Submitted:
12 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Iron Ore Tailings
1.2. The Use of Wastes in Earthen Components
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Collection
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Soil-IOT Compatibility Analysis
3. Results
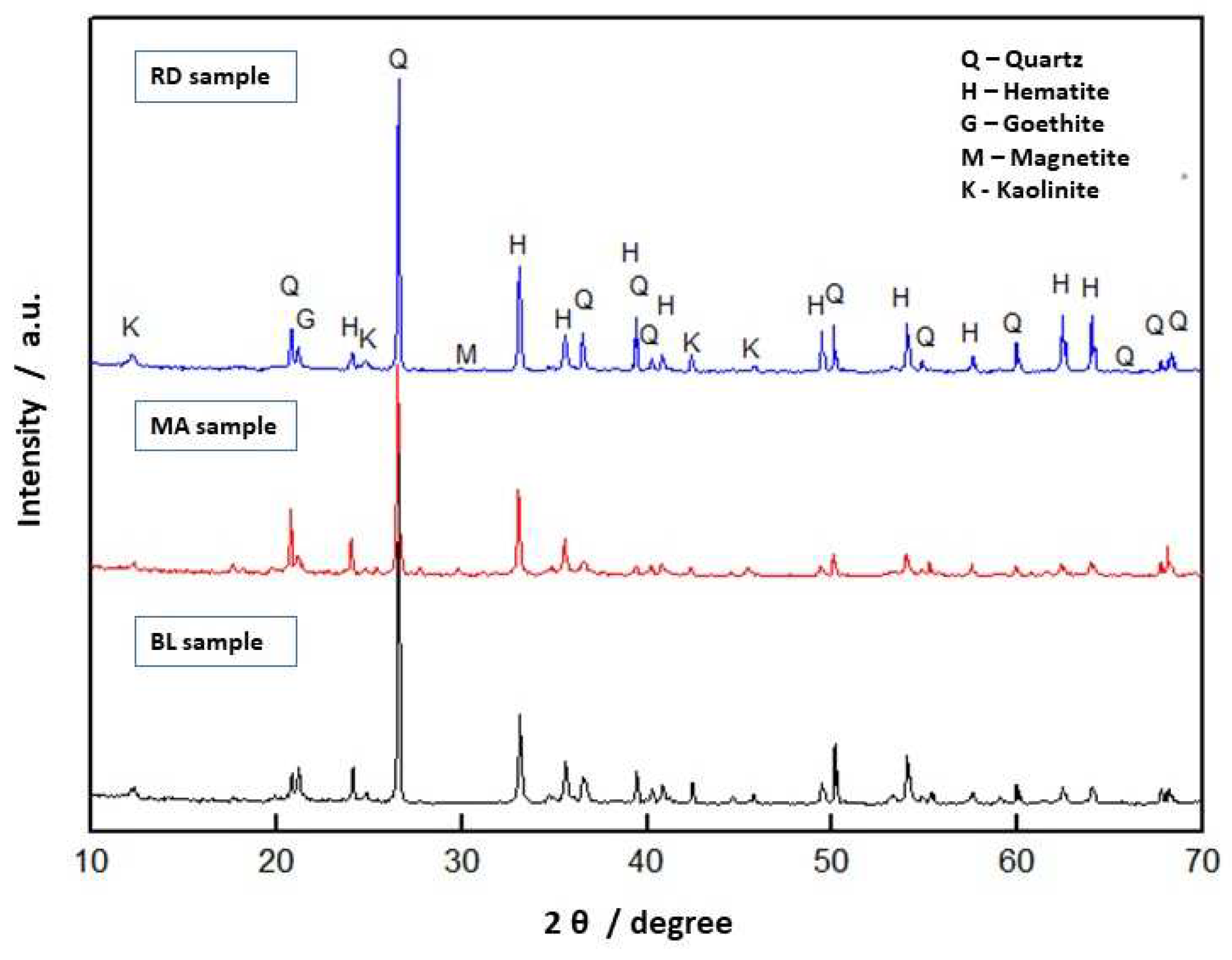
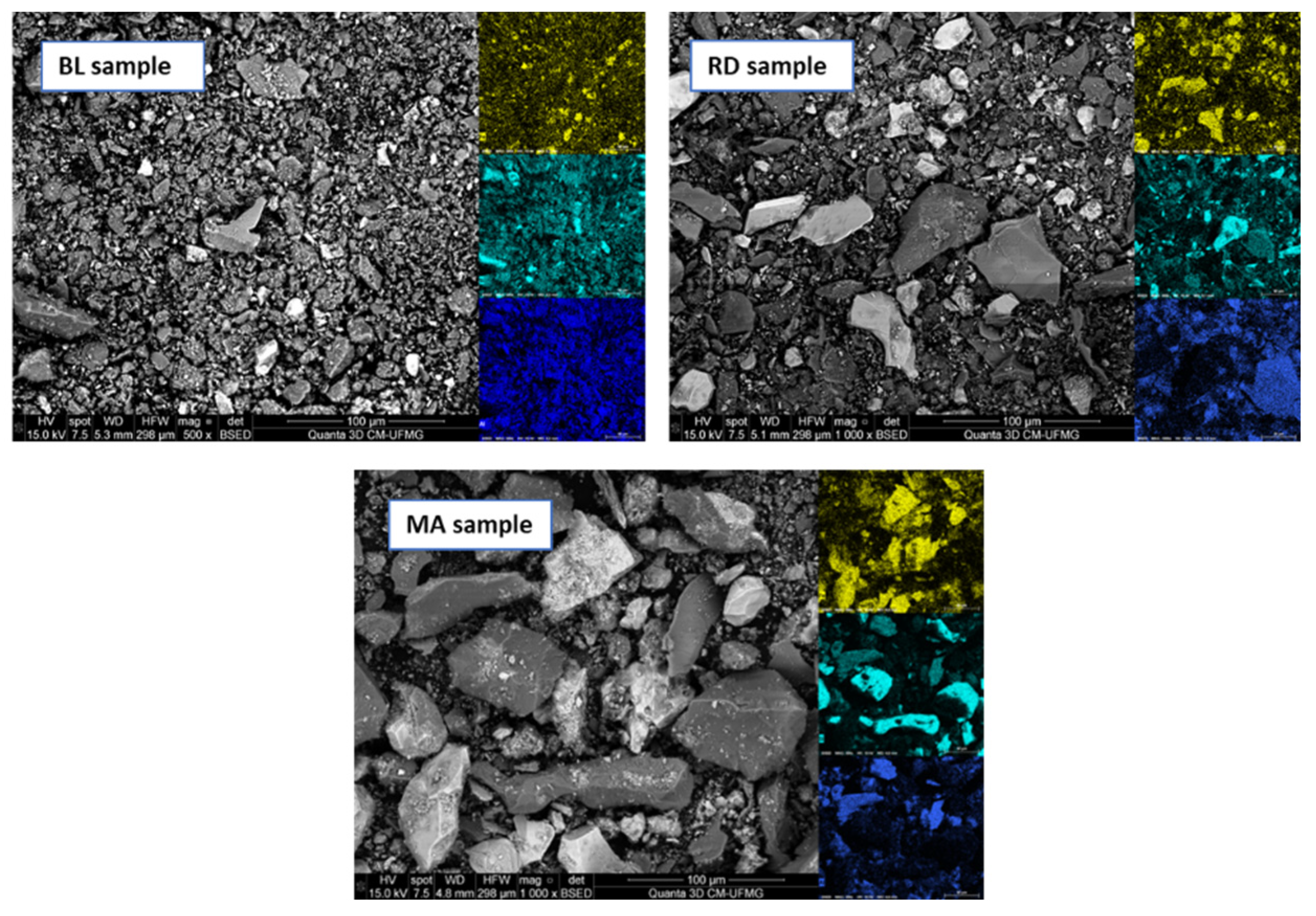
3.1. IOT Samples Characterization and Analysis
3.2. Soil-IOT Compatibility to Produce RE
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY. Mineral Commodity Summaries; U.S. Geological Survey, 2020; p. 89.
- IBRAM – Instituto Brasileiro de mineração. Riscos e Oportunidades de Negócios em Mineração e Metais no Brasil. 2021. Available online: https://ibram.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Estudo-Mineracao-e-Metais_EY-e-IBRAM_Versao-050421.pdf. (accessed on 2 November 2021). (in portuguese).
- IPT - Instituto de Pesquisas Tecnológicas. Rejeitos de mineração. Available online: http://www.ipt.br/noticias_interna.php?id_noticia=1043%3E. (accessed on 11 June 2021). (in portuguese).
- IPEA – Instituto de Pesquisa e Economia Aplicada. Diagnóstico dos Resíduos Sólidos da Atividade de Mineração de Substâncias Não-Energéticas. Available online: https://repositorio.ipea.gov.br/bitstream/11058/7702/1/RP_Diagn%C3%B3stico_2012.pdf. (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- ANM – Agência Nacional de Mineração. Classificação de Barragens de Mineração. 2020. Available online: http://www.anm.gov.br/assuntos/barragens/plano-de-seguranca-de-barragens.
- O TEMPO. Vale começa obra para descaracterizar mais uma barragem a montante em MG. O Tempo, 17 mar. 2023. Available online: https://encurtador.com.br/gEHO8 (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- LACAZ, F. A. C.; PORTO, M. F. S.; PINHEIRO, T. M. M. Tragédias brasileiras contemporâneas: o caso do rompimento da barragem de rejeitos de Fundão/Samarco. Revista Brasileira de Saúde Ocupacional 2017, 42, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOMES, L. E. O.; CORREA, L. B.; SA, F.; NETO, R. R.; BERNARDINO, A. F. The impacts of the Samarco mine tailing spill on the Rio Doce estuary, Eastern Brazil. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2017, 120, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FUNDAÇÃO RENOVA. Retomada das Atividades na Fazenda Floresta. Available online: https://www.fundacaorenova.org/noticia/retomada-das-atividades-na-fazenda-floresta/ (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- ASSIS, D. M.; QUEIROGA, F. O. C. S.; MENDES, J. C. Utilização de rejeito de barragem de minério de ferro na fabricação de tijolos maciços. A revista científica da FaSaR 2018, 3, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- CARRASCO, E. V. M.; MAGALHAES, M. D. C.; SANTOS, W. J. D.; ALVES, R. C.; MANTILLA, J. N. R. Characterization of mortars with iron ore tailings using destructive and nondestructive tests. Construction and Building Materials 2017, 131, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SHETTIMA, A. U.; HUSSIN, M. W.; AHMAD, Y.; MIRZA, J. Evaluation of iron ore tailings as replacement for fine aggregate in concrete. Construction and Building Materials 2016, 120, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YUNHONG, C.; FEI, H.; WENCHUAN, L.; RUI, L.; GUANGLU, L.; JINGMING, W. Test research on the effects of mechanochemically activated iron tailings on the compressive strength of concrete. Construction and Building Materials 2016, 118, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MORAIS, C. F.; BELO, B. R.; BEZERRA, A. C. S.; LOURA, R. M.; PORTO, M. P.; BESSA, S. A. L. Thermal and mechanical analyses of colored mortars produced using Brazilian iron ore tailings. Construction and Building Materials 2021, 268, 121073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GALVÃO, J. L. B.; ANDRADE, H. D.; BRIGOLINI, G. J.; PEIXOTO, R. A. F.; MENDES, J. C. Reuse of iron ore tailings from tailings dams as pigment for sustainable paints. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 200, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, R.; ZHOU, Y.; LI, C.; LI, S.; HUANG, Z. Recycling of industrial waste iron tailings in porous bricks with low thermal conductivity. Construction and Building Materials 2019, 213, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MENDES, B. C.; PEDROTI, L. G.; FONTES, M. P. F.; RIBEIRO, J. C. L.; VIEIRA, C. M. F.; PACHECO, A. A.; AZEVEDO, A. R. G. Technical and environmental assessment of the incorporation of iron ore tailings in construction clay bricks. Construction and Building Materials 2019, 227, 116669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BESSA, S. A. L.; MIRANDA, M. A.; ARRUDA, E. A. M.; BEZERRA, A. C. S.; SACHT, H. M. Produção e avaliação de microconcretos com rejeito de minério de ferro para a fabricação de componentes construtivos. Materia-Rio de Janeiro 2022, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEFÁVERI, K. C. S.; SANTOS, L. F.; CARVALHO, J. M. F.; PEIXOTO, R. A. F.; SILVA, G. J. B. Iron ore tailing-based geopolymer containing glass wool residue: A study of mechanical and microstructural properties. Construction and Building Materials 2019, 220, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DUAN, P.; YAN, C.; ZHOU, W.; REN, D. Development of fly ash and iron ore tailing based porous geopolymer for removal of Cu (II) from wastewater. Ceramics International 2016, 42, 13507–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KURANCHIE, F. A.; SHUKLA, S. K.; HABIBI, D. Utilization of iron ore mine tailings for the production of geopolymer bricks. International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment 2016, 30, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OBENAUS-EMLER, R.; FALAH, M.; ILLIKAINEN, M. Assessment of mine tailings as precursors for alkali-activated materials for on-site applications. Construction and Building Materials 2020, 246, 118470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LAGE, G. T. L.; VIMIEIRO, J. I. C.; MATIAS, L. M.; COSTA, J. M.; BATISTA, G. E. F.; BESSA, S.A.L. Caracterização do sedimento de rejeito de minério de ferro para uso como estabilizante da taipa de pilão. In 4º Congresso Luso-Brasileiro de Materiais de Construção Sustentáveis, 2022, Salvador; Anais do 4º CLBMCS. Salvador: UFBA; 2022; pp. 620–633. [Google Scholar]
- SEGURA, F. R.; NUNES, E. A.; PANIZ, F. P.; PAULELLI, A. C. C.; RODRIGUES, G. B.; BRAGA, G. U. L.; PEDREIRA, W. D.; BARBOSA, F.; CERCHIARO, G.; SILVA, F. F.; BATISTA, B. L. Potential risks of the residue from Samarco's mine dam burst (Bento Rodrigues, Brazil). Environmental Pollution 2016, 218, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ALMEIDA, C.A.; OLIVEIRA, A.F.; PACHECO, A.A.; LOPES, R.P.; NEVES, A.A.; QUEIROZA, M.E.L.R. Characterization and evaluation of sorption potential of the iron mine waste after Samarco dam disaster in Doce River basin – Brazil. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, R.; ZHOU, Y.; LI, C.; LI, S.; HUANG, Z. Recycling of industrial waste iron tailings in porous bricks with low thermal conductivity. Construction and Building Materials 2019, 213, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MACHADO, M. S. M. M.; SANTOS, A. M. M.; FREIRE, C. B.; GUIMARÃES, A. C. P. D.; LAMEIRAS, F. S. Blocks for civil construction made with the sediment deposited in the Candonga Dam. Metallurgy and Materials 2019, 72, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FIGUEIREDO, M. D.; LAMEIRAS, F. S.; ARDISSON, J. D.; ARAÚJO, M. H.; TEXEIRA, A. P. C. Tailings from Fundão Tragedy: Physical–Chemical Properties of the Material That Remains by Candonga Dam. Integr. Environ Assess Management 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COUTO, F. R.; FERREIRA, A. M.; PONTES, P. P.; MARQUES, A. R. Physical, Chemical and Microbiological Characterization of the Soils Contaminated by Iron Ore Tailing Mud After Fundão Dam Disaster In Brazil. Applied soil ecology 2021, 158, 103811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DUARTE, E. B.; NEVES, M. A.; DE OLIVEIRA, F. B.; MARTINS, M. E.; DE OLIVEIRA, C. H. R.; BURAK, D. L.; ORLANDO, M. T. D.; RANGEL, C. V. G. T. Trace metals in Rio Doce sediments before and after the collapse of the Fundão iron ore tailing dam, Southeastern Brazil. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MINKE, G. Manual de construção com terra: uma arquitetura sustentável; B4 Editores: São Paulo, 2015; (in Portuguese). 225p. [Google Scholar]
- ARRIGONI, A.; GRILLET, A.C.; PELOSATO, R.; DOTELLI, G.; BECKETT, C. T. S.; WOLOSZYN, M.; CIANCIO, D. Reduction of rammed earth’s hygroscopic performance under stabilization: an experimental investigation. Building and Environment 2017, 115, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HOFFMANN, M. V.; MINTO, F. C. N.; HEISE, A. F. Taipa de Pilão. In Técnicas de construção com terra; NEVES, C., FARIA, O. B., Eds.; FEB-UNESP / PROTERRA: Bauru, 2011; pp. 46–60. (in Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- DA ROCHA, C. G.; CONSOLI, N. C.; DALLA ROSA JOHANN, A. Greening stabilized rammed earth: Devising more sustainable dosages based on strength controlling equations. Journal of Cleaner Production 2014, 66, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIDDIQUA, S.; BARRETO, P. N. M. Chemical stabilization of rammed earth using calcium carbide residue and fly ash. Construction and Building Materials 2018, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MUNOZ, P.; LETELIER, V.; MUNOZ, L.; BUSTAMANTE. Adobe bricks reinforced with paper e pulp wastes improving thermal and mechanical properties. Construction and Building Materials 2020, 254, 119314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OLACIA, E.; PISELLO, A. L.; CHIODO, V.; MAISANO, S.; FRAZZICA, A.; CABEZA, L. F. Sustainable adobe bricks with seagrass fibres. Mechanical and thermal properties characterization. Construction And Building Materials 2020, 239, 117669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEEK, A. H.; BECKETT, C. T. S.; ELCHALAKANI, M. Reinforcement corrosion in cement and alternatively stabilised rammed earth materials. Construction and Building Materials 2021, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KARIYAWASAM, K. K.G.K.D.; JAYASINGHE, C. Cement stabilized rammed earth as a sustainable construction material. Construction and Building Material 2016, 105, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VENKATARAMA REDDY, B.; LEUZINGER, G.; SREERAM, V. S. Low embodied energy cement stabilised rammed earth building - A case study. Energy and Buildings. 2014, 68, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KOSARIMOVAHHED, M.; TOUFIGH, V. Sustainable usage of waste materials as stabilizer in rammed earth structures. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GIUFFRIDA, G.; CAPONETTO, R.; CUOMO, M. An overview on contemporary rammed earth buildings: Technological advances in production, construction, and material characterization. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; Institute of Physics Publishing, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- IPHAN. Inventário nacional de bens imóveis e sítios urbanos tombados; IPHAN: Brasília, v. 82 E-book; 2007; Available online: https://livraria.senado.leg.br/inventarionacional-de-bens-imoveis-e-sitios-urbanos-tombados-vol-82. (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- LAGE, G. T. L.; NOGUEIRA, J. A. W.; SARAIVA, S. H. M.; BESSA, S. A. L. Arquitetura de terra em regiões afetadas pelo rompimento da barragem de Fundão. In TerraBrasil 2022 - Congresso de Arquitetura e Construção com Terra no Brasil, 8., 2022, Florianópolis. Anais [...]; (in Portuguese). TerraBrasil: UFSC: Florianópolis, 2022; pp. 232–244. (in Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR NM 45; Aggregates - Determination of the unit weight and air-void contends. Rio de Janeiro, 2006. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR NM 23; Portland cement and other powdered materials - determination of specific gravity. Rio de Janeiro, 2000. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR NM 30; Fine aggregate - Test method for water absorption. Rio de Janeiro, 2000. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 10004; Solid waste – Classification. Rio de Janeiro, 2004. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 10005; Procedure for obtention leaching extract of solid wastes. Rio de Janeiro, 2004. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 10006; Procedure for obtention leaching extract of solid wastes. Rio de Janeiro, 2004. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 6459Solo - Determinação do limite de liquidez, Rio de Janeiro, 2016. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 7180; Solo - Determinação do limite de plasticidade. Rio de Janeiro, 2016. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 17014; taipa de pilão: requisitos, procedimentos e controle. Rio de Janeiro, 2022. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 7181; Solo – Análise granulométrica. Rio de Janeiro, 2018. (In Portuguese)
- BRITISH STANDARD. EN 197-1; Cement Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, 2011.
- GUETTALA, A., ABIBSI, A., & HOUARI, H. Durability study of stabilized earth concrete under both laboratory and climatic conditions exposure. Construction and Building Materials, 20, 119-127. [CrossRef]
- GRAMLICH, A. N. A concise history of the use of the rammed earth building technique including information on methods of preservation, repair, and maintenance. Tese. Eugene: University of Oregon.
- KHADKA, B. Rammed earth, as a sustainable and structurally safe green building: a housing solution in the era of global warming and climate change. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering, 21, 119–136. [CrossRef]
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 7182; Solo – Ensaio de compactação. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, 2022. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 12024; Solo-cimento - moldagem e cura de corpos-de-prova cilíndricos - Procedimento. Rio de Janeiro, 2012. (In Portuguese)
- CIANCIO, D.; JAQUIN, P.; WALKER, P. Advances on the assessment of soil suitability for rammed earth. Construction and Building Materials 2013, 42, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 12025; Solo-cimento - Ensaio de compressão simples de corpos de prova cilíndricos - Método de ensaio. Rio de Janeiro, 2012. (In Portuguese)
- ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 7215; Cimento Portland - Determinação da resistência à compressão de corpos de prova cilíndricos. Rio de Janeiro, 2019. (In Portuguese)
- THOMMES, M.; KANEKO, K.; NEIMARK, A. V.; OLIVIER, J. P.; RODRIGUEZ-REINOSO, F.; ROUQUEROL, J.; SING, K. S. W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure and Applied Chemistry 2015, 87, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PENA, E. Q.; VIEIRA, C. B.; SILVA, C. A.; SESHADRI, V.; ARAÚJO, F. G. S. Caracterização de parâmetros de porosidade de concentrados de minérios de ferro pelo método de adsorção de nitrogênio. Tecnologia em Metalurgia e Materiais. 2008, 4, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SING, K. S. W.; EVERETT, D. H.; HAUL, R. A. W.; MOSCOU, L.; PIEROTTI, R. A.; ROUQUÉROL, J.; SIEMIENIEWSKA, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Applied Chemistry 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FONTES, W. C.; MENDES, J. C.; SILVA, S. N.; PEIXOTO, R. A. F. Mortars for laying and coating produced with iron ore tailings from tailing dams. Construction and Building Materials 2016, 112, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SILVA, R. A.; SOARES, E.; OLIVEIRA, D. V.; MIRANDA, T.; CRISTELO, N. M.; LEITÃO, D. Mechanical characterisation of dry-stack masonry made of CEBs stabilised with alkaline activation. Construction and Building Materials 2015, 75, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TAIZ, L.; ZEIGER, E. Plant Physiology, The Benjamim/ Cummings Publishing Company, Inc.: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1991.
- ORLANDO, M. T. D.; GALVÃO, E. S.; CAVICHINI, A. S.; RANGEL, C. V. G. T. R.; ORLANDO, C. G. P.; GRILO, C. F.; SOARES, J.; OLIVEIRA, K. S. S.; SÁ, F.; JUNIOR, A. C.; BASTOS, A. C.; QUARESMA, V. S. Tracing iron ore tailings in the marine environment: An investigation of the Fundão dam failure. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HATJE, V.; PEDREIRA, R. M. A.; REZENDE, C. E.; SCHETTINI, C. A. F.; SOUZA, G. C.; MARIN, D. C.; HACKSPACHER, P. C. The environmental impacts of one of the largest tailing dam failures worldwide. Scientific Reports London: Nature Publishing Group. 2017, 7, 10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DAUCE, P. D.; CASTRO, G. B.; LIMA, M. M. F.; LIMA, R. M. F. Characterisation and magnetic concentration of an iron ore tailings. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2019, 8, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANDRADE, L. C. R. de. Caracterização de rejeitos de mineração de ferro, in natura e segregados, para aplicação como material de construção civil. 2014. 96 f. Tese (Doutorado em Engenharia Civil) - Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Viçosa. 2014 (In Portuguese).
- BASTOS, L. A. C.; SILVA, G. C.; MENDES, J. C.; PEIXOTO, R. A. F. Using Iron Ore Tailings from Tailing Dams as Road Material. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 2016, 28, 04016102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, N.; TANG, B.; LIU, X. Cementitious activity of iron ore tailing and its utilization in cementitious materials, bricks and concrete. Construction and Building Materials 2021, 288, 123022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YANG, M.; SUN, J.; DUN, C.; DUAN, Y.; MENG, Z. Cementitious activity optimization studies of iron tailings powder as a concrete admixture. Construction and Building Materials 2020, 265, 120760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BENEZET, J. C.; BENHASSAINE, A. Grinding and pozzolanic reactivity of quartz powders. Powder Technology 1999, 105, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FERNANDEZ, R.; MARTIRENA, F.; SCRIVENER K., L. The origin of the pozzolanic activity of calcined clay minerals: A comparison between kaolinite, illite and montmorillonite. Cement and Concrete Research 2011, 41, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TAN, X.; WANG, W.; LONG, S.; YANG, C.; XU, F. Effects of calcination on mineralogical properties and reactivity of acidic aluminum sulfate residue. Materials Letters 2020, 258, 126810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHAO, S.; FAN, J.; SUN, W. Utilization of iron ore tailings as fine aggregate in ultra-high performance concrete. Construction and Building Materials 2014, 50, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEDAVID, B.A.; GOMES, C. I.; MACHADO, G. Microscopia eletrônica de varredura: aplicações e preparação de amostras: materiais poliméricos, metálicos e semicondutores; EDIPUCRS: Porto Alegre, 2007. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- BOTTINO, F.; MILAN, J. A. M.; CUNHA-SANTINO, M. B.; BIANCHINI, I. Influence of the residue from an iron mining dam in the growth of two macrophyte species. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GOMES, M.I.; GONÇALVES, T. D.; FARIA, P. Unstabilized Rammed Earth: Characterization of Material Collected from Old Constructions in South Portugal and Comparison to Normative Requirements. International Journal of Architectural Heritage 2013, 8, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PACHECO-TORGAL, F. & JALALI, S. Earth construction: Lessons from the past for future eco-efficient construction. Construction and Building Materials 2011, 29, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AVILA, F.; PUERTAS, E.; GALLEGO, R. Characterization of the mechanical and physical properties of unstabilized rammed earth: A review. Construction and Building Materials 2021, 270, 121435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUSÉBIO, A.P.J. Reabilitação e Melhoramento de Paredes de Terra Crua-Taipa. Tese de Mestrado em Construção; Universidade Técnica de Lisboa, Instituto Superior Técnico: Portugal, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- JAYASINGHE, C.; KAMALADASA, N. Compressive strength characteristics of cement stabilized rammed earth walls. Construction and Building Materials. 2007, 21, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norma E.080 (2017). Diseño y construcción con tierra reforzada. Perú: Ministerio de Vivienda, Construcción y Saneamiento. Available online: https://www.sencico.gob.pe/descargar.php?idFile=3478.
- NZS 4297; Engineering design of earth buildings. Earth Building Association of New Zealand: Nova Zelandia, 1998.
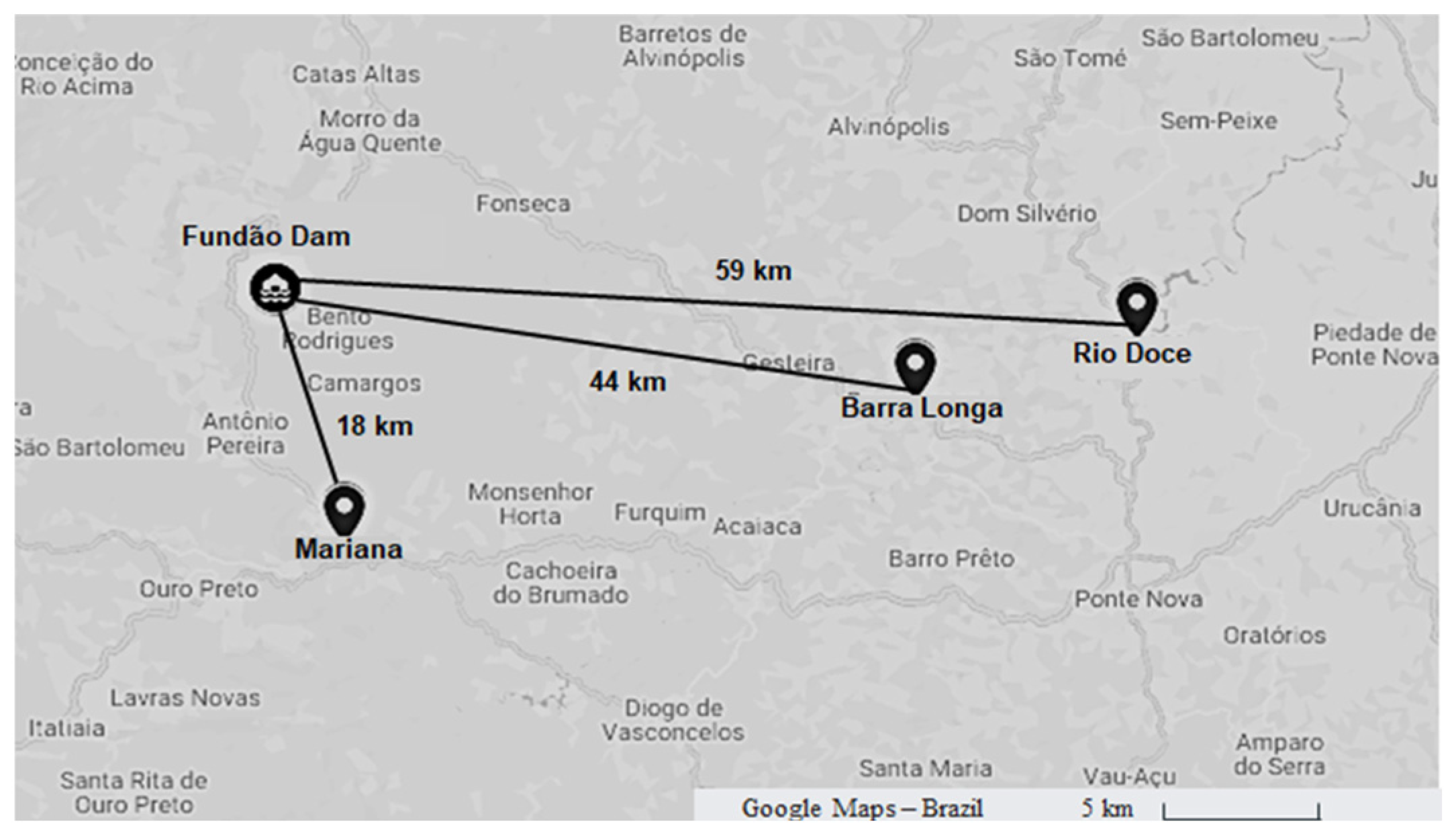
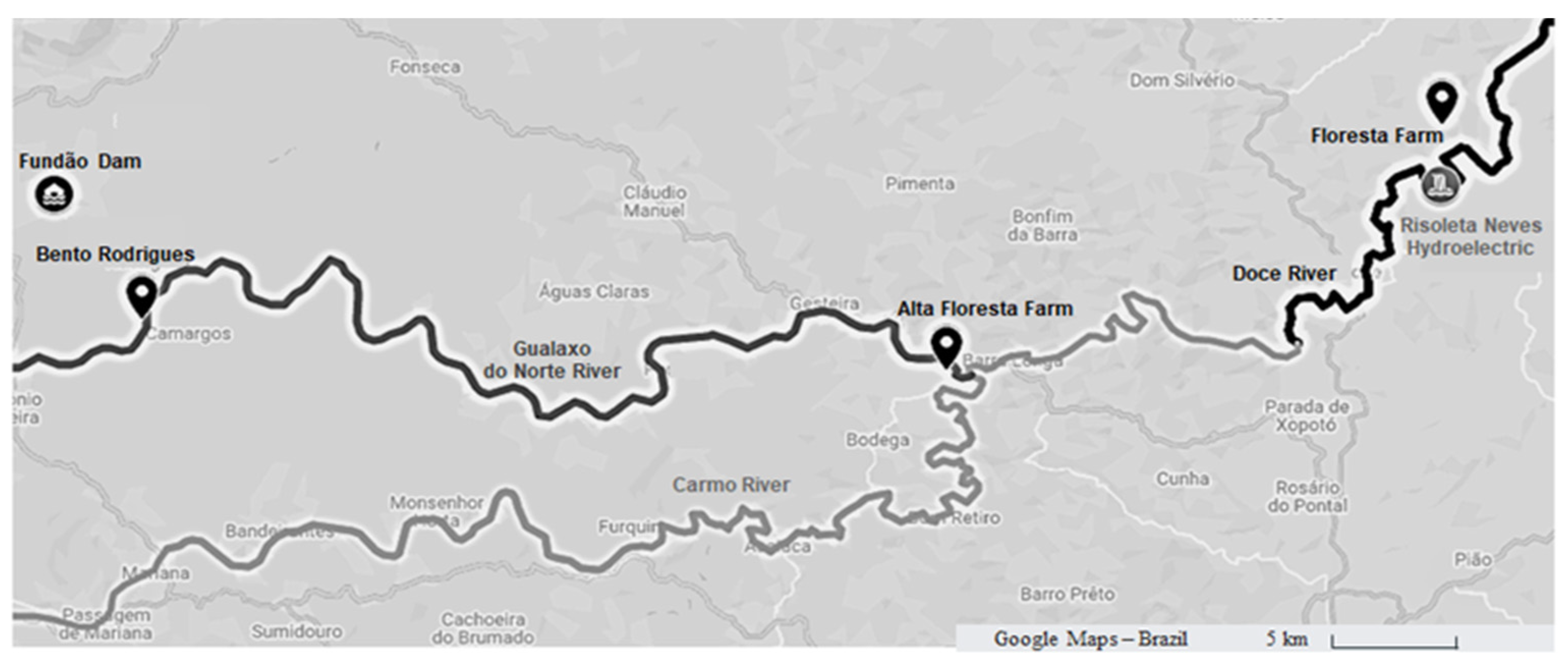
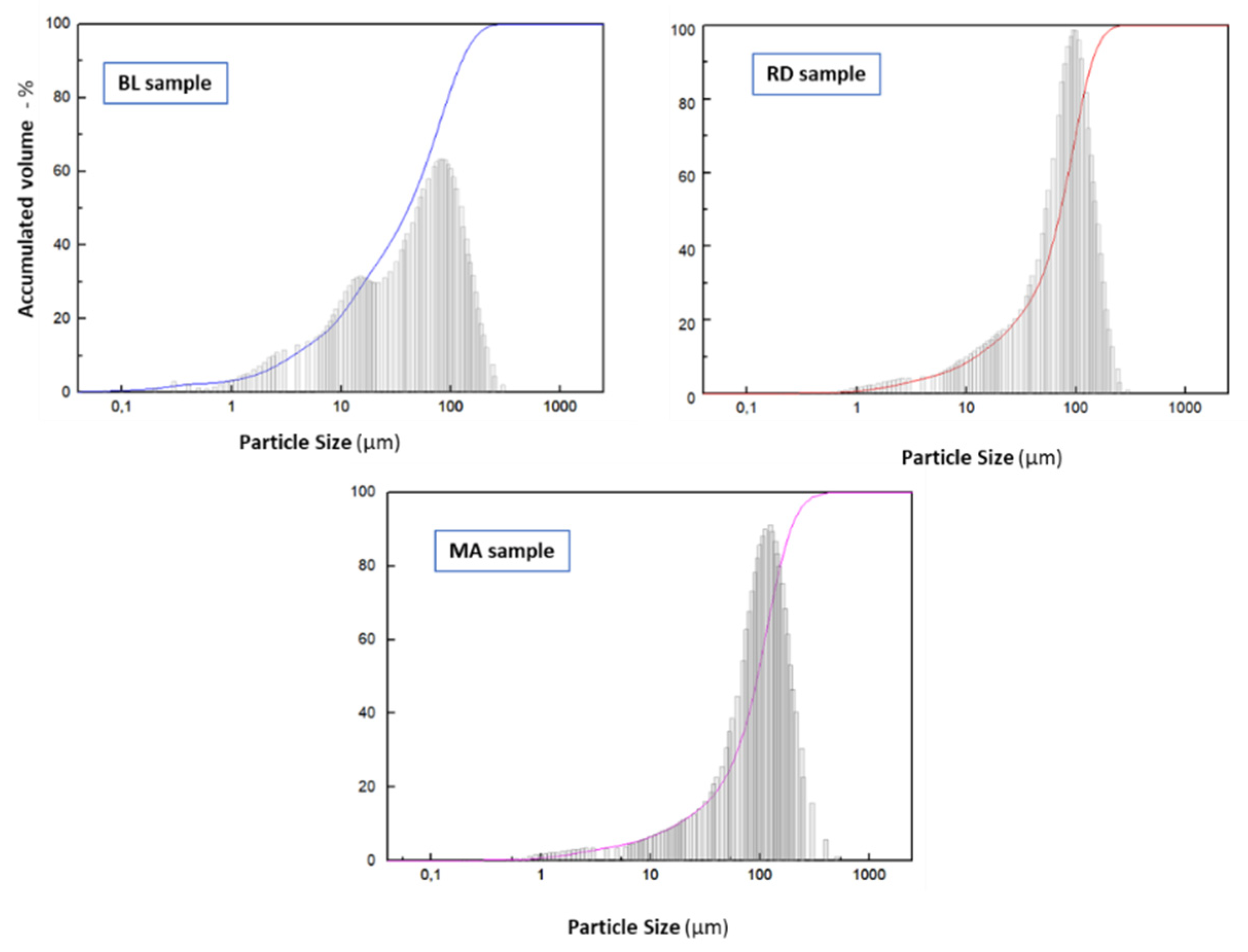
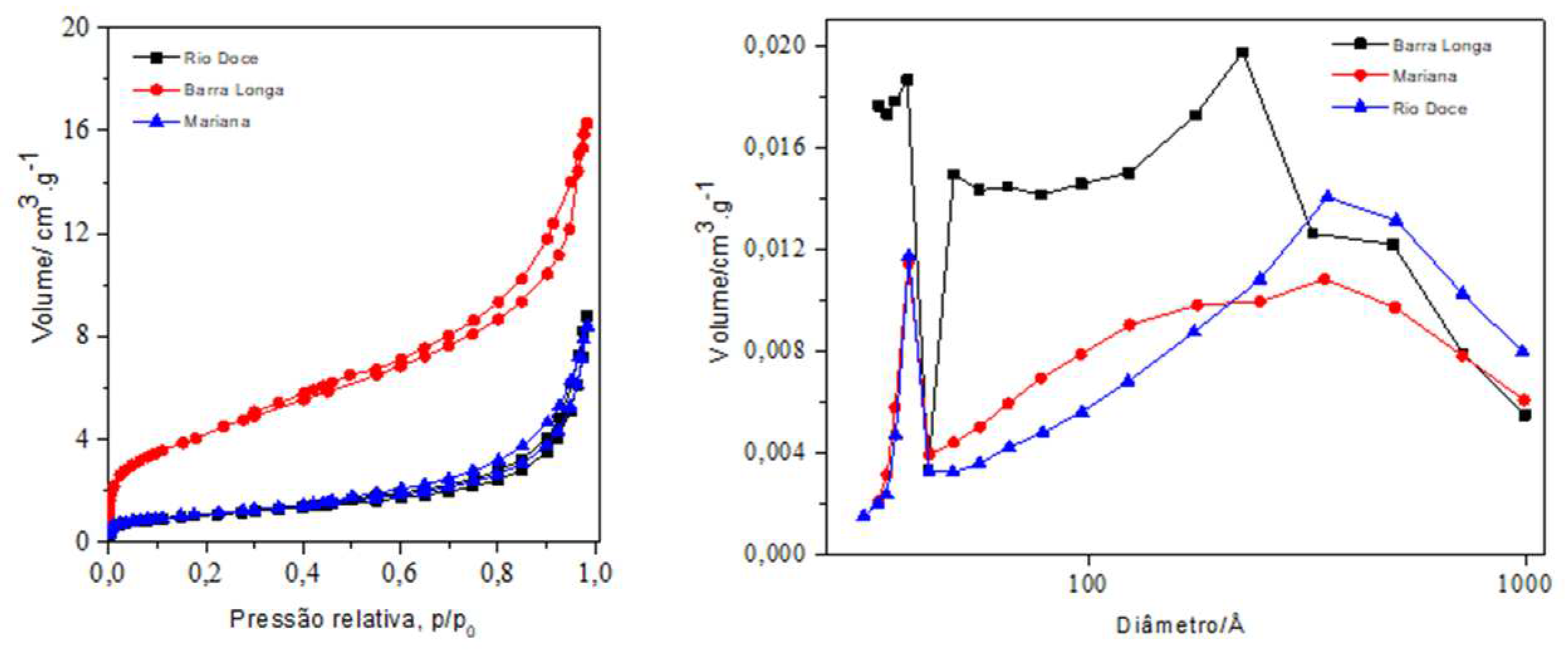
| Group | Mix | Soil (%) | IOT sediment (%) | Portland Cement (%) |
| G1 | T0-0 | 100.0 | - | - |
| T10-0 | 90.0 | 10.0 | ||
| T20-0 | 80.0 | 20.0 | ||
| T40-0 | 60.0 | 40.0 | ||
| G2 | T0-5 | 100.0 | - | 5.0 |
| T10-5 | 90.0 | 10.0 | ||
| T20-5 | 80.0 | 20.0 | ||
| T40-5 | 60.0 | 40.0 |
| Samples | Specific surface area (m²/g) | Pore volume (cm3/g) | Pore diameter (mm) |
| MA Sample | 3.60 | 0.013 | 3.864 |
| RD Sample | 3.26 | 0.013 | 3.873 |
| BL Sample | 7.28 | 0.020 | 3.300 |
| Samples | Physical tests | |||
| Specific mass (g/cm³) | Unit mass (kg/m3) | Ev (%) | Water absorption (%) | |
| MA Sample | 2.93 | 1526.50 | 66.9 | 2.97 |
| RD Sample | 2.82 | 1498.70 | 64.5 | 3.33 |
| BL Sample | 2.79 | 1368.47 | 64.2 | 7.52 |
|
Samples |
Composition (%) | ||||||
| SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | K2O | MnO | CaO | |
| MA Sample | 78.13 | 8.88 | 1.09 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.04 |
| RD Sample | 76.85 | 8.46 | 2.49 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 0.24 |
| BL Sample | 67.05 | 9.57 | 6.39 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 0.21 |
| Specific mass (kg/m³) | 2340 | Liquidity Limit (%) | 53 |
| Unit mass (kg/m³) | 1012 | Plasticity Limit (%) | 31 |
| Volume of voids (%) | 57.50 | Plasticity Index (%) | 22 |
| Granulometry (%) | |||
| Clay | 55.5 | ||
| Sand | 28.0 | ||
| Average diameter (μm) | 26.4 | ||
| Mixture | Compressive strength (MPa) | Standard deviation | Coefficient of variation (%) |
| T0-0 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 11.55 |
| T10-0 | 1.12 | 0.13 | 11.90 |
| T20-0 | 1.24 | 0.05 | 4.07 |
| T40-0 | 1.80 | 0.15 | 8.53 |
| T0-5 | 1.35 | 0.14 | 10.63 |
| T10-5 | 1.07 | 0.11 | 9.91 |
| T20-5 | 1.27 | 0.15 | 12.20 |
| T40-5 | 1.57 | 0.08 | 4.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





