Submitted:
14 December 2023
Posted:
21 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Fungal Isolates
2.2. Fungal Cultures and DNA Extraction
2.3. PCR and Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
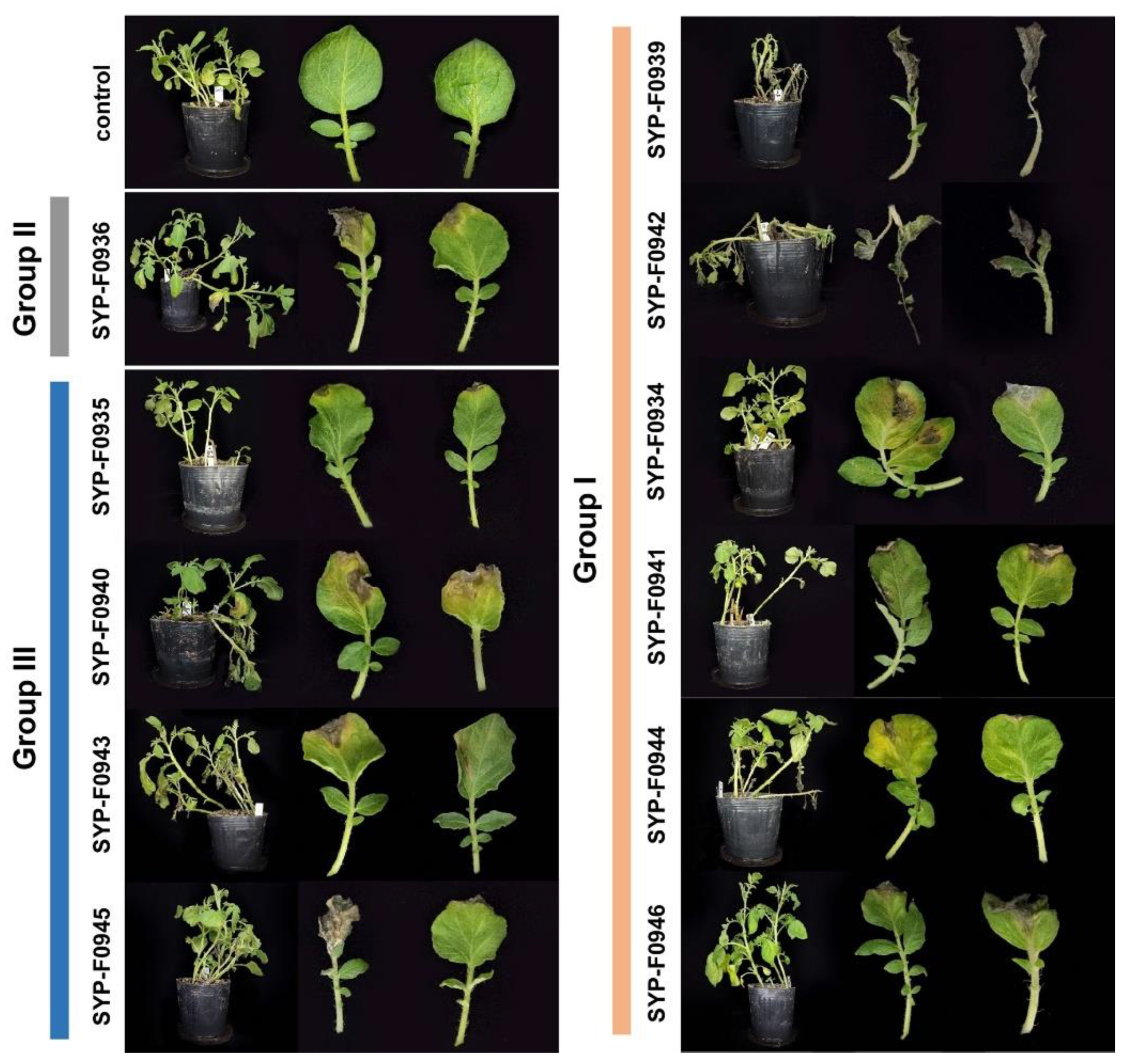
2.5. Pathogenicity Test
2.6. Virulence Test on Commercial Cultivars
2.7. In Vitro Screening of Fungicide Sensitivity
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
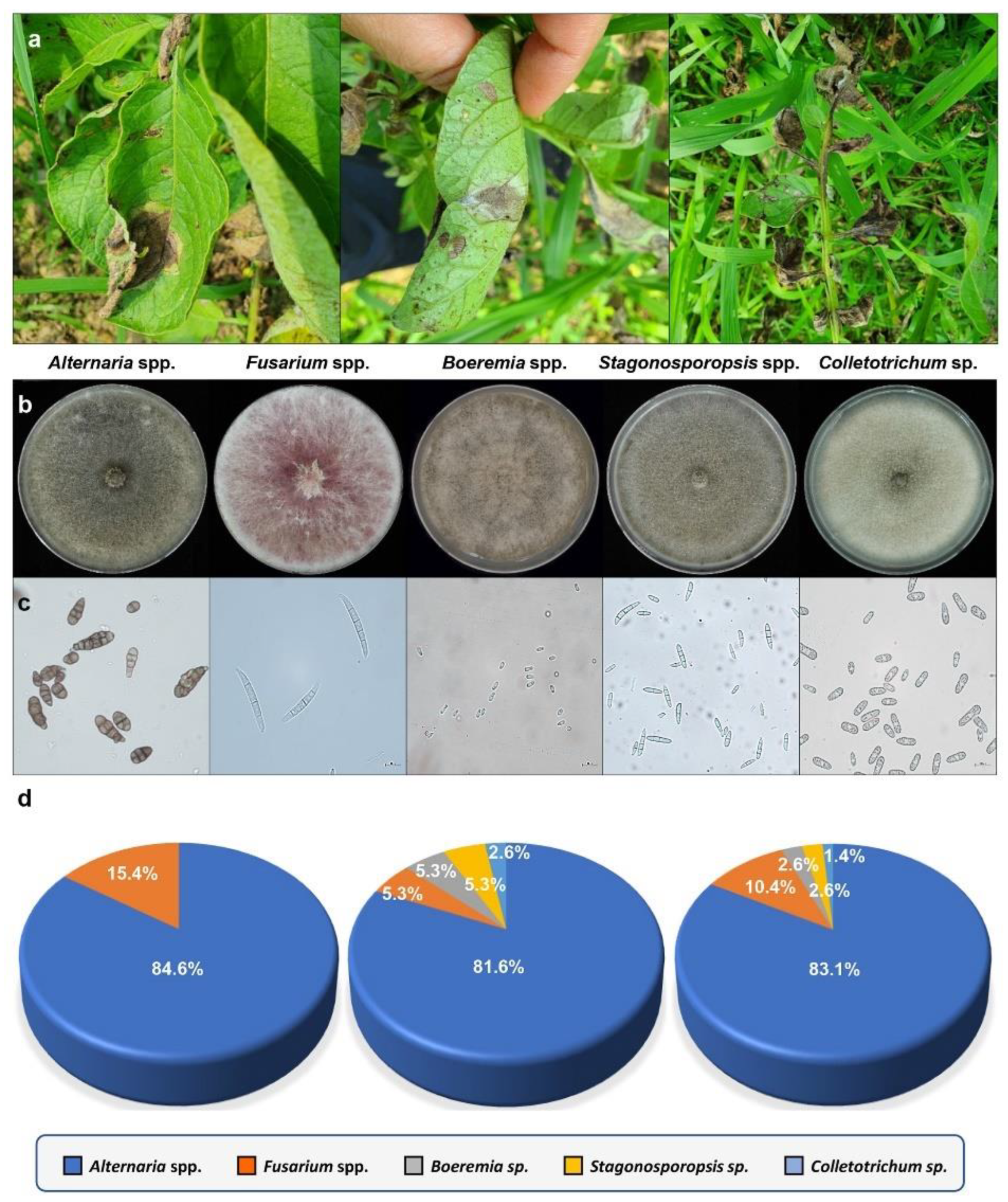
3.1. Collection of Fungal Isolates from Potatoes with Brown Leaf Spot Disease
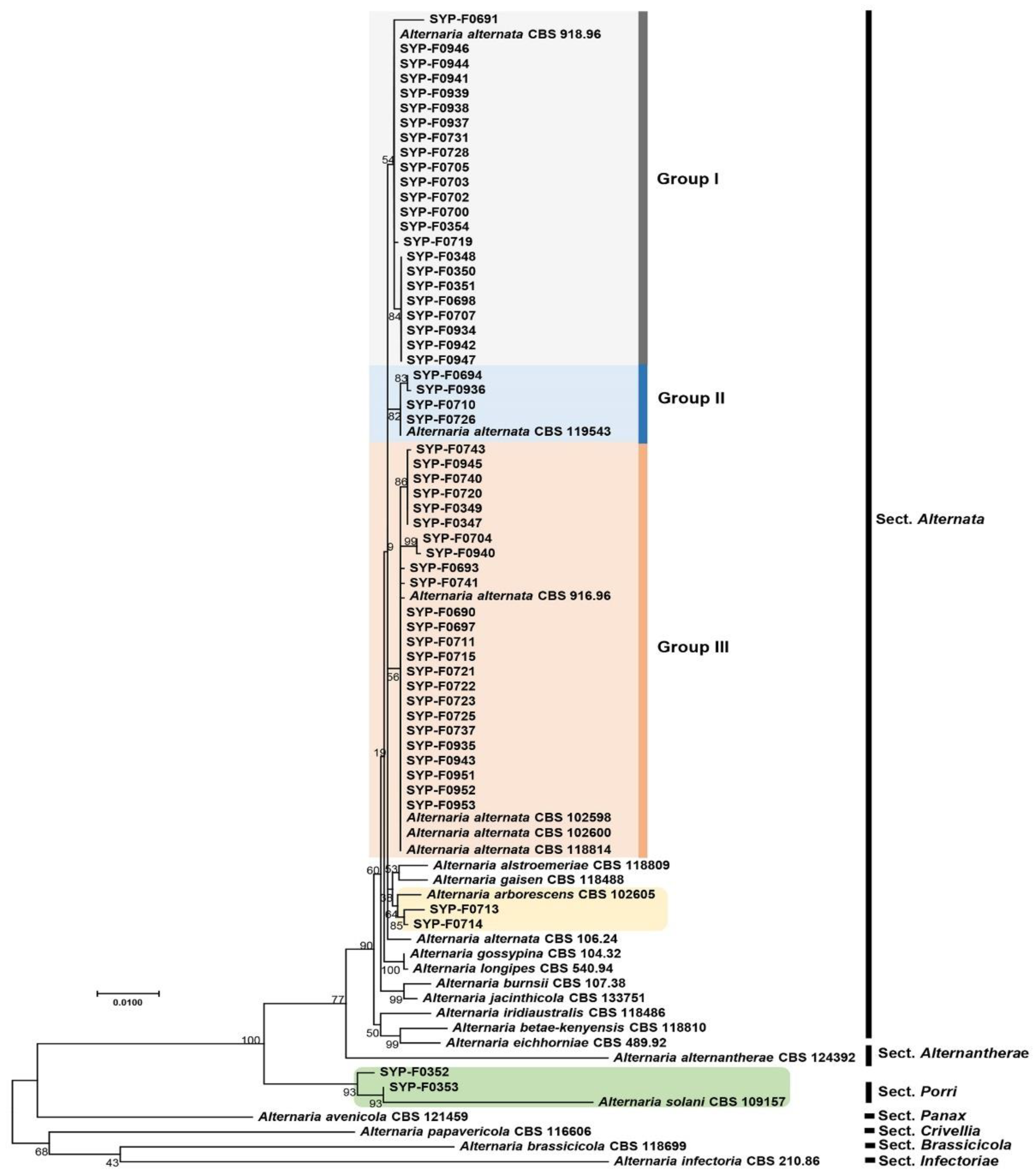
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Alternaria spp. Isolates Using Seven Barcoding Genes
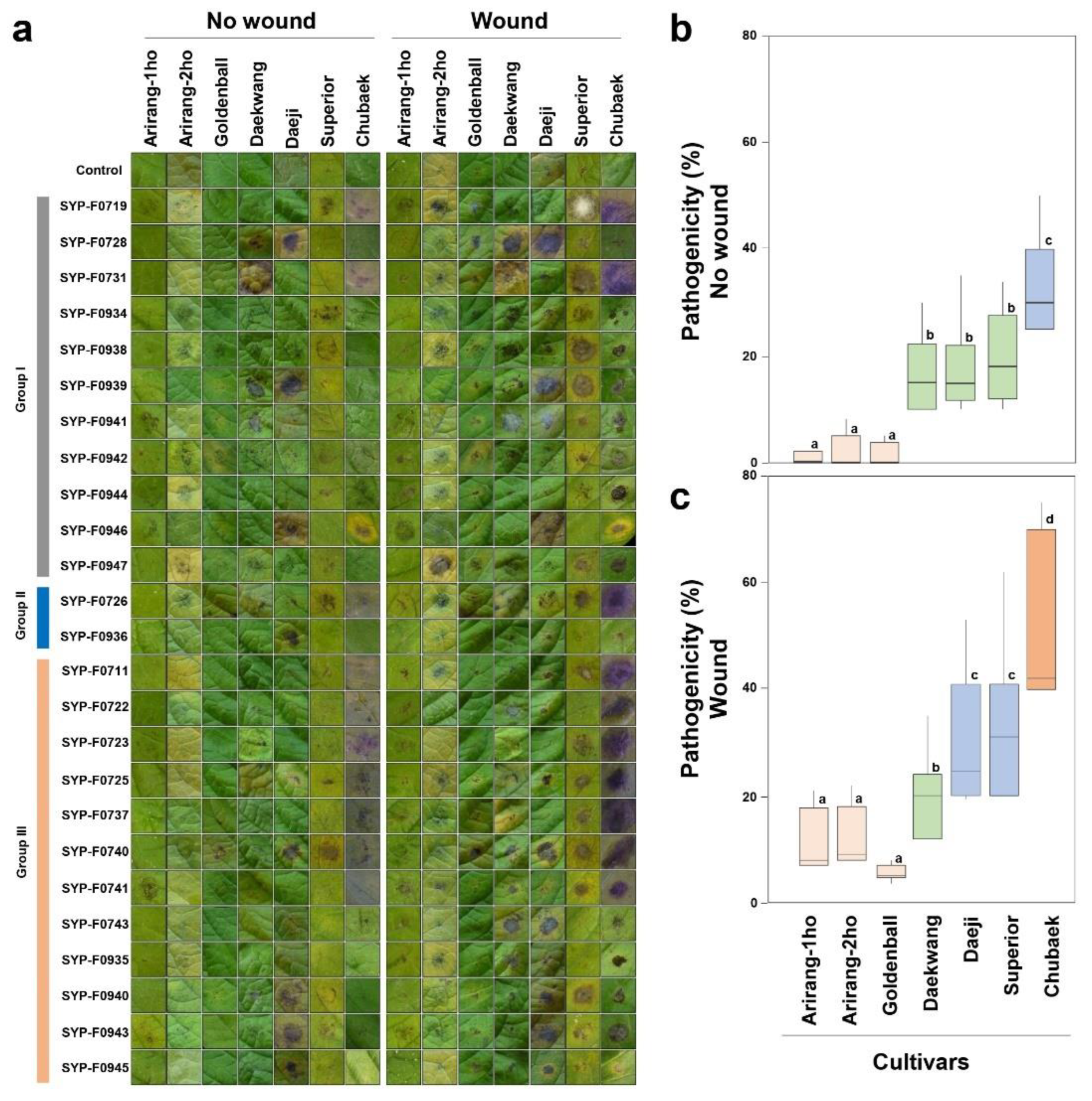
3.3. Pathogenicity Test
3.4. Virulence Test on Commercial Cultivars
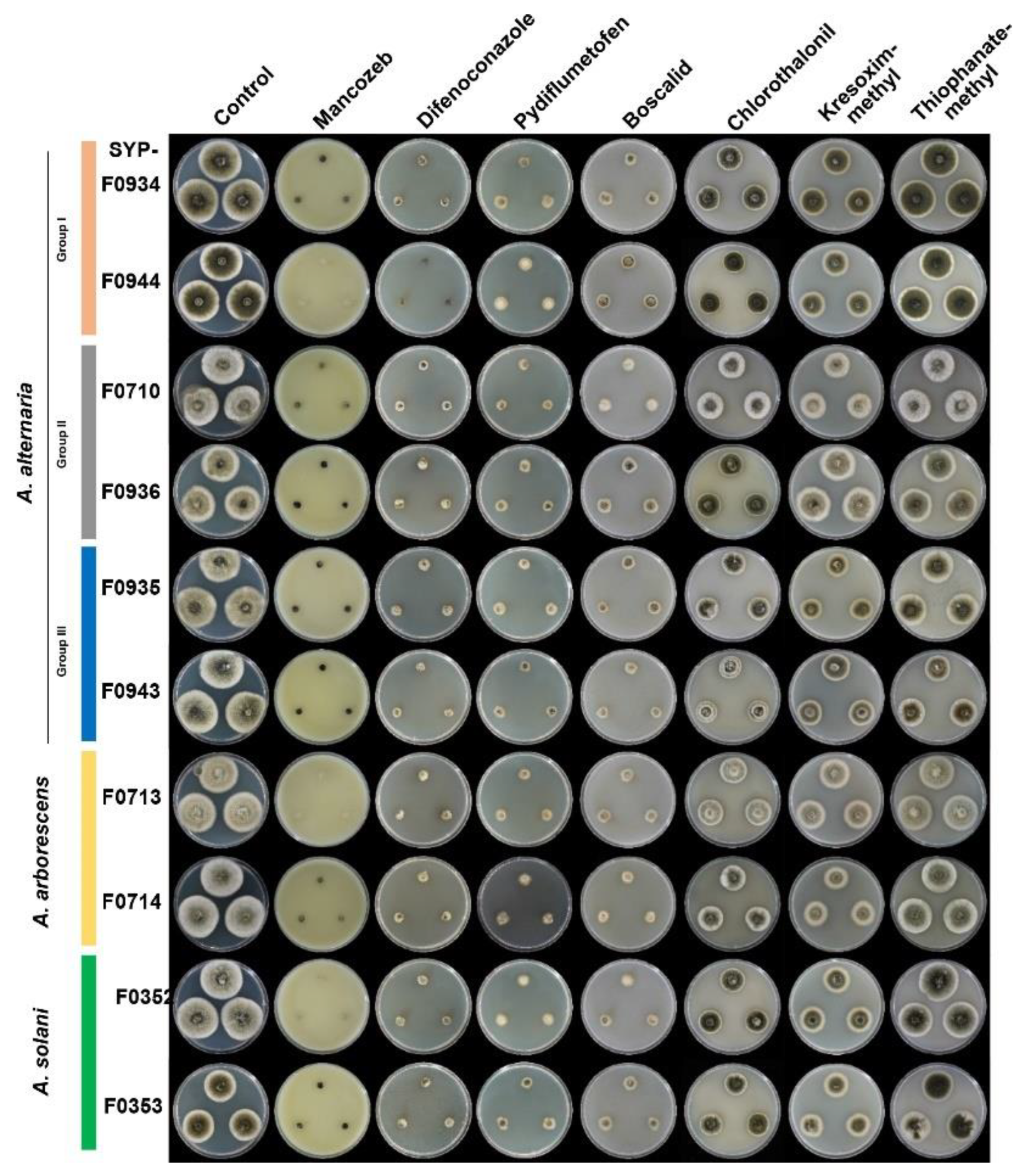
3.5. Selection of Appropriate Fungicides for Potato Brown Spot Disease in Korea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng:, H.H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, T.Y.; Wu, X.H. Characterization of Alternaria species associated with potato foliar disease in China. Plant Pathol. 2016, 64, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Waals, J.E.; Korsten, L.; Slippers, B. Genetic diversity among Alternaria solani isolated from potatoes in South Africa. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Jeung, M.-H.; Choi, E.D.; Park, J.; Park, S.-Y. First report of brown spot caused by Alternaria alternata on potato (Solanum tuberosum) in Korea. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, W.R.; Loria, R.; Franc, G.D.; Weingartner, D.P. Compendium of potato diseases, Second Edition; The American Phytopathological Society: St, Paul, MN, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dorby, S.; Dinoor, A.; Prusky, D.; Barkaigolan, R. Pathogenicity of Alternaria alternata on potato in Israel. Phytopathology 1984, 74, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, K.L.; Miles, T.D.; Wharton, P.S. Assessing fungicide resistance in population of Alternaria in Idaho potato fields. Crop Prot. 2013, 49, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, M.J.; Kirk, W. Enhance resistance to Alternaria alternata causing pototo brown leaf spot disease by using some plant defense inducers. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2012, 52, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomma, B.P. Alternaria spp.: From general saprophyte to specific parasite. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2003, 4, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.T.M.S.; Berbee, M.L.; Simmons, E.G.; Cardoso, C.R.; Reis, A.; Maffia, L.A.; Mizubuti, E.S.G. First report of Alternaria tomatophila and A. grandis causing early blight on tomato and potato in Brazil. New Des. Rep. 2010, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymon, L.S.; Cummings, T.F.; Johnson, D.A. Identification and aggressiveness of three Alternaria spp. on potato foliage in the US Northwest. Plant Dis. 2016, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woudenberg, J.H.; Seidl, M.F.; Groenewald, J.Z.; de Vries, M.; Stielow, J.B.; Thomma, B.P.; Crous, P.W. Alternaria section Alternaria: Species, formae speciales or pathotypes? Stud. Mycol. 2015, 82, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woudenberg, J.H.; Truter, M.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. Large-spored Alternaria pathogens in section Porri disentangled. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 79, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Meinholz, K.; Cleveland, K.; Jordan, S.A.; Gevens, A.J. Diversity and virulence of Alternaria spp. causing potato early blight and brown spot in Wisconsin. Phytopathology 2018, 109, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.W.; Zhu, W.; He, M.H.; Wu, E.J.; Duan, G.H.; Xie, Y.K.; Jin, Y.J.; Yang, L.N.; Shang, L.P.; Zhan, J. Population genetic analysis reveals cryptic sex in the phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria alternata. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, M.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, Y.-H. A quick and safe method for fungal DNA extraction. Plant Pathol. J. 2009, 25, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoog, G.S.; Gerrits van den Ende, A.H. Molecular diagnostics of clinical strains of filamentous Basidiomycetes. Mycoses. 1998, 41, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics; Academic Press: New York, 1990; Volume 18, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Berbee, M.L.; Pirseyedi, M.; Hubbard, S. Cochliobolus phylogenetics and the origin of known, highly virulent pathogens, inferred from ITS and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene sequences. Mycologia 1999, 91, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Donnell, K.; Kistler, H.C.; Cigelnik, E.; Ploetz, R.C. Multiple evolutionary origins of the fungus causing Panama disease of banana: Concordant evidence from nuclear and mitochondrial gene genealogies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1998, 95, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, G.H.; Sung, J.M.; Hywel-Jones, N.L.; Spatafora, J.W. A multi-gene phylogeny of Clavicipitaceae (Ascomycota, Fungi): Identification of localized incongruence using a combinational bootstrap approach. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 44, 1204–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA polymerse II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.G.; Cramer, R.A.; Lawrence, C.B.; Pryor, B.M. Alt a 1 allergen homologs from Alternaria and related taxa: Analysis of phylogenetic content and secondary structure. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2005, 42, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, M.; Peever, T.L.; Pryor, B.M. An expanded multilocus phylogeny does not resolve morphological species within the small-spored Altemrnaria species complex. Mycologia 2009, 101, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlon, A.; Taylor, M.; Dick, J. Agar dilution susceptibility testing; CRC Press: The journal CRC Press eBooks, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gorai, P.S.; Ghosh, R.; Konra, S.; Mandal, N.C. Biological control of early blight disease of potato caused by Alternaria alternata EBP3 by an endophytic bacterial strain Bacillus velenzensis SEB1. Biol. Control 2021, 156, 104551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrios, G.N. Plant Patholgy 5th edition; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Edin, E.; Liljeroth, E.; Andersson, B. Long term field sampling in Sweden reveal a shift in occurrence of cytochrome b genotype and amino acid substitution F129L in Alternaria solani, together with a high incidence of the G143A substitution in Alternaria alternata. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 155, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandecasteelea, M.; Landschoota, S.; Carrettea, J.; Verwaerena, J.; Hofte, M.; Audenaerta, K.; Haesaert, G. Species prevalence and disease progression studies demonstrate a seasonal shift in the Alternaria population composition on potato. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, J.P.; Truter, M.; van der Waals, J.E. First report of resistance to QoI fungicides in Alternaria alternata isolates from potato in South Africa. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokaeva, L.Y.; Belosokhov, A.F.; Doeva, L.Y.; Skolotneva, E.S.; Elansky, S.N. Distribution of Alternaria species on blighted potato and tomato leaves in Russia. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2018, 125, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Locusa | Primer | Primer Sequence (5’-3’) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | V9G | TTACGTCCCTGCCCTTTGTA | [16] |
| ITS4 | CCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC | [17] | |
| gapdh | gpd1 | CAACGGCTTCGGTCGCATTG | [18] |
| gpd2 | GCCAAGCAGTTGGTTGTGC | [18] | |
| tef1 | EF1-728F | CATCGAGAAGTTCGAGAAGG | [19] |
| EF1-986R | TAC TTG AAG GAA CCC TTA CC | [19] | |
| EF2 | GGARGTACCAGTSATCATGTT | [20] | |
| rpb2 | RPB2-5F2 | GGGGWGAYCAGAAGAAGGC | [21] |
| fRPB2-7cR | CCCATRGCTTGTYYRCCCAT | [22] | |
| Alt a 1 | Alt-For | ATGCAGTTCACCACCATCGC | [23] |
| Alt-Rev | ACGAGGGTGAYGTAGGCGTC | [23] | |
| endoPG | PG3 | TACCATGGTTCTTTCCGA | [24] |
| PG2b | GAGAATTCRCARTCRTCYTGRTT | [24] | |
| OPA10-2 | OPA 10-2R | GATTCGCAGCAGGGAAACTA | [24] |
| OPA 10-2L | TCGCAGTAAGACACA TTCTACG | [24] |
| Chemical Name | Target Site | Group Name | Formulation (%) |
Final conc. of Fungicide on the Medium (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mancozeb | Multi-site contact activity |
Dithiocarbamates | 75 | 1,500 |
| Chlorothalonil | Chloronitriles | 75 | 1,253 | |
| Difenoconazole | Inhibit sterol biosynthesis in membrane | C14-methylase in sterol biosynthesis | 10 | 34 |
| Pydiflumetofen | “Complex II” Succinate dehydrogenase |
Succinate-dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI) | 18.35 | 46 |
| Boscalid | 49.30 | 328 | ||
| Krexosim-methyl | Inhibit mitochondrial respiration | Quinone outside inhibitor (QoI) | 40.20 | 148 |
| Thiophanate-methyl | B1 tubulin polymerization |
Methyl benzimidazole carbamates (MBC) | 70 | 700 |
| Isolates | The Closest Matched GenBank Taxa | GenBank Accession nos. | Query Over |
Percent | Collected Regions | Date of Isolation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYP-F0690 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0691 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0693 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0694 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0697 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0698 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0700 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0701 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0702 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0703 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0704 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0705 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0706 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0707 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0696 | Fusarium acuminatum | MT635295.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0688 | Fusarium equiseti | MT560375.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0689 | Fusarium equiseti | MT560375.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0692 | Fusarium equiseti | MT560375.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0708 | Fusarium equiseti | MT560375.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0709 | Fusarium equiseti | MT560375.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | June 26, 2020 |
| SYP-F0347 | Alternaria alternata | MH992147.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | July 22, 2020 |
| SYP-F0348 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | July 22, 2020 |
| SYP-F0349 | Alternaria alternata | KX816031.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | July 22, 2020 |
| SYP-F0350 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 99.81 | Goseong | July 22, 2020 |
| SYP-F0351 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Goseong | July 22, 2020 |
| SYP-F0354 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Baengnyeongdo | July 22, 2020 |
| SYP-F0352 | Alternaria solani | MT498268.1 | 100 | 100 | Baengnyeongdo | July 22, 2020 |
| SYP-F0353 | Alternaria solani | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Baengnyeongdo | July 22, 2020 |
| SYP-F0937 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0938 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0939 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0940 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0941 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0942 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0943 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0944 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0945 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0946 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0947 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 27, 2020 |
| SYP-F0710 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0711 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0712 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0715 | Alternaria alternata | OR687203.1 | 100 | 99.61 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0716 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0717 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0718 | Alternaria alternata | MT524302.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0719 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0720 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0721 | Alternaria alternata | OR734592.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0722 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0723 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0725 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0726 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0728 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0729 | Alternaria alternata | OK315470.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0731 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0737 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0740 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0741 | Alternaria alternata | ON599295.1 | 100 | 98.33 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0742 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0743 | Alternaria alternata | MT498268.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0934 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0935 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0936 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0713 | Alternaria arborescens | MT212228.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0714 | Alternaria arborescens | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0745 | Alternaria longipes | MT524302.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0736 | Boeremia exigua | KY555024.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0733 | Boeremia exigua | MT397284.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0730 | Colletotrichum nymphaeae | LC435466.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0732 | Fusarium equiseti | MK752407.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0734 | Fusarium graminearum | OR346117.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0724 | Stagonosporopsis dennisii | OQ158929.1 | 100 | 99.18 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0727 | Stagonosporopsis dennisii | OK315470.1 | 100 | 100 | Yeoncheon | June 22, 2021 |
| SYP-F0951 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Baengnyeongdo | July 19, 2021 |
| SYP-F0952 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Baengnyeongdo | August 1, 2021 |
| SYP-F0953 | Alternaria alternata | OR787445.1 | 100 | 100 | Baengnyeongdo | August 1, 2021 |
| Isolates | Control | Mancozeb | Defenoconazole | Pydiflumetofen | Boscalid | Chlorothalonil | Krexoxim-methyl | Thiophanate-methyl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYP-F0934 | 0.0±0.0g,*,# | 100.0±0.0a | 90.0±1.6b | 77.3±4.2c | 77.3±1.6c | 46.4±1.6d | 38.2±3.1e | 14.6±3.1f |
| SYP-F0944 | 0.0±0.0g | 100.0±0.0a | 96.3±1.6b | 75.7±1.6c | 72.9±1.6c | 58.0±2.8d | 39.3±3.2e | 20.6±1.6f |
| SYP-F0945 | 0.0±0.0f | 100.0±0.0a | 90.5±1.6b | 84.8±3.3c | 81.0±1.6c | 41.9±1.6d | 44.8±4.4d | 25.7±2.9e |
| SYP-F0936 | 0.0±0.0g | 100.0±0.0a | 87.3±2.5b | 75.8±1.9c | 68.1±1.9d | 40.0±1.0e | 3.2±1.9g | 10.9±1.7f |
| SYP-F0935 | 0.0±0.0f | 100.0±0.0a | 83.7±2.7b | 77.3±1.6bc | 80.0±5.7c | 51.9±1.6d | 55.5±1.6d | 28.2±1.6e |
| SYP-F0943 | 0.0±0.0f | 100.0±0.0a | 92.6±1.6b | 82.4±4.2c | 80.6±2.8c | 56.5±3.2d | 50.0±2.8e | 45.4±4.2e |
| SYP-F0713 | 0.0±0.0h | 100.0±0.0a | 88.1±0.0c | 97.0±0.0b | 74.3±1.7d | 41.6±1.7e | 32.7±3.4f | 13.9±0.0g |
| SYP-F0714 | 0.0±0.0f | 100.0±0.0a | 90.0±8.7b | 76.0±3.0c | 80.0±1.7c | 44.9±1.7d | 43.9±1.7d | 14.9±1.7e |
| SYP-F0352 | 0.0±0.0g | 100.0±0.0a | 89.0±2.8b | 79.8±1.6c | 79.8±1.6c | 52.2±1.6d | 43.1±1.6e | 14.6±7.3f |
| SYP-F0353 | 0.0±0.0f | 98.7±2.2a | 73.1±20.0b | 74.4±2.2b | 66.7±2.2b | 37.2±2.2c | 25.6±2.2c | 5.1±2.2d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





