Submitted:
05 December 2023
Posted:
13 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and material models
2.2. Methods
2.2.1 Topology optimization
2.2.1.1 Unidisciplinary topology optimization considering constant anisotropy
2.2.1.2 Multidisciplinary topology optimization considering variable anisotropy
| Algorithm 1. Multidisciplinary topology optimization. | |||
| Input: BCstruct, BCinjMold, MPinjMold, MPmatrix+fiber, OPtopoOpt, th, δmap, Vdef, εobj, geo.stp (Optional) | |||
| Output: topoOptStruct.stl | |||
| write materialProperties.txt ← MPfiber+matrix | |||
| write topoParameters.txt ← OPtopoOpt | |||
| meshstruct, designelements, frozenelements = AnsysWorkbench_Mesh(BCstruct, geo.stp); | |||
| write designRegionMesh.ans ← meshstruct, design.txt ← designelements, frozen.txt ← frozenelements; | |||
| g = 1; | |||
| counter_epsilon = 0; | |||
| while (counter_epsilon < Kε) do | |||
| if g == 1 then | |||
| reducedMesh.ans = designRegionMesh.ans; | |||
| else | |||
| domain_mesh_reduced = delete_elements(designRegionMesh.ans, th, (density.txt)g-1); | |||
| write reducedMesh.ans ← domain_mesh_reduced | |||
| end if | |||
| meshinjMold, A = AutodeskMoldFlow(reducedMesh.ans, BCinjMold, MPinjMold); | |||
| write meshMoldFlow.pat ← meshinjMold, fiberOrientMoldFlow.xml ← A; | |||
| A’ = DigimatMAP(fiberOrientMoldFlow.xml, meshMoldFlow.pat, designRegionMesh.ans, δ); | |||
| write fiberOrientAnsys.xml ← A’; | |||
| KEL = AnisoTopo(materialProperties.txt, fiberOrientAnsys.xml, topoPararmeters.txt, designRegionMesh.ans, design.txt, frozen.txt); | |||
| write apdl_pre.txt ← KEL; | |||
| if g == 1 then | |||
| Wg = AnsysWorkbench_StructuralAnalysis(designRegionMesh.ans, apdl_pre.txt, BCstruct); | |||
| else | |||
| Wg = AnsysWorkbench_StructuralAnalysis(designRegionMesh.ans, apdl_pre.txt, BCstruct, ρ); | |||
| εg = |(Wg - Wg-1)/Wg-1| | |||
| if εg <= εobj then | |||
| counter_epsilon ++ | |||
| else | |||
| counter_epsilon = 0 | |||
| end if | |||
| end if | |||
| ρ = AnsysWorkbench_TopologyOptimization_Iteration(designRegionMesh.ans, design.txt, frozen.txt, Vdef, topoPara, apdl_pre.txt, Wg) | |||
| write density.topo ← ρ; | |||
| Convert density.topo to (density.txt)g with HDFView(); | |||
| g++ | |||
| end while | |||
| topoOptStruct = delete_elements(designRegionMesh.ans, th, (density.txt)g-1); | |||
| write topoOptStruct.stl ← topoOptStruct | |||
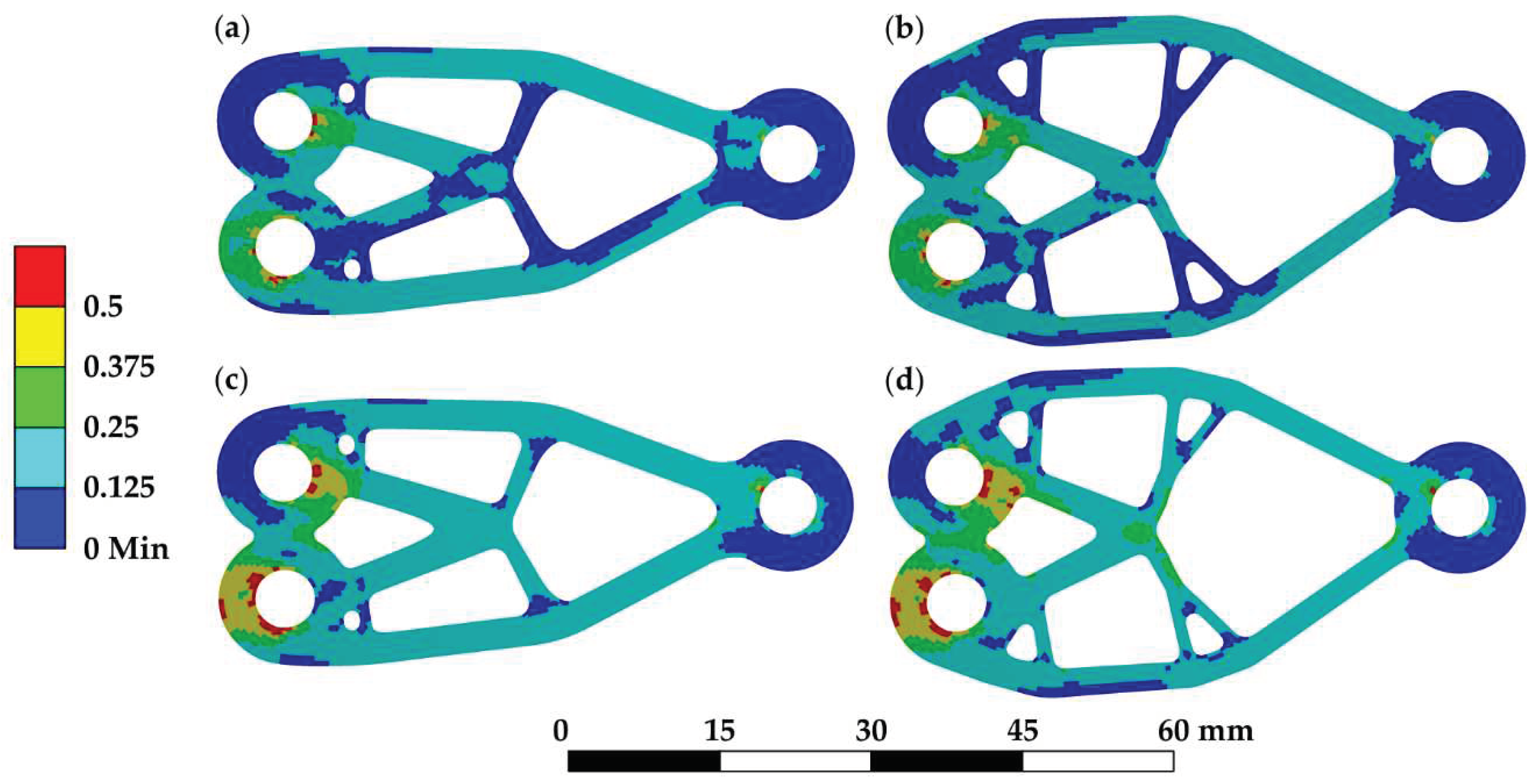
2.2.2 Metric for evaluating structure design quality of composite materials
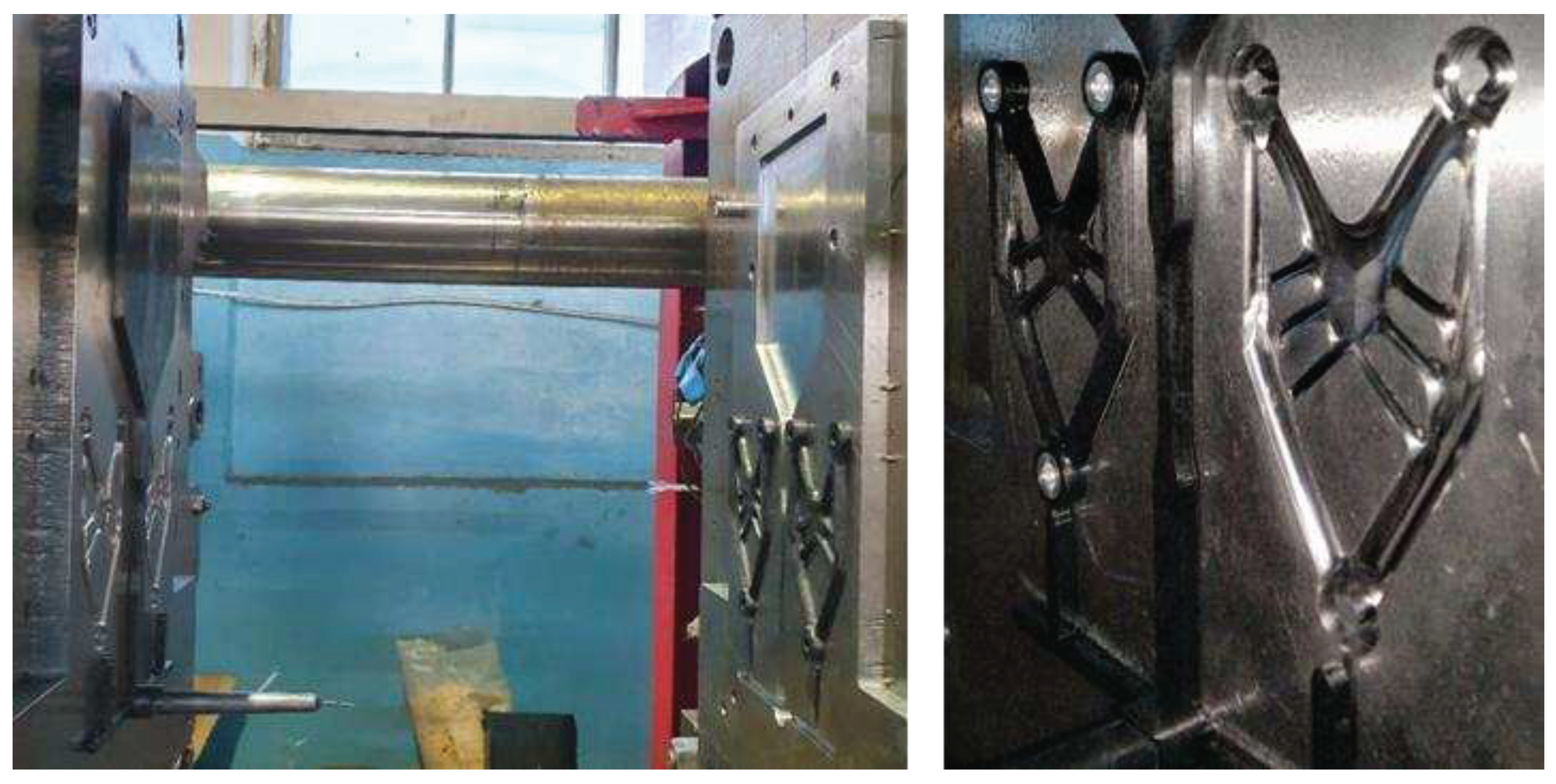
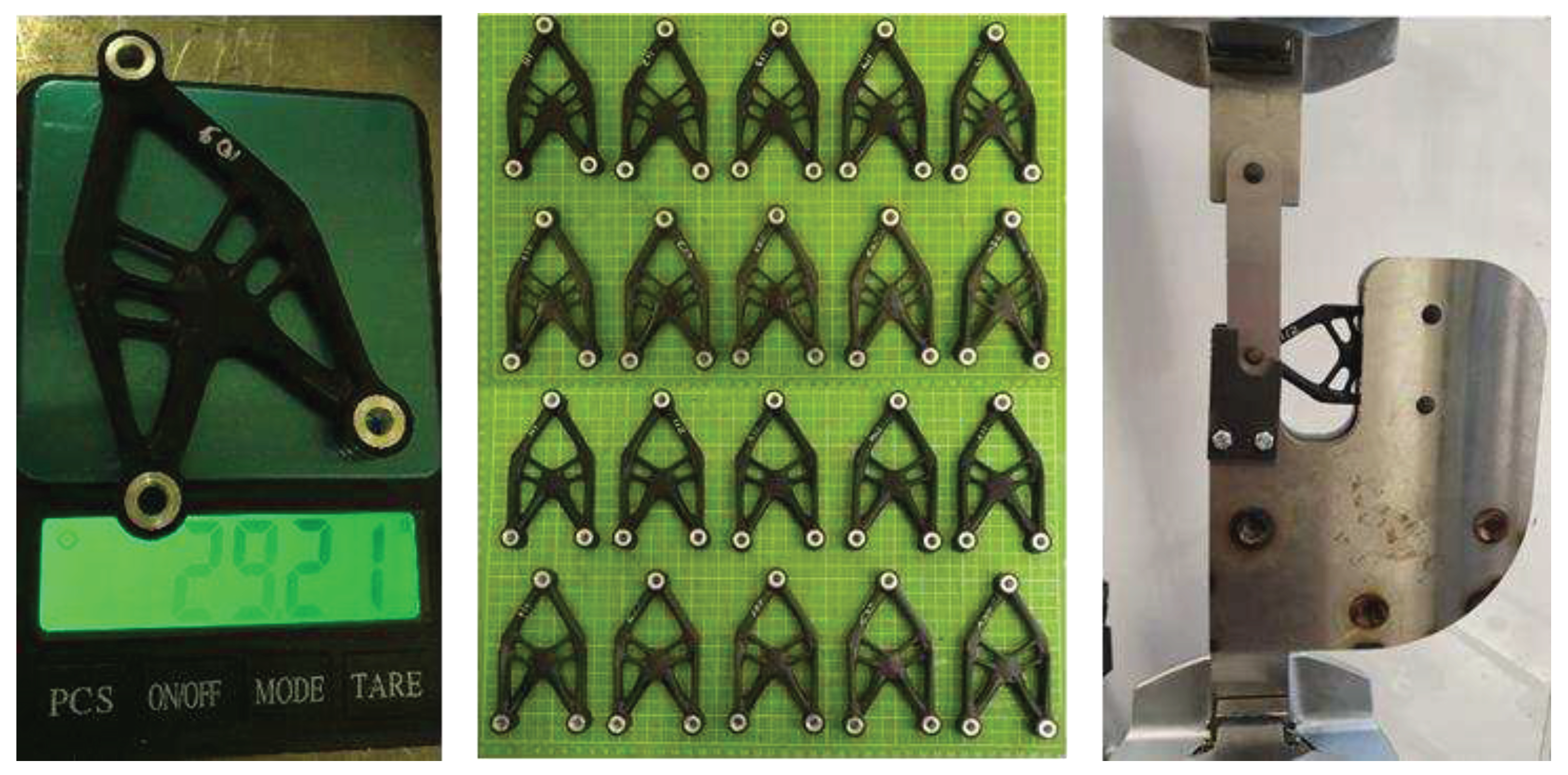
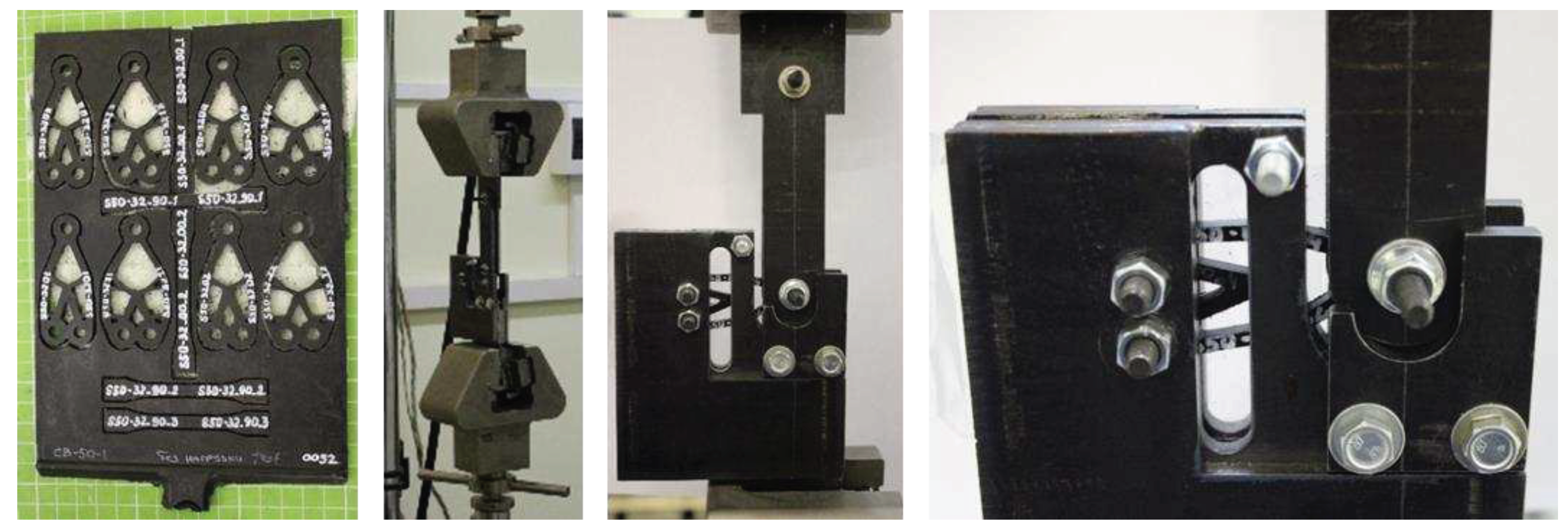
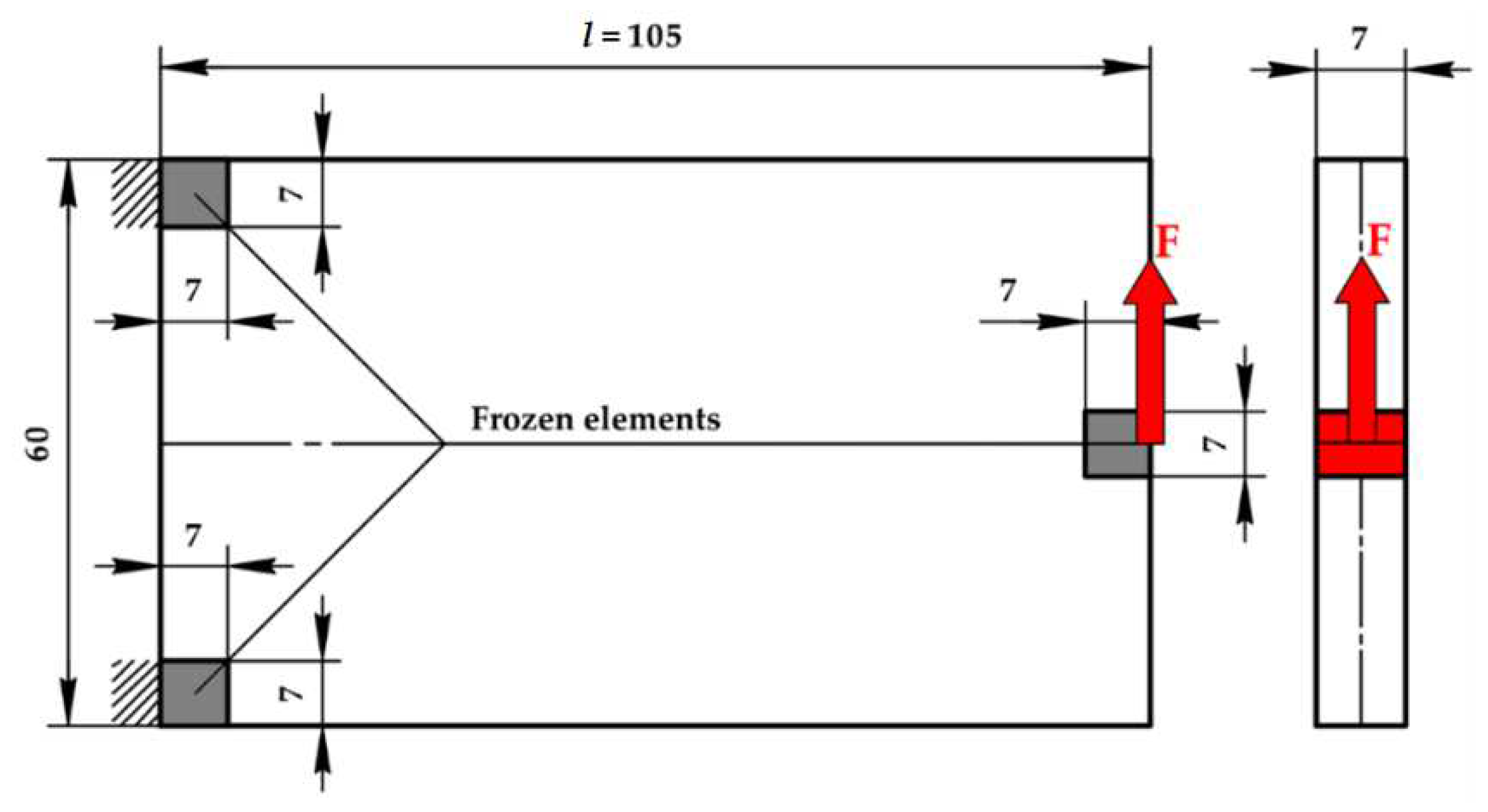
2.2.3 Brackets manufacturing and load testing technique
3. Results
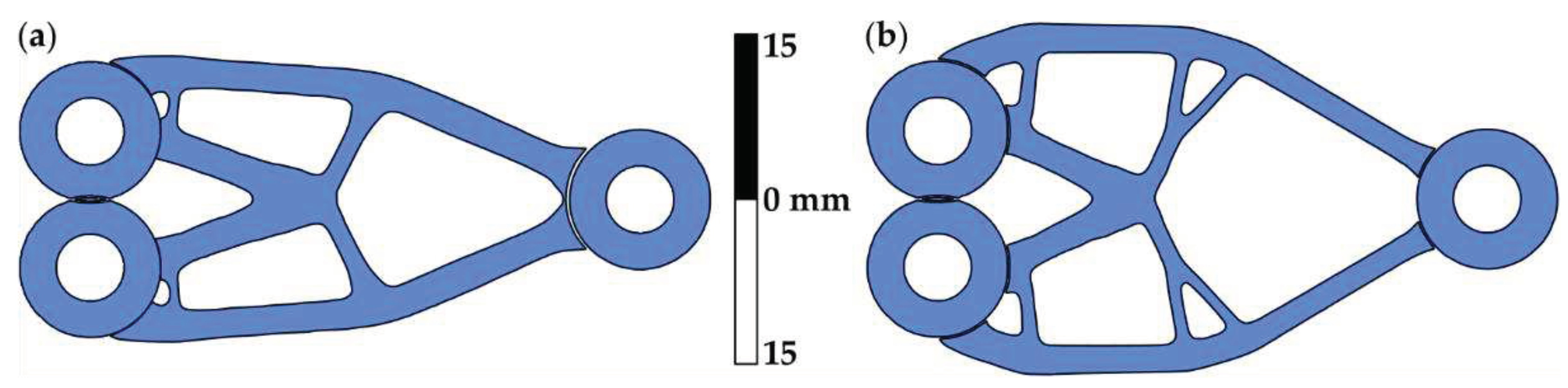
3.1. Topology optimal two-dimensional structures
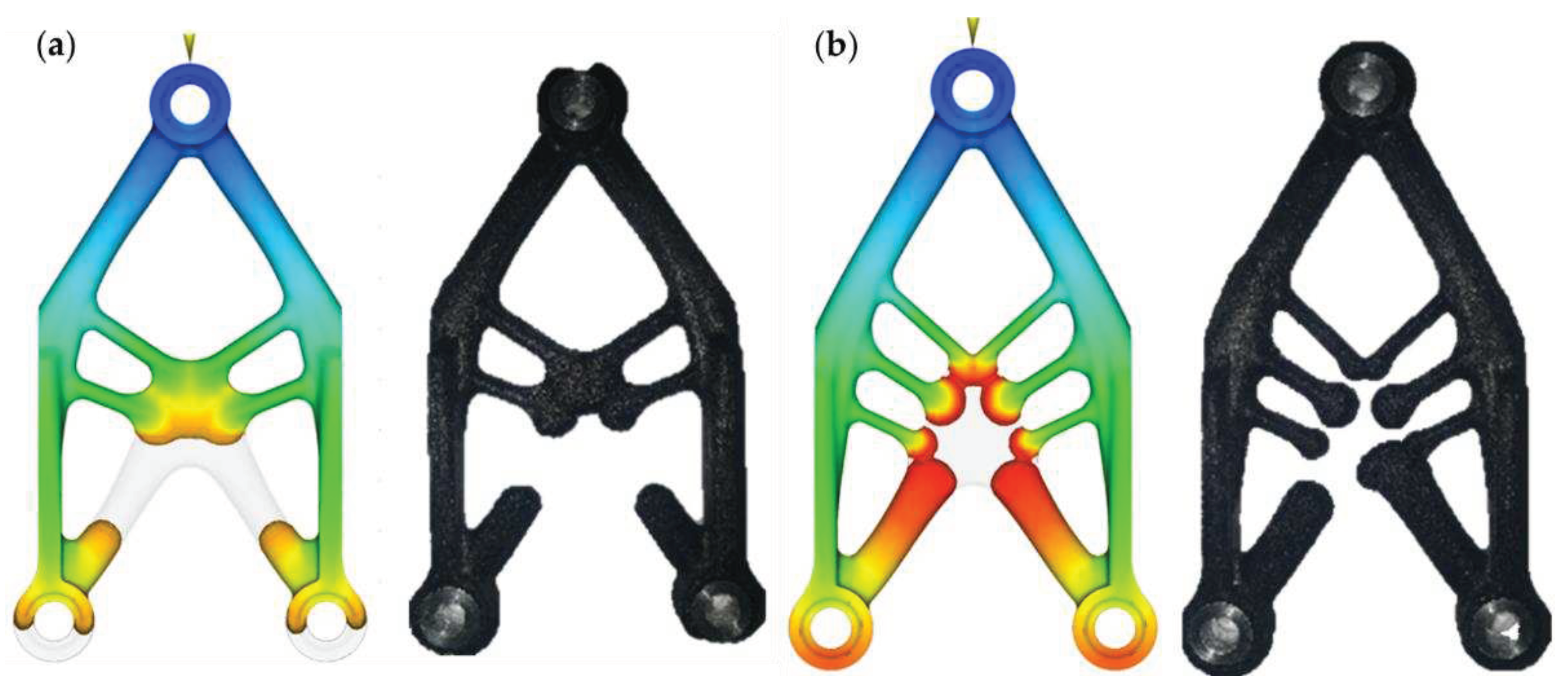
3.1.1. Topology optimization and structural arrangement quality assessment
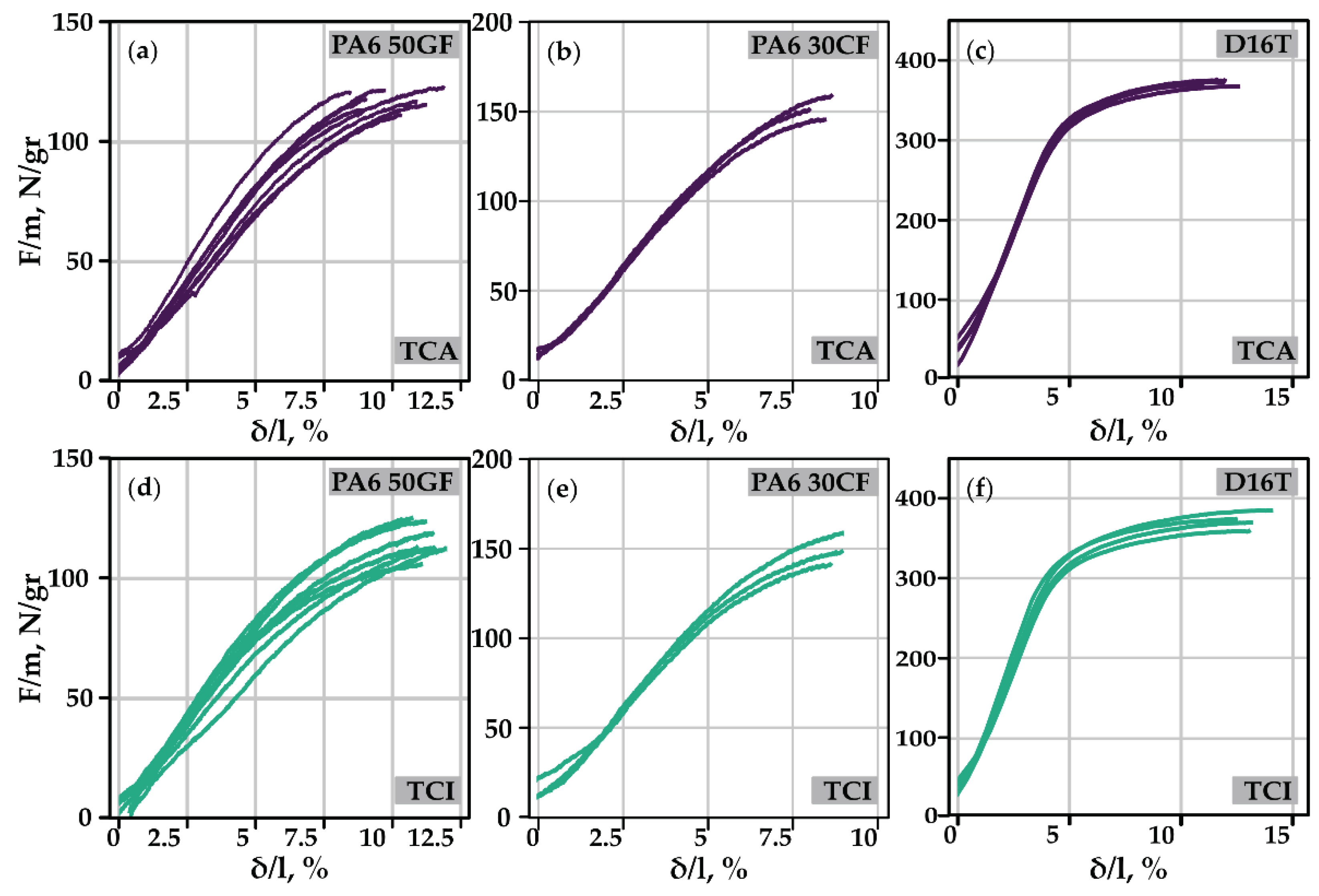
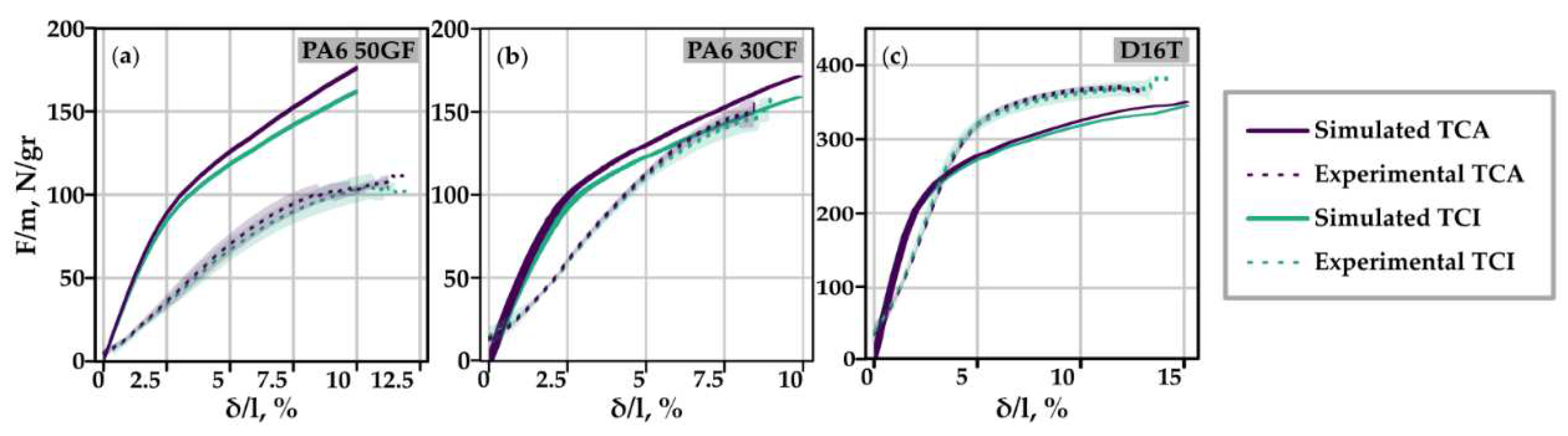
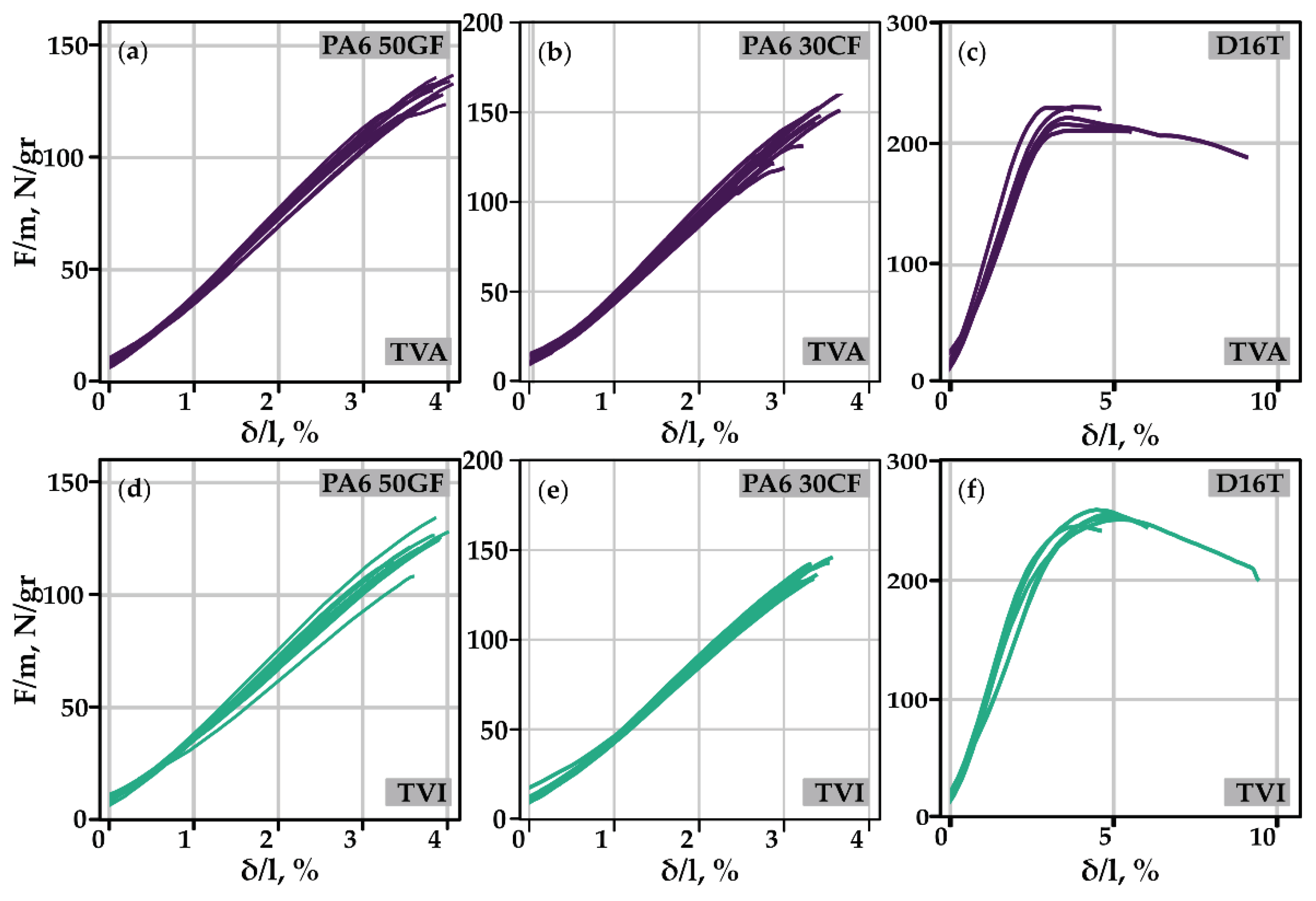
3.1.2. Experimental verification
3.2. Topology-optimal three-dimensional structures
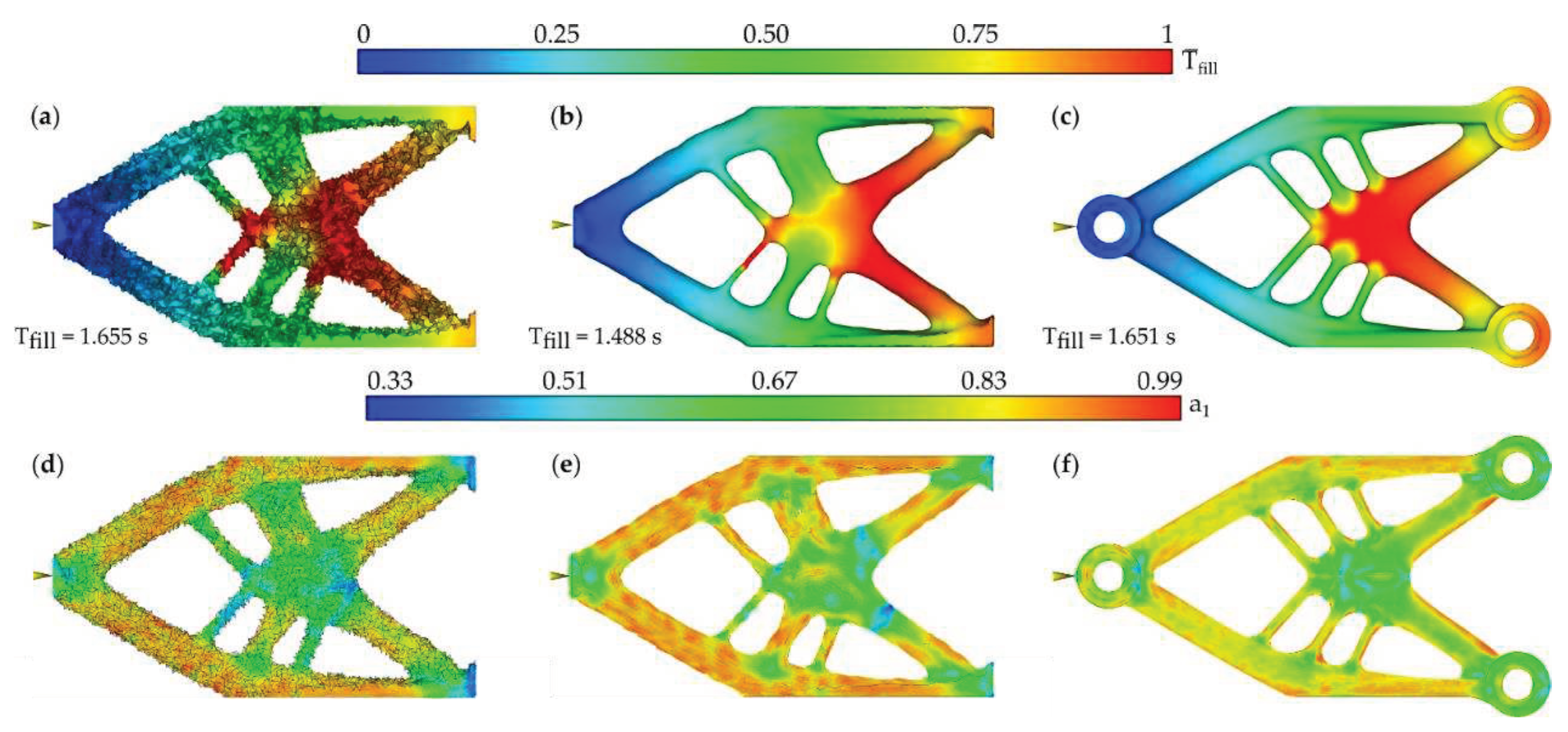
3.2.1. Topology optimization and topology assessment
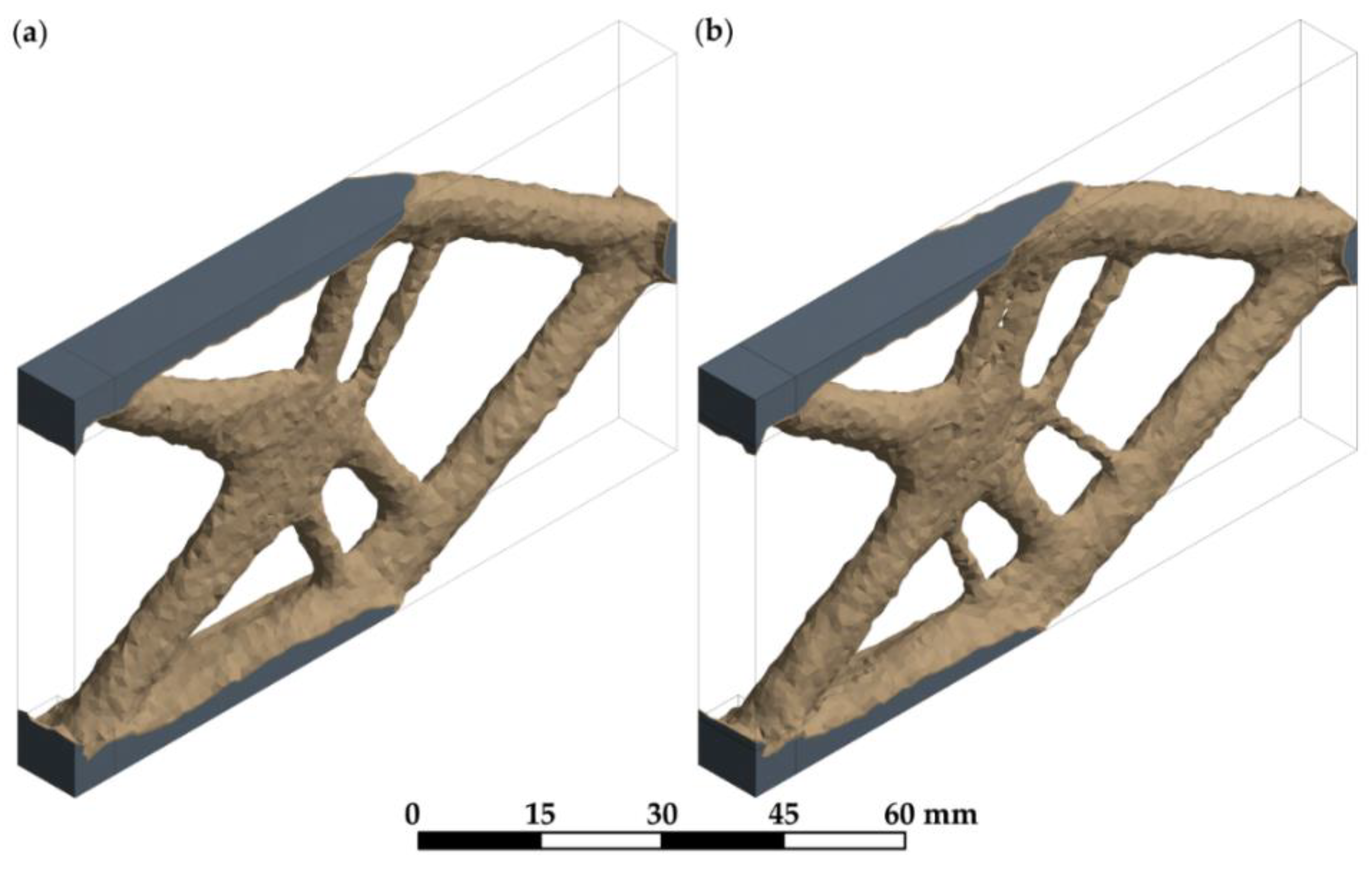
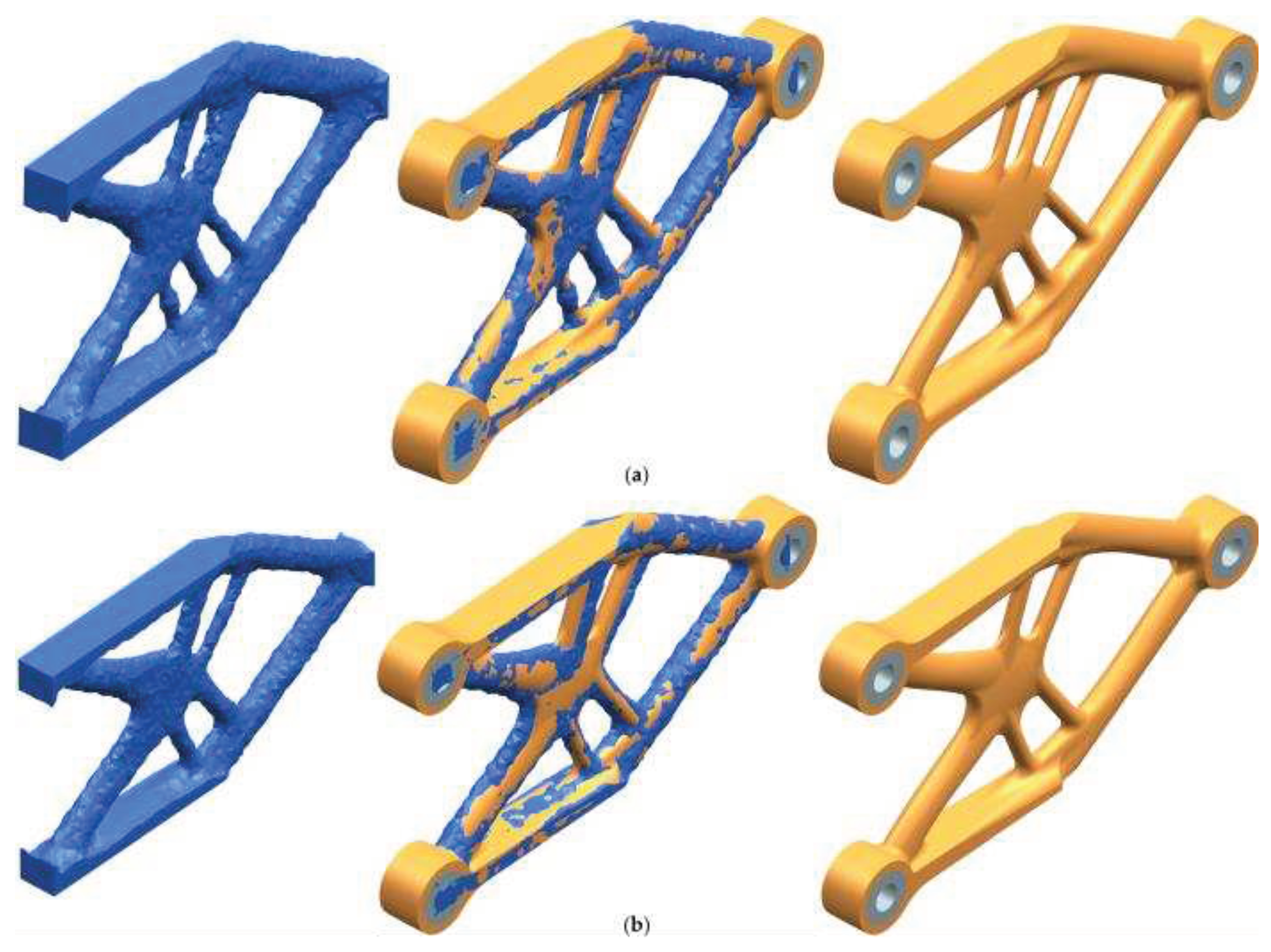
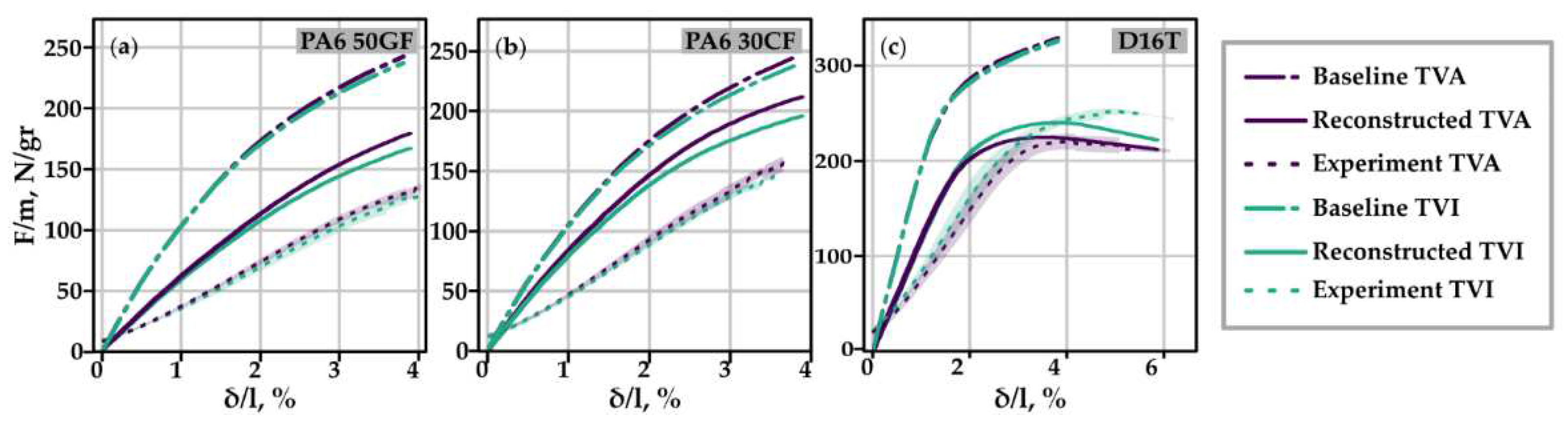
3.1.2. Topology reconstruction
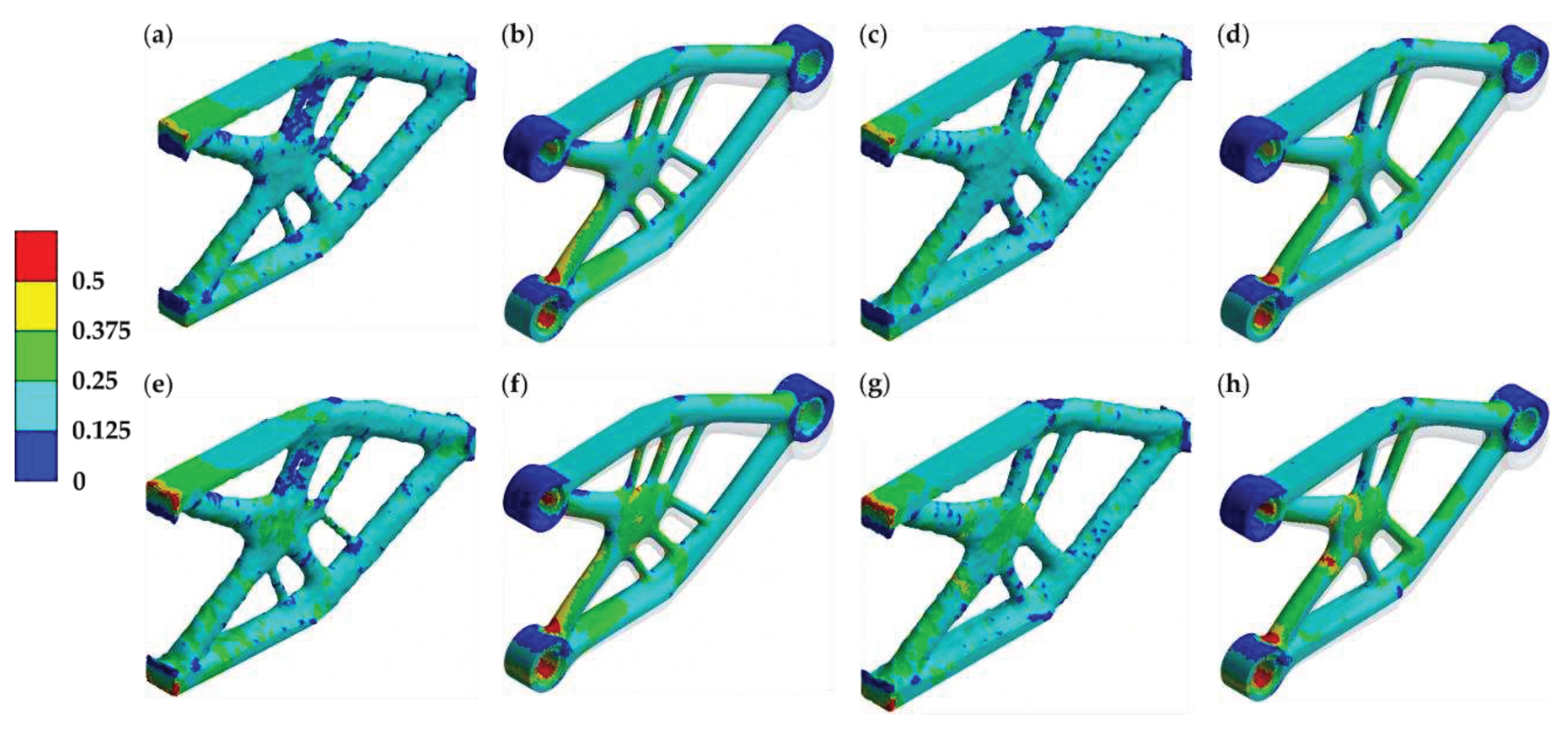
3.2.3. Experimental validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhitomirskiy, G. Konstruktsiya Samoletov: Uchebnoye Posobiye [Aircraft Structure: Textbook], 4th ed.; Mashinostroyeniye: Moscow, 2018; ISBN 978-5-9500364-8-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yendogur, A. Proyektirovaniye Aviatsionnykh Konstruktsiy: Proyektirovaniye Konstruktsiy Detaley i Uzlov [Aircraft Structural Design: Structural Design of Parts and Assemblies]; MAI-Print: Moscow, 2009; ISBN 9785703521038. [Google Scholar]
- Kobelev, V. Design and Analysis of Composite Structures for Automotive Applications: Chassis and Drivetrain. ISBN 9781119513841.
- Spacecraft Structures; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-75552-4.
- Alejandro Ortiz Morales, F.; Bejarano, W.; Zorto, F.; Mejuto, J.; Ortiz, F.; Bejarano Diana Rosales, W. Chassis Optimization of a 1U Cubesat Made in a Developing Country Estudio Arqueoastronómico Del Parque Arqueológico de El Puente View Project Participación Científica En La Misión a Marte MEIGA-METNET-PRECURSOR View Project Chassis Optimization of a 1U Cubesat Made in a Developing Country.
- Feng, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, W.; Xie, Y.; Yu, T.; Hao, Y. Optimal Design of Space Assembly Microsatellite Structure Based on Sequential Quadratic Programming. Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe2009.
- Kawachi, T.; Kimoto, N.; Tsunemi, Y. Stiffness Increase and Weight Reduction Based on Stiffness Evaluation Techniques.
- Formula_1_-_technical_regulations_-_2022_-_iss_9_-_2022-02-18.
- Huh, J.; Kwon, S. A Practical Design Approach for a Single-Stage Sounding Rocket to Reach a Target Altitude. Aeronautical Journal 2022, 126, 1084–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, S. Aircraft Cost Analysis. In General Aviation Aircraft Design; Elsevier, 2014; pp. 33–53. [Google Scholar]
- Vasigh Bijan and Azadian, F. Aircraft Financial and Operational Efficiencies. In Aircraft Valuation in Volatile Market Conditions: Guiding Toward Profitability and Prosperity; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 113–163. ISBN 978-3-030-82450-1. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.; Singh, H.V.; Mishra, L. Improvement In Design Of Engines To Reduce Emissions In Aircarft And Increase Fuel Efficiency. In Outcomes Of Best Practices In Classroom Research; L Ordine Nuovo Publication: New Delhi, 2021 ISBN 978-93-92995-10-1.
- Peters, M.; Kumpfert, J.; Ward, C.H.; Leyens, C. Titanium Alloys for Aerospace Applications. Adv Eng Mater 2003, 5, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.-C.; Chang, R.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H. Numerical Investigations of Fiber Orientation Models for Injection Molded Long Fiber Composites.
- Advanced Aerospace Materials; Buhl, H., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1992; ISBN 978-3-642-50161-6. [Google Scholar]
- Garvey, R.E.; Andriulli, J.B.; Mckeever, J.W. Minimum-Gage, Maximum-Stiffness Graphite/ Thermoplastic Spacecraft Structures.
- Maleki, H.; Durães, L.; Portugal, A. An Overview on Silica Aerogels Synthesis and Different Mechanical Reinforcing Strategies. J Non Cryst Solids 2014, 385, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwary, A.; Kumar, R.; Chohan, J.S. A Review on Characteristics of Composite and Advanced Materials Used for Aerospace Applications. In Proceedings of the Materials Today: Proceedings, Elsevier Ltd; 2021; Vol. 51, pp. 865–870. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Hu, C. Design, Preparation and Properties of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Ultra-High Temperature Ceramic Composites for Aerospace Applications: A Review. J Mater Sci Technol 2017, 33, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalgiri, P.D. Composite Materials for Aerospace Applications. 1999; Vol. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, A.; Budholiya, S.; Raj, S.A.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Hui, D.; Shah, A.U.M.; Safri, S.N.A. Review on Nanocomposites Based on Aerospace Applications. Nanotechnol Rev 2021, 10, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Fierro, D.; Bustamante-Torres, M.; Bravo-Plascencia, F.; Esquivel-Lozano, A.; Ruiz, J.-C.; Bucio, E. Recent Trends in Magnetic Polymer Nanocomposites for Aerospace Applications: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, A.; Upma; Shukla, S.K.; Thakur, N.; Debnath, A.; Mangla, B. Advanced Polymeric Materials for Aerospace Applications. In Aerospace Polymeric Materials; Wiley, 2022; pp. 117–136.
- Sokolowski, W.M.; Tan, S.C. Advanced Self-Deployable Structures for Space Applications. J Spacecr Rockets 2007, 44, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, H.; Liu, L.; Leng, J. Shape Memory Polymers and Their Composites in Aerospace Applications: A Review. Smart Mater Struct 2014, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutis, C. Fibre Reinforced Composites in Aircraft Construction. Progress in Aerospace Sciences 2005, 41, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.A. Study On 3d Printing With Fiber Reinforcement And Its Aerospace Applications.
- Öztoprak, N. Novel AA7075/AA2124-SiC-17p Laminated Structures for Aerospace Applications: A Comparative Study into the Mechanical Performance of PA6 and PA66 Composite Interlayers. Journal of Composite Materials 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neveu, F.; Cornu, C.; Olivier, P.; Castanié, B. Manufacturing and Impact Behaviour of Aeronautic Overmolded Grid-Stiffened Thermoplastic Carbon Plates. Compos Struct 2022, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevo Applications. Available online: https://arevo.com/applications?lang=en (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Aircraft Seat Support | Anisoprint. Available online: https://anisoprint.com/cases/aircraft-seat-support/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Composite Tool for Turbine Blade Production | Anisoprint. Available online: https://anisoprint.com/cases/composite-tool-for-wind-blade-production/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- D2-Concepts.
- Kassapoglou, C. Design and Analysis of Composite Structures; Wiley, 2013; ISBN 9781118401606.
- Lake, M.S. NASA Technical Paper 3210 Stiffness and Strength Tailoring in Uniform Space-Filling Truss Structures. 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Campo, G.A.; Vettorello, A.; Giacalone, M. Optimization Methodology for Continuous Heterogeneous Structures: A Preliminary Design of an Engine Mounting Bracket. In Proceedings of the Key Engineering Materials, Trans Tech Publications Ltd; 2020; Vol. 827, pp. 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev, V. v.; Barynin, V.A.; Razin, A.F. Anisogrid Composite Lattice Structures - Development and Aerospace Applications. Compos Struct 2012, 94, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolaeva, N.S.; Castro, M.B.G.; Kandachar, P. v. Materials Selection for an Automotive Structure by Integrating Structural Optimization with Environmental Impact Assessment. Mater Des 2004, 25, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienz, J.; Luege, M.; Fuerle, F. Continuous Optimization in Aerospace Structures. In Encyclopedia of Aerospace Engineering; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2010.
- Pettit, C.L.; Grandhi, R. v Multidisciplinary Optimization of Aerospace Structures with High Reliability. 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Komarov, V.A.; Kishov, E.A.; Kurkin, E.I.; Charkviani, R. v. Aircraft Composite Spoiler Fitting Design Using the Variable Density Model. In Proceedings of the Procedia Computer Science, Elsevier; 2015; Vol. 65, pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Komarov, V.; Kurkin, E.; Spirina, M.; Kishov, E. Estimation of Weight Efficiency of Topologically Optimal Aerospace Structures. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies, RAST 2019, June 1 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.; pp. 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, M.; Behdinan, K. Design Optimization of Multifunctional Aerospace Structures. In Advanced Multifunctional Lightweight Aerostructures; Design, Development, and Implementation; Wiley, 2021; pp. 93–108.
- Zhu, J.H.; Zhang, W.H.; Xia, L. Topology Optimization in Aircraft and Aerospace Structures Design. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 2016, 23, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, H.; Zheng, S. Multidisciplinary Topology Optimization for Reduction of Sloshing in Aircraft Fuel Tanks Based on SPH Simulation. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2018, 58, 1719–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maute, K.; Reich, G.W. Integrated Multidisciplinary Topology Optimization Approach to Adaptive Wing Design. J Aircr 2006, 43, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarov, A. Osnovy Proyektirovaniya Silovykh Konstruktsiy [Fundamentals of Load-Carrying Structure Design]; Kuybyshev book publ.: Kuybyshev, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Komarov, V. Ratsional’noye Proyektirovaniye Silovykh Aviatsionnykh Konstruktsiy [Rational Design of Load-Carrying Aircraft Structures]. D. in Technical Sciences thesis, Kuibyshev Aviation Institute: Kuibyshev, 1974.
- Komarov, V. Proyektirovaniye Silovykh Skhem Aviatsionnykh Konstruktsiy [Design of Load-Carrying Diagrams of Aircraft Structures]. In Aktual’nyye problemy aviatsionnoy nauki i tekhniki [Actual Problems of Aviation Science and Technology]; Lavrentyev, M., Ed.; Mashinostroyeniye: Moscow, 1984; p. 278. [Google Scholar]
- Komarov, V. Design of Aircraft Structures on the Basis of Discrete Models. In Optimal Design: Theory and Applications to Materials and Structures; Vasiliev, V., Gurdal, Z., Eds.; Technomic Publishing Company: Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1999; p. 330. ISBN 9781566766869. [Google Scholar]
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. Generating Optimal Topologies in Structural Design Using a Homogenization Method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 1988, 71, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P. Optimization of Structural Topology, Shape, and Material; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1995; ISBN 978-3-662-03117-9. [Google Scholar]
- de Luca, A.; Caputo, F. A Review on Analytical Failure Criteria for Composite Materials. AIMS Mater Sci 2017, 4, 1165–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, F.; Washington, G. A Study of Failure Criteria of Fibrous Composite Materials. 2001. [Google Scholar]
- HD-R138 091 A Survey Of Macroscopic Failure Criteria For Composite.
- Komarov, V.A.; Weisshaar, T.A. New Approach to Improving the Aircraft Structural Design Process. J Aircr 2002, 39, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarov, V.A. Dimensionless Criterion of Power Perfection of a Structure. Mechanics of Solids 2018, 53, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarov, V.A. Design and material. Ontology of designing 2023, 13, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Kawamoto, A.; Kondoh, T.; Dede, E.M.; Lee, J.; Song, Y.; Kikuchi, N. Inverse Design of Structure and Fiber Orientation by Means of Topology Optimization with Tensor Field Variables. Compos B Eng 2019, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapetrou, V.S.; Patel, C.; Tamijani, A.Y. Stiffness-Based Optimization Framework for the Topology and Fiber Paths of Continuous Fiber Composites. Compos B Eng 2020, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z. A Review on the Topology Optimization of the Fiber-Reinforced Composite Structures. Aerospace technic and technology 2021, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caivano, R.; Tridello, A.; Paolino, D.; Chiandussi, G. Topology and Fibre Orientation Simultaneous Optimisation: A Design Methodology for Fibre-Reinforced Composite Components. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part L: Journal of Materials: Design and Applications 2020, 234, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.L.F.; Salas, R.A.; Nelli Silva, E.C.; Reddy, J.N. Topology Optimization of Fibers Orientation in Hyperelastic Composite Material. Compos Struct 2020, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, B.C. Multi-Objective Optimization of an Automotive Body Component with Fiber-Reinforced Composites. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2018, 58, 2203–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospald, F.; Herzog, R. SIMP Based Topology Optimization for Injection Molding of SFRPs. In Proceedings of the SIMP based Topology Optimization for Injection Molding of SFRPs, Braunschweig, June 2017; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Folgar, F.; Tucker III, C.L. Orientation Behavior of Fibers in Concentrated Suspensions. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites 1984, 3, 98–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advani, S.G.; Tucker, C.L. The Use of Tensors to Describe and Predict Fiber Orientation in Short Fiber Composites. J Rheol (N Y N Y) 1987, 31, 751–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkin, E.; Kishov, E. Programma AnisoTopo Postroyeniya Anizotropnykh Matrits Zhestkosti Elementov v Zadachakh Topologicheskoy Optimizatsii Konstruktsiy Iz Korotkoarmirovannykh Kompozitsionnykh Materialov [AnisoTopo Program for Constructing Anisotropic Stiffness Matrices of Elements in Problems of Topological Optimization of Structures from Short-Reinforced Composite Materials] 2021.
- Armamid PA6 GF 50-1 TDS TDS. Available online: https://polyplastic-compounds.ru/images/pdf/Armamid/Armamid_PA6_GF_50-1.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- Kurkin, E.; Spirina, M. Accuracy of the Short Fibers Reinforced Composite Material Plasticity Models. J Phys Conf Ser 2021, 12040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamma Plast UPA 6 30 M TDS. Available online: https://gamma-plast.ru/poliamid/uglenapolnenniy/poliamid-upa-6-30-m/ (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- Kurkin, E.; Spirina, M.; Espinosa Barcenas, O.U.; Kurkina, E. Calibration of the PA6 Short-Fiber Reinforced Material Model for 10% to 30% Carbon Mass Fraction Mechanical Characteristic Prediction. Polymers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GOST 4784-97: Aluminium and wrought aluminium alloys. Grades.
- Plastics – Determination of Tensile Properties – Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics; Geneva, CH, 2012; Vol. 2012.
- Komarov, V.; Kurkin, E.; Spirina, M.; Chertykovtseva, V. Multi-Level Computational-Experimental System For The Analysis Of Strength And Stiffness Of Elements Of Structures From Composites Reinforced By Short Fibers. Izvestiya of Samara Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences 2017, 6, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kurkin, E.I.; Kishov, E.A.; Lukyanov, O.E.; Espinosa Barcenas, O.U. Technique of Considering the Material Anisotropy in Topology Optimization of Short Fibers Composite Structures. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, June 21 2021; IOP Publishing Ltd; Vol. 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, G.P.; Weng, G.J. The Effect of Aspect Ratio of Inclusions on the Elastic Properties of Unidirectionally Aligned Composites. Polymer Composites 1984, 5, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. Mathematical Simplification of the Tandon–Weng Approach to the Mori–Tanaka Model for Es-timating the Young’s Modulus of Clay/Polymer Nanocomposites. JOM 2017, 69, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, A.A. Finite Element Estimates of Viscoelastic Stiffness of Short Glass Fiber Reinforced Composites. Composite Structures 2017, 171, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
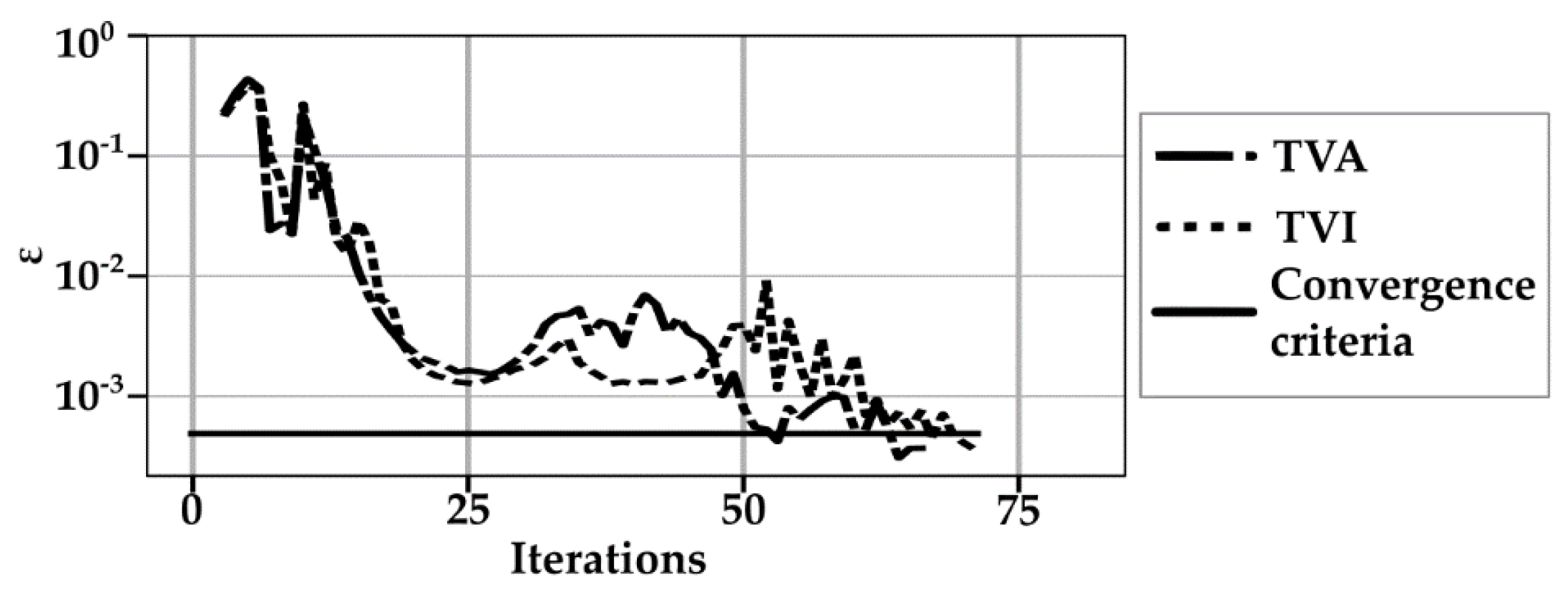
- Ghoreishi, S.N.; Clausen, A.; Joergensen, B.N. Termination Criteria in Evolutionary Algorithms: A Survey. In Proceedings of the IJCCI 2017 - Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence; SciTePress, 2017; pp. 373–384. [Google Scholar]
- Komarov, V.; Spirina, M.; Kurkin, E.; Kishov, E. Estimation of Weight Efficiency of Topologically Optimal Aerospace Structures.
- Guest, J.K.; Lotfi, R.; Gaynor, A.T.; Jalalpour, M. Structural Topology Optimization: Moving Beyond Linear Elastic Structural Topology Optimization: Moving Beyond Linear Elastic Design Objectives Design Objectives Original Citation Original Citation “Structural Topology Optimization-Moving beyond Linear Elastic Design Objectives”; 2012.
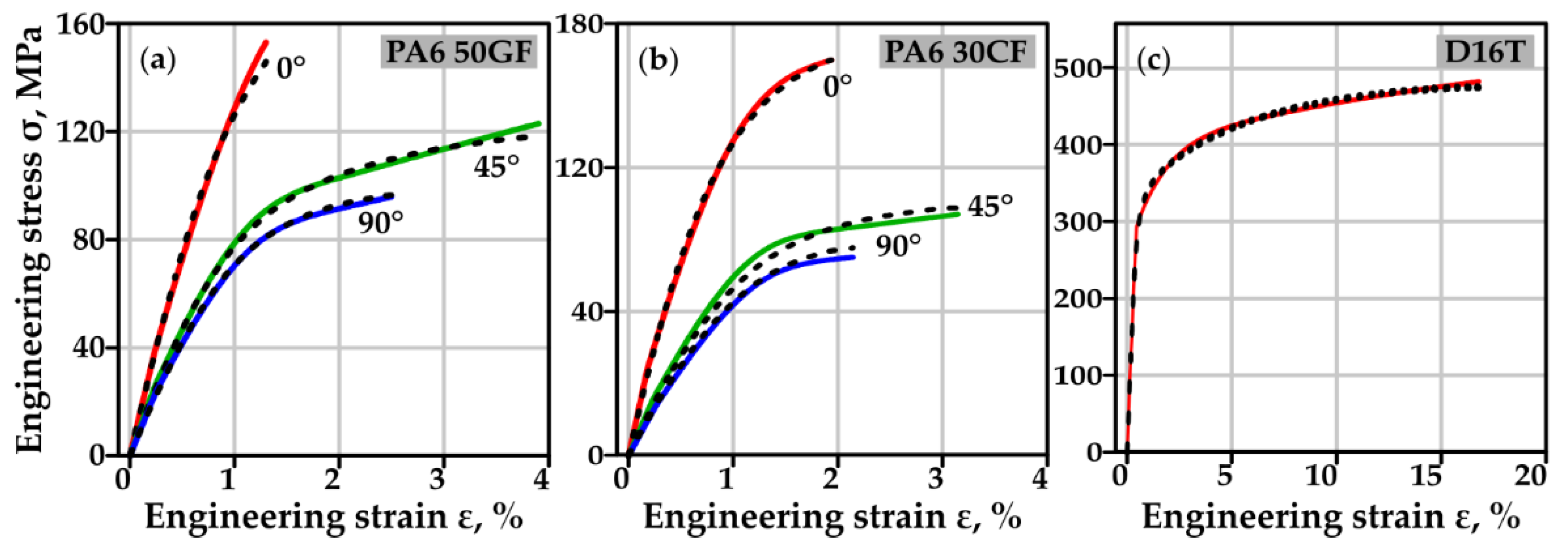
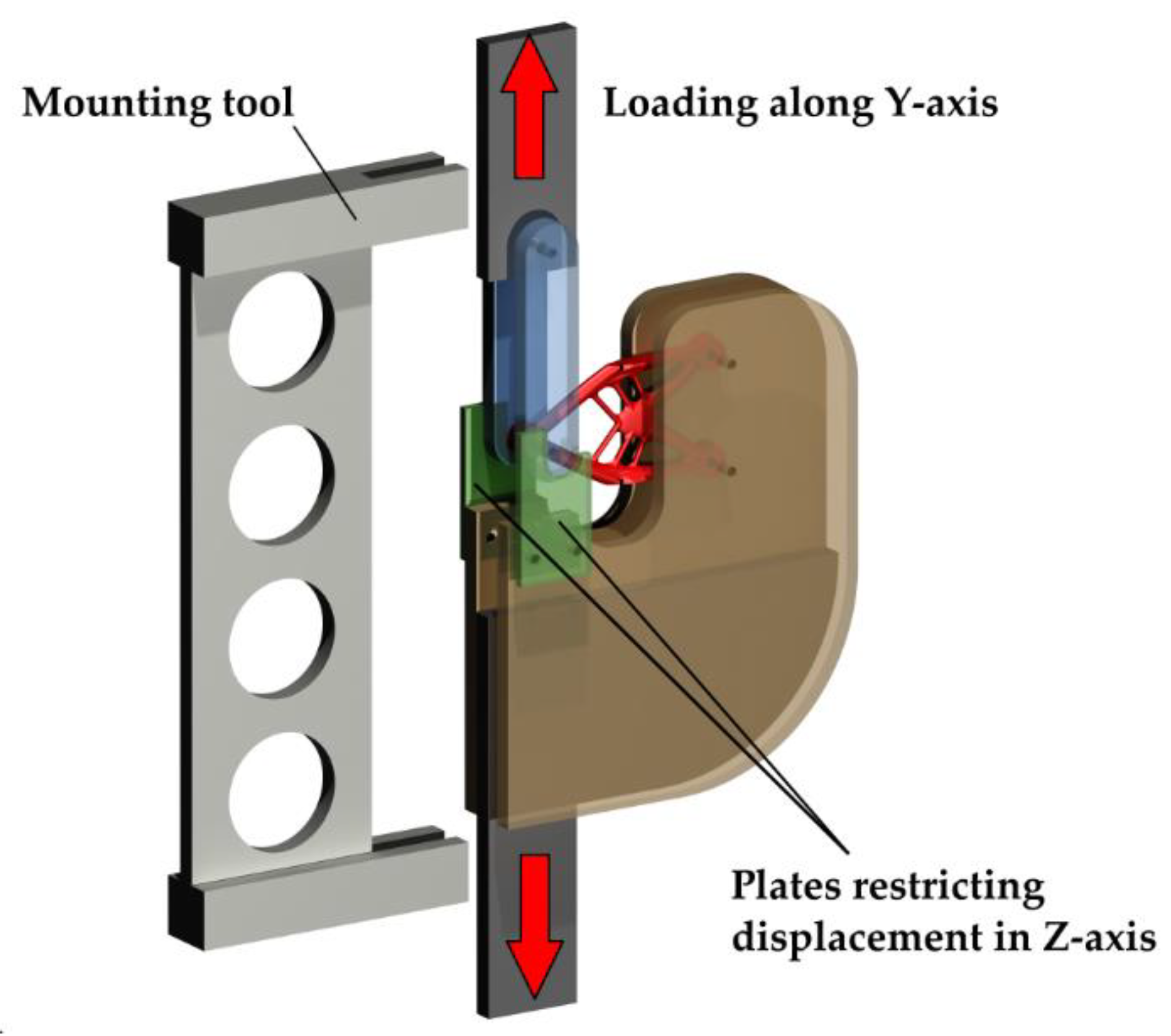
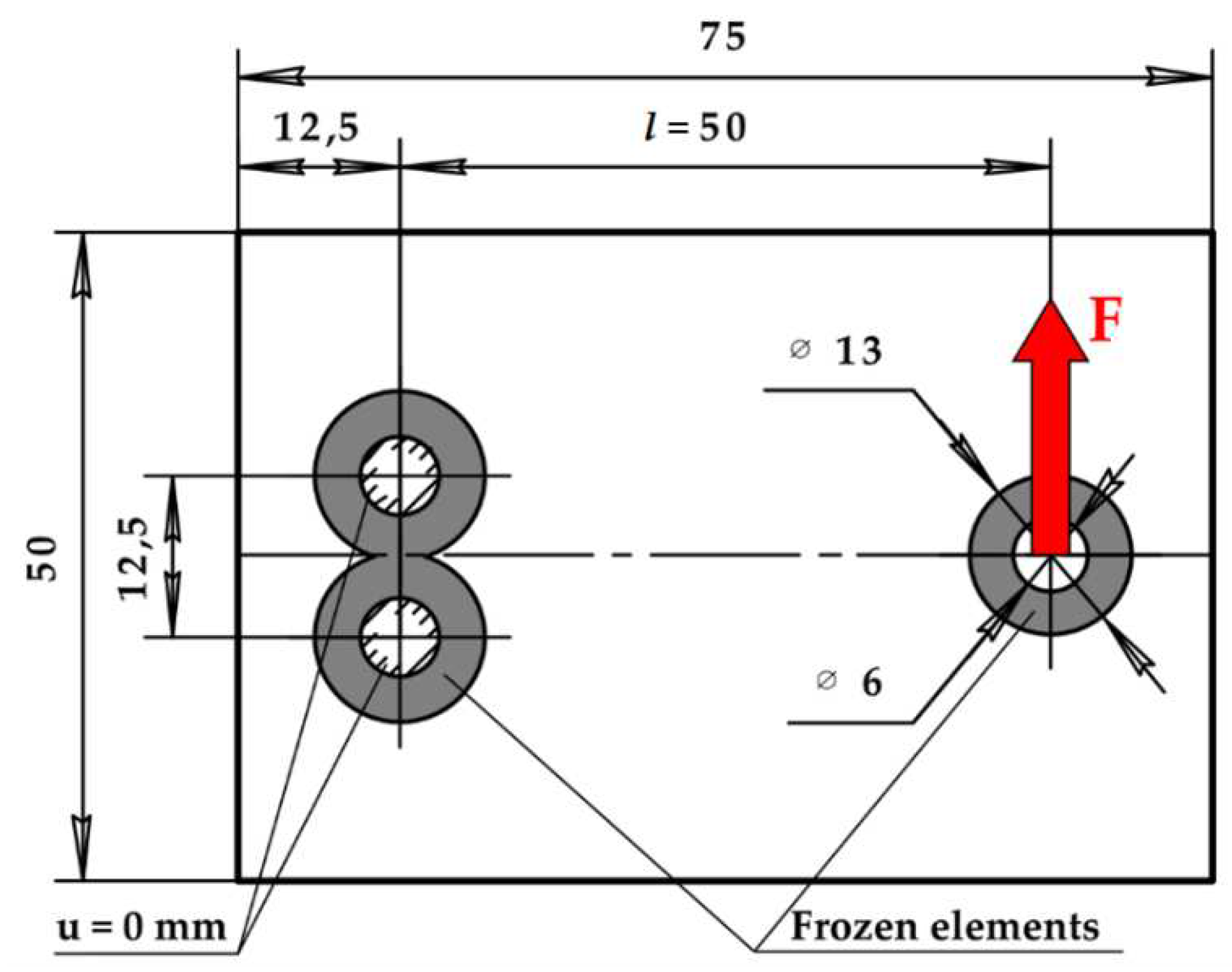
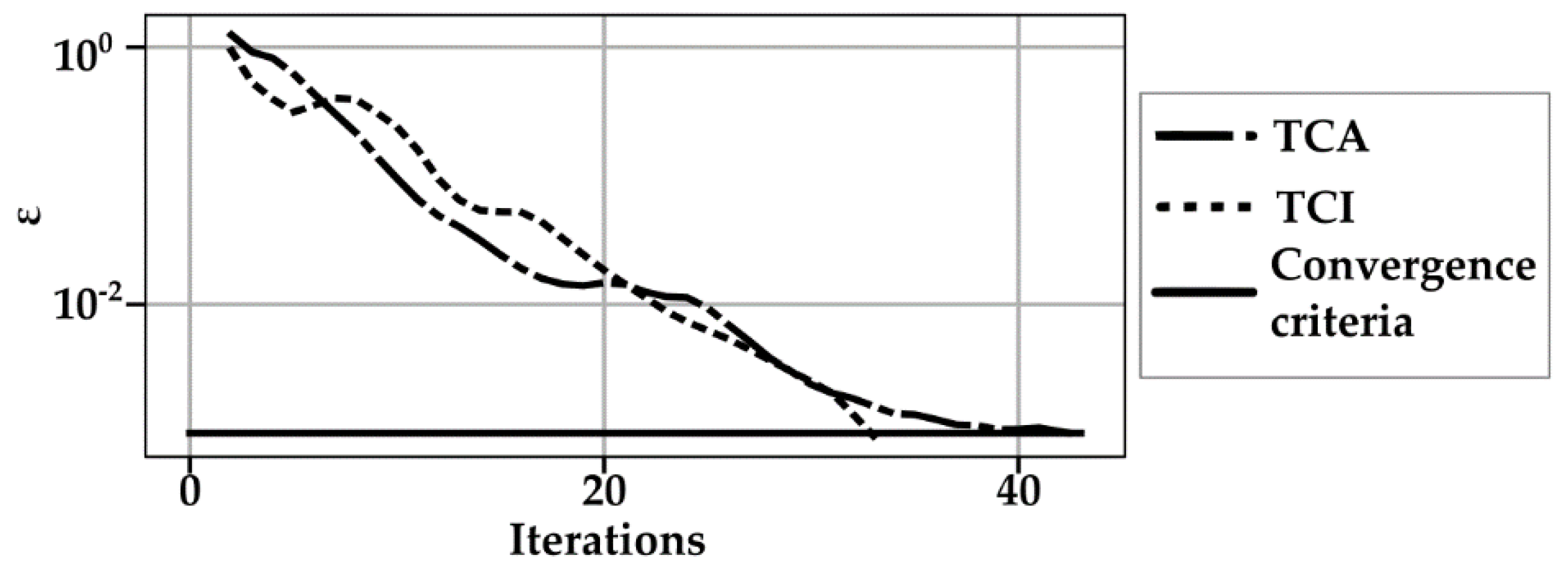

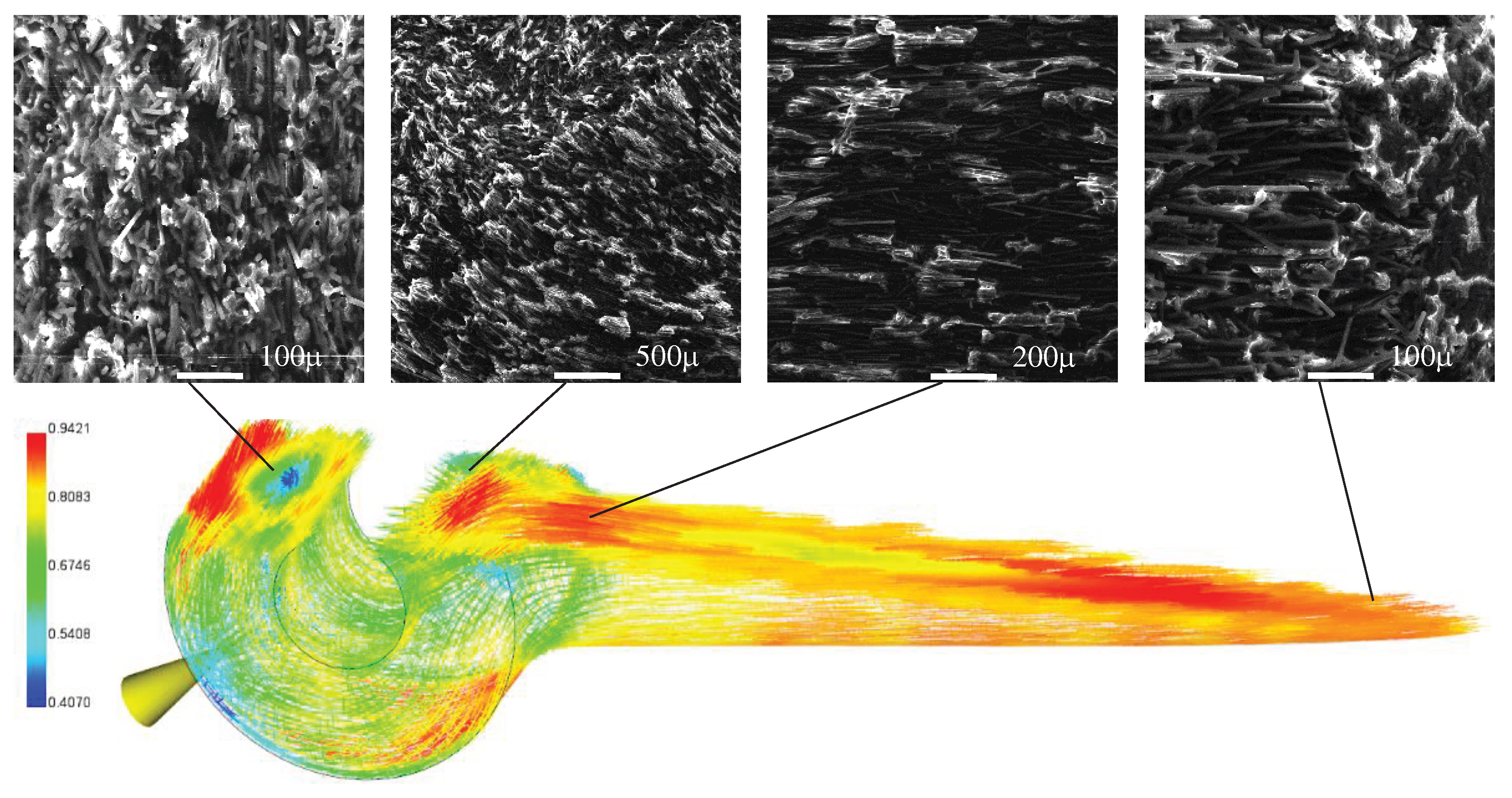

| Characteristics | Material | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PA 50GF | PA 30CF | D16T | |
| Matrix phase | |||
| Matrix density, kg/m3 | 1148 | 2770 | |
| Young’s modulus, Em (MPa) | 4911 | 3994 | 66059 |
| Poisson’s coefficient, υm | 0.372 | 0.372 | 0.330 |
| Yield stress, σy (MPa) | 17.21 | 14.5 | 294.48 |
| Hardening modulus, R∞ (MPa) | 37.1 | 37.00 | 109.51 |
| Hardening exponent, m | 371.21 | 458.30 | 75.72 |
| Linear hardening modulus, k (MPa) | 313.02 | 188.40 | 1107.60 |
| Reinforcement phase | |||
| Fiber density, kg/m3 | 2550 | 1780 | - |
| Young’s modulus, Ef (MPa) | 72000 | 230000 | - |
| Poisson’s coefficient, υf | 0.22 | 0.20 | - |
| Fibers’, AR | 13.58 | 16.54 | - |
| Wt. % | 30 | 50 | - |
| Material ultimate tensile strength | |||
| Longitudinal, X (MPa) | 153.31 | 169.35 | 476 |
| Transverse, Y (MPa) | 97.82 | 85.07 | - |
| Transverse shear strength, S (MPa) | 83.90 | 66.33 | - |
| Topology | m, g | f, N | CK | CKTH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA6 50GF | ||||||
| TCA | 4.655 | 326.8 | 5.2928 | 5.6994 | ||
| TCI | 4.658 | 326.1 | 5.2482 | 5.8285 | ||
| PA6 30CF | ||||||
| TCA | 3.779 | 264.5 | 5.3407 | 6.7438 | ||
| TCI | 3.781 | 264.7 | 5.2874 | 7.1127 | ||
| D16T | ||||||
| TCA | 8.146 | 570.3 | 5.1964 | - | ||
| TCI | 8.152 | 570.6 | 5.2287 | - | ||
| Topology | Normalized specific stiffness, N/gr | Percentage change from TCA to TCI, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCA | TCI | ||
| PA6 50GF | 3883 | 3661 | 6.06 |
| PA6 30CF | 4621 | 4194 | 10.18 |
| D16T | 11474 | 11654 | -1.54 |
| Material | Average, N/gr | Standard deviation, N/gr |
Coefficient of variation, % | Percentage change from TCA to TCI, % |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TVA | TVI | TVA | TVI | TVA | TVI | ||
| PA6 50GF | 1551 | 1479 | 140 | 167 | 9.03 | 11.26 | 4.87 |
| PA6 30CF | 1833 | 1737 | 52 | 96 | 2.84 | 5.54 | 5.53 |
| D16T | 7192 | 7584 | 76 | 406 | 1.06 | 5.36 | -5.17 |
| Topology | Baseline | Reconstructed | Percentage difference from baseline to reconstructed |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m, g | f, N | CKeq | CKTH | m, g | f, N | CKeq | CKTH | CKeq | CKTH | |
| PA6 50GF | ||||||||||
| TVA | 22.94 | 1606 | 3.3183 | 3.4341 | 25.59 | 1791 | 3.5230 | 3.6541 | 5.98% | 6.21% |
| TVI | 23.24 | 1627 | 3.3214 | 3.4437 | 26.17 | 1832 | 3.5481 | 3.6926 | 6.60% | 6.98% |
| PA6 30CF | ||||||||||
| TVA | 18.62 | 1304 | 3.3225 | 3.6881 | 20.76 | 1448 | 3.5273 | 3.9025 | 5.98% | 5.65% |
| TVI | 18.86 | 1320 | 3.3238 | 3.7103 | 21.24 | 1481 | 3.5539 | 3.9799 | 6.69% | 7.01% |
| D16T | ||||||||||
| TVA | 40.15 | 2810 | 3.3122 | - | 47.34 | 3314 | 3.5707 | - | 7.51% | - |
| TVI | 40.66 | 2846 | 3.3176 | - | 48.36 | 3386 | 3.5892 | - | 7.86% | - |
| Material | Topology | Normalized specific stiffness, N/gr | Percentage change from TVA to TVI, % |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TVA | TVI | |||
| PA6 50GF | Baseline | 7250 | 7187 | 0.88 |
| Reconstructed | 5500 | 5260 | 4.56 | |
| PA6 30CF | Baseline | 8993 | 8924 | 0.77 |
| Reconstructed | 7209 | 6893 | 4.58 | |
| D16T | Baseline | 19737 | 19869 | -0.66 |
| Reconstructed | 11838 | 11613 | 1.92 | |
| Material | Average, N/gr |
Standard deviation, N/ gr |
Coefficient of variation, % |
Percentage change from TVA to TVI, % |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TVA | TVI | TVA | TVI | TVA | TVI | ||
| PA6 50GF | 3529 | 3289 | 179 | 267 | 5.09 | 8.13 | 7.30 |
| PA6 30CF | 4533 | 4290 | 216 | 187 | 4.77 | 4.36 | 5.66 |
| D16T | 7293 | 7875 | 775 | 1150 | 10.63 | 14.60 | -7.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





