Submitted:
21 December 2023
Posted:
21 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- (1)
- How do metabolic resources (nutrients, machinery, and bioenergetics) constrain the cell?
- (2)
-
How do cells allocate resources to coordinate activity across molecular processes?Building on these concepts to understand multicellularity (Figure 2b), we ask:
- (3)
- How do trade-offs imposed by resource constraints affect cellular decision-making, leading to cell specialization?
- (4)
- How do specialized cells with distinct tasks coordinate within multicellular systems to achieve higher-order functions?
2. Main
2.1. Cellular Resources Constrain Phenotype
2.1.1. Nutrients: resources informing allocation
2.1.2. Machinery: resources actuating allocation
2.1.3. Bioenergy: resources fueling allocation
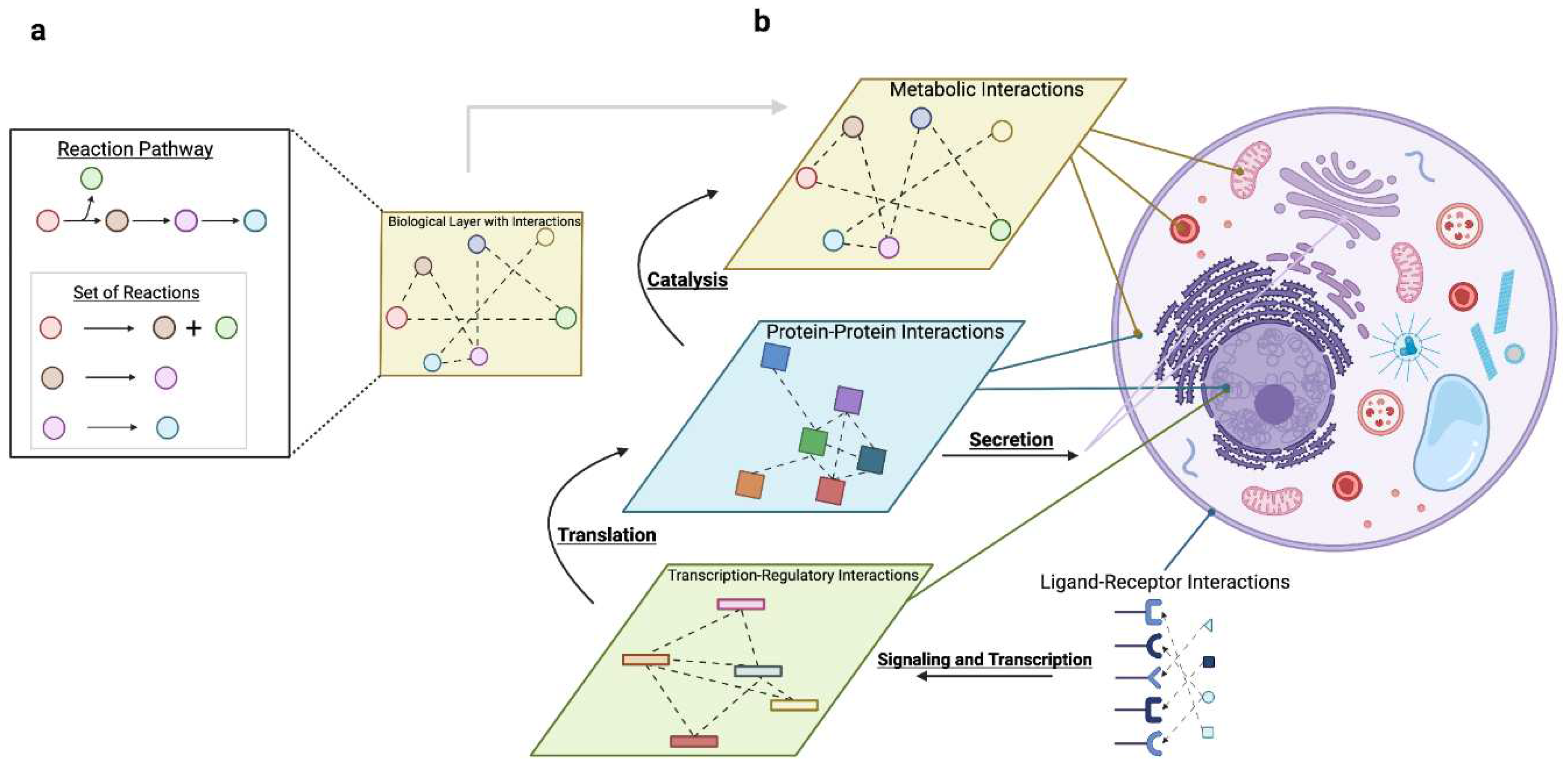
2.2. Molecular Processes Coordinate Resources
2.2.1. Gene Expression: Coordinating mRNA with Protein
2.2.2. Actuation: Coordinating Protein with Metabolism
2.2.3. Communication: Coordinating Signaling and Secretion with Gene Expression
2.3. Trade-offs Occur Due to Multiple Objectives
2.3.1. Context-specific Trade-offs Underlie Cellular Decision-Making
2.3.2. Cells Hedge for Future Contexts
2.4. Multicellularity: From Cells to Organisms
2.4.1. Division of Labor Distributes Resource Burdens
2.4.2. Coordination Enables Higher-Order Functions
2.4.3. Resource Competition Maintains Homeostasis
3. Conclusions
4. Appendix
4.1. Appendix A: Resource Constraints and Growth
4.1.1. Growth Phenotypes Depend On Gene Expression
4.1.2. Energy Budgets are Balanced Between Growth and NGAM
4.2. Appendix B: Systems Biology Approaches to Understand Resource Allocation
4.3. Appendix C: Resource Allocation Affects the Whole-Organism
4.4. Appendix D: Further Insights into Growth and Maintenance
4.4.1. Microbial Shifts in Energy Metabolism at High Growth Rate
4.4.2. Energetic Trade-offs Beyond Proteome Allocation
4.4.3. Growth and NGAM Scale to Whole-Organisms
4.5. Appendix E: Modeling Machinery Activity and Abundance to Couple Protein with Metabolism
4.5.1. Saturation
4.5.2. Resource Loading
4.5.3. Thermodynamics

5. Glossary
- Cellular context: A combination of the current intracellular state (e.g., genomic variants, cell type, and machinery concentrations and localization) and extracellular cues from the microenvironment (e.g., nutrients and communicatory molecules) that together inform cellular decision-making and change as a function of factors such as time, space, and disease.
- Cell specialization: The extent to which a cell is optimized for the performance of a specific, single objective.
- Division of labor: A resource allocation strategy in which multicellular systems distribute multiple objectives across cells with varying degrees of specialization.
- Fitness: The efficiency by which a system uses its resource budget to achieve its objective; mathematically, this is the extent to which the system minimizes resource costs while simultaneously maximizing its objectives.
- Hedging: Resource allocated in preparation for future objectives, particularly at the cost of a current objective.
- Information Transfer: The extent to which the output depends on or is informed by the input (e.g., mutual information).
- Machinery: The macromolecular products of anabolism and gene expression, often enzymes, that catalyze and enable cell functions.
- Machinery-limiting: The flux through a reaction is limited by saturation of the machinery.
- Nutrient-limiting: The flux through a reaction is limited by the availability of a metabolic substrate (nutrient or downstream intermediate).
- Objective: The biological goal that a cell or system is trying to achieve (e.g., motility, proliferation, and differentiation) through the integration of its various biological activities.
- Optimality: The maximization of an objective that is constrained by the resource budget.
- Resource budget: The total quantity of a resource (i.e., nutrient, machinery, and bioenergy) that is available to the cell for use.
- Resource cost: The total quantity of resources that are consumed or sequestered for biological activities contributing to the cell objective.
- Resource loading: Competition in the cell for a shared and often limiting resource (e.g., competition between mRNA transcripts for ribosome).
- Response Time: The time between when the pathway senses the input and when it generates the output.
- Signal Amplification: The magnitude change in the output relative to the magnitude change in the input.
- Signaling Crosstalk: the interaction of shared components between signaling pathways, particularly in the presence of multiple inputs and/or outputs, which requires resource sharing across the signaling network
- Signaling Modularity: A set of signaling components that can convert inputs to outputs while limiting retroactivity (i.e., instances in which the inputs and the outputs are not unidirectional).
- Sensing Precision: The ability of a signaling pathway to accurately convert a given input to the desired output with limited variance, also known as “noise mitigation”.
- Parameter Robustness: The change in the output response given a change to one of the system’s parameters (e.g. binding affinities).
- Pareto optimality: A state in which increasing performance of one objective can only occur by decreasing the performance of another objective due to resource constraints, leading to trade-offs.
6. Highlighted References
- PMID 22068332: This article demonstrates that proteome allocation strategies minimize machinery costs by high expression of proteins with conserved functions and lower expression of proteins involved in context-specific and multicellular processes such as cell signaling and communication.
- PMID 32859923: This article quantifies relative ATP levels in relation to genome-wide machinery abundance across three conditions, highlighting the metabolic flexibility of bioenergetic pathways, distinguishing between machinery- or substrate-limited reactions, and identifying relationships between bioenergetics and growth.
- PMID 25745177: This article uses a model of gene expression to show the variable contributions of macromolecular abundance, synthesis rates, and degradation rates on differential protein expression in non-steady-state conditions.
- PMID 33173034: This article uses a model of gene expression that accounts for resource loading to demonstrate that, in engineered mammalian circuits, transcriptional resources limit protein abundance.
- PMID 26575626: This article quantifies the energetic costs of various steps of gene expression, showing that protein translation consumes a considerable fraction of the energy consumed during gene expression, and it also argues that the bioenergy budget scales (across prokaryotes to eukaryotes) with cell size when accounting for the total lifetime of the cell.
- PMID 31519914: This article provides a unique example of mammalian cell-decision making that optimizes for non-growth phenotypes (in this case, motility) by choosing migratory paths that will be less energetically costly.
- PMID 27951527: This article introduces the concept of a gene-specific, tissue-independent PTR that indicates that coupling between transcript and protein processes is affected by gene-intrinsic features.
- PMID 31896772: This article creates a mammalian genome-scale model that couples metabolism with the secretory pathway, demonstrating that trade-offs occur between cell growth and protein secretion.
- PMID 30638811: This article identifies Pareto fronts from single-cell measurements in tissue, showing that cells have varying extents of specialization according to their spatial location, resulting in division of labor that optimizes tissue-level function.
- PMID 29398113: This article shows how cell communication via growth factor signaling works in combination with constraints to maintain tissue compositional homeostasis.
- PMID 35421362: This article demonstrates how cells employ combinatorial strategies to efficiently communicate by only expressing a small number of ligands.
- PMID 10878248: This article adapts supply-demand analysis from economics to metabolism, showing that reaction flux and metabolite concentration are independently controlled to maintain homeostatic concentrations of metabolites across contexts.
- PMID 22308336: This article presents a theory for how specialization is favored by evolution due to context-specificity and synergistic effects.
- PMID 14550310: This article shows that humans regulate diet to intake balanced macronutrient ratios and prioritize protein when a balanced diet is not possible.
7. Figure Captions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FBA | flux balance analysis |
| GEM | genome-scale model |
| M-Model | genome-scale metabolic model |
| ME-Model | genome scale model of metabolism and expression |
| NGAM | non-growth associated maintenance |
| ODE | ordinary differential equation |
| RBA | resource balance analysis |
| WCM | whole-cell model |
References
- Aceto, N. , Bardia, A., Miyamoto, D.T., Donaldson, M.C., Wittner, B.S., Spencer, J.A., Yu, M., Pely, A., Engstrom, A., Zhu, H., Brannigan, B.W., Kapur, R., Stott, S.L., Shioda, T., Ramaswamy, S., Ting, D.T., Lin, C.P., Toner, M., Haber, D.A., Maheswaran, S., 2014. Circulating tumor cell clusters are oligoclonal precursors of breast cancer metastasis. Cell 158, 1110–1122. [CrossRef]
- Adler, M. , Chavan, A.R., Medzhitov, R., 2023a. Tissue Biology: In Search of a New Paradigm. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 39, 67–89. [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.I. , Bonduriansky, R., 2014. Why do the well-fed appear to die young? A new evolutionary hypothesis for the effect of dietary restriction on lifespan. Bioessays 36, 439–450. [CrossRef]
- Adler, M. , Korem Kohanim, Y., Tendler, A., Mayo, A., Alon, U., 2019. Continuum of Gene-Expression Profiles Provides Spatial Division of Labor within a Differentiated Cell Type. Cell Syst 8, 43–52.e5. [CrossRef]
- Adler, M. , Moriel, N., Goeva, A., Avraham-Davidi, I., Mages, S., Adams, T.S., Kaminski, N., Macosko, E.Z., Regev, A., Medzhitov, R., Nitzan, M., 2023b. Emergence of division of labor in tissues through cell interactions and spatial cues. Cell Rep. 42, 112412. [CrossRef]
- Adler, M. , Szekely, P., Mayo, A., Alon, U., 2017. Optimal Regulatory Circuit Topologies for Fold-Change Detection. Cell Syst 4, 171–181.e8. [CrossRef]
- Aiello, L.C. , Wheeler, P., 1995. The Expensive-Tissue Hypothesis: The Brain and the Digestive System in Human and Primate Evolution. Current Anthropology 36, 199–221. [CrossRef]
- Al-Bassam, M.M. , Kim, J.-N., Zaramela, L.S., Kellman, B.P., Zuniga, C., Wozniak, J.M., Gonzalez, D.J., Zengler, K., 2018. Optimization of carbon and energy utilization through differential translational efficiency. Nat. Commun. 9, 4474. [CrossRef]
- Alle, H. , Roth, A., Geiger, J.R.P., 2009. Energy-efficient action potentials in hippocampal mossy fibers. Science 325, 1405–1408. [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.L. , Taatjes, D.J., 2015. The Mediator complex: a central integrator of transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 155–166. [CrossRef]
- Almet, A.A. , Cang, Z., Jin, S., Nie, Q., 2021. The landscape of cell-cell communication through single-cell transcriptomics. Curr Opin Syst Biol 26, 12–23. [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R. , Brocas, I., Carrillo, J.D., 2013. Resource Allocation in the Brain. Rev. Econ. Stud. 81, 501–534. [CrossRef]
- Alon, U. , 2019. Multi-Objective Optimality in Biology, in: An Introduction to Systems Biology. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Second edition. | Boca Raton, Fla. : CRC Press, [2019], pp. 249–272.
- Alon, U. , 2007. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat. Rev. Genet. 8, 450–461. [CrossRef]
- Alon, U. , 2006. An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits. CRC Press.
- Alves, R. , Salvadó, B., Milo, R., Vilaprinyo, E., Sorribas, A., 2021. Maximization of information transmission influences selection of native phosphorelay architectures. PeerJ 9, e11558. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.R. , Raubenheimer, D., Hessen, D.O., Jensen, K., Gentleman, W.C., Mayor, D.J., 2020. Geometric Stoichiometry: Unifying Concepts of Animal Nutrition to Understand How Protein-Rich Diets Can Be “Too Much of a Good Thing.” Front. Ecol. Evol. 8. [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, S. , Miskovic, L., Hatzimanikatis, V., 2016. iSCHRUNK--In Silico Approach to Characterization and Reduction of Uncertainty in the Kinetic Models of Genome-scale Metabolic Networks. Metab. Eng. 33, 158–168. [CrossRef]
- Arendt, D. , 2008. The evolution of cell types in animals: emerging principles from molecular studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 868–882. [CrossRef]
- Argüello, R.J. , Combes, A.J., Char, R., Gigan, J.-P., Baaziz, A.I., Bousiquot, E., Camosseto, V., Samad, B., Tsui, J., Yan, P., Boissonneau, S., Figarella-Branger, D., Gatti, E., Tabouret, E., Krummel, M.F., Pierre, P., 2020. SCENITH: A Flow Cytometry-Based Method to Functionally Profile Energy Metabolism with Single-Cell Resolution. Cell Metab. 32, 1063–1075.e7. [CrossRef]
- Armingol, E. , Baghdassarian, H.M., Martino, C., Perez-Lopez, A., Aamodt, C., Knight, R., Lewis, N.E., 2022a. Context-aware deconvolution of cell-cell communication with Tensor-cell2cell. Nat. Commun. 13, 3665. [CrossRef]
- Armingol, E. , Larsen, R.O., Cequeira, M., Baghdassarian, H., Lewis, N.E., 2022b. Unraveling the coordinated dynamics of protein- and metabolite-mediated cell-cell communication. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Armingol, E. , Officer, A., Harismendy, O., Lewis, N.E., 2021. Deciphering cell-cell interactions and communication from gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 22, 71–88. [CrossRef]
- Attwell, D. , Laughlin, S.B., 2001. An energy budget for signaling in the grey matter of the brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 21, 1133–1145. [CrossRef]
- Austin, D.W. , Allen, M.S., McCollum, J.M., Dar, R.D., Wilgus, J.R., Sayler, G.S., Samatova, N.F., Cox, C.D., Simpson, M.L., 2006. Gene network shaping of inherent noise spectra. Nature 439, 608–611. [CrossRef]
- Azzout-Marniche, D. , Gaudichon, C., Blouet, C., Bos, C., Mathé, V., Huneau, J.-F., Tomé, D., 2007. Liver glyconeogenesis: a pathway to cope with postprandial amino acid excess in high-protein fed rats? Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 292, R1400–7. [CrossRef]
- Baghdassarian, H. , Blackstone, S.A., Clay, O.S., Philips, R., Matthiasardottir, B., Nehrebecky, M., Hua, V.K., McVicar, R., Liu, Y., Tucker, S.M., Randazzo, D., Deuitch, N., Rosenzweig, S., Mark, A., Sasik, R., Fisch, K.M., Pimpale Chavan, P., Eren, E., Watts, N.R., Ma, C.A., Gadina, M., Schwartz, D.M., Sanyal, A., Werner, G., Murdock, D.R., Horita, N., Chowdhury, S., Dimmock, D., Jepsen, K., Remmers, E.F., Goldbach-Mansky, R., Gahl, W.A., O’Shea, J.J., Milner, J.D., Lewis, N.E., Chang, J., Kastner, D.L., Torok, K., Oda, H., Putnam, C.D., Broderick, L., 2023. Variant and Response to Ruxolitinib in an Autoinflammatory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 388, 2241–2252. [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.E. , 2020. Emerging mechanisms of cell competition. Nat. Rev. Genet. 21, 683–697. [CrossRef]
- Barclay, C.J. , 2015. Energetics of contraction. Compr. Physiol. 5, 961–995. [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.P. , Sontag, E.D., 2013. The energy costs of insulators in biochemical networks. Biophys. J. 104, 1380–1390. [CrossRef]
- Basan, M. , 2018. Resource allocation and metabolism: the search for governing principles. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 45, 77–83. [CrossRef]
- Basan, M. , Hui, S., Okano, H., Zhang, Z., Shen, Y., Williamson, J.R., Hwa, T., 2015. Overflow metabolism in Escherichia coli results from efficient proteome allocation. Nature 528, 99–104. [CrossRef]
- Bashor, C.J. , Hilton, I.B., Bandukwala, H., Smith, D.M., Veiseh, O., 2022. Engineering the next generation of cell-based therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 21, 655–675. [CrossRef]
- Battich, N. , Stoeger, T., Pelkmans, L., 2015. Control of Transcript Variability in Single Mammalian Cells. Cell 163, 1596–1610. [CrossRef]
- Baysoy, A. , Bai, Z., Satija, R., Fan, R., 2023. The technological landscape and applications of single-cell multi-omics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 24, 695–713. [CrossRef]
- Beard, D.A. , Qian, H., 2007. Relationship between thermodynamic driving force and one-way fluxes in reversible processes. PLoS One 2, e144. [CrossRef]
- Beck, M. , Schmidt, A., Malmstroem, J., Claassen, M., Ori, A., Szymborska, A., Herzog, F., Rinner, O., Ellenberg, J., Aebersold, R., 2011. The quantitative proteome of a human cell line. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 549. [CrossRef]
- Beltman, J.G.M. , van der Vliet, M.R., Sargeant, A.J., de Haan, A., 2004. Metabolic cost of lengthening, isometric and shortening contractions in maximally stimulated rat skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol. Scand. 182, 179–187. [CrossRef]
- Bender, D.A. , 2012. The metabolism of “surplus” amino acids. Br. J. Nutr. 108 Suppl 2, S113–21. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Moshe, S. , Itzkovitz, S., 2019. Spatial heterogeneity in the mammalian liver. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16, 395–410. [CrossRef]
- Bennett, N.K. , Nguyen, M.K., Darch, M.A., Nakaoka, H.J., Cousineau, D., Ten Hoeve, J., Graeber, T.G., Schuelke, M., Maltepe, E., Kampmann, M., Mendelsohn, B.A., Nakamura, J.L., Nakamura, K., 2020. Defining the ATPome reveals cross-optimization of metabolic pathways. Nat. Commun. 11, 4319. [CrossRef]
- Bergström, M. , Hultman, E., 1988. Energy cost and fatigue during intermittent electrical stimulation of human skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 65, 1500–1505. [CrossRef]
- Bisschop, P.H. , De Sain-Van Der Velden, M.G.M., Stellaard, F., Kuipers, F., Meijer, A.J., Sauerwein, H.P., Romijn, J.A., 2003. Dietary carbohydrate deprivation increases 24-hour nitrogen excretion without affecting postabsorptive hepatic or whole body protein metabolism in healthy men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 3801–3805. [CrossRef]
- Björkeroth, J. , Campbell, K., Malina, C., Yu, R., Di Bartolomeo, F., Nielsen, J., 2020. Proteome reallocation from amino acid biosynthesis to ribosomes enables yeast to grow faster in rich media. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117, 21804–21812. [CrossRef]
- Blecher-Gonen, R. , Bost, P., Hilligan, K.L., David, E., Salame, T.M., Roussel, E., Connor, L.M., Mayer, J.U., Bahar Halpern, K., Tóth, B., Itzkovitz, S., Schwikowski, B., Ronchese, F., Amit, I., 2019. Single-Cell Analysis of Diverse Pathogen Responses Defines a Molecular Roadmap for Generating Antigen-Specific Immunity. Cell Syst 8, 109–121.e6. [CrossRef]
- Bonnans, C. , Chou, J., Werb, Z., 2014. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 786–801. [CrossRef]
- Bonny, A.R. , Kochanowski, K., Diether, M., El-Samad, H., 2020. Stress-Induced Transient Cell Cycle Arrest Coordinates Metabolic Resource Allocation to Balance Adaptive Tradeoffs. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Brand, A. , Singer, K., Koehl, G.E., Kolitzus, M., Schoenhammer, G., Thiel, A., Matos, C., Bruss, C., Klobuch, S., Peter, K., Kastenberger, M., Bogdan, C., Schleicher, U., Mackensen, A., Ullrich, E., Fichtner-Feigl, S., Kesselring, R., Mack, M., Ritter, U., Schmid, M., Blank, C., Dettmer, K., Oefner, P.J., Hoffmann, P., Walenta, S., Geissler, E.K., Pouyssegur, J., Villunger, A., Steven, A., Seliger, B., Schreml, S., Haferkamp, S., Kohl, E., Karrer, S., Berneburg, M., Herr, W., Mueller-Klieser, W., Renner, K., Kreutz, M., 2016. LDHA-Associated Lactic Acid Production Blunts Tumor Immunosurveillance by T and NK Cells. Cell Metab. 24, 657–671. [CrossRef]
- Brückner, A. , Badroos, J.M., Learsch, R.W., Yousefelahiyeh, M., Kitchen, S.A., Parker, J., 2021. Evolutionary assembly of cooperating cell types in an animal chemical defense system. Cell 184, 6138–6156.e28. [CrossRef]
- Bryan, A.K. , Hecht, V.C., Shen, W., Payer, K., Grover, W.H., Manalis, S.R., 2014. Measuring single cell mass, volume, and density with dual suspended microchannel resonators. Lab Chip 14, 569–576. [CrossRef]
- Buccitelli, C. , Selbach, M., 2020. mRNAs, proteins and the emerging principles of gene expression control. Nat. Rev. Genet. 21, 630–644. [CrossRef]
- Bulusu, V. , Prior, N., Snaebjornsson, M.T., Kuehne, A., Sonnen, K.F., Kress, J., Stein, F., Schultz, C., Sauer, U., Aulehla, A., 2017. Spatiotemporal Analysis of a Glycolytic Activity Gradient Linked to Mouse Embryo Mesoderm Development. Dev. Cell 40, 331–341.e4. [CrossRef]
- Buttgereit, F. , Brand, M.D., 1995. A hierarchy of ATP-consuming processes in mammalian cells. Biochem. J 312 ( Pt 1), 163–167. [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L. , Grilli, J., Osella, M., Kempes, C.P., Lagomarsino, M.C., Ciandrini, L., 2022. Protein degradation sets the fraction of active ribosomes at vanishing growth. PLoS Comput. Biol. 18, e1010059. [CrossRef]
- Cambridge, S.B. , Gnad, F., Nguyen, C., Bermejo, J.L., Krüger, M., Mann, M., 2011. Systems-wide proteomic analysis in mammalian cells reveals conserved, functional protein turnover. J. Proteome Res. 10, 5275–5284. [CrossRef]
- Cantó, C. , Jiang, L.Q., Deshmukh, A.S., Mataki, C., Coste, A., Lagouge, M., Zierath, J.R., Auwerx, J., 2010. Interdependence of AMPK and SIRT1 for metabolic adaptation to fasting and exercise in skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 11, 213–219. [CrossRef]
- Carey, B.W. , Finley, L.W.S., Cross, J.R., Allis, C.D., Thompson, C.B., 2015. Intracellular α-ketoglutarate maintains the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Nature 518, 413–416. [CrossRef]
- Carr, E.L. , Kelman, A., Wu, G.S., Gopaul, R., Senkevitch, E., Aghvanyan, A., Turay, A.M., Frauwirth, K.A., 2010. Glutamine uptake and metabolism are coordinately regulated by ERK/MAPK during T lymphocyte activation. J. Immunol. 185, 1037–1044. [CrossRef]
- Cavigliasso, F. , Dupuis, C., Savary, L., Spangenberg, J.E., Kawecki, T.J., 2020. Experimental evolution of post-ingestive nutritional compensation in response to a nutrient-poor diet. Proc. Biol. Sci. 287, 20202684. [CrossRef]
- Cell design in bacteria as a convex optimization problem, 2011.. Automatica 47, 1210–1218. [CrossRef]
- Cermak, N. , Olcum, S., Delgado, F.F., Wasserman, S.C., Payer, K.R., A Murakami, M., Knudsen, S.M., Kimmerling, R.J., Stevens, M.M., Kikuchi, Y., Sandikci, A., Ogawa, M., Agache, V., Baléras, F., Weinstock, D.M., Manalis, S.R., 2016. High-throughput measurement of single-cell growth rates using serial microfluidic mass sensor arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 34, 1052–1059. [CrossRef]
- Cham, C.M. , Driessens, G., O’Keefe, J.P., Gajewski, T.F., 2008. Glucose deprivation inhibits multiple key gene expression events and effector functions in CD8+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 38, 2438–2450. [CrossRef]
- Cham, C.M. , Gajewski, T.F., 2005. Glucose availability regulates IFN-gamma production and p70S6 kinase activation in CD8+ effector T cells. J. Immunol. 174, 4670–4677. [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, A. , Navlakha, S., 2019. Neural arbors are Pareto optimal. Proc. Biol. Sci. 286, 20182727. [CrossRef]
- Chaneton, B. , Hillmann, P., Zheng, L., Martin, A.C.L., Maddocks, O.D.K., Chokkathukalam, A., Coyle, J.E., Jankevics, A., Holding, F.P., Vousden, K.H., Frezza, C., O’Reilly, M., Gottlieb, E., 2012. Serine is a natural ligand and allosteric activator of pyruvate kinase M2. Nature 491, 458–462. [CrossRef]
- Chang, A. , Jeske, L., Ulbrich, S., Hofmann, J., Koblitz, J., Schomburg, I., Neumann-Schaal, M., Jahn, D., Schomburg, D., 2021. BRENDA, the ELIXIR core data resource in 2021: new developments and updates. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, D498–D508. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H. , Qiu, J., O’Sullivan, D., Buck, M.D., Noguchi, T., Curtis, J.D., Chen, Q., Gindin, M., Gubin, M.M., van der Windt, G.J.W., Tonc, E., Schreiber, R.D., Pearce, E.J., Pearce, E.L., 2015. Metabolic Competition in the Tumor Microenvironment Is a Driver of Cancer Progression. Cell 162, 1229–1241. [CrossRef]
- Chantranupong, L. , Wolfson, R.L., Sabatini, D.M., 2015. Nutrient-sensing mechanisms across evolution. Cell 161, 67–83. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K. , Gao, Y., Mih, N., O’Brien, E.J., Yang, L., Palsson, B.O., 2017. Thermosensitivity of growth is determined by chaperone-mediated proteome reallocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114, 11548–11553. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. , McConnell, B.O., Gayatri Dhara, V., Mukesh Naik, H., Li, C.-T., Antoniewicz, M.R., Betenbaugh, M.J., 2019. An unconventional uptake rate objective function approach enhances applicability of genome-scale models for mammalian cells. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 5, 25. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. , Nielsen, J., 2019. Energy metabolism controls phenotypes by protein efficiency and allocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 116, 17592–17597. [CrossRef]
- Cheong, R. , Rhee, A., Wang, C.J., Nemenman, I., Levchenko, A., 2011. Information transduction capacity of noisy biochemical signaling networks. Science 334, 354–358. [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S. , Narayanan, B., Moret, M., Hatzimanikatis, V., Miskovic, L., 2023. Generative machine learning produces kinetic models that accurately characterize intracellular metabolic states. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. , Talalay, P., 1977. A simple generalized equation for the analysis of multiple inhibitions of Michaelis-Menten kinetic systems. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 6438–6442. [CrossRef]
- Clavería, C. , Giovinazzo, G., Sierra, R., Torres, M., 2013. Myc-driven endogenous cell competition in the early mammalian embryo. Nature 500, 39–44. [CrossRef]
- Clissold, F.J. , Tedder, B.J., Conigrave, A.D., Simpson, S.J., 2010. The gastrointestinal tract as a nutrient-balancing organ. Proc. Biol. Sci. 277, 1751–1759. [CrossRef]
- Cotter, S.C. , Simpson, S.J., Raubenheimer, D., Wilson, K., 2011. Macronutrient balance mediates trade-offs between immune function and life history traits. Functional Ecology. [CrossRef]
- Covert, M.W. , 2017. Fundamentals of Systems Biology: From Synthetic Circuits to Whole-cell Models. CRC Press.
- Csárdi, G. , Franks, A., Choi, D.S., Airoldi, E.M., Drummond, D.A., 2015. Accounting for experimental noise reveals that mRNA levels, amplified by post-transcriptional processes, largely determine steady-state protein levels in yeast. PLoS Genet. 11, e1005206. [CrossRef]
- Dahal, S. , Zhao, J., Yang, L., 2021. Genome-scale Modeling of Metabolism and Macromolecular Expression and Their Applications. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 25, 931–943. [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z. , Zheng, W., Locasale, J.W., 2022. Amino acid variability, tradeoffs and optimality in human diet. Nat. Commun. 13, 6683. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Novaes, A. , Borges, F.T., Maquigussa, E., Varela, V.A., Dias, M.V.S., Boim, M.A., 2019. Influence of high glucose on mesangial cell-derived exosome composition, secretion and cell communication. Sci. Rep. 9, 6270. [CrossRef]
- Davidi, D. , Milo, R., 2017. Lessons on enzyme kinetics from quantitative proteomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 46, 81–89. [CrossRef]
- Davidi, D. , Noor, E., Liebermeister, W., Bar-Even, A., Flamholz, A., Tummler, K., Barenholz, U., Goldenfeld, M., Shlomi, T., Milo, R., 2016. Global characterization of in vivo enzyme catalytic rates and their correspondence to in vitro kcat measurements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113, 3401–3406. [CrossRef]
- Dekel, E. , Alon, U., 2005. Optimality and evolutionary tuning of the expression level of a protein. Nature 436, 588–592. [CrossRef]
- Di Blasi, R. , Marbiah, M.M., Siciliano, V., Polizzi, K., Ceroni, F., 2021. A call for caution in analysing mammalian co-transfection experiments and implications of resource competition in data misinterpretation. Nat. Commun. 12, 2545. [CrossRef]
- Di Blasi, R. , Pisani, M., Tedeschi, F., Marbiah, M.M., Polizzi, K., Furini, S., Siciliano, V., Ceroni, F., 2023. Resource-aware construct design in mammalian cells. Nat. Commun. 14, 3576. [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. , Elowitz, M.B., 2019. Constitutive splicing and economies of scale in gene expression. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 26, 424–432. [CrossRef]
- Domenzain, I. , Sánchez, B., Anton, M., Kerkhoven, E.J., Millán-Oropeza, A., Henry, C., Siewers, V., Morrissey, J.P., Sonnenschein, N., Nielsen, J., 2022. Reconstruction of a catalogue of genome-scale metabolic models with enzymatic constraints using GECKO 2.0. Nat. Commun. 13, 3766. [CrossRef]
- Dourado, H. , Mori, M., Hwa, T., Lercher, M.J., 2021. On the optimality of the enzyme-substrate relationship in bacteria. PLoS Biol. 19, e3001416. [CrossRef]
- Du, B. , Yang, L., Lloyd, C.J., Fang, X., Palsson, B.O., 2019. Genome-scale model of metabolism and gene expression provides a multi-scale description of acid stress responses in Escherichia coli. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15, e1007525. [CrossRef]
- Du, F. , Zhu, X.-H., Zhang, Y., Friedman, M., Zhang, N., Ugurbil, K., Chen, W., 2008. Tightly coupled brain activity and cerebral ATP metabolic rate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 6409–6414. [CrossRef]
- Edelman, G.M. , Gally, J.A., 2001. Degeneracy and complexity in biological systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 13763–13768. [CrossRef]
- Edfors, F. , Danielsson, F., Hallström, B.M., Käll, L., Lundberg, E., Pontén, F., Forsström, B., Uhlén, M., 2016. Gene-specific correlation of RNA and protein levels in human cells and tissues. Mol. Syst. Biol. 12, 883. [CrossRef]
- Efeyan, A. , Comb, W.C., Sabatini, D.M., 2015. Nutrient-sensing mechanisms and pathways. Nature 517, 302–310. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.J. , Gomez, N.C., Levorse, J., Mertz, A.F., Ge, Y., Fuchs, E., 2019. Distinct modes of cell competition shape mammalian tissue morphogenesis. Nature 569, 497–502. [CrossRef]
- Elowitz, M.B. , Levine, A.J., Siggia, E.D., Swain, P.S., 2002. Stochastic gene expression in a single cell. Science 297. [CrossRef]
- Elsemman, I.E. , Rodriguez Prado, A., Grigaitis, P., Garcia Albornoz, M., Harman, V., Holman, S.W., van Heerden, J., Bruggeman, F.J., Bisschops, M.M.M., Sonnenschein, N., Hubbard, S., Beynon, R., Daran-Lapujade, P., Nielsen, J., Teusink, B., 2022. Whole-cell modeling in yeast predicts compartment-specific proteome constraints that drive metabolic strategies. Nat. Commun. 13, 801. [CrossRef]
- Fan, J. , Kamphorst, J.J., Mathew, R., Chung, M.K., White, E., Shlomi, T., Rabinowitz, J.D., 2013. Glutamine-driven oxidative phosphorylation is a major ATP source in transformed mammalian cells in both normoxia and hypoxia. Mol. Syst. Biol. 9, 712. [CrossRef]
- Farhan, H. , Rabouille, C., 2011. Signalling to and from the secretory pathway. J. Cell Sci. 124, 171–180. [CrossRef]
- Feist, A.M. , Palsson, B.O., 2010. The biomass objective function. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 13, 344–349. [CrossRef]
- Felton, A.M. , Felton, A., Wood, J.T., Foley, W.J., Raubenheimer, D., Wallis, I.R., Lindenmayer, D.B., 2009. Nutritional Ecology of Ateles chamek in lowland Bolivia: How Macronutrient Balancing Influences Food Choices. Int. J. Primatol. 30, 675–696. [CrossRef]
- Ferguson-Stegall, L. , McCleave, E., Ding, Z., Doerner, P.G., Iii, Liu, Y., Wang, B., Healy, M., Kleinert, M., Dessard, B., Lassiter, D.G., Kammer, L., Ivy, J.L., 2011. Aerobic exercise training adaptations are increased by postexercise carbohydrate-protein supplementation. J. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 623182. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B. , Dieckmann, U., Taborsky, B., 2011. When to store energy in a stochastic environment. Evolution 65, 1221–1232. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B. , Taborsky, B., Dieckmann, U., 2009. Unexpected patterns of plastic energy allocation in stochastic environments. Am. Nat. 173, E108–20. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.S. , Fiedler, A.K., Kernfeld, E.M., Genga, R.M.J., Bastidas-Ponce, A., Bakhti, M., Lickert, H., Hasenauer, J., Maehr, R., Theis, F.J., 2019. Inferring population dynamics from single-cell RNA-sequencing time series data. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 461–468. [CrossRef]
- Foreman, R. , Wollman, R., 2020. Mammalian gene expression variability is explained by underlying cell state. Mol. Syst. Biol. 16, e9146. [CrossRef]
- Francis, K. , Palsson, B.O., 1997. Effective intercellular communication distances are determined by the relative time constants for cyto/chemokine secretion and diffusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 94, 12258–12262. [CrossRef]
- Frei, T. , Cella, F., Tedeschi, F., Gutiérrez, J., Stan, G.-B., Khammash, M., Siciliano, V., 2020. Characterization and mitigation of gene expression burden in mammalian cells. Nat. Commun. 11, 4641. [CrossRef]
- French, S.S. , Dearing, M.D., Demas, G.E., 2011. Leptin as a physiological mediator of energetic trade-offs in ecoimmunology: implications for disease. Integr. Comp. Biol. 51, 505–513. [CrossRef]
- Funk, L. , Su, K.-C., Ly, J., Feldman, D., Singh, A., Moodie, B., Blainey, P.C., Cheeseman, I.M., 2022. The phenotypic landscape of essential human genes. Cell. [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D. , Belmonte, D., Deurenberg, P., Wang, Z., Krasnow, N., Pi-Sunyer, F.X., Heymsfield, S.B., 1998. Organ-tissue mass measurement allows modeling of REE and metabolically active tissue mass. Am. J. Physiol. 275, E249–58. [CrossRef]
- Ganeshan, K. , Nikkanen, J., Man, K., Leong, Y.A., Sogawa, Y., Maschek, J.A., Van Ry, T., Chagwedera, D.N., Cox, J.E., Chawla, A., 2019. Energetic Trade-Offs and Hypometabolic States Promote Disease Tolerance. Cell 177, 399–413.e12. [CrossRef]
- Gazestani, V.H. , Pramparo, T., Nalabolu, S., Kellman, B.P., Murray, S., Lopez, L., Pierce, K., Courchesne, E., Lewis, N.E., 2019. A perturbed gene network containing PI3K-AKT, RAS-ERK and WNT-β-catenin pathways in leukocytes is linked to ASD genetics and symptom severity. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 1624–1634. [CrossRef]
- Gerashchenko, M.V. , Peterfi, Z., Yim, S.H., Gladyshev, V.N., 2021. Translation elongation rate varies among organs and decreases with age. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, e9. [CrossRef]
- Geri, J.B. , Oakley, J.V., Reyes-Robles, T., Wang, T., McCarver, S.J., White, C.H., Rodriguez-Rivera, F.P., Parker, D.L., Jr, Hett, E.C., Fadeyi, O.O., Oslund, R.C., MacMillan, D.W.C., 2020. Microenvironment mapping via Dexter energy transfer on immune cells. Science 367, 1091–1097. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. , Körte, A., Serafini, G., Yadav, V., Rodenfels, J., 2022. Developmental energetics: Energy expenditure, budgets and metabolism during animal embryogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. [CrossRef]
- Gingold, H. , Pilpel, Y., 2011. Determinants of translation efficiency and accuracy. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 481. [CrossRef]
- Giunta, G. , Tostevin, F., Tănase-Nicola, S., Gerland, U., 2022. Optimal spatial allocation of enzymes as an investment problem. Communications Physics 5, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Glancy, B. , Balaban, R.S., 2021. Energy metabolism design of the striated muscle cell. Physiol. Rev. 101, 1561–1607. [CrossRef]
- Glancy, B. , Willis, W.T., Chess, D.J., Balaban, R.S., 2013. Effect of calcium on the oxidative phosphorylation cascade in skeletal muscle mitochondria. Biochemistry 52, 2793–2809. [CrossRef]
- Goelzer, A. , Fromion, V., 2019. RBA for eukaryotic cells: foundations and theoretical developments. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Goelzer, A. , Fromion, V., 2017. Resource allocation in living organisms. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 45, 945–952.
- Goldsby, H.J. , Dornhaus, A., Kerr, B., Ofria, C., 2012. Task-switching costs promote the evolution of division of labor and shifts in individuality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109, 13686–13691. [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Pinilla, F. , 2011. The combined effects of exercise and foods in preventing neurological and cognitive disorders. Prev. Med. 52 Suppl 1, S75–80. [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S. , Dash, S., Maranas, C., 2020. K-FIT: An accelerated kinetic parameterization algorithm using steady-state fluxomic data. Metab. Eng. 61, 197–205. [CrossRef]
- Govern, C.C. , Ten Wolde, P.R., 2014. Optimal resource allocation in cellular sensing systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111, 17486–17491. [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, L.H. , Schueler, M., Munschauer, M., Mastrobuoni, G., Chen, W., Kempa, S., Dieterich, C., Landthaler, M., 2014. MOV10 Is a 5’ to 3' RNA helicase contributing to UPF1 mRNA target degradation by translocation along 3' UTRs. Mol. Cell 54, 573–585. [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J. , Robinson, J.L., Zetterberg, H., Nielsen, J., 2022. Brain energy metabolism is optimized to minimize the cost of enzyme synthesis and transport. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.M. , Feizi, A., Li, S., Kallehauge, T.B., Hefzi, H., Grav, L.M., Ley, D., Baycin Hizal, D., Betenbaugh, M.J., Voldborg, B., Faustrup Kildegaard, H., Min Lee, G., Palsson, B.O., Nielsen, J., Lewis, N.E., 2020. Genome-scale reconstructions of the mammalian secretory pathway predict metabolic costs and limitations of protein secretion. Nat. Commun. 11, 68. [CrossRef]
- Gyorgy, A. , Jiménez, J.I., Yazbek, J., Huang, H.-H., Chung, H., Weiss, R., Del Vecchio, D., 2015. Isocost Lines Describe the Cellular Economy of Genetic Circuits. Biophys. J. 109, 639–646. [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, M. , Caicedo, J.C., Cimini, B.A., Carpenter, A.E., Singh, S., 2022. High-dimensional gene expression and morphology profiles of cells across 28,000 genetic and chemical perturbations. Nat. Methods 19, 1550–1557. [CrossRef]
- Halpern, K.B. , Shenhav, R., Matcovitch-Natan, O., Toth, B., Lemze, D., Golan, M., Massasa, E.E., Baydatch, S., Landen, S., Moor, A.E., Brandis, A., Giladi, A., Avihail, A.S., David, E., Amit, I., Itzkovitz, S., 2017. Single-cell spatial reconstruction reveals global division of labour in the mammalian liver. Nature 542, 352–356. [CrossRef]
- Handly, L.N. , Pilko, A., Wollman, R., 2015. Paracrine communication maximizes cellular response fidelity in wound signaling. Elife 4, e09652.
- Harber, M.P. , Konopka, A.R., Jemiolo, B., Trappe, S.W., Trappe, T.A., Reidy, P.T., 2010. Muscle protein synthesis and gene expression during recovery from aerobic exercise in the fasted and fed states. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 299, R1254–62. [CrossRef]
- Harber, M.P. , Schenk, S., Barkan, A.L., Horowitz, J.F., 2005. Effects of dietary carbohydrate restriction with high protein intake on protein metabolism and the somatotropic axis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90, 5175–5181. [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G. , Ross, F.A., Hawley, S.A., 2012. AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 251–262. [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, M. , Spriet, L.L., 2020. Skeletal muscle energy metabolism during exercise. Nat Metab 2, 817–828. [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.W. , Bennett, E.J., 2016. Proteome complexity and the forces that drive proteome imbalance. Nature 537, 328–338. [CrossRef]
- Hart, Y. , Sheftel, H., Hausser, J., Szekely, P., Ben-Moshe, N.B., Korem, Y., Tendler, A., Mayo, A.E., Alon, U., 2015. Inferring biological tasks using Pareto analysis of high-dimensional data. Nat. Methods 12, 233–5, 3 p following 235. [CrossRef]
- Haschemi, A. , Kosma, P., Gille, L., Evans, C.R., Burant, C.F., Starkl, P., Knapp, B., Haas, R., Schmid, J.A., Jandl, C., Amir, S., Lubec, G., Park, J., Esterbauer, H., Bilban, M., Brizuela, L., Pospisilik, J.A., Otterbein, L.E., Wagner, O., 2012. The sedoheptulose kinase CARKL directs macrophage polarization through control of glucose metabolism. Cell Metab. 15, 813–826. [CrossRef]
- Hasenstaub, A. , Otte, S., Callaway, E., Sejnowski, T.J., 2010. Metabolic cost as a unifying principle governing neuronal biophysics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107, 12329–12334. [CrossRef]
- Hausser, J. , Mayo, A., Keren, L., Alon, U., 2019. Central dogma rates and the trade-off between precision and economy in gene expression. Nat. Commun. 10, 68. [CrossRef]
- Headley, M.B. , Bins, A., Nip, A., Roberts, E.W., Looney, M.R., Gerard, A., Krummel, M.F., 2016. Visualization of immediate immune responses to pioneer metastatic cells in the lung. Nature 531, 513–517. [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, D. , Campeau, A., Lloyd, C.J., Phaneuf, P.V., Hefner, Y., Carrillo-Terrazas, M., Feist, A.M., Gonzalez, D.J., Palsson, B.O., 2020. Kinetic profiling of metabolic specialists demonstrates stability and consistency of in vivo enzyme turnover numbers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117, 23182–23190. [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, D. , Lloyd, C.J., Mih, N., Ha, Y., Zielinski, D.C., Haiman, Z.B., Desouki, A.A., Lercher, M.J., Palsson, B.O., 2018. Machine learning applied to enzyme turnover numbers reveals protein structural correlates and improves metabolic models. Nat. Commun. 9, 5252. [CrossRef]
- Hefzi, H. , Lewis, N., 2017. Mammalian cells devoid of lactate dehydrogenase activity. World Patent. 2017192437:A1.
- Herculano-Houzel, S. , 2011. Scaling of brain metabolism with a fixed energy budget per neuron: implications for neuronal activity, plasticity and evolution. PLoS One 6, e17514. [CrossRef]
- Hewson-Hughes, A.K. , Colyer, A., Simpson, S.J., Raubenheimer, D., 2016. Balancing macronutrient intake in a mammalian carnivore: disentangling the influences of flavour and nutrition. R Soc Open Sci 3, 160081. [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B. , Peterson, C.M., Bourgeois, B., Thomas, D.M., Gallagher, D., Strauss, B., Müller, M.J., Bosy-Westphal, A., 2018. Human energy expenditure: advances in organ-tissue prediction models. Obes. Rev. 19, 1177–1188. [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.M. , Nesser, N.K., Johnson-Camacho, K., Jeffress, M., Johnson, A., Boniface, C., Spencer, S.E.F., Lu, Y., Heiser, L.M., Lawrence, Y., Pande, N.T., Korkola, J.E., Gray, J.W., Mills, G.B., Mukherjee, S., Spellman, P.T., 2017. Context Specificity in Causal Signaling Networks Revealed by Phosphoprotein Profiling. Cell Syst 4, 73–83.e10. [CrossRef]
- Hinzpeter, F. , Tostevin, F., Gerland, U., 2019. Regulation of reaction fluxes via enzyme sequestration and co-clustering. J. R. Soc. Interface 16, 20190444. [CrossRef]
- Hitze, B. , Hubold, C., van Dyken, R., Schlichting, K., Lehnert, H., Entringer, S., Peters, A., 2010. How the selfish brain organizes its supply and demand. Front. Neuroenergetics 2, 7. [CrossRef]
- Hofmeyr, J.S. , Cornish-Bowden, A., 2000. Regulating the cellular economy of supply and demand. FEBS Lett. 476, 47–51. [CrossRef]
- Hogan, M.C. , Ingham, E., Kurdak, S.S., 1998. Contraction duration affects metabolic energy cost and fatigue in skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 274, E397–402. [CrossRef]
- Holzhütter, H.-G. , 2004. The principle of flux minimization and its application to estimate stationary fluxes in metabolic networks. Eur. J. Biochem. 271, 2905–2922. [CrossRef]
- Hosios, A.M. , Hecht, V.C., Danai, L.V., Johnson, M.O., Rathmell, J.C., Steinhauser, M.L., Manalis, S.R., Vander Heiden, M.G., 2016. Amino Acids Rather than Glucose Account for the Majority of Cell Mass in Proliferating Mammalian Cells. Dev. Cell 36, 540–549. [CrossRef]
- Hrovatin, K. , Fischer, D.S., Theis, F.J., 2022. Toward modeling metabolic state from single-cell transcriptomics. Mol Metab 57, 101396. [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. , Zhou, P., Wei, J., Long, L., Shi, H., Dhungana, Y., Chapman, N.M., Fu, G., Saravia, J., Raynor, J.L., Liu, S., Palacios, G., Wang, Y.-D., Qian, C., Yu, J., Chi, H., 2021. In vivo CRISPR screening reveals nutrient signaling processes underpinning CD8+ T cell fate decisions. Cell 184, 1245–1261.e21. [CrossRef]
- Hui, S. , Silverman, J.M., Chen, S.S., Erickson, D.W., Basan, M., Wang, J., Hwa, T., Williamson, J.R., 2015. Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals a simple strategy of global resource allocation in bacteria. Mol. Syst. Biol. 11, 784. [CrossRef]
- Hukelmann, J.L. , Anderson, K.E., Sinclair, L.V., Grzes, K.M., Murillo, A.B., Hawkins, P.T., Stephens, L.R., Lamond, A.I., Cantrell, D.A., 2016. The cytotoxic T cell proteome and its shaping by the kinase mTOR. Nat. Immunol. 17, 104–112. [CrossRef]
- Hu, K. , Yu, Y., 2017. Metabolite availability as a window to view the early embryo microenvironment in vivo. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 84, 1027–1038. [CrossRef]
- Ingolia, N.T. , Lareau, L.F., Weissman, J.S., 2011. Ribosome profiling of mouse embryonic stem cells reveals the complexity and dynamics of mammalian proteomes. Cell 147, 789–802. [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y. , Kawamata, Y., Harada, M., Kobayashi, M., Fujii, R., Fukusumi, S., Ogi, K., Hosoya, M., Tanaka, Y., Uejima, H., Tanaka, H., Maruyama, M., Satoh, R., Okubo, S., Kizawa, H., Komatsu, H., Matsumura, F., Noguchi, Y., Shinohara, T., Hinuma, S., Fujisawa, Y., Fujino, M., 2003. Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells through GPR40. Nature 422, 173–176. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K. , Simpson, S.J., Nielsen, V.H., Hunt, J., Raubenheimer, D., Mayntz, D., 2014. Nutrient-specific compensatory feeding in a mammalian carnivore, the mink, Neovison vison. Br. J. Nutr. 112, 1226–1233. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H. , Tombor, B., Albert, R., Oltvai, Z.N., Barabási, A.L., 2000. The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature 407, 651–654. [CrossRef]
- Jerby-Arnon, L. , Regev, A., 2022. DIALOGUE maps multicellular programs in tissue from single-cell or spatial transcriptomics data. Nat. Biotechnol. 40, 1467–1477. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.A. , Raubenheimer, D., Rothman, J.M., Clarke, D., Swedell, L., 2013. 30 days in the life: daily nutrient balancing in a wild chacma baboon. PLoS One 8, e70383. [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.D. , Qian, Y., Siciliano, V., DiAndreth, B., Huh, J., Weiss, R., Del Vecchio, D., 2020. An endoribonuclease-based feedforward controller for decoupling resource-limited genetic modules in mammalian cells. Nat. Commun. 11, 5690. [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, M. , Rooney, M.S., Mertins, P., Przybylski, D., Chevrier, N., Satija, R., Rodriguez, E.H., Fields, A.P., Schwartz, S., Raychowdhury, R., Mumbach, M.R., Eisenhaure, T., Rabani, M., Gennert, D., Lu, D., Delorey, T., Weissman, J.S., Carr, S.A., Hacohen, N., Regev, A., 2015. Immunogenetics. Dynamic profiling of the protein life cycle in response to pathogens. Science 347, 1259038. [CrossRef]
- Kafri, M. , Metzl-Raz, E., Jona, G., Barkai, N., 2016. The Cost of Protein Production. Cell Rep. 14, 22–31. [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R. , Sanghvi, J.C., Macklin, D.N., Gutschow, M.V., Jacobs, J.M., Bolival, B., Jr, Assad-Garcia, N., Glass, J.I., Covert, M.W., 2012. A whole-cell computational model predicts phenotype from genotype. Cell 150, 389–401. [CrossRef]
- Keren, L. , Hausser, J., Lotan-Pompan, M., Vainberg Slutskin, I., Alisar, H., Kaminski, S., Weinberger, A., Alon, U., Milo, R., Segal, E., 2016. Massively Parallel Interrogation of the Effects of Gene Expression Levels on Fitness. Cell 166, 1282–1294.e18. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S. , Spann, R.A., Münzberg, H., Yu, S., Albaugh, V.L., He, Y., Berthoud, H.-R., Morrison, C.D., 2021. Protein Appetite at the Interface between Nutrient Sensing and Physiological Homeostasis. Nutrients 13. [CrossRef]
- Khurana, P. , Burudpakdee, C., Grupp, S.A., Beier, U.H., Barrett, D.M., Bassiri, H., 2021. Distinct Bioenergetic Features of Human Invariant Natural Killer T Cells Enable Retained Functions in Nutrient-Deprived States. Front. Immunol. 12, 700374. [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, T.B.L. , 2017. The Disposable Soma Theory, in: The Evolution of Senescence in the Tree of Life. Cambridge University Press, pp. 23–39. [CrossRef]
- Kistner, T.M. , Pedersen, B.K., Lieberman, D.E., 2022. Interleukin 6 as an energy allocator in muscle tissue. Nat Metab 4, 170–179. [CrossRef]
- Kiweler, N. , Delbrouck, C., Pozdeev, V.I., Neises, L., Soriano-Baguet, L., Eiden, K., Xian, F., Benzarti, M., Haase, L., Koncina, E., Schmoetten, M., Jaeger, C., Noman, M.Z., Vazquez, A., Janji, B., Dittmar, G., Brenner, D., Letellier, E., Meiser, J., 2022. Mitochondria preserve an autarkic one-carbon cycle to confer growth-independent cancer cell migration and metastasis. Nat. Commun. 13, 2699. [CrossRef]
- Klein, D. , Palla, G., Lange, M., Klein, M., Piran, Z., Gander, M., Meng-Papaxanthos, L., Sterr, M., Bastidas-Ponce, A., Tarquis-Medina, M., Lickert, H., Bakhti, M., Nitzan, M., Cuturi, M., Theis, F.J., 2023. Mapping cells through time and space with moscot. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Kleinridders, A. , Ferris, H.A., Reyzer, M.L., Rath, M., Soto, M., Manier, M.L., Spraggins, J., Yang, Z., Stanton, R.C., Caprioli, R.M., Kahn, C.R., 2018. Regional differences in brain glucose metabolism determined by imaging mass spectrometry. Mol Metab 12, 113–121. [CrossRef]
- Klumpe, H.E. , Langley, M.A., Linton, J.M., Su, C.J., Antebi, Y.E., Elowitz, M.B., 2022. The context-dependent, combinatorial logic of BMP signaling. Cell Syst. [CrossRef]
- Kochanowski, K. , Sander, T., Link, H., Chang, J., Altschuler, S.J., Wu, L.F., 2021. Systematic alteration of in vitro metabolic environments reveals empirical growth relationships in cancer cell phenotypes. Cell Rep. 34, 108647. [CrossRef]
- Kol, S. , Ley, D., Wulff, T., Decker, M., Arnsdorf, J., Schoffelen, S., Hansen, A.H., Jensen, T.L., Gutierrez, J.M., Chiang, A.W.T., Masson, H.O., Palsson, B.O., Voldborg, B.G., Pedersen, L.E., Kildegaard, H.F., Lee, G.M., Lewis, N.E., 2020. Multiplex secretome engineering enhances recombinant protein production and purity. Nat. Commun. 11, 1908. [CrossRef]
- Kon, S. , Ishibashi, K., Katoh, H., Kitamoto, S., Shirai, T., Tanaka, S., Kajita, M., Ishikawa, S., Yamauchi, H., Yako, Y., Kamasaki, T., Matsumoto, T., Watanabe, H., Egami, R., Sasaki, A., Nishikawa, A., Kameda, I., Maruyama, T., Narumi, R., Morita, T., Sasaki, Y., Enoki, R., Honma, S., Imamura, H., Oshima, M., Soga, T., Miyazaki, J.-I., Duchen, M.R., Nam, J.-M., Onodera, Y., Yoshioka, S., Kikuta, J., Ishii, M., Imajo, M., Nishida, E., Fujioka, Y., Ohba, Y., Sato, T., Fujita, Y., 2017. Cell competition with normal epithelial cells promotes apical extrusion of transformed cells through metabolic changes. Nat. Cell Biol. 19, 530–541. [CrossRef]
- Korem, Y. , Szekely, P., Hart, Y., Sheftel, H., Hausser, J., Mayo, A., Rothenberg, M.E., Kalisky, T., Alon, U., 2015. Geometry of the Gene Expression Space of Individual Cells. PLoS Comput. Biol. 11, e1004224. [CrossRef]
- Kroll, A. , Rousset, Y., Hu, X.-P., Liebrand, N.A., Lercher, M.J., 2023. Turnover number predictions for kinetically uncharacterized enzymes using machine and deep learning. Nat. Commun. 14, 4139. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-C. , Chiang, A.W.T., Baghdassarian, H.M., Lewis, N.E., 2021. Dysregulation of the secretory pathway connects Alzheimer’s disease genetics to aggregate formation. Cell Syst 12, 873–884.e4. [CrossRef]
- Kuzawa, C.W. , 2007. Developmental origins of life history: growth, productivity, and reproduction. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 19, 654–661. [CrossRef]
- Kuzawa, C.W. , Chugani, H.T., Grossman, L.I., Lipovich, L., Muzik, O., Hof, P.R., Wildman, D.E., Sherwood, C.C., Leonard, W.R., Lange, N., 2014. Metabolic costs and evolutionary implications of human brain development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111, 13010–13015. [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.K.M. , Dick, T.J.M., Biewener, A.A., Wakeling, J.M., 2021. Task-dependent recruitment across ankle extensor muscles and between mechanical demands is driven by the metabolic cost of muscle contraction. J. R. Soc. Interface 18, 20200765. [CrossRef]
- Lailvaux, S.P. , Husak, J.F., 2017. Predicting Life-History Trade-Offs with Whole-Organism Performance. Integr. Comp. Biol. 57, 325–332. [CrossRef]
- Lailvaux, S.P. , Husak, J.F., 2014. The life history of whole-organism performance. Q. Rev. Biol. 89, 285–318. [CrossRef]
- Lane, N. , Martin, W., 2010. The energetics of genome complexity. Nature 467, 929–934. [CrossRef]
- Lan, G. , Sartori, P., Neumann, S., Sourjik, V., Tu, Y., 2012. The energy-speed-accuracy tradeoff in sensory adaptation. Nat. Phys. 8, 422–428. [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.C. , Kann, M.C., Bailey, S.R., Haradhvala, N.J., Llopis, P.M., Bouffard, A.A., Scarfó, I., Leick, M.B., Grauwet, K., Berger, T.R., Stewart, K., Anekal, P.V., Jan, M., Joung, J., Schmidts, A., Ouspenskaia, T., Law, T., Regev, A., Getz, G., Maus, M.V., 2022. CAR T cell killing requires the IFNγR pathway in solid but not liquid tumours. Nature 604, 563–570. [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, M.-C. , Bigot, A., Jensen, S.S., Dennis, J.L., Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A., Lainé, J., Gache, V., Furling, D., Jensen, O.N., Voit, T., Mouly, V., Coulton, G.R., Butler-Browne, G., 2012. In-depth analysis of the secretome identifies three major independent secretory pathways in differentiating human myoblasts. J. Proteomics 77, 344–356. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.C. , Fragala, M.S., Kavouras, S.A., Queen, R.M., Pryor, J.L., Casa, D.J., 2017. Biomarkers in Sports and Exercise: Tracking Health, Performance, and Recovery in Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 31, 2920–2937. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M. , Gianchandani, E.P., Eddy, J.A., Papin, J.A., 2008. Dynamic analysis of integrated signaling, metabolic, and regulatory networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 4, e1000086. [CrossRef]
- Lennie, P. , 2003. The cost of cortical computation. Curr. Biol. 13, 493–497. [CrossRef]
- Lerman, J.A. , Hyduke, D.R., Latif, H., Portnoy, V.A., Lewis, N.E., Orth, J.D., Schrimpe-Rutledge, A.C., Smith, R.D., Adkins, J.N., Zengler, K., Palsson, B.O., 2012. In silico method for modelling metabolism and gene product expression at genome scale. Nat. Commun. 3, 929. [CrossRef]
- Lestas, I. , Vinnicombe, G., Paulsson, J., 2010. Fundamental limits on the suppression of molecular fluctuations. Nature 467, 174–178. [CrossRef]
- Levy, W.B. , Baxter, R.A., 1996. Energy efficient neural codes. Neural Comput. 8, 531–543. [CrossRef]
- Lewin, N. , Swanson, E.M., Williams, B.L., Holekamp, K.E., 2017. Juvenile concentrations of IGF -1 predict life-history trade-offs in a wild mammal. Functional Ecology. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.E. , Hixson, K.K., Conrad, T.M., Lerman, J.A., Charusanti, P., Polpitiya, A.D., Adkins, J.N., Schramm, G., Purvine, S.O., Lopez-Ferrer, D., Weitz, K.K., Eils, R., König, R., Smith, R.D., Palsson, B.Ø., 2010a. Omic data from evolved E. coli are consistent with computed optimal growth from genome-scale models. Mol. Syst. Biol. 6, 390. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.E. , Nagarajan, H., Palsson, B.O., 2012. Constraining the metabolic genotype-phenotype relationship using a phylogeny of in silico methods. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 10, 291–305. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.E. , Schramm, G., Bordbar, A., Schellenberger, J., Andersen, M.P., Cheng, J.K., Patel, N., Yee, A., Lewis, R.A., Eils, R., König, R., Palsson, B.Ø., 2010b. Large-scale in silico modeling of metabolic interactions between cell types in the human brain. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 1279–1285. [CrossRef]
- Liebermeister, W. , Noor, E., Flamholz, A., Davidi, D., Bernhardt, J., Milo, R., 2014. Visual account of protein investment in cellular functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111, 8488–8493. [CrossRef]
- Li, F. , Yuan, L., Lu, H., Li, G., Chen, Y., Engqvist, M.K.M., Kerkhoven, E.J., Nielsen, J., 2022. Deep learning-based kcat prediction enables improved enzyme-constrained model reconstruction. Nature Catalysis 5, 662–672. [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-W. , Burkhardt, D., Gross, C., Weissman, J.S., 2014. Quantifying absolute protein synthesis rates reveals principles underlying allocation of cellular resources. Cell 157, 624–635. [CrossRef]
- Li, J. , Cai, Z., Vaites, L.P., Shen, N., Mitchell, D.C., Huttlin, E.L., Paulo, J.A., Harry, B.L., Gygi, S.P., 2021. Proteome-wide mapping of short-lived proteins in human cells. Mol. Cell 81, 4722–4735.e5. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J. , Bickel, P.J., Biggin, M.D., 2014. System wide analyses have underestimated protein abundances and the importance of transcription in mammals. PeerJ 2, e270. [CrossRef]
- Lin, J. , Amir, A., 2018. Homeostasis of protein and mRNA concentrations in growing cells. Nat. Commun. 9, 4496. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. , Mac Gabhann, F., Popel, A.S., 2012. Effects of fiber type and size on the heterogeneity of oxygen distribution in exercising skeletal muscle. PLoS One 7, e44375. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. , Duclos, G., Sun, B., Lee, J., Wu, A., Kam, Y., Sontag, E.D., Stone, H.A., Sturm, J.C., Gatenby, R.A., Austin, R.H., 2013. Minimization of thermodynamic costs in cancer cell invasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 1686–1691. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. , Beyer, A., Aebersold, R., 2016. On the Dependency of Cellular Protein Levels on mRNA Abundance. Cell 165, 535–550. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. , Yao, L., Mori, Y., Sun, S.X., 2019. On the energy efficiency of cell migration in diverse physical environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 116, 23894–23900. [CrossRef]
- Long, L. , Wei, J., Lim, S.A., Raynor, J.L., Shi, H., Connelly, J.P., Wang, H., Guy, C., Xie, B., Chapman, N.M., Fu, G., Wang, Y., Huang, H., Su, W., Saravia, J., Risch, I., Wang, Y.-D., Li, Y., Niu, M., Dhungana, Y., Kc, A., Zhou, P., Vogel, P., Yu, J., Pruett-Miller, S.M., Peng, J., Chi, H., 2021. CRISPR screens unveil signal hubs for nutrient licensing of T cell immunity. Nature 600, 308–313. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.A. , Brennan, A.J., Whisstock, J.C., Voskoboinik, I., Trapani, J.A., 2012. Protecting a serial killer: pathways for perforin trafficking and self-defence ensure sequential target cell death. Trends Immunol. 33, 406–412. [CrossRef]
- Lunt, S.Y. , Muralidhar, V., Hosios, A.M., Israelsen, W.J., Gui, D.Y., Newhouse, L., Ogrodzinski, M., Hecht, V., Xu, K., Acevedo, P.N.M., Hollern, D.P., Bellinger, G., Dayton, T.L., Christen, S., Elia, I., Dinh, A.T., Stephanopoulos, G., Manalis, S.R., Yaffe, M.B., Andrechek, E.R., Fendt, S.-M., Vander Heiden, M.G., 2015. Pyruvate kinase isoform expression alters nucleotide synthesis to impact cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 57, 95–107. [CrossRef]
- Lutter, M. , Nestler, E.J., 2009. Homeostatic and hedonic signals interact in the regulation of food intake. J. Nutr. 139, 629–632. [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M. , Marinov, G.K., 2015. The bioenergetic costs of a gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112, 15690–15695. [CrossRef]
- Macklin, D.N. , Ahn-Horst, T.A., Choi, H., Ruggero, N.A., Carrera, J., Mason, J.C., Sun, G., Agmon, E., DeFelice, M.M., Maayan, I., Lane, K., Spangler, R.K., Gillies, T.E., Paull, M.L., Akhter, S., Bray, S.R., Weaver, D.S., Keseler, I.M., Karp, P.D., Morrison, J.H., Covert, M.W., 2020. Simultaneous cross-evaluation of heterogeneous datasets via mechanistic simulation. Science 369. [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.H. , Verway, M.J., Johnson, R.M., Roy, D.G., Steadman, M., Hayes, S., Williams, K.S., Sheldon, R.D., Samborska, B., Kosinski, P.A., Kim, H., Griss, T., Faubert, B., Condotta, S.A., Krawczyk, C.M., DeBerardinis, R.J., Stewart, K.M., Richer, M.J., Chubukov, V., Roddy, T.P., Jones, R.G., 2019. Metabolic Profiling Using Stable Isotope Tracing Reveals Distinct Patterns of Glucose Utilization by Physiologically Activated CD8 T Cells. Immunity 51, 856–870.e5. [CrossRef]
- Magkos, F. , Hjorth, M.F., Astrup, A., 2020. Diet and exercise in the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 16, 545–555. [CrossRef]
- Mah, C.K. , Ahmed, N., Lopez, N., Lam, D., Monell, A., Kern, C., Han, Y., Prasad, G., Cesnik, A.J., Lundberg, E., Zhu, Q., Carter, H., Yeo, G.W., 2023. Bento: A toolkit for subcellular analysis of spatial transcriptomics data. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudabadi, G. , Phillips, R., Lynch, M., Milo, R., 2019. Defining the Energetic Costs of Cellular Structures. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Marchingo, J.M. , Cantrell, D.A., 2022. Protein synthesis, degradation, and energy metabolism in T cell immunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 19, 303–315. [CrossRef]
- Markin, C.J. , Mokhtari, D.A., Sunden, F., Appel, M.J., Akiva, E., Longwell, S.A., Sabatti, C., Herschlag, D., Fordyce, P.M., 2021. Revealing enzyme functional architecture via high-throughput microfluidic enzyme kinetics. Science 373. [CrossRef]
- Martins Conde, P. do R., Sauter, T., Pfau, T., 2016. Constraint Based Modeling Going Multicellular. Front Mol Biosci 3, 3. [CrossRef]
- Matamoro-Vidal, A. , Levayer, R., 2019. Multiple Influences of Mechanical Forces on Cell Competition. Curr. Biol. 29, R762–R774. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P. , Schwab, D.J., 2012. Energetic costs of cellular computation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109, 17978–17982. [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, B.A. , Bennett, N.K., Darch, M.A., Yu, K., Nguyen, M.K., Pucciarelli, D., Nelson, M., Horlbeck, M.A., Gilbert, L.A., Hyun, W., Kampmann, M., Nakamura, J.L., Nakamura, K., 2018. A high-throughput screen of real-time ATP levels in individual cells reveals mechanisms of energy failure. PLoS Biol. 16, e2004624. [CrossRef]
- Metzl-Raz, E. , Kafri, M., Yaakov, G., Soifer, I., Gurvich, Y., Barkai, N., 2017. Principles of cellular resource allocation revealed by condition-dependent proteome profiling. Elife 6. [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, T.P. , Pessa, H.K.J., Caldez, M.J., Fuhrer, T., Diril, M.K., Sauer, U., Kaldis, P., Björklund, M., 2014. Identification of transcriptional and metabolic programs related to mammalian cell size. Curr. Biol. 24, 598–608. [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.H. , Hamill, J., 2015. Optimal footfall patterns for cost minimization in running. J. Biomech. 48, 2858–2864. [CrossRef]
- Milo, R. , Phillips, R., 2015. Cell biology by the numbers. Garland Science, London, England. [CrossRef]
- Mitchel, J. , Grace Gordon, M., Perez, R.K., Biederstedt, E., Bueno, R., Ye, C.J., Kharchenko, P.V., 2023. Tensor decomposition reveals coordinated multicellular patterns of transcriptional variation that distinguish and stratify disease individuals. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Mori, M. , Hwa, T., Martin, O.C., De Martino, A., Marinari, E., 2016. Constrained Allocation Flux Balance Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 12, e1004913. [CrossRef]
- Mosier, J.A. , Wu, Y., Reinhart-King, C.A., 2021. Recent advances in understanding the role of metabolic heterogeneities in cell migration. Fac Rev 10, 8. [CrossRef]
- Munding, E.M. , Shiue, L., Katzman, S., Donohue, J.P., Ares, M., Jr, 2013. Competition between pre-mRNAs for the splicing machinery drives global regulation of splicing. Mol. Cell 51, 338–348.
- Munsky, B. , Neuert, G., van Oudenaarden, A., 2012. Using gene expression noise to understand gene regulation. Science 336, 183–187. [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, N. , Wisniewski, J.R., Geiger, T., Cox, J., Kircher, M., Kelso, J., Pääbo, S., Mann, M., 2011. Deep proteome and transcriptome mapping of a human cancer cell line. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 548. [CrossRef]
- Nagle, M.P. , Tam, G.S., Maltz, E., Hemminger, Z., Wollman, R., 2021. Bridging scales: From cell biology to physiology using in situ single-cell technologies. Cell Syst 12, 388–400. [CrossRef]
- Nagrath, D. , Avila-Elchiver, M., Berthiaume, F., Tilles, A.W., Messac, A., Yarmush, M.L., 2007. Integrated energy and flux balance based multiobjective framework for large-scale metabolic networks. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35, 863–885. [CrossRef]
- Neurohr, G.E. , Terry, R.L., Lengefeld, J., Bonney, M., Brittingham, G.P., Moretto, F., Miettinen, T.P., Vaites, L.P., Soares, L.M., Paulo, J.A., Harper, J.W., Buratowski, S., Manalis, S., van Werven, F.J., Holt, L.J., Amon, A., 2019. Excessive Cell Growth Causes Cytoplasm Dilution And Contributes to Senescence. Cell 176, 1083–1097.e18. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P. , Sheng, R., Murray, E., Ito, Y., Bruck, M., Biellak, C., An, K., Lynce, F., Dillon, D.A., Magbanua, M.J.M., Huppert, L.A., Hammerlindl, H., Esserman, L., Rosenbluth, J.M., Ahituv, N., 2023. Implantation of engineered adipocytes that outcompete tumors for resources suppresses cancer progression. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, A. , Nielsen, J., Palsson, B.O., 2017. Metabolic Models of Protein Allocation Call for the Kinetome. Cell Syst 5, 538–541. [CrossRef]
- Noor, E. , Bar-Even, A., Flamholz, A., Reznik, E., Liebermeister, W., Milo, R., 2014. Pathway thermodynamics highlights kinetic obstacles in central metabolism. PLoS Comput. Biol. 10, e1003483. [CrossRef]
- Noor, E. , Flamholz, A., Bar-Even, A., Davidi, D., Milo, R., Liebermeister, W., 2016. The Protein Cost of Metabolic Fluxes: Prediction from Enzymatic Rate Laws and Cost Minimization. PLoS Comput. Biol. 12, e1005167. [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.J. , Lerman, J.A., Chang, R.L., Hyduke, D.R., Palsson, B.Ø., 2013. Genome-scale models of metabolism and gene expression extend and refine growth phenotype prediction. Mol. Syst. Biol. 9, 693. [CrossRef]
- Opdam, S. , Richelle, A., Kellman, B., Li, S., Zielinski, D.C., Lewis, N.E., 2017. A Systematic Evaluation of Methods for Tailoring Genome-Scale Metabolic Models. Cell Syst 4, 318–329.e6. [CrossRef]
- Ori, A. , Iskar, M., Buczak, K., Kastritis, P., Parca, L., Andrés-Pons, A., Singer, S., Bork, P., Beck, M., 2016. Spatiotemporal variation of mammalian protein complex stoichiometries. Genome Biol. 17, 47. [CrossRef]
- Orth, J.D. , Thiele, I., Palsson, B.Ø., 2010. What is flux balance analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 245–248. [CrossRef]
- Palm, W. , Thompson, C.B., 2017. Nutrient acquisition strategies of mammalian cells. Nature 546, 234–242. [CrossRef]
- Palsson, B.Ø. , 2015. Systems Biology: Constraint-based Reconstruction and Analysis.
- Pantaleon, M. , Scott, J., Kaye, P.L., 2008. Nutrient sensing by the early mouse embryo: hexosamine biosynthesis and glucose signaling during preimplantation development. Biol. Reprod. 78, 595–600. [CrossRef]
- Papin, J.A. , Palsson, B.O., 2004a. Topological analysis of mass-balanced signaling networks: a framework to obtain network properties including crosstalk. J. Theor. Biol. 227, 283–297. [CrossRef]
- Papin, J.A. , Palsson, B.O., 2004b. The JAK-STAT signaling network in the human B-cell: an extreme signaling pathway analysis. Biophys. J. 87, 37–46. [CrossRef]
- Parenteau, J. , Maignon, L., Berthoumieux, M., Catala, M., Gagnon, V., Abou Elela, S., 2019. Introns are mediators of cell response to starvation. Nature 565, 612–617. [CrossRef]
- Peters, A. , 2011. The selfish brain: Competition for energy resources. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 23, 29–34. [CrossRef]
- Peters, A. , Schweiger, U., Pellerin, L., Hubold, C., Oltmanns, K.M., Conrad, M., Schultes, B., Born, J., Fehm, H.L., 2004. The selfish brain: competition for energy resources. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 28, 143–180. [CrossRef]
- Peth, A. , Nathan, J.A., Goldberg, A.L., 2013. The ATP costs and time required to degrade ubiquitinated proteins by the 26 S proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 29215–29222. [CrossRef]
- Pinkard, H. , Baghdassarian, H., Mujal, A., Roberts, E., Hu, K.H., Friedman, D.H., Malenica, I., Shagam, T., Fries, A., Corbin, K., Krummel, M.F., Waller, L., 2021. Learned adaptive multiphoton illumination microscopy for large-scale immune response imaging. Nat. Commun. 12, 1916. [CrossRef]
- Poganik, J.R. , Zhang, B., Baht, G.S., Tyshkovskiy, A., Deik, A., Kerepesi, C., Yim, S.H., Lu, A.T., Haghani, A., Gong, T., Hedman, A.M., Andolf, E., Pershagen, G., Almqvist, C., Clish, C.B., Horvath, S., White, J.P., Gladyshev, V.N., 2023. Biological age is increased by stress and restored upon recovery. Cell Metab. [CrossRef]
- Polychronidou, M. , Hou, J., Babu, M.M., Liberali, P., Amit, I., Deplancke, B., Lahav, G., Itzkovitz, S., Mann, M., Saez-Rodriguez, J., Theis, F., Eils, R., 2023. Single-cell biology: what does the future hold? Mol. Syst. Biol. 19, e11799. [CrossRef]
- Popovic, D. , Koch, B., Kueblbeck, M., Ellenberg, J., Pelkmans, L., 2018. Multivariate Control of Transcript to Protein Variability in Single Mammalian Cells. Cell Syst 7, 398–411.e6. [CrossRef]
- Pulido, C. , Ryan, T.A., 2021. Synaptic vesicle pools are a major hidden resting metabolic burden of nerve terminals. Sci Adv 7, eabi9027. [CrossRef]
- Qin, C. , Xiang, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, R., Liu, Z., Li, T., Sun, Z., Ouyang, X., Zong, Y., Zhang, H.M., Ouyang, Q., Qian, L., Lou, C., 2023. Precise programming of multigene expression stoichiometry in mammalian cells by a modular and programmable transcriptional system. Nat. Commun. 14, 1500. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X. , Zhu, D.Y., Yao, J., Jing, Z., Zuo, L., Wang, M., Min, K.H. (joseph), Pan, H., Wang, S., Liao, S., Lai, Y., Hao, S., Lu, Y.R., Hill, M., Martin-Rufino, J.D., Weng, C., Riera-Escandell, A.M., Chen, M., Wu, L., Zhang, Y., Wei, X., Li, M., Huang, X., Xiang, R., Yang, Z., Liu, C., Xia, T., Liang, Y., Xu, J., Hu, Q., Hu, Y., Zhu, H., Li, Y., Chen, A., Esteban, M.A., Gu, Y., Lauffenburger, D.A., Xu, X., Liu, L., Weissman, J.S., Liu, S., Bai, Y., 2022. Spateo: multidimensional spatiotemporal modeling of single-cell spatial transcriptomics. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Rabani, M. , Levin, J.Z., Fan, L., Adiconis, X., Raychowdhury, R., Garber, M., Gnirke, A., Nusbaum, C., Hacohen, N., Friedman, N., Amit, I., Regev, A., 2011. Metabolic labeling of RNA uncovers principles of RNA production and degradation dynamics in mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 436–442. [CrossRef]
- Raj, A. , Peskin, C.S., Tranchina, D., Vargas, D.Y., Tyagi, S., 2006. Stochastic mRNA Synthesis in Mammalian Cells. PLoS Biol. 4, e309. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez Flores, R.O. , Lanzer, J.D., Dimitrov, D., Velten, B., Saez-Rodriguez, J., 2023. Multicellular factor analysis of single-cell data for a tissue-centric understanding of disease. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Rathmell, J.C. , Vander Heiden, M.G., Harris, M.H., Frauwirth, K.A., Thompson, C.B., 2000. In the absence of extrinsic signals, nutrient utilization by lymphocytes is insufficient to maintain either cell size or viability. Mol. Cell 6, 683–692. [CrossRef]
- Reefman, E. , Kay, J.G., Wood, S.M., Offenhäuser, C., Brown, D.L., Roy, S., Stanley, A.C., Low, P.C., Manderson, A.P., Stow, J.L., 2010. Cytokine secretion is distinct from secretion of cytotoxic granules in NK cells. J. Immunol. 184, 4852–4862. [CrossRef]
- Reinfeld, B.I. , Madden, M.Z., Wolf, M.M., Chytil, A., Bader, J.E., Patterson, A.R., Sugiura, A., Cohen, A.S., Ali, A., Do, B.T., Muir, A., Lewis, C.A., Hongo, R.A., Young, K.L., Brown, R.E., Todd, V.M., Huffstater, T., Abraham, A., O’Neil, R.T., Wilson, M.H., Xin, F., Tantawy, M.N., Merryman, W.D., Johnson, R.W., Williams, C.S., Mason, E.F., Mason, F.M., Beckermann, K.E., Vander Heiden, M.G., Manning, H.C., Rathmell, J.C., Rathmell, W.K., 2021. Cell-programmed nutrient partitioning in the tumour microenvironment. Nature 593, 282–288. [CrossRef]
- Ren, X. , Zhong, G., Zhang, Q., Zhang, L., Sun, Y., Zhang, Z., 2020. Reconstruction of cell spatial organization from single-cell RNA sequencing data based on ligand-receptor mediated self-assembly. Cell Res. 30, 763–778. [CrossRef]
- Reuveni, S. , Ehrenberg, M., Paulsson, J., 2017. Ribosomes are optimized for autocatalytic production. Nature 547, 293–297. [CrossRef]
- Rode, K.D. , Robbins, C.T., 2000. Why bears consume mixed diets during fruit abundance. Canadian Journal of Zoology 78, 1640–1645. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Caso, C. , 2013. Can cell mortality determine division of labor in tissue organization? J. Theor. Biol. 332, 161–170. [CrossRef]
- Rolfe, D.F. , Brown, G.C., 1997. Cellular energy utilization and molecular origin of standard metabolic rate in mammals. Physiol. Rev. 77, 731–758. [CrossRef]
- Rondelez, Y. , 2012. Competition for catalytic resources alters biological network dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 018102. [CrossRef]
- Rooyackers, O.E. , Adey, D.B., Ades, P.A., Nair, K.S., 1996. Effect of age on in vivo rates of mitochondrial protein synthesis in human skeletal muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93, 15364–15369. [CrossRef]
- Rothman, J.M. , Raubenheimer, D., Chapman, C.A., 2011. Nutritional geometry: gorillas prioritize non-protein energy while consuming surplus protein. Biol. Lett. 7, 847–849. [CrossRef]
- Rueffler, C. , Hermisson, J., Wagner, G.P., 2012. Evolution of functional specialization and division of labor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109, E326–35. [CrossRef]
- Rues, S. , Lenz, J., Türp, J.C., Schweizerhof, K., Schindler, H.J., 2008. Forces and motor control mechanisms during biting in a realistically balanced experimental occlusion. Arch. Oral Biol. 53, 1119–1128. [CrossRef]
- Saez-Rodriguez, J. , Kremling, A., Gilles, E.D., 2005. Dissecting the puzzle of life: modularization of signal transduction networks. Comput. Chem. Eng. 29, 619–629. [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S. , Aurich, M.K., Jonsson, J.J., Thiele, I., 2014. Membrane transporters in a human genome-scale metabolic knowledgebase and their implications for disease. Front. Physiol. 5, 91. [CrossRef]
- Sale, C. , Saunders, B., Hudson, S., Wise, J.A., Harris, R.C., Sunderland, C.D., 2011. Effect of β-alanine plus sodium bicarbonate on high-intensity cycling capacity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 43, 1972–1978. [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S. , Kabeer, F., Ceglia, N., Andronescu, M., Williams, M.J., Campbell, K.R., Masud, T., Wang, B., Biele, J., Brimhall, J., Gee, D., Lee, H., Ting, J., Zhang, A.W., Tran, H., O’Flanagan, C., Dorri, F., Rusk, N., de Algara, T.R., Lee, S.R., Cheng, B.Y.C., Eirew, P., Kono, T., Pham, J., Grewal, D., Lai, D., Moore, R., Mungall, A.J., Marra, M.A., IMAXT Consortium, McPherson, A., Bouchard-Côté, A., Aparicio, S., Shah, S.P., 2021. Clonal fitness inferred from time-series modelling of single-cell cancer genomes. Nature 595, 585–590. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, B.J. , Zhang, C., Nilsson, A., Lahtvee, P.-J., Kerkhoven, E.J., Nielsen, J., 2017. Improving the phenotype predictions of a yeast genome-scale metabolic model by incorporating enzymatic constraints. Mol. Syst. Biol. 13, 935. [CrossRef]
- Sartori, P. , Pigolotti, S., 2015. Thermodynamics of error correction. Phys. Rev. X. 5. [CrossRef]
- Schell, J.C. , Wisidagama, D.R., Bensard, C., Zhao, H., Wei, P., Tanner, J., Flores, A., Mohlman, J., Sorensen, L.K., Earl, C.S., Olson, K.A., Miao, R., Waller, T.C., Delker, D., Kanth, P., Jiang, L., DeBerardinis, R.J., Bronner, M.P., Li, D.Y., Cox, J.E., Christofk, H.R., Lowry, W.E., Thummel, C.S., Rutter, J., 2017. Control of intestinal stem cell function and proliferation by mitochondrial pyruvate metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 19, 1027–1036. [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, S. , Reggiani, C., 2011. Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol. Rev. 91, 1447–1531. [CrossRef]
- Schilling, C.H. , Letscher, D., Palsson, B.O., 2000. Theory for the systemic definition of metabolic pathways and their use in interpreting metabolic function from a pathway-oriented perspective. J. Theor. Biol. 203, 229–248. [CrossRef]
- Schindler, H.J. , Rues, S., Türp, J.C., Schweizerhof, K., Lenz, J., 2007. Jaw clenching: muscle and joint forces, optimization strategies. J. Dent. Res. 86, 843–847. [CrossRef]
- Schink, S.J. , Christodoulou, D., Mukherjee, A., Athaide, E., Brunner, V., Fuhrer, T., Bradshaw, G.A., Sauer, U., Basan, M., 2022. Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis specialization in microbes is driven by biochemical constraints of flux sensing. Mol. Syst. Biol. 18, e10704. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.A. , Fisher-Wellman, K.H., Neufer, P.D., 2021. From OCR and ECAR to energy: Perspectives on the design and interpretation of bioenergetics studies. J. Biol. Chem. 297, 101140. [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.L. , An, S., 2017. Spatial Organization of Metabolic Enzyme Complexes in Cells. Biochemistry 56, 3184–3196. [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, R. , Zamboni, N., Zampieri, M., Heinemann, M., Sauer, U., 2012. Multidimensional optimality of microbial metabolism. Science 336, 601–604. [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S. , Schuster, R., Heinrich, R., 1991. Minimization of intermediate concentrations as a suggested optimality principle for biochemical networks. II. Time hierarchy, enzymatic rate laws, and erythrocyte metabolism. J. Math. Biol. 29, 443–455. [CrossRef]
- Schwanhäusser, B. , Busse, D., Li, N., Dittmar, G., Schuchhardt, J., Wolf, J., Chen, W., Selbach, M., 2011. Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 473, 337–342. [CrossRef]
- Scott, M. , Gunderson, C.W., Mateescu, E.M., Zhang, Z., Hwa, T., 2010. Interdependence of cell growth and gene expression: origins and consequences. Science 330, 1099–1102. [CrossRef]
- Seki, T. , Yang, Y., Sun, X., Lim, S., Xie, S., Guo, Z., Xiong, W., Kuroda, M., Sakaue, H., Hosaka, K., Jing, X., Yoshihara, M., Qu, L., Li, X., Chen, Y., Cao, Y., 2022. Brown-fat-mediated tumour suppression by cold-altered global metabolism. Nature 608, 421–428. [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, N. , Jones, R.D., Weiss, R., Del Vecchio, D., 2021. Context-aware synthetic biology by controller design: Engineering the mammalian cell. Cell Syst 12, 561–592. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. , Dinh, H.V., Cruz, E., Call, C.M., Baron, H., Ryseck, R.-P., Pratas, J., Subramanian, A., Fatma, Z., Weilandt, D., Dwaraknath, S., Xiao, T., Hendry, J.I., Tran, V., Yang, L., Yoshikuni, Y., Zhao, H., Maranas, C.D., Wühr, M., Rabinowitz, J.D., 2022. Proteome capacity constraints favor respiratory ATP generation. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. , Zhou, M., Cai, D., Filho, D.A., Fernandes, G., Cai, Y., de Sousa, A.F., Tian, M., Kim, N., Lee, J., Necula, D., Zhou, C., Li, S., Salinas, S., Liu, A., Kang, X., Kamata, M., Lavi, A., Huang, S., Silva, T., Do Heo, W., Silva, A.J., 2022. CCR5 closes the temporal window for memory linking. Nature 606, 146–152. [CrossRef]
- Shoval, O. , Sheftel, H., Shinar, G., Hart, Y., Ramote, O., Mayo, A., Dekel, E., Kavanagh, K., Alon, U., 2012. Evolutionary trade-offs, Pareto optimality, and the geometry of phenotype space. Science 336, 1157–1160. [CrossRef]
- Shvartsman, S.Y. , Hagan, M.P., Yacoub, A., Dent, P., Wiley, H.S., Lauffenburger, D.A., 2002. Autocrine loops with positive feedback enable context-dependent cell signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 282, C545–59. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.J. , Batley, R., Raubenheimer, D., 2003. Geometric analysis of macronutrient intake in humans: the power of protein? Appetite 41, 123–140. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.J. , Raubenheimer, D., 2005. Obesity: the protein leverage hypothesis. Obes. Rev. 6, 133–142. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.J. , Raubenheimer, D., 1993. A multi-level analysis of feeding behaviour: the geometry of nutritional decisions. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 342, 381–402. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. , Cuervo, A.M., 2011. Autophagy in the cellular energetic balance. Cell Metab. 13, 495–504. [CrossRef]
- Smiley, P. , Levin, M., 2022. Competition for finite resources as coordination mechanism for morphogenesis: An evolutionary algorithm study of digital embryogeny. Biosystems. 221, 104762. [CrossRef]
- Smillie, C.S. , Biton, M., Ordovas-Montanes, J., Sullivan, K.M., Burgin, G., Graham, D.B., Herbst, R.H., Rogel, N., Slyper, M., Waldman, J., Sud, M., Andrews, E., Velonias, G., Haber, A.L., Jagadeesh, K., Vickovic, S., Yao, J., Stevens, C., Dionne, D., Nguyen, L.T., Villani, A.-C., Hofree, M., Creasey, E.A., Huang, H., Rozenblatt-Rosen, O., Garber, J.J., Khalili, H., Desch, A.N., Daly, M.J., Ananthakrishnan, A.N., Shalek, A.K., Xavier, R.J., Regev, A., 2019. Intra- and Inter-cellular Rewiring of the Human Colon during Ulcerative Colitis. Cell 178, 714–730.e22. [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. , Grima, R., 2018. Single-cell variability in multicellular organisms. Nat. Commun. 9, 345. [CrossRef]
- Soeters, M.R. , Soeters, P.B., Schooneman, M.G., Houten, S.M., Romijn, J.A., 2012. Adaptive reciprocity of lipid and glucose metabolism in human short-term starvation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 303, E1397–407. [CrossRef]
- Soflaee, M.H. , Kesavan, R., Sahu, U., Tasdogan, A., Villa, E., Djabari, Z., Cai, F., Tran, D.H., Vu, H.S., Ali, E.S., Rion, H., O’Hara, B.P., Kelekar, S., Hallett, J.H., Martin, M., Mathews, T.P., Gao, P., Asara, J.M., Manning, B.D., Ben-Sahra, I., Hoxhaj, G., 2022. Purine nucleotide depletion prompts cell migration by stimulating the serine synthesis pathway. Nat. Commun. 13, 2698. [CrossRef]
- Solon-Biet, S.M. , Cogger, V.C., Pulpitel, T., Heblinski, M., Wahl, D., McMahon, A.C., Warren, A., Durrant-Whyte, J., Walters, K.A., Krycer, J.R., Ponton, F., Gokarn, R., Wali, J.A., Ruohonen, K., Conigrave, A.D., James, D.E., Raubenheimer, D., Morrison, C.D., Le Couteur, D.G., Simpson, S.J., 2016. Defining the Nutritional and Metabolic Context of FGF21 Using the Geometric Framework. Cell Metab. 24, 555–565. [CrossRef]
- Son, S. , Stevens, M.M., Chao, H.X., Thoreen, C., Hosios, A.M., Schweitzer, L.D., Weng, Y., Wood, K., Sabatini, D., Vander Heiden, M.G., Manalis, S., 2015. Cooperative nutrient accumulation sustains growth of mammalian cells. Sci. Rep. 5, 17401. [CrossRef]
- Stefl, S. , Nishi, H., Petukh, M., Panchenko, A.R., Alexov, E., 2013. Molecular mechanisms of disease-causing missense mutations. J. Mol. Biol. 425, 3919–3936. [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W. , Elser, J.J., 2017. Ecological Stoichiometry. Princeton University Press.
- Su, C.J. , Murugan, A., Linton, J.M., Yeluri, A., Bois, J., Klumpe, H., Langley, M.A., Antebi, Y.E., Elowitz, M.B., 2022. Ligand-receptor promiscuity enables cellular addressing. Cell Syst 13, 408–425.e12. [CrossRef]
- Szekely, P. , Sheftel, H., Mayo, A., Alon, U., 2013. Evolutionary tradeoffs between economy and effectiveness in biological homeostasis systems. PLoS Comput. Biol. 9, e1003163. [CrossRef]
- Taggart, J.C. , Li, G.-W., 2018. Production of Protein-Complex Components Is Stoichiometric and Lacks General Feedback Regulation in Eukaryotes. Cell Syst 7, 580–589.e4. [CrossRef]
- Tepper, N. , Noor, E., Amador-Noguez, D., Haraldsdóttir, H.S., Milo, R., Rabinowitz, J., Liebermeister, W., Shlomi, T., 2013. Steady-state metabolite concentrations reflect a balance between maximizing enzyme efficiency and minimizing total metabolite load. PLoS One 8, e75370. [CrossRef]
- Thiele, I. , Jamshidi, N., Fleming, R.M.T., Palsson, B.Ø., 2009. Genome-scale reconstruction of Escherichia coli’s transcriptional and translational machinery: a knowledge base, its mathematical formulation, and its functional characterization. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5, e1000312.
- Thiele, I. , Palsson, B.Ø., 2010. A protocol for generating a high-quality genome-scale metabolic reconstruction. Nat. Protoc. 5, 93–121. [CrossRef]
- Thiele, I. , Sahoo, S., Heinken, A., Hertel, J., Heirendt, L., Aurich, M.K., Fleming, R.M., 2020. Personalized whole-body models integrate metabolism, physiology, and the gut microbiome. Mol. Syst. Biol. 16, e8982. [CrossRef]
- Thornburg, Z.R. , Bianchi, D.M., Brier, T.A., Gilbert, B.R., Earnest, T.M., Melo, M.C.R., Safronova, N., Sáenz, J.P., Cook, A.T., Wise, K.S., Hutchison, C.A., 3rd, Smith, H.O., Glass, J.I., Luthey-Schulten, Z., 2022. Fundamental behaviors emerge from simulations of a living minimal cell. Cell 185, 345–360.e28. [CrossRef]
- Tian, L. , Chen, F., Macosko, E.Z., 2023. The expanding vistas of spatial transcriptomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 41, 773–782. [CrossRef]
- Tillin, N.A. , Pain, M.T.G., Folland, J.P., 2012. Contraction type influences the human ability to use the available torque capacity of skeletal muscle during explosive efforts. Proc. Biol. Sci. 279, 2106–2115. [CrossRef]
- Toda, S. , Frankel, N.W., Lim, W.A., 2019. Engineering cell-cell communication networks: programming multicellular behaviors. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 52, 31–38. [CrossRef]
- Torrent, M. , Chalancon, G., de Groot, N.S., Wuster, A., Madan Babu, M., 2018. Cells alter their tRNA abundance to selectively regulate protein synthesis during stress conditions. Sci. Signal. 11. [CrossRef]
- Tuller, T. , Carmi, A., Vestsigian, K., Navon, S., Dorfan, Y., Zaborske, J., Pan, T., Dahan, O., Furman, I., Pilpel, Y., 2010. An evolutionarily conserved mechanism for controlling the efficiency of protein translation. Cell 141, 344–354. [CrossRef]
- Umberger, B.R. , Gerritsen, K.G.M., Martin, P.E., 2003. A model of human muscle energy expenditure. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 6, 99–111. [CrossRef]
- Urlacher, S.S. , Ellison, P.T., Sugiyama, L.S., Pontzer, H., Eick, G., Liebert, M.A., Cepon-Robins, T.J., Gildner, T.E., Snodgrass, J.J., 2018. Tradeoffs between immune function and childhood growth among Amazonian forager-horticulturalists. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115, E3914–E3921. [CrossRef]
- van Albada, S.B. , ten Wolde, P.R., 2007. Enzyme localization can drastically affect signal amplification in signal transduction pathways. PLoS Comput. Biol. 3, 1925–1934. [CrossRef]
- Vandenbogaerde, T.J. , Hopkins, W.G., 2011. Effects of acute carbohydrate supplementation on endurance performance: a meta-analysis. Sports Med. 41, 773–792. [CrossRef]
- van Helvert, S. , Storm, C., Friedl, P., 2018. Mechanoreciprocity in cell migration. Nat. Cell Biol. 20, 8–20. [CrossRef]
- Vannini, N. , Girotra, M., Naveiras, O., Nikitin, G., Campos, V., Giger, S., Roch, A., Auwerx, J., Lutolf, M.P., 2016. Specification of haematopoietic stem cell fate via modulation of mitochondrial activity. Nat. Commun. 7, 13125. [CrossRef]
- van Noordwijk, A.J. , de Jong, G., 1986. Acquisition and Allocation of Resources: Their Influence on Variation in Life History Tactics. The American Naturalist 128, 137–142. [CrossRef]
- Veldhorst, M.A.B. , Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S., Westerterp, K.R., 2009. Gluconeogenesis and energy expenditure after a high-protein, carbohydrate-free diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 90, 519–526. [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C. , Marcotte, E.M., 2012. Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 227–232. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A. , Regev, A., Yosef, N., 2016. Revealing the vectors of cellular identity with single-cell genomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 34, 1145–1160. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A. , Wang, C., Fessler, J., DeTomaso, D., Avila-Pacheco, J., Kaminski, J., Zaghouani, S., Christian, E., Thakore, P., Schellhaass, B., Akama-Garren, E., Pierce, K., Singh, V., Ron-Harel, N., Douglas, V.P., Bod, L., Schnell, A., Puleston, D., Sobel, R.A., Haigis, M., Pearce, E.L., Soleimani, M., Clish, C., Regev, A., Kuchroo, V.K., Yosef, N., 2021. Metabolic modeling of single Th17 cells reveals regulators of autoimmunity. Cell 184, 4168–4185.e21. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. , Eraslan, B., Wieland, T., Hallström, B., Hopf, T., Zolg, D.P., Zecha, J., Asplund, A., Li, L.-H., Meng, C., Frejno, M., Schmidt, T., Schnatbaum, K., Wilhelm, M., Ponten, F., Uhlen, M., Gagneur, J., Hahne, H., Kuster, B., 2019. A deep proteome and transcriptome abundance atlas of 29 healthy human tissues. Mol. Syst. Biol. 15, e8503. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. , Delfarah, A., Gelbach, P.E., Fong, E., Macklin, P., Mumenthaler, S.M., Graham, N.A., Finley, S.D., 2022. Elucidating tumor-stromal metabolic crosstalk in colorectal cancer through integration of constraint-based models and LC-MS metabolomics. Metab. Eng. 69, 175–187. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. , Liu, R., Hawkins, M., Barzilai, N., Rossetti, L., 1998. A nutrient-sensing pathway regulates leptin gene expression in muscle and fat. Nature 393, 684–688. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-L. , Kuznets-Speck, B., Broderick, J., Hinczewski, M., 2022. The price of a bit: energetic costs and the evolution of cellular signaling. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. , Ying, Z., Bosy-Westphal, A., Zhang, J., Schautz, B., Later, W., Heymsfield, S.B., Müller, M.J., 2010. Specific metabolic rates of major organs and tissues across adulthood: evaluation by mechanistic model of resting energy expenditure. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 92, 1369–1377. [CrossRef]
- Way, J.C. , Collins, J.J., Keasling, J.D., Silver, P.A., 2014. Integrating biological redesign: where synthetic biology came from and where it needs to go. Cell 157, 151–161. [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.C. , Noakes, T.D., Chacko, S.K., Swart, J., Kohn, T.A., Smith, J.A.H., 2016. Gluconeogenesis during endurance exercise in cyclists habituated to a long-term low carbohydrate high-fat diet. J. Physiol. 594, 4389–4405. [CrossRef]
- Wegrzyn, J.L. , Bark, S.J., Funkelstein, L., Mosier, C., Yap, A., Kazemi-Esfarjani, P., La Spada, A.R., Sigurdson, C., O’Connor, D.T., Hook, V., 2010. Proteomics of dense core secretory vesicles reveal distinct protein categories for secretion of neuroeffectors for cell-cell communication. J. Proteome Res. 9, 5002–5024. [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, M. , Schlegl, J., Hahne, H., Gholami, A.M., Lieberenz, M., Savitski, M.M., Ziegler, E., Butzmann, L., Gessulat, S., Marx, H., Mathieson, T., Lemeer, S., Schnatbaum, K., Reimer, U., Wenschuh, H., Mollenhauer, M., Slotta-Huspenina, J., Boese, J.-H., Bantscheff, M., Gerstmair, A., Faerber, F., Kuster, B., 2014. Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome. Nature 509, 582–587. [CrossRef]
- Wroble, K.A. , Trott, M.N., Schweitzer, G.G., Rahman, R.S., Kelly, P.V., Weiss, E.P., 2019. Low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet impairs anaerobic exercise performance in exercise-trained women and men: a randomized-sequence crossover trial. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 59, 600–607. [CrossRef]
- Wu, A. , Ying, Z., Gomez-Pinilla, F., 2008. Docosahexaenoic acid dietary supplementation enhances the effects of exercise on synaptic plasticity and cognition. Neuroscience 155, 751–759. [CrossRef]
- Xia, J. , Sánchez, B.J., Chen, Y., Campbell, K., Kasvandik, S., Nielsen, J., 2022. Proteome allocations change linearly with the specific growth rate of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under glucose limitation. Nat. Commun. 13, 2819. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. , Mih, N., Anand, A., Park, J.H., Tan, J., Yurkovich, J.T., Monk, J.M., Lloyd, C.J., Sandberg, T.E., Seo, S.W., Kim, D., Sastry, A.V., Phaneuf, P., Gao, Y., Broddrick, J.T., Chen, K., Heckmann, D., Szubin, R., Hefner, Y., Feist, A.M., Palsson, B.O., 2019. Cellular responses to reactive oxygen species are predicted from molecular mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 116, 14368–14373. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. , Yurkovich, J.T., Lloyd, C.J., Ebrahim, A., Saunders, M.A., Palsson, B.O., 2016. Principles of proteome allocation are revealed using proteomic data and genome-scale models. Sci. Rep. 6, 36734. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. , Heinemann, M., Howard, J., Huber, G., Iyer-Biswas, S., Le Treut, G., Lynch, M., Montooth, K.L., Needleman, D.J., Pigolotti, S., Rodenfels, J., Ronceray, P., Shankar, S., Tavassoly, I., Thutupalli, S., Titov, D.V., Wang, J., Foster, P.J., 2021. Physical bioenergetics: Energy fluxes, budgets, and constraints in cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y. , Zhang, L., Zhu, T., Deng, S., Ma, B., Lv, H., Shan, X., Cheng, H., Jiang, K., Zhang, T., Meng, B., Mei, B., Li, W.-G., Li, F., 2021. Reconsolidation of a post-ingestive nutrient memory requires mTOR in the central amygdala. Mol. Psychiatry 26, 2820–2836. [CrossRef]
- Yeo, G.H.T. , Saksena, S.D., Gifford, D.K., 2021. Generative modeling of single-cell time series with PRESCIENT enables prediction of cell trajectories with interventions. Nat. Commun. 12, 3222. [CrossRef]
- Yewdell, J.W. , 2001. Not such a dismal science: the economics of protein synthesis, folding, degradation and antigen processing. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 294–297. [CrossRef]
- Yizhak, K. , Le Dévédec, S.E., Rogkoti, V.M., Baenke, F., de Boer, V.C., Frezza, C., Schulze, A., van de Water, B., Ruppin, E., 2014. A computational study of the Warburg effect identifies metabolic targets inhibiting cancer migration. Mol. Syst. Biol. 10, 744. [CrossRef]
- Youk, H. , Lim, W.A., 2014. Secreting and sensing the same molecule allows cells to achieve versatile social behaviors. Science 343, 1242782. [CrossRef]
- Zanotelli, M.R. , Rahman-Zaman, A., VanderBurgh, J.A., Taufalele, P.V., Jain, A., Erickson, D., Bordeleau, F., Reinhart-King, C.A., 2019. Energetic costs regulated by cell mechanics and confinement are predictive of migration path during decision-making. Nat. Commun. 10, 4185. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. , Goliwas, K.F., Wang, W., Taufalele, P.V., Bordeleau, F., Reinhart-King, C.A., 2019. Energetic regulation of coordinated leader-follower dynamics during collective invasion of breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 116, 7867–7872. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-P. , Cheng, Z., Liu, F., Wang, W., 2007. Linking fast and slow positive feedback loops creates an optimal bistable switch in cell signaling. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 76, 031924. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R. , Zhang, Y., Tsuji, T., Gao, X., Wagner, A., Yosef, N., Chen, H., Zhang, L., Tseng, Y.-H., Chen, K., 2022. MEBOCOST: Metabolite-mediated Cell Communication Modeling by Single Cell Transcriptome. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X. , Franklin, R.A., Adler, M., Carter, T.S., Condiff, E., Adams, T.S., Pope, S.D., Philip, N.H., Meizlish, M.L., Kaminski, N., Medzhitov, R., 2022. Microenvironmental Sensing by Fibroblasts Controls Macrophage Population Size. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X. , Franklin, R.A., Adler, M., Jacox, J.B., Bailis, W., Shyer, J.A., Flavell, R.A., Mayo, A., Alon, U., Medzhitov, R., 2018. Circuit Design Features of a Stable Two-Cell System. Cell 172, 744–757.e17. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J. , Thompson, C.B., 2019. Metabolic regulation of cell growth and proliferation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 436–450. [CrossRef]
- Zisman, A. , Peroni, O.D., Abel, E.D., Michael, M.D., Mauvais-Jarvis, F., Lowell, B.B., Wojtaszewski, J.F., Hirshman, M.F., Virkamaki, A., Goodyear, L.J., Kahn, C.R., Kahn, B.B., 2000. Targeted disruption of the glucose transporter 4 selectively in muscle causes insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. Nat. Med. 6, 924–928. [CrossRef]
- Zwick, R.K. , Kasparek, P., Palikuqi, B., Viragova, S., Weichselbaum, L., McGinnis, C.S., McKinley, K.L., Rathnayake, A., Vaka, D., Nguyen, V., Trentesaux, C., Reyes, E., Gupta, A.R., Gartner, Z.J., Locksley, R.M., Gardner, J.M., Itzkovitz, S., Boffelli, D., Klein, O.D., 2023. Epithelial zonation along the mouse and human small intestine defines five discrete metabolic domains. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
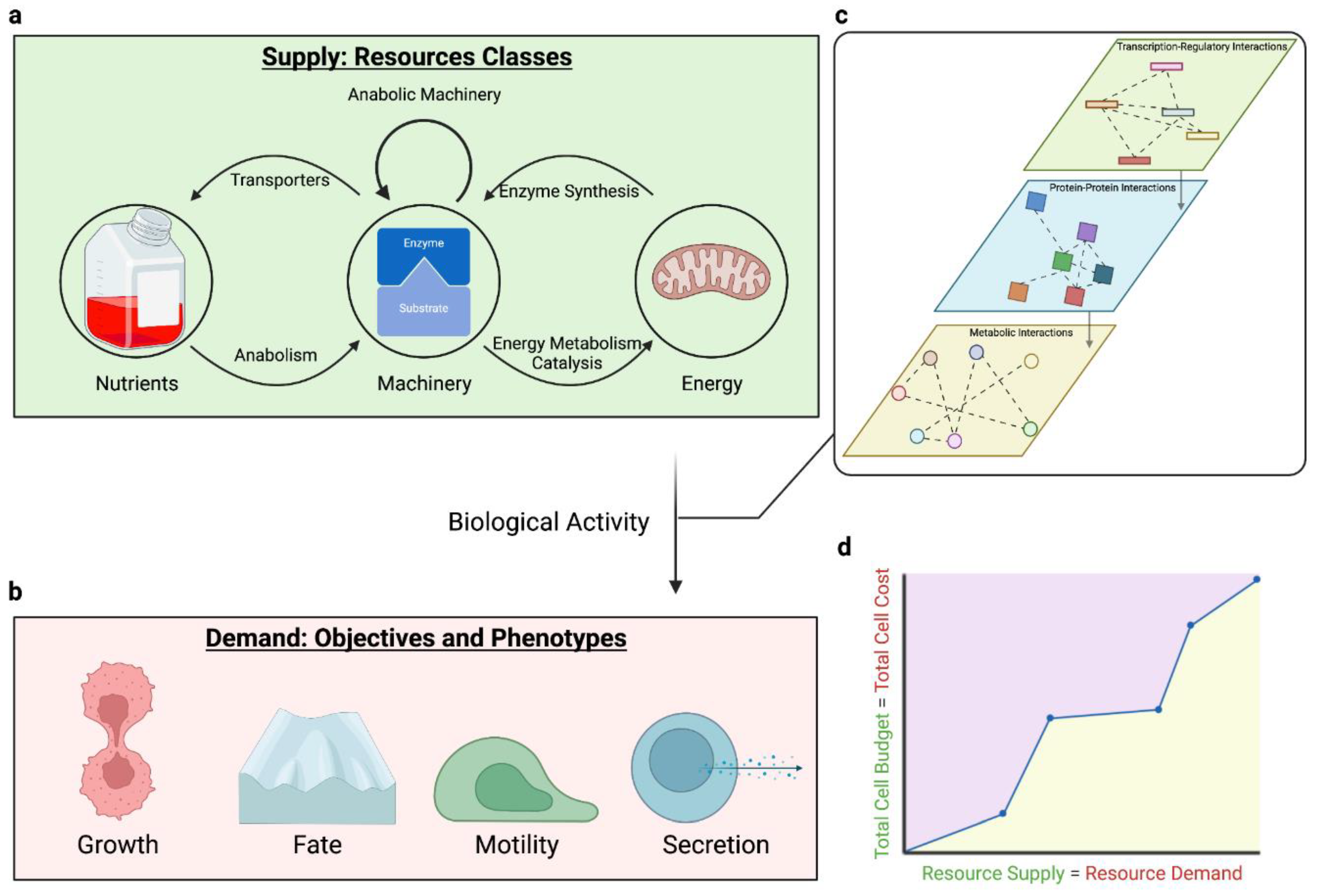
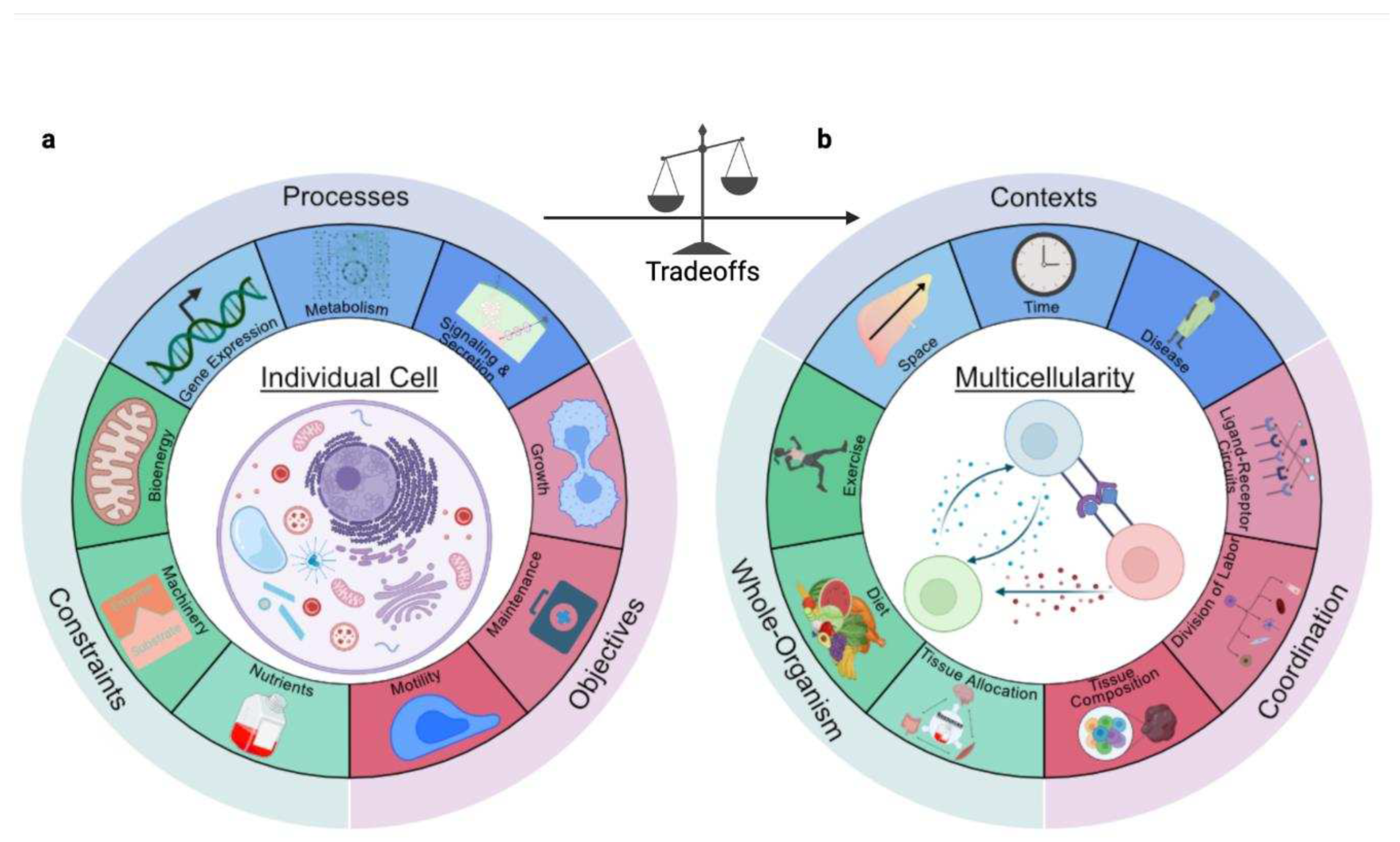
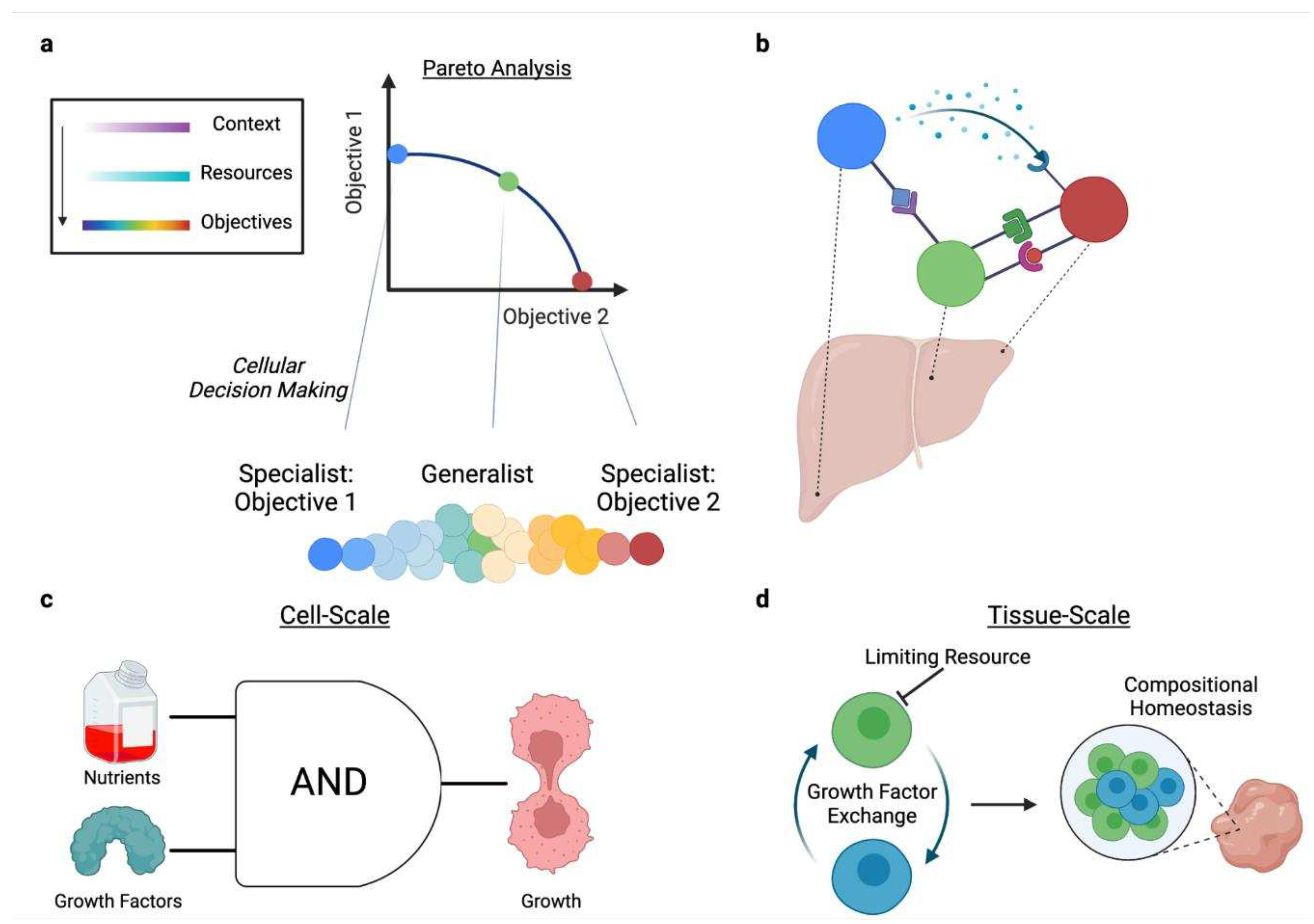
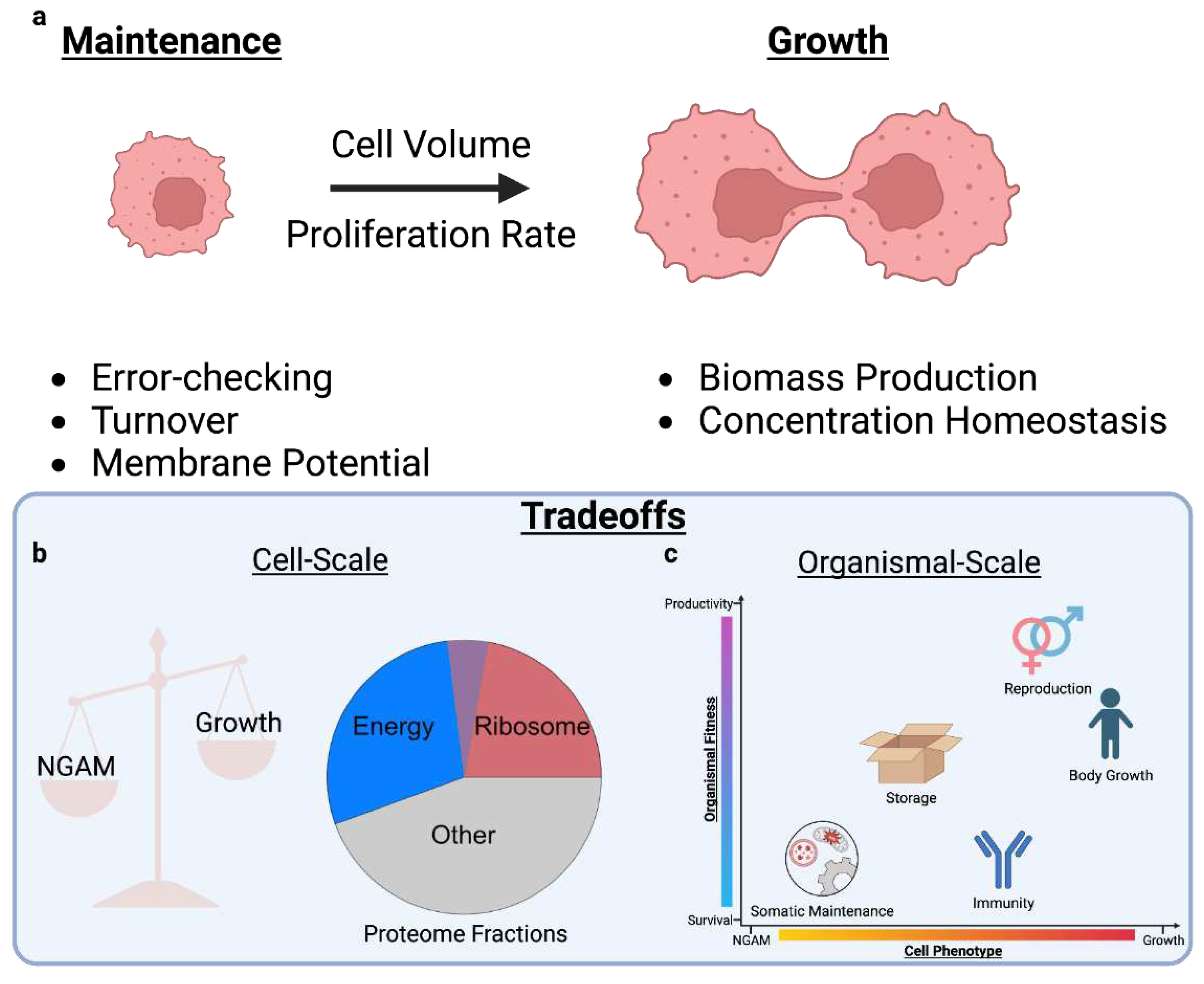
| Disease | Resource Allocation Concept | Reference |
| Aging | Context-dependent machinery synthesis rates | (Gerashchenko et al., 2021; Rooyackers et al., 1996) |
| Aging | Organismal-scale trade-offs | (Kirkwood, 2017) |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Machinery constraints | (Kuo et al., 2021) |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Multicellular GEMs | (Lewis et al., 2010b) |
| Autoimmunity | GEMs | (Wagner et al., 2021) |
| Cancer | Resource constraints on cell migration | (Kiweler et al., 2022; Soflaee et al., 2022; Yizhak et al., 2014) |
| Cancer | Multi-objective optimality | (Hart et al., 2015) |
| Cancer | Multicellular nutrient constraints and GEMs | (J. Wang et al., 2022) |
| Cancer | Multicellular bioenergy constraints | (Liu et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2019) |
| Cancer | Multicellular resource competition | (Brand et al., 2016; Chang et al., 2015; Nguyen et al., 2023; Reinfeld et al., 2021; Seki et al., 2022) |
| Diabetes | Nutrient and machinery constraints | (Zisman et al., 2000) |
| Obesity | Nutrient imbalances | (Dai et al., 2022; Simpson and Raubenheimer, 2005) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




