solution - which contains 5 mg of MTT in 1 mL of PBS - was added to every well, including the untreated controls. After that, the 96-well plates were incubated for four hours at 37 °C with 5% CO2. After removing an 85 µL aliquot of the medium from each well, 50 µL of DMSO was added, thoroughly mixed and the wells were incubated for 10 minutes at 37°C. The number of live cells was next ascertained by measuring the optical density at 590 nm using a micro plate reader (Sun Rise, TECAN, Inc., USA). [(ODt/ODc)]x100% was the formula used to get the viability percentage; ODt stands for the mean optical density of the wells treated with the tested sample, and ODc for the mean optical density of the cells that were left untreated. The survival curve of each tumor cell line following treatment with the designated substance is obtained by plotting the relationship between remaining cells and compound concentration. Using graphic plots of the dose response curve for each concentration, the cytotoxic concentration (CC50), or the concentration needed to cause toxic effects in 50% of intact cells, was determined using Graphpad Prism software (San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results and discussion
Table 1 contains some physical and analytical details on the separated MHB and its Zn(II) complex. Various physicochemical methods were used to validate the structural formula of the produced molecules.
3.1. Sample Characterization
3.1.1. Structural determination of the ligand, MHB
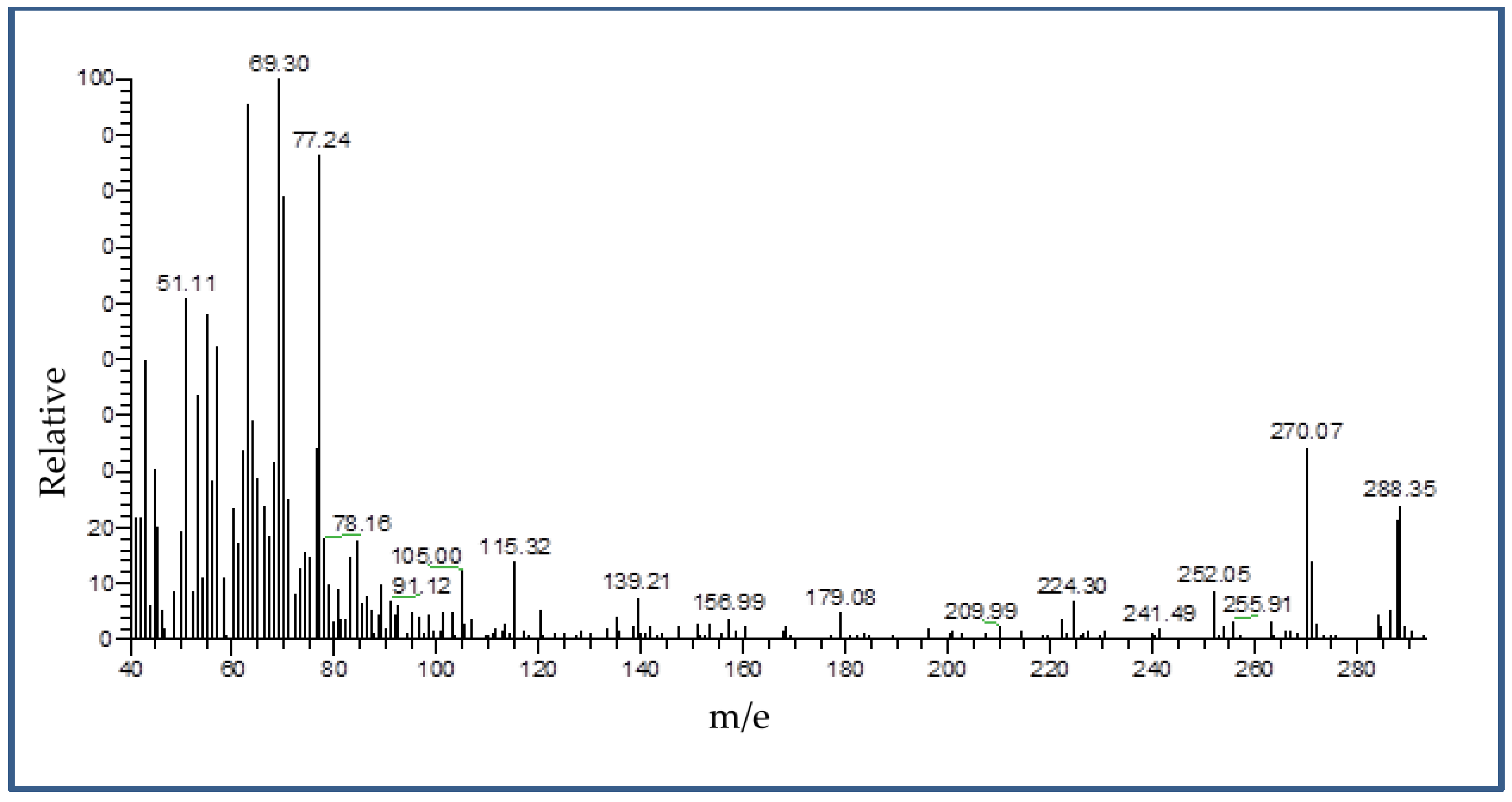
Mass spectrum: The purity and predicted molecular weight of the compound have been emphasized throughout the mass spectrum (
Figure 1). The molecular ion peak for the MHB was at m/e = 288.35 [(C
15H
12O
6), calculated m/e = 288.35].
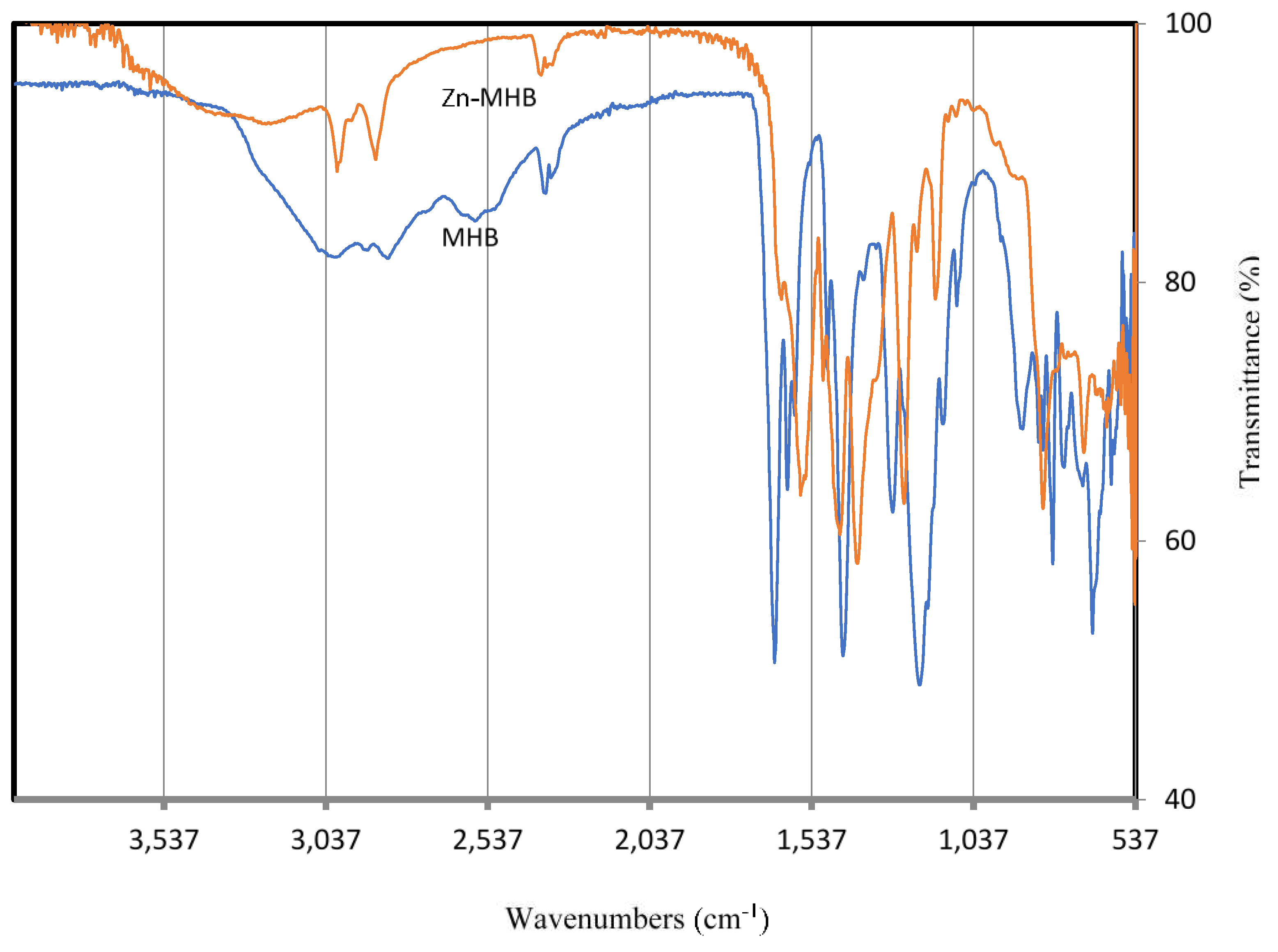
IR spectrum: The spectrum data (
Figure 2,
Table 2) exhibited υ(C-O)
phenolic, ν(OH)
phenolic, δ(OH)
phenolic and υ(C=O)
caroxylic at 1281, 3150, 1200 and 1648 cm
-1, respectively [27]. It is believed that the presence of phenolic OH at the lower site (3150 cm
-1) indicates that intermolecular H-bonding (O–H.O-H) between related molecules. The widening form of υOH
phenolic provides support for this suggestion, whereas the band resulting from intramolecular hydrogen bonds is sharp. The significant reduction in frequency reveals how strong the link is. The broad band at 2395-2650 cm
-1 confirms the presence of the intermolecular hydrogen bond among MHB molecules.
Absorption of the (C=O)
carboxyl is lower than typical position (1700-1730 cm
-1) due to the presence of MHB as dimer (intermolecular hydrogen bonding) and internal conjugation (the lone pair on the carboxyl's OH is in delocalization with C=O). Four bands associated to aromatic (C=C) vibrations were also found at 1609, 1585, 1489, and 1435 cm
-1. Moreover,
Figure 2 shows the locations of additional bands corresponding to the phenyl rings at 791 cm
-1 (out of plane deformation), υCH
aromatic (near 3033 cm
-1) and methylene (-CH
2-) groups (υCH
asym= 2905, υCH
sym = 2836 and δCH
rocking = 754 cm
-1).
NMR spectrum: According to a prior report [1], the 1H NMR spectra of MHB revealed signals at 3.8 (CH2, d), 11.2 (COOH, s, broad), 11.6 (phenolic OH, s, broad) and 6.7 - 7.9 (aromatic protons, m). The correct locations of–OH groups and –COOH, where the labile protons can be replaced by deuterium, were demonstrated by disappearing signals of -COOH and -OH following addition of D2O. In accordance with IR findings, the spectral widening of the phenolic OH and COOH signals provided support the formation of hydrogen bonds between these groups.
3.1.2. Structural determination of the complex, Zn-MHB
Along with their diamagnetism and white color, the ZnII (d10 configuration) could be regarded as a limit for the spectroscopic description of Zn derivatives due to their diamagnetism and white color. Conversely, the lack of ligand field stabilization might provide extremely flexible coordination geometry that is exclusively controlled by the ligands' charge and steric hindrance. [28,29].
IR spectrum: A comparison of the IR spectrum of the complex with this of MHB (
Figure 2,
Table 2) signified that MHB acts as a tetradentate ligand chelating two zinc ions via the deprotonated phenolic (-OH) and carboxyl (COOH) groups. The following evidences support this suggestion: (1) The negative shift of υ(C-O) band (MHB:1281 → Zn-MHB: 1248 cm
-1). (2) Disappearance of υ and δ(OH)
phenolic in the ligand upon complexation. (3) The carbonyl group (C=O) of the carboxyl (L: 1648 cm
-1,
Table 2) disappears and the carbonyl of the carboxylate appears instead at 1554 cm
-1. (4) Obscure of broad band assigned to the intermolecular H-bond of COOH in ligand (2395-2650 cm
-1) points to breakage of this bond by coordination with zinc. The persistence of two additional bands in the range 600-620 cm
-1, centered at 618 and 624 due to (Zn-O) [30], is further evidence for the coordination of phenolic and carboxylic oxygen. On the other hand, the coordinated ethanol and water in the complex are indicated by the stretching vibrations observed within 3450 - 3550 cm
-1 (υOH
ethanol, υOH
water) and two somewhat weaker bands assigned to rocking (OH
water, 870 cm
-1) and wagging (OH
water, 614 cm
-1) vibrations.
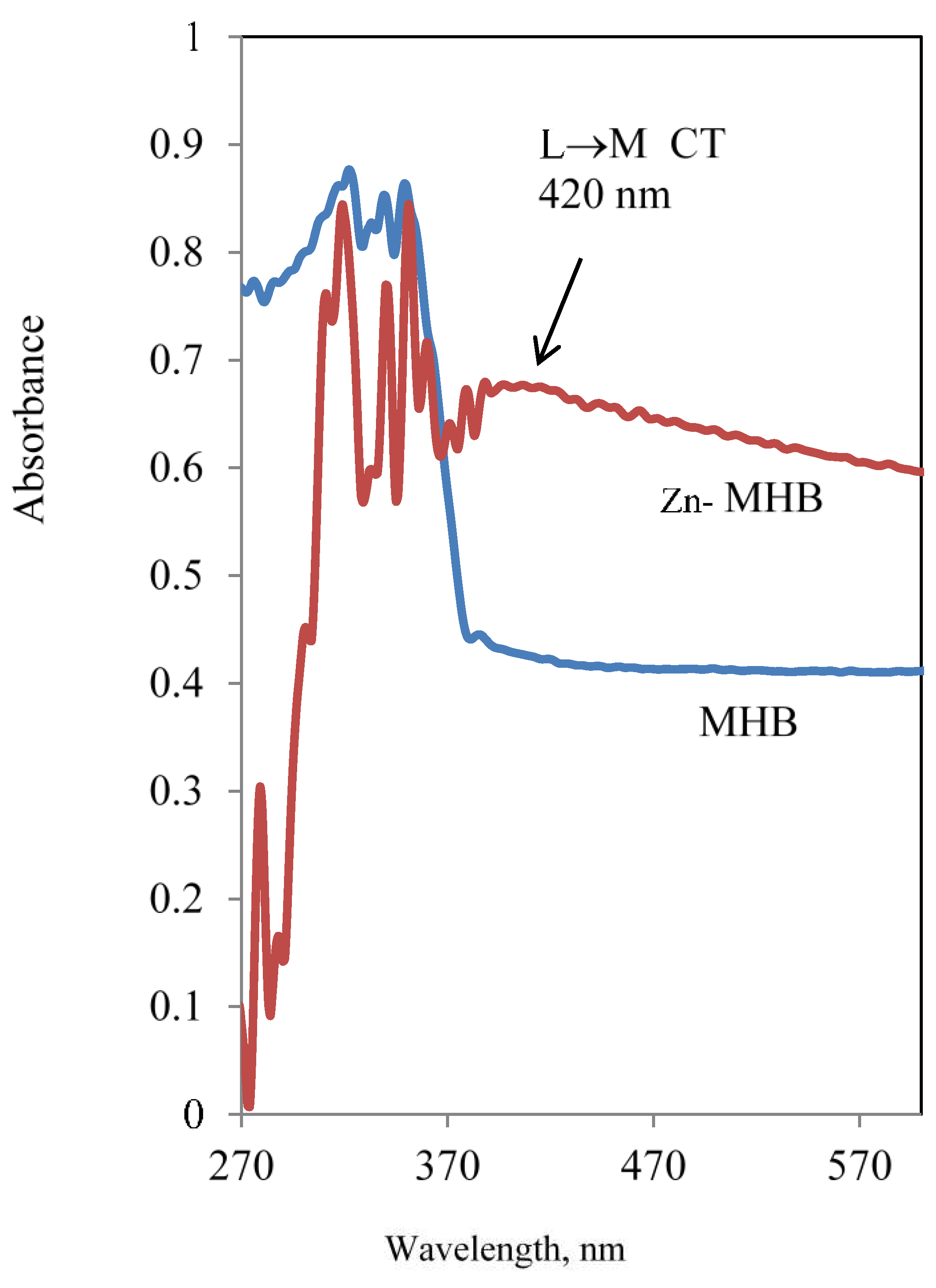
UV-Vis spectrum: The electronic spectrum of the MHB and Zn-MHB were scanned and shown in
Figure 3. MHB gave five peaks centered at 361, 351, 341, 319, 280 associated with n→π* (C=O)
carboxyl, n→π* phenolic OH, π→π* (C=O), π→π* phenolic and π→π* (phenyl) transitions, respectively. The π→π* and n→π* transitions were suggested for phenolic OH considering it is in delocalization with the carboxyl group's C=O. As well known, Zn(II) complexes does not display d–d transitions due to their fully filled d
10 configuration, however they frequently show charge transfer spectra. The same MHB peak locations with a slight shift were visible in the Zn-MHB electronic spectrum, along with peak of absorption at 420 nm due to L to M charge transfer (LMCT). The existence of the latter new CT band is consistent with complex having a tetrahedral structure [31] and confirmed coordination of MHB with Zn(II) ion.
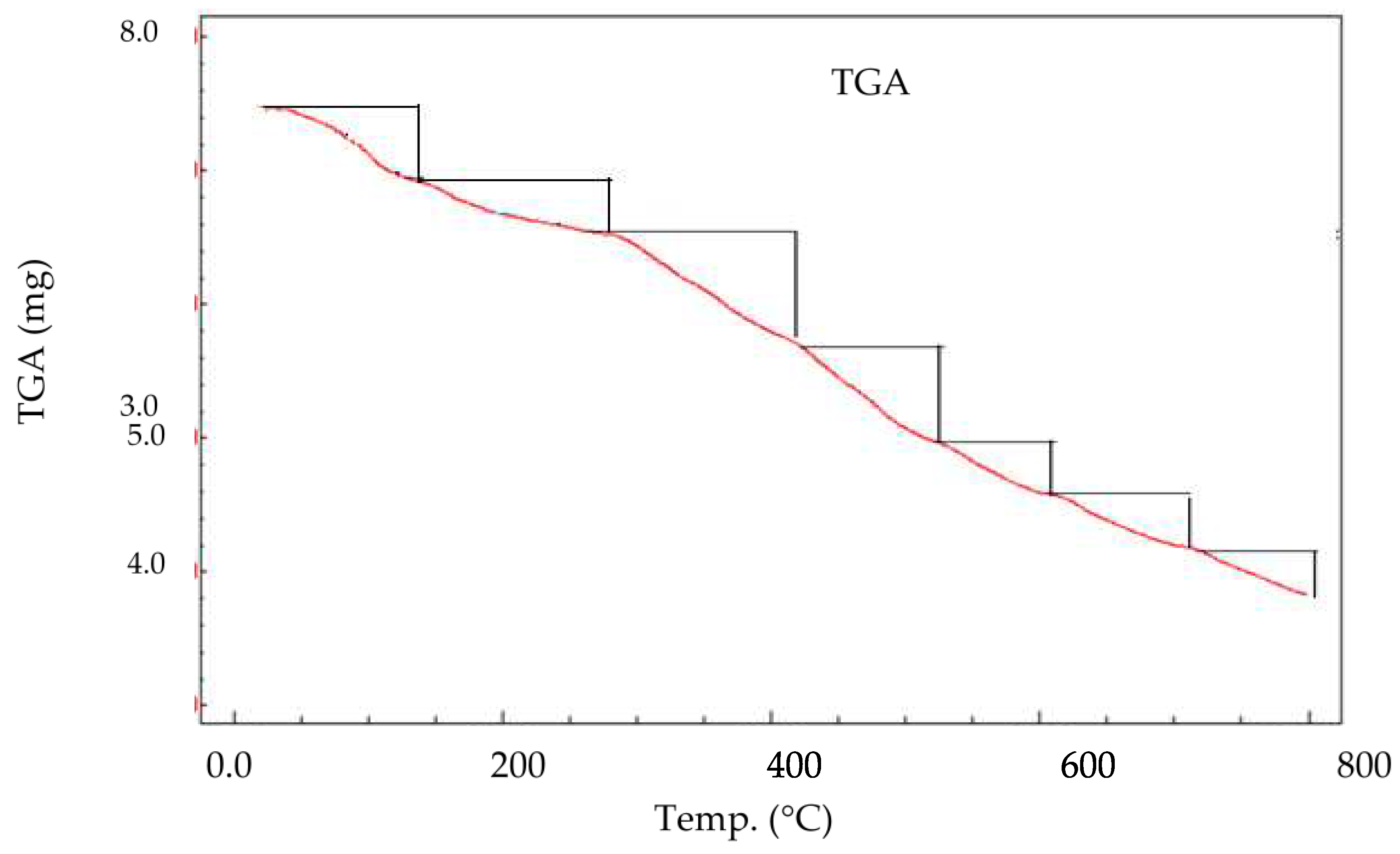
Thermogravimetric analysis: The thermogram of the Zn-MHB has been studied. The TG curves up to 800 °C (
Figure 4) revealed several weight loss steps. The first one (40-110 °C) is caused by the elimination of crystalline water molecules (found/calculated = 6.6/6.2)%, the second weight loss stage (110-280 °C) arise from removal of coordinated two water molecules (found/calculated = 6.7/6.2)% whereas the third weight loss step (280-400 °C) comes from elimination of coordinated ethanol (found/calculated = 14.4/15.9)%. The other four peaks are the result of the Zn(II) complex decomposition, which produces metal oxides in the last stage.
In light of the results mentioned above, the logical structure of the Zn(II) chelate is displayed in
Scheme 1. A tetrahedral confirmation for Zn-MHB is supported by the fact that Zn(II) ion is a late transition metal with full d valence electrons, meaning that a stable 18-electron complex may be produced through 4-coordination number.
3.1.3. Powder XRD studies
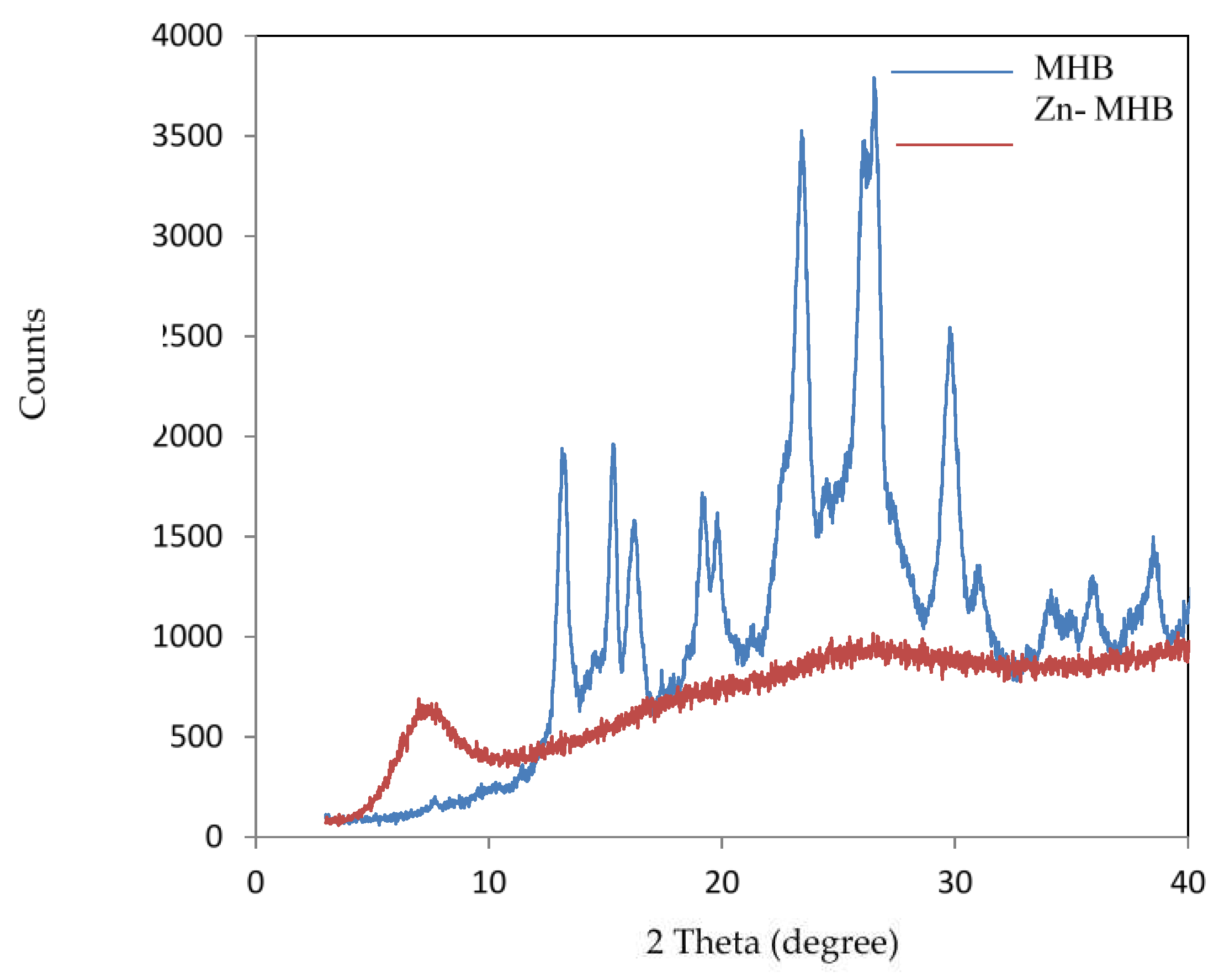
X-ray diffraction pattern are recorded for MHB and Zn(II) complex. The patterns of the samples are presented in the
Figure 5 and the diffraction data include the inter-planar distances d (Å) and crystallite size are given in
Table 2. The findings show that the MHB is crystalline, i.e., it has a single geometric shape with a distinct repeating pattern of its constituent molecules. The purity, single phase nature and crystallinity of the MHB particles are really indicated by the well-defined, sharp peaks in the XRD patterns [32]. The fact that Zn-MHB's diffraction patterns differ significantly from those of the ligand indicates that the chelation
process was successful. The XRD pattern of Zn-MHB indicated an amorphous character, suggesting that the constituent particles are arranged randomly. Specific melting temperature of MHB proved that MHB is crystalline material. In X-ray diffraction and crystallography, the Scherrer equation [33] is a formula used to estimate the smallest size or diameter of a nanogranule; it is not relevant in limits larger than 200 nm. The Debye– Scherrer equation is
where: λ = wavelength of X-ray radiation (Cu Kα=1.54 Å), β = the line broadening at full width at half maximum height (FWHM) in radians, k=constant taken as 0.94, θ = diffraction angle in degree and D = average crystallite size (Å),. The MHB and Zn-MHB crystallite sizes were found to be 14.4 and 2.5 nm, respectively.
3.1.4. Optical properties
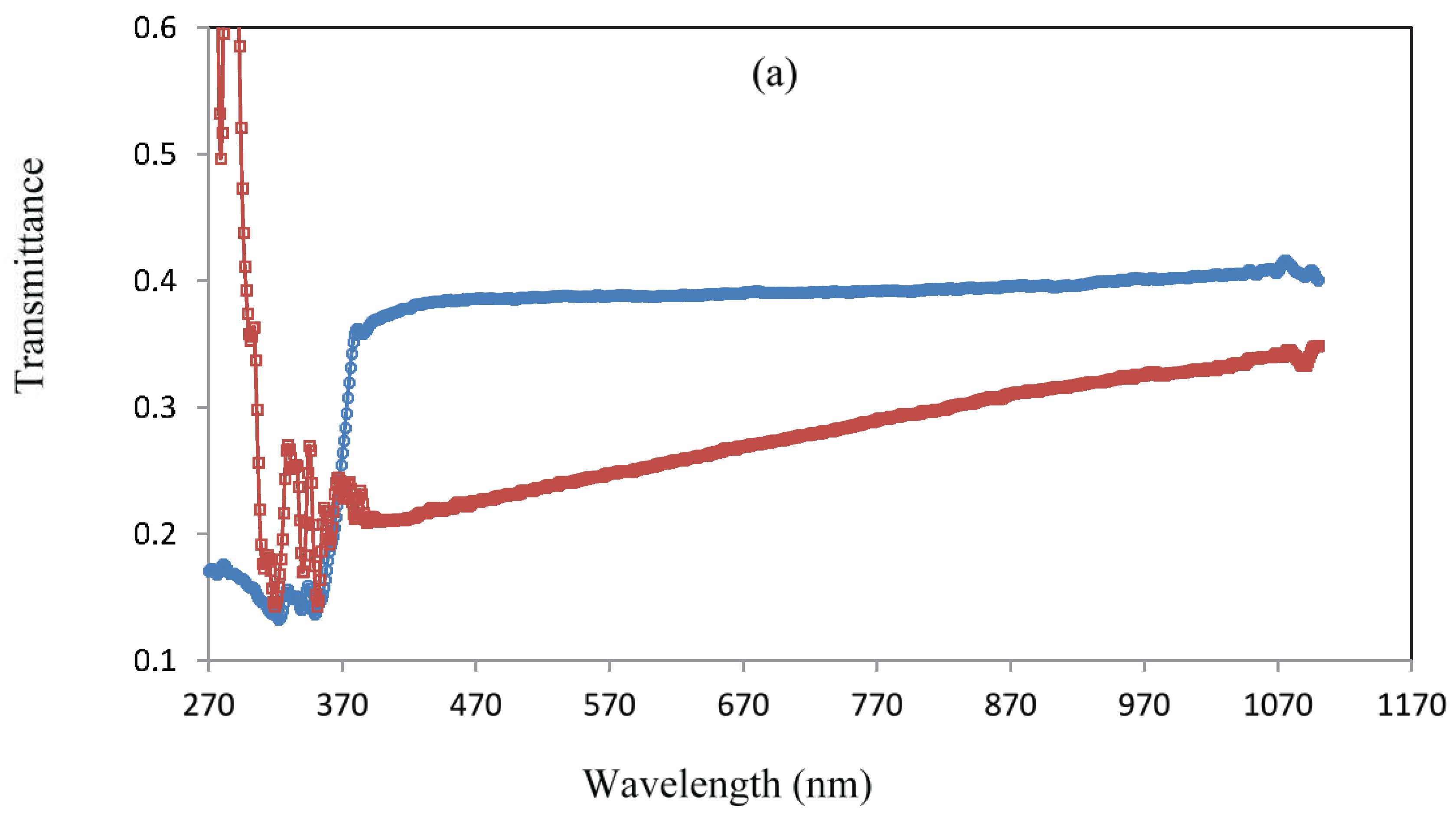
Transmittance spectrum measurements have been used to study the compounds' optical characteristics.
Figure 6a shows the transmittance that was obtained. The energy gap (E
g) is the amount of energy required to move an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. Both the resultant electron in the conduction band and the electron hole in the valence band are free to migrate inside the crystal lattice and carry out electrical current conductivity. Small band gaps (0.1 to <⁚ 4 electron volts, eV) are found in semiconductors, big band gaps (> 4 eV) are found in insulators, and Conductors have very small band gaps or none at all because the valence and conduction bands overlap to produce a continuous band. Since the band gap value determines the material's optical characteristics, or its capacity to absorb light or photon energy, it was necessary to measure it. The values of the indirect optical band gap were computed and are displayed in
Figure 6b. The MHB and Zn-MHB were discovered to have E
g values of 3.23 and 3.16 eV, respectively. The result indicates that the conduction of ligand and complex resemble ZnO (E
g=3.37), GaN (E
g=3.4) and ZnSe (E
g=2.7) [34]. As reported in literature [35], it could be explain the slightly higher E
g values of MHB in comparison to its analogous Zn(II) complex. Through the acceptance of ligand electrons in its shell, zinc tends to increase ligand mobilization. It can be found that after chelation; the localized levels' width is increased, resulting in a reduced band gap. It is noteworthy to emphasize that a small band gap facilitates electronic transitions between the HOMO-LUMO energy states, increasing the molecule's electro-conductivity [36]. The MHB and Zn(II) complex both have band gap values lie in the range of semiconductors and could be employed in applications of optoelectronic [37].
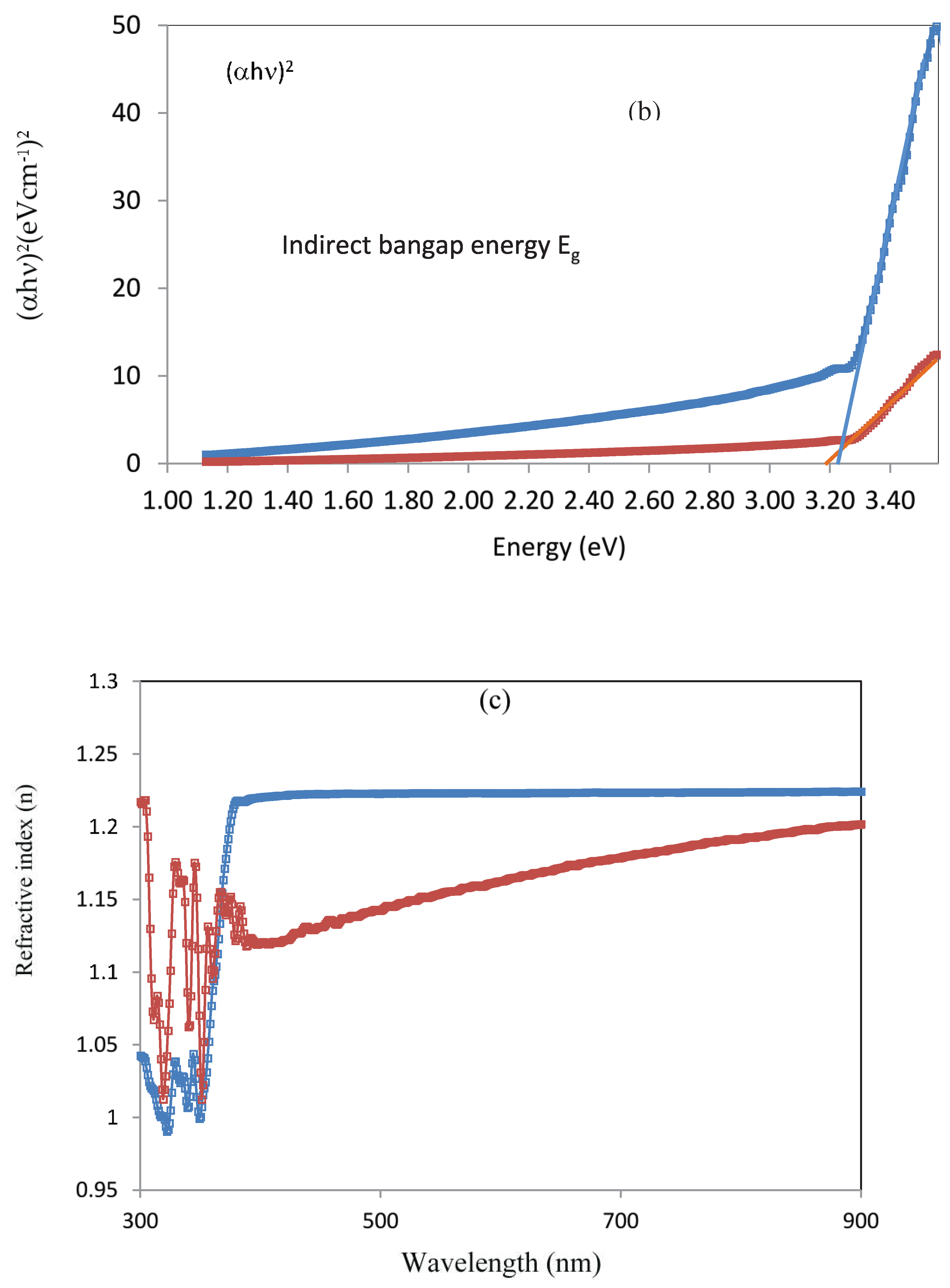
The refractive index, which controls the speed of light in media other than a vacuum, is an essential property for optical applications. The smaller the refractive index (n), the higher the light travels within the substance. The evaluation of optical materials' refractive indices is crucial for their application in optic devices, such as switches and modulators. Furthermore, one important physical characteristic that is commonly used in chemistry to assess purity is the refractive index. The subsequent relationship has been used to estimate the reflectance:
The refractive index values (n) of the compounds may be approximately expressed by the relation [38,39],
r is the usual reflectance in this case. The changes in n values with λ,nm of the incident light are shown in
Figure 6c. Because of certain interactions between photons and electrons, it is seen that the refractive index changes as the incident light beam's wavelength varies [40]. Additionally, this figure shows how complexation affects the refractive index of the free ligand where the chelation leads to a difference in the n values. It is evident from the data in
Figure 6c that the refractive index rises gradually until it remains almost constant.
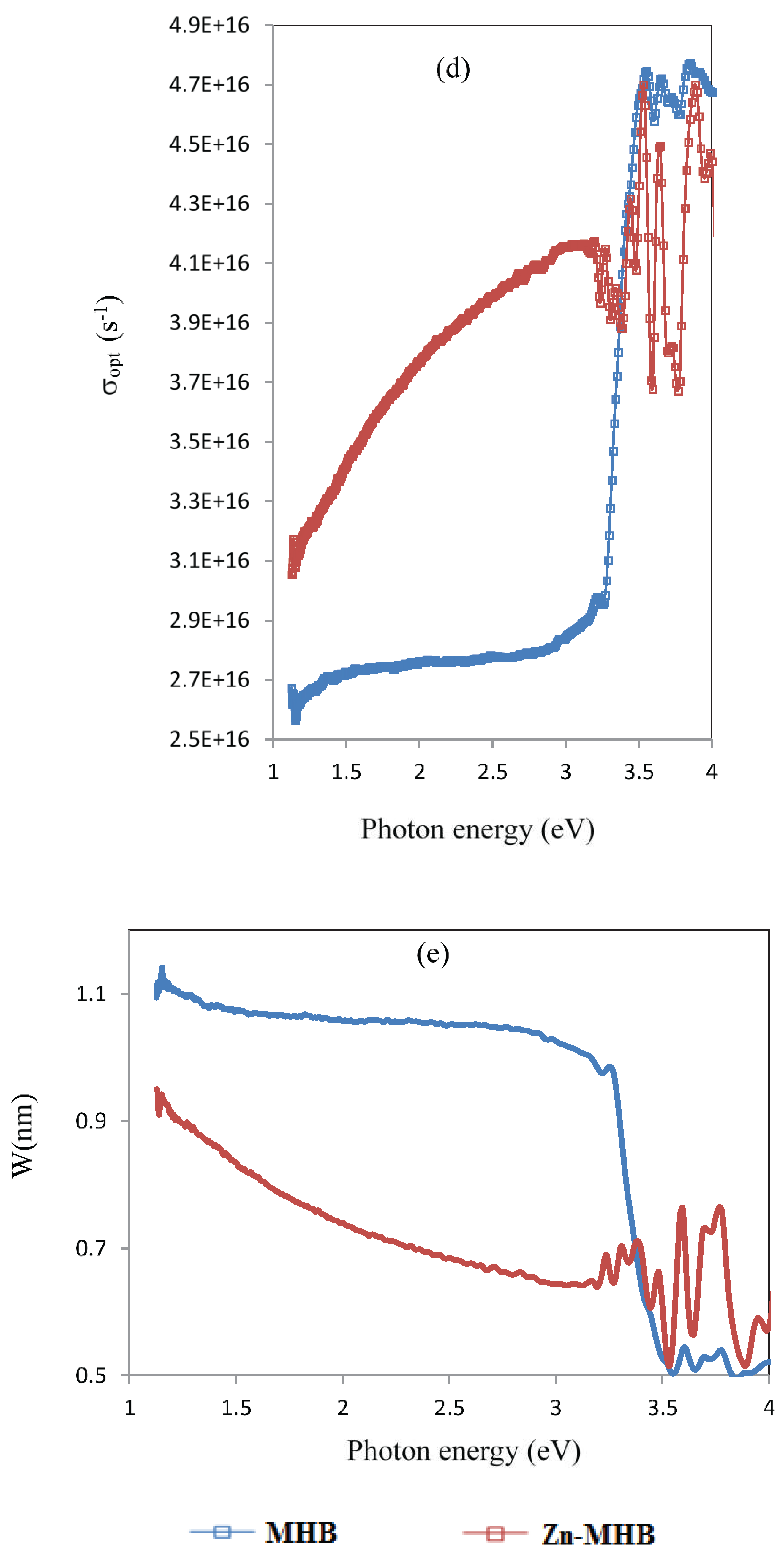
The optical conductivity (σ
opt) depends on the values of n and frequency/wavelength of incident light and is given from [41]
where ν, λ, k, c, n, α and A stand for the frequency, wavelength, extinction coefficient, light velocity, refractive index, absorption coefficient and absorption, respectively.
Figure 6d displays the variation of σ
opt as a function of photon energy (hv). The diagram illustrates precisely how, for two compounds, the ligand's conductivity is nearly constant and the complex's σ
opt value increases with photon energy or light frequency in the range of 1 to 3. After this, the ligand conductivity increases in comparison to the complex, which seems to change depending on the incident light frequency.
How far light can go through a compound is determined by its penetration depth. This depth—also known as skin depth—is reached when the material's internal radiation intensity drops to roughly 37% of its initial level. The relationship has been used to determine the light penetration depth (W) through the ligand and zinc complex is:
where the wavelength and extinction coefficient are denoted by k and λ, respectively. As a result, depending on the characteristics of the material and the radiation's wavelength, electromagnetic radiation may either go away instantly or penetrate a substance very deeply. Actually, depth can provide the details with greater significance and insight.
Figure 6e displays the fluctuation of W vs photon energy. Until the photon energy is 3.3, the penetration distance of the ligand is higher than that of the complex after which the opposite happens.
Figure 6.
Variation of optical parameters for ligand and complex (a) transmittance, T, (b) band gap energy, Eg, (c) refractive index, n (d) optical conductivity, σopt and (e) penetration depth, W. .
Figure 6.
Variation of optical parameters for ligand and complex (a) transmittance, T, (b) band gap energy, Eg, (c) refractive index, n (d) optical conductivity, σopt and (e) penetration depth, W. .
3.1.5. Morphological Studies on the MHB and Zn-MHB
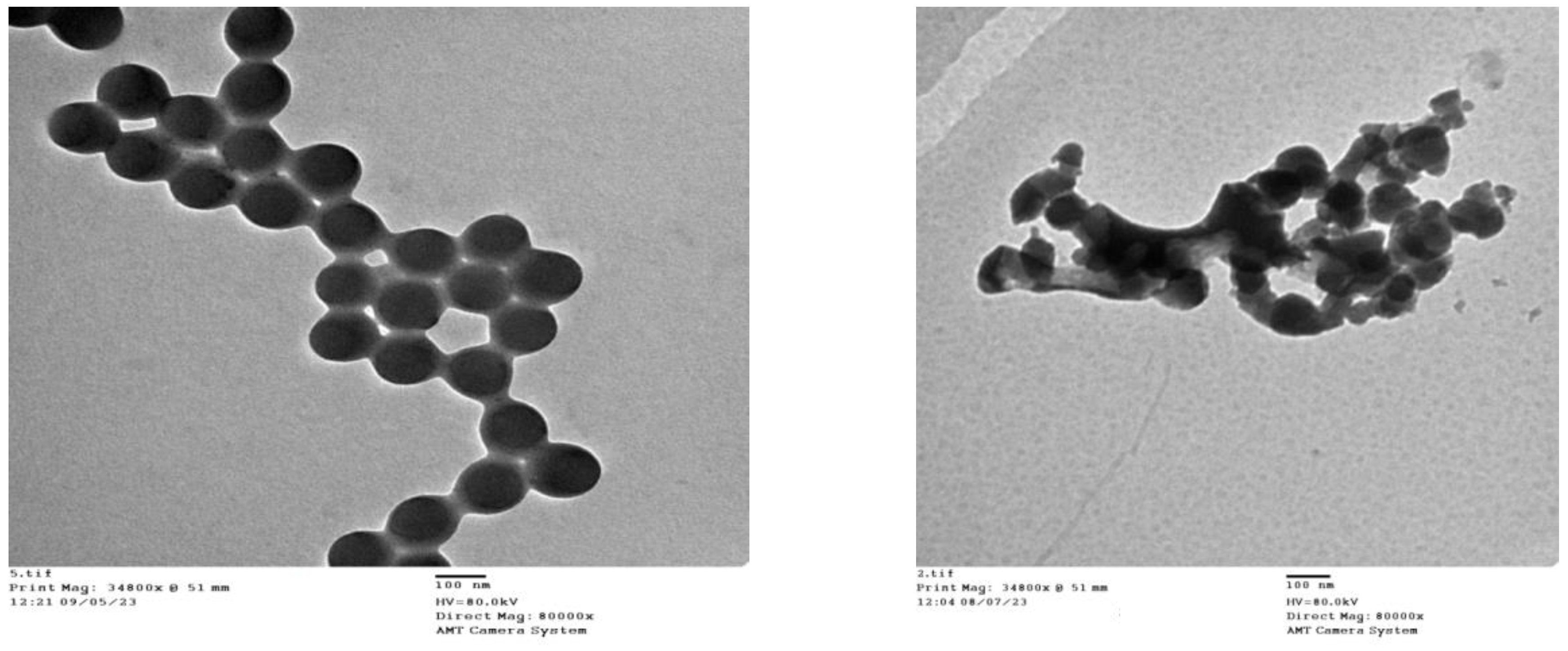
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis [42] was carried out to study the morphological properties and the TEM images at the same magnification are shown in
Figure 7. The TEM micrographs of both MHB and Zn-MHB exhibited regular spherical structures. While some of the Zn-MHB particles are heterogeneously dispersed and aggregated, the MHB particles appear to be mono-crystalline, non-aggregated, and evenly distributed. The obtained outcome is in good agreement with the XRD findings. The nanostructure of the
complex in comparison to the ligand was further verified by the TEM pictures, where MHB and Zn-MHB give average particle sizes of 116 and 95 nm, respectively. In fact, the chelation-induced change of ligand particles into zero dimensional (0-D) nanoparticles might be regarded as a successful outcome. Nano scale of the Zn-MHB points to the possibility of utilizing the produced Zn(II) complex in nanotechnology, in the field of medicine, environmental remediation and as quantum dots especially its band gap (Eg) locates in semiconductor rang.
3.1.6. Antibacterial investigation
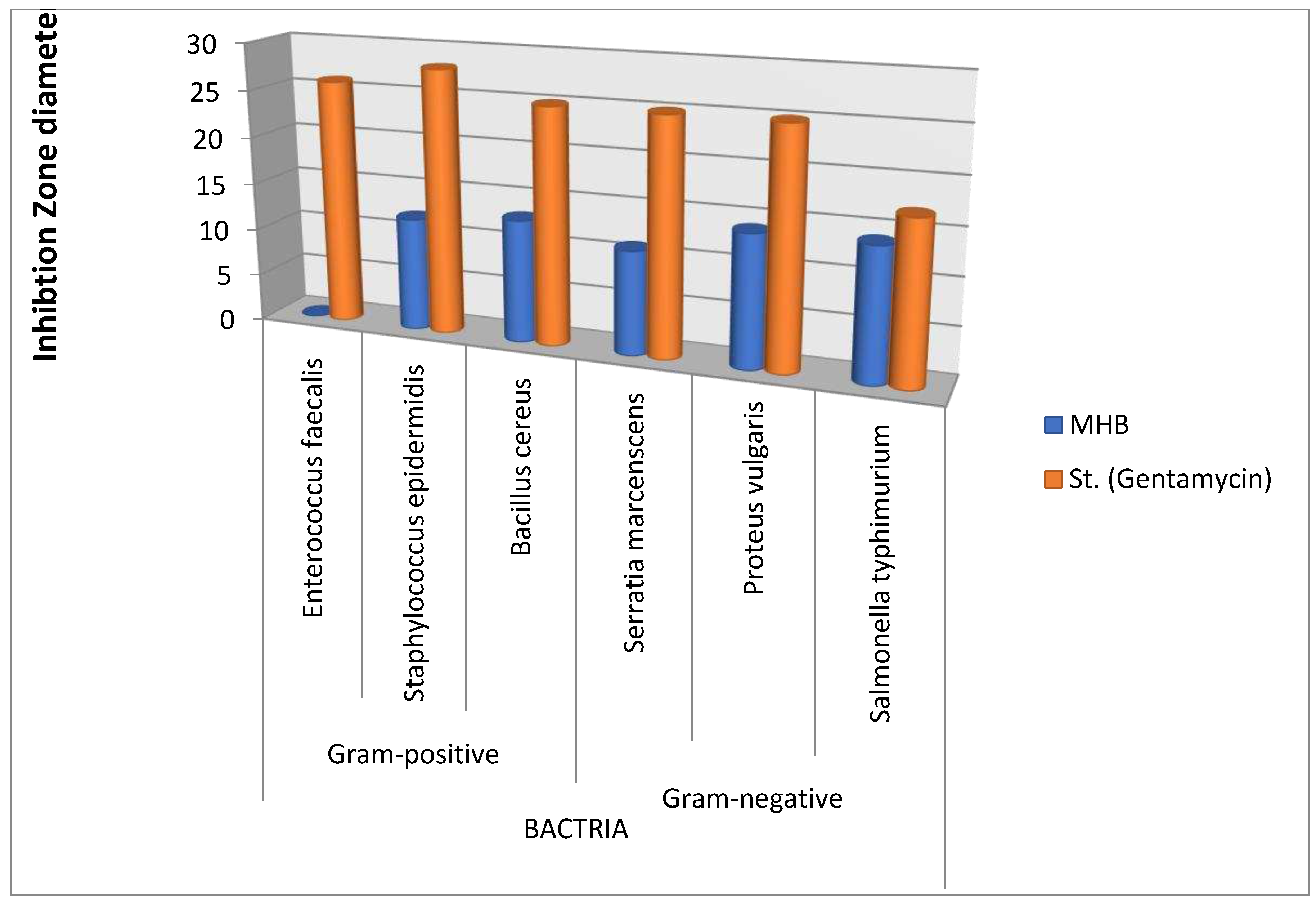
Antimicrobial evaluation of MHB was carried out while its corresponding Zn(II) complex was not due to its insolubility as mentioned in experimental section. Screening of antimicrobial activity of synthesized MHB exhibits no activity against enterococcus faecalis, high activity against salmonella typhimurium and moderate activity towards other examined bacteria (
Figure 8). While the MHB did not exhibit greater activity than the reference, it exhibited beneficial activity against the tested strains of several bacteria, especially salmonella. Salmonella infections in animals used for food production are a severe public health problem since animal foods are thought to be a major source of human illness. Eggs and meat from chickens and other food animals are the most frequently found causes of infection. Salmonellosis outbreaks in humans have also been linked to milk and dairy products. Infected water may also contaminate fruits and vegetables, which could also be a source of infection. Within 24 hours of infection, s. typhimurium-caused salmonellosis in people and food animals is characterized by severe intestinal inflammation, fever and diarrhea. Because salmonella can use a variety of virulence factors to overcome colonization resistance and cause intestinal inflammation, it is dangerous [43]. According to what was said, the increased efficacy of MHB against Salmonella typhimurium in comparison to gentamycin may be regarded as a distinguishing characteristic. The ability of MHB to permeate lipid membranes and blocked the metal binding sites in microbial enzymes serves as an example of how effective it is against bacteria. [44,45]. This behavior led to destroy the enzymes and hence impedes the formation of proteins necessary for further growth of the organisms [46].
3.1.7. Cytotoxic assay
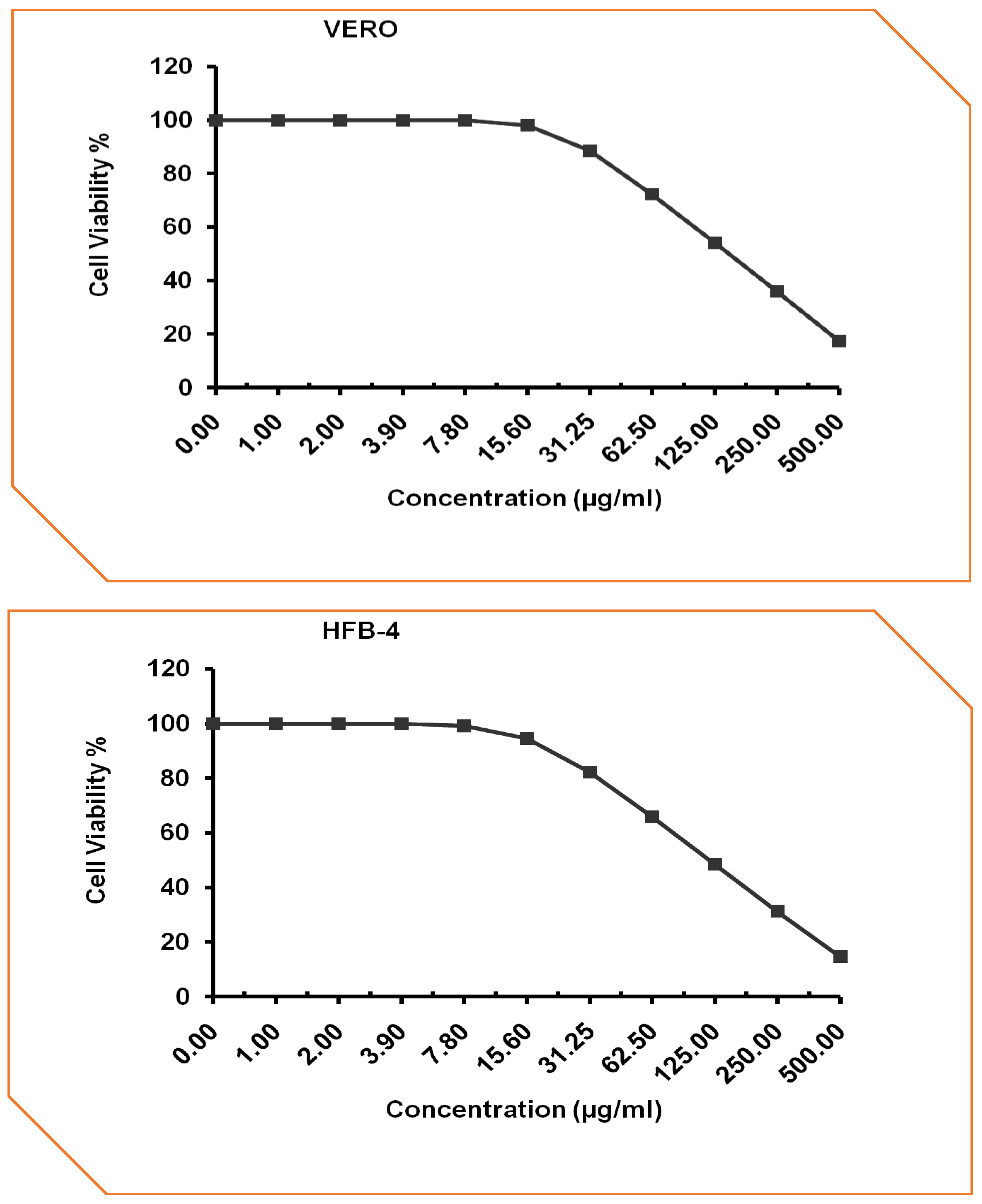
Exposure to excess doses of chemical compounds or drugs may cause many health problems such as skin rashes, burns, damage to the kidneys and lungs, impact on the central nervous system, cancer, and many more. To get a preliminary indication of the cytotoxic of MHB in normal cells, MHB was evaluated against normal mammalian cell lines including African Green Monkey Kidney (VERO) and Human normal melanocytes of skin (HFB4). The cell viability values are exhibited in
Figure 9. The concentration needed to destroy 50% of healthy cells (CC
50) was estimated. Human normal melanocytes had a CC
50 of 119.45 ± 6.31 µg/ ml, however mammalian cells from African green monkey kidney showed lesser sensitivity (153.85 ± 10.47 µg/ml). In general, the MHB was practically devoid of significant cytotoxic activity in normal mammalian cell [47]. Of course this result was speculated as MHB mimic hydroxybenzoic acid to a large extent and hydroxybenzoic acid is a natural substance employed in a variety of medicinal formulations as well as food and cosmetic additives [48,49].
4. Conclusions
3,3’-Methylenebis[2-hydroxybenzoic acid] can be created from formaldehyde, salicylic acid and sulfuric acid. Different methods can be used to identify the MHB and associated Zn(II) complex, including elemental studies (C, H, M), FT-IR, mass, NMR, and UV-Vis. Comparing theoretical and experimental elemental analysis percentages (C, H, and M%) reveals that the isolated Zn(II) complex's composition matches well with the suggested formulae. The Zn(II)-3,3'-methylenebis[2-hydroxybenzoic acid] complex (Zn-MHB) has tetrahedral conformation. The compounds' optical transmittance, band gap, and optical constants were studied. As the current compounds' energy gap values fall within the range of semiconductors, they could soon be employed as raw materials for solar radiation harvesting solar cell applications. After chelation, the optical band gap and refractive index values differ. It appears that the optical conductivity and penetration depth of the compounds depend on the frequency or photon energy. The antibacterial activity of the studied MHB ligand against particular types of bacteria has been evaluated (six microorganisms). The results of the study showed that the ligand had a reasonable effect and might stop some bacteria from creating proteins, especially salmonella typhimurium. Additionally, free MHB had negligible cytotoxic effects on VERO and HFB-4, two types of typical mammalian cells. This was expected because the structure of the naturally occurring chemical salicylic acid is similar to that of MHB.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Jouf University through the Fast-track Research Funding Program.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
- Kahl, L. Ber 1898, 31, 143. [CrossRef]
- Takashi, H.; Takaaki, H.; Hyozo, S.; Alan, P.M.; Kaipenchery, A.K.; Simon, G.B.; Kata, M.M.; Tatjana, S.; Nazar, S.A.E.; Hong-Sik, H.; Galina, G.T.; Richard, A.B. Molecular design of lipophilic disalicylic acid compounds with varying spacers for selective lead(II) extraction. Talanta 2000, 52, 385–396. [Google Scholar]
- Clemmensen, E.; Heitman, A.H.C. Methylenedisalicylic acid and its reaction with bromine and iodine, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1911, 33, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, J. Rauner. Def. Pub! U.S. Pat. 878,020. Chem. Abstr 1970, 73, 125729. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, R.P.; Karampurwala, A.M.; Shah, J.R. Physicochemical studies on square planar Co2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ chelate polymers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 1980, 87, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kaltenberg, J.; Plum, J.L.; Ober-Blobaum, J.L.; Honscheid, A.; Rink, L.; Haase, H. Zinc signals promote IL-2-dependent proliferation of T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.M.; Bernhardt, M.L.; Kong, B.Y.; Ahn, R.W.; Vogt, S.; Woodruf, T.K.; O’Halloran, T.V. Zinc sparks are triggered by fertilization and facilitate cell cycle resumption in mammalian eggs. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, F.; Zheng, J.M. Syntheses, structures, and magnetic properties of a series of het-erotri-, tetra- and pentanuclear LnIII–CoII compounds. Polymers 2019, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.M.; Zhang, N.N.; Liu, C.S.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wang, X.D.; Du, M.A. Mixed-cluster approach for building a highly porous cobalt(II) isonicotinic acid framework: gas sorption properties and computational analyses. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 2379–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.D.; Guo, X.Z.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, S.S. Metal(II) coordination polymers derived from mixed 4-imidazole ligands and carboxylates: syntheses, topological structures, and properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Chen, Y.G.; Tang, G.; Liu, S.X. Polynuclear complexes of main group and transition metals with polyaminopolycarboxylate and polyoxometalate. Dalton Trans 2012, 41, 9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Niu, C.; Ni, J. Study on mixed ligand complexes of rare earth with nitrilotriacetic acid and amino acid. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry 1990, 3, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Trevin, S.; Bedioui, F.; Gomez, M.G.; Charreton, C.B. Electro polymerized nickel Micro cyclic complex - base films design and elctro-catalytic application. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Sherif, E.M. Methylenedisalicylic acid as a bio corrosion inhibitor for aluminum in concentrated sodium chloride solutions. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 19193–19203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Cano, H.J.; Robles-Contreras, A. Basic aspects of the mechanisms of bacterial resistance. Rev Med MD 2013, 4, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Kantouch, A.; Atef El-Sayed, A.; Salama, M.; Abou El-Kheir, A.; Mowafi, S. Disalicylic acid and some of its derivatives as antibacterial agents for viscose fabric. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yishan, F.; Jianxin, F.; Chunjing, T.; Pengfei, L.; Bo, C. Mechanical properties and antibacterial activities of novel starch-based composite films incorporated with disalicylic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Ghezzi, L.; Spepi, A.; Agnolucci, M.; Cristani, C.; Giovannetti, M.; Tiné, M.R.; Duce, C. Kinetics of release and antibacterial activity of disalicylic acid loaded into halloysite nanotubes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, M.; Kanamathareddy, S. Synthesis of the covalent hydrate of the incorrectly assumed structure of aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA). Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 1491–1498, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, M.S.; Ahmed, A.H. Ship-in-a-bottle synthesis and physicochemical studies on zeolite encapsulated Mn(II), Mn(III)-semicarbazone complexes: Application in the heterogeneous hydroxylation of benzene. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, N.F.; Davis, E.A. Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Hassan, A.M.; Gumaa, H.A.; Mohamed, B.H.; Eraky, A.M. Physicochemical studies on some selected oxaloyldihydrazones and their novel palladium(II) complexes along with using oxaloyldihydrazones as corrosion resistants. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2017, 47, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Hassan, A.M.; Gumaa, H.A.; Mohamed, B.H.; Eraky, A.M.; Omran, A.A. Copper(II)-oxaloyldihydrazone complexes: Physico-chemicalstudies; energy band gap and inhibition evaluation of free oxaloyldihydrazones toward the corrosion of copper metal in acidic medium. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4287–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindler, J.A.; Howard, B.J.; Keiser, J.F. Antimicrobial agents and Susceptibility testing. In Clinical and pathogenic Microbiology; Howard, B.J., Ed.; Mosby-Year Book Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Abo-Ashour, M.F.; Eldehna, W.M.; Nocentini, A.; Bonardi, A.; Bua, S.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Elaasser, M.M.; Kryštof, V.; Jorda, R.; Gratteri, P.; Abou-Seri, S.M.; Supuran, C.T. 3-Hydrazinoisatin-based benzenesulfonamides as novel carbonic anhydrase inhibitors endowed with anticancer activity: Synthesis, in vitro biological evaluation and in silico insights. Eur J Med Chem. 2019, 184, 111768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomha, S.M.; Riyadh, S.M.; Mahmmoud, E.A.; Elaasser, M.M. Synthesis and Anticancer Activities of Thiazoles, 1,3-Thiazines, and Thiazolidine Using Chitosan-Grafted-Poly(vinylpyridine) as Basic Catalyst. Heterocycles 2015, 91, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.M.; Ahmed, A.H.; Mohamed, T.A.; Mohamed, B.H. Chelates and corrosion inhibition of newly synthesized Schiff bases derived from o- tolidine. Transit. Met. Chem. 2007, 32, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinari, C.; Lorenzotti, A.; Pellei, M.; Santini, C. Zinc(II), cadmium(II) and mercury(II) derivatives of bis(4-halopyrazol-1-yl)alkanes: synthesis, spectroscopic characterization and behaviour in solution. Polyhedron 1997, 16, 3435–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Butcher, R.J.; Porchia, M.; De Franco, M.; Marzano, C.; Gandin, V.; Tisato, F. Synthesis and characterization of mixed-ligand Zn(II) and Cu(II) complexes including polyamines and dicyano-dithiolate(2-): In vitro cytotoxic activity of Cu(II) compounds. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 498, 119098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R.A.; Basumatary, D.; Arjun, K.D.; Kumar, A. Synthesis and spectral characterization of zinc(II), copper(II), nickel(II) and manganese(II) complexes derived from bis(2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde) malonoyldihydrazone, Transit. Met. Chem. 2007, 32, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, H.; Çakir, Ü.; Otludil, B.; Uğraş, H.İ. Synthesis, spectral and biological studies of Mnn(II), NiII), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes with a tetradentate Schiff base ligand. complexation studies and the determination of stability constants (Ke). Synth. React. Inorg. Met-org Chem. 2001, 31, 1323–1337, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseyphus, R.S.; Nair, M.S. Synthesis, characterization and biological studies of some Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes derived from indole-3-carboxaldehyde and glycylglycine, as Schiff base ligand. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 3, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A. The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streetman, B.G. Solid State electronic Devices, 5th ed.; New Jersey: Prentice, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Karipcin, F.; Dede, B.; Caglar, Y.; Hur, D.; Ilican, S.; Caglar, M.; Sahin, Y. A new dioxime ligand and its trinuclear copper(II) complex: Synthesis, characterization and optical properties. Opt. Commun. 2007, 272, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.K.; Pandey, O.P.; Srivastava, B.K.; Sharma, V. Trends in Structural Mechanics: Theory, Practice. Transit. Met. Chem. 1998, 23, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, N.; Gündüz, B.; Körkoca, H.; Adigüzel, R.; Çolak, N.; Buldurun, K. Study of structure and spectral characteristics of the zinc(II) and copper(II) complexes with 5,5-dimethyl-2-(2-(3-nitrophenyl)hydrazono)cyclohexane-1,3-dione and their effects on optical properties and the developing of the energy band gap and investigation of antibacterial activity. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2014, 58, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gittleman, J.I.; Sichel, E.K.; Arie, Y. Composite semiconductors: Selective absorbers of solar energy. Sol. Energy Mater. 1979, 1, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmokhtar, A.; Yahiaoui, A.; Hachemaoui, A.I.; Abdelghani, B.; Sahli, N.; Belbachir, M. ANovelPoly{(2,5-diylfuran)(benzylidene)}:Anew Synthetic Approach and Electronic Properties. ISRN Physical Chemistry 2012, 7, 781879. [Google Scholar]
- Yakuphanoglu, F.; Erten, H. Refractive index dispersion and analysis of the optical constants of an ionomer thin film. Optica. Applicata. 2005, 4, 969–976. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, T.C.; Podder, J. Synthesis and characterization of Zn- incorporated TiO2 thin flms: impact of crystallite size on X-ray line broadening and bandgap tuning. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, B.H.; Ahmed, H.Y.; Gazzar, E.M.E.; Badawy, M.M.M. Enhancement the Mycosynthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles by Using Gamma Radiation. Dose-Response: An International Journal 2021, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrega, A.; Vila, J. Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium skills to succeed in the host: virulence and regulation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 308–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H. N,N`-bis[2-hydroxynaphthylidene]/[2-methoxybenzylidene]amino]oxamides and their divalent manganese complexes: Isolation, spectral characterization, morphology, antibacterial and cytotoxicity against leukemia cells. Open Chem. 2020, 18, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Hassan, A.M.; Gumaa, H.A.; Mohamed, B.H.; Eraky, A.M. Nickel(II)-oxaloyldihydrazone complexes: Characterization, indirect band gap energy and antimicrobial evaluation. Cogent Chem. 2016, 2, 1142820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, P.; Reddy, K.L. Synthesis, spectral characterization, morphology, biological activity and DNA cleavage studies of metal complexes with chromone Schiff base. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohareb, R.M.; EL-Sharkawy, K.A.; Al Farouk, F.O. Synthesis, cytotoxicity against cancer and normal cell lines of novel hydrazide–hydrazine derivatives bearing 5H-chromen-5-one. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 1885–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G.J.; Graham, A.B.; Lawrence, J.R.; Wiles, D.; Paterson, J.R. Salicylic acid acid in soups prepared from organically and non-organically grown vegetables. Eur. J. Nutr. 2001. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, W.P., III; Brody, H.J. Advances in chemical peeling. Dermatol. Clin. 1997, 15, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).