Submitted:
21 December 2023
Posted:
22 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
| Acronym | Definition |
|---|---|
|
IoT |
Internet of Things |
| IoE | Internet of Everything |
| CUPS | Control Plane and User Plane Separation |
| LPWA | Low Power Wide Area |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| NR | New Radio |
| MIMO | Multiple input, Multiple output |
| HD | High Definition |
| M2M | Machine to Machine |
| UP | User Plane |
| PCRF | Policy and Charging Rules Function |
| OCS | Online Charging System |
| SDN | Software Defined Network |
| VNF | Virtual Network Function |
| OSI | Open Systems Interconnection |
| PSM | Power Saving Mode |
| eDRX | Extended Discontinuous Reception |
| PDN | Packet Data Network |
| UE | User Equipment |
| MME | Mobility Management Entity |
| HLC | High Latency Communication |
| MT | Mobile Terminated |
| AES | Advanced Encryption Standard |
| ECC | Eliptic Curve Cryptography |
| LoRA | Long Range |
| MTC | Machine-Type Communication |
| PGW | PDN Gateway |
| IPv4 | Internet Protocol 4 |
| IPv6 | Internet Protocol 6 |
| RAN | Radio Access Network |
| SeGW | Security Gateways |
| O&M | Operation and Maintenance |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
| ML WUR AI |
Machine Learning Wakeup Radio Artificial Intelligence |
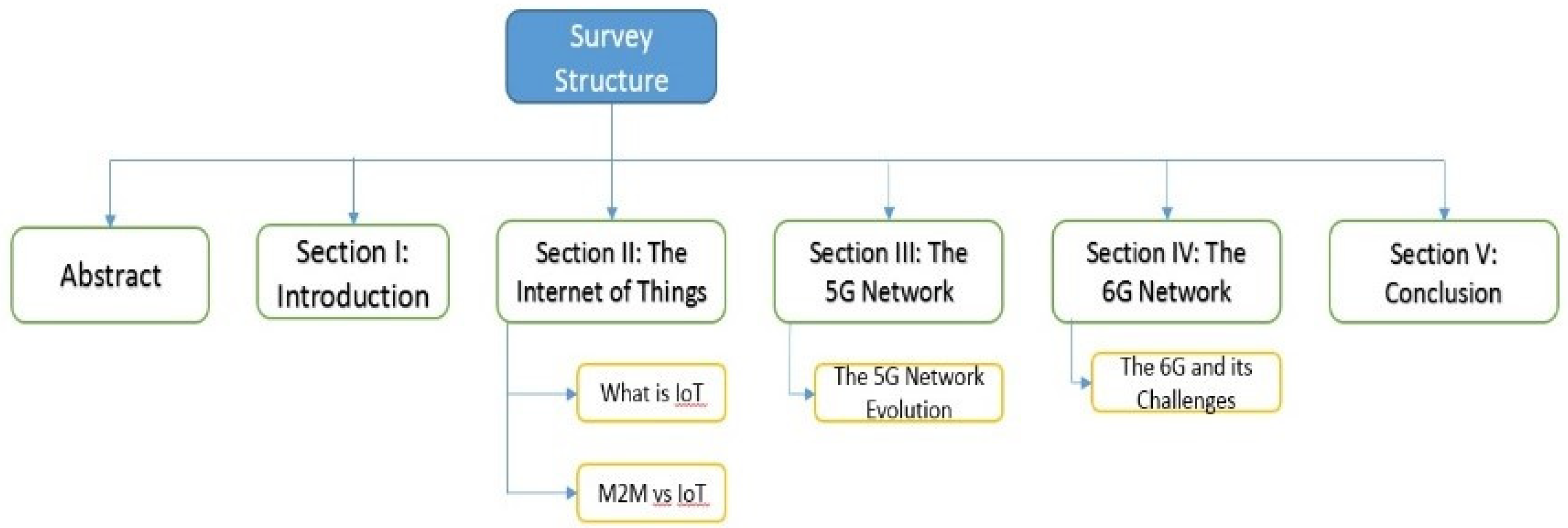
2. The Internet of Things
2.1. What is IOT
- The technical characteristics of the IoT devices such as CPU, memory capacity, signal level, operating system, battery capacity and power consumption of the processor.
- The network topology of the IoT devices system determining the amount of the information passing through.
- The functional characteristics of the IoT devices such as data transfer protocols, security and encryption methods used.
- The frequency and transmission of the collected data.
- CPU frequency
- Transmitted packet size
- Channel bitrate
- Total number of processed algorithm commands
- Sleep mode timeframe
- The channel bit rate
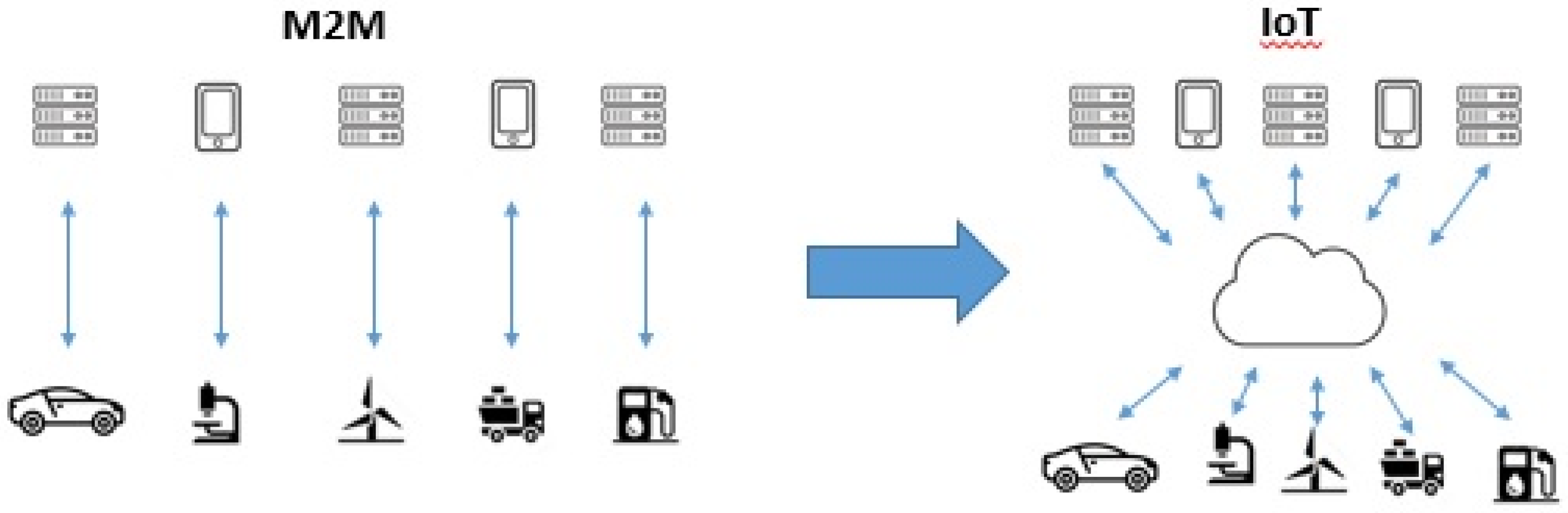
2.2. M2M vs IoT
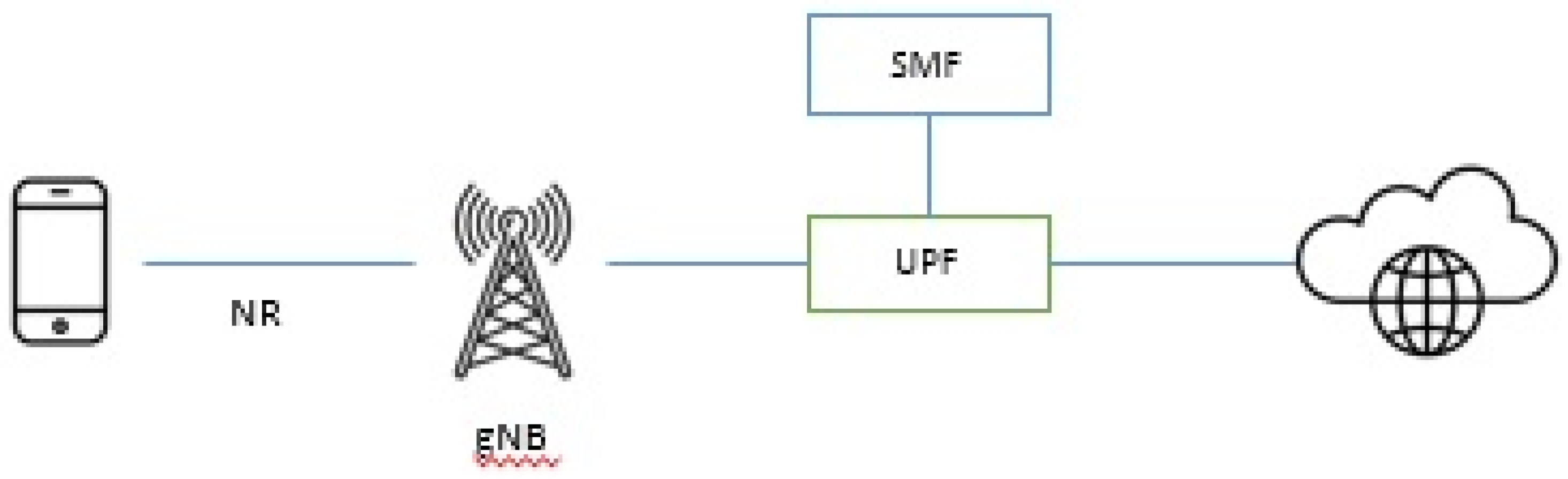
3. The 5G Network
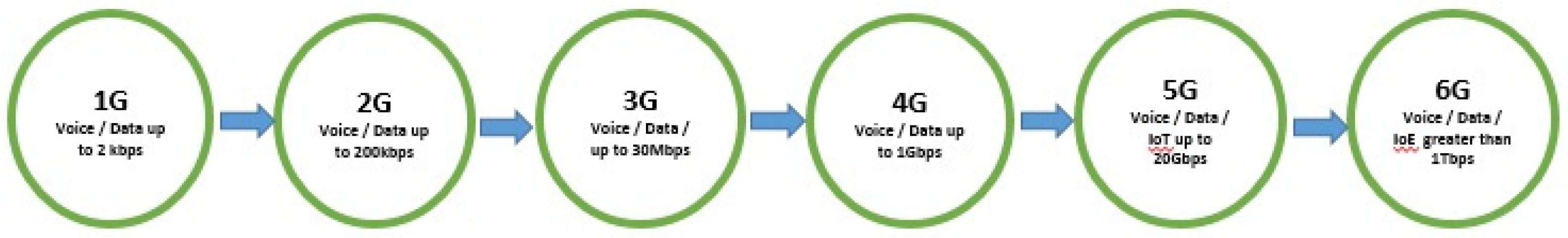
3.1. The 5G Network Evolution
4. The 6G Network
4.1. The 6G and its challenges
5. Conclusions
References
- Knyazev, N.S.; Chechetkin, V.A.; Letavin, D.A. Comparative analysis of standards for Low-power Wide-area Network. 2017 Systems of Signal Synchronization, Generating and Processing in Telecommunications, 2017 (SINKHROINFO), Kazan, 2017.
- Dinh, C. Nguyen, Ming Ding, Pubudu N. Pathirana, Aruna Seneviratne, Jun Li, Dusit Niyato, Fellow, IEEE, Octavia Dobre, Fellow, IEEE, and H. Vincent Poor, Fellow, IEEE, 2022. “6G Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Survey”.
- Veena, S. Chakravarthi, 2011. “Internet of Things and M2M Communication Technologies”, Architecture and Practical Design Approach to IoT in Industry 4.0, ISBN 978-3-030-79272-5, Pages 15-18.
- Stefan Rommer, Peter Hedman, Magnus Olsson, Lars Frid, Shabnam Sultana, Catherine Mulligan, 2019. “5G Core Networks” Powering Digitalization, ISBN 978-0-08-103009-7, Pages 89-102.
- Wakunami, K.; et al. Projection-type see-through holographic three-dimensional display. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daji Qiao, & Shin, K. G. (n.d.), 2005. “Smart power-saving mode for IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs”. Proceedings IEEE 24th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies.
- Fan, X.-N. , Hu, Q.-S., & Cao, G.-J, (2019). “Grouping-Based Extended Discontinuous Reception with Adjustable eDRX Cycles for Smart Grid”. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm).
- Sultan, I.; Mir, B.J.; Banday, M.T. Analysis and Optimization of Advanced Encryption Standard for the Internet of Things. 2020 seventh International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 2020.
- Almuhammadi, S.; Al-Hejri, I. A comparative analysis of AES common modes of operation. In 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering (CCECE), 2017.
- Ievgeniia Kuzminykh, Maryna Yevdokymenko, Vladimir Sokolov, 2022. “Encryption Algorithms in IoT: Security vs Lifetime, How long the device will live?”.
- Samuel, A. , & Sipes, C, (2019). “Making Internet of Things Real”. IEEE Internet of Things Magazine.
- Praveen Kumar Reddy Maddikunta, Quoc-Viet Pham, Dinh C. Nguyen, Thien Huynh-The, Ons Aouedi, Gokul Yenduri, Sweta Bhattacharya, Thippa Reddy Gadekallu, 2022. “Incentive techniques for the Internet of Things: A survey”.
- Samuel Greengard, MIT Press, 2015, “The Internet of Things”, ISBN 0262527731, 9780262527736.
- Carles Anton-Haro and Mischa Dohler, 2015 “Machine-to-machine (M2M) Communications, Architecture, Performance and Applications”, ISBN 978-1-78242-110-8.
- Mehmood, Y.; Görg, C.; Muehleisen, M.; Timm-Giel, A. Mobile m2m communication architectures, upcoming challenges, applications, and future directions. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2015, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazis, V. A survey of standards for machine-to-machine and the internet of things. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut. 2017, 19, 482–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavimi, F.; Chen, H.H. M2m communications in 3GPP LTE/LTE-a networks: Architectures, service requirements, challenges, and applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut. 2015, 17, 525–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Hedman, P.; Zisimopoulos, H. Machine type communications in 3GPP systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.C.; Lien, S.Y. Machine-to-machine communications: Technologies and challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. 2014, 18, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.K.; Verma, R.; Prakash, A.; Agrawal, A.; Naik, K.; Tripathi, R.; Alsabaan, M.; Khalifa, T.; Abdelkader, T.; Abogharaf, A. Machine-to-machine (m2m) communications: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 66, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Kumar, A.; Ristaniemi, T.; Chong, P.H.J. Machine-to-machine communication and research challenges: A survey. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 97, 3569–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherine Mohamed Abd El-Kader, Hanan Hussein, 2019. “Fundamental and Supportive Technologies for 5G Mobile Networks” ISBN 9781799811541.
- Afif Osseiran, Jose F. Monserrat, Patrick Marsch, 2016. “5G Mobile and Wireless Communications Technology”, ISBN 978-1-107-13009-8.
- Saad, Z. Asif, 2018. “5G Mobile Communications, Concepts and Technologies”, ISBN 9780429466342.
- Jonathan Rodriguez, 2015. “Fundamentals of 5G Mobile Networks”, ISBN 9781118867525.
- Wei Xiang, Kan Zheng, Xuemin (Sherman) Shen, 2017. “5G Mobile Communications”, ISBN 978-3-319-34208-5.
- Brandon Satrom, “Demystifying LoRa and LoraWAN Wireless Network Protocols”, 2022. https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/technical-articles/demystifying-lora-network-and-lorawan-network-wireless-network-protocols/.
- Wikipedia, “LoRa”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LoRa.
- Semtech, “AN1200.22 LoRa Modulation Basics”. https://www.semtech.com/uploads/documents/an1200.22.pdf.
- Qoitech, “How Spreading Factor affects LoRaWAN device battery life”. https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/article/how-spreading-factor-affects-lorawan-device-battery-life.
- Yang Yang, Xu Chen, Rui Tan, Yong Xiao, 2021. “Intelligent IoT for the digital world”, ISBN 9781119593553.
- Yang Yang, Xiliang Luo, Xiaoli Chu, Ming Tuo Zhou, 2019. “Fog-Enabled Intelligent IoT Systems”, ISBN 978-3-030-23185-9.
- Ayman ElNashar, Mohamed A. El-saidny, 2018. “Practical Guide to LTE-A, VoLTE and IoT: Paving the way towards 5G”, ISBN 9781119063308.
- Soumya Ranjan Nayak, Biswa Mohan Sahoo, Muthukumaran Malarvel, Jibitesh Mishra, 2021. “Smart Sensor Networks Using AI for Industry 4.0: Applications and New Opportunities”, ISBN 978-1-003-14502-8.
- Bharat, S. Chaudhari, Marco Zennaro, 2020. “LPWAN Technologies for IoT and M2M Applications”, ISBN 978-0-12-818880-4.
- Ghavimi, F.; Chen, H.H. M2M communications in 3GPP LTE/LTEA networks: Architectures, service requirements, challenges and applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tuts. 2015, 17, 525–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, C.; Bodinier, Q.; Farhang, A.; Marchetti, N.; Bader, F.; DaSilva, L.A. Enabling Asynchronous Machine-Type D2D Communication Using Multiple Waveforms in 5G. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2018, 2327–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrii Solomitckii, Margarita Gapeyenko, Vasilii Semkin, Sergey Andreev, and Yevgeni Koucheryavy, 2018. “Technologies for Efficient Amateur Drone Detection in 5G, Millimeter-Wave Cellular Infrastructure”, IEEE Communication magazine.
- S. M. Ahsan Kazmi, Latif U. Khan, Nguyen H. Tran, Choong Seon Hong, 2019. “Network Slicing for 5G and Beyond Networks”, ISBN 978-3-030-16170-5.
- Qiang Ye, Weihua Zhuang, 2021. “Inteligent Resource Management for Network Slicing in 5G and Beyond”, ISBN 978-3-030-88666-0.
- Anwer Al-Dulaimi, Xianbin Wang, Chih-Lin I, 2018. “5G Networks: Fundamental Requirements, Enabling Technologies, and Operations Management”, ISBN 9781119332732.
- Jyrki T., J. Penttinen, 2021. “5G Second Phase Explained: The 3GPP Release 16 Enhancements”, ISBN 9781119645566.
- Jyrki T., J. Penttinen, 2019. “5G Explained: Security and Deployment of Advanced Mobile Communications”, ISBN 978119275701.
- 3GPP, “Control and User Plane Separation of EPC nodes (CUPS)”. https://www.3gpp.org/cups.
- Sassan Ahmadi, 2018. “5G NR, Architecture, Technology, Implementation, and Operation of 3GPP New Radio Standards”, ISBN 978-0-08-102267-2.
- Zoran, S. Bojkovic, Dragorad A. Milovanovic, Tulsi Pawan Fowdur, 2020. “5G Multimedia Communication, Technology, Multiservices and Deployment”, ISBN 978-1-003-09645-0.
- Khaldoun Al Agha, Guy Pujolle, Tara Ali Yahiya, 2001. “Mobile and Wireless Networks”, ISBN 978-1-84821-714-0.
- Martin Maier, Amin Ebrahimzadeh, 2020. “Toward 6G: A New Era of Convergence”, ISBN 9781119658030.
- Bharathy, A.M. Viswa, Alhadidi, Basim, 2022. “Challenges and Risks Involved in Deploying 6G and NextGen Networks”, ISBN 9781668438060.
- Zakria Qadir, Khoa N. Le, Nasir Saeed, Hafiz Suliman Munawar, 2022. “Towards 6G Internet of Things: Recent advantages, use cases, and open challenges”. [CrossRef]
- Xianzhong Xie, Bo Rong, Michel Kadoch, 2021. “6G Wireless Communications and Mobile Networking”, ISBN 978-1-68108-796-2.
- Jonathan Rodriguez, Christos Verikoukis, John S. Vardakas, Nikos Passas, 2021. “Enabling 6G Mobile Networks”, ISBN 978-3-030-74648-3.
- Yulei Wu, Sukhdeep Singh, Tarik Taleb, Abhishek Roy, Harpreet S. Dhillon, Madhan Raj Kanagarathinam, Aloknath De, 2021. “6G Mobile Wireless Networks”, ISBN 798-3-030-72777-2.
- Mangesh, M. Ghonge, Ramchandra Sharad Mangrulkar, Pradip M. Jawandhiya, Nitin Goje, 2021. “Future Trends in 5G and 6G: Challenges, Architecture, and Applications”, ISBN 978-1-003-17515-5.
- Mladen Božanić, Saurabh Sinha, 2021. “Mobile Communication Networks: 5G and a Vision of 6G”, ISBN 978-3-030-69273-5.
- Hu L, Xie N, Kuang Z; et al. 2012. “Review of Cyber-Physical System Architecture”, international symposium on object component service oriented real time distributed computing, pp.25-30.
- DOCOMO Press Release, 2019. “DOCOMO, AGC and Ericsson achieve world’s first 5G communication using glass antenna for 28 GHz”.
- DOCOMO Press Release, 2020. “DOCOMO conducts world’s first successful trial of transparent dynamic metasurface”.
- Bresson, G.; Alsayed, Z.; Yu, L.; Glaser, S. Simultaneous localization and mapping: A survey of current trends in autonomous driving. IEEE Trans Intell Veh 2017, 2, 194–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, K.; Berndt, H. 6G Vision and Requirement. IEEE Vehic. Teh. Mag. 2018, 13, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Amirabadi Mohammad, Kahaei Mohammad Hossein and Alireza Nezamalhosseini S. Deep learning based detection technique for FSO communication systems. S. Phys. Commun. 2020, 43, 101229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W. Accelerating federated learning via momentum gradient descent. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2020, 31, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, J.; Xia, P.; Zhao, S.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Hanzo, L. Charg-ing unplugged: Will distributed laser charging for mobile wireless power transfer work? IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2016, 11, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaventura, A.; Carvalho, N. A low-power wakeup radio for application in WSN-based indoor location systems. Int. J. Wireless Inf. Netw. 2013, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





