1. Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most prevalent forms of atrial arrhythmias among adult patients, with rising incidence due to an aging society. Age, in tandem with heart failure (HF), is linked to the emergence of AF, and vice versa. The concurrent presence of both conditions significantly amplifies mortality risks.1 The Framingham Heart Study found that 37% of patients with newly diagnosed AF had HF and 57% of patients with newly diagnosed HF had AF.2 These findings underscore the importance of identifying HF or its risk factors in patients with AF. In this regard, plasma brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) emerges as a well-established indicator of congestive HF, capable of detecting HF in its early stages. Elevated BNP levels in patients pose a risk of HF development, irrespective of their underlying heart disease and the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) value.3
BNP is frequently used as a surrogate marker to discern subtle changes in LV function arising from AF, making it a crucial indicator in assessing responses to specific AF treatment, such as catheter ablation (CA). While CA for AF improves patients’ quality of life (QOL), the clinical utility of BNP levels on the QOL benefit after CA remains uncertain. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to investigate the association of baseline plasma BNP levels and QOL changes after undergoing CA in AF patients without a history of clinical HF.
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
We obtained patient data from the Keio interhospital Cardiovascular Studies-atrial fibrillation (KiCS-AF) registry. In brief, the KiCS-AF registry4 is a prospective, multicenter, registry-based cohort study designed to collect data on the clinical variables and outcomes of consecutive patients with AF from 11 hospitals within the Tokyo metropolitan area of Japan from September 2012 to May 2018 (UMIN 000022229). The Atrial Fibrillation Effect on Quality-of-Life (AFEQT) questionnaires5 were administered to all patients at the baseline visit and at the 1-year follow-up visit or by mail, if possible. Yearly follow-up examinations were performed for all patients through chart reviews, mail, and phone interviews. Data quality assurance was achieved through systematic validation that highlighted outliers and data completeness, and the clinical research coordinators in each institution answered all inquiries regarding data entry.4 To ensure consecutive case enrollment, the senior study coordinator (I.U.) and investigator (S.Ko.) performed on-site auditing to ensure proper registration of each eligible patient. The registry was conducted per the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Institutional review board/ethics committee approval was obtained from all the study sites. All patients provided written informed consent.4
2.2. Studied Patients
The study flowchart is illustrated in
Figure 1. A total of 3313 consecutive patients with AF were registered in this study. Among those, 1157 patients underwent CA for AF within 1 year after registration, and the 1-year follow-up data of 1077 patients were available. Of those, data regarding plasma BNP levels were available in 963 patients. The exclusion criteria were left atrial (LA) diameter ≥60 mm by transthoracic echocardiogram, or a 12-lead electrocardiogram at registration showing a rhythm other than the sinus rhythm (SR) or AF. A firstly diagnosed AF was also excluded, since these patients are known to have a recurrence rate of 50% in 1 year after undergoing CA and is performed in less than 3% of patients.
6 Finally, we analzyed 491 patients non-HF (mean age, 61 ± 10 years; 385 (78%) males; and 378 (77%) patients with paroxysmal AF (PAF)). HF was defined as having a history of HF, an LVEF of ≤40%, or a plasma BNP level of ≥100 pg/mL
7. Enrolled patients were divided into quartiles based on their plasma BNP levels (normal, ≤18.4 pg/ml
8) before undergoing CA as follows: Q1: 1.32–18.5 pg/mL, Q2: 18.7–37.7 pg/mL, Q3: 37.9–63.5 pg/mL, and Q4: 63.8–99.8 pg/mL.
In this study, the primary aim of performing CA was to ensure that all pulmonary veins are electrically isolated and SR is restored. Performing an additional ablation procedure and prescribing postoperative antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs) depended on the operator. After ablation, all patients received anticoagulation therapy for at least 6 months.
2.3. Assessment of Patients’ Health Status
We evaluated the patient-reported health status at the time of registration (before CA) and 1 year after registration (after CA) using the AFEQT questionnaire.5 The AFEQT consists of four conceptual domains (symptoms, daily activities, treatment concern, and satisfaction), and its global score was used to measure the patient’s AF-specific health status in this study. This score ranges from 0 to 100, where 100 indicates the best AF-related health status and 0 indicates the worst. A culturally and linguistically translated version of the AFEQT for Japan was used.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, and categorical variables are presented as numbers and percentages. Comparisons among the quartiles were performed using the one-way analysis of variance for continuous variables and the Kruskal–Wallis test for ordinal variables. Differences between the groups were compared using the Student’s t-test or Mann–Whitney U test. Changes in the AFEQT scores before and after CA were analyzed by multivariable linear regression with generalized estimating equations to account for relevant factors, including the baseline AFEQT score (per 1-point increase), age (per 1-year increase), PAF presence, beta blocker use, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). In this study, all 491 patients analyzed had effective BNP data. A p-value of <0.05 was considered significant. These analyses were performed using EZR software (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan).
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of non-HF groups stratified by quartiles based on BNP levels. Patients with higher BNP levels were found to be older, with ages ranging from 57±10 years in Q1 to 64±10 years in Q4 (p<0.001). This age difference correlated with a higher CHADS2-Vasc score, increasing from 1.1±1.1 in Q1 to 1.7±1.3 in Q4 (p<0.005). The higher BNP groups also exhibited a lower prevalence of PAF, with percentages decreasing from 96% in Q1 to 57% in Q4 (p<0.001). Furthermore, patients in the higher BNP quartiles were more frequently prescribed beta blockers, with percentages rising from 33% in Q1 to 53% in Q4 (p<0.01). Conversely, the distribution of patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, a history of cerebral infarction or transient ischemic attack, and the prescription of AADs, along with the percentage of male patients, remained comparable across the quartiles.
As for the echocardiographic variables, the higher BNP groups exhibited noteworthy differences. The LA diameter increased from 3.7±0.6 in Q1 to 4.0±0.7 in Q4 (p<0.001) among the higher BNP quartiles. Concomitantly, the LA appendage flow velocity showed a decrease from 67±21 in Q1 to 52±21 in Q4 (p<0.001) within the same quartile comparison.
3.2. Improvement in AFEQT Score
Prior to undergoing CA, the lower BNP group exhibited lower overall AFEQT scores in both the symptom and treatment concern domains, as indicated in
Table 1. However, following CA, AFEQT scores became comparable across all domains, as shown in
Table 2. Notably, in comparison to the scores pre-CA, all quartiles demonstrated a significant increase in the total AFEQT score within each domain (data not shown).
Moreover, the lower BNP quartile displayed a noteworthy enhancement in the overall AFEQT score, particularly in the symptom and treatment concern domains, after undergoing CA (
Table 2). After adjusting for the clinically relevant factors including baseline AFEQT score (Supplemental
Table 1) and confounding factors such as age, beta blocker use, eGFR, and PAF (Supplemental
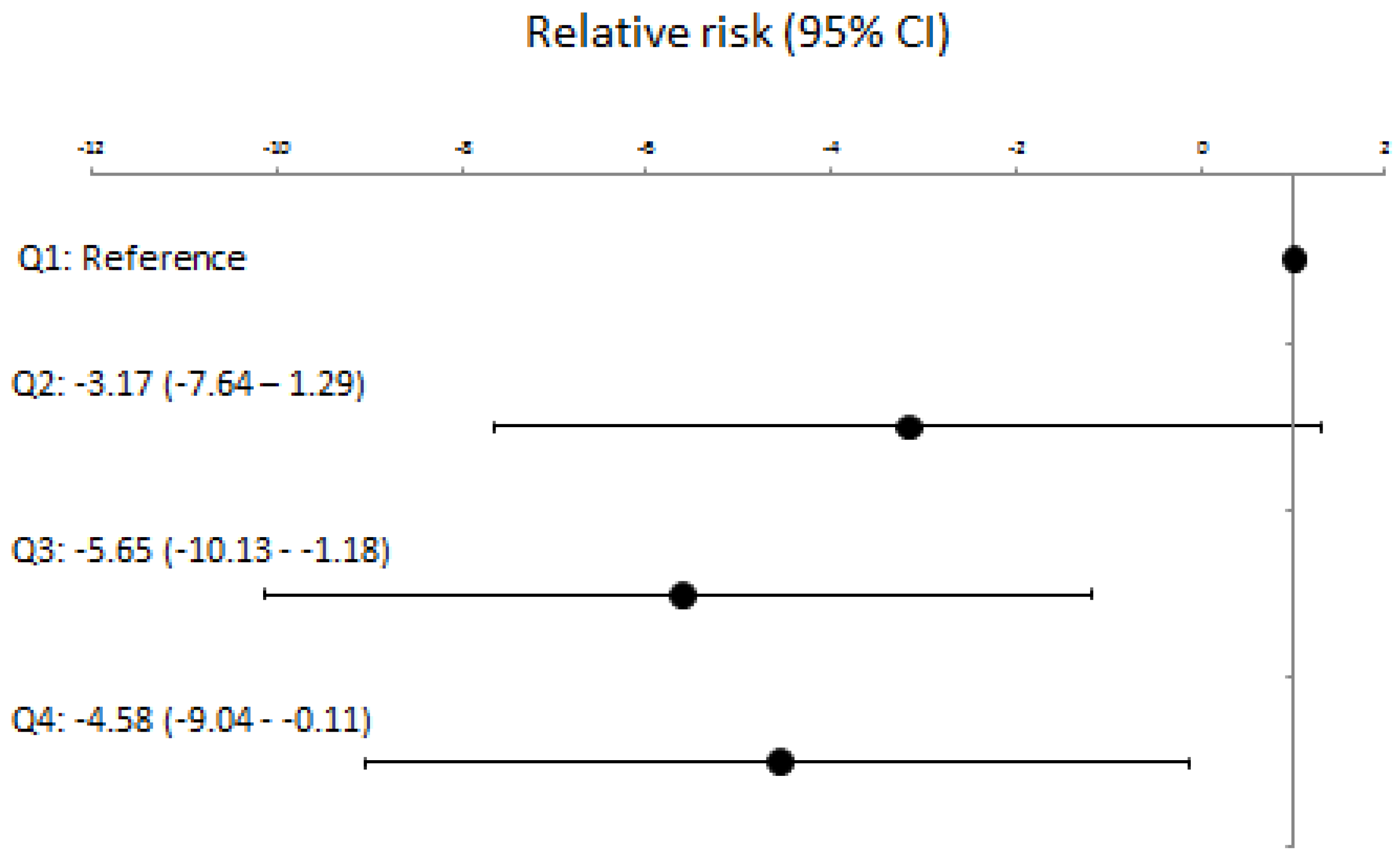
Table 2), lower baseline BNP levels scores were significantly associated with greater AFEQT score improvement at 1 year (
Figure 2), especially for the symptom and treatment concern domains (Supplemental Figure).
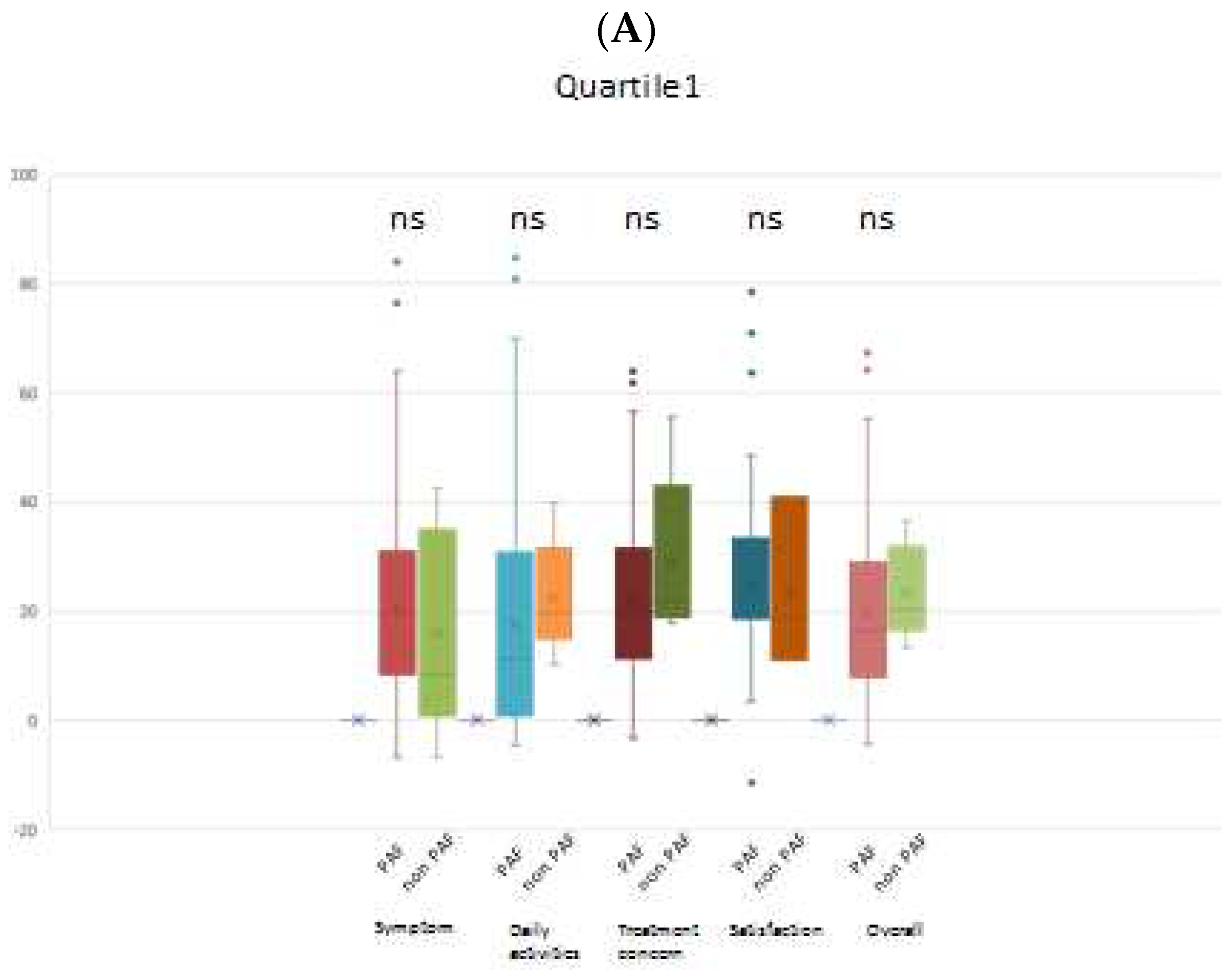
Furthermore, a comparison between normal and abnormal BNP groups revealed that the normal BNP (≤18.4 pg/ml) group experienced a significant improvement in QOL, evident in the overall AFEQT score and the symptom and treatment concern domains (
Table 4).
3.4. Comparative Analysis of PAF and Non-PAF Groups
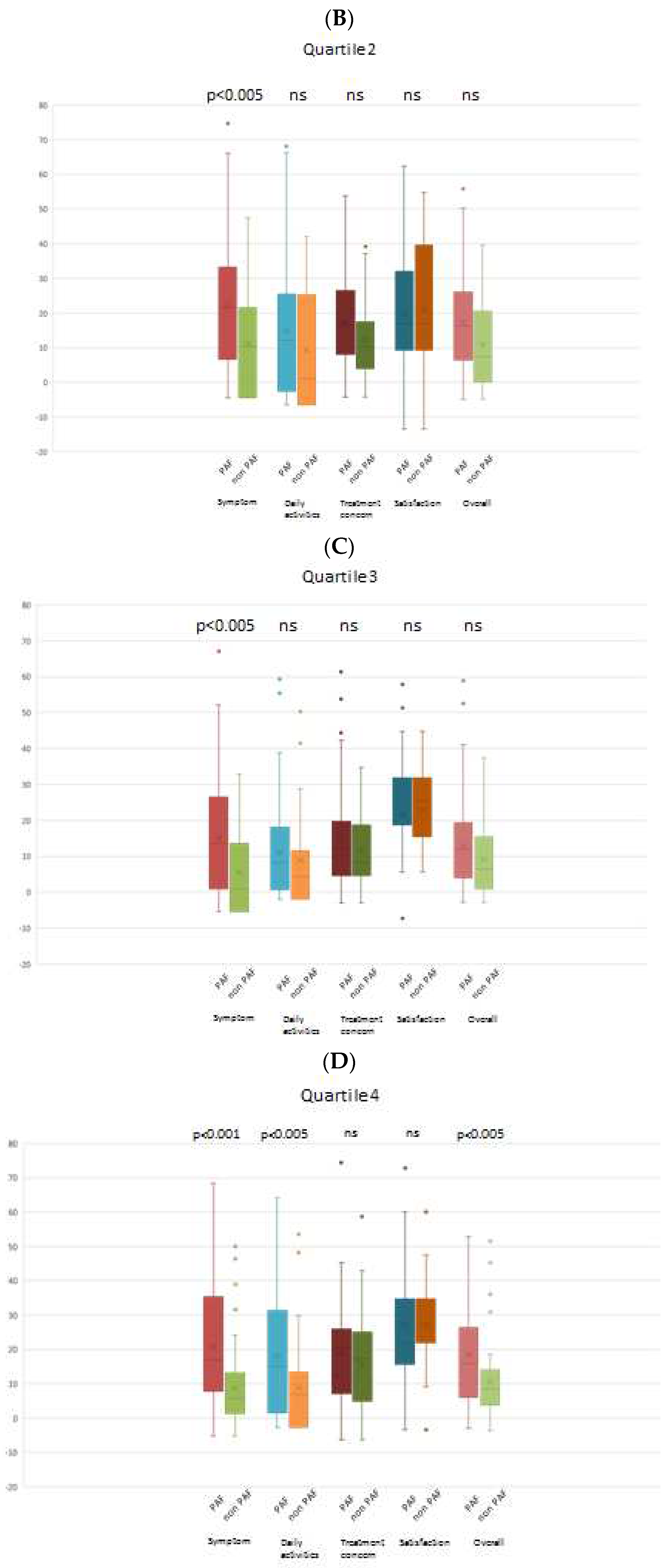
When comparing the PAF and non-PAF groups, it was observed that changes in the AFEQT score across all domains were not significantly different in quartile 1 (lowest BNP group). However, in the other quartiles (higher BNP groups), a noteworthy finding emerged: the PAF group demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in the AFEQT score, particularly in the symptom domain. Importantly, this trend persisted even after adjusting for the baseline AFEQT score. Intriguingly, patients with PAF in the highest BNP group exhibited a significantly greater improvement in both the overall AFEQT score and the daily activities domain, as illustrated in
Figure 3.
4. Discussion
This study represents the inaugural investigation to reveal a positive correlation between baseline lower plasma BNP levels and enhanced QOL in non-HF patients who underwent CA for AF. Specifically, those with lower plasma BNP levels achieved higher scores in the symptom and treatment concern domains of the AFEQT.
While the effectiveness of CA for AF in patients with HF has been extensively explored, limited knowledge exists regarding the extent of QOL improvement and the influence of plasma BNP levels before CA in patients without HF. This study contributes novel insights into the interplay between plasma BNP levels and QOL after CA in non-HF patients with AF, shedding light on a previously unexplored aspect of this therapeutic intervention. Previously, the CASTLE-AF trial showed that performing CA for AF in patients with HF reduced the mortality from any cause and hospitalization for worsening HF.9 The disappearance of an atrial kick is widely known to cause reduced cardiac function. Furthermore, the target heart rate in patients with AF10, the irregularity of cardiac rhythm during AF11, and the neuroendocrine function of the atrium12 have been recognized as key determinant factors for adverse effects in patients with HF. Restoration of SR through CA in patients with congestive HF significantly improved their QOL.13 The CAMTAF trial also showed an improvement in the LVEF and HF symptoms among patients with persistent AF after CA.14 A systematic review15 showed that performing CA for AF significantly improved the patient’s QOL both physically and mentally, and patients without recurrence had a greater improvement in their QOL than those who experienced recurrence. Even among patients with asymptomatic AF, maintenance of SR by CA was reported to improve their QOL, exercise performance, and plasma BNP levels.16
Among patients with non-HF, elevated N-terminal prohormone BNP levels were reported to be correlated with stroke, all-cause death, and hospitalization for HF.17 An increased plasma BNP level is known to correlate not only with an increased incidence of AF18 but also with elevated mortality rate19. Furthermore, the BNP level decreases after successful CA for AF and correlates with the atrial arrhythmia burden after AF ablation.20
In our current investigation, recognizing that plasma BNP levels tend to rise in patients with AF, patients demonstrating normal BNP levels and presenting with PAF were considered to possess unimpaired cardiac function, coupled with a relatively infrequent occurrence of AF episodes, notably without recent manifestations. This subgroup of patients demonstrated a favorable response to CA for AF, resulting in a notable improvement in their AFEQT score. Analysis of individual domains of the AFEQT questionnaire, particularly the symptom domain, revealed that lower BNP levels were indicative of a reduced AF burden. This suggests that patients with lower BNP levels may not have become accustomed to the presence of AF and might become more aware of it in the future. Verma et al. reported that the ratio of asymptomatic to symptomatic AF had increased after CA.21 Previous studies have stated that younger patients22 and those with PAF23 tended to be more symptomatic to AF. Similarly, our study data showed that patients with lower BNP levels, including younger individuals and those with PAF, exhibited greater symptomatic responses to AF.
Regarding the treatment concern domain, we noted only a marginal increase in plasma BNP levels shortly after the onset of AF. It is conceivable that these patients may have experienced anxiety, fearing the onset of AF at any moment or as a potential side effect of treatment. However, the degree of QOL improvement in the daily activities and satisfaction domains was comparable among the quartiles. Yanagisawa et al.24 reported that CA improved the number of maximum daily steps performed in parallel in patients with PAF and those with non-PAF. Dissatisfaction among patients with CA for AF has been attributed not only to procedural failure but also to excessive pain experienced during the procedure.25
Concerning the type of AF, CA for PAF in patients without HF resulted in a greater improvement in QOL than in those with non-PAF among the higher BNP groups. This enhancement in QOL after CA was similar between patients with PAF and those with non-PAF in the lowest BNP group. These individuals were considered to be in the early stages of AF, and their AF burden was comparable. Generally, PAF is more amenable to treatment than non-PAF using CA. In this study, as higher BNP quartiles included a greater number of patients with non-PAF, the magnitude of QOL improvement among the patients in lower BNP quartiles was greater than that among those in higher BNP quartiles. This outcome may reflect the proportion of patients with PAF and the success of SR restoration after CA.
Charitakis et al.26 reported that anxiety and LA dilatation predicted the occurrence of arrhythmia-related symptoms. However, the present study yielded conflicting results as patients in the lower BNP groups, characterized by a smaller LA diameter, exhibited lower AFEQT scores in both the treatment concern (reflecting the severity of anxiety) and symptom domains. This discrepancy may be attributed to the higher proportion of patients with PAF enrolled in our study (77% vs. 37%). Consequently, individuals with a smaller LA diameter in this group may not have become accustomed to AF and, as a result, experienced lower QOL due to AF attacks rather than HF symptoms caused by atrial enlargement.
This study included patients with both PAF and non-PAF, suggesting potential benefits from CA in terms of QOL. The presence of normal BNP levels, indicative of an earlier stage of AF regardless of its type, suggests an optimal opportunity for achieving the best response to CA. Furthermore, performing CA for AF in its early stage is believed to arrest the progression of the condition before developing HF.
5. Limitations
This study is subject to certain limitations. Unmeasured confounding factors, such as the patient's psychiatric status or frailty, may have influenced the results. The primary focus of this study was on the improvement in QOL through CA for AF. Additionally, the relationship between the actual percentage of SR restoration and QOL improvement remains unclear. To address this unresolved question, the consideration of an implantable loop recorder may provide valuable insights.
6. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that individuals with non-HF and AF exhibiting lower BNP levels experience a more substantial improvement in QOL following CA compared to those with higher BNP levels. Moreover, patients in the lowest BNP group exhibited enhanced QOL after CA, regardless of the type of AF. Therefore, considering the improvement in QOL, CA should be regarded as a viable option for individuals in the early stages of AF, particularly those with normal BNP levels.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.T.; methodology, S.T.; software, T.K.; validation, S.Ko, T.K., I.U.; formal analysis, S.Ka, S.Ko; investigation, S.Ka; resources, S.Ko; data curation, N.I.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Ka; writing—review and editing, N.I., S.Ko; visualization, S.Ka; supervision, Y.K., D.S., K.F., K.N., M.I., S.T. ; project administration, S.T.; funding acquisition, S.Ko. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant nos. 20H03915, 16H05215, and 16KK0186) and by an unrestricted research grant from Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The registry was conducted per the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Institutional review board/ethics committee approval was obtained from all the study sites.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Dr Ikemura received an unrestricted research grant for the Department of Cardiology, Keio University School of Medicine from Bristol Myer Squibb. Dr Kohsaka received an unrestricted research grant for the Department of Cardiology at Keio University School of Medicine from Novartis and AstraZeneca; and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr Kimura received grants from Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd. Dr Takatsuki received grants and personal fees from Bayer and received personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo and Bristol-Myers Squibb. The remaining authors have no disclosures to report.
References
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Leip, E.P.; Wolf, P.A.; D'Agostino, R.B.; Murabito, J.M.; Kannel, W.B.; Benjamin, E.J. Temporal relations of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure and their joint influence on mortality: The framingham heart study. Circulation 2003, 107, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhanakrishnan, R.; Wang, N.; Larson, M.G.; Magnani, J.W.; McManus, D.D.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ellinor, P.T.; Cheng, S.; Vasan, R.S.; Lee, D.S.; Wang, T.J.; Levy, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Ho, J.E. Atrial fibrillation begets heart failure and vice versa: Temporal associations and differences in preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. Circulation 2016, 133, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukoyama, M.; Nakao, K.; Saito, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Hosoda, K.; Suga, S.; Shirakami, G.; Jougasaki, M.; Imura, H. Increased human brain natriuretic peptide in congestive heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 757–758. [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura, N.; Spertus, J.A.; Kimura, T.; Mahaffey, K.; Piccini, J.P.; Inohara, T.; Ueda, I.; Tanimoto, K.; Suzuki, M.; Nakamura, I.; Akaishi, M.; Mitamura, H.; Fukuda, K.; Takatsuki, S.; Kohsaka, S. Cohort profile: Patient characteristics and quality-of-life measurements for newly-referred patients with atrial fibrillation-keio interhospital cardiovascular studies-atrial fibrillation (kics-af). BMJ Open 2019, 9, e032746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spertus, J.; Dorian, P.; Bubien, R.; Lewis, S.; Godejohn, D.; Reynolds, M.R.; Lakkireddy, D.R.; Wimmer, A.P.; Bhandari, A.; Burk, C. Development and validation of the atrial fibrillation effect on quality-of-life (afeqt) questionnaire in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2011, 4, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, K.H.; Kerr, C.R.; Connolly, S.J.; Klein, G.; Boone, J.A.; Green, M.; Sheldon, R.; Talajic, M.; Dorian, P.; Newman, D. New-onset atrial fibrillation: Sex differences in presentation, treatment, and outcome. Circulation 2001, 103, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B.; Coats, A.J.; Tsutsui, H.; Abdelhamid, M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Albert, N.; Anker, S.D.; Atherton, J.; Böhm, M.; Butler, J.; Drazner, M.H.; Felker, G.M.; Filippatos, G.; Fonarow, G.C.; Fiuzat, M.; Gomez-Mesa, J.E.; Heidenreich, P.; Imamura, T.; Januzzi, J.; Jankowska, E.A.; Khazanie, P.; Kinugawa, K.; Lam, C.S.P.; Matsue, Y.; Metra, M.; Ohtani, T.; Francesco Piepoli, M.; Ponikowski, P.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Sakata, Y.; SeferoviĆ, P.; Starling, R.C.; Teerlink, J.R.; Vardeny, O.; Yamamoto, K.; Yancy, C.; Zhang, J.; Zieroth, S. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: A report of the heart failure society of america, heart failure association of the european society of cardiology, japanese heart failure society and writing committee of the universal definition of heart failure. Journal of cardiac failure. 2021.
- Tsutsui, H.; Isobe, M.; Ito, H.; Okumura, K.; Ono, M.; Kitakaze, M.; Kinugawa, K.; Kihara, Y.; Goto, Y.; Komuro, I.; Saiki, Y.; Saito, Y.; Sakata, Y.; Sato, N.; Sawa, Y.; Shiose, A.; Shimizu, W.; Shimokawa, H.; Seino, Y.; Node, K.; Higo, T.; Hirayama, A.; Makaya, M.; Masuyama, T.; Murohara, T.; Momomura, S.I.; Yano, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Akiyama, M.; Anzai, T.; Ishihara, S.; Inomata, T.; Imamura, T.; Iwasaki, Y.K.; Ohtani, T.; Onishi, K.; Kasai, T.; Kato, M.; Kawai, M.; Kinugasa, Y.; Kinugawa, S.; Kuratani, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Tanaka, A.; Toda, K.; Noda, T.; Nochioka, K.; Hatano, M.; Hidaka, T.; Fujino, T.; Makita, S.; Yamaguchi, O.; Ikeda, U.; Kimura, T.; Kohsaka, S.; Kosuge, M.; Yamagishi, M.; Yamashina, A. Jcs 2017/jhfs 2017 guideline on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure- digest version. Circ. J. : Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2019, 83, 2084–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrouche, N.F.; Brachmann, J.; Andresen, D.; Siebels, J.; Boersma, L.; Jordaens, L.; Merkely, B.; Pokushalov, E.; Sanders, P.; Proff, J.; Schunkert, H.; Christ, H.; Vogt, J.; Bänsch, D. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation with heart failure. New Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaya, G.; Al-Khazaali, A.; Arora, R. Heart rate as a biomarker in heart failure: Role of heart rate lowering agents. American journal of therapeutics. 2017, 24, e532–e539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melenovsky, V.; Hay, I.; Fetics, B.J.; Borlaug, B.A.; Kramer, A.; Pastore, J.M.; Berger, R.; Kass, D.A. Functional impact of rate irregularity in patients with heart failure and atrial fibrillation receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozakowska-Kaplon, B.; Opolski, G. Atrial natriuretic peptide level after cardioversion of chronic atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2002, 83, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.F.; Jaïs, P.; Sanders, P.; Garrigue, S.; Hocini, M.; Sacher, F.; Takahashi, Y.; Rotter, M.; Pasquié, J.L.; Scavée, C.; Bordachar, P.; Clémenty, J.; Haïssaguerre, M. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in congestive heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.J.; Berriman, T.J.; Diab, I.; Kamdar, R.; Richmond, L.; Baker, V.; Goromonzi, F.; Sawhney, V.; Duncan, E.; Page, S.P.; Ullah, W.; Unsworth, B.; Mayet, J.; Dhinoja, M.; Earley, M.J.; Sporton, S.; Schilling, R.J. A randomized controlled trial of catheter ablation versus medical treatment of atrial fibrillation in heart failure (the camtaf trial). Circulation. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.G.; Shim, J.; Choi, J.I.; Kim, Y.H. Radiofrequency catheter ablation improves the quality of life measured with a short form-36 questionnaire in atrial fibrillation patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagishita, A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Sato, H.; Yamashita, S.; Hirao, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Hirao, K. Efficacy of catheter ablation and concomitant antiarrhythmic drugs on the reduction of the arrhythmia burden in patients with long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2017, 10, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamatani, Y.; Iguchi, M.; Ueno, K.; Aono, Y.; Esato, M.; Tsuji, H.; Wada, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Ogawa, H.; Abe, M.; Morita, S.; Akao, M. Prognostic significance of natriuretic peptide levels in atrial fibrillation without heart failure. Heart (Br. Card. Soc. ) 2021, 107, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.W.; Hsu, J.C.; Toomu, A.; Fox, S.; Maisel, A.S. Clinical applications of biomarkers in atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- York MK, Gupta DK, Reynolds CF, Farber-Eger E, Wells QS, Bachmann KN, Xu M, Harrell FE, Jr., Wang TJ. B-type natriuretic peptide levels and mortality in patients with and without heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2079–2088.
- Hussein, A.A.; Saliba, W.I.; Martin, D.O.; Shadman, M.; Kanj, M.; Bhargava, M.; Dresing, T.; Chung, M.; Callahan, T.; Baranowski, B.; Tchou, P.; Lindsay, B.D.; Natale, A.; Wazni, O.M. Plasma b-type natriuretic peptide levels and recurrent arrhythmia after successful ablation of lone atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2011, 123, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Champagne, J.; Sapp, J.; Essebag, V.; Novak, P.; Skanes, A.; Morillo, C.A.; Khaykin, Y.; Birnie, D. Discerning the incidence of symptomatic and asymptomatic episodes of atrial fibrillation before and after catheter ablation (discern af): A prospective, multicenter study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, M.R.; Lavelle, T.; Essebag, V.; Cohen, D.J.; Zimetbaum, P. Influence of age, sex, and atrial fibrillation recurrence on quality of life outcomes in a population of patients with new-onset atrial fibrillation: The fibrillation registry assessing costs, therapies, adverse events and lifestyle (fractal) study. Am. Heart J. 2006, 152, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, L.S.; Brodsky, M.; Schron, E.; Chung, M.; Rocco, T.; Jr Lader, E.; Constantine, M.; Sheppard, R.; Holmes, D.; Mateski, D.; Floden, L.; Prasun, M.; Greene, H.L.; Shemanski, L. Quality of life in atrial fibrillation: The atrial fibrillation follow-up investigation of rhythm management (affirm) study. Am. Heart J. 2005, 149, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, S.; Inden, Y.; Fujii, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Tomomatsu, T.; Mamiya, K.; Okamoto, H.; Murohara, T.; Shibata, R. Early improvement of daily physical activity after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in an accelerometer assessment: A prospective pilot study. Annals of noninvasive electrocardiology : The official journal of the International Society for Holter and Noninvasive Electrocardiology, Inc. 2021;26:e12807.
- Ezzat, V.A.; Chew, A.; McCready, J.W.; Lambiase, P.D.; Chow, A.W.; Lowe, M.D.; Rowland, E.; Segal, O.R. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation-patient satisfaction from a single-center uk experience. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. : Int. J. Arrhythm. Pacing 2013, 37, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charitakis, E.; Barmano, N.; Walfridsson, U.; Walfridsson, H. Factors predicting arrhythmia-related symptoms and health-related quality of life in patients referred for radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation: An observational study (the smurf study). JACC. Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).