1. Introduction
In deep underground engineering, seepage actions are frequent and their consequences are usually notable. The performance reduction of the support scheme and therefore the longevity of deep-buried structures are among the major effects of seepage actions in tunnel engineering. It is recognized that long-term effects of seepage actions are precursors of many failures in deep rock tunnels. This is due by the fact that stresses and displacements in underground tunnels can be increased by the actions of seepage [
1]. In such situations, as related by Otsu et al. [
2], it is required to reasonably assess the stability of tunnels facing seepage problems. In fact, worse instability events can be happened under hydromechanical coupling when water propagates and concentrates in the existing interstices of tunnel surrounding rocks [
3]. In deep soft rock strata, water seepage effects are even of huge concern and remain an open pertinent topic. This is because hydration is one of the most determining factors of soft rock alteration mechanism. Precisely, water seepage hastens the deterioration of soft rock constituents such as clay minerals and argillaceous cement, and put the tunnels in extremely dangerous conditions. Therefore, it is essential to adequately and accurately discuss the effects of seepage actions in the support structure of deeply buried tunnels in order to better guarantee their long-term safety and stability.
Abundant research results exist on the effects of water seepage in deeply buried tunnels. For instance, from an elastic, homogeneous and isotropic rocky media, Nam and Bobet [
4] revealed that, at a tunnel face, the extent and distribution of radial deformations can be significantly increased due to the water seepage. Combining theoretical and numerical analyses under the conditions of seepage forces, an analytical solution for ground convergence has been proposed by Shin et al. [
5] to forecast the stability of deep tunnels where the host rocks are reinforced with grout and rock bolts. But a specific case has not been detailed for accurate application of this solution. Wang et al. [
6] analysed elastoplastically the surrounding rocks of deep tunnels via twin shear unified strength theory under seepage conditions. Their results show that, for proper tunnel support structure design and stability control, seepage actions are one of the major factors that need to be adequately taken into account. Based on strain-softening rock masses and nonlinear Hoek-Brown failure criterion, Fahimifar et al. [
7] proposed an elasto-plastic model to analyze the effects of seepage forces in deep-buried tunnels. Although they have presented some examples for the validation of their model, it remains difficult to accurately apply their solution in deep soft rock tunnels built in complex geomechanical and hydrological conditions. Using a bolted tunnel face and under seepage flow conditions, a computational method were developed by Perazzelli et al. [
8] to study the stability of lined tunnels. Nonetheless, such calculation method can be better applied to approximate support schemes of deep rock tunnels. On their sides and considering seepage forces, Jin-feng et al. [
9] employed two failure criteria (Generalized Hoek-Brown and Mohr-Coulomb) to establish analytic solutions for evaluating the displacements and plastic radii of circular tunnels working in rock masses exhibiting elastic-plastic and elastic-brittle–plastic behaviors. According to their outcomes, water seepage greatly affects the deformation of rock tunnels. However, it remains difficult to adequately apply such solutions in realistic case studies due to their complicated mathematical expressions. By considering the effects of water seepage actions, Yang et al. [
10] studied the long-term stability of deep soft rock tunnels mainly lodged in chlorite schist. Under such conditions, they proposed a visco-elastoplastic rheological model that can describe the comportment of the mentioned soft rock and designed an appropriate support structure aiming at ensuring durably the safety and stability of deep tunnels which are mainly bedded in chlorite schist. Analytical model for determining external stresses in tunnel lining has been established by Yan et al. [
11] by combining seepage flow and elastic theories. Their results mainly shown that the evolution of rock permeability coefficient governs the peak permissible drainage flow along the tunnel environments. Using the conformal mapping techniques, Chen et al. [
12] proposed workable analytical solutions of anisotropic and steady seepage field for deep grouted and lined tunnels. Nevertheless, since the exact rock types hosting such tunnels are not clearly provided, this makes it difficult to accurately employ such solutions in a given study case. Taking into consideration the upper bound theorem of the limit analysis, Di et al. [
13] studied the stability of tunnels from an analytical solution combined with an extension of Fourier series and numerical method for the tunnel face seepage field. Such a solution is very interesting for assessing the stability of tunnel face taking into account the effects of water seepage. Recently, Guo et al. [
14] proposed an analytical method to predict the seepage field around twin tunnels by expanding the Schwartz alternating method associated with issues related to multi-connected domains. Their solutions are suited to deep-buried tunnels crossing diverse rock types possessing different mechanical properties.
Since water seepage is a typical engineering concern [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21], which generally generates durable unwanted actions in deep rock tunnels [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26], they need to be thoroughly taken into account in deep rock engineering. Indeed, water seepage can induce seepage pressure which will endanger the support structure of the tunnels. Markedly, such seepage pressures may produce tensile force which should be supported by the primary support such as the rock bolts and cable bolts [
27]. Thereby, for long-term safety and stability reasons, as explained by Yang et al. [
28], the lining structure of deeply buried tunnels can be designed taking into account the seepage field existing around the surrounding rocks. However, based on realistic cases, in-depth discussions on the actions and consequences of water seepage are not yet abundant in the literature.
In this paper, the seepage actions and its consequences in deep-buried tunnels are analytically discussed, taking the surrounding rocks of the Weilai Tunnel in Guangxi province of China as a case study. The research gaps can be substantially filled by the study of this tunnel which presents complex host rocks where common major engineering problems exist. The main objective of this paper is to show how the actions of seepage affect the support structure and the stability of deep-buried tunnels built in soft rock environments. This paper can provide in-depth understanding of seepage effects on deep underground structures and can serve as a very good reference for related research studies.
2. Project Overview, Engineering Context and Rock Parameters
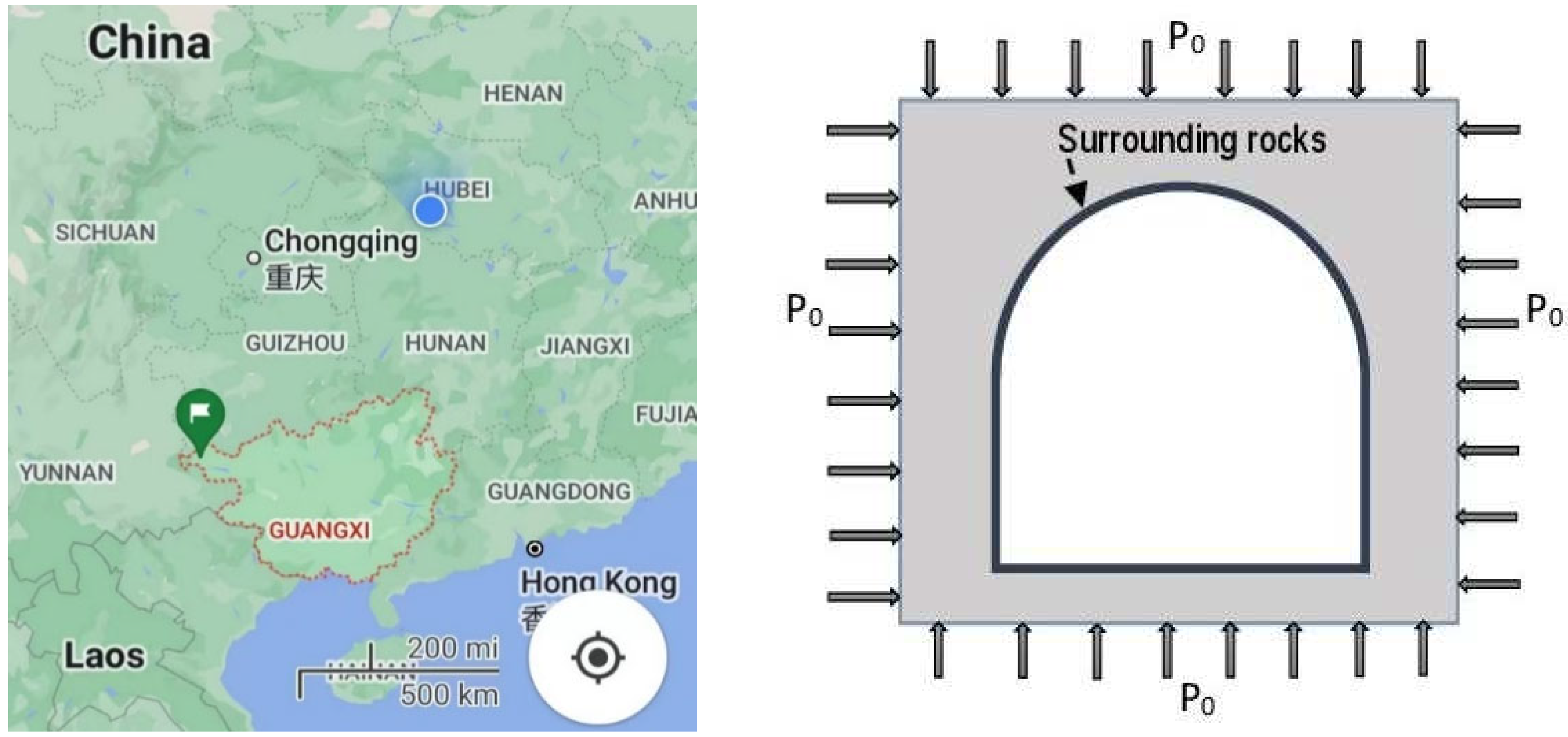
Given its complex conditions in terms of geology and hydrology, the Weilai Tunnel situated in Guangxi province of China is taken as the research substance. It is buried at a depth of 105 m, and is part of the Tianxi Expressway project, and is connected to the G357 national highway. The Weilai Tunnel has two lanes, the right one having a length of 662 m and the left one having a length of 686 m. The starting and ending stakes of the right and left lanes are respectively indicated by K114+422~K115+084 and Z4K114+424~Z4K115+110. Drill-and-blast excavation method has been employed with controlled sequence during the construction of the Weilai Tunnel. A location map of this tunnel and its surrounding rock situation is shown in
Figure 1.
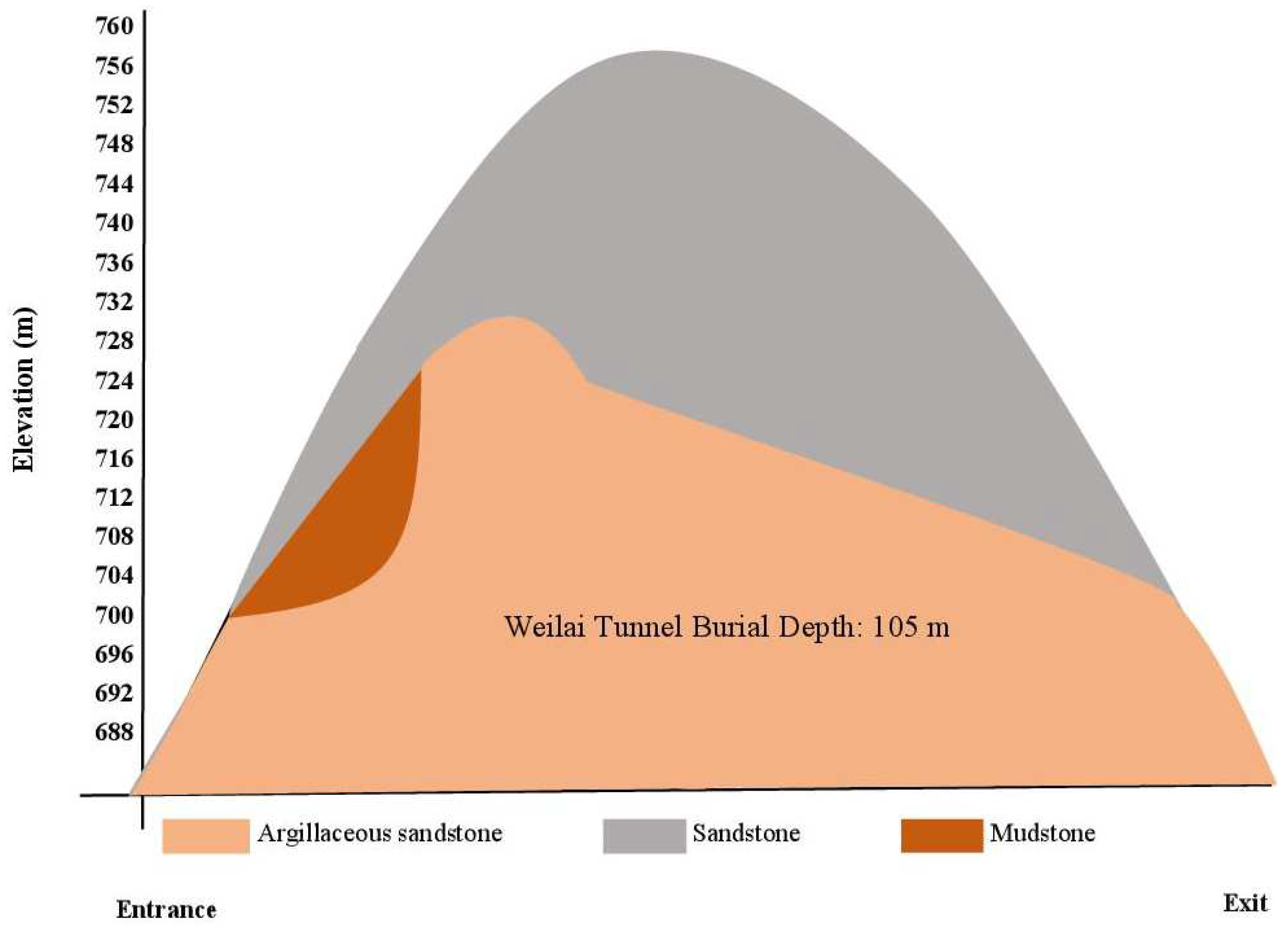
Figure 2 schematically illustrates the main rock types located in the tunnel alignment. The most predominant surrounding rock of this tunnel is argillaceous sandstone which is broken, according to a revelation made by a relevant geological survey.
Groundwater is relatively rich in the tunnel site due to the existence of aquifers which are close to the tunnel surroundings and the presence of broken rock types. Considerable groundwater ingresses were triggered in the excavated region during the construction of this tunnel. Relevant measures have been taken to deal with these groundwater influxes. However, over time, water seepage will be inevitably occurred in the host rocks [
29], and it will be a significant issue regarding the long-term safety and stability of the Weilai Tunnel.
Research results related to many rock parameters are rich. For the surrounding rocks of the studied tunnel, the parameters characteristics in dry and wet conditions are displayed in
Table 1 and
Table 2, referring to Frenelus and Peng [
30]. Note that, in wet conditions, most rock parameters are diminished. Additional parameters of the surrounding rocks and that of the tunnel radius are presented in
Table 3, based on relevant engineering reports.
3. Adopted Mechanical Model of the Tunnel and Seepage Pressure Determination
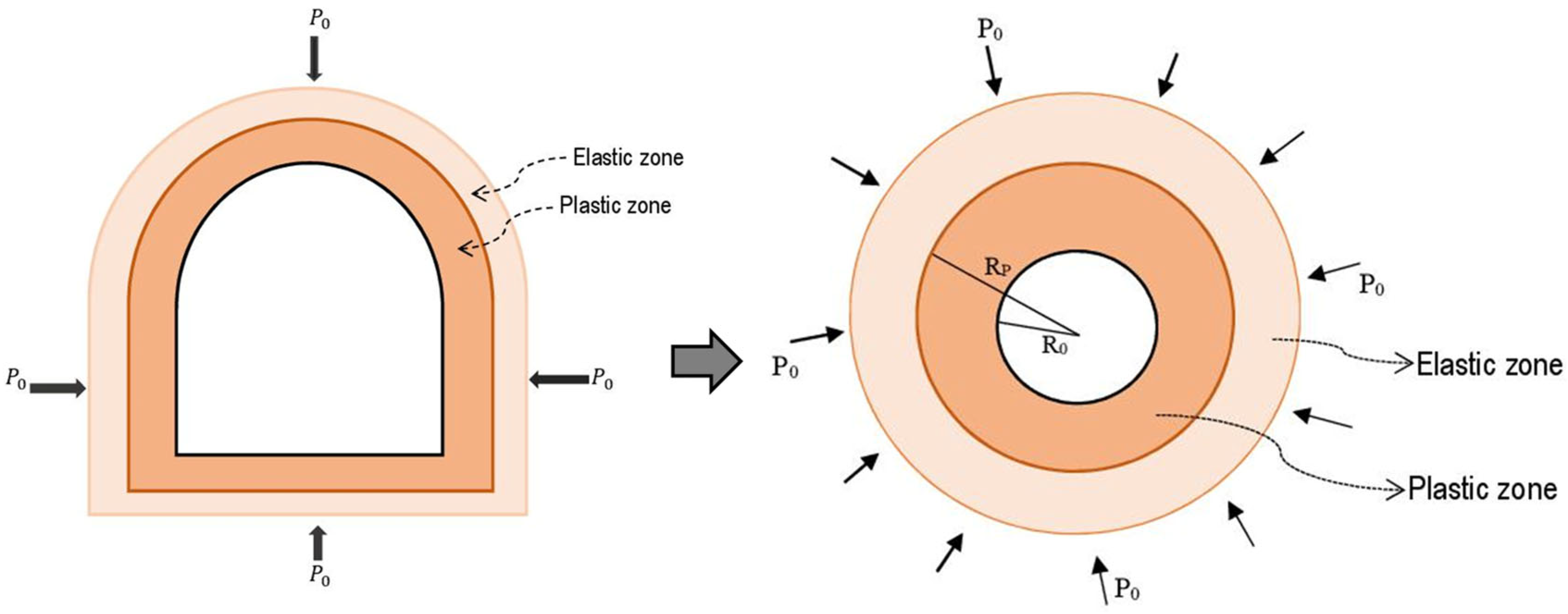
Two main parts describe the geometry of the actual tunnel cross section such as an upper part which is semi-circular, and a lower part which is rectangular. For convenience of computation and analysis, the whole tunnel is treated as a circular section, in accordance with Peng et al. [
31].
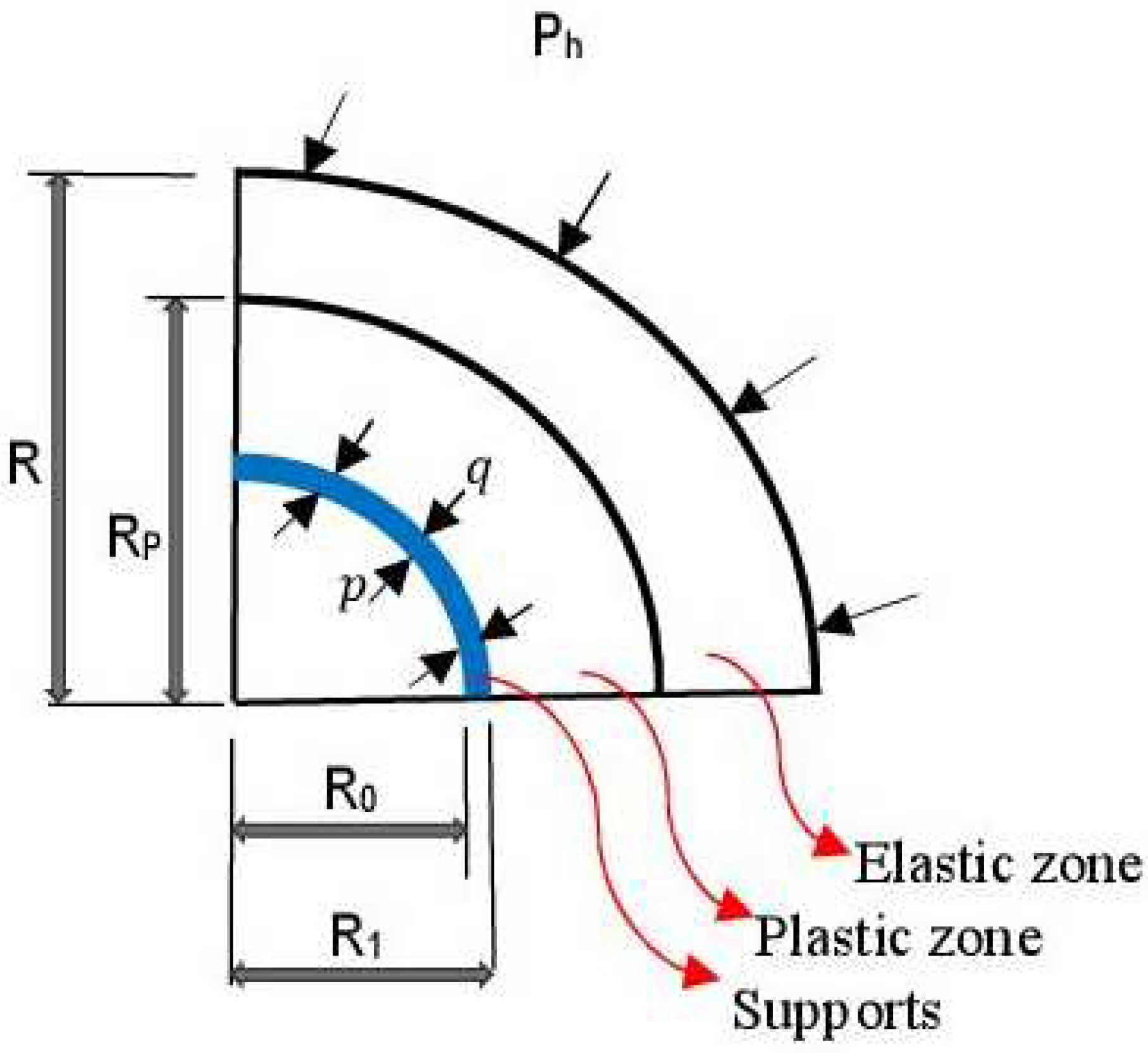
Figure 3 displays the adopted mechanical model of the Weilai Tunnel.
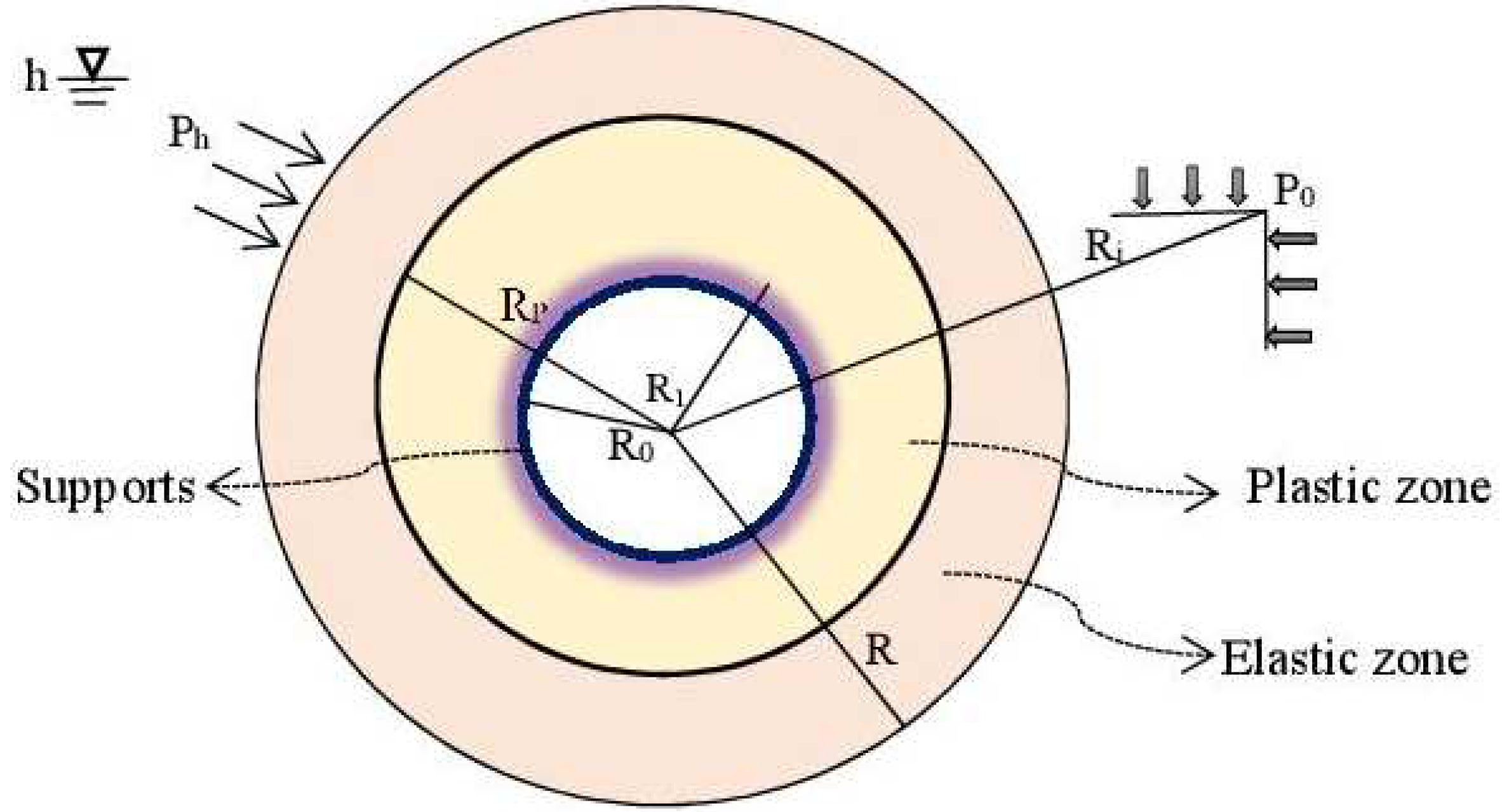
An initial hydrostatic pressure
is assumed to be existed along the host rocks of the tunnel. The initial seepage field that exists around the tunnel induces an external hydraulic pressure
. One represents by
the hydraulic head which is at infinity. One denotes by
the radius of the tunnel just after excavation, by
the effective radius of the tunnel after placement of secondary lining, while
represents the distance between the tunnel center and the boundary of the plastic zone. Subsequently,
is assumed to be the distance between the tunnel center and the infinity. The adopted mechanical model of the studied tunnel under seepage states is presented in
Figure 4.
Indisputably, due to the external pressure of water, a seepage field exist and will disturb the support structure performance. As the tunnel is lined, a stable symmetric seepage field is taken into consideration. Moreover, the permeability of the lining structure and that of the surrounding rocks are also considered. Indeed, referring to Tunç and Tunç [
32], the differential equations of the seepage pressure (
) can be read as below:
The relevant boundary conditions can be written as follows:
Here stands for the seepage pressure which is existed at the interface between the host rocks and the lining.
The continuity and limit conditions are put forward when solving the Equation (1). Hence, the seepage pressure can be found equal to:
By representing the apparent density of groundwater by
, and the permeability coefficients of the linings and the surrounding rocks respectively by
and
. The seepage rate of the linings (
) and that of the surrounding rocks (
) can be evaluated as follows:
At the interface between the host rocks and the linings, it is assumed that the water seepage operates at consistent rate. Indeed, The union of Equations (3) and (4) yields:
4. Stress and Displacement Examination
It is of utmost importance to examine the stresses and displacements of the host rocks confronting the actions of water seepage. Around deep-buried tunnels, the stress field is impacted not only by excavation disturbance, but also by seepage actions. For stability reasons, suitable examination in terms of elasto-plastic behavior is really needed. In this sense, as displayed in
Figure 5, the adopted mechanical model traduces the interaction existing between the host rocks and the supports.
The host rocks and the linings will interact continually during the life cycle of the tunnel, as illustrated in
Figure 5. Since the states of stresses and strains are pivotal in the study the stability of tunnels, they have to be adequately examined. To this end, it is assumed that a pressure
is exerted by the surrounding rocks. In the other hand, a pressure
is thus exerted by the support structures, in terms of reaction. Affected by diverse continuous actions such as seepage pressure, support reaction, and their own pressures, the surrounding rocks of the tunnel will deform plastically with the passage of time.
4.1. Examination of Stress in the Plastic Zone
As displayed in the adopted mechanical model, a plastic zone exists along the surrounding rocks of the Weilai Tunnel. The support structures have the ability of reducing the pressure of water seepage around the tunnel. To better take into account such a reduction, a coefficient
is introduced. Thereby, referring to Zou and Li [
33] and Li et al. [
34], and considering the reduction of the water seepage pressure, the equation traducing the stress equilibrium in the plastic zone can be written as below:
It is worth noting that the plastic conditions are generated by the combined actions of rock-supports, water seepage pressure and surrounding rock pressure. Under such conditions, the Mogi-Coulomb strength criterion can be employed [
35]. The rock mass is defined by its internal friction angle
and its cohesion
. Moreover, the effective radial stress (
) and the circumferential stress (
) are linked as follows:
The parameters A and B are defined as below:
Here
and
are parameters related to Mogi-Coulomb strength criterion [
35], and are defined as follows:
The parameter
traduces a coefficient of the principal stress and is defined as follows:
Referring to Li et al. [
34] and taking
, and by replacing Equations (5) and (7) into the Equation (6), the obtained first-order nonlinear differential equation is solved where two parameters
and
are defined as follows:
Accordingly, the plastic stresses exerted on the surrounding rocks can be written as follows:
Here stands for the reaction force of the lining to the host rocks.
4.2. Examination of Stress in the Elastic Zone
In deep underground engineering, it is widely assumed that the elastic zone can be characterized by a tick-walled cylinder. Consequently, the total elastic radial stress (
), and the total elastic circumferential stress (
) exerted by the host rocks can be computed using Kirsch equations [
36,
37] as follows below:
Here the radial stress of the rocks near the elastic-plastic boundary is designed by ; the coefficient of lateral pressure is denoted by ; the existing angle between the tunnel center line, the vertical direction and the calculated point is represented by .
Due to the water pressure and considering that such pressure is uniformly distributed in all directions (
), the total elastic radial stress (
), and the total circumferential stress (
) generated by the surrounding rocks can be converted to the following equations:
5. Examining the Plastic Radius and the Displacement of the Host Rocks
One key factor for opining on the stability of a deeply-buried tunnel is the plastic radius. To do so, it should be reasonably assessed under seepage conditions. The plastic zone must be secured adequately by the support structures in order to guarantee the long-term stability of the tunnel. The extent of the plastic radius is schematically illustrated in
Figure 4. It should be reminded that the stresses are continue, and at the elastic-plastic interface, the total plastic stress is equal to the total elastic stress. Hence, the following can written as below:
Moreover, at the aforesaid interface,
. By simply solving the equation (5.17), it can be found the following:
Thereby, the radius of the plastic zone is given as below:
As shown in Equation (17) that the radius of the plastic zone rely on several factors. Mainly, it is affected by the reaction force of the tunnel support and the pressure of water seepage.
Around deep-buried tunnels, displacements are inevitable and are categorized into elastic and plastic zones, due to the elastic and plastic zones of the surrounding rocks. The plastic radius provides the scope of plastic deformation around the tunnel. In the elastic zone, the displacements can be estimated by means of elastic theory where the strain can be obtained as below:
Here and represent respectively radial and tangential strain; stands for the rock elastic modulus, represents Poisson’s coefficient.
Geometric formula can link strain and displacement as follows:
Hence, in the elastic zone, at
, the displacement (
) of host rocks can be evaluated as follows:
Here stands for the Poisson’s ratio of the rock mass; represents the rock elastic modulus.
Likewise, in the elastic zone, at
, the host rock displacement (
) is computed as follows:
6. Consideration on the Coupled Effect of Softening and Seepage
As already mentioned, the rocks that surround the tunnel is soft and broken. The softening is amplified by the excavation effects such the inevitable complex load-unload [
38], as well as by the water seepage. Consequently, it is more than important to take into consideration the coupling effects of softening and seepage. To this end, it should be reminded that elastic and plastic zones are formed around the tunnel after rock excavation, as already stated. Under the circumstances of softening and seepage, the plastic zone can be appropriately decomposed. Indeed, since rocks typically loss their strength in deep underground engineering [
39,
40,
41,
42,
43], the plastic residual zone and plastic softening zone are the two main components of the plastic zone. Representing by
and
respectively the radius of the plastic residual zone and that of the softening zone, the adopted mechanical model is schematically illustrated in
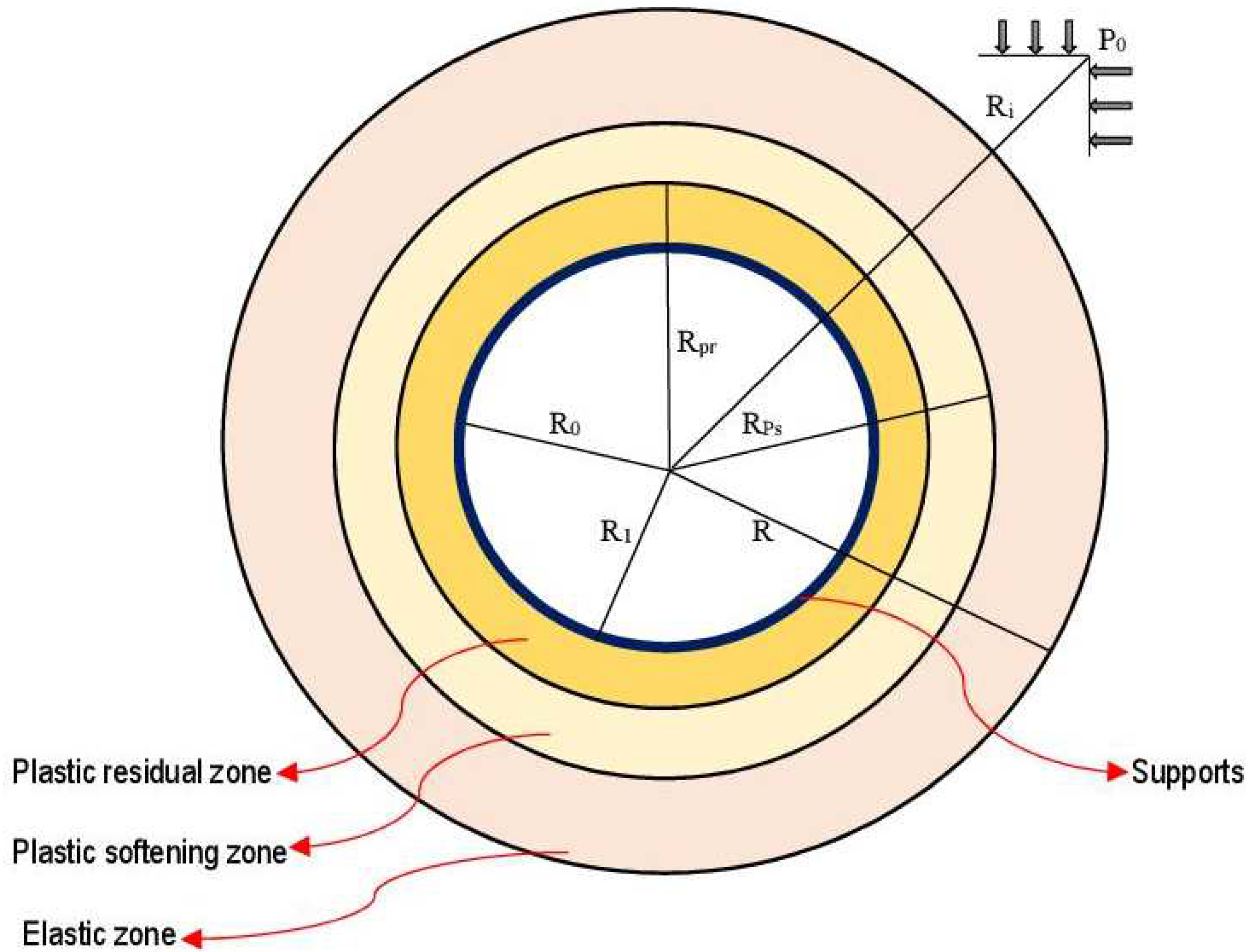
Figure 6.
As presented through
Figure 6, the surrounding rocks affected by high stress and water seepage conditions are divided into three zones namely plastic residual zone, plastic softening zone and elastic zone. Concretely, the elastic zone is formed rapidly in stressed host rocks. Nonetheless, the plastic softening zone describes the conditions of the surrounding rocks in which the stress overtakes the maximum strength of the rock massif. Concerning the plastic residual zone, it is inevitably created because of the progressive deformation of the plastic softening zone. It is worth mentioning that the scope of the plastic deformation along the tunnel surrounding rocks is reflected by the plastic radius.
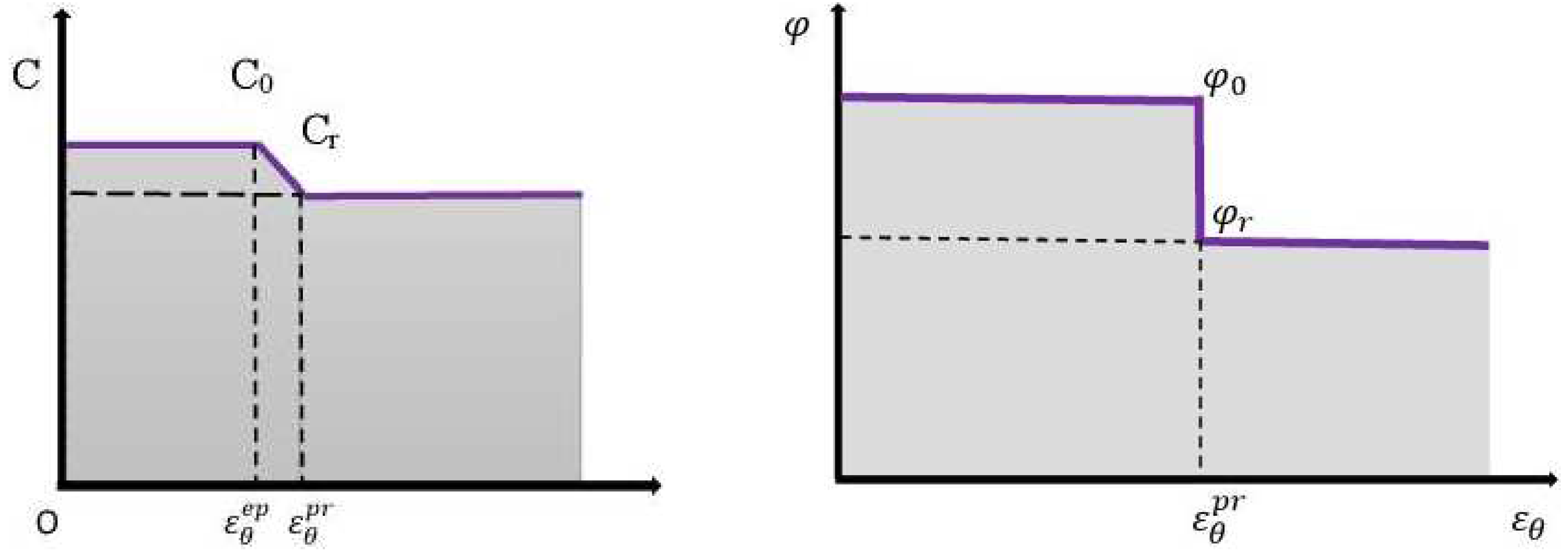
Rock mechanical properties are affected by softening. However, the rock mechanical properties mostly affected by softening are the internal friction angle and the cohesion. To show how these properties are affected by softening, the strain-softening model is introduced as displayed in
Figure 7 where C
0 stands for the maximum cohesion, C
r is the residual cohesion,
denotes critical tangential strain at the boundary of elastic zone and plastic softening zone,
represents the critical tangential strain at the plastic residual zone/plastic softening zone boundary.
According to the model presented in
Figure 7, and by taking into consideration a relevant linear decreasing functions
and
for the cohesion and internal friction angle respectively, one can be write [
42]:
Here stands for the softening parameter; while the parameter reflecting the plastic softening. In this sense, the elastic stage of the tunnel host rocks is reflected at .
It is considered that the groundwater flow is incompressible and the seepage field is stable. The pore water pressure (
) which depends on the water gravity (
), and the coefficient of non-uniform permeability (
) can be expressed as follows:
Where and represents permeability coefficient in horizontal and vertical directions respectively.
In the plastic residual zone and the softening zone, the continuity equation is put forward to calculate the plane seepage field as below:
Here
and
are respectively seepage flow velocity in horizontal and vertical directions of the tunnel. Stable seepage flow obeys Darcy’s law, and the seepage velocity can be given as below:
Thereby, the aforesaid velocities can be written as follows:
The angle (
) is taken into account. It is an angle located between the radius
and the horizontal axis with coordinate defined as:
On the basis of Equation (25), the seepage equations can be written as:
Then, by solving the Equation (29), and taking into account that:
If isotropic states (
) are put forward, the pore water pressure can be found as follows:
Likewise, in the case of non-isotropic states (
), the pore water pressure can be written as:
6.1. Stress and Plastic Radius in the Plastic Residual Zone
In the plastic residual zone, the coefficient of seepage water pressure (
) is taking into account, and the stress balance can be written as below:
In general,
for the safety and stability of surrounding rocks. At the interface of the plastic residual zone and plastic softening zone, it should be reminded that
. Moreover, it is assumed that such an interface is subjected to a maximum principal stress
. The plastic tangential residual stress can be written as follows:
Here stands for the residual reaction force of the lining to the host rocks.
Also, at the interface between the plastic residual zone and the plastic softening zone, the radial stress is
, and it is similar to the tangential stress. The radius of the plastic residual zone can be written as follows:
6.2. Stress and Plastic Radius in the Plastic Softening Zone
Similar to the plastic residual zone, the stress in plastic softening zone conforms to the Equation (33). The maximum tangential stress of the plastic softening zone (
) can be written as below:
In the limit of the plastic softening zone where
, the tangential stress is equal to the plastic stress
. Hence, the plastic softening zone radius can be written as follows:
6.3. Stress in the Elastic Zone
As already illustrated, a virgin in-situ stress
is applied to the elastic zone. At the boundary between the elastic zone and the plastic softening zone, the radial stress is represented by
. The stress in the elastic zone can be computed as:
7. Parametric Study and Discussions
The main factors of the analytical solutions are appropriately examined. An adequate parametric study is conducted to show the relevance of the presented analytical approaches. In fact, for proper engineering practice, parametric study is of great importance. It provides the ability to evaluate diverse key parameters that have a strong influence on the trend and interpretation of analytical or closed solutions. Moreover, it also allows us to better understand the established theoretical and analytical models. Thereby, parametric studies constitute solid keys for appropriate and in-depth discussions on the analytical solutions proposed in engineering fields. Hence, it is more than important to carry out parametric investigations on the proposed analytical models. Such parametric investigations are associated by pertinent calculations. The flowchart of the computations is shown in
Figure 8. The calculation results are presented in
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11,
Figure 12,
Figure 13,
Figure 14,
Figure 15 and
Figure 16.
7.1. Variation of Plastic Radius with Support Pressure
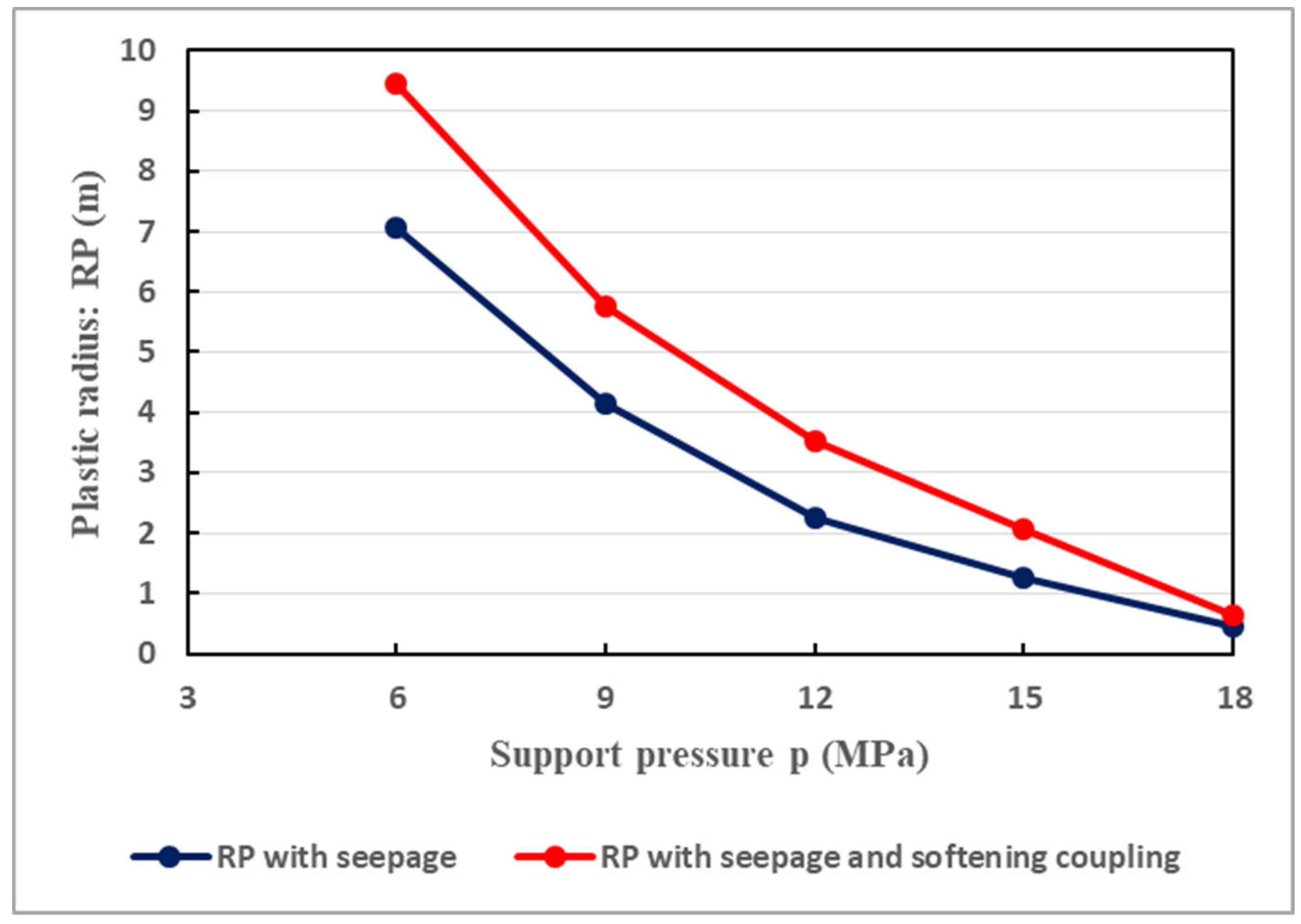
Figure 9 illustrates the relationship between the plastic radius and the support resistance (
) when the principal stress coefficient is not accounted. It is shown that the plastic radius undergoes progressive reduction by the augmentation of support resistance. This conforms well to the actual situation. In fact, the safety and stability of the surrounding rocks greatly rely on the resistance of the tunnel support structure. For instance, as it can interpreted in
Figure 9, when the resistance of the support structure is 9 MPa, the extent of the plastic radius can reach 4 m. However, when the support resistance is 15 MPa, the scope of the plastic radius is less than 2 m; while when the support resistance is 18 MPa, the extent of the plastic radius is very low, under solely the action of seepage. Nonetheless, the coupled action of seepage and softening can somewhat change the tendency. Indeed, under such conditions, when the support has a resistance of 9 MPa, the plastic radius is significant. Significant plastic radius (2 m) is still observed even when the support has a resistance of 15 MPa. This illustrates the great important of coupled effects of seepage and softening in deformation of the tunnel. Thus, the support scheme resistance of the tunnel has to be great enough in order to effectively deal with the coupling actions of seepage and softening.
7.2. Variation of Plastic Radius with Principal Stress Coefficient
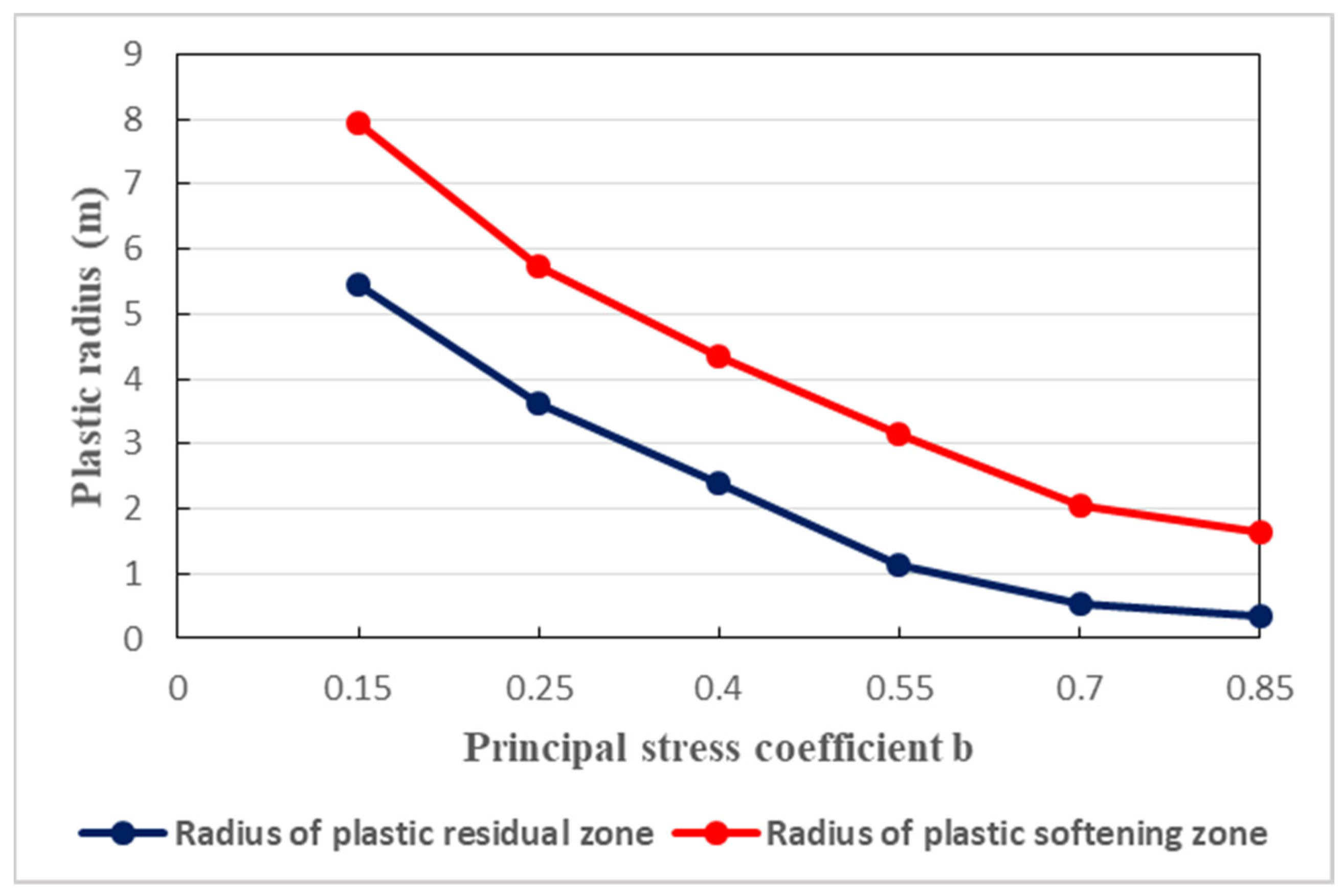
The relationship between the radius of the plastic zone and the principal stress coefficient b is presented in
Figure 10. In fact, with the increase in the principal stress coefficient b, remarkable decrease of the plastic zone radius is observed. For b = 0.15, the radius of the plastic softening zone is found to be approximately 8 m; while it is 3 m when b = 0.55. When b = 0.85, the radius of the plastic softening zone is less than 2 m. Indeed, given the definition of the principal stress coefficient, it is necessary to control the difference ratios of the relative stresses in order to limit the extent of the radius of the plastic zone. It is worth noting the plastic zone radius which traduces the extent of the deformation around the surrounding rocks, varies with several factors. Reducing such extent is of particular consideration regarding the tunnel stability. To this end, effective countermeasures must be adopted. In deep underground engineering, the most suitable principal stress coefficient is important for the reduction of the plastic zone radius. It should be highlighted better control of the plastic zone radius necessitates sufficient reduction of plastic zone radius. The lower the plastic radius, the lower the deformation of the tunnel, and therefore the longer the operation of the tunnel can be maintained with safety and stability.
7.3. Variation of Pore Water Pressure in the Surrounding Rocks
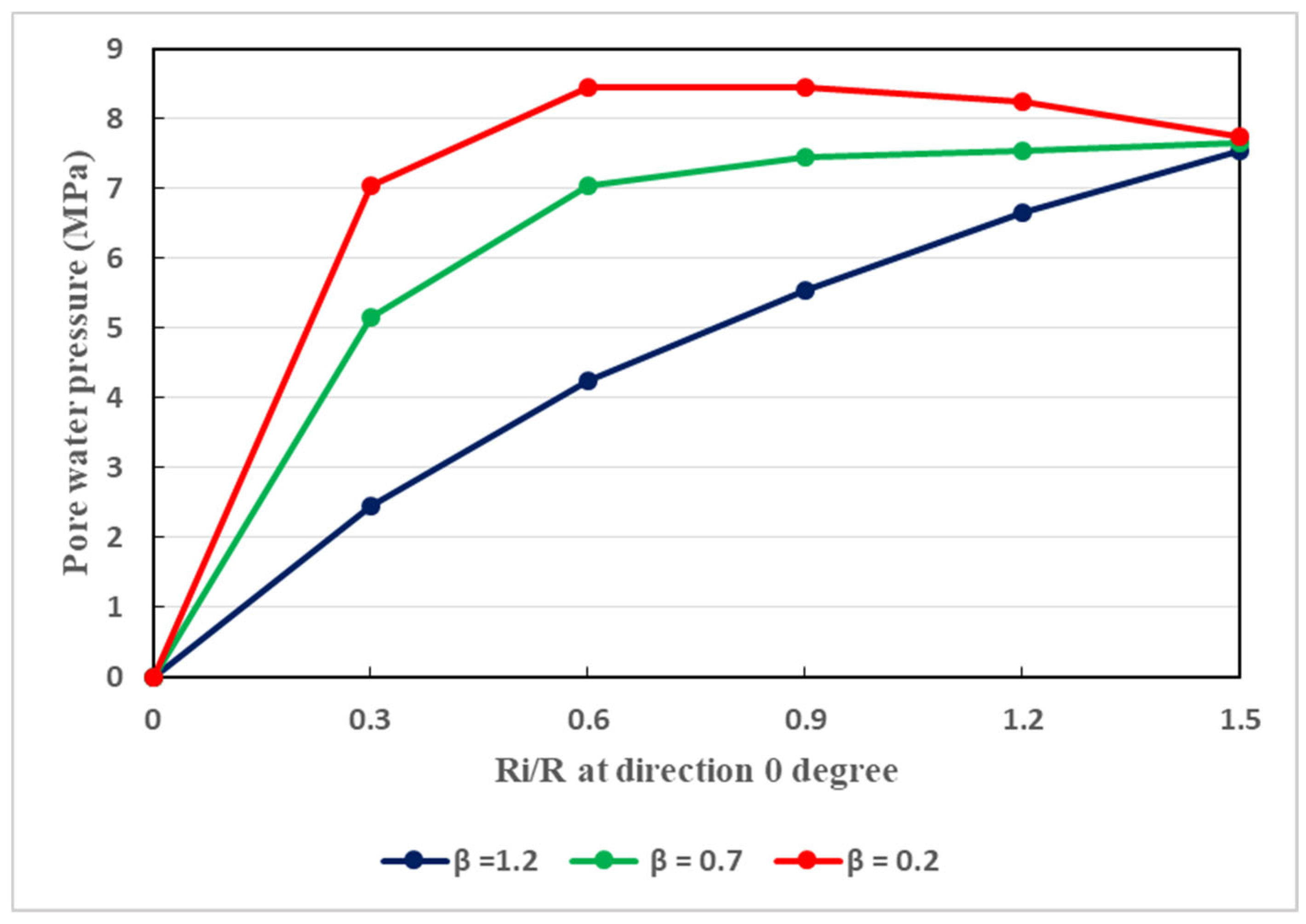
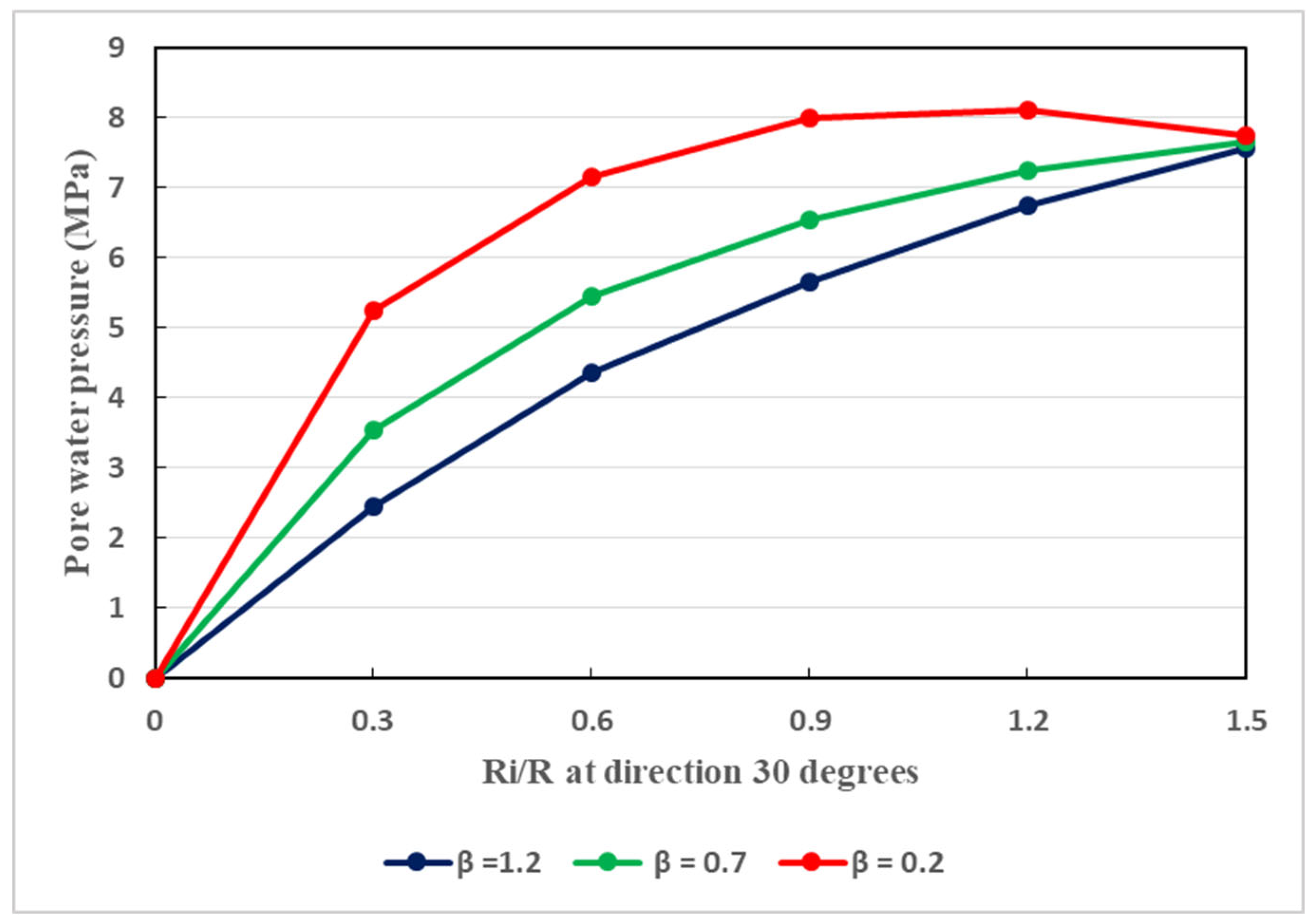
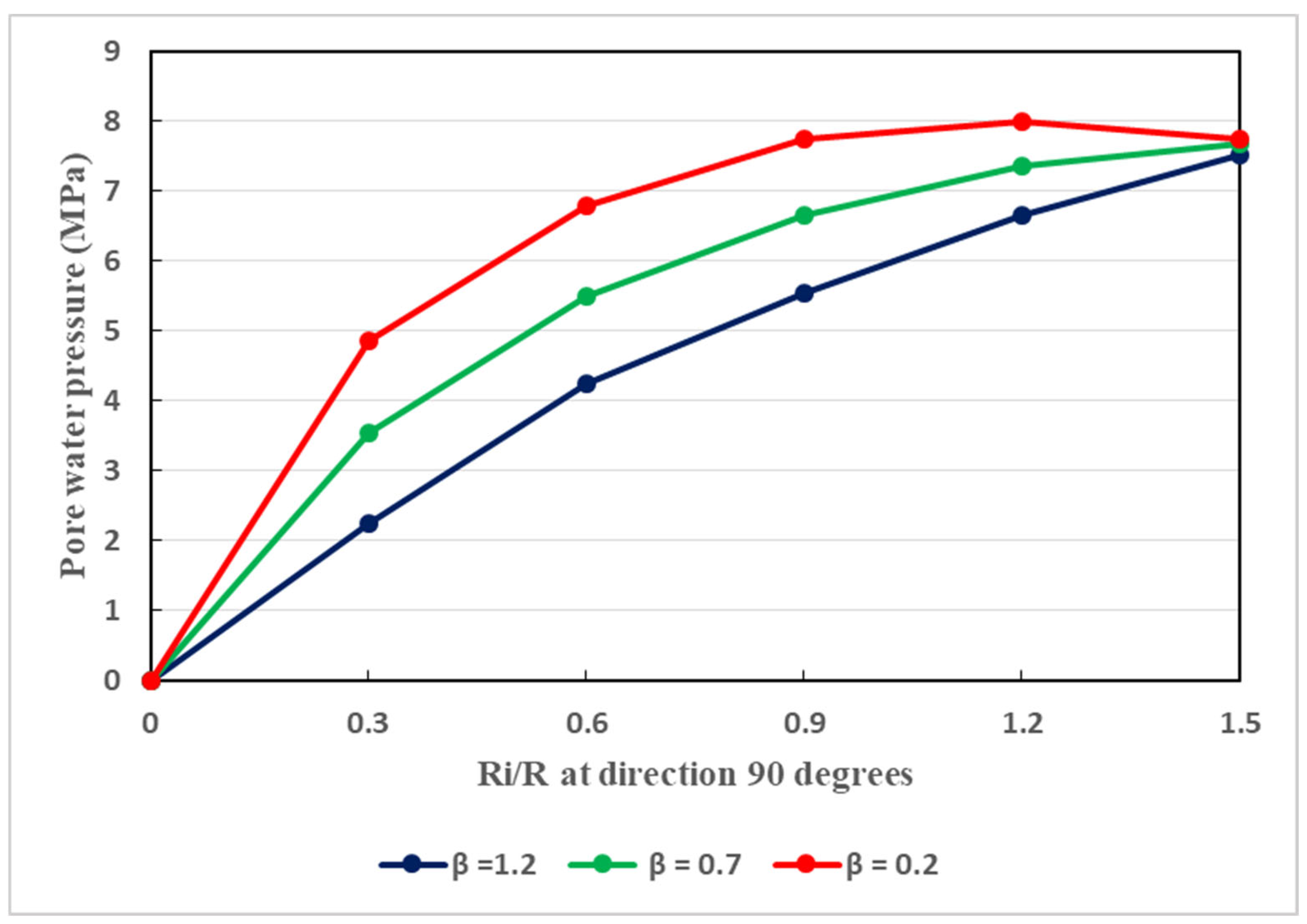
The host rocks of the tunnel is naturally anisotropic. Aiming at taking into consideration this feature, three different values of the permeability coefficient (
) are considered, as it is shown in
Figure 11,
Figure 12 and
Figure 13. It can be interpreted that, in the directions of 0°, 30°, and 90°, the tendencies in pore water pressure change are nearly same. Specifically, in all directions, there is gradual increase in pore water pressure as the permeability coefficient increases. However, the evolution rate in the direction of 90° is slightly quicker as shown in
Figure 13. Indeed,
Figure 13 illustrates the development of pore water pressure at a direction of 90°. Such a direction traduces the vertical direction in which, when the permeability coefficient is augmented, the pore pressure may be developed faster than that in the horizontal direction. Globally, in the vertical and horizontal directions, the seepage behavior is not isotropic when the permeability coefficient is changed. Owing to the existence of broken soft rocks in the environment of the tunnel, the permeability coefficient cannot be constant. It can be said that, in the aforesaid directions, the seepage is mainly anisotropic. Its effects are notable and thus cannot be overlooked regarding the stability of the tunnel. Water seepage effects are very pronounced at great depth. In any direction, water seepage has influences on the stability of the tunnel. To effectively withstand water seepage actions, reasonable support structure is required.
It is also observed that the ratios of different radii increase as the water pressure increases. During the rainy periods which in Guangxi, water pressure can be increased easily, and can enhance the tunnel plastic zone radii. In such circumstances, the bond between the host rocks and the support system can be deteriorated considerably. This can be more marked in the plastic residual zone and plastic softening zone where the increase in plastic radius is rapid. In fact, in such zones, the rocks are less resistant than those in the elastic zones. Real-time inspection is strongly recommended for such tunnel in order to better control any increase of its plastic radius. Therefore, effective remedial measures in right time can be ensured.
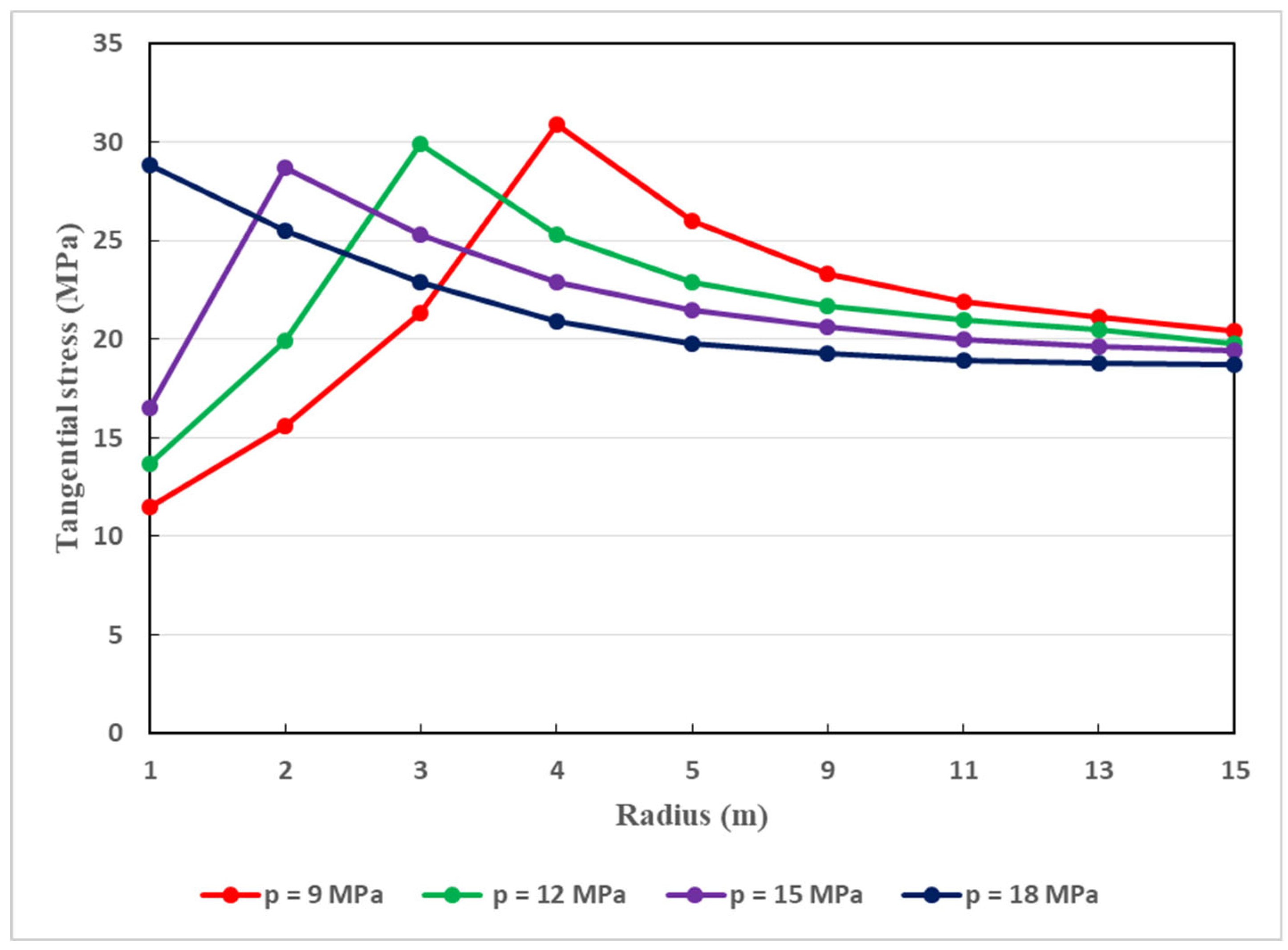
7.4. Variation of Tangential Stress in Surrounding Rocks
Thorough the tunnel, the tangential stresses exist. It is important to study their dissemination along the host rocks of the Weilai Tunnel, as illustrated in
Figure 14. In fact, with regard to the plastic radius, and considering different values of support pressure, under the coupled actions of seepage and softening, the dissemination of the tangential stress is revealed in
Figure 14. On the one hand, in the vicinity of tunnel face, the tangential stress increases rapidly as the support pressure increases. After reaching its maximum values, the tangential stress decreases progressively. This is explained by the fact that, along the host rocks of the tunnel, the support pressures exert great effect on the distribution of tangential stress. In fact, the latter can be reduced more easily with the highest support pressures. For instance, a support pressure of 18 MPa can be better suited in decreasing the tangential stress along the host rocks of the tunnel. This is another key reason showing that deep-buried tunnels which are constructed in complex soft rocky environments require strong support structure. The supports must be able to generate and maintain reasonable values of the tangential stress around the tunnel for as long as possible since the longevity of the supports is of particular consideration. In fact, it should be noted that the longevity of deep-buried tunnel support structures can be diminished not only by water seepage, but also another relevant factors such as rock creep [
44].
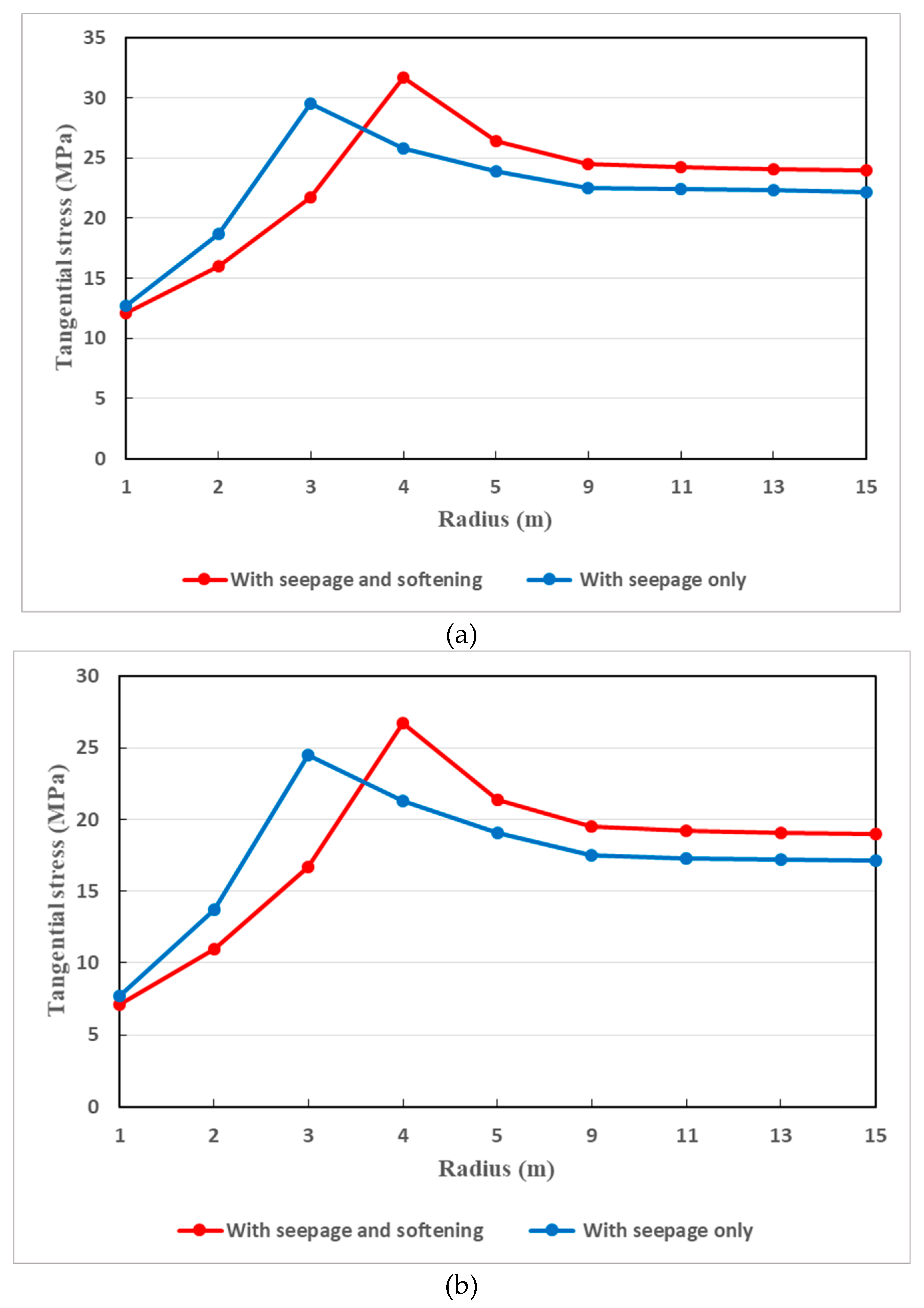
It is also very important to compare the dissemination of tangential stress in two pertinent situations.
Figure 15a,b gives such a comparison where coupled actions of seepage and softening and with seepage actions solely are taken into consideration. In coupling actions of seepage and softening, it can be seen that there is remarkable decrease of tangential stress. Undoubtedly, this can be understood since the disintegration of rocks is more marked when the coupled actions of seepage and softening is considered.
In fact, the strength of the host rocks is further impaired in such situations. In other words, by the coupling effect of seepage and softening, the tangential stress of the surrounding rocks is reduced when the seepage filed is taken into consideration at the tunnel face. That is, at the tunnel face, the tangential stress under such a coupling effect is less than that with seepage only. But as one moves away from the tunnel face, the tangential stress is somewhat greater under the combined of seepage and softening than under the effect of seepage solely. This is really conform to the actual situation where the tangential stress of the surrounding rocks is higher under the aforesaid coupling effect.
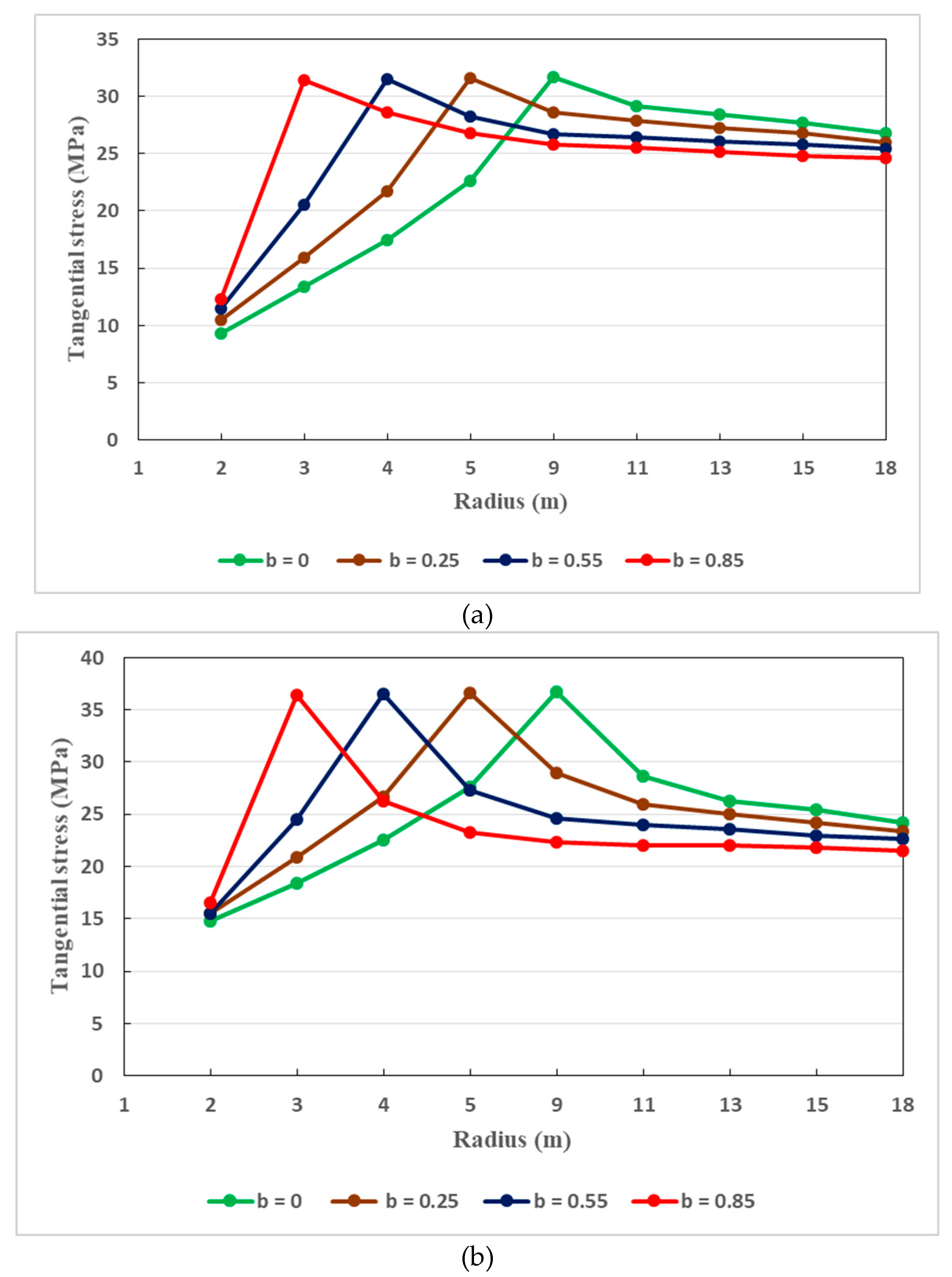
Figure 16a,b presents the variation of tangential stress in the tunnel host rocks with regard to the principal stress coefficient under a support pressure of 9 MPa and 15 MPa respectively. The tangential stress increases rapidly when the principal stress coefficient (b) increases. After reaching its maximum value, the tangential stress reduces gradually along the tunnel surrounding rocks. This can be understood that the tangential stress is strongly influenced by the principal stress coefficient.
Note that, around the host rocks, the tangential stress evolves following mainly two stages, under the influence of the principal stress coefficient. In the first stage, it increases quickly as the principal stress coefficient b increases. Then, in the second stage, it becomes stable when the tangential stress attains its maximum value. However, its tendency varies with the value of the principal stress coefficient b. Also, the principal stress coefficient plays a major role in the distribution of the tangential stress along the surrounding rocks. Appropriate value of the principal stress coefficient should therefore be taken into consideration in order to get adequate distribution of the tangential stress around the tunnel surrounding rocks.
7.5. Implications
It is important to highlight that seepage actions are inevitable in deep-buried tunnels constructed in complex soft rock strata. Indeed, over time, the support components of these tunnels will experience reduced rigidity [
45,
46]. The most pronounced is that seepage can be coupled with stresses [
47], and can thus provoke more adverse effects on the stability of deep soft rock tunnels. Likewise, the combined effects of seepage and material softening are very detrimental to the tunnel safety and stability. Suitable countermeasures should be adopted to ensure the long-term safety and stability of deep soft rock tunnels facing seepage problems. On the one hand, the support structure must be of highest strength possible to properly perform its function in seepage conditions. For instance, typical primary support such as rock bolts and cable bolts are generally prone to degradation due to water seepage-induced corrosion. In such situations, its performance will be easily diminished. If adequate measures are not taken in right time, the primary support will be heavily corroded and the secondary support will become the main support structure of the tunnel, which is very unfavorable. On the other hand, cracks can extend into the secondary support when exposed to seepage. Note that the secondary support material for deeply buried tunnels is generally concrete or reinforced concrete [
48], which can also be degraded by the action of water seepage [
49]. It should remembered that water seepage is the cause of many structural problems in deep rock engineering [
50,
51], and is certain to appear over time even when the most appropriate grouting techniques are applied to the host rocks [
20]. Hence, at any time, the need to guarantee the safety and stability of deeply buried tunnels is of huge consideration. All structural components of such tunnels should be monitored using appropriate remote sensors [
52]. In fact, structural health monitoring based on automation and smart techniques is becoming indispensable for accurate prediction of tunnel safety and stability [
53,
54,
55,
56,
57]. In addition, the monitoring system must be sufficient to provide all the required information regarding the health status of the tunnel. Thereby, relevant decisions in real time can be adopted to continuously guarantee safe operation of deeply buried tunnels. In fact, insufficient monitoring should be avoided because it generally results in unfavorable conditions for the safety of deep soft rock tunnels [
58]. In the case of the Weilai Tunnel which suffers from water seepage problems, comprehensive long-term monitoring carried out by reliable remote sensing techniques is strongly recommended.
8. Conclusions
The stability of deeply buried tunnels constructed in complex soft rocky media is greatly affected by water seepage actions. In this research study, water seepage actions and their consequences are analytically discussed based mainly on Mogi-Coulomb strength criterion and elasto-plastic approaches. The main conclusions are as follows:
To effectively withstand the inevitable severe consequences caused by seepage actions, the support scheme of deep-buried tunnels particularly constructed in soft rock environments must be of highest resistance possible. It is thus necessary to design such supports according to the complexity related to the concerned rocky environments which confront the seepage actions.
Plastic softening zone and plastic residual zone are two constituents of the plastic zone of deeply buried tunnels. Their radius decreases by increasing the resistance of the support structure, under seepage conditions and under combined effects of seepage and softening.
The combined effects of water seepage and material softening are very dangerous for the tunnel safety and stability. Such effects have the consequences of significantly increasing the plastic radii of deep soft rock tunnels. It is revealed that the more strongly the tunnel is supported, the more its plastic radii and therefore its deformations are reduced.
In terms of scope, the plastic zone radii of deep soft rock tunnels is considerably affected by the principal stress coefficient. In fact, the highest values of principal stress coefficient are favorable to small plastic radii. Accordingly, appropriate values of such coefficient must be adopted to ensure reasonable dissemination of tangential stress along the tunnel which must be durably safe and stable.
Throughout the surrounding rocks of deeply buried tunnels, the dissemination of pore water pressure is strongly affected by the uneven permeability coefficient under anisotropic seepage states. This conforms well to the actual situation where the host rocks are broken and therefore the seepage field is mainly anisotropic. Thereby, seepage actions cannot be ignored since they can affect the stability of deep soft rock tunnels in any direction.
Owing to the inevitable severe consequences of seepage actions, deep-buried tunnels constructed in complex soft rocky media must be adequately monitored at all times even if their support schemes are sufficiently resistant. In fact, proper long-term monitoring can effectively guarantee the safety and stability of such structures at all times. In this sense, reliable remote sensors are promising.
Supplementary Materials
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.F.; methodology, W.F.; software, W.F.; validation, HP; formal analysis, J.Z.; investigation, W.F.; resources, W.F.; data curation, W.F; writing—original draft preparation, W.F; writing—review and editing, W.F; visualization, J.Z.; supervision, H.P.; project administration, H.P.; funding acquisition, H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded the Special Topics of National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2022YFC3005603-01.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fernandez, G., Alvarez Jr, T.A. Seepage-Induced Effective Stresses and Water Pressures around Pressure Tunnels. J. Geotech. Eng. 1994, 120 (1), 108-28. [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, H., Ohnishi, Y., Taki, H., Kamemura, K. A study on problems associated with finite element excavation analysis by the stress-flow coupled method. Int. J. Num. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 1999, 23, 1473-1492. [CrossRef]
- Rutqvist, J., Stephansson, O. The role of hydromechanical coupling in fractured rock engineering. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 7–40. [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.W., Bobet, A. Radial Deformations Induced by Groundwater Flow on Deep Circular Tunnels. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2007, 40, 23–39. [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.J., Song, K.-I. Lee, I.M. Cho, G.-C., Interaction between tunnel supports and ground convergence - Consideration of seepage forces. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48 (3), 394-405. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y., Wang, X.-H., Chen, J.-R. Elastoplastic Analysis of Surrounding Rocks of Submarine Tunnel with Consideration of Seepage. J. Highway Transport. Research Develop. 2013, 7(2), 73. [CrossRef]
- Fahimifar, A., Ghadami, H., Ahmadvand, M. An elasto-plastic model for underwater tunnels considering seepage body forces and strain-softening behavior. Eur. J. Environ. Civil Eng. 2015, 19(2), 129-151. [CrossRef]
- Perazzelli, P., Leone, T., Anagnostou, G.. Tunnel face stability under seepage flow conditions. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 43, 459-469. [CrossRef]
- Jin-feng, Z., Shuai-shuai, L., Yuan, X., Han-cheng, D., Lian-heng, Z. Theoretical Solutions for a Circular Opening in an Elastic–brittle–plastic Rock Mass Incorporating the Out-of-plane Stress and Seepage Force. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20(2), 687-701. [CrossRef]
- Yang, F., Zhang, C., Zhou, H., Liu, N., Zhang, Y., Muhammad Usman Azhar, Feng Dai. The long-term safety of a deeply buried soft rock tunnel lining under inside-to-outside seepage conditions. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 67, 132-146. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q., Zhang, C., Wu, W., Zhang, Y., Ma T. Analytical Solution for the External Stress Acting on the Lining in a Deep-Buried Circular TBM Tunnel Considering the Seepage Field. J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 2019, 60, 176–185. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q., Liang, L., Zou, B., Xu, C., Kong, B., Ma, J. Analytical Solutions of Steady a Seepage Field for Deep-Buried Tunnel with Grouting Ring Considering Anisotropic Flow. J. Marine Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1861. [CrossRef]
- Di, Q., Li, P., Zhang, M., Zhang, Q., Wang, X. Analysis of face stability for tunnels under seepage flow in the saturated ground. Ocean Eng. 2022, 266, Part 1, 112674. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.F., Wang, H.N., Jiang, M.J. An exact analytical approach for determining the seepage field around underwater twin tunnels with linings. Transport. Geotech. 2023, 42, 101050. [CrossRef]
- Wongsaroj, J., Soga, K., Mair, R.J. Modelling of long-term ground response to tunnelling under St James’s Park, London. Géotechnique 2007, 57(1), 75–90. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y., Yu, Z., Zhou, Z. Simulating Groundwater Inflow in the Underground Tunnel with a Coupled Fracture-Matrix Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18(11), 1557-1561. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y., Li, Y.A., Lin, J.L., Ruan, C.K., Chen, S.J., Tang, H.M., Duan, W.H. Towards microstructure-based analysis and design for seepage water in underground engineering: Effect of image characteristics. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 93, 103086. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K., Dou, L., Gong, S., Song, S., Chai, Y., Li, J., Ma, X. Mechanical behavior of sandstones under water rock interactions. Geomech. Eng. 2022, 29(6), 627-643. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Zhou, Z., Yang, J., Pang, S., Geng, J., Li, W., Zhang, X. Creep properties of siltstone-like materials with different unloading confining pressures under seepage. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 949916. [CrossRef]
- Peng, H., Frenelus, W., Zhang, J. Key factors influencing analytical solutions for predicting groundwater inflows in rock tunnels. Water Supply 2022, 22(11), 7982-8013. [CrossRef]
- El Tani, M., Kamali, A., Gholami, M.A. Analytic Assessment of the Water Table Drawdown, Seepage, and Back Pressure at Rudbar PSPP. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 2227–2243. [CrossRef]
- Gong, B., Jiang, Y., Okatsu, K., Wu, X., Teduka, J., Aoki, K. The Seepage Control of the Tunnel Excavated in High-Pressure Water Condition Using Multiple Times Grouting Method. Processes 2018, 6, 159. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Yin, T. A Coupled CFD–DEM Simulation of Slurry Infiltration and Filter Cake Formation during Slurry Shield Tunneling. Infrastructures 2018, 3, 15. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Li, Z., Jing, H., Li, Y., Wang, M. Study on the seepage characteristics of deep buried tunnels under variable high-pressure water heads. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 1477–1487. [CrossRef]
- Ding, W., Tan, A.S., Zhu, R., Jiang, H., Zhang, Q. Study on the Damage Process and Numerical Simulation of Tunnel Excavation in Water-Rich Soft Rock. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8906. [CrossRef]
- Kacimov, A.R., Obnosov, Y.V., Šimůnek, J. Seepage to staggered tunnels and subterranean cavities: Analytical and HYDRUS modeling. Adv. Water Resources 2022, 164, 104182. [CrossRef]
- Niu, X. Key Technologies of the Hydraulic Structures of the Three Gorges Project. Engineering 2016, 2, 340–349. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2016.03.006.
- Yang, G., Wang, X., Wang, X., Cao, Y. Analyses of Seepage Problems in a Subsea Tunnel Considering Effects of Grouting and Lining Structure. Marine Geores. Geotechnol. 2016, 34, 1, 65-70. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-H. Hydraulic Structures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 755–812. [CrossRef]
- Frenelus, W., Peng, H. Evaluating the Time-Dependent Behavior of Deeply Buried Tunnels in Soft Rock Environments and Relevant Measures Guaranteeing Their Long-Term Stability. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10542. [CrossRef]
- Peng, K., Yi, G., Luo, S., Si, X. Stress Analysis and Spalling Failure Simulation on Surrounding Rock of Deep Arch Tunnel. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6474. [CrossRef]
- Tunç, C., Tunç, O. A note on the stability and boundedness of solutions to non-linear differential systems of second order. J. Assoc. Arab Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 24, 169–175. [CrossRef]
- Zou, J, Li S. Theoretical solution for displacement and stress in strain-softening surrounding rock under hydraulic-mechanical coupling. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2015, 58, 1401–1413. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F., Du, S.J., Chen, B. Unified analytical solution for deep circular tunnel with consideration of seepage pressure, grouting and lining. J. Central South Univ. 2017, 24, 1483−1493. [CrossRef]
- Al-Ajmi, A.M., Zimmerman, R.W. Stability analysis of vertical boreholes using the Mogi–Coulomb failure criterion. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2006, 43, 1200-1211, 2006. [CrossRef]
- Komurlu E., Kesimal A., Hasanpour R. In situ horizontal stress effect on plastic zone around circular underground openings excavated in elastic zones. Geomech. Eng. 2015, 8 (6), 783-799. [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z., Yang, J., Wang, Z., Liu, H. The Plastic Zone of Tunnel Surrounding Rock under Unequal Stress in Two Directions Based on the Unified Strength. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8842153. [CrossRef]
- Frenelus, W., Peng, H., Zhang, J. Creep Behavior of Rocks and Its Application to the Long-Term Stability of Deep Rock Tunnels. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8451. [CrossRef]
- Sterpi D. An analysis of geotechnical problems involving strain softening effects. In. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 1999, 23, 1427-1454. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S., Yin, S., Wu, Z. Strain-softening analysis of a spherical cavity. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 2012, 36, 182–202. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F., Qian, D. Difference solution for a circular tunnel excavated in strain-softening rock mass considering decayed confinement. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 82, 66–81. [CrossRef]
- Zareifard, M.R., Shekari M.R. Comprehensive solutions for underwater tunnels in rock masses with different GSI values considering blast-induced damage zone and seepage forces. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 96, 236–268. [CrossRef]
- Song, F. Modelling time-dependent plastic behaviour of geomaterials. PhD Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Frenelus, W., Peng, H., Zhang, J. An Insight from Rock Bolts and Potential Factors Influencing Their Durability and the Long-Term Stability of Deep Rock Tunnels. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10943. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Q., Li, S.C., Li, L.P., Shi, S.S., Zhou, Z.Q., Gao, C.L. Design of a Displacement Monitoring System Based on Optical Grating and Numerical Verification in Geomechanical Model Test of Water Leakage of Tunnel. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 2097–2108. [CrossRef]
- Baji, H., Li, C.Q., Scicluna, S., Dauth, J. Risk-cost optimised maintenance strategy for tunnel structures. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 69, 72–84. [CrossRef]
- Elgamal, A., Elfaris, N. Stability of Shield-Bored Tunnel for the Challenge of Nile Crossing. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 147. [CrossRef]
- Wu, G., Chen, W., Tian, H., Jia, S., Yang, J., Tan, X. Numerical evaluation of a yielding tunnel lining support system used in limiting large deformation in squeezing rock. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 439. [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Lambert, M.F.; Simpson, A.R.; Zecchin, A.C. Detection of Localized Deterioration Distributed along Single Pipelines by Reconstructive MOC Analysis. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 190–198. [CrossRef]
- Hognestad, H.O., Kieffer, S. Pre-excavation grouting in rock tunneling – Dealing with high groundwater pressures. Geomech. Tunn. 2019, 12, 141-146. [CrossRef]
- Xu, S., Ma, E., Lai, J., Yang, Y., Liu, H., Yang, C., Hu, Q. Diseases failures characteristics and countermeasures of expressway tunnel of water-rich strata: A case study. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 134, 106056. [CrossRef]
- Frenelus, W., Peng, H. Towards Long-Term Monitoring of the Structural Health of Deep Rock Tunnels with Remote Sensing Techniques. Fratt. Ed. Integrità Strutt. 2023, 66, 56-87. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X., Shi, P., Zhou, X., Liu, W., Yang, H, Wang, T., Yan, M., Fan, W. A novel vision measurement system for health monitoring of tunnel structures. Mech. Advanced Mater. Struct. 2022, 29 (15), 2208-2218. [CrossRef]
- Moser, F., Lienhart, W., Woschitz, H., Schuller, H. Long-term monitoring of reinforced earth structures using distributed fiber optic sensing. J. Civil Struct. Health Monit. 2016, 6, 321–327. [CrossRef]
- Monsberger, C.M., Bauer, P., Buchmayer, F., Lienhart, W. Large-scale distributed fiber optic sensing network for short and long-term integrity monitoring of tunnel linings. J. Civil Struct. Health Monit. 2022, 12, 1317–1327. [CrossRef]
- Kane, W.F., Peters, D.C., Speirer, R.A. Remote Sensing in Investigation of Engineered Underground Structures. J. Geotech. Eng. 1996, 122 (8), 674-681. [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, K., Najafi, M., Kaushal, V., Covilakam, M. Development of a Decision Support Tool for Inspection and Monitoring of Large-Diameter Steel and Prestressed Concrete Cylinder Water Pipes. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2022, 13(1), 04021067. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y., Zhou. J., Zhang. B., Wang, H., Huang, M. Statistical analysis of major tunnel construction accidents in China from 2010 to 2020. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104460. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Relevant details: a) A view of location map of the Weilai Tunnel; b) Excavated section subject to an initial hydrostatic stress field .
Figure 1.
Relevant details: a) A view of location map of the Weilai Tunnel; b) Excavated section subject to an initial hydrostatic stress field .
Figure 2.
Main rock types along the Weilai Tunnel alignment.
Figure 2.
Main rock types along the Weilai Tunnel alignment.
Figure 3.
Adopted mechanical model of the Weilai Tunnel.
Figure 3.
Adopted mechanical model of the Weilai Tunnel.
Figure 4.
Mechanical model of the supported tunnel under seepage states.
Figure 4.
Mechanical model of the supported tunnel under seepage states.
Figure 5.
Mechanical model of the tunnel for elasto-plastic examination.
Figure 5.
Mechanical model of the tunnel for elasto-plastic examination.
Figure 6.
Illustration of plastic residual zone and plastic softening zone around the surrounding rocks of deep tunnels.
Figure 6.
Illustration of plastic residual zone and plastic softening zone around the surrounding rocks of deep tunnels.
Figure 7.
Tunnel surrounding rocks and its strain-softening model.
Figure 7.
Tunnel surrounding rocks and its strain-softening model.
Figure 8.
Calculation flowchart.
Figure 8.
Calculation flowchart.
Figure 9.
Variation of plastic radius with the support resistance when the principal stress coefficient is not accounted.
Figure 9.
Variation of plastic radius with the support resistance when the principal stress coefficient is not accounted.
Figure 10.
Principal stress coefficient b and plastic zone radius.
Figure 10.
Principal stress coefficient b and plastic zone radius.
Figure 11.
Relationship between the pore water pressure and the ratio of plastic radii at different values of the permeability, considering a direction of
Figure 11.
Relationship between the pore water pressure and the ratio of plastic radii at different values of the permeability, considering a direction of
Figure 12.
Relationship between the pore water pressure and the ratio of plastic radii at different values of the permeability, considering a direction of
Figure 12.
Relationship between the pore water pressure and the ratio of plastic radii at different values of the permeability, considering a direction of
Figure 13.
Relationship between the pore water pressure and the ratio of plastic radii at different values of the permeability, considering a direction of
Figure 13.
Relationship between the pore water pressure and the ratio of plastic radii at different values of the permeability, considering a direction of
Figure 14.
Relationship between the tangential stress of the host rocks and the support reaction (p) under coupled actions of softening and seepage.
Figure 14.
Relationship between the tangential stress of the host rocks and the support reaction (p) under coupled actions of softening and seepage.
Figure 15.
(a). Dissemination of tangential stress around the tunnel surrounding rocks when the support pressure is 9 MPa (principal stress coefficient not accounted). (b). Dissemination of tangential stress around the tunnel surrounding rocks when the support pressure is 15 MPa (principal stress coefficient not accounted).
Figure 15.
(a). Dissemination of tangential stress around the tunnel surrounding rocks when the support pressure is 9 MPa (principal stress coefficient not accounted). (b). Dissemination of tangential stress around the tunnel surrounding rocks when the support pressure is 15 MPa (principal stress coefficient not accounted).
Figure 16.
(a). Dissemination of tangential stress around the tunnel surrounding rocks when the support pressure is 9 MPa, for different values of principal stress coefficient. (b) Dissemination of tangential stress around the tunnel surrounding rocks when the support pressure is 15 MPa, for different values of principal stress coefficient.
Figure 16.
(a). Dissemination of tangential stress around the tunnel surrounding rocks when the support pressure is 9 MPa, for different values of principal stress coefficient. (b) Dissemination of tangential stress around the tunnel surrounding rocks when the support pressure is 15 MPa, for different values of principal stress coefficient.
Table 1.
Average basic values of the parameters characteristics of argillaceous sandstone in dry states around the tunnel.
Table 1.
Average basic values of the parameters characteristics of argillaceous sandstone in dry states around the tunnel.
| Rock type |
Uniaxial compressive strength (MPa) |
Elastic Modulus (GPa) |
Poisson’s ratio |
Cohesion (MPa) |
Internal friction angle (°) |
Density (g/cm3) |
| Argillaceous sandstone |
10 |
2.2 |
0.23 |
5.06 |
30 |
0.24 |
Table 2.
Average basic values of the parameters characteristics of argillaceous sandstone in wet states.
Table 2.
Average basic values of the parameters characteristics of argillaceous sandstone in wet states.
| Rock type |
Uniaxial compressive strength (MPa) |
Elastic Modulus (GPa) |
Poisson’s ratio |
Cohesion (MPa) |
Internal friction angle (°) |
Density (g/cm3) |
| Argillaceous sandstone |
6.6 |
0.62 |
0.39 |
0.93 |
7.5 |
0.38 |
Table 3.
Additional Parameter characteristics of the tunnel and its host rocks.
Table 3.
Additional Parameter characteristics of the tunnel and its host rocks.
| Relevant parameter characteristics |
Unit |
Value |
| Initial hydrostatic stress |
MPa |
10 |
| Hydraulic pressure |
MPa |
5 |
| Residual internal friction angle |
degree |
5.3 |
| Residual cohesion |
kPa |
0.61 |
| Plastic softening parameter |
--- |
0.005 |
| Tunnel excavation radius |
m |
6 |
| Tunnel net radius |
m |
5 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).