Submitted:
11 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We explored the critical features of generative learning and the capabilities of generative models, highlighting their effectiveness in creating new data compared to discriminative models [7]. This comparison is further enriched by a detailed examination of how generative models operate.
- We provide a concise overview of GANs, focusing on their data generation capabilities and architecture. It includes examining various models and techniques that generate diverse image and text data across domains using GANs.
- Next, we comprehensively review various methods for generating synthetic cyber attack data using GANs.
- Finally, we assess the value of synthetically generated attack data by conducting experiments with the NSL-KDD dataset. Specifically, we examine the characteristics of DoS attacks and gauge how well GAN-generated data can improve the training of intrusion detection systems for real-world cyber-attack mitigation.
2. Modeling Techniques
2.1. Generative models
2.2. Discriminative models
2.3. Difference between Generative and Discriminative Models
2.4. Why Generative models?
2.5. How Generative Models work?
2.6. How Generative Models generate data?
| Generative Models | Discriminative Models |
|---|---|
| Learn the underlying data distribution | Learn the decision boundary between different classes of the data |
| Model the joint probability distribution between the input and output data | Model the conditional probability distribution of the output given the input |
| Can generate new data from the learned distribution | Cannot generate new data from the learned decision boundary |
| Used for tasks such as image and audio synthesis, text generation, and anomaly detection | Used for tasks such as classification, regression, and object recognition |
| Make no assumptions about the data | Use prior assumptions about the data |
| Examples include VAE, GAN, and RBM | Examples include Logistic Regression, SVM, and Neural Networks |
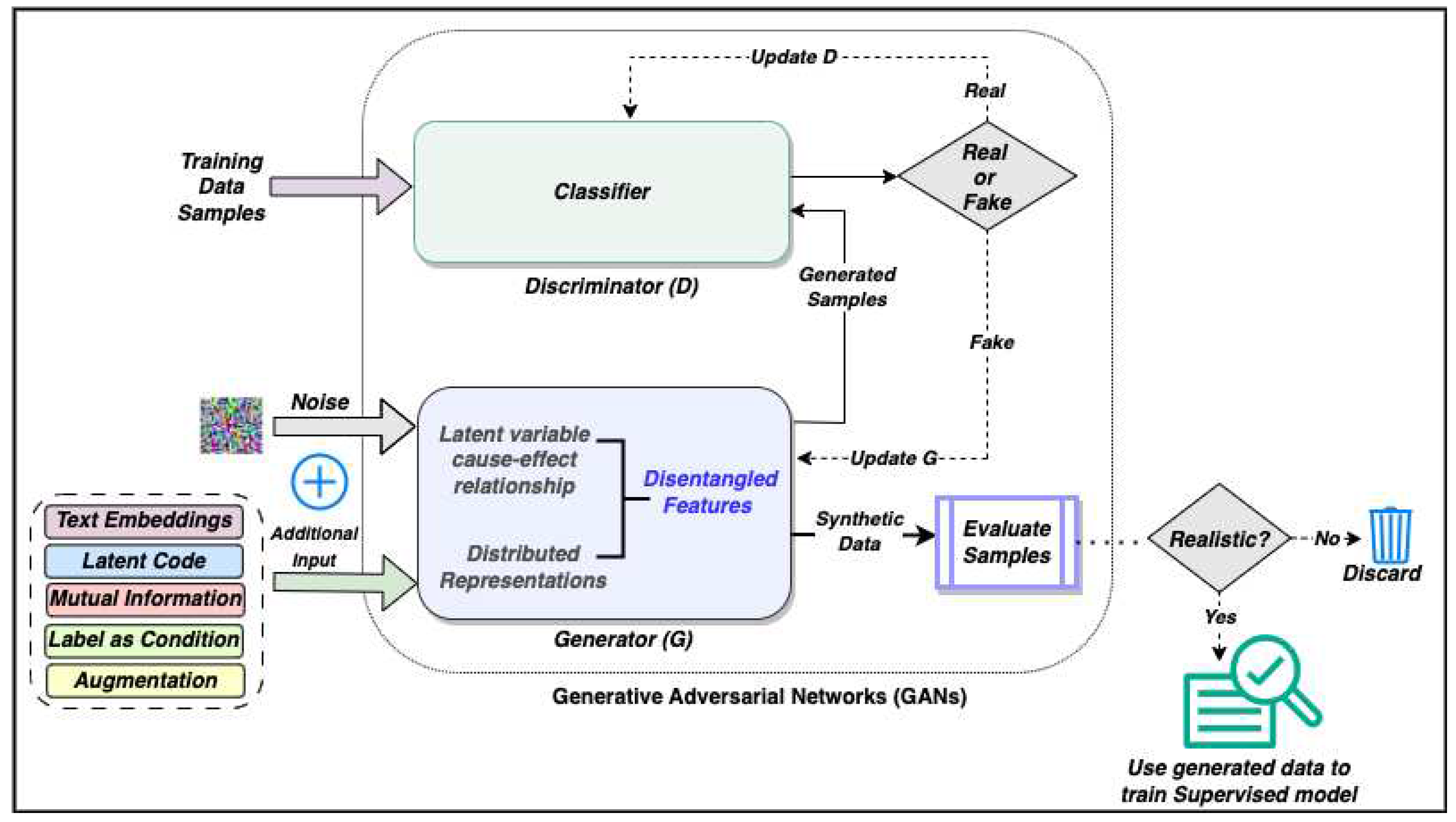
3. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
3.1. Construction of Networks
3.2. Cost Function
3.3. Training of Networks
- False Negative - The input is real but the discriminator gives the output as fake: The real data is given to the discriminator. The generator is not involved in this step. The discriminator makes a mistake and classifies the input as fake. This is a training error and the weights of the discriminator are updated using backpropagation.
- True Negative - The input is fake and the discriminator gives the output as fake: The generator generates some fake data from random noise in latent space. If the discriminator recognizes this as fake, there is no need to update the discriminator. The weights of the generator should be updated using backpropagation using the loss function value.
- False Positive - The input is fake but the discriminator gives the output as real. The discriminator should be updated. The loss function is used to update the weights of discriminator.
4. Generating Data using GANs
4.1. Different techniques in GAN for generating data
4.2. Generating images
4.3. Generating tabular synthetic data
4.3.1. Airline Passenger Name Record (PNR) generation
4.3.2. Synthesizing fake tables
5. Generating Cyber Attack data using GAN
5.1. Flow-based Network Traffic Generation
5.2. Cyber Intrusion Alert Data Synthesis
5.3. Generating Attack Data using Adversarial Examples
5.3.1. MalGAN: Generating Malware Adversarial Examples using GAN
5.3.2. IDSGAN: Generating Adversarial Examples against Intrusion Detection System
6. Analysis of GAN generated Synthetic Attack Data
7. Discussion
8. Conclusion
References
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2014, pp. 2672–2680.
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Communications of the ACM 2020, 63, 139–144.
- Shahriar, S. GAN computers generate arts? a survey on visual arts, music, and literary text generation using generative adversarial network. Displays 2022, p. 102237. [CrossRef]
- Yinka-Banjo, C.; Ugot, O.A. A review of generative adversarial networks and its application in cybersecurity. Artificial Intelligence Review 2020, 53, 1721–1736. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Pan, Y. Generative adversarial networks: A survey toward private and secure applications. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–38.
- Hu, W.; Tan, Y. Generating adversarial malware examples for black-box attacks based on GAN. Data Mining and Big Data: 7th International Conference, DMBD 2022, Beijing, China, November 21–24, 2022, Proceedings, Part II. Springer, 2023, pp. 409–423.
- Jordan, A.; others. On discriminative vs. generative classifiers: A comparison of logistic regression and naive bayes. Advances in neural information processing systems 2002, 14, 841.
- Lee, H.W.; Lim, K.Y.; Grabowski, B.L. Generative learning: Principles and implications for making meaning. In Handbook of research on educational communications and technology; Routledge, 2008; pp. 111–124.
- Nallapati, R. Discriminative models for information retrieval. Proceedings of the 27th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, 2004, pp. 64–71.
- Oussidi, A.; Elhassouny, A. Deep generative models: Survey. 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Computer Vision (ISCV), 2018, pp. 1–8. doi:10.1109/ISACV.2018.8354080.
- Webb, G.I. Naïve Bayes. Encyclopedia of machine learning 2010, 15, 713–714.
- Pearl, J. Bayesian networks; UCLA: Department of Statistics, UCLA, 2011.
- Clifford, P. Markov random fields in statistics. Disorder in physical systems: A volume in honour of John M. Hammersley 1990, pp. 19–32.
- Eddy, S.R. Hidden markov models. Current opinion in structural biology 1996, 6, 361–365.
- Izenman, A.J. Linear discriminant analysis. In Modern multivariate statistical techniques; Springer, 2013; pp. 237–280.
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. nature 2015, 521, 436–444.
- Fahlman, S.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Sejnowski, T.J. Massively parallel architectures for Al: NETL, Thistle, and Boltzmann machines. National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI, 1983.
- Fischer, A.; Igel, C. An introduction to restricted Boltzmann machines. Iberoamerican congress on pattern recognition. Springer, 2012, pp. 14–36.
- Hinton, G.E. Deep belief networks. Scholarpedia 2009, 4, 5947.
- Salakhutdinov, R.; Hinton, G. Deep boltzmann machines. Artificial intelligence and statistics. PMLR, 2009, pp. 448–455.
- Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Deep, narrow sigmoid belief networks are universal approximators. Neural computation 2008, 20, 2629–2636. [CrossRef]
- Bontrager, P.; Togelius, J. Fully differentiable procedural content generation through generative playing networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.05259 2020.
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M.; others. An introduction to variational autoencoders. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning 2019, 12, 307–392.
- Nikolenko, S.I. Synthetic data for deep learning; Vol. 174, Springer, 2021.
- Caruana, R.; Niculescu-Mizil, A. An empirical comparison of supervised learning algorithms. Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning, 2006, pp. 161–168.
- Wright, R.E. Logistic regression. Reading and Understanding Multivariate Statistics 1995, pp. 217–244.
- Joachims, T. Svmlight: Support vector machine. SVM-Light Support Vector Machine http://svmlight. joachims. org/, University of Dortmund 1999, 19.
- Kröse, B.; Krose, B.; van der Smagt, P.; Smagt, P. An introduction to neural networks; The University of Amsterdam, 1993.
- Peterson, L.E. K-nearest neighbor. Scholarpedia 2009, 4, 1883.
- Phyu, T.N. Survey of classification techniques in data mining. Proceedings of the international multiconference of engineers and computer scientists, 2009, Vol. 1.
- Bernardo, J.; Bayarri, M.; Berger, J.; Dawid, A.; Heckerman, D.; Smith, A.; West, M. Generative or discriminative? getting the best of both worlds. Bayesian statistics 2007, 8, 3–24.
- Minka, T. Discriminative models, not discriminative training. Technical report, Technical Report MSR-TR-2005-144, Microsoft Research, 2005.
- Theis, L.; Oord, A.v.d.; Bethge, M. A note on the evaluation of generative models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.01844 2015.
- Amit, I.; Matherly, J.; Hewlett, W.; Xu, Z.; Meshi, Y.; Weinberger, Y. Machine learning in cyber-security-problems, challenges and data sets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.07858 2018.
- Barlow, H.B. Unsupervised learning. Neural computation 1989, 1, 295–311.
- Zhu, X.; Goldberg, A.B. Introduction to semi-supervised learning. Synthesis lectures on artificial intelligence and machine learning 2009, 3, 1–130.
- Khosravi, P.; Choi, Y.; Liang, Y.; Vergari, A.; Broeck, G.V.d. On tractable computation of expected predictions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.02182 2019.
- Huang, C.W.; Touati, A.; Dinh, L.; Drozdzal, M.; Havaei, M.; Charlin, L.; Courville, A. Learnable explicit density for continuous latent space and variational inference. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.02248 2017.
- Frey, B.J.; Hinton, G.E.; Dayan, P.; others. Does the wake-sleep algorithm produce good density estimators? Advances in neural information processing systems. Citeseer, 1996, pp. 661–670.
- Karhunen, J. Nonlinear independent component analysis. ICA: Principles and Practice 2001, pp. 113–134.
- Hammersley, J. Monte carlo methods; Springer Science & Business Media, 2013.
- Tran, D.; Ranganath, R.; Blei, D. Hierarchical implicit models and likelihood-free variational inference. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, 30.
- Ching, W.K.; Ng, M.K. Markov chains. Models, algorithms and applications 2006.
- Wang, H.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, B.; Peng, J. Machine learning basics. Deep learning 2016, pp. 98–164.
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2013, 35, 1798–1828.
- Arora, S.; Khandeparkar, H.; Khodak, M.; Plevrakis, O.; Saunshi, N. A theoretical analysis of contrastive unsupervised representation learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.09229 2019.
- Hodson, T.O.; Over, T.M.; Foks, S.S. Mean squared error, deconstructed. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2021, 13, e2021MS002681. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. CmSalGAN: RGB-D salient object detection with cross-view generative adversarial networks. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 2020, 23, 1343–1353. [CrossRef]
- Goudet, O.; Kalainathan, D.; Caillou, P.; Guyon, I.; Lopez-Paz, D.; Sebag, M. Causal generative neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.08936 2017.
- Zhou, G.; Yao, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, K. On the opportunity of causal deep generative models: A survey and future directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.12351 2023.
- Kügelgen, J.; Mey, A.; Loog, M.; Schölkopf, B. Semi-supervised learning, causality, and the conditional cluster assumption. Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. PMLR, 2020, pp. 1–10.
- Han, T.; Tu, W.W.; Li, Y.F. Explanation consistency training: Facilitating consistency-based semi-supervised learning with interpretability. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2021, Vol. 35, pp. 7639–7646. [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, T.; Mount, D.M.; Netanyahu, N.S.; Piatko, C.; Silverman, R.; Wu, A.Y. The analysis of a simple k-means clustering algorithm. Proceedings of the sixteenth annual symposium on Computational geometry, 2000, pp. 100–109.
- Kramer, O.; Kramer, O. K-nearest neighbors. Dimensionality reduction with unsupervised nearest neighbors 2013, pp. 13–23.
- De Ville, B. Decision trees. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics 2013, 5, 448–455.
- Cho, Y.; Saul, L. Kernel methods for deep learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2009, 22.
- Sennrich, R. Modelling and optimizing on syntactic n-grams for statistical machine translation. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics 2015, 3, 169–182. [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E. Distributed representations 1984.
- Hinton, G.E.; Ghahramani, Z. Generative models for discovering sparse distributed representations. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 1997, 352, 1177–1190. [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06434 2015.
- Li, T.; Ortiz, J.M. Generative Adversarial Network 1011.
- Ratliff, L.J.; Burden, S.A.; Sastry, S.S. Characterization and computation of local Nash equilibria in continuous games. 2013 51st Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton). IEEE, 2013, pp. 917–924.
- Sun, F.; Xie, X. Deep non-parallel hyperplane support vector machine for classification. IEEE Access 2023. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Xie, G.S.; Li, X.; Mei, T.; Liu, C.L. A Survey on Learning to Reject. Proceedings of the IEEE 2023, 111, 185–215. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, Y.; Cheong, K.H. Permutation Jensen–Shannon divergence for Random Permutation Set. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 119, 105701. [CrossRef]
- Wildberger, J.; Guo, S.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Schölkopf, B. On the Interventional Kullback-Leibler Divergence. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.05380 2023.
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J. Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196 2017.
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.1784 2014.
- Denton, E.L.; Chintala, S.; Fergus, R.; others. Deep generative image models using a laplacian pyramid of adversarial networks. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2015, pp. 1486–1494.
- Burt, P.; Adelson, E. The Laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. IEEE Transactions on communications 1983, 31, 532–540. [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Nair, V.; Hinton, G. Cifar-10 (canadian institute for advanced research). URL http://www. cs. toronto. edu/kriz/cifar. html 2010, 5.
- Song, F.Y.Y.Z.S.; Xiao, A.S.J. LSUN: Construction of a Large-scale Image Dataset using Deep Learning with Humans in the Loop. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.03365 2015.
- Liu, Z.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face attributes in the wild. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2015, pp. 3730–3738.
- Wang, Z.; Simoncelli, E.P.; Bovik, A.C. Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. The Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, 2003. Ieee, 2003, Vol. 2, pp. 1398–1402. [CrossRef]
- Bowles, C.; Chen, L.; Guerrero, R.; Bentley, P.; Gunn, R.; Hammers, A.; Dickie, D.A.; Hernández, M.V.; Wardlaw, J.; Rueckert, D. Gan augmentation: Augmenting training data using generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.10863 2018.
- Sixt, L.; Wild, B.; Landgraf, T. Rendergan: Generating realistic labeled data. Frontiers in Robotics and AI 2018, 5, 66. [CrossRef]
- Wario, F.; Wild, B.; Couvillon, M.J.; Rojas, R.; Landgraf, T. Automatic methods for long-term tracking and the detection and decoding of communication dances in honeybees. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 2015, 3, 103. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Metaxas, D.N. Stackgan: Text to photo-realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2017, pp. 5907–5915.
- Reed, S.E.; Akata, Z.; Mohan, S.; Tenka, S.; Schiele, B.; Lee, H. Learning what and where to draw. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2016, pp. 217–225.
- Wah, C.; Branson, S.; Welinder, P.; Perona, P.; Belongie, S. The caltech-ucsd birds-200-2011 dataset, 2011.
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. European conference on computer vision. Springer, 2014, pp. 740–755.
- Nilsback, M.E.; Zisserman, A. Automated flower classification over a large number of classes. 2008 Sixth Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics & Image Processing. IEEE, 2008, pp. 722–729.
- Salimans, T.; Goodfellow, I.; Zaremba, W.; Cheung, V.; Radford, A.; Chen, X. Improved techniques for training gans. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2016, pp. 2234–2242.
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016, pp. 2818–2826.
- Chen, X.; Duan, Y.; Houthooft, R.; Schulman, J.; Sutskever, I.; Abbeel, P. Infogan: Interpretable representation learning by information maximizing generative adversarial nets. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2016, pp. 2172–2180.
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [CrossRef]
- Netzer, Y.; Wang, T.; Coates, A.; Bissacco, A.; Wu, B.; Ng, A.Y. Reading digits in natural images with unsupervised feature learning. NIPS workshop on deep learning and unsupervised feature Learning, 2011.
- Vinod, B. The continuing evolution: Customer-centric revenue management. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 2008, 7, 27–39. [CrossRef]
- Mottini, A.; Lheritier, A.; Acuna-Agost, R. Airline passenger name record generation using generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.06657 2018.
- Voigt, P.; Von dem Bussche, A. The eu general data protection regulation (gdpr). A Practical Guide, 1st Ed., Cham: Springer International Publishing 2017. [CrossRef]
- Bellemare, M.G.; Danihelka, I.; Dabney, W.; Mohamed, S.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; Hoyer, S.; Munos, R. The cramer distance as a solution to biased wasserstein gradients. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.10743 2017.
- Wang, R.; Fu, B.; Fu, G.; Wang, M. Deep & cross network for ad click predictions. In Proceedings of the ADKDD’17; 2017; pp. 1–7.
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein gan. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.07875 2017.
- Ajalloeian, A.; Stich, S.U. Analysis of SGD with Biased Gradient Estimators. arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.00051 2020.
- Székely, G.J. E-statistics: The energy of statistical samples. Bowling Green State University, Department of Mathematics and Statistics Technical Report 2003, 3, 1–18.
- Guo, C.; Berkhahn, F. Entity embeddings of categorical variables. arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.06737 2016.
- Lilliefors, H.W. On the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality with mean and variance unknown. Journal of the American statistical Association 1967, 62, 399–402.
- Park, N.; Mohammadi, M.; Gorde, K.; Jajodia, S.; Park, H.; Kim, Y. Data synthesis based on generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.03384 2018.
- LA.
- Adult. UCI Machine Learning Repository, 1996. [CrossRef]
- Health.
- Airline.
- Shokri, R.; Stronati, M.; Song, C.; Shmatikov, V. Membership inference attacks against machine learning models. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). IEEE, 2017, pp. 3–18.
- Bhuyan, M.H.; Bhattacharyya, D.K.; Kalita, J.K. Network anomaly detection: methods, systems and tools. Ieee communications surveys & tutorials 2013, 16, 303–336. [CrossRef]
- Khraisat, A.; Gondal, I.; Vamplew, P.; Kamruzzaman, J. Survey of intrusion detection systems: techniques, datasets and challenges. Cybersecurity 2019, 2, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Shahid Khan, A.; Wai Shiang, C.; Abdullah, J.; Ahmad, F. Network intrusion detection system: A systematic study of machine learning and deep learning approaches. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies 2021, 32, e4150. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Han, H. A systematic literature review of methods and datasets for anomaly-based network intrusion detection. Computers & Security 2022, p. 102675. [CrossRef]
- Bulusu, S.; Kailkhura, B.; Li, B.; Varshney, P.K.; Song, D. Anomalous Instance Detection in Deep Learning: A Survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.06979 2020.
- Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, D. A survey of network traffic generation 2015.
- Lin, Z.; Jain, A.; Wang, C.; Fanti, G.; Sekar, V. Using GANs for sharing networked time series data: Challenges, initial promise, and open questions. Proceedings of the ACM Internet Measurement Conference, 2020, pp. 464–483.
- Xu, S.; Marwah, M.; Arlitt, M.; Ramakrishnan, N. Stan: Synthetic network traffic generation with generative neural models. Deployable Machine Learning for Security Defense: Second International Workshop, MLHat 2021, Virtual Event, August 15, 2021, Proceedings 2. Springer, 2021, pp. 3–29.
- Ring, M.; Schlör, D.; Landes, D.; Hotho, A. Flow-based network traffic generation using generative adversarial networks. Computers & Security 2019, 82, 156–172. [CrossRef]
- Ring, M.; Wunderlich, S.; Grüdl, D.; Landes, D.; Hotho, A. Flow-based benchmark data sets for intrusion detection. Proceedings of the 16th European conference on cyber warfare and security, 2017, pp. 361–369.
- Ring, M.; Dallmann, A.; Landes, D.; Hotho, A. Ip2vec: Learning similarities between ip addresses. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW). IEEE, 2017, pp. 657–666.
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781 2013.
- Cheng, A. PAC-GAN: Packet Generation of Network Traffic using Generative Adversarial Networks. 2019 IEEE 10th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON). IEEE, 2019, pp. 0728–0734.
- Shahid, M.R.; Blanc, G.; Jmila, H.; Zhang, Z.; Debar, H. Generative deep learning for Internet of Things network traffic generation. 2020 IEEE 25th Pacific Rim International Symposium on Dependable Computing (PRDC). IEEE, 2020, pp. 70–79.
- Yin, Y.; Lin, Z.; Jin, M.; Fanti, G.; Sekar, V. Practical gan-based synthetic ip header trace generation using netshare. Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2022 Conference, 2022, pp. 458–472.
- Myneni, S.; Chowdhary, A.; Sabur, A.; Sengupta, S.; Agrawal, G.; Huang, D.; Kang, M. DAPT 2020-constructing a benchmark dataset for advanced persistent threats. Deployable Machine Learning for Security Defense: First International Workshop, MLHat 2020, San Diego, CA, USA, August 24, 2020, Proceedings 1. Springer, 2020, pp. 138–163.
- Sweet, C.; Moskal, S.; Yang, S.J. On the Variety and Veracity of Cyber Intrusion Alerts Synthesized by Generative Adversarial Networks. ACM Transactions on Management Information Systems (TMIS) 2020, 11, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Sweet, C.; Moskal, S.; Yang, S.J. Synthetic intrusion alert generation through generative adversarial networks. MILCOM 2019-2019 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM). IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–6.
- Gulrajani, I.; Ahmed, F.; Arjovsky, M.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A.C. Improved training of wasserstein gans. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2017, pp. 5767–5777.
- Belghazi, M.I.; Baratin, A.; Rajeswar, S.; Ozair, S.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Hjelm, R.D. Mine: mutual information neural estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.04062 2018.
- Munaiah, N.; Pelletier, J.; Su, S.H.; Yang, S.J.; Meneely, A. A Cybersecurity Dataset Derived from the National Collegiate Penetration Testing Competition. HICSS Symposium on Cybersecurity Big Data Analytics, 2019.
- Szegedy, C.; Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Bruna, J.; Erhan, D.; Goodfellow, I.; Fergus, R. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6199 2013.
- Papernot, N.; McDaniel, P.; Jha, S.; Fredrikson, M.; Celik, Z.B.; Swami, A. The limitations of deep learning in adversarial settings. 2016 IEEE European symposium on security and privacy (EuroS&P). IEEE, 2016, pp. 372–387.
- Papernot, N.; McDaniel, P.; Goodfellow, I.; Jha, S.; Celik, Z.B.; Swami, A. Practical black-box attacks against machine learning. Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Asia conference on computer and communications security, 2017, pp. 506–519.
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Shlens, J.; Szegedy, C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6572 2014.
- Hu, W.; Tan, Y. Generating adversarial malware examples for black-box attacks based on gan. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.05983 2017.
- Lin, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xue, Z. Idsgan: Generative adversarial networks for attack generation against intrusion detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.02077 2018.
- Papernot, N.; McDaniel, P.; Goodfellow, I. Transferability in machine learning: from phenomena to black-box attacks using adversarial samples. arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.07277 2016.
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Wu, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Network intrusion detection based on supervised adversarial variational auto-encoder with regularization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 42169–42184. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, K. GAN-based imbalanced data intrusion detection system. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing 2021, 25, 121–128. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lei, K. IGAN-IDS: An imbalanced generative adversarial network towards intrusion detection system in ad-hoc networks. Ad Hoc Networks 2020, 105, 102177. [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, M.H.; Haque, N.I.; Rahman, M.A.; Alonso, M. G-ids: Generative adversarial networks assisted intrusion detection system. 2020 IEEE 44th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC). IEEE, 2020, pp. 376–385.
- Schneier, B. Attack trees. Dr. Dobb’s journal 1999, 24, 21–29.
- Gadyatskaya, O.; Trujillo-Rasua, R. New directions in attack tree research: catching up with industrial needs. Graphical Models for Security: 4th International Workshop, GraMSec 2017, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, August 21, 2017, Revised Selected Papers 4. Springer, 2018, pp. 115–126.
- Wideł, W.; Audinot, M.; Fila, B.; Pinchinat, S. Beyond 2014: Formal Methods for Attack Tree–based Security Modeling. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 2019, 52, 1–36.
- Kholgh, D.K.; Kostakos, P. PAC-GPT: A novel approach to generating synthetic network traffic with GPT-3. IEEE Access 2023. [CrossRef]
- Gadyatskaya, O.; Papuc, D. ChatGPT Knows Your Attacks: Synthesizing Attack Trees Using LLMs. International Conference on Data Science and Artificial Intelligence. Springer, 2023, pp. 245–260.

| Data Type | Model | Method | Generated Data Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Images | DCGAN [60] | Vector Arithmetic Manipulation | Low, suffers from Mode Collapse |
| CGAN [68] | Label as condition | Improved Quality | |
| LAPGAN [69] | Conditional GAN with Laplacian Pyramid | High-resolution Realistic Images | |
| PGGAN) [67] | Focus on finer-scale details | High quality Synthetic Images | |
| RenderGAN [76] | Image Augmentation | Realistic Labeled Images | |
| StackGANs [78] | Generate images from a text description using Text Embedding | Good quality images, evaluated using Inception Score | |
| InfoGAN [85] | Use Mutual Information as condition | Model can disentangle variations, improved generated images | |
| Tabular | PNR generation [89] | Use Cramer GAN [91] | Evaluated using Jensen-Shannon divergence (JSD), Realistic data generated |
| Table-GANs [98] | Use 3 CNNs, additional classifier to increase synthetic records integrity | Models trained using synthetic data performed well |
| DoS | R2L | U2R | Probe |
|---|---|---|---|
| back | ftp_write | buffer_overflow | ipsweep |
| land | guess_passwd | loadmodule | nmap |
| pod | imap | perl | portsweep |
| smurf | multihop | rootkit | satan |
| teardrop | phf | ||
| spy | |||
| warezclient | |||
| warezmaster |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





