Submitted:
18 December 2023
Posted:
20 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
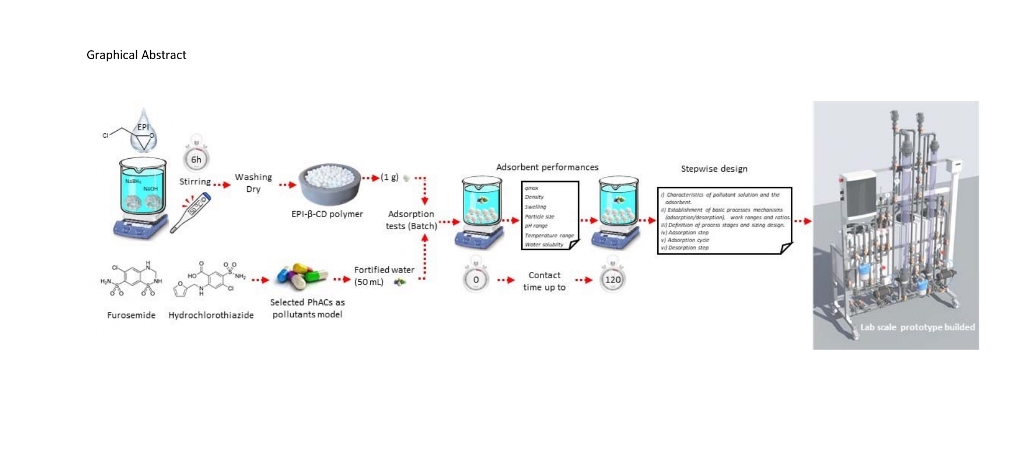
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and discussion
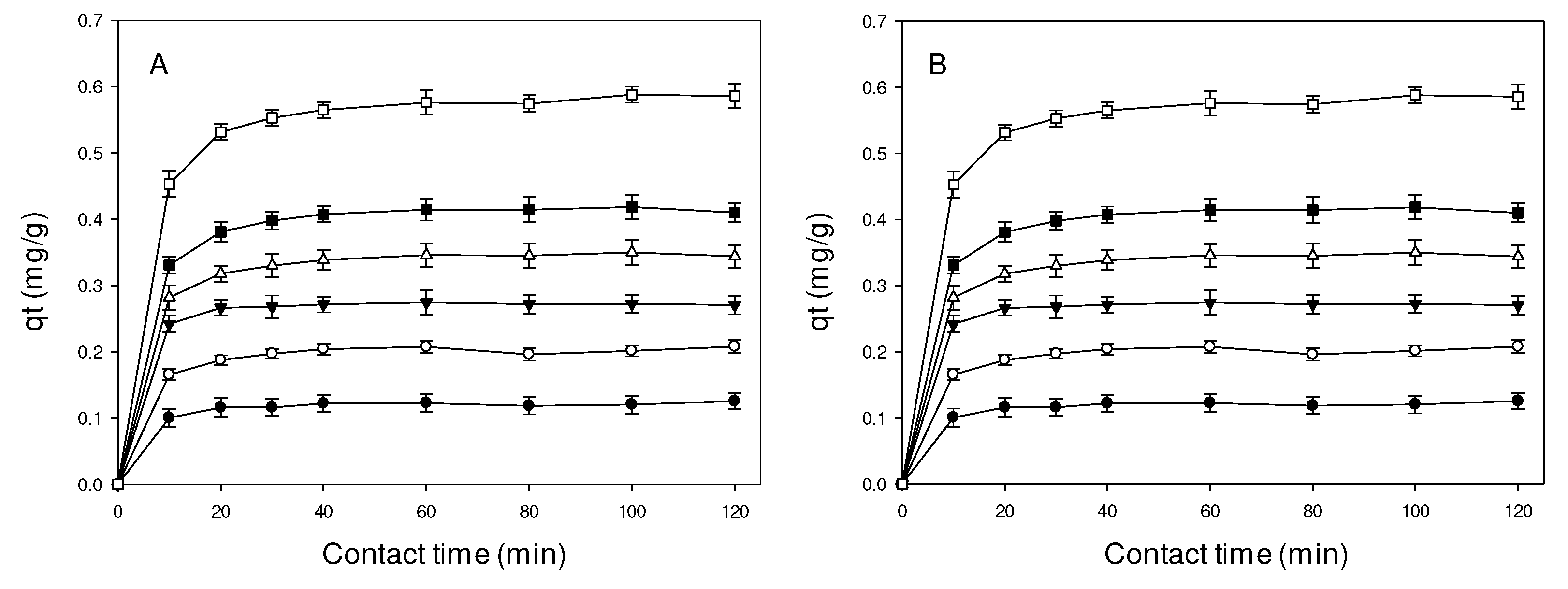
2.1. Effect contact time
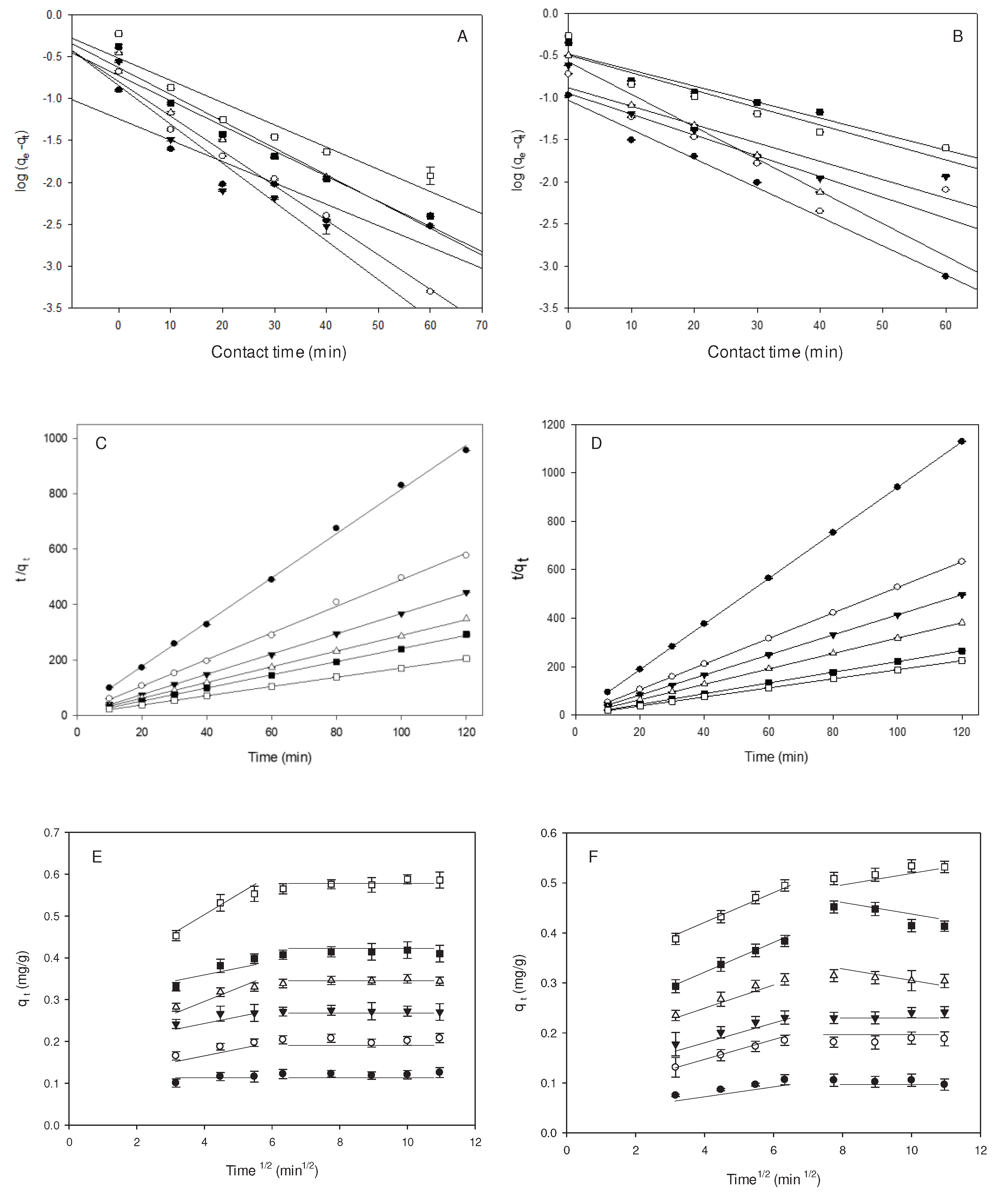
2.2. Kinetic Analysis
2.3. Adsorption equilibrium
| Isotherm | Parameter | Furosemide | Hydrochlorothiazide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | KF (L/g) | 0.044 | 0.029 |
| nF | 0.817 | 0.737 | |
| R2 | 0.991 | 0.905 | |
| Langmuir | qmax(mg/g) | 1.282 | 0.844 |
| KL | 0.050 | 0.038 | |
| aL | 0.039 | 0.045 | |
| ∆G | -16919.810 | -16730.651 | |
| R2 | 0.516 | 0.514 | |
| RL | 0.838-0.564 | 0.817-0.527 | |
| Tempkin | aT | 0.525 | 0.448 |
| bT (kJ/mol) | 6.890 | 6.79 | |
| R2 | 0.943 | 0.872 |
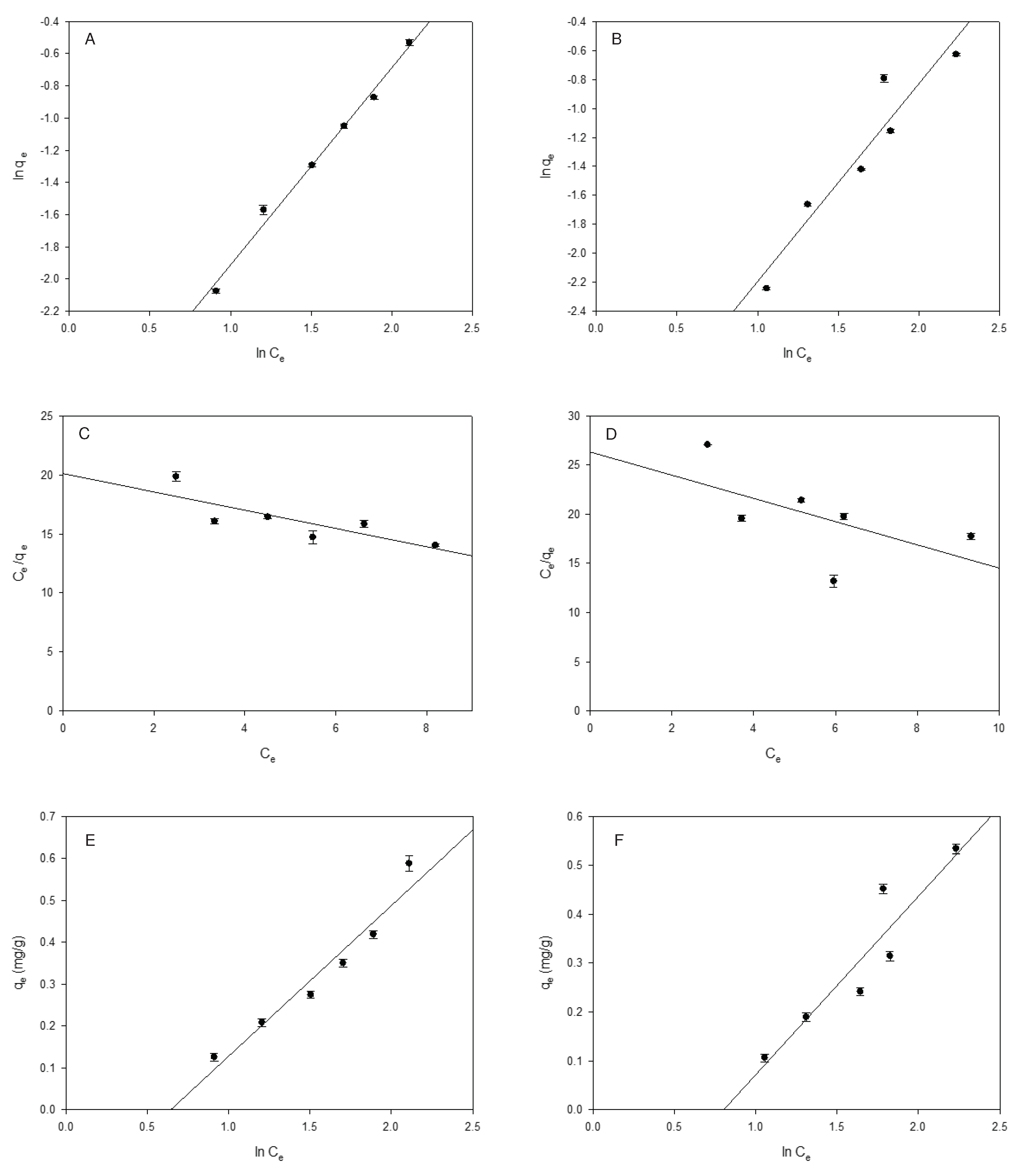
2.4. Thermodynamic parameters
2.5. Polymer reusability
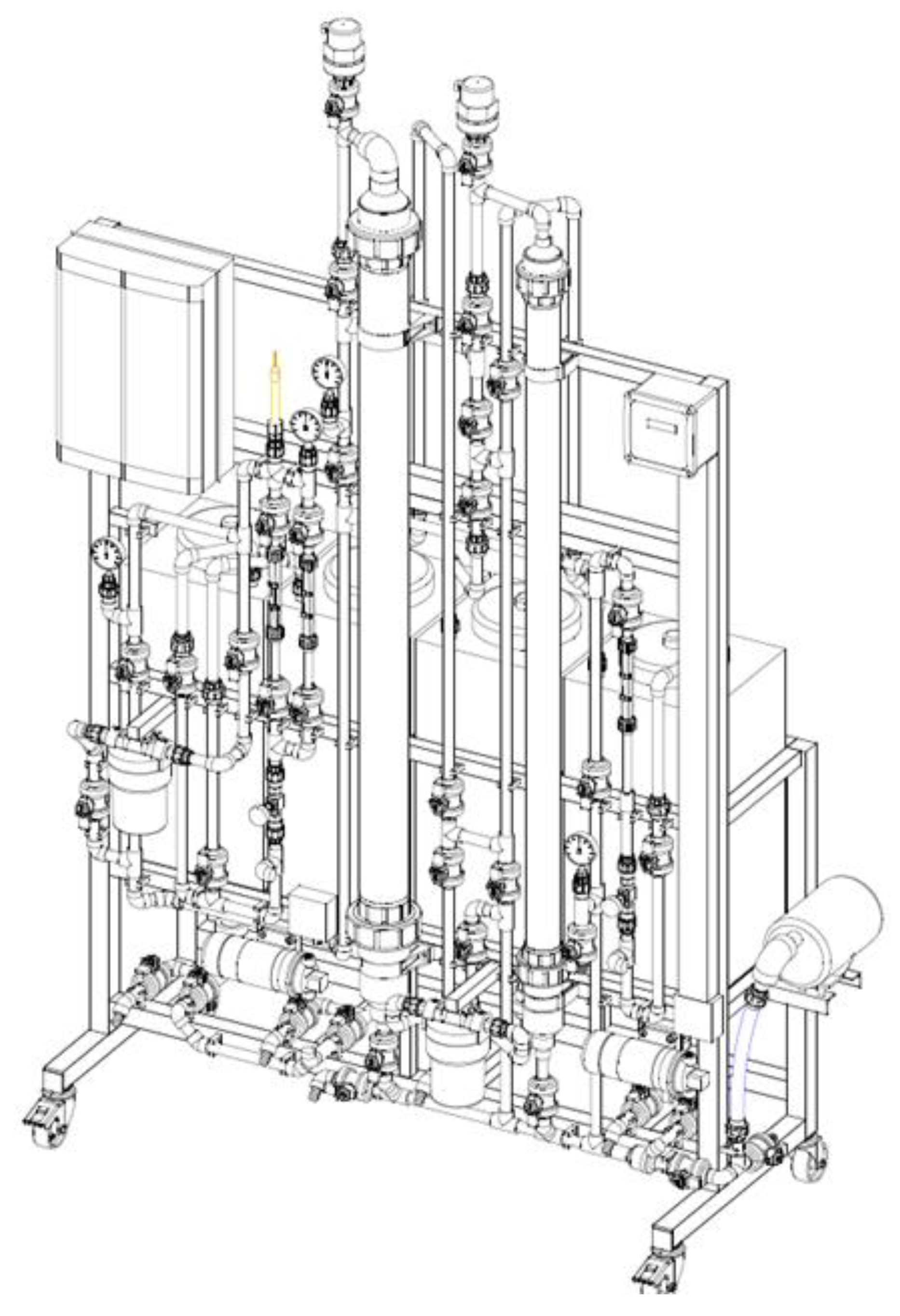
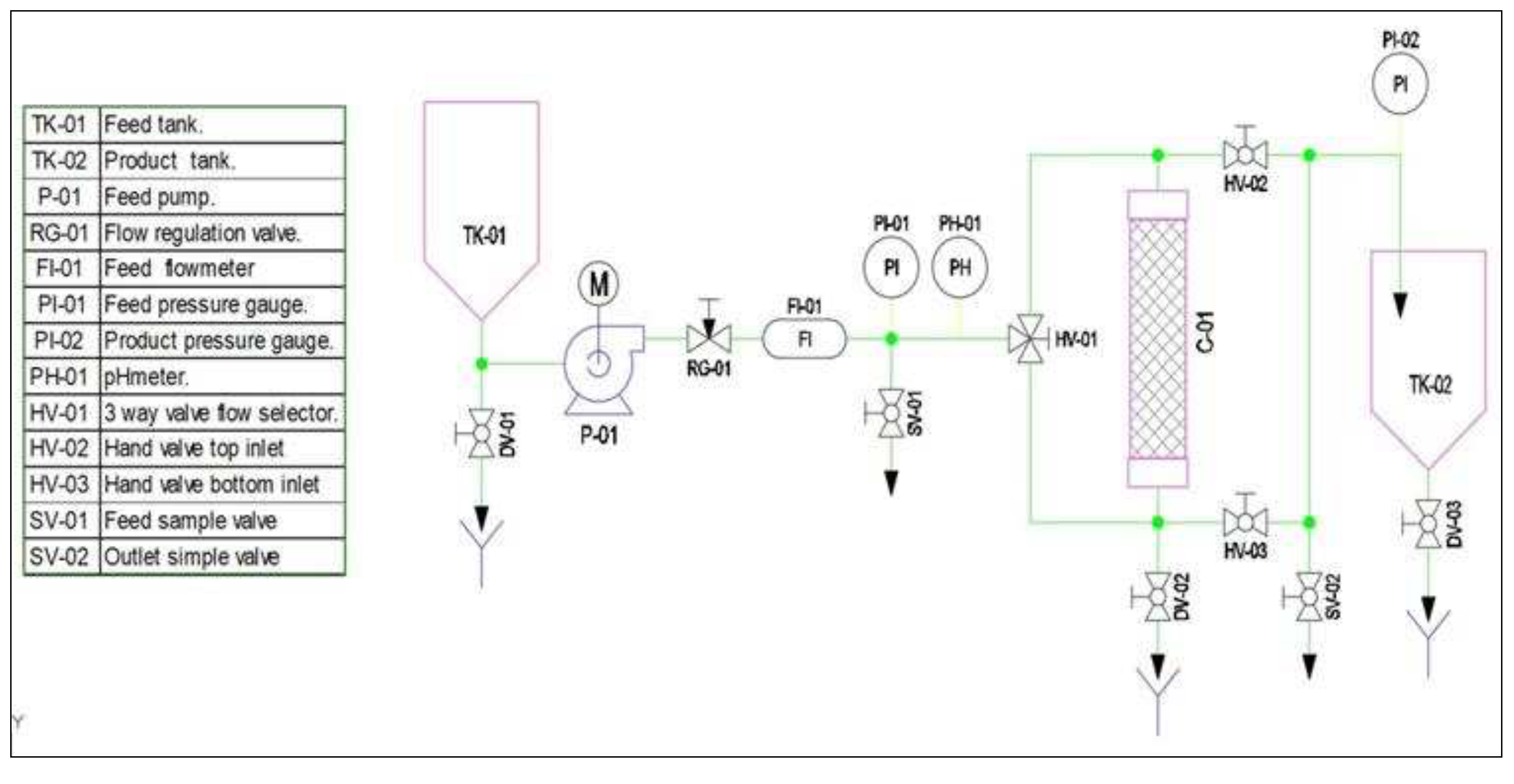
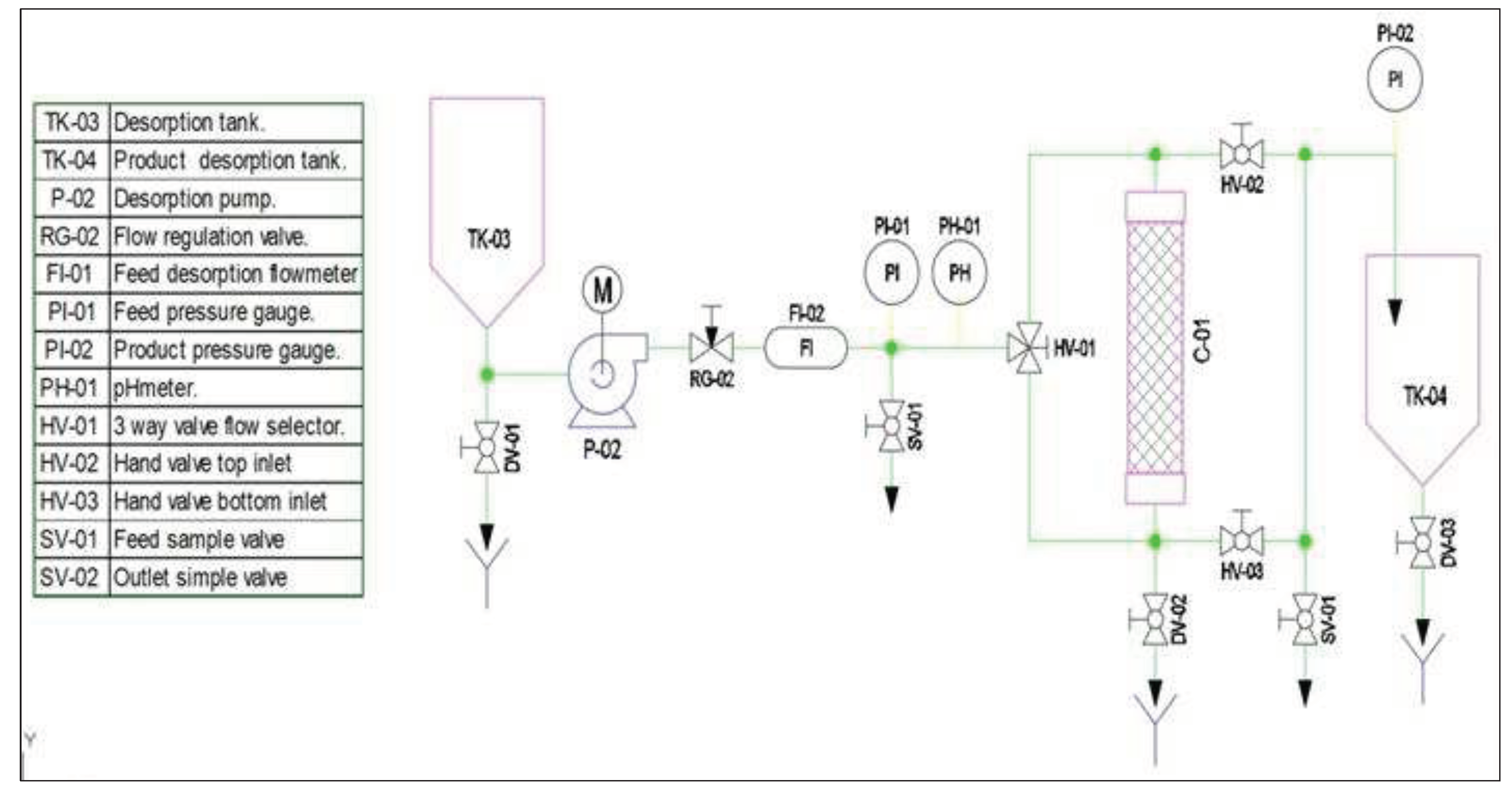
2.6. Design continuous flow Prototype Adsorption
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| qmax (furosemide) (mg/g) | 1.282 |
| qmax (hydrochlorothiazide) (mg/g) | 0.844 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.06 |
| Swelling | 4 ± 1 |
| Particle size (mm) | 0.1→0.3 |
| Stability range (pH) | 2→11 |
| Temperature range (ºC) | 5→35 |
| Solubilty in H2O | Insoluble |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Adsorbent Volume (L) | 1→3 |
| Column diameter | To define |
| Adsorbent bed depth (mm) | 150→550 |
| Adsorbent expansion (%) | Up to 100 |
| Contact time (min) | 1→7.5 |
| Loading flow rate (BV/h) | 8→40 |
| Desorbent flow rate (BV/h) | 2→5 |
| Desorbent contact time (min) | 20→60 |
| Desorbent displacement (BV of water) | 2→4 |
| Final rinse (BV service flow rate) | 2→10 |
| Column size design calculations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Ø90 mm | Ø63 mm | ||
| Flow (L/h) | 8 | 40 | 8 | 40 |
| Flow rate (m/h) | 1.43 | 7.17 | 3.10 | 15.51 |
| Ad volume (L) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| BV (BV/h) | 8 | 40 | 8 | 40 |
| Area (m²) | 0.0056 | 0.0056 | 0.0026 | 0.0026 |
| Bed depth (m) | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| Expansion (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Column height (m) | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.78 | 0.78 |
| Contact time (min) | 7.5 | 1.5 | 7.5 | 1.5 |
| Flow (L/h) | 16 | 80 | 16 | 80 |
| Flow rate (m/h) | 2.87 | 14.33 | 6.20 | 31.02 |
| Ad volume (L) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| BV (BV/h) | 8 | 40 | 8 | 40 |
| Area (m²) | 0.0056 | 0.0056 | 0.0026 | 0.0026 |
| Bed depth (m) | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.78 | 0.78 |
| Expansion (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Column height (m) | 0.72 | 0.72 | 1.55 | 1.55 |
| Contact time (min) | 7.5 | 1.5 | 7.5 | 1.5 |
| Flow (L/h) | 24 | 120 | 24 | 120 |
| Flow rate (m/h) | 4.30 | 21.50 | 9.31 | 46.54 |
| Ad volume (L) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| BV (BV/h) | 8 | 40 | 8 | 40 |
| Area (m²) | 0.0056 | 0.0056 | 0.0026 | 0.0026 |
| Bed depth (m) | 0.54 | 0.54 | 1.16 | 1.16 |
| Expansion (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Column height (m) | 1.07 | 1.07 | 2.33 | 2.33 |
| Contact time (min) | 7.5 | 1.5 | 7.5 | 1.5 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| PhACs concentration (mg/L) | 5→20 |
| Tank volume of PhACs solution (L) | 50 |
| Amount PhACs concentration (mg) | 250→1000 |
| β-CDs-EPI qmax (furosemide) (mg/g) | 1.282 |
| β-CDs-EPI qmax (hydrochlorothiazide) (mg/g) | 0.844 |
| β-CDs-EPI volume (L) | 1→3 |
| β-CDs-EPI weight (g/column) | 1,060→3,180 |
| Amount β-CDs-EPI qmax (furosemide) (mg) | 1,358→3,846 |
| Amount β-CDs-EPI qmax (hydrochlorothiazide) (mg) | 894→2,683 |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and reagents
3.2. Epichlorohydrin-β-cyclodextrin polymer preparation
3.3. Diuretics solution preparation
3.4. Adsorption experiments
3.5. Kinetics analysis
3.6. Isotherms analysis
3.8. Polymer reusability
3.9. Design of a pilot-scale prototype cyclodextrin polymer adsorption of pollutants
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Gosling, S.N.; Kummu, M.; Flörke, M.; Pfister, S.; et al. Water scarcity assessments in the past, present, and future. Earth’s Future. 2017, 5, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Fang, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Future global urban water scarcity and potential solutions. Nature Communications. 2021, 12, 4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Parliament. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Communities 2000, 327, 1–72. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2000/60/oj.
- European Commission. Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 August 2013 amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as regards priority substances in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Community 2013, 1–17. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2013:226:0001:0017:en:PDF.
- World Health Organization. State of the World’s Sanitation: An Urgent Call to Transform Sanitation for Better Health, Environments, Economies and Societies. New York (NY): United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) and the World Health Organization. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240014473.
- Lopez-Pacheco, I.Y.; Silva-Nunez, A.; Salinas-Salazar, C.; Arevalo-Gallegos, A.; Lizarazo-Holguin, L.A.; Barcelo, D.; et al. Anthropogenic contaminants of high concern: Existence in water resources and their adverse effects. Science of the Total Environment. 2019, 690, 1068–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauve, S.; Desrosiers, M. A review of what is an emerging contaminant. Chemistry Central Journal. 2014, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, B.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Research. 2015, 7, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissen, V.; Mol, H.; Klumpp, E.; Umlauf, G.; Nadal van der Ploeg, M.; et al. Emerging pollutants in the environment: A challenge for water resource management. International Soil Water Conservation Research. 2015, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991 concerning urban waste-water treatment. Official Journal of the European Communities 1991. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:31991L0271.
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environmental Chemistry Letters. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudri, B.S.; Al-Awadhi, T.; Charabi, Y.; Al-Nasiri, N. Wastewater treatment, reuse, and disposal-associated effects on environment and health. Water Environment Research. 2020, 92, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Farjadfard, S.; Esmaeili, H.; Saberi, M.; Sahebi, S.; Dobaradaran, S.; Ramavandi, B. Characteristics and performance of Cd, Ni, and Pb bio-adsorption using Callinectes sapidus biomass: real wastewater treatment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2019, 26, 6336–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhri, V.; Jafari, A.; Vahed, F.L.; Su, C.H.; Pirouzfar, V. Polysaccharides as eco-friendly bio-adsorbents for wastewater remediation: Current state and future perspective. Journal of Water Process Engineering. 2023, 54, 103980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia-Salvador, A.; Pellicer, J.A.; Fortea, M.I.; Gómez-López, V.M.; Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Gabaldón, J.A. Adsorption of Direct Blue 78 using chitosan and cyclodextrins as adsorbents. Polymers 2019, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchêne, D.; Bochot, A. Thitry years with cyclodextrins. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2016, 514, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G. Review: a history of cyclodextrins. Chemical Reviews. 2014, 114, 10940–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansook, P.; Ogawa, N.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins: structure, physicochemical properties and pharmaceutical applications. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2018, 535, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Louzao, R.; Lucas-Abellán, C.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; Cerón-Carrasco, J.P.; Gabaldón, J.A.; López-Miranda, S.; Yañez-Gascón, M.J.; Asín-Lorca, M.; Núñez-Delicado, E. Encapsulation of finasteride with native and modified γ-cyclodextrins. Extensive characterization of the complexes. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2020, 587, 119619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Hua, S.; Tian, Y.; Jiayue, L. Cyclodextrin-based adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from wastewater: a review. Environmental Science and Polutation Research. 2021, 28, 1317–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G. Cyclodextrin–epichlorohydrin polymers synthesis, characterization and applications to wastewater treatment: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Crini, G. Environmental applications of water-insoluble β-cyclodextrin–epichlorohydrin polymers. Progress in Polymer Science. 2013, 38, 344–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Repo, E.; Yin, D.; Chen, L.; Kalliola, S.; Tang, J.; Iakovleva, E.; Tam, C.K.; Sillanpää, M. One-pot synthesis of trifunctional chitosan-EDTA-β-cyclodextrin polymer for simultaneous removal of metals and organic micropollutants. Scientific Reports. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpkird, T.; Manaprasertsak, A.; Penkitti, A.; Sinthuvanich, C.; Singchuwong, T.; Leepasert, T. A novel chitosan-citric acid crosslinked beta-cyclodextrin nanocarriers for insoluble drug delivery. Carbohydrate Research. 2020, 498, 108184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Nasir, M. Effective removal of acetaminophen from aqueous solution using Ca (II)-doped chitosan/β-cyclodextrin composite. Journal of Molecular Liquids. 2020, 301, 112454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsbaiee, A.; Smith, B.J.; Xiao, L.; Ling, Y.; Helbling, D.E.; Dichtel, W.R. Rapid removal of organic micropollutants from water by a porous β-cyclodextrin polymer. Nature 2016, 529, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, V.; Gubitosa, J.; Signorile, R.; Fini, P.; Cecone, C.; Matencio, A.; Trotta, F.; Cosma, P. Cyclodextrin nanosponges as adsorbent material to remove hazardous pollutants from water: The case of ciprofloxacin. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2021, 411, 128514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Long, F.; Pan, X. A versatile β-cyclodextrin and polyethyleneimine bi-functionalized magnetic nanoadsorbent for simultaneous capture of methyl orange and Pb (II) from complex wastewater. Chemosphere. 2019, 216, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Jakariya, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Kurasaki, M.; Saito, T. Remediation of water pollution with native cyclodextrins and modified cyclodextrins: A comparative overview and perspectives. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2019, 355, 920–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.S.; Selvarajan, E.; Subramaniam, K.; Mathimani, T.; Seethappan, S.; Pugazhendhi, A. Synthesized β-cyclodextrin modified graphene oxide (β-CD-GO) composite for adsorption of cadmium and their toxicity profile in cervical cancer (HeLa) cell lines. Process Biochemistry. 2020, 93, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeraro, P.; Gabaldón, J.; Fini, P.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Pellicer, J.A.; Rizzi, V.; Cosma, P. Removal of an azo textile dye from wastewater by cyclodextrin-epichlorohydrin polymers; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; Volume 303. [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer, J.A.; Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Fortea, M.I.; Hernández, J.A.; Lucas-Abellán, C.; Mercader-Ros, M.T.; Serrano-Martínez, A.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Cosma, P.; Fini, P.; Franco, E. Removing of Direct Red 83: 1 using α-and HP-α-CDs polymerized with epichlorohydrin: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Dyes and Pigments. 2018, 149, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Yu, H.; Xie, W. A versatile β-cyclodextrin functionalized silver nanoparticle monolayer for capture of methyl orange from complex wastewater. Chinese Chemical Letters. 2020, 31, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romita, R.; Rizzi, V.; Semeraro, P.; Gubitosa, J.; Gabaldón, J.A.; Gorbe MI, F.; Gómez, V.M.; Cosma, P.; Fini, P. Operational parameters affecting the atrazine removal from water by using cyclodextrin based polymers as efficient adsorbents for cleaner technologies. Environmental Technology & Innovation. 2019, 16, 100454. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Li, L.; Xu, D.; Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Metal–organic framework preparation using magnetic graphene oxide–β-cyclodextrin for neonicotinoid pesticide adsorption and removal. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2017, 175, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Cai, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Adsorption mechanism-based screening of cyclodextrin polymers for adsorption and separation of pesticides from water. Water Research. 2011, 45, 3499–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Morte, T.; Gómez-López, V.M.; Lucas-Abellán, C.; Martínez-Alcalá, I.; Ayuso, M.; Martínez-López, S.; Montemuro, N.; Pérez, S.; Barceló, D.; Fini p Cosma, P.; Cerón, J.P.; Forte, M.I.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Gabaldón, J.A. Removal and toxicity evaluation of a diverse group of drugs from water by a cyclodextrin polymer/pulsed light system. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2021, 402, 123504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenyvesi, É.; Barkács, K.; Gruiz, K.; Varga, E.; Kenyeres, I.; Záray, G.; Szente, L. Removal of hazardous micropollutants from treated wastewater using cyclodextrin bead polymer–A pilot demonstration case. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2020, 383, 121181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzeri, G.; Matias, P.M.; Murtinho, D.; Valente, A.J. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: Overview and opportunities. Frontiers in Chemistry. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicer, J.; Rodríguez-López, M.; Fortea, M.; Lucas-Abellán, C.; Mercader-Ros, M.; López-Miranda, S.; Gómez-López, V.; Semeraro, P.; Cosma, P.; Fini, P.; et al. Adsorption Properties of β- and Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrins Cross-Linked with Epichlorohydrin in Aqueous Solution. A Sustainable Recycling Strategy in Textile Dyeing Process. Polymers 2019, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Winterton, P.; Fourmentin, S.; Wilson, L.D.; Fenyvesi, E.; Crini, G. Water-insoluble β-cyclodextrin–epichlorohydrin polymers for removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions by sorption processes using batch studies: A review of inclusion mechanisms. Progress in Polymer Science. 2018, 78, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemine, K.; Łukasik, N.; Gazda, M.; Nowak, I. β-cyclodextrin-containing polymer based on renewable cellulose resources for effective removal of ionic and non-ionic toxic organic pollutants from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2021, 2021 418, 126286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Gimbert, F.; Robert, C.; Martel, B.; Adam, O.; Morin-Crini, N.; De Giorgi, F.; Badot, P.-M. The Removal of Basic Blue 3 from Aqueous Solutions by Chitosan-Based Adsorbent: Batch Studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2008, 153, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Asthana, A.; Singh, A.K.; Chakraborty, R.; Vidya, S.S.; Susan MA, B.H.; Carabineiro, S.A. Adsorption of cationic dyes, drugs and metal from aqueous solutions using a polymer composite of magnetic/β-cyclodextrin/activated charcoal/Na alginate: Isotherm, kinetics and regeneration studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2021, 409, 124840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.-T.; Shi, L.-Q.; Shen, H.; Chen, X.; Xie, K.-P. Equilibrium, Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies for Removal of Tetracycline Antibiotics by Adsorption onto Hazelnut Shell Derived Activated Carbons from Aqueous Media. RSC Advances. 2016, 6, 109983–109991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.J.; Wang, J.S.; Liu, Y.G.; Li, X.; Zeng, G.M.; Bao, Z.L.; Zeng, X.-X.; Chen, A.W.; Long, F. Adsorption of chromium (VI) by ethylenediamine-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan resin: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2011, 185, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, X. The Unit Problem in the Thermodynamic Calculation of Adsorption Using the Langmuir Equation. Chemical Engineering Communications. 2014, 201, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia-Salvador, A.; Pellicer, J.A.; Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Gómez-López, V.M.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Gabaldón, J.A. Egg By-Products as a Tool to Remove Direct Blue 78 Dye from Wastewater: Kinetic, Equilibrium Modeling, Thermodynamics and Desorption Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G.; Peindy, H.N.; Gimbert, F.; Robert, C. Removal of CI Basic Green 4 (Malachite Green) from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption Using Cyclodextrin-Based Adsorbent: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Separation and Purification Technology. 2007, 53, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie Der Sogenannten Adsorption Geloster Stoffe. K. Sven. Vetensk. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. Kinetic Models for the Sorption of Dye from Aqueous Solution by Wood. Process Safety and Environmental Protection. 1998, 76, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-S. Review of Second-Order Models for Adsorption Systems. ChemInform. 2006, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.J., Jr.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. Journal of the Sanitary Engineering Division. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the Adsorption in Solution. Journal of Physical Chemistry. 1906, 57, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The Constitution and Fundamental Properties of Solids and Liquids. Part I. Solids. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.I. Kinetics of Ammonia Synthesis on Promoted Iron Catalysts. Acta Physiochimica. URSS 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Pellicer, J.A.; Gómez-Morte, T.; Auñón, D.; Gómez-López, V.M.; Yáñez-Gascón, M.J.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á.; Cerón-Carrasco, J.P.; Crini, G.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Gabaldón, J.A. Removal of an azo dye from wastewater through the use of two technologies: Magnetic cyclodextrin polymers and pulsed light. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022, 23, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





