Submitted:
12 December 2023
Posted:
13 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. An Overview of GK and GKAs
3. Dorzagliatin (also known as Sinogliatin, HMS-5552 or RO-5305552)
3.1. Dorzagliatin: Mechanisms of Action
3.2. Dorzagliatin: Pre-Clinical Studies
3.3. Dorzagliatin: Clinical Studies
| Pre-Clinical Studies | |||||
| Reference | Animal | Duration (weeks) | Interventions | Primary findings | |
| 2017, Wang et al. [1] | Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats with T2DM | 4 | Control, diabetic, 10mg/kg, 30mg/kg | Reduction in FPG by ∼18% (10mg/kg) and 23% (30mg/kg) Reduction in FINS: 28.40 mU/L (10mg/kg) and 18.74 mU/L (30mg/kg) Levels of TC and TG unchanged Increase in FG: 43 pg/ml (10mg/kg) and 51 pg/ml (30mg/kg) Reduction in OGTT: 9 mmol/L (10mg/kg) and 7 mmol/L (30mg/kg) compared to diabetic rats Increased expression of GK-immuno-positive cells and insulin (Western blot) |
|
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Reference | Total Participants (N) | Duration (weeks) | Study design | Interventions | Primary findings |
| 2016, Xu et al. [52] | 60 (31 M, 29 F) | XXX | Phase Ia: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, administered to healthy subjects | Six dose-cohorts (5, 10, 15, 25, 35, and 50 mg), 10 randomized subjects (8 receiving HMS5552 and 2 receiving placebo) | HMS5552 at doses up to 50 mg in healthy subjects is safe and well-tolerated Dose-related glucose-lowering effects and post-prandial insulin secretion AE: belching, dizziness, palpitation, cold sweat, and proteinuria No Hypoglycemia |
| 2018, Zhu et al. [55] | 24 (17 M, 7 F) | 4 | T2DM patients randomized at 1:1 ratio to receive two concentrations of dorzagliatin | 75 mg QD, 75 mg BID | Overall, QD treatment was better than BID Decrease in HBA1c , FPG and PPG Increase in C-peptide Reduction in AUC Increase in HOMA2 parameter %B Increase in the dynamic state parameter ΔC30 /ΔG30 Hypoglycemia: 17% |
| 2018, Zhu et al. [50,56] | 258 (154 M, 104 F) | 12 | Phase II: Multicenter, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled T2DM patients on were on a diet and exercise regimen; drug naïve or previously treated with Metformin or α-glucosidase inhibitor monotherapy |
75 or 100 mg QD, 50 or 75 mg BID, Placebo | Decrease in HbA1c, FPG and PPG particularly in patients received 100 QD or 75 BID AE: URTi, hyperuricemia, dizziness Hypoglycemia 6% in all studied groups |
| 2020-2022, Zhu et al. (SEED trial) [57,58] | 463 (301 M, 162 F) | 52 | Phase III: Multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled (24 weeks), open-label (28 weeks) study T2DM drug naïve patients |
75 mg BID, Placebo | Decrease in HbA1c and FPG at week 24, sustain through week 52 Increase in HOMA2-β AE: URTi, hyperlipidemia, proteinuria, abnormal hepatic function, hypertension Hypoglycemia 0.3% in all studied groups |
| 2022, Yang et al. (DAWN trial) [59] | 767 (475 M, 292 F) | 52 | Phase III: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled (24 weeks), open-label (28 weeks) study T2DM add-on therapy to metformin |
75 mg BID, Placebo, Add on metformin 1500 mg | Decrease in HbA1c < 7% in 44.4% patients at week 24 Decrease in FPG and HOMA2-IR Increase in HOMA2-β Hypoglycemia 0.3%, no weight gain in all studied groups |
| 2022, Miao et al. [60] | 17 (7 M, 10 F) | ½ | Open-label, single-dose, sequential two-part, parallel-group Study 8 Non-dialysis ESRD, including 1 T2DM; 9 Healthy volunteers |
25 mg QD | End-stage renal insufficiency does not affect dorzagliatin efficacy. Dorzagliatin absorption is rapid peak plasma concentration (Cmax) 1.25–2.5 hr post dose Dorzagliatin elimination half-life (t1/2) for dorzagliatin is 4.5–8.6 hr |
| 2023, Chow et al. [61] | 18 (6 M, 12 F) | 2 | Phase II: Randomized, double-blind, cross-over study 8 GCK-MODY; 10 T2DM |
Single dose First group: 75 mg dorzagliatin (first visit), placebo (second visit) Second group: Placebo (first visit), 75mg dorzagliatin (second visit) |
GCK-MODY, dorzagliatin significantly increased absolute and incremental second phase ISRs Dorzagliatin improves β-cell glucose sensitivity in GCK-MODY Dorzagliatin increases basal Prehepatic insulin secretion rates in T2DM Dorzagliatin restores GK enzymatic activity |
| 2023, Zeng et al. [62] (DREAM, longitudinal SEED study) | 69 (48 M, 21 F) | 52 | Phase III: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled (24 weeks), open-label (28 weeks) stud Patients who completed the SEED trial (56), who achieved stable glycemic control with potential to sustain drug-free remission Glycemic control status was assessed at weeks 0, 12, 26, 39 and 52. |
T2DM remission, glycemic control status was assessed at weeks 0, 12, 26, 39 and 52. | Dorzagliatin leads to stable glycemic control and drug-free remission in drug-naïve patients with T2DM Dorzagliatin sustains HbA1c and FPG levels and glucose homeostasis Dorzagliatin maintains the steady-state β-cell function and insulin resistance |
| 2023, Chen et al, [63] | 15 | 2 | Phase I: open-label, single-sequence, multiple-dose, single-center Dorzagliatin + Sitagliptin in obese T2DM patients |
Day 1-5: Sitagliptin 100 mg QD on Day 1-5 Day 6-10: Sitagliptin 100 mg QD and dorzagliatin 75 mg BID Day 11-15: dorzagliatin 75 mg BID alone |
Combination treatment did not increase AE and well-tolerated in T2DM No pharmacokinetic interactions between dorzagliatin and sitagliptin Improvement of glycemic control under combination conditions |
4. TTP399 (Also known as Cadisegliatin)
4.1. TTP399: Mechanisms of Action
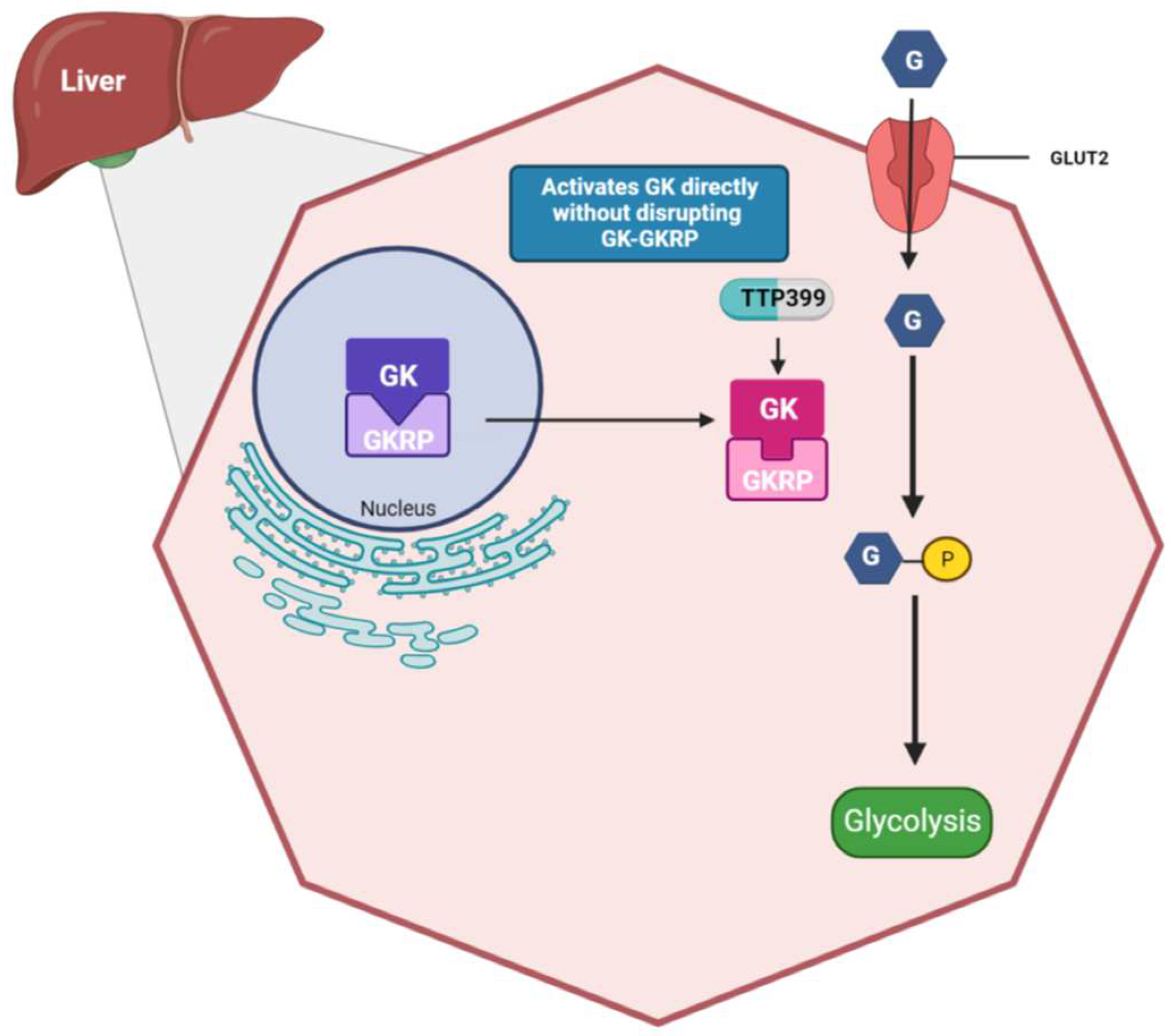
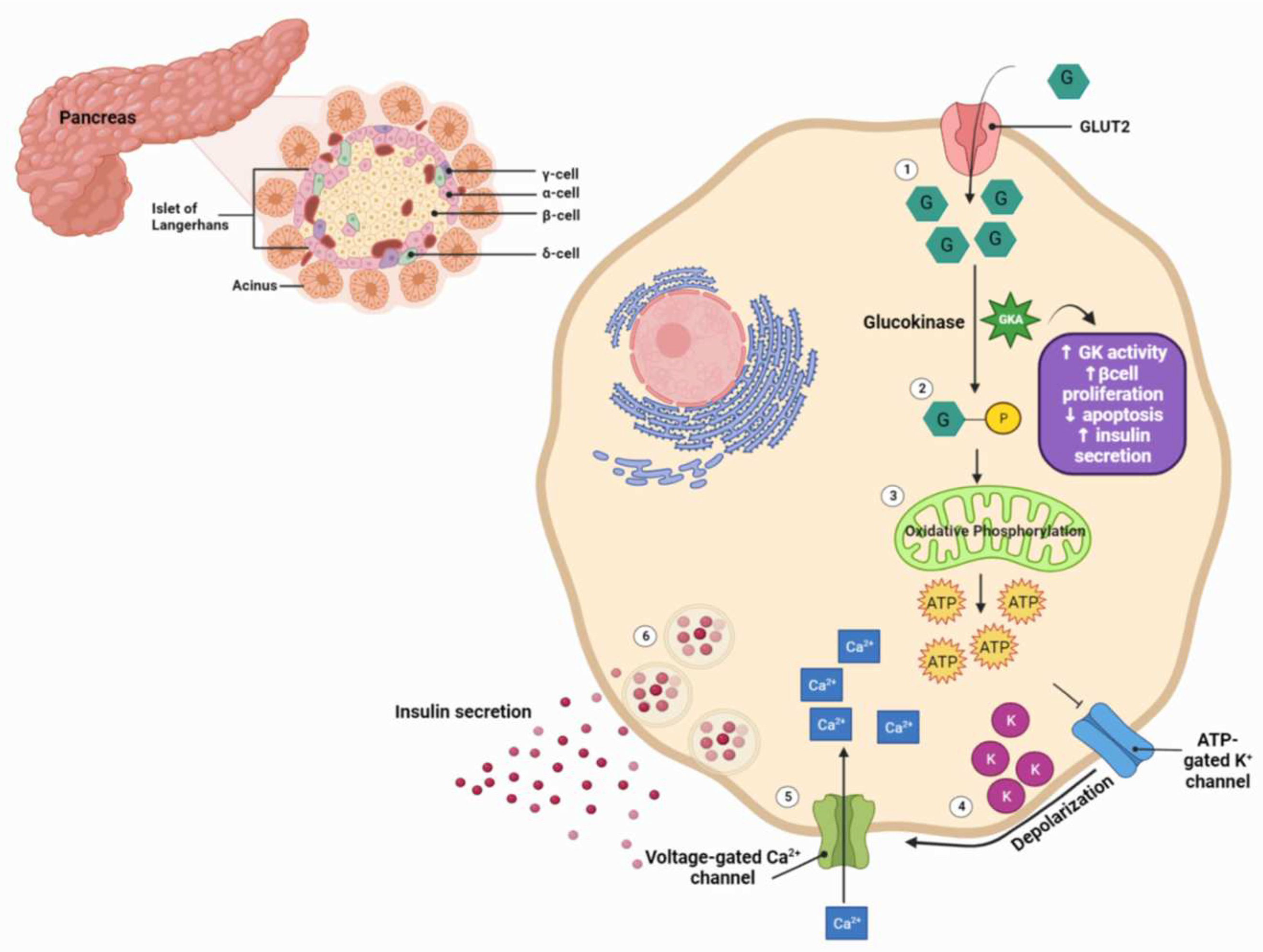
4.2. TTP399: Pre-Clinical Studies
4.3. TTP399: Clinical Studies
| Pre-Clinical Studies | |||||
| Reference | Animal | Duration (Weeks) | Interventions | Primary findings | |
| 2019, Vella et al. (AGATA trial) [51] | Umea ob/ob mice with T2DM | 4 | 75, 150 mg/kg | Reduction in HbA1c from baseline (week 4) 0.76 ± 0.14% (75 mg/kg); 1.23 ± 0.28% (150 mg/kg) Lower blood glucose Reduced weight gain 0.5 g with 150 mg/kg per day Reduced TG concentrations |
|
| 2019, Vella et al. (AGATA trial) [51] | Gottingen minipigs with T2DM | 13 | 50 mg/kg ± Add on Metformin 500 mg BID | Reduced plasma glucose levels | |
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Reference | Total Participants (N) | Duration (Weeks) | Study design | Interventions | Primary findings |
| 2019, Vella et al. (AGATA trial) [51] | 190 (101 M, 89 F) T2DM |
24 | Phase II b, randomized, double-blind, placebo and active-controlled, parallel group | TTP399 400 mg QD TTP399 800 mg QD Sitagliptin 100 mg QD Placebo ± add-on Metformin |
Reduction in HbA1c from baseline Decrease in FG concentrations Increase in HDL-C Lower blood glucose No change in body weight, no hypoglycemia |
| 2021, Klein K.R. et al. (The Simplici-T1 trial) [66,67] | Part 1: 20 (7 M, 13 F) Part 2: 85 (47 M, 38 F) All T2DM |
12 | Phase 1b/2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Part 1: T1DM on insulin pump therapy and continuous glucose monitoring (CSII) Part 2: T1DM with a broader range of T1DM severity, multiple daily injections of insulin or CSII. |
TTP399 800 mg QD Placebo |
Reduction in HbA1c, Improved daytime TIR Reduced plasma β-hydroxybutyrate and urinary ketones No adverse events |
| 2022, Klein K.R. et al. [68] | 23 (10 M, 13 F) T1DM |
1-1 ½ | Phase 1, double-blinded, randomized, parallel-grouped, placebo-controlled multiple-dose study T1DM using insulin pump therapy |
IWT test, ketogenesis induction, TTP399 800 mg QD | Reduction in FPG Elevated Serum bicarbonate, lower urine acetoacetate No increase in BHB concentrations Reduction in the incidence of DKA during acute insulin withdrawal. |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Duan, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xi, S. Effects of a Novel Glucokinase Activator, HMS5552, on Glucose Metabolism in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of diabetes research 2017, 2017, 5812607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Cusi, K.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; et al. 4. Comprehensive Medical Evaluation and Assessment of Comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes care 2023, 46 (Suppl. 1), S49–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, A.D.; Harris-Hayes, M.; Schootman, M. Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetes-related complications. Physical therapy 2008, 88, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Samouda, H. Clinical and biological risk factors associated with inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Endocrine Disorders 2022, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, S.R.; Peyrot, M.; Oates, S.K.; Taylor, A.D. Hypoglycemia in patient with type 2 diabetes treated with insulin: it can happen. BMJ open diabetes research & care 2020, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Susilawati, E.; Levita, J.; Susilawati, Y.; Sumiwi, S.A. Review of the Case Reports on Metformin, Sulfonylurea, and Thiazolidinedione Therapies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Medical sciences (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Magno, L.; Di Pastena, F.; Bordone, R.; Coni, S.; Canettieri, G. The Mechanism of Action of Biguanides: New Answers to a Complex Question. Cancers 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebovitz, H.E. Thiazolidinediones: the Forgotten Diabetes Medications. Current Diabetes Reports 2019, 19, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasson, J.-L.; Josse, R.G.; Gomis, R.; Hanefeld, M.; Karasik, A.; Laakso, M. Acarbose for prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus: the STOP-NIDDM randomised trial. The Lancet 2002, 359, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minis, E.; Stanford, F.C.; Mahalingaiah, S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and safety in the preconception period. Current opinion in endocrinology, diabetes, and obesity 2023, 30, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J.; Nauck, M.A. The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. The Lancet 2006, 368, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccardi, F.; Webb, D.R.; Htike, Z.Z.; Youssef, D.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism 2016, 18, 783–794. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes A. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020. Diabetes care 2020, 43 (Suppl. 1), S98–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle-Delgado, K.; Chamberlain, J.J.; Shubrook, J.H.; Skolnik, N.; Trujillo, J. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Synopsis of the 2020 American Diabetes Association’s Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes Clinical Guideline. Ann Intern Med 2020, 173, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corathers, S.D.; Peavie, S.; Salehi, M. Complications of diabetes therapy. Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America 2013, 42, 947–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlas, D. International diabetes federation. In IDF Diabetes Atlas, 7th edn Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2015; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo, R.A. From the Triumvirate to the Ominous Octet: A New Paradigm for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 2009, 58, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajchenberg, B.L. β-Cell Failure in Diabetes and Preservation by Clinical Treatment. Endocrine Reviews 2007, 28, 187–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retnakaran, R.; Pu, J.; Emery, A.; Harris, S.B.; Reichert, S.M.; Gerstein, H.C.; McInnes, N.; Kramer, C.K.; Zinman, B. Determinants of sustained stabilization of beta-cell function following short-term insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes. Nature communications 2023, 14, 4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, J.; Ferré, P.; Foufelle, F. Mechanisms by which carbohydrates regulate expression of genes for glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes. Annual review of nutrition 1997, 17, 325–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschinsky, F.M. Regulation of Pancreatic β-Cell Glucokinase: From Basics to Therapeutics. Diabetes 2002, 51 (Suppl. 3), S394–S404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa Maheshvare, M.; Raha, S.; König, M.; Pal, D. A pathway model of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the pancreatic β-cell. Frontiers in endocrinology 2023, 14, 1185656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Marchand, S.J.; Piston, D.W. Glucose suppression of glucagon secretion: metabolic and calcium responses from α-cells in intact mouse pancreatic islets. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2010, 285, 14389–14398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.E.; Newgard, C.B. Mechanisms controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2021, 22, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakis, M.J.; Carlson, O.; Michopoulos, S.; Doyle, M.E.; Juhaszova, M.; Petraki, K.; Egan, J.M. Human duodenal enteroendocrine cells: source of both incretin peptides, GLP-1 and GIP. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2006, 290, E550–E559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matschinsky, F.M.; Wilson, D.F. The Central Role of Glucokinase in Glucose Homeostasis: A Perspective 50 Years After Demonstrating the Presence of the Enzyme in Islets of Langerhans. Front Physiol 2019, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn-Meynell, A.A.; Routh, V.H.; Kang, L.; Gaspers, L.; Levin, B.E. Glucokinase is the likely mediator of glucosensing in both glucose-excited and glucose-inhibited central neurons. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.S.; Kang, G.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, B.H.; Koo, S.H. Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Experimental & molecular medicine 2016, 48, e218. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, A.; Omori, K.; Terauchi, Y. Glucokinase activation or inactivation: Which will lead to the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Diabetes, obesity & metabolism 2021, 23, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Fu, H.; Kang, F.; Ning, G.; Ni, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q. β-Cell glucokinase expression was increased in type 2 diabetes subjects with better glycemic control. Journal of diabetes 2023, 15, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willms, B.; Ben-Ami, P.; Söling, H. Hepatic enzyme activities of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in diabetes of man and laboratory animals. Hormone and Metabolic Research 1970, 2, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, J.F.; Triester, S.; Patel, V.K.; Tapscott, E.B.; Frazier, N.L.; Dohm, G.L. Liver glucokinase: decreased activity in patients with type II diabetes. Hormone and metabolic research = Hormon- und Stoffwechselforschung = Hormones et metabolisme 1995, 27, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agius, L. Glucokinase and molecular aspects of liver glycogen metabolism. The Biochemical journal 2008, 414, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Schaftingen, E.; Veiga-da-Cunha, M.; Niculescu, L. The regulatory protein of glucokinase. Biochem Soc Trans 1997, 25, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.S.; Torres, T.P.; Catlin, R.L.; Donahue, E.P.; Shiota, M. A defect in glucose-induced dissociation of glucokinase from the regulatory protein in Zucker diabetic fatty rats in the early stage of diabetes. American journal of physiology Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2007, 292, R1381–R1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, V.A.; Arden, C.; Lange, A.J.; Agius, L. Contributions of glucokinase and phosphofructokinase-2/fructose bisphosphatase-2 to the elevated glycolysis in hepatocytes from Zucker fa/fa rats. American journal of physiology Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2007, 293, R618–R625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, K. Mutations in pancreatic ss-cell Glucokinase as a cause of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia and neonatal diabetes mellitus. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2010, 11, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakera, A.J.; Steele, A.M.; Gloyn, A.L.; Shepherd, M.H.; Shields, B.; Ellard, S.; Hattersley, A.T. Recognition and Management of Individuals With Hyperglycemia Because of a Heterozygous Glucokinase Mutation. Diabetes care 2015, 38, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osbak, K.K.; Colclough, K.; Saint-Martin, C.; Beer, N.L.; Bellanne-Chantelot, C.; Ellard, S.; Gloyn, A.L. Update on mutations in glucokinase (GCK), which cause maturity-onset diabetes of the young, permanent neonatal diabetes, and hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Hum Mutat 2009, 30, 1512–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antal, Z. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY): Genetic Causes, Clinical Characteristics, Considerations for Testing, and Treatment Options. Endocrines 2021, 2, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellard, S.; Thomas, K.; Edghill, E.L.; Owens, M.; Ambye, L.; Cropper, J.; Little, J.; Strachan, M.; Stride, A.; Ersoy, B.; et al. Partial and whole gene deletion mutations of the GCK and HNF1A genes in maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2313–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagen, J.V.; Bjørkhaug, L.; Molnes, J.; Ræder, H.; Grevle, L.; Søvik, O.; Molven, A.; Njølstad, P.R. Diagnostic screening of MODY2/GCK mutations in the Norwegian MODY Registry. Pediatric diabetes 2008, 9, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanik, J.; Dusatkova, P.; Cinek, O.; Valentinova, L.; Huckova, M.; Skopkova, M.; Dusatkova, L.; Stanikova, D.; Pura, M.; Klimes, I.; et al. De novo mutations of GCK, HNF1A and HNF4A may be more frequent in MODY than previously assumed. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agius, L. Targeting hepatic glucokinase in type 2 diabetes: weighing the benefits and risks. Diabetes 2009, 58, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J. New hope for glucokinase activators in type 2 diabetes? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018, 6, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, X. Glucokinase and glucokinase activator. Life Metabolism 2023, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschinsky, F.M. GKAs for diabetes therapy: why no clinically useful drug after two decades of trying? Trends in pharmacological sciences 2013, 34, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Terauchi, Y. Present status of clinical deployment of glucokinase activators. Journal of diabetes investigation 2015, 6, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. Investigational insulin secretagogues for type 2 diabetes. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 2016, 25, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Gan, S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Dong, X.; Song, W.; Zeng, J.; Wang, G.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Dorzagliatin monotherapy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: a dose-ranging, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018, 6, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, A.; Freeman, J.L.R.; Dunn, I.; Keller, K.; Buse, J.B.; Valcarce, C. Targeting hepatic glucokinase to treat diabetes with TTP399, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator. Sci Transl Med 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sheng, L.; Chen, W.; Yuan, F.; Yang, M.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Choi, J.; Zhao, G.; Hu, T.; et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of novel glucokinase activator HMS5552: results from a first-in-human single ascending dose study. Drug Des Devel Ther 2016, 10, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yao, C.; Shang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Meng, F. Insights into the binding of dorzagliatin with glucokinase: A molecular dynamics simulation. Journal of Theoretical and Computational Chemistry 2020, 19, 2050027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.; Li, C. Comparative docking assessment of glucokinase interactions with its allosteric activators. Current chemical genomics 2008, 2, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.X.; Zhu, D.L.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Jin, X.W.; Hu, T.X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.G.; Zhao, G.Y.; Ren, S.; et al. : Dorzagliatin (HMS5552), a novel dual-acting glucokinase activator, improves glycaemic control and pancreatic beta-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 28-day treatment study using biomarker-guided patient selection. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism 2018, 20, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, C.; Sr Tianxin, H.; Li, Y.-G.; Zhao, G.; Hou, X.; Sr Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Group, H.S. Pharmacodynamics Post-Hoc Analysis of Glucose Kinase Activator Dorzagliatin (HMS5552)—Twelve Weeks Treatment in T2D Patients in China. Diabetes 2018, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. 182-OR: a novel dual-acting glucokinase activator (GKA) dorzagliatin (HMS5552) achieved primary efficacy endpoint with good safety profiles in T2DM patients after 24 weeks of treatment in a phase III monotherapy trial. Diabetes 2020, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Zeng, J.; Gan, S.; Dong, X.; Yang, J.; Lin, X.; Cai, H.; Song, W.; et al. : Dorzagliatin in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Nature medicine 2022, 28, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhu, D.; Gan, S.; Dong, X.; Su, J.; Li, W.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, W.; Yao, M.; Song, W.; et al. Dorzagliatin add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Nature medicine 2022, 28, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Fu, P.; Ren, S.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, C.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, C.; Qian, Y.; et al. Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics and safety of dorzagliatin, a novel dual-acting glucokinase activator. Clin Transl Sci 2022, 15, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.; Wang, K.; Lim, C.K.P.; Tsoi, S.T.F.; Fan, B.; Poon, E.; Luk, A.O.Y.; Ma, R.C.W.; Ferrannini, E.; Mari, A.; et al. Dorzagliatin, a Dual-Acting Glucokinase Activator, Increases Insulin Secretion and Glucose Sensitivity in Glucokinase Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young and Recent-Onset Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2023, 72, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Gan, S.; Mi, N.; Liu, Y.; Su, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, F.; Dong, X.; Han, M.; et al. Diabetes remission in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes after dorzagliatin treatment: A prospective cohort study. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism 2023, 25, 2878–2887. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Fang, Z.; Feng, L.; He, B.; Zou, Q.; Tracey, G.J. A phase I open-label clinical trial to study drug-drug interactions of Dorzagliatin and Sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Nature communications 2023, 14, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, A.; Vella, A. TTP399: an investigational liver-selective glucokinase (GK) activator as a potential treatment for type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2019, 28, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebernitz, G.R.; Beaulieu, V.; Dale, B.A.; Deacon, R.; Duttaroy, A.; Gao, J.; Grondine, M.S.; Gupta, R.C.; Kakmak, M.; Kavana, M.; et al. Investigation of functionally liver selective glucokinase activators for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2009, 52, 6142–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.R.; Freeman, J.L.R.; Dunn, I.; Dvergsten, C.; Kirkman, M.S.; Buse, J.B.; Valcarce, C. Simplici Trg: The SimpliciT1 Study: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 1b/2 Adaptive Study of TTP399, a Hepatoselective Glucokinase Activator, for Adjunctive Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes care 2021, 44, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 56(th) EASD Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes: 21-25 September 2020. Diabetologia 2020, 63 (Suppl. 1), 1–485. [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.R.; Boeder, S.C.; Freeman, J.L.R.; Dunn, I.; Dvergsten, C.; Madduri, S.; Giovannetti, E.R.; Valcarce, C.; Buse, J.B.; Pettus, J.H. Impact of the hepatoselective glucokinase activator TTP399 on ketoacidosis during insulin withdrawal in people with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2022, 24, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tong, K.; Yin, S.; Hu, G.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, P.; Zhou, M.; Jian, W. Efficacy and safety of dorzagliatin for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022, 9, 1041044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





