Submitted:
05 December 2023
Posted:
06 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Diets, Experimental design and Animal management
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Growth performance
2.4. Real-Time PCR analysis
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. The growth performance of broilers challenged with LPS
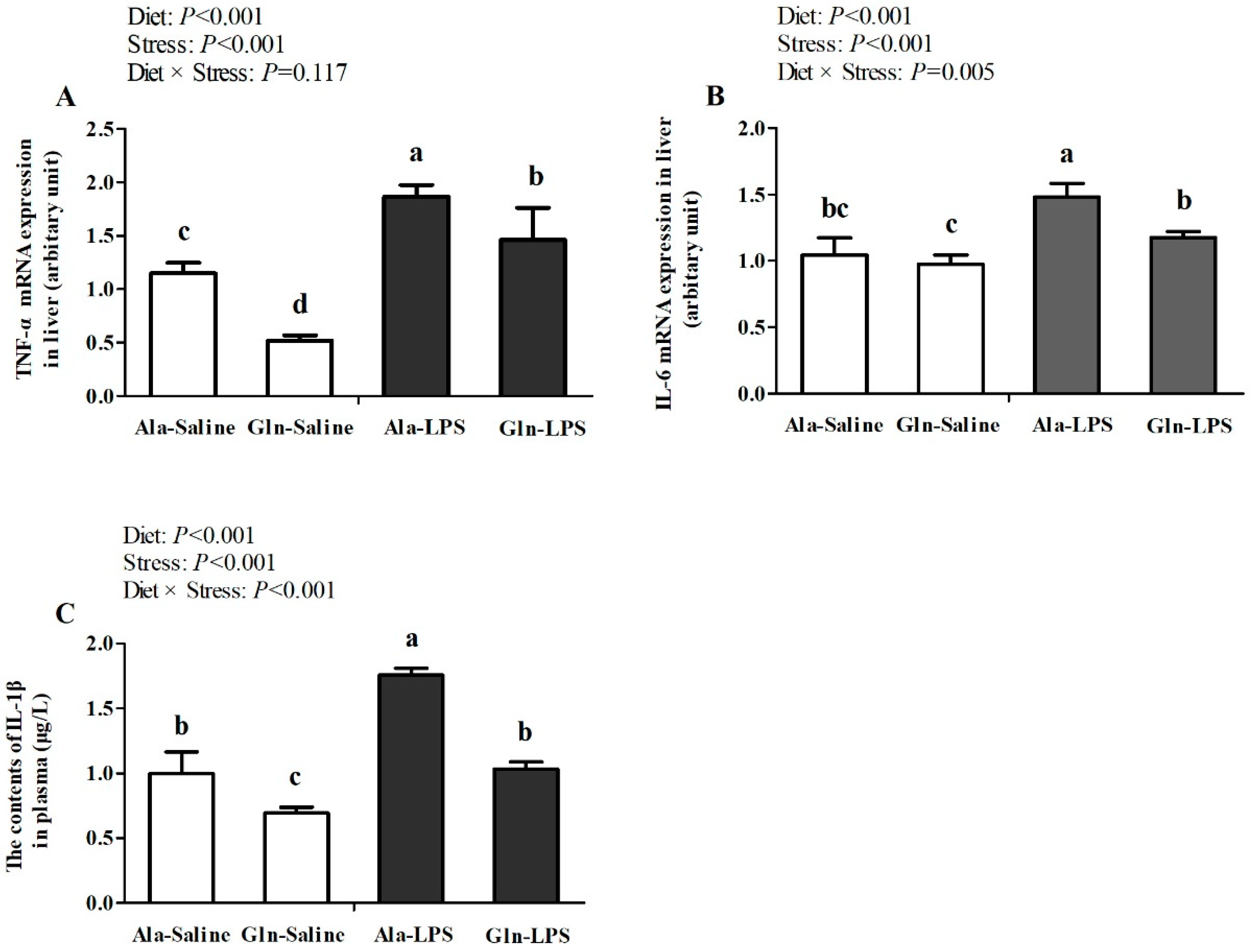
3.2. mRNA expression of TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β in liver
3.3. The activities of ALT and AST in muscle of broilers
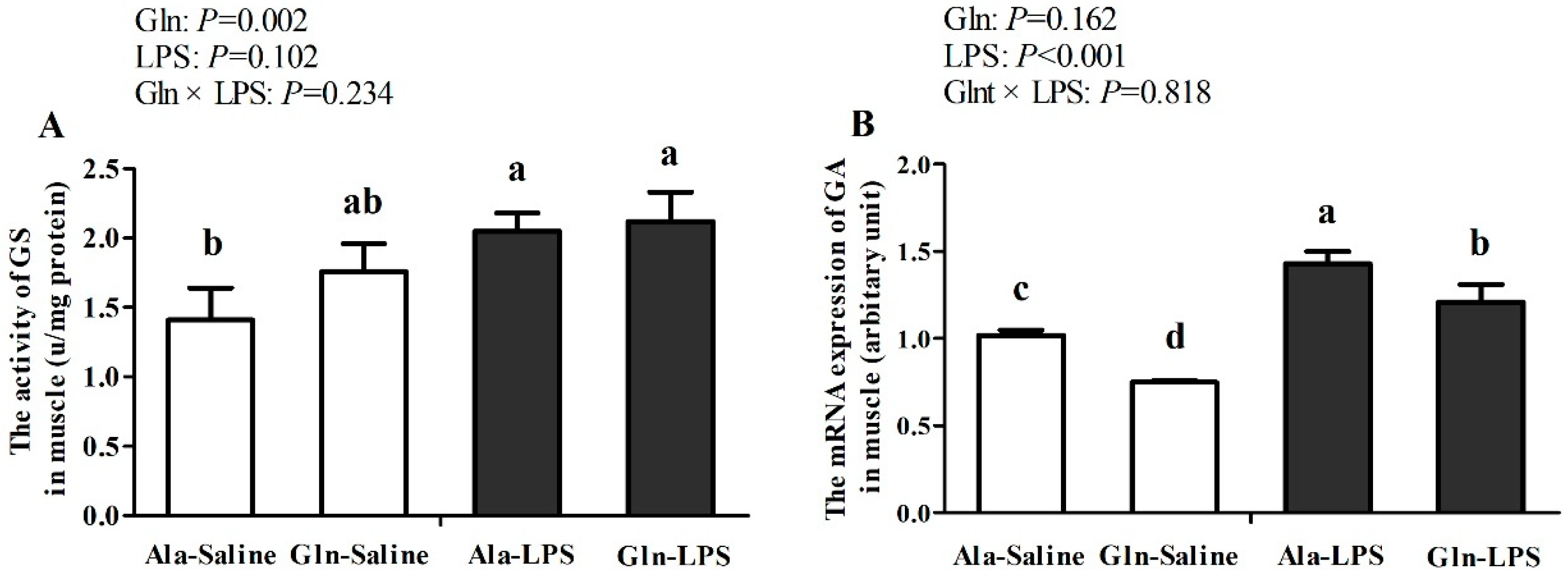
3.4. GS activity and mRNA expression of GA in Pecloralis Muscles of broilers
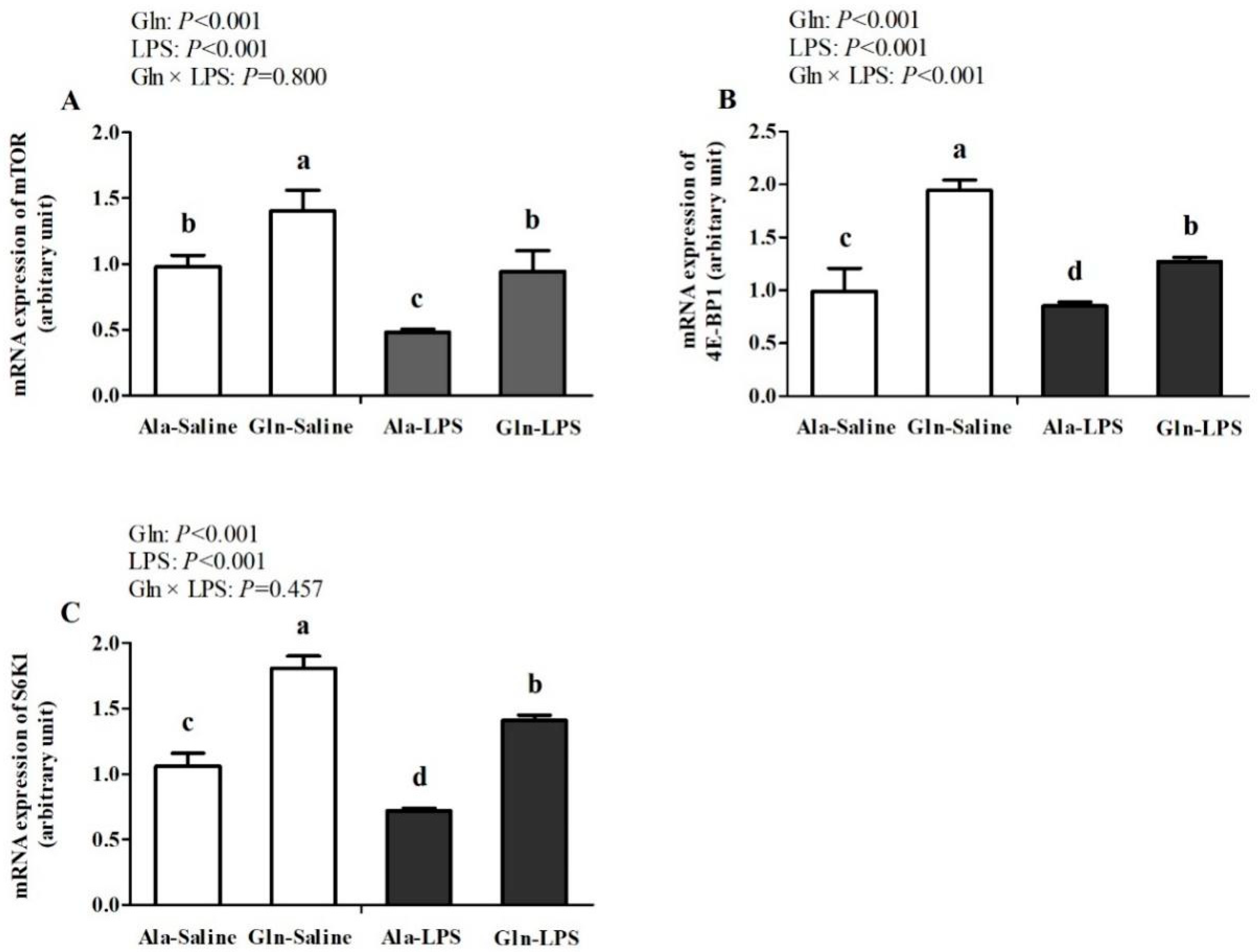
3.5. mTOR signaling molecules in muscle
3.6. mRNA expression of Akt/FOXO signals mediated by TLR4
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- Liu K. X., Zhen W. R., Bai D. Y., Tan H. Q., He X. L., Li Y. Q., Liu Y. H., Zhang Y., Ito K., Zhang B. K., Ma Y. B. Lipopolysaccharide-induced immune stress negatively regulates broiler chicken growth the COX-2-PGE-EP4 signaling pathway. Frontiers in immunology 2023, 14, 1193798. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi S., Shao J. J., Qu Y. W., Hu W. D., Ma Y., Cao L. T. Hepatic transcriptomics and metabolomics indicated pathways associated with immune stress of broilers induced by lipopolysaccharide. Poultry science 2022, 101, 102199. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu Y. P., Li Q., Liu J. S., Liu Y. L., Xu Y. L., Zhang R. Q., Yu Y., Wang Y. X., Yang C. M. Integrating Serum Metabolome and Gut Microbiome to Evaluate the Benefits of Lauric Acid on Lipopolysaccharide- Challenged Broilers. Frontiers in immunology 2021, 12, 759323. [CrossRef]
- Lee Y., Lee S. H., Gadde U. D., Oh S. T., Lee S. J., Lillehoj H. S. Dietary Allium hookeri reduces inflammatory response and increases expression of intestinal tight junction proteins in LPS-induced young broiler chicken. Research in veterinary science 2017, 112, 149–55. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang B. L.., Zhong Q Z., Liu N., Song P. Y., Zhu P., Zhang C. C., Sun Z. W. Dietary Glutamine Supplementation Alleviated Inflammation Responses and Improved Intestinal Mucosa Barrier of LPS-Challenged Broilers. Animals 2022, 12, 1729. [CrossRef]
- Orellana R. A., Suryawan A., Wilson F. A., Gazzaneo M. C., Fiorotto M. L., Nguyen H. V., Davis T. A. Development aggravates the severity of skeletal muscle catabolism induced by endotoxemia in neonatal pigs. American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative comparative physiology 2012, 302, R682-90. [CrossRef]
- Zhang B., Yu C., Lin M., Fu Y., Zhang L., Meng M., Xing S., Li J., Sun H., Gao F. Regulation of skeletal muscle protein synthetic and degradative signaling by alanyl-glutamine in piglets challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Nutrition 2015, 31, 749–56. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai S. F., Wang L. K., Wen A. Y., Wang L. X., Jin G. M. Dietary glutamine supplementation improves growth performance, meat quality and colour stability of broilers under heat stress. British poultry science 2009, 50, 333–40. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai X., Wang K., Khan R., U, Zhang C., Hu H. Effect of Glutamine on the Growth Performance, Oxidative Stress, and Nrf2/p38 MAPK Expression in the Livers of Heat-Stressed Broilers. Animals 2023, 13, 652. [CrossRef]
- Wu Q. J.., Zhu D. D., Wang D. D.., Zhang B B., Ren A., Zhang Z. B. Effects of dietary supplementation with glutamine on the lymphocyte proliferation and intestinal immune gene expression in broiler chickens infected with Salmonella Enteritidis. Research in veterinary science 2021, 139, 18–24. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang B. L., Liu N., Hao M. L., Xie Y. X., Song P. Y. Effects of substitution of soybean meal with rapeseed meal and glutamine supplementation on growth performance, intestinal morphology, and intestinal mucosa barrier of Qiandongnan Xiaoxiang Chicken. Animal bioscience 2022, 35, 1711–24. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing S., Zhang B. L., Lin M., Zhou P., Li J. L., Zhang L., Gao F., Zhou G. H. Effects of alanyl-glutamine supplementation on the small intestinal mucosa barrier in weaned piglets. Asian-Australasian journal of animal sciences 2017, 30, 236–45. [CrossRef]
- Xue G. D., Barekatain R., Wu S. B., Choct M., Swick R. A. Dietary L-glutamine supplementation improves growth performance, gut morphology, and serum biochemical indices of broiler chickens during necrotic enteritis challenge. Poultry science 2018, 97, 1334–41. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou J., Chen H. H., Du J. T., Tai H. R., Han X. J., Huang N., Wang X. B., Gong H., Yang M. Y., Xiao H. Y. Glutamine Availability Regulates the Development of Aging Mediated by mTOR Signaling and Autophagy. Frontiers in pharmacology 2022, 13, 924081. [CrossRef]
- Yi D., Hou Y. Q., Wang L.., Ouyang W. J., Long M. H., Zhao D., Ding B. Y., Liu Y. L., Wu G. Y. L-Glutamine enhances enterocyte growth via activation of the mTOR signaling pathway independently of AMPK. Amino acids 2015, 47, 65–78. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak K. J., Schmittgen T. D.. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2-△△Ct Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–8. [CrossRef]
- Tang J., Xu Lq., Zeng Y. W., Gong F. Effect of gut microbiota on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. International immunopharmacology 2021, 91, 107272. [CrossRef]
- Ruan D., Wu S. W., Fouad A. M., Zhu Y. W., Huang W. J., Chen Z. L., Gou Z. Y., Wang Y. B., Han Y. Q., Yan S. J.., Zheng C. T., Jiang S. Q.. Curcumin alleviates LPS-induced intestinal homeostatic imbalance through reshaping gut microbiota structure and regulating group 3 innate lymphoid cells in chickens. Food function 2022, 13, 11811–24. [CrossRef]
- Kampman-van de Hoek E., Sakkas P., Gerrits W. J., van den Borne J. J., van der Peet-Schwering C. M., Jansman A. J. Induced lung inflammation and dietary protein supply affect nitrogen retention and amino acid metabolism in growing pigs. British journal of nutrition 2015, 113, 414–25. [CrossRef]
- Zhang W. H., Jiang Y., Zhu Q. F., Gao F., Dai S. F., Chen J., Zhou G. H. Sodium butyrate maintains growth performance by regulating the immune response in broiler chickens. British poultry science 2011, 52, 292–301. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang L., Liu G., Zhu X. Q., Luo Y., Shang Y. X., Gu X. L. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of leonurine hydrochloride after lipopolysaccharide challenge in broiler chicks. Poultry science 2019, 98, 1648–57. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai S. F., Bai X., Zhang D., Hu H., Wu X. Z.., Wen A. Y., He S. J., Zhao L. Dietary glutamine improves meat quality, skeletal muscle antioxidant capacity and glutamine metabolism in broilers under acute heat stress. Journal of applied animal research 2018, 46, 1412–7. [CrossRef]
- Wu Q. J., Wang Y. Q., Qi Y. X. Influence of procyanidin supplementation on the immune responses of broilers challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Animal science journal 2017, 88, 983–90. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramires C. C., Balbinot D. T., Cidral-Filho F. J., Dias D. V., Dos Santos A. R., da Silva M. D. Acupuncture reduces peripheral and brainstem cytokines in rats subjected to lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Acupuncture in medicine 2021, 39, 376–84. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang L., Liu G., Liang X. R., Wang M. M., Zhu X. Q., Luo Y., Shang Y. X., Yang J. Q., Zhou P., Gu X. L. Effects of berberine on the growth performance, antioxidative capacity and immune response to lipopolysaccharide challenge in broilers. Animal science journal 2019, 90, 1229–38. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achamrah N., Déchelotte P., Coëffier M. Glutamine and the regulation of intestinal permeability: from bench to bedside. Current opinion in clinical nutrition metabolic care 2017, 20, 86–91. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang B. L., Lin M., Yu C. N., Li J. L., Zhang L., Zhou P., Yang W. W., Gao F., Zhou G. H. Alanyl-glutamine supplementation regulates mTOR and ubiquitin proteasome proteolysis signaling pathways in piglets. Nutrition 2016, 32, 1123–31. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsholme E. A., Parry-Billings M. Properties of glutamine release from muscle and its importance for the immune system. Journal of parenteral enteral nutrition 1990, 14, 63S–7S. [CrossRef]
- Cruzat V., Macedo Rogero M. M., Noel Keane K. N., Curi R. C., Newsholme P. Glutamine: Metabolism and Immune Function, Supplementation and Clinical Translation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1564. [CrossRef]
- Labow B. I., Souba W. W., Abcouwer S. F.. Mechanisms governing the expression of the enzymes of glutamine metabolism--glutaminase and glutamine synthetase. Journal of nutrition 2001, 131, 2467S–74S. [CrossRef]
- Karinch A. M., Pan M., Lin C. M., Strange R., Souba W. W. Glutamine metabolism in sepsis and infection. Journal of Nutrition 2001, 131, 2531S–50S. [CrossRef]
- Xiao Y. P., Li X. Y., Wu T. X., Yang L., Hong Q. H., Yang C. M., Chen A. G. Effects of dietary glutamine supplementation on nutrient absorption and activity of enzymes involved in glutamine metabolism and energy production in the jejunum of weaned piglets. Journal of animal and vetrinary advances 2012, 11, 1441–9. [CrossRef]
- Cao Y., Liu S., Liu K. X., Abbasi I. H. R., Cai C., Yao J. Molecular mechanisms relating to amino acid regulation of protein synthesis. Nutrition research reviews 2019, 32, 183–91. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost R. A., Lang C. H. mTOR signaling in skeletal muscle during sepsis and inflammation: where does it all go wrong? Physiology 2011, 26, 83–96. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklin P., Bergman P., Zhang B. L., Triantafellow E., Wang H., Nyfeler B., Yang H. D., Hild M., Kung C., Wilson C.., Myer V. E., MacKeigan J. P., Porter J. A., Wang Y. K., Cantley L. C., Finan P. M., Murphy L. O.. Bidirectional transport of amino acids regulates mTOR and autophagy. Cell 2009, 136, 521–34. [CrossRef]
- Xi P. B., Jiang Z. Y., Dai Z. L., Li X. L., Yao K., Zheng C. T., Lin Y. C., Wang J. J., Wu G. Y. Regulation of protein turnover by L-glutamine in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Journal of nutritional biochemistry 2012, 23, 1012–7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecker S. H., Goldberg A. L., Mitch W. E. Protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in normal and disease states. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006, 17, 1807–19. [CrossRef]
- Franch H. A., Price S. R. Molecular signaling pathways regulating muscle proteolysis during atrophy. Current opinion in clinical nutrition metabolic care 2005, 8, 271–5. [CrossRef]
- Crossland H., Constantin-Teodosiu D., Gardiner S. M., Constantin D., Greenhaff P. L. A potential role for Akt/FOXO signalling in both protein loss and the impairment of muscle carbohydrate oxidation during sepsis in rodent skeletal muscle. Journal of physiology 2008, 586, 5589–600. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle A., Zhang G.., Abdel Fattah E. A., Eissa N. T., Li Y. P. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced muscle catabolism via coordinate activation of ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy-lysosome pathways. FASEB 2011, 25, 99–110. [CrossRef]
- Crossland H., Constantin-Teodosiu D., Greenhaff P. L., Gardiner S. M. Low-dose dexamethasone prevents endotoxaemia-induced muscle protein loss and impairment of carbohydrate oxidation in rat skeletal muscle. Journal of physiology 2010, 588, 1333–47. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan H. W. S.., Sim A. Y. L., Long Y. C. Glutamine metabolism regulates autophagy-dependent mTORC1 reactivation during amino acid starvation. Nature communications 2017, 8, 338. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambertucci A. C.., Lambertucci R. H., Hirabara S. M., Curi R., Moriscot A. S., Alba-Loureiro T. C., Guimarães-Ferreira L., Levada-Pires A. C., Vasconcelos D. A., Sellitti D. F., Pithon-Curi T. C. Glutamine supplementation stimulates protein-synthetic and inhibits protein-degradative signaling pathways in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats. PloS one 2012, 7, e50390. [CrossRef]
| Ingredients (g/kg diet) | Nutrient content (g/kg diet) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Maize | 563.0 | Crude protein‡ | 210.8 |
| Wheat bran | 51.30 | Metabolism energy(MJ/kg) | 121.2 |
| Soybean meal | 285.0 | Calcium(%) | 10.00 |
| Corn gluten meal | 43.0 | Phosphorus(%) | 4.50 |
| DL-Methionine | 1.50 | DL-Methionine(%) | 8.60 |
| Phytase | 0.40 | L-Lysine(%) | 10.60 |
| Choline | 1.50 | Threonine(%) | 8.0 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 18.70 | ||
| Limestone | 12.60 | ||
| Salt | 1.50 | ||
| Soybean oil | 16.50 | ||
| Vitamin and mineral premix† | 5.00 |
| Genes | ID | Primers sequences(5’-3’) | Product size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAFbx | NM_001030956.1 | F: GCCAGTACCACTTCACAGACAGAC R: GCGTGTCACCATACTGCTCCTTC |
132 |
| MuRF1 | XM_424369.4 | F: GAACGACCGCATCCAGACCATC R: TCCGTCTTCTTCTCCTCCAGCAG |
138 |
| FOXO1 | NM_204328.1 | F: GACCTCATCACCAAGGCCATCG R: GCACGCTCTTGACCATCCACTA |
85 |
| Akt | NM_205055.1 | F: GGCTACAAGGAACGACCGCAAG R: TACTGTGGTCCACTGGAGGCATC |
141 |
| TLR4 | NM_001030693.1 | F: TTCGGTTGGTGGACCTGAATCTTG R: ACAGCTTCTCAGCAGGCAATTCC |
114 |
| GA | NM_001031248.1 | F: TCCTCGCAGAGAAGGTGGTGATC R: TACGTGCAATGCTGTTCGTGAGTC |
154 |
| S6K1 | NM_001030721.1 | F: GTTCAGGCTCACCCGTTCTTCAG R: TGGCTCACATCCTCTTCAGATTGC |
107 |
| FOXO4 | XM_015278657.2 | F: CAACGTTCCACCACCCGTGA R: TGGAGGCAGATTGCTGGGTA |
101 |
| TNF-α | NM_204267.1 | F: TGTGTATGTGCAGCAACCCG R: AACAACCAGCTATGCACCCC |
178 |
| mTOR | XM_417614.6 | F: AACCACTGCTCGCCACAATGC R: CATAGGATCGCCACACGGATTAGC |
120 |
| 4E-BP1 | XM_424384.6 | F: GACCGTAAGTTCCTGATGGAGTGC R: ATTGGGCTGGTAACACCTGGAATG |
92 |
| IL-1β | NM_204524.1 | F: AAGCCTCGCCTGGATTCTAG R: TCAGGTCGCTGTCAGCAAAG |
90 |
| IL-6 | NM_204628.1 | F: TCCCTCCTCGCCAATCTGAA R: AAATAGCGAACGGCCCTCAC |
80 |
| β-actin | NM_205518.1 | F: ATTGTCCACCGCAAATGCTTC R: AAATAAAGCCATGCCAATCTCGTC |
113 |
| Treatment | ALT(u/g of protein) | AST(u/g of protein) |
|---|---|---|
| Ala-Saline | 2.93 | 22.97 |
| Ala-LPS | 2.43 | 16.49 |
| Gln-Saline | 3.05 | 27.79 |
| Gln-LPS | 2.68 | 24.63 |
| SEM Main Effect Diet Ala Gln Stress Saline LPS P Value |
0.542 2.68 2.87 2.99 2.56 |
4.587 19.73b 26.21a 25.38a 20.56b |
| Gln | 0.603 | <0.001 |
| LPS | 0.236 | 0.002 |
| Gln × LPS | 0.848 | 0.160 |
| Treatment | TLR4 | Akt | FOXO4 | FOXO1 | MAFbx | MuRF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ala-Saline | 1.00c | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.04b | 1.0 | 1.07c |
| Ala-LPS | 1.43a | 0.59 | 1.42 | 2.93a | 1.4 | 2.81a |
| Gln-Saline | 0.86d | 1.39 | 0.92 | 0.94b | 0.69 | 1.03c |
| Gln-LPS | 1.01b | 0.96 | 1.11 | 1.28b | 1.14 | 1.47b |
| SEM Main Effect Diet Ala Gln Stress Saline LPS P Value |
0.234 1.22a 0.94b 0.93b 1.22a |
0.301 0.80b 1.18a 1.20a 0.78b |
0.249 1.21a 1.02b 0.96b 1.27a |
0.868 1.99a 1.11b 0.99b 2.11a |
0.292 1.29a 0.92b 0.89b 1.32a |
0.762 1.94a 1.25b 1.05b 2.14a |
| Gln | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| LPS | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Gln × LPS | 0.002 | 0.932 | 0.091 | <0.001 | 0.266 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




