Submitted:
29 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
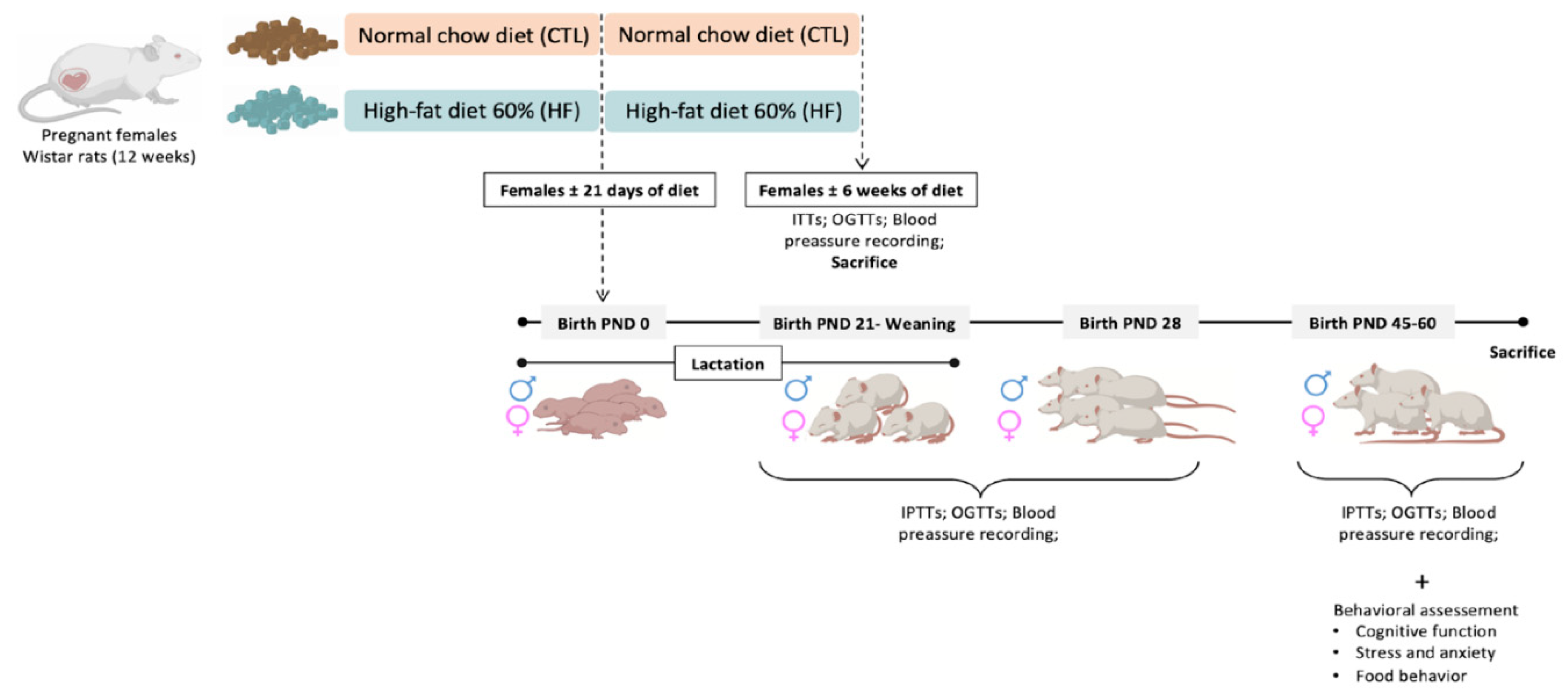
2.1. Animals
2.2. Metabolic Evaluation
2.2.1. Intravenous Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT)
2.2.2. Intraperitoneal Insulin Tolerance Test (ipITT)
2.2.3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
2.3. Behavioral Assessment
2.3.1. Open Field (OF)
2.3.2. Y Maze
2.3.3. Elevated Plus Maze (EPM)
2.3.4. Light Dark Box (LDB)
2.3.5. Novel Object Recognition (NOR)
2.3.6. Block Test
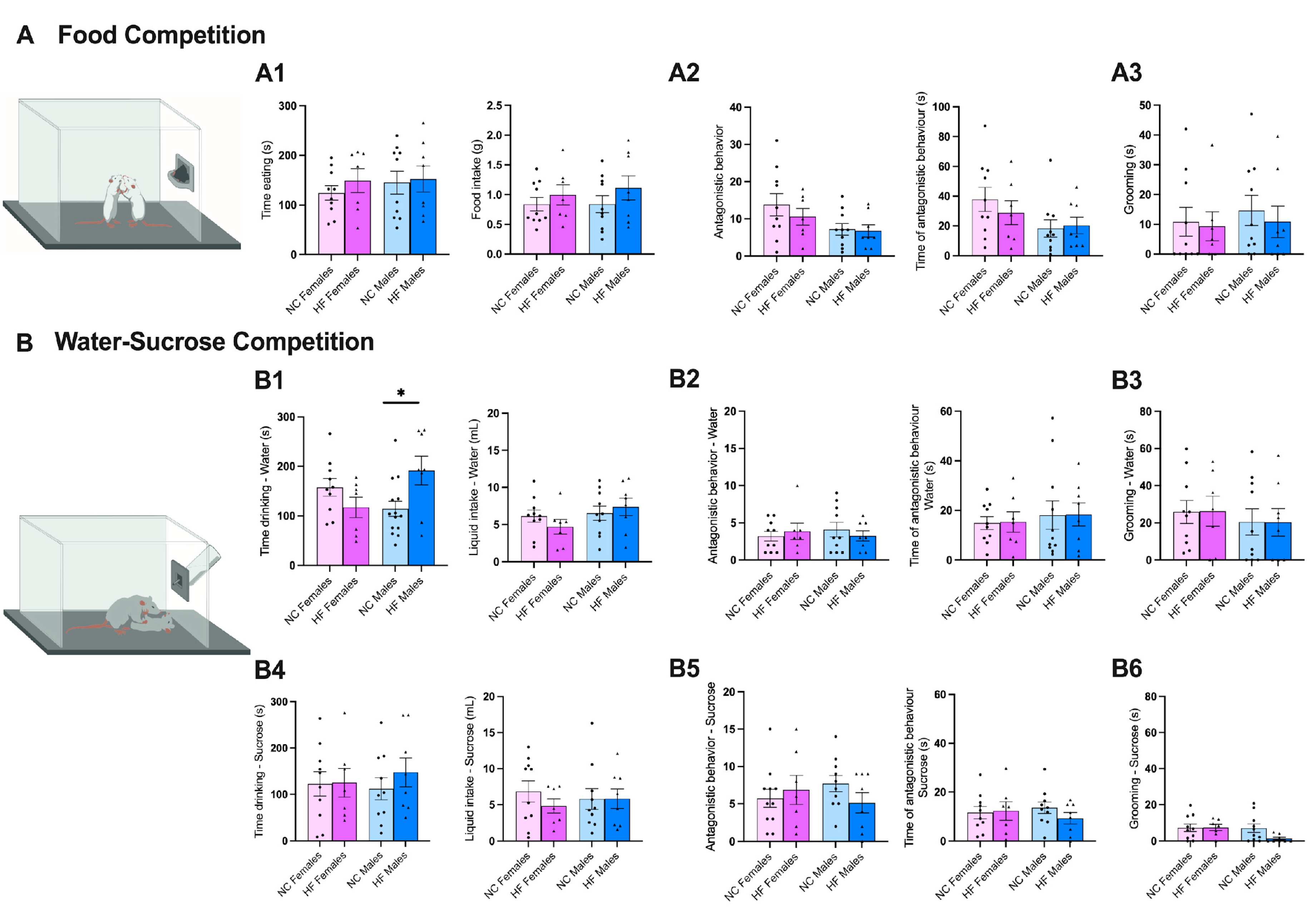
2.3.7. Food Competition
2.3.8. Water/Sucrose Competition
2.4. Ex Vivo Analysis
2.4.1. Tissue Lysate Preparation and Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
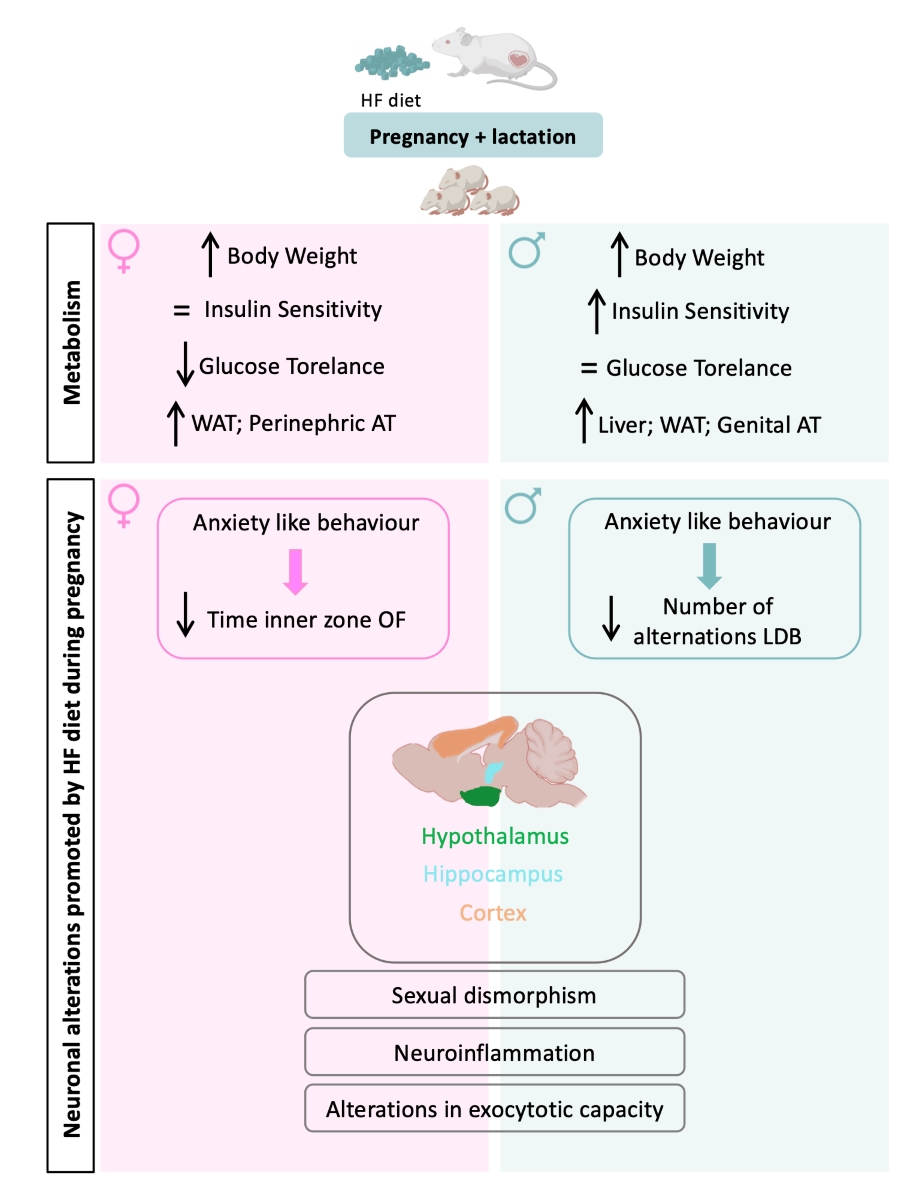
3.1. Effect of Overnutrition during Pregnancy and Lactation on Metabolic Parameters in the Mothers
3.2. Effect of Overnutrition during Pregnancy and Lactation on Metabolic Function in the Offspring
3.2.1. Insulin Action and Glucose Homeostasis
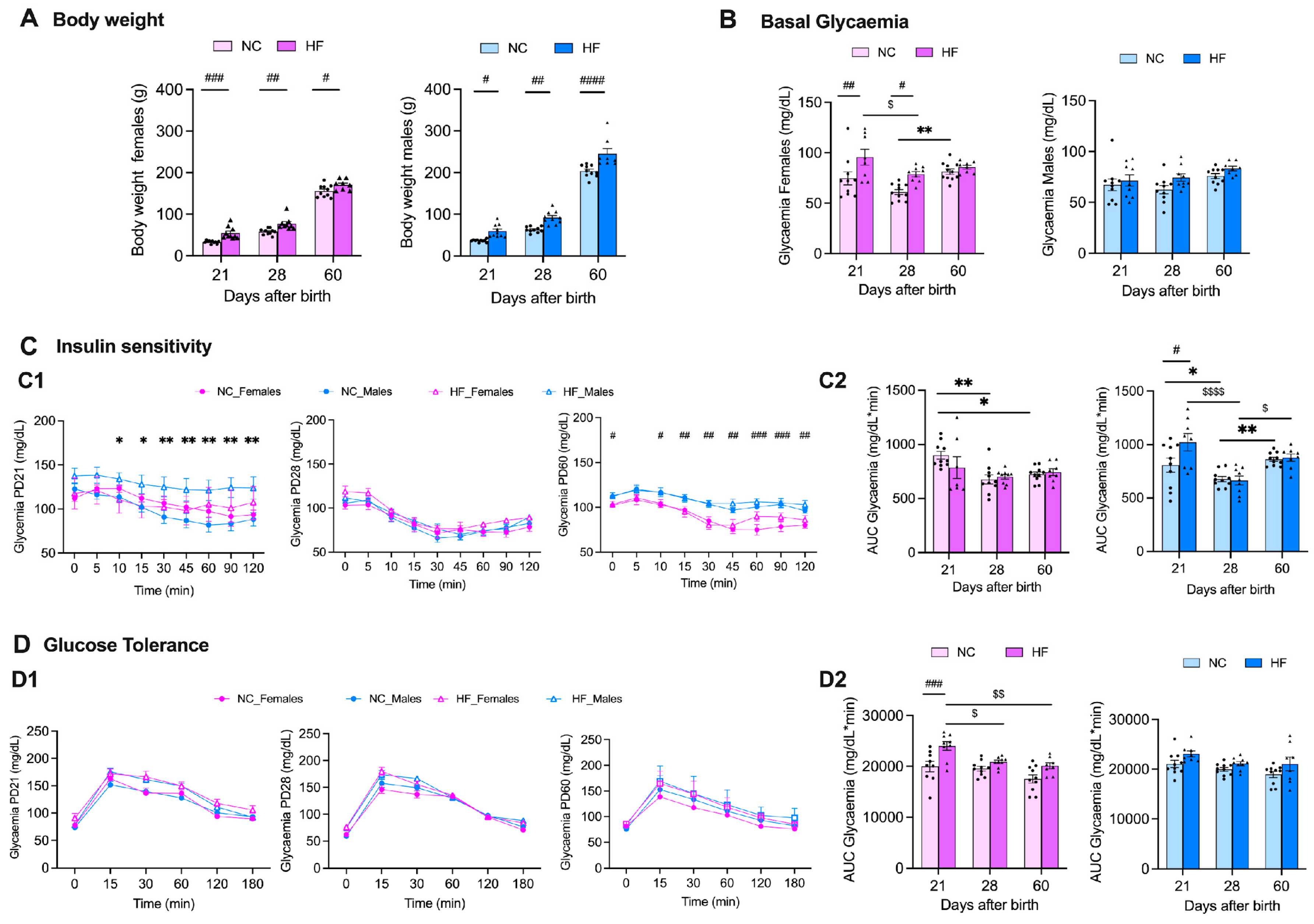
3.2.2. Liver and Adipose Tissue Depots Weight
| Liver | Visceral AT | Perinephric AT | Genital AT | Brown AT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC Females PD21 | 0.963 ± 0.066 | 0.262 ± 0.026 | 0.105 ± 0.017 | 0.128 ± 0.015 | 0.087 ± 0.010 |
| HF Females PD21 | 1.646 ± 0.139 | 0.278 ± 0.039 | 0.222 ± 0.026 | 0.318 ± 0.098 | 0.130 ± 0.021 |
| NC Females PD28 | 0.978 ± 0.056 | 0.257 ± 0.021 | 0.139 ± 0.012 | 0.114 ± 0.012 | 0.103 ± 0.009 |
| HF Females PD28 | 1.965 ± 0.115 | 0.344 ± 0.042 | 0.303 ± 0.053 | 0.286 ± 0.050 | 0.143 ± 0.015 |
| NC Females PD60 | 1.892 ± 0.118 | 0.406 ± 0.038 | 0.196± 0.017 | 0.214 ± 0.033 | 0.135 ± 0.009 |
| HF Females PD60 | 2.670 ± 0.158 | 0.527 ± 0.055 *** | 0.374 ± 0.068 ** | 0.472 ± 0.075 | 0.139 ± 0.010 |
| NC Males PD21 | 2.286 ± 0.086 | 0.376 ± 0.042 | 0.376 ± 0.059 | 0.305 ± 0.033 | 0.146 ± 0.016 |
| HF Males PD21 | 2.717 ± 0.126 ** | 0.561 ± 0.043 | 0.472 ± 0.042 | 0.528 ± 0.054 | 0.144 ± 0.012 |
| NC Males PD28 | 4.872 ± 0.405 | 1.029 ± 0.135 | 1.109 ± 0.212 | 1.993 ± 0.405 | 0.249 ± 0.025 |
| HF Males PD28 | 4.566 ± 0.178 | 1.472 ± 0.065 | 1.879 ± 0.281 | 2.183 ± 0.386 | 0.226 ± 0.026 |
| NC Males PD60 | 6.377 ± 0.326 | 1.216 ± 0.182 | 2.599 ± 0.381 | 2.324 ± 0.375 | 0.269 ± 0.025 |
| HF Males PD60 | 7.218 ± 0.465 * | 1.864 ± 0.152 ** | 3.162 ± 0.422 | 3.642 ± 0.503 ** | 0.284 ± 0.026 |
3.3. Effect of Overnutrition during Pregnancy and Lactation on Behaviour Phenotype in the Offspring
3.3.1. Anxiety and Stress
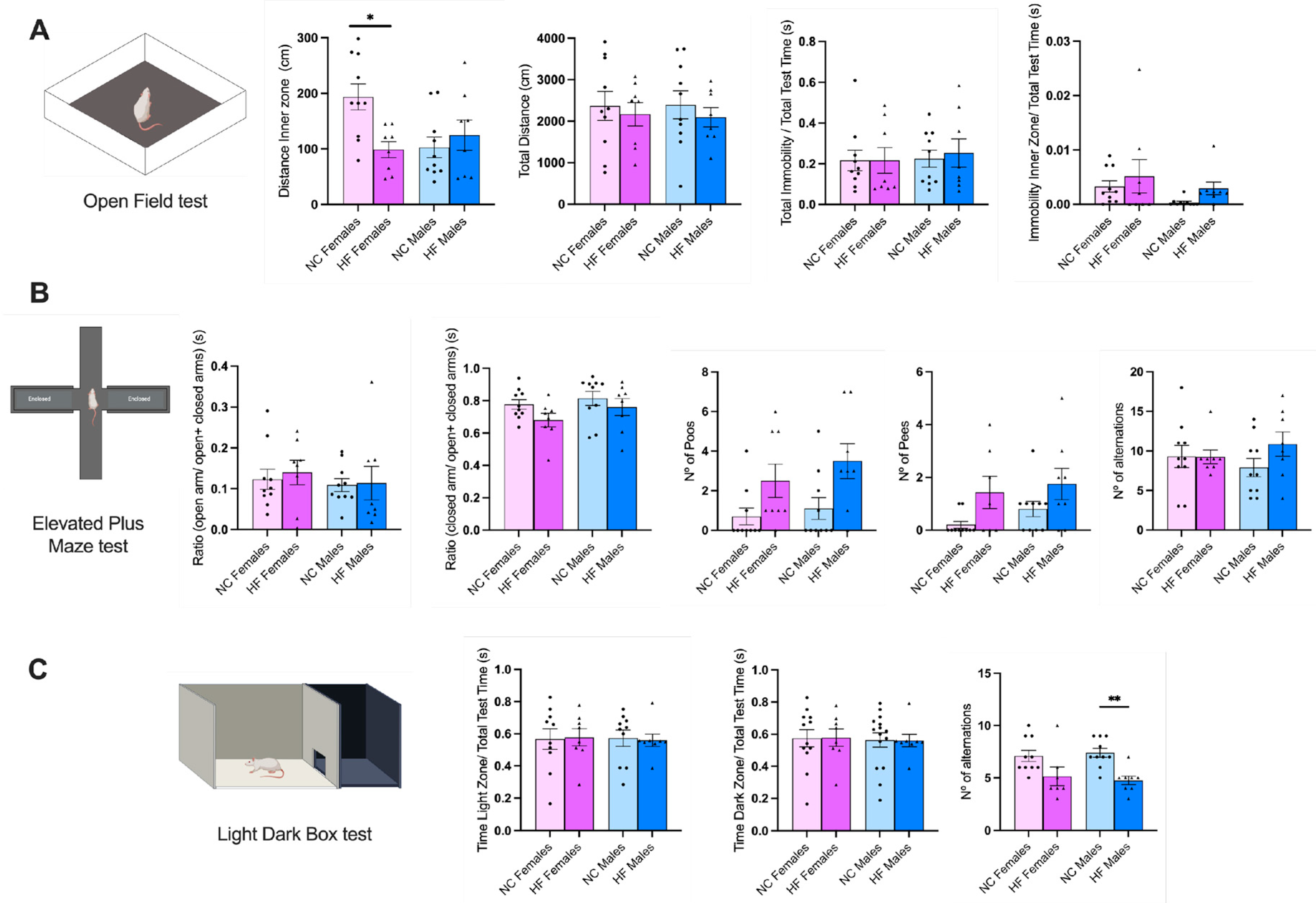
3.3.2. Memory and Learning
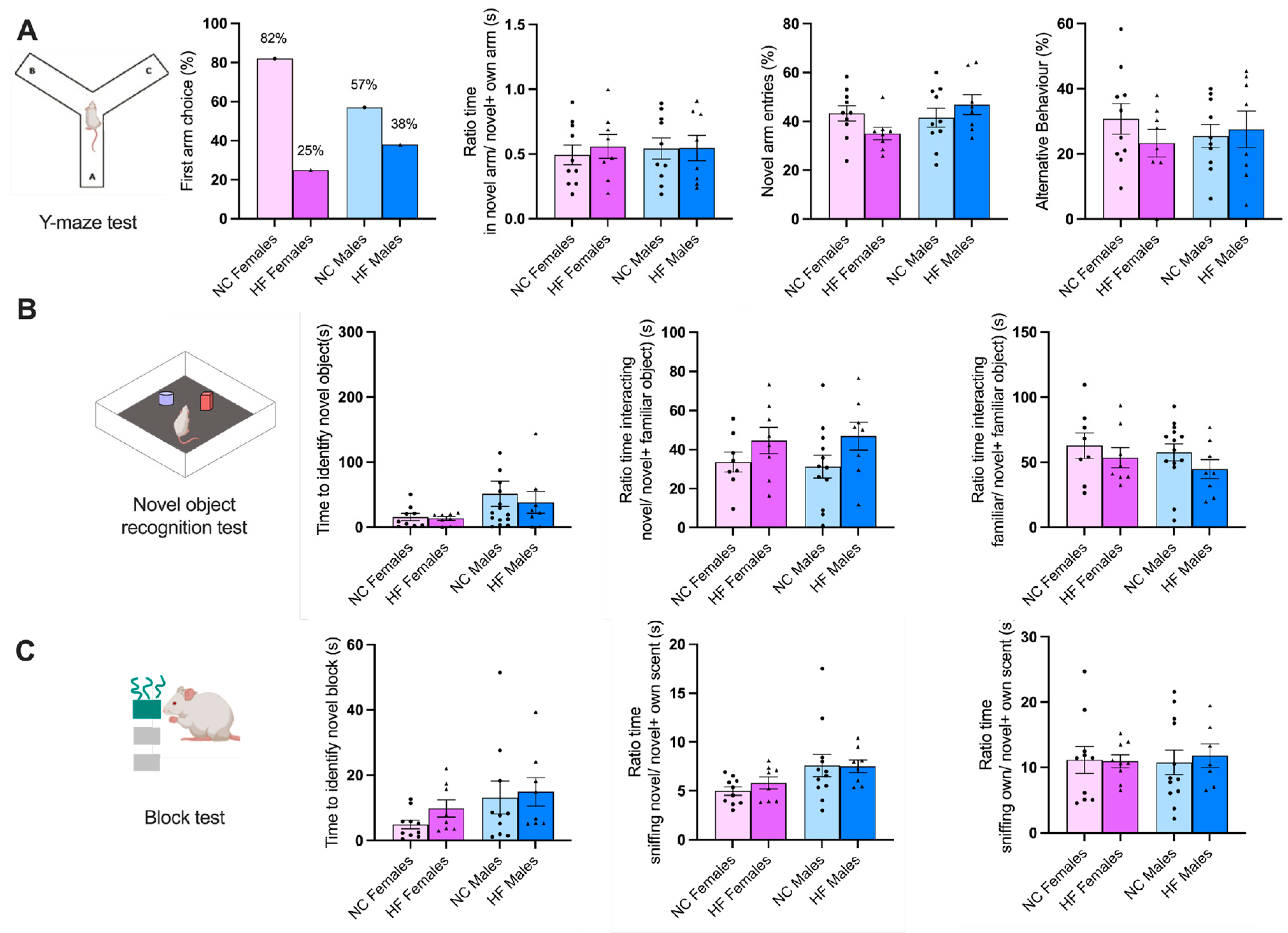
3.3.3. Food/Drink Behavior
3.4. Effect of Overnutrition during Pregnancy and Lactation on Hypothalamic, Hippocampal and Prefrontal Markers of Synaptic Transmission, Metabolic Signaling and Inflammation
3.4.1. Protein Markers of Synaptic Transmission on the Hypothalamus, Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex
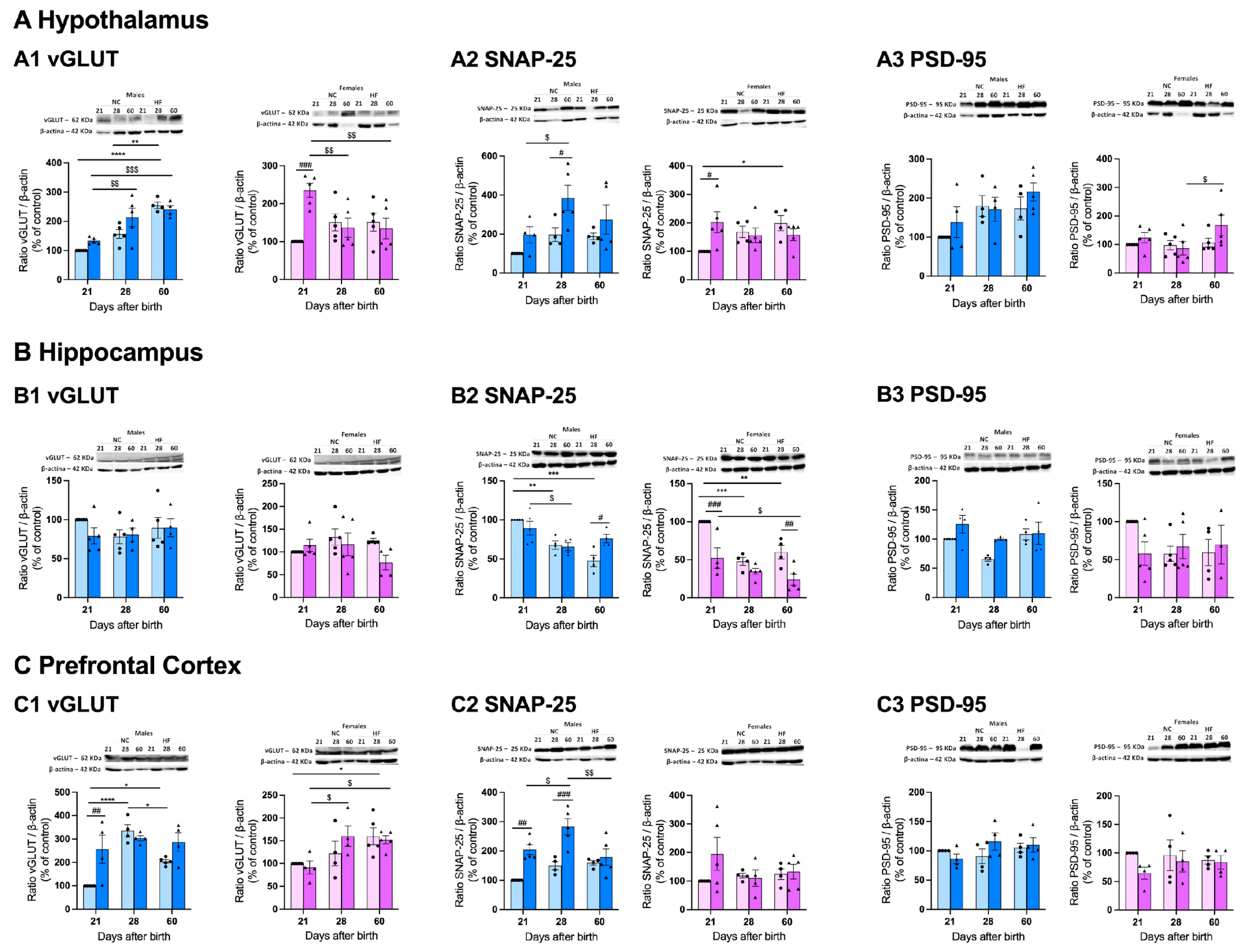
3.4.2. Protein Markers of Metabolism on the Hypothalamus, Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex
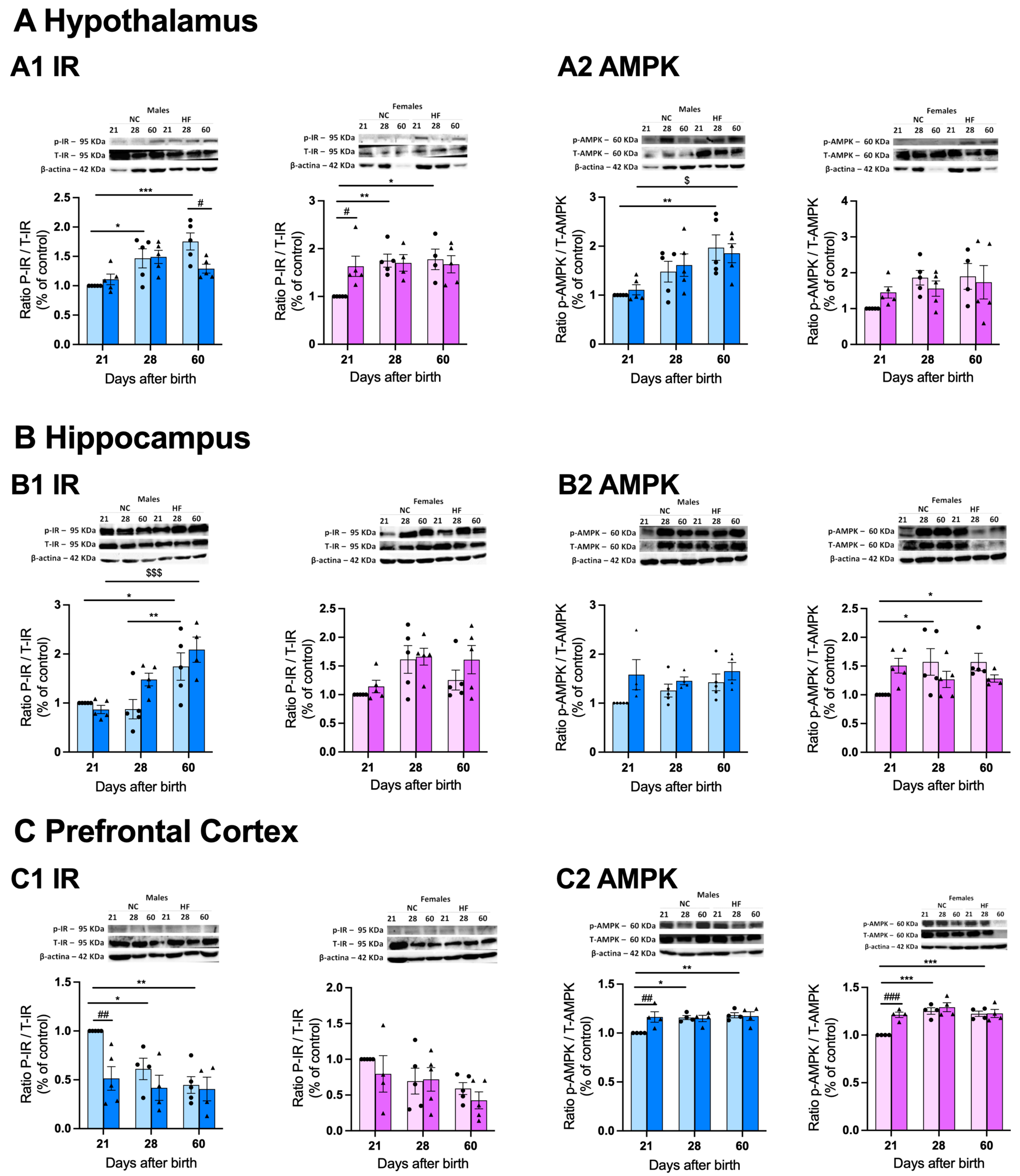
3.4.3. Protein Markers of Inflammation on the Hypothalamus, Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex
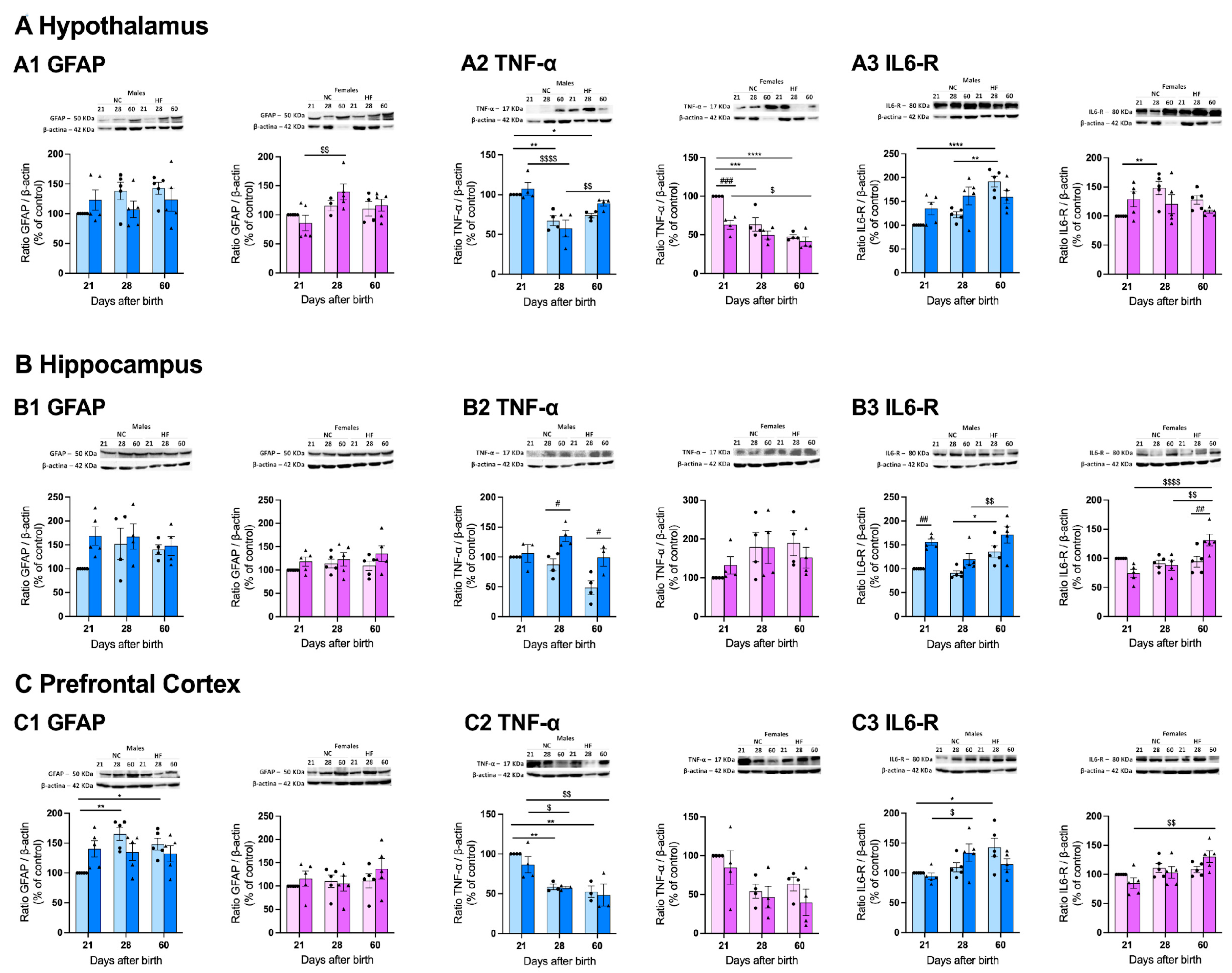
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Overnutrition during Pregnancy and Lactation on Metabolic Function in the Offspring
4.2. Effect of Overnutrition during Pregnancy and Lactation on Behaviour and CNS Functions in the Offspring
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alberti, K. G. M. M. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; National heart, lung, and blood institute; American heart association; World heart federation; International atherosclerosis society; And international association for the study of obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M. Metabolic syndrome: Is it time to add the central nervous system? Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D. J. P. The origins of the developmental origins theory. Journal of Internal Medicine 2007, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, A. , Patro-Małysza, J., Kimber-Trojnar, Ż., Marciniak, B., Oleszczuk, J., and Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Fetal programming of the metabolic syndrome. Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2017, 56, 2133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, C. M. and Friedman, J. E. Maternal modifiers of the infant gut microbiota: Metabolic consequences. Journal of Endocrinology 2017, 235, R1–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jašarević, E. Howard, C. D. Misic. Stress during pregnancy alters temporal and spatial dynamics of the maternal and offspring microbiome in a sex-specific manner. Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D. et al., “Exposure to Obesogenic Environments during Perinatal Development Modulates Offspring Energy Balance Pathways in Adipose Tissue and Liver of Rodent Models. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, B. , Liber, A., Zalewski, B., Poston, L., Szajewska, H. and Koletzko, B. Maternal and paternal body mass index and offspring obesity: A systematic review. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism 2013, 63, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaro, A. Baptista, F. I. and Matafome, P. Programming of future generations during breastfeeding: The intricate relation between metabolic and neurodevelopment disorders. Life Sciences 2022, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leddy, M. A. , Power, M. L. and Schulkin, J. The Impact of Maternal Obesity on Maternal and Fetal Health. 2008.
- Hyatt H., W. Zhang, Y. Hood, W. R. and Kavazis, A. N. Lactation has persistent effects on a mother’s metabolism and mitochondrial function. Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, G. C. Ural, S. H. and Hajnal, A. Differential effects of maternal high fat diet during pregnancy and lactation on taste preferences in rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, A. et al. Associations between visceral adipose tissue, inflammation and sex steroid concentrations in men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2013, 78, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokras, N. and Dalla, C. Preclinical sex differences in depression and antidepressant response: Implications for clinical research. Journal of Neuroscience Research 2017, 95, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzillo, L. U. and Hamdy, O. Evaluation of Insulin Sensitivity in Clinical Practice and in Research Settings. Nutrition Reviews 2003, 61, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M. J. , Sacramento, J. F. Gonzalez, C. Guarino, M. P., Monteiro, E. C. and Conde, S. V. Carotid body denervation prevents the development of insulin resistance and hypertension induced by hypercaloric diets. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibenhener M., L. and Wooten, M. C. Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. Journal of Visualized Experiments 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmkuhl, A. M. E. , Dirr, R. and Fleming, S. M. Olfactory assays for mouse models of neurodegenerative disease. Journal of Visualized Experiments 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A. , Bauer, B., Abner, E. L., Ashkenazy-Frolinger, T. and Hartz, A. M. S. A comprehensive behavioral test battery to assess learning and memory in 129S6/ Tg2576 mice. PLoS One 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M. B. Synaptic signaling in learning and memory. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2016, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrow, A. P. , Stranahan, A. Suchecki, M. D. and Yunes, R. Neuroendocrine Regulation of Anxiety: Beyond the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Journal of Neuroendocrinology 2016, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. , Koyama, Y., and S. Shimada, “Inflammation From Peripheral Organs to the Brain: How Does Systemic Inflammation Cause Neuroinflammation? Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2022, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, E. and Kim, Y. K. Neuroinflammation-associated alterations of the brain as potential neural biomarkers in anxiety disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neniskyte, U. , Vilalta, A. and Brown, G. C. Tumour necrosis factor alpha-induced neuronal loss is mediated by microglial phagocytosis. FEBS Lett 2014, 588, 2952–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor B., A. , et al., “Corrigendum to ‘Alpha-Synuclein-induced DNA Methylation and Gene Expression in Microglia’ [Neuroscience 468 (2021) 186–198] (Neuroscience (2021) 468 (186–198), (S0306452221002748), (10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.05.027)). Neuroscience 2022, 492, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boberg, J. et al., “Comparison of female rat reproductive effects of pubertal versus adult exposure to known endocrine disruptors. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Garrido M., A. , et al., “Early overnutrition sensitizes the growth hormone axis to the impact of diet-induced obesity via sex-divergent mechanisms. Sci Rep 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şanlı, E. and Kabaran, S. Maternal Obesity, Maternal Overnutrition and Fetal Programming: Effects of Epigenetic Mechanisms on the Development of Metabolic Disorders. Curr Genomics 2019, 20, 419–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco M., E. and Josefson, J. L. Hyperglycemia During Pregnancy and Long-Term Offspring Outcomes. Current Diabetes Reports 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen E., D. et al., “Epigenetics and epigenomics: Implications for diabetes and obesity. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, J. , Chen, P. J., and Xiao, W. H. Mechanism of increased risk of insulin resistance in aging skeletal muscle. Diabetology and Metabolic Syndrome 2020, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, L. M. , Nagao, M., Kusinski, L. C., Fernandez-Twinn D. S., Eliasson, L., and Ozanne S. E. Exposure to maternal obesity programs sex differences in pancreatic islets of the offspring in mice. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- “MCN-16-e13031”.
- Melo, B. F. , Sacramento, J. F., Capucho, A. M., Sampaio-Pires, D., Prego, C. S., and Conde, S. V. Long-Term Hypercaloric Diet Consumption Exacerbates Age-Induced Dysmetabolism and Carotid Body Dysfunction: Beneficial Effects of CSN Denervation. Front Physiol 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M. , Han, G., Mossayebi, E., Beall, M. H., and Ross, M. G., “552: Programmed insulin resistance of offspring of obese mothers. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2017, 216, S325–S326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingrone, G. et al., “Influence of maternal obesity on insulin sensitivity and secretion in offspring. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1872–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Beld, A. W. , Kaufman, J. M., Zillikens, M. C., S. Lamberts, W. J., Egan, J. M. and van der Lely, A. J. The physiology of endocrine systems with ageing. The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology 2018, 6, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M. et al., “Obesity and abnormal glucose tolerance in offspring of diabetic mothers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, S. , Vieira, N., Marques, F., Costa, P. S., Sousa, N. and Palha, J. A. The effect of high-fat diet on rat’s mood, feeding behavior and response to stress. Transl Psychiatry 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XIANG, A. et al., “251-OR: Maternal Diabetes during Pregnancy and Incidence of Depression and Anxiety in Offspring from Childhood to Young Adulthood. Diabetes 2022, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabji, F. On: Wed. Gene Expr 2018, 13, 311–319, Available: www.cognizantcommunication.com. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, R. W. , Miller, B. R., and DiAntonio, A. Increased vesicular glutamate transporter expression causes excitotoxic neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 2011, 41, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendining, K. A. , Fisher, L. C. and Jasoni, C. L. Maternal high fat diet alters offspring epigenetic regulators, amygdala glutamatergic profile and anxiety. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 96, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbas, O. et al., “Neurobehavioral effects of long-term maternal fructose intake in rat offspring. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 2018, 69, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi,Y. et al., “Agrp-negative arcuate NPY neurons drive feeding under positive energy balance via altering leptin responsiveness in POMC neurons. Cell Metab 2023, 35, 979–995. [CrossRef]
- Qu, N. et al., “A POMC-originated circuit regulates stress-induced hypophagia, depression, and anhedonia. Mol Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1006–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenman, Y. et al. Postnatal Ablation of POMC Neurons Induces an Obese Phenotype Characterized by Decreased Food Intake and Enhanced Anxiety-Like Behavior. Molecular Endocrinology 2013, 27, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmann, F. and Holzer, P. Neuropeptide Y: A stressful review. Neuropeptides 2016, 55, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H. Molecular Mechanisms of Hypothalamic Insulin Resistance. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESLER, M. , “Sympathetic nervous system and insulin resistance: from obesity to diabetes. Am J Hypertens 2001, 14, S304–S309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B. and Cheng, K. 2018. Hypothalamic AMPK as a Mediator of Hormonal Regulation of Energy Balance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kola, B. Role of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in the Control of Appetite. J Neuroendocrinol 2008, 20, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, M. M. , and Shaw, R. J. The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nat Cell Biol 2011, 13, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Z. , Wang, Y. X. and Jiang, C. L. Inflammation: The common pathway of stress-related diseases. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 2017, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, K. E. , McCracken, Buck, K. D. J., Davis, R. L., Sloan, D. K., and Curtis, K. S. Relationship Between Circulating Metabolic Hormones and Their Central Receptors During Ovariectomy-Induced Weight Gain in Rats. Front Physiol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagundes, C. P. , Bennett, J. M., Derry, H. M., and Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K. House. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humberg, A. et al., Preterm birth and sustained inflammation: consequences for the neonate Network, German Center for Lung Research and Priming Immunity at the beginning of life (PRIMAL) Consortium. Semin Immunopathol 2020, 42, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, C. et al., Immature anti-inflammatory response in neonates. Clin Exp Immunol 2004, 135, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A. , Vega, W., Sivanathan, de S., St-Cyr, S. and McGowan, P. Maternal high-fat diet alters anxiety behavior and glucocorticoid signaling in adolescent offspring. Neuroscience 2014, 272, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H. L. et al., A peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-δ agonist provides neuroprotection in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2013, 240, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovac, H. , Grubić Kezele, T. and Radošević-Stašić, B. Expression Profiles of Metallothionein I/II and Megalin in Cuprizone Model of De- and Remyelination. Neuroscience 2018, 388, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| NC MOTHERS | HF MOTHERS | |
|---|---|---|
| Body Weight (g) | 243.2 ± 5.122 | 236.8 ± 2.577 |
| Basal Glycaemia (mg/dL) | 69.14 ± 1.792 | 78.88 ± 3.573 * |
| kITT (% glucose/min) | 4.864 ± 0.3957 | 1.849 ± 0.3188 **** |
| AUC Glycaemia (mg/dL*min) | 18138 ± 417.4 | 19612 ± 594.9 |
| Liver (g/kg) | 0.0280 ± 0.001 | 0.0289 ± 0.001 |
| Visceral Adipose Tissue (g/kg) | 0.0057 ± 0.002 | 0.0066 ± 0.002 |
| Perinephric Adipose Tissue (g/kg) | 0.0153 ± 0.002 | 0.0171 ± 0.004 |
| Genital Adipose Tissue (g/kg) | 0.0232 ± 0.002 | 0.0254 ± 0.002 |
| Brown Adipose Tissue (g/kg) | 0.0007 ± 0.000 | 0.0016 ± 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





