Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
01 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and discussion
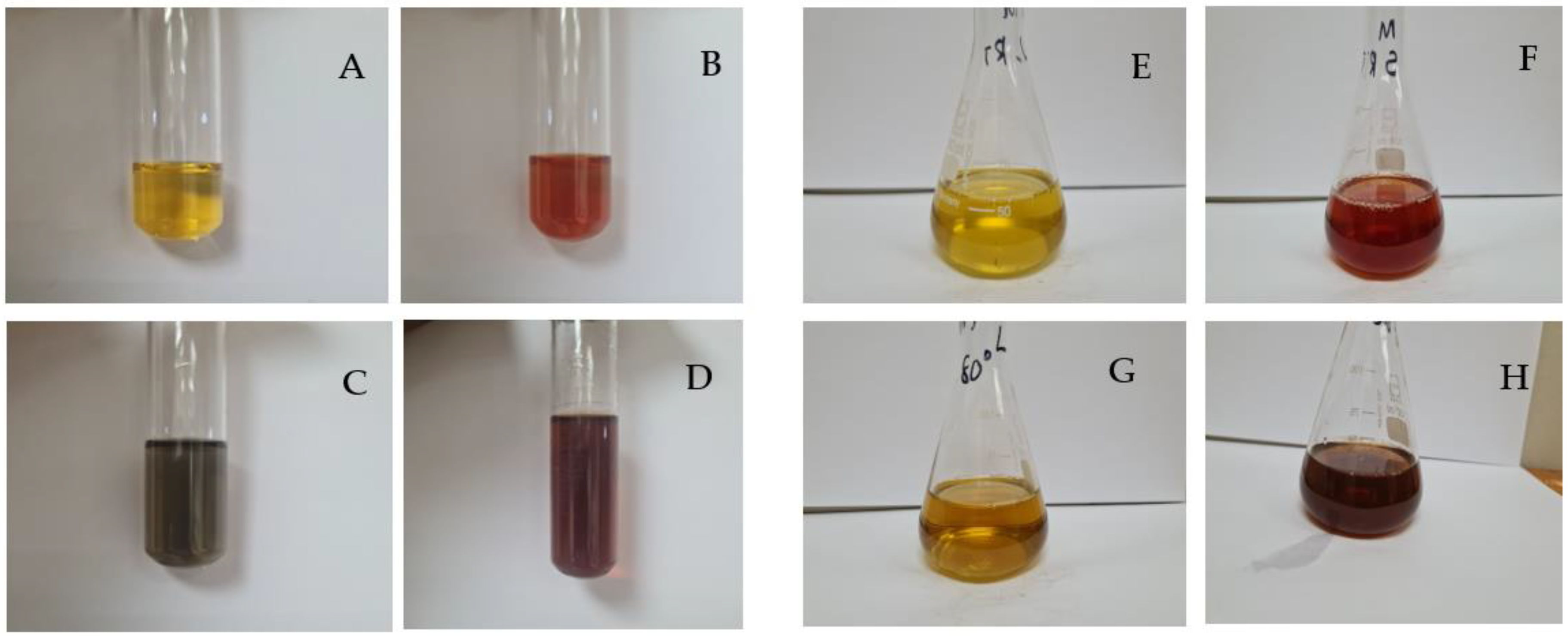
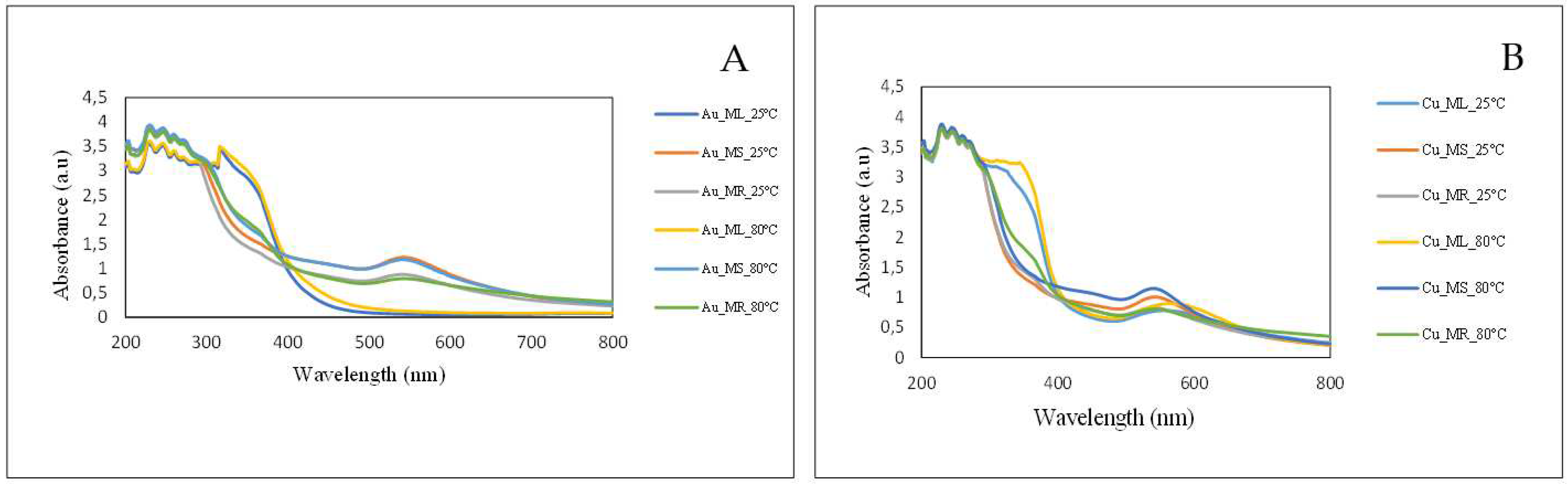
2.1. Visual and UV-Vis Spectroscopic Analysis
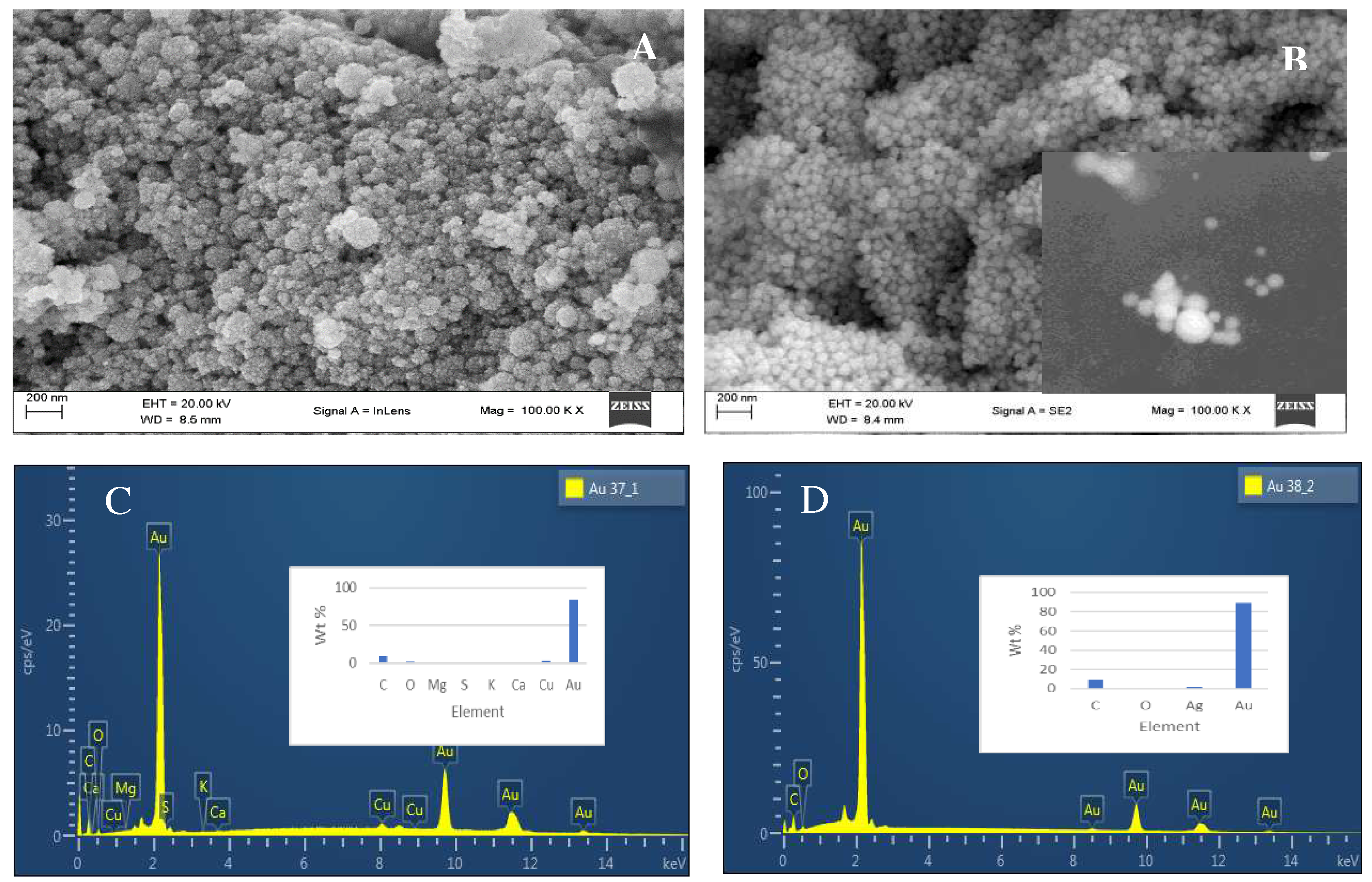
2.2. Morphology of synthesised nanoparticles using Scanning electron microscopy and Energy dispersive X-ray Analysis
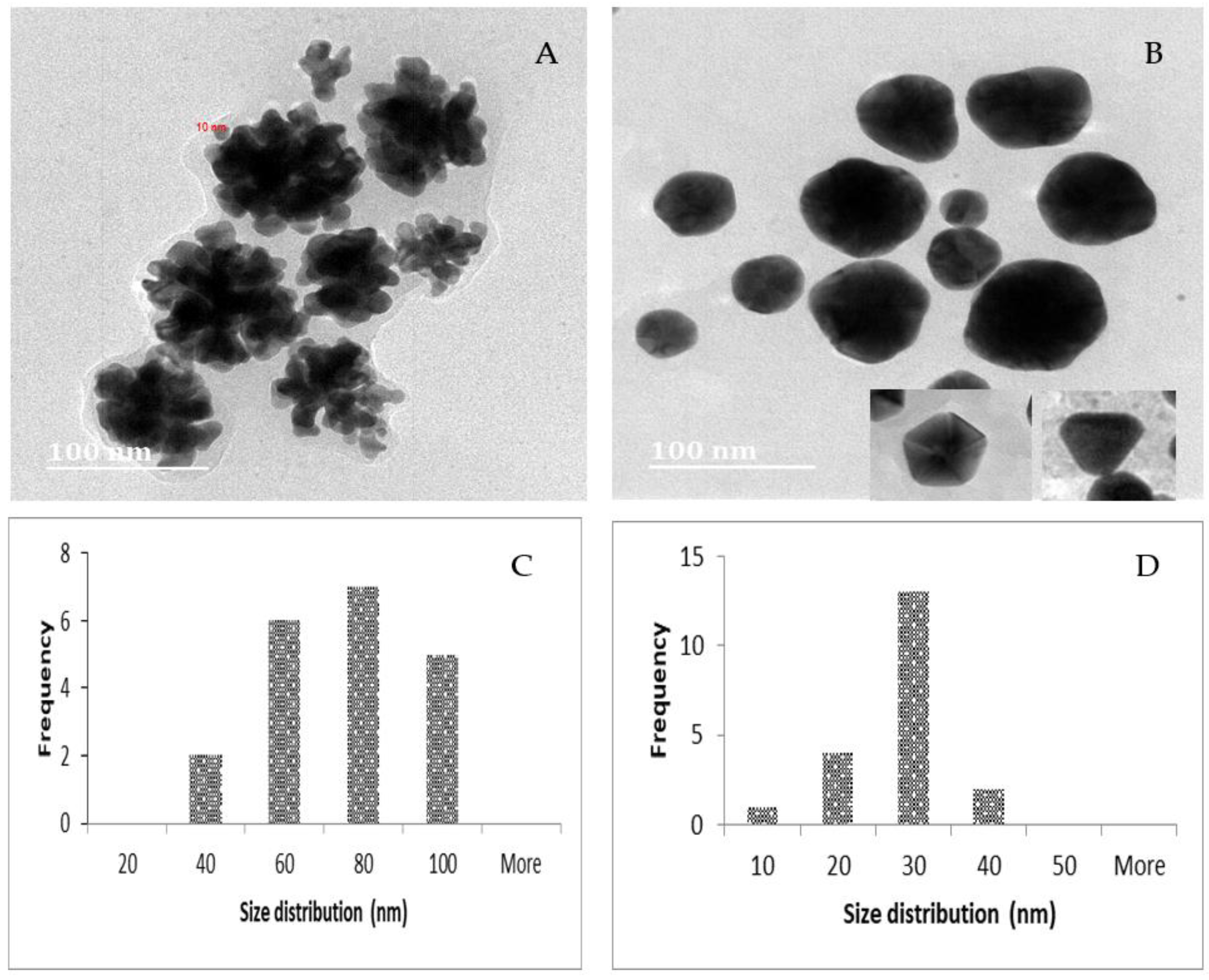
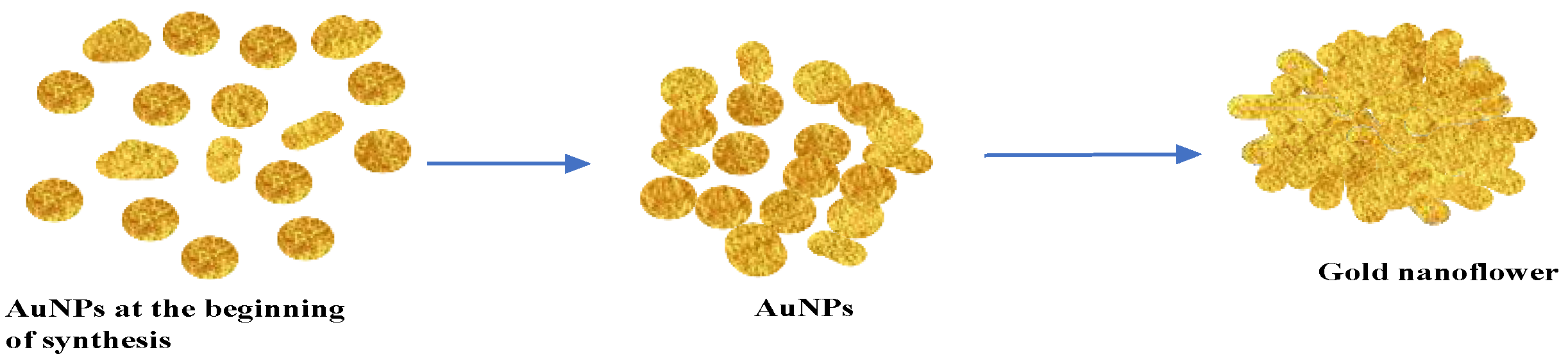
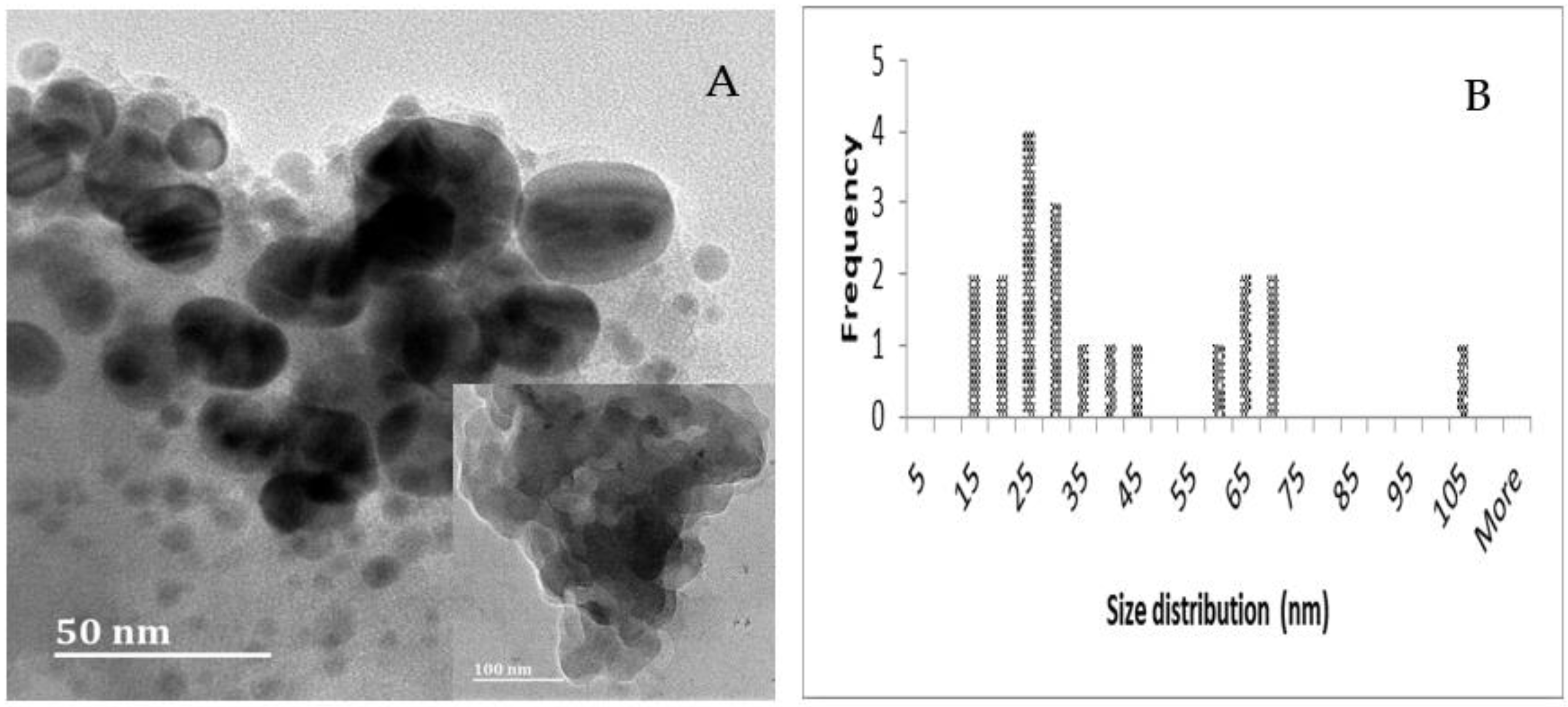
2.3. TEM, Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
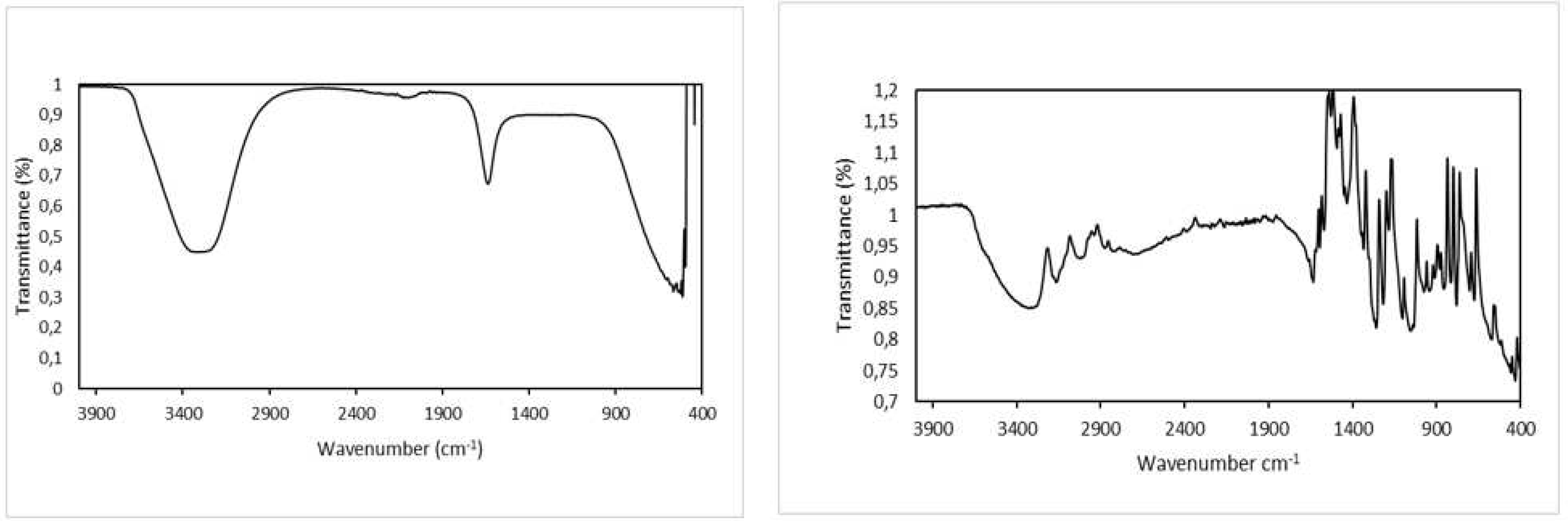
2.4. FTIR Analysis
2.5. Antibacterial Activity of AuNPs and CuNPs
3. Materials and methods
3.1. Collection of plant material
Extraction
3.2. Synthesis of nanoparticles
3.3. Characterisation
3.3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of AuNPs and CuNPs
3.3.2. Scanning electron microscopy analysis and energy dispersive x-ray microanalysis
3.3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy analysis and Measurements of Zeta Potential
3.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis
3.4. Antibacterial Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malike, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Nanotechnology: A revolution in modern industry. Molecules. 2023, 28, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications, and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczyglewska, P.; Feliczak-Guzik, A.; Nowak, I. Nanotechnology–General Aspects: A Chemical Reduction Approach to the Synthesis of Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2023, 28, 4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh., J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. Green synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnology. 2018, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Which metals are green for catalysis? Comparison of the toxicities of Ni, Cu, Fe, Pd, Pt, Rh, and Au salts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12150–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, C.; Pluchery, O. Gold nanoparticles in the past: before the nanotechnology era gold nanoparticles for physics, chemistry, and biology (Singapore: World Scientific Publishing). 2012, p 1-28.
- Chiang, M.C.; Nicol, C.J.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, S.J.; Yen, C.; Huang, R.N. Nanogold induces anti-inflammation against oxidative stress induced in human neural stem cells exposed to amyloid-beta peptide. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 145, 104992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leary, J. Attaching Biomolecules to Nanoparticles (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press). 2022, p 103-121.
- Kulkarni, D.; Sherkar, R.; Shirsathe, C.; Sonwane, R.; Varpe, N.; Shelke, S.; More, M.P.; Pardeshi, S.R.; Dhaneshwar, G.; Junnuthula, V.; Dyawanapelly, S. Biofabrication of nanoparticles: sources, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Front. bioeng. biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1159193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheny, D.S.; Joseph, M.; Daizy, P. Phytosynthesis of Au, Ag and Au-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles using aqueous extract and dried leaf of Anacardium occidentale. Spectrochim. Acta A. 2011, 79, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechyen, C.; Ponsanti, K.; Tangnorawich, B.; Ngernyuang, N. Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by Spondias dulcis (Anacardiaceae) peel extract and its cytotoxic activity in human breast cancer cell. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhumaydhi, F.A. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using extract of Pistacia chinensis and their in vitro and in vivo biological activities. J. Nanomater. 2022, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, M.C.; Teodora, M.; Lucian, M. Copper nanoparticles: Synthesis and characterization, physiology, toxicity, and antimicrobial applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, E.K.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J. Large-scale production of carbon-coated copper nanoparticles for sensor applications. Nanotechnology. 2006, 17, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhou, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, R.; Fu, Y.; Jiao, T. Facile biosynthesis and grown mechanism of gold nanoparticles in Pueraria lobata extract. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. 2019, 567, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Vieyra, C.; Olguin, M.T.; Gutiérrez-Segura, E.; López-Tellez, G. Comparison of Ag, Cu and Zn nanoparticles obtained using Aloe vera extract and gamma ionizing radiation. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2020, 18, 289–314. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Madasamy, M.; Mahendran, V. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Cissus vitiginea and its antioxidant and antibacterial activity against urinary tract infection pathogens. Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, B.; Kurian, M.; Krishna, S.; Athira, T.S. Biochemical synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Zingiber officinalis and Curcuma longa: Characterization and antibacterial activity study. Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 25, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, C.S.; Kumar, J.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Ramesh, P.L.N.; Zin, T.; Rao, U.M. 2020 Antibacterial and anticancer potential of Brassica oleracea var acephala using biosynthesised copper nanoparticles. Med. J. Malaysia. 2020, 75, 677. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shubhashree, K.R.; Reddy, R.; Gangula, A.K.; Nagananda, G.S.; Badiya, P.K.; Ramamurthy, S.S.; Reddy, N. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using aqueous extracts from Hyptis suaveolens (L). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 280, 125795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroyi, A. Lannea discolor: its botany, ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties. Asian. J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwamatope, B.; Tembo, D.; Kampira, E.; Maliwichi-Nyirenda, C.; Ndolo, V. Seasonal variation of phytochemicals in four selected medicinal plants. Pharmacognosy. Res. 2021, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, B.M.; Ali, E.M. Therapeutic Potential of Green Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles Using Extract of Leptadenia hastata against Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Fungi. 2022, 8, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; He, Z.; Curtin, J.F.; Byrne, H.J.; Tian, F. A novel, rapid, seedless, in situ synthesis method of shape and size controllable gold nanoparticles using phosphates. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebig, F.; Henning, R.; Sarhan, R.M.; Prietzel, C.; Bargheer, M.; Koetz, J. A new route to gold nanoflowers. Nanotechnology. 2018, 29, 185603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Mei, S.; Ma, H.; Chen, X. Ultrasound-assisted green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using citrus peel extract and their enhanced anti-inflammatory activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 83, 105940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mthembu, S.B.; Akintayo, D.C.; Moodley, B.; Gumbi, B.P. Development of gold plasmonic nanoparticles for detection of polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride at Umgeni water treatment plants: An optimised study and case application. Heliyon. 2023, 9, e17136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.E.; Abu-Yousef, I.A.; Majdalawieh, A.F.; Narasimhan, S.; Poltronieri, P. Green synthesis of encapsulated copper nanoparticles using a hydroalcoholic extract of Moringa oleifera leaves and assessment of their antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Molecules. 2022, 25, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.Y. Near-infrared-responsive cancer photothermal and photodynamic therapy using gold nanoparticles. Polym. 2018, 10, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjad, R.; Mubeen, B.; Ali, S.S.; Imam, S.S.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alzarea, S.I.; Rasool, R.; Ullah, I.; Nadeem, M.S.; Kazmi, I. Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Fortunella margarita leaves. Polym. 2021, 13, 4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, B.J.; Ayodele, O.O.; Olubambi, P.A. Sintering of nanocrystalline materials: Sintering parameters. Heliyon. 2023, 9, e14070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.B.; Wang, J.F.; Chuang, K.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Chang, K.C.; Ma, C.M. Preparing Copper Nanoparticles and Flexible Copper Conductive Sheets. Nanomater. 2022, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwax, N.; Choi, S.H.; Dastgeer, G.; Humayoun, U.B.; Kumar, M.; Nawaz, A.; Jeong, D.I.; Zaidi, S.F.; Yoon, D.H. Synthesis of citrate-capped copper nanoparticles: A low temperature sintering approach for the fabrication of oxidation stable flexible conductive film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 542, 148609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, C.; Atalar, M.N. Firat Baran, M.; Baran, A. Environmentally friendly rapid synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Artemisia absinthium plant extract and application of antimicrobial activities. JIST. 2021, 11, 365. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Gul, S.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, M.A.; Asiri, A.M.; Khan, S.B. Green synthesis of zerovalent copper nanoparticles for efficient reduction of toxic azo dyes congo red and methyl orange. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajanlal, P.R.; Sreeprasad, T.S.; Samal, A.K.; Pradeep, T. Anisotropic nanomaterials: structure, growth, assembly, and functions. Nano. Rev. 2011, 2, 5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakhmola, A.; Vecchione, R.; Gentile, F.; Profeta, M.; Manikas, A.C.; Battista, E.; Netti, P.A. Experimental and theoretical study of biodirected green synthesis of gold nanoflowers. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 14, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ren, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; Shu, M.; Yang, H.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, Y. Detection of aflatoxin B1 with immunochromatographic test strips: enhanced signal sensitivity using gold nanoflowers. Talanta. 2015, 142, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borah, D.; Hazarika, M.; Tailor, P.; Silva, A.R.; Chetia, B.; Singaravelu, G.; Das, P. Starch-templated biosynthesis of gold nanoflowers for in vitro antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onmaz, N.E.; Demirezen, Yilmaz, D.; Imre, K.; Morar, A.; Gungor, C.; Yilmaz, S.; Gundog, D.A.; Dishan, A.; Herman, V.; Gungor, G. Green synthesis of gold nanoflowers using Rosmarinus officinalis and Helichrysum italicum extracts: Comparative studies of their antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities. Antibiotics. 2022, 11, 1466. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh, A.R.; Kim, B.S. Flower-like biogenic gold nanostructures for improved catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluchery, O.; Remita, H.; Schaming, D. Demonstrative experiments about gold nanoparticles and nanofilms: an introduction to nanoscience. Gold Bull. 2013, 46, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, R.; Yuhi, T.; Nagatani, N.; Endo, T.; Kerman, K.; Takamura, Y.; Tamiya, E. A novel enhancement assay for immunochromatographic test strips using gold nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merza, K.S.; Al-Attabi, H.D.; Abbas, Z.M.; Yusr, H. A Comparative Study on Methods for Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles. Green. Sustain. Chem. 2011, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, V.M.; Hoffmeier, J.C.; Yazgan, I.; Sadik, O.A. Seedless synthesis and SERS characterization of multi-branched gold nanoflowers using water soluble polymers. Nanoscale. 2017, 9, 8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabestarian, H.; Homayouni-Tabrizi, M.; Soltani, M.; Namvar, F.; Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R.; Shabestarian, H. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using sumac aqueous extract and their antioxidant activity. Mater. Res. 2016, 20, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donga, S.; Bhadu, G.R.; Chanda, S. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer activities of gold nanoparticles green synthesized using Mangifera indica seed aqueous extract. Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Y.; Jang, H.K.; Kim, B.S. Biological synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Magnolia kobus and Diopyros kaki leaf extracts. Process. Biochem. 2009, 44, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, H.; Bibi, S.; Singh, I.; Hasan, M.M.; Khan, M.S.; Yousafi, Q.; Baig, AA.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam.; Emran, T.B.; Cavalu, S. Green metallic nanoparticles: biosynthesis to applications. Front. bioeng. biotechnol. 2022, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; Habtemariam, S. Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnology. 2018, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawande, M.B.; Goswami, A.; Felpin, F.X.; Asefa, T.; Huang, X.; Silva, R.; Zou, X.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Cu and Cu-based nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3722–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizochenko, N.; Mikolajczyk, A.; Syzochenko, M.; Puzyn, T.; Leszczynski, J. Zeta potentials (ζ) of metal oxide nanoparticles: A meta-analysis of experimental data and a predictive neural network modelling. NanoImpact. 2021, 22, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, H.C.; Desalegn, T.; Kassa, M.; Abebe, B.; Assefa, T. Synthesis of green copper nanoparticles using medicinal plant Hagenia abyssinica (Brace) JF Gmel leaf extract: Antimicrobial properties. J. Nanomater. 2020, 1, 3924081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P. Reactive oxygen species-related nanoparticle toxicity in the biomedical field. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yougbare, S.; Chang, T.K.; Tan, S.H.; Kuo, J.C.; Hsu, P.H.; Su, C.Y.; Kuo, T.R. Antimicrobial gold nanoclusters: Recent developments and future perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Zarei, M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chiang, W.H.; Lai, C.W.; Gholami, A. Gold nanostars-diagnosis, bioimaging and biomedical applications. Drug Metab. Rev. 2020, 52, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okkeh, M.; Bloise, N.; Restivo, E.; De Vita, L.; Pallavicini, P.; Visai, L. Gold nanoparticles: can they be the next magic bullet for multidrug-resistant bacteria? Nanomater. 2021, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umadevi, M.; Rani, T.; Balkrishnan, T.; Ramanibai, R. Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles under an ultrasonic field. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 4, 1491. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K.; Setyawati, M.I.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Antimicrobial Gold Nanoclusters. ACS Nano. 2017, 11, 6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovati, D.; Albini, B.; Galinetto, P.; Grisoli, P.; Bassi, B.; Pallavicini, P.; Dacarro, G.; Taglietti, A. High Stability Thiol-Coated Gold Nanostars Monolayers with Photo-Thermal Antibacterial Activity and Wettability Control. Nanomater. 2019, 9, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes de Oca-Vásquez, G.; Solano-Campos, F.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R.; López-Mondéjar, R.; Odriozola, I.; Vera, A.; Moreno, J.L.; Bastida, F. Environmentally relevant concentrations of silver nanoparticles diminish soil microbial biomass but do not alter enzyme activities or microbial diversity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qamar, H.; Rehman, S.; Chauhan, D.K.; Tiwari, A.K.; . Upmanyu, V. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Copper Oxide Nanomaterial Derived from Momordica charantia. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020, 15, 2541–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry ed, Meyers, R.A.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., USA, 2000; P 10815.
- Madikizela, B.; Ndhlala, AR.; Finnie, J.F.; Staden, J.V. In vitro antimicrobial activity of extracts from plants used traditionally in South Africa to treat tuberculosis and related symptoms. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2013, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AuNFs and NPs (µg/ml) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | Extracts (µg/ml) | G | HAuCl4(1 mM) | |
| P. aeruginosa | 250 | 125 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 125 | 62,5 | 7,81 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 7,8 | 500 |
| K. pneumoniae | 250 | 125 | 125 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 62,5 | 125 | 15,62 | 15,62 | 1000 | 1000 | 0 | 0 | 7,81 | 62,5 | 0 | 1000 | 7,8 | 500 |
| E. coli | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 125 | 62,5 | 15,62 | 15,62 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 0 | 1000 | 7,8 | 500 |
| B. subtilis | 250 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 15,62 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 15,62 | 15,62 | 7,81 | 0 | 1000 | 7,8 | 1000 |
| S. aureus | 62,5 | 62,5 | 0 | 62,5 | 62,5 | 0 | 15,62 | 62,5 | 125 | 250 | 250 | 500 | 500 | 250 | 500 | 250 | 250 | 0 | 1000 | 7,8 | 1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





