Submitted:
27 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Generalized Elastic Model with Active Brownian Particle
2. Fractional Langevin Equation
3. h-autocorrelation Function
4. Mean Square Displacement
4.1. AOUP’s MSD
4.1.1.
-
.We can split the integral and solve the first one [119]:Hence we integrate the second by parts and we expand the resulting trigonometric functions for small argumentsBy evaluating the remaining integrals we obtain the final result
-
.The integral (35) is in this caseIntegrating by parts we haveWe can neglect the second and split the first into two contributionsThen we can retain only the first one, as the second is nearly zero, and expand the sine for small arguments, getting [119]
-
.This case is the easier to be handled. Expanding the cosine for small arguments in (35) yields
4.1.2.
-
.From (36), after integrating by parts, it is obtainedThe major contributions to the integrals appearing in (44) come from , hence may be properly approximated to
-
.We recap from the expression (40), neglecting the second integral on the RHS and retaining only the contributions coming from in the first:
-
.As in the previous situations the main contributions to the integral in (35) will arise from , henceBy integration by parts it becomesand, using the methods of improper integrals [121], the final result is
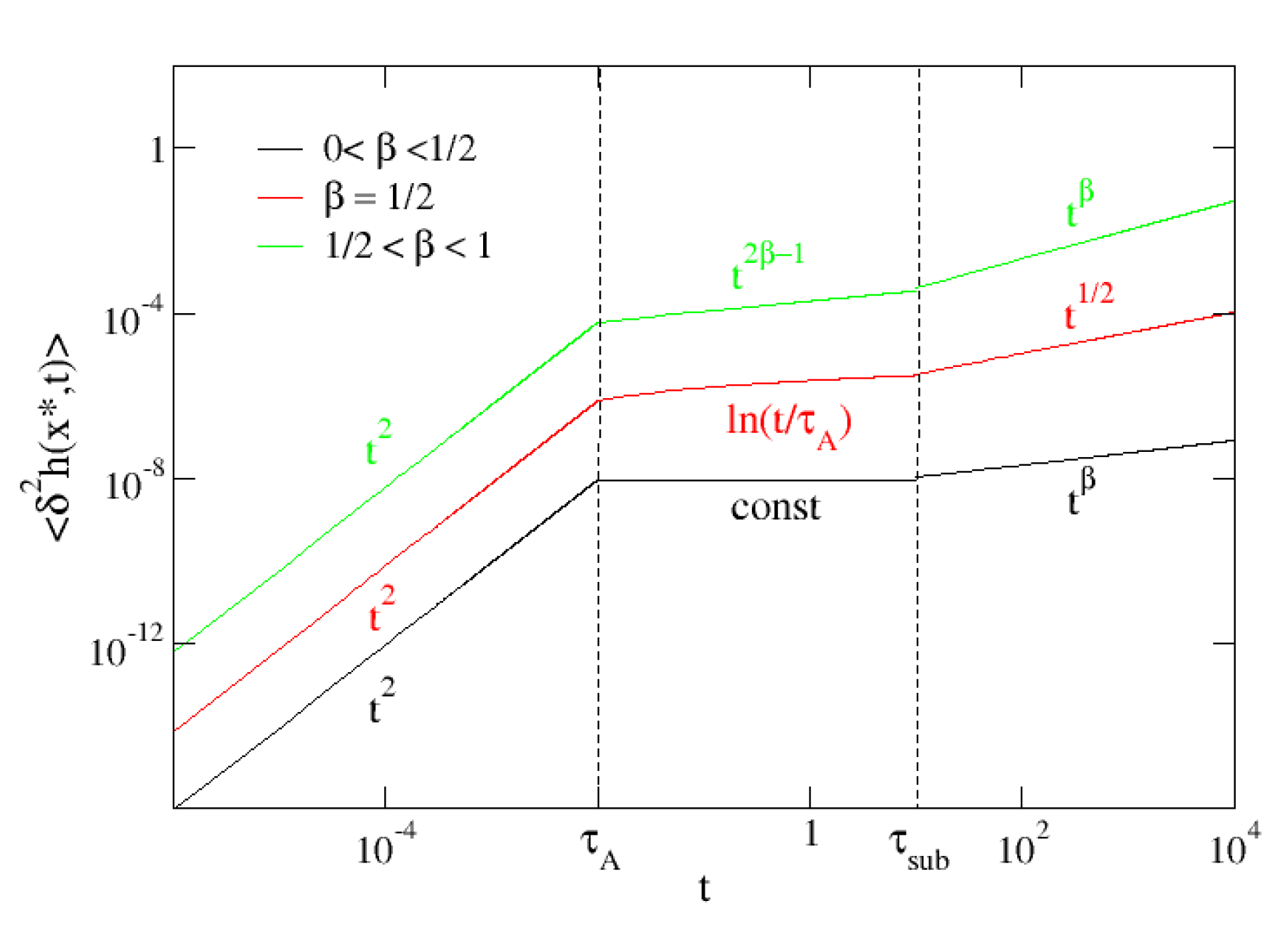
4.2. MSD at a Generic Position
-
.Probes very close to the AOUP exhibit an initial thermal subdiffusive behavior . Subsequently, the probe at behaves identically to the AOUP.
-
.
-
.Probes that satisfy this condition, i.e., probes far away from the AOUP, are not influenced by the action of the active force.
5. Concluding Remarks
References
- Bechinger, C.; Di Leonardo, R.; Löwen, H.; Reichhardt, C.; Volpe, G.; Volpe, G. Active particles in complex and crowded environments. Reviews of Modern Physics 2016, 88, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.C.; Joanny, J.F.; Ramaswamy, S.; Liverpool, T.B.; Prost, J.; Rao, M.; Simha, R.A. Hydrodynamics of soft active matter. Reviews of modern physics 2013, 85, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgeti, J.; Winkler, R.G.; Gompper, G. Physics of microswimmers—single particle motion and collective behavior: a review. Reports on progress in physics 2015, 78, 056601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanczuk, P.; Bär, M.; Ebeling, W.; Lindner, B.; Schimansky-Geier, L. Active Brownian particles: From individual to collective stochastic dynamics. The European Physical Journal Special Topics 2012, 202, 1–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, S. The mechanics and statistics of active matter. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2010, 1, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.W. Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 14th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques, 1987, pp. 25–34.
- Olfati-Saber, R. Flocking for multi-agent dynamic systems: Algorithms and theory. IEEE Transactions on automatic control 2006, 51, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czirók, A.; Barabási, A.L.; Vicsek, T. Collective motion of self-propelled particles: Kinetic phase transition in one dimension. Physical Review Letters 1999, 82, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzin, I.D.; Ioannou, C.C.; Demirel, G.; Gross, T.; Torney, C.J.; Hartnett, A.; Conradt, L.; Levin, S.A.; Leonard, N.E. Uninformed individuals promote democratic consensus in animal groups. science 2011, 334, 1578–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Escudero, A.; de Polavieja, G. Collective animal behavior from Bayesian estimation and probability matching. Nature Precedings 2011, pp. 1–1.
- Couzin, I.D.; Krause, J.; et al. Self-organization and collective behavior in vertebrates. Advances in the Study of Behavior 2003, 32, 10–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, H.C. E. coli in Motion; Springer, 2004.
- Lauga, E.; Goldstein, R.E. Dance of the microswimmers. Physics Today 2012, 65, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthäus, F.; Jagodič, M.; Dobnikar, J.E. coli superdiffusion and chemotaxis—search strategy, precision, and motility. Biophysical journal 2009, 97, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.L.; Libchaber, A. Particle diffusion in a quasi-two-dimensional bacterial bath. Physical review letters 2000, 84, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leptos, K.C.; Guasto, J.S.; Gollub, J.P.; Pesci, A.I.; Goldstein, R.E. Dynamics of enhanced tracer diffusion in suspensions of swimming eukaryotic microorganisms. Physical Review Letters 2009, 103, 198103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal, N.; Weihs, D. Experimental evidence of strong anomalous diffusion in living cells. Physical Review E 2010, 81, 020903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wang, B.; Granick, S. Memoryless self-reinforcing directionality in endosomal active transport within living cells. Nature Materials 2015, 14, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal, N.; Lechtman-Goldstein, D.; Weihs, D. Particle tracking in living cells: a review of the mean square displacement method and beyond. Rheologica Acta 2013, 52, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.A.; Suzuki, R.; Schaller, V.; Aranson, I.S.; Bausch, A.R.; Frey, E. Random bursts determine dynamics of active filaments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2015, 112, 10703–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacci, J.; Cottin-Bizonne, C.; Ybert, C.; Bocquet, L. Sedimentation and effective temperature of active colloidal suspensions. Physical Review Letters 2010, 105, 088304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howse, J.R.; Jones, R.A.; Ryan, A.J.; Gough, T.; Vafabakhsh, R.; Golestanian, R. Self-motile colloidal particles: from directed propulsion to random walk. Physical review letters 2007, 99, 048102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfus, R.; Baudry, J.; Roper, M.L.; Fermigier, M.; Stone, H.A.; Bibette, J. Microscopic artificial swimmers. Nature 2005, 437, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierno, P.; Golestanian, R.; Pagonabarraga, I.; Sagués, F. Controlled swimming in confined fluids of magnetically actuated colloidal rotors. Physical review letters 2008, 101, 218304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Fischer, P. Controlled propulsion of artificial magnetic nanostructured propellers. Nano letters 2009, 9, 2243–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bricard, A.; Caussin, J.B.; Desreumaux, N.; Dauchot, O.; Bartolo, D. Emergence of macroscopic directed motion in populations of motile colloids. Nature 2013, 503, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Leonardo, R. Controlled collective motions. Nature materials 2016, 15, 1057–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Han, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Luijten, E.; Granick, S. Reconfiguring active particles by electrostatic imbalance. Nature materials 2016, 15, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiguchi, D.; Iwasawa, J.; Jiang, H.R.; Sano, M. Flagellar dynamics of chains of active Janus particles fueled by an AC electric field. New Journal of Physics 2018, 20, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, C.; Paoluzzi, M.; Angelani, L.; Di Leonardo, R. Memory-less response and violation of the fluctuation-dissipation theorem in colloids suspended in an active bath. Scientific reports 2017, 7, 17588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor, É.; Nardini, C.; Cates, M.E.; Tailleur, J.; Visco, P.; Van Wijland, F. How far from equilibrium is active matter? Physical review letters 2016, 117, 038103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, C.; Paoluzzi, M.; Pellicciotta, N.; Lepore, A.; Angelani, L.; Di Leonardo, R. Generalized energy equipartition in harmonic oscillators driven by active baths. Physical review letters 2014, 113, 238303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cates, M.E.; Tailleur, J. Motility-induced phase separation. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2015, 6, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverey, J.F.; Jeon, J.H.; Bao, H.; Leippe, M.; Metzler, R.; Selhuber-Unkel, C. Superdiffusion dominates intracellular particle motion in the supercrowded cytoplasm of pathogenic Acanthamoeba castellanii. Scientific reports 2015, 5, 11690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budrene, E.O.; Berg, H.C. Dynamics of formation of symmetrical patterns by chemotactic bacteria. Nature 1995, 376, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, M.P.; Levitov, L.S.; Budrene, E.O. Physical mechanisms for chemotactic pattern formation by bacteria. Biophysical journal 1998, 74, 1677–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, A.K.; Klymko, K.; GrandPre, T.; Geissler, P.L. Phase diagram of active Brownian spheres: Crystallization and the metastability of motility-induced phase separation. Physical review letters 2021, 126, 188002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alert, R.; Casademunt, J.; Joanny, J.F. Active turbulence. Annual Review of Condensed Matter Physics 2022, 13, 143–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafri, Y.; da Silveira, R.A. Steady-state chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Physical review letters 2008, 100, 238101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tailleur, J.; Cates, M. Statistical mechanics of interacting run-and-tumble bacteria. Physical review letters 2008, 100, 218103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Isaac, E.; Fodor, É.; Visco, P.; Van Wijland, F.; Gov, N.S. Modeling the dynamics of a tracer particle in an elastic active gel. Physical Review E 2015, 92, 012716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Ten Hagen, B.; Kaiser, A.; Wu, M.; Cui, H.; Silber-Li, Z.; Löwen, H. Non-Gaussian statistics for the motion of self-propelled Janus particles: Experiment versus theory. Physical Review E 2013, 88, 032304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.P.; Wittmann, R.; Löwen, H. Active Ornstein–Uhlenbeck model for self-propelled particles with inertia. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2021, 34, 035101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprini, L.; Marconi, U.M.B.; Wittmann, R.; Löwen, H. Dynamics of active particles with space-dependent swim velocity. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprenger, A.R.; Caprini, L.; Löwen, H.; Wittmann, R. Dynamics of active particles with translational and rotational inertia. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2023, 35, 305101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprini, L.; Bettolo Marconi, U.M.; Wittmann, R.; Löwen, H. Active particles driven by competing spatially dependent self-propulsion and external force. SciPost Physics 2022, 13, 065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, N.; Chakrabarti, R. Chain reconfiguration in active noise. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical 2016, 49, 195601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKintosh, F.C.; Janmey, P.A. Actin gels. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 1997, 2, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenstecken, T.; Gompper, G.; Winkler, R.G. Conformational properties of active semiflexible polymers. Polymers 2016, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.; Babel, S.; ten Hagen, B.; von Ferber, C.; Löwen, H. How does a flexible chain of active particles swell? The Journal of chemical physics 2015, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.K.; Singh, S.P. Behavior of active filaments near solid-boundary under linear shear flow. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 4008–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Cherstvy, A.G.; Kim, W.K.; Metzler, R. Facilitation of polymer looping and giant polymer diffusivity in crowded solutions of active particles. New Journal of Physics 2015, 17, 113008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaki, S.; Chakrabarti, R. Enhanced diffusion, swelling, and slow reconfiguration of a single chain in non-Gaussian active bath. The Journal of chemical physics 2019, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikola, N.; Solon, A.P.; Kafri, Y.; Kardar, M.; Tailleur, J.; Voituriez, R. Active particles with soft and curved walls: Equation of state, ratchets, and instabilities. Physical review letters 2016, 117, 098001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, J.; Valeriani, C.; Cacciuto, A. Activity-induced collapse and reexpansion of rigid polymers. Physical Review E 2014, 90, 062312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, S.C.; Spakowitz, A.J.; Theriot, J.A. Nonthermal ATP-dependent fluctuations contribute to the in vivo motion of chromosomal loci. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2012, 109, 7338–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronshtein, I.; Kepten, E.; Kanter, I.; Berezin, S.; Lindner, M.; Redwood, A.B.; Mai, S.; Gonzalo, S.; Foisner, R.; Shav-Tal, Y.; et al. Loss of lamin A function increases chromatin dynamics in the nuclear interior. Nature communications 2015, 6, 8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstein, I.; Israel, Y.; Kepten, E.; Mai, S.; Shav-Tal, Y.; Barkai, E.; Garini, Y. Transient anomalous diffusion of telomeres in the nucleus of mammalian cells. Physical review letters 2009, 103, 018102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colin, A.; Singaravelu, P.; Théry, M.; Blanchoin, L.; Gueroui, Z. Actin-network architecture regulates microtubule dynamics. Current Biology 2018, 28, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, T.; Chen, D.T.; DeCamp, S.J.; Heymann, M.; Dogic, Z. Spontaneous motion in hierarchically assembled active matter. Nature 2012, 491, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, R.; Sano, K.I.; Ijiro, K.; Osada, Y. Chemically cross-linked microtubule assembly shows enhanced dynamic motions on kinesins. RSC Advances 2014, 4, 32953–32959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speckner, K.; Stadler, L.; Weiss, M. Anomalous dynamics of the endoplasmic reticulum network. Physical Review E 2018, 98, 012406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sparkes, I.; Ashwin, P. Structure and dynamics of ER: minimal networks and biophysical constraints. Biophysical Journal 2014, 107, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, D.; Tardin, C.; Schmidt, C.F.; MacKintosh, F.C. Nonequilibrium mechanics of active cytoskeletal networks. Science 2007, 315, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonn-Segev, A.; Bernheim-Groswasser, A.; Roichman, Y. Dynamics in steady state in vitro acto-myosin networks. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2017, 29, 163002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sonn-Segev, A.; Bernheim-Groswasser, A.; Roichman, Y. Scale dependence of the mechanics of active gels with increasing motor concentration. Soft matter 2017, 13, 7352–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köster, D.V.; Husain, K.; Iljazi, E.; Bhat, A.; Bieling, P.; Mullins, R.D.; Rao, M.; Mayor, S. Actomyosin dynamics drive local membrane component organization in an in vitro active composite layer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2016, 113, E1645–E1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celli, J.; Gregor, B.; Turner, B.; Afdhal, N.H.; Bansil, R.; Erramilli, S. Viscoelastic properties and dynamics of porcine gastric mucin. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.E.; Turner, B.S.; Rubinstein, M.; McKinley, G.H.; Ribbeck, K. A rheological study of the association and dynamics of MUC5AC gels. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3654–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, D.; Xu, T.; Xing, W.; Ge, X.; Fang, L.; Wang, K.; Ren, F.; Lu, X. Mussel-inspired contact-active antibacterial hydrogel with high cell affinity, toughness, and recoverability. Advanced Functional Materials 2019, 29, 1805964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherstvy, A.G.; Thapa, S.; Wagner, C.E.; Metzler, R. Non-Gaussian, non-ergodic, and non-Fickian diffusion of tracers in mucin hydrogels. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 2526–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, A.; Granek, R.; Elbaum, M. Enhanced diffusion in active intracellular transport. Physical Review Letters 2000, 85, 5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.H.; Tejedor, V.; Burov, S.; Barkai, E.; Selhuber-Unkel, C.; Berg-Sørensen, K.; Oddershede, L.; Metzler, R. In vivo anomalous diffusion and weak ergodicity breaking of lipid granules. Physical review letters 2011, 106, 048103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, T.; Head, D.A.; Schmidt, C.F.; Mizuno, D. Non-Gaussian athermal fluctuations in active gels. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3234–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkin, G.; DeCamp, S.J.; Chen, D.T.; Sanchez, T.; Dogic, Z. Tunable dynamics of microtubule-based active isotropic gels. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 2014, 372, 20140142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; Kanduč, M.; Roa, R.; Dzubiella, J. Tuning the permeability of dense membranes by shaping nanoscale potentials. Physical review letters 2019, 122, 108001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seisenberger, G.; Ried, M.U.; Endress, T.; Buning, H.; Hallek, M.; Bräuchle, C. Real-time single-molecule imaging of the infection pathway of an adeno-associated virus. Science 2001, 294, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y.; Noguchi, A.; Kishino, A.; Yanagida, T. Sliding movement of single actin filaments on one-headed myosin filaments. Nature 1987, 326, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amblard, F.; Maggs, A.C.; Yurke, B.; Pargellis, A.N.; Leibler, S. Subdiffusion and anomalous local viscoelasticity in actin networks. Physical review letters 1996, 77, 4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, I.; Gardel, M.; Reichman, D.; Weeks, E.R.; Valentine, M.; Bausch, A.; Weitz, D.A. Anomalous diffusion probes microstructure dynamics of entangled F-actin networks. Physical review letters 2004, 92, 178101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, T.D.; Cooper, J.A. Actin, a central player in cell shape and movement. science 2009, 326, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.S.; Moon, H.C.; Jeon, J.H.; Park, H.Y. Neuronal messenger ribonucleoprotein transport follows an aging Lévy walk. Nature communications 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihs, D.; Mason, T.G.; Teitell, M.A. Bio-microrheology: a frontier in microrheology. Biophysical journal 2006, 91, 4296–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, C. Out-of-equilibrium microrheology inside living cells. Physical review letters 2008, 101, 028101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahana, A.; Kenan, G.; Feingold, M.; Elbaum, M.; Granek, R. Active transport on disordered microtubule networks: The generalized random velocity model. Physical Review E 2008, 78, 051912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kam, Z.; Carlton, P.M.; Xu, L.; Sedat, J.W.; Blackburn, E.H. Rapid telomere motions in live human cells analyzed by highly time-resolved microscopy. Epigenetics & chromatin 2008, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Stadler, L.; Weiss, M. Non-equilibrium forces drive the anomalous diffusion of telomeres in the nucleus of mammalian cells. New Journal of Physics 2017, 19, 113048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.; Park, G.; Goo, J.; Lee, J.; Park, T.L.; Shim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, W.K.; Jeong, C. Effects of transcription-dependent physical perturbations on the chromosome dynamics in living cells. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2022, 10, 822026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesbolatova, A.K.; Arai, R.; Sakaue, T.; Kimura, A. Formulation of chromatin mobility as a function of nuclear size during C. elegans embryogenesis using polymer physics theories. Physical Review Letters 2022, 128, 178101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, R.D.; Hotani, H. Formation of membrane networks in vitro by kinesin-driven microtubule movement. The Journal of cell biology 1988, 107, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Gov, N. Dynamics of active semiflexible polymers. Biophysical journal 2014, 107, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isele-Holder, R.E.; Elgeti, J.; Gompper, G. Self-propelled worm-like filaments: spontaneous spiral formation, structure, and dynamics. Soft matter 2015, 11, 7181–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isele-Holder, R.E.; Jäger, J.; Saggiorato, G.; Elgeti, J.; Gompper, G. Dynamics of self-propelled filaments pushing a load. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 8495–8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, A.; Adhikari, R. Filament actuation by an active colloid at low Reynolds number. New Journal of Physics 2017, 19, 033021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, R.; Winkler, R.G.; Gompper, G. Flow-induced helical coiling of semiflexible polymers in structured microchannels. Physical review letters 2012, 109, 178101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, A.; Löwen, H. Unusual swelling of a polymer in a bacterial bath. The Journal of chemical physics 2014, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Hou, Z. Configuration dynamics of a flexible polymer chain in a bath of chiral active particles. The Journal of chemical physics 2019, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Hou, Z. Motion transition of active filaments: Rotation without hydrodynamic interactions. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.; Thakur, S. Coarse-grained simulations of an active filament propelled by a self-generated solute gradient. Physical Review E 2016, 93, 032508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, N. Crowding-activity coupling effect on conformational change of a semi-flexible polymer. Polymers 2019, 11, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathyusha, K.; Henkes, S.; Sknepnek, R. Dynamically generated patterns in dense suspensions of active filaments. Physical Review E 2018, 97, 022606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, V.; Locatelli, E.; Malgaretti, P. Globulelike conformation and enhanced diffusion of active polymers. Physical review letters 2018, 121, 217802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, Ö.; Isele-Holder, R.E.; Elgeti, J.; Gompper, G. Collective dynamics of self-propelled semiflexible filaments. Soft matter 2018, 14, 4483–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, L.; Caprini, L.; Cecconi, F. How a local active force modifies the structural properties of polymers. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 2594–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.; Durang, X.; Lee, O.c.; Jeon, J.H. Anomalous diffusion of active Brownian particles cross-linked to a networked polymer: Langevin dynamics simulation and theory. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 9188–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Joo, S.; Sakaue, T.; Jeon, J.H. Nonequilibrium diffusion of active particles bound to a semi-flexible polymer network: simulations and fractional Langevin equation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.05851 2023.
- Taloni, A.; Chechkin, A.; Klafter, J. Generalized elastic model yields a fractional Langevin equation description. Physical review letters 2010, 104, 160602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taloni, A.; Chechkin, A.; Klafter, J. Correlations in a generalized elastic model: Fractional Langevin equation approach. Physical Review E 2010, 82, 061104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimm, B.H. Dynamics of polymer molecules in dilute solution: viscoelasticity, flow birefringence and dielectric loss. The journal of chemical physics 1956, 24, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbas, A.A.; Marichev, O.I.; Samko, S.G. Fractional integrals and derivatives (theory and applications), 1993.
- Saichev, A.I.; Zaslavsky, G.M. Fractional kinetic equations: solutions and applications. Chaos: an interdisciplinary journal of nonlinear science 1997, 7, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taloni, A.; Chechkin, A.; Klafter, J. Unusual response to a localized perturbation in a generalized elastic model. Physical Review E 2011, 84, 021101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taloni, A.; Chechkin, A.; Klafter, J. Generalized elastic model: fractional Langevin description, fluctuation relation and linear response. Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena 2013, 8, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taloni, A.; et al. Kubo fluctuation relations in the generalized elastic model. Advances in Mathematical Physics 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, J.; Song, T.; Jeon, J.H. Langevin dynamics driven by a telegraphic active noise. Frontiers in Physics 2019, 7, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samko, S.G. Fractional integrals and derivatives. Theory and applications 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional differential equations: an introduction to fractional derivatives, fractional differential equations, to methods of their solution and some of their applications; Elsevier, 1998.
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A.; Romer, R.H. Handbook of mathematical functions with formulas, graphs, and mathematical tables, 1988.
- Gradshteyn, I.S.; Ryzhik, I.M. Table of integrals, series, and products; Academic press, 2014.
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Van Ness, J.W. Fractional Brownian motions, fractional noises and applications. SIAM review 1968, 10, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, G.H. Divergent series; Vol. 334, American Mathematical Soc., 2000.
- Taloni, A.; Chechkin, A.; Klafter, J. Generalized elastic model: Thermal vs. non-thermal initial conditions—Universal scaling, roughening, ageing and ergodicity. Europhysics Letters 2012, 97, 30001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanović, D.; Rabin, Y. Dynamics of active Rouse chains. Soft matter 2017, 13, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanović, D. Properties of Rouse polymers with actively driven regions. The Journal of chemical physics 2018, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, T.; Saito, T. Active diffusion of model chromosomal loci driven by athermal noise. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, D. Anomalous polymer dynamics is non-Markovian: memory effects and the generalized Langevin equation formulation. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment 2010, 2010, P06011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, D. Generalized Langevin equation formulation for anomalous polymer dynamics. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment 2010, 2010, L02001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



