Submitted:
29 November 2023
Posted:
29 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Peptides
2.2. Mycobacterial Culture
2.3. Peptide Screening
2.4. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration
3. Results
3.1. Determining the Time to Positivity (TTP) for All 171 Single Substitutions of Peptide 14D
3.2. Verification of the Screen with Purified Peptides
3.3. Determining the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Selected Peptides with A Strong Inhibitory Effect
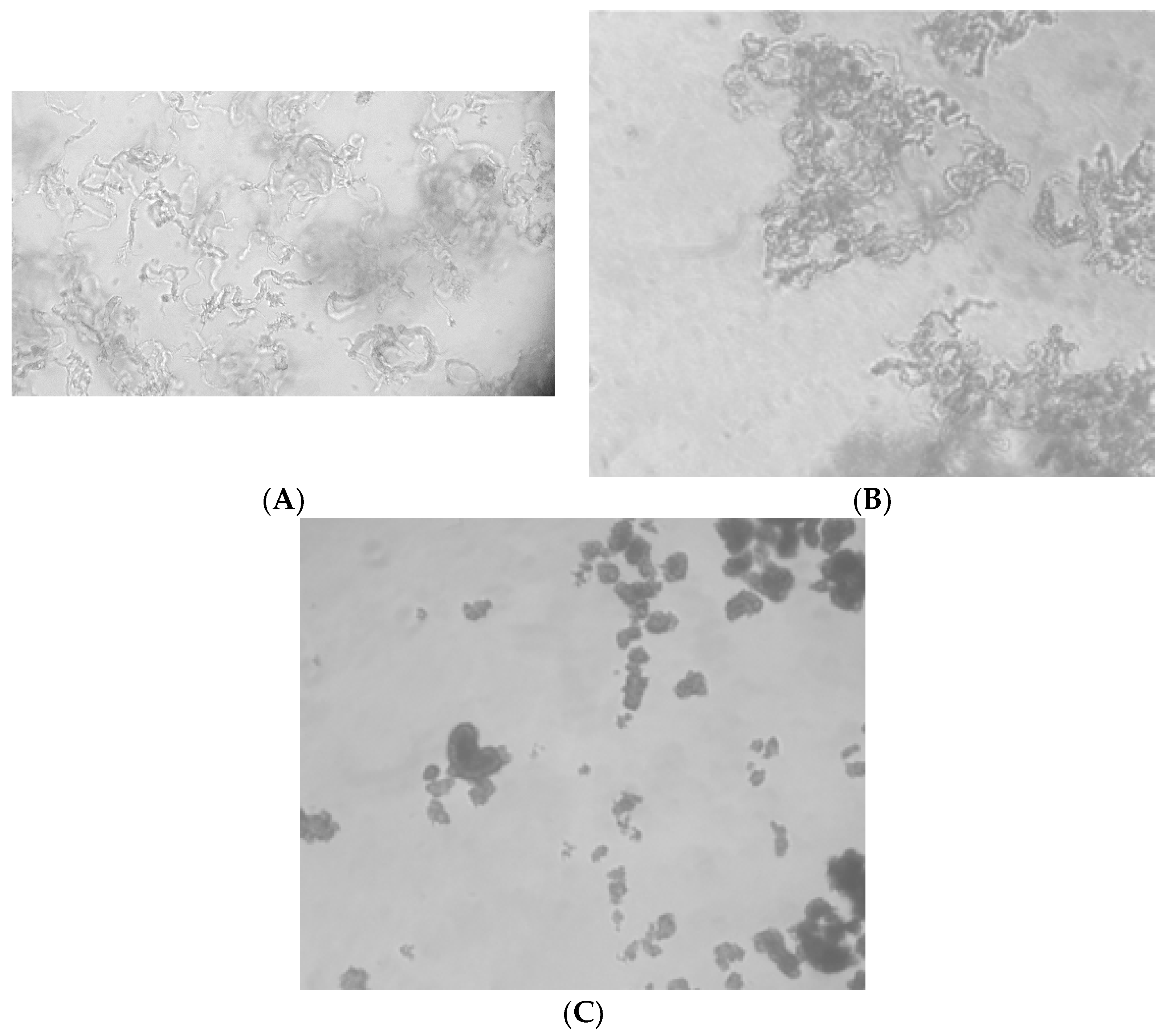
3.4. Observing Changes in Cord Formation in the Presence of Peptides at 10 µg/mL
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Tuberculosis - Key Facts Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Gill, C.M.; Dolan, L.; Piggott, L.M.; McLaughlin, A.M. New Developments in Tuberculosis Diagnosis and Treatment. Breathe 2022, 18. [CrossRef]
- Sibandze, D.B.; Kay, A.; Dreyer, V.; Sikhondze, W.; Dlamini, Q.; DiNardo, A.; Mtetwa, G.; Lukhele, B.; Vambe, D.; Lange, C.; et al. Rapid Molecular Diagnostics of Tuberculosis Resistance by Targeted Stool Sequencing. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Dong, F.; Shi, C.; Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Lao, X.; Zheng, H. DRAMP 2.0, an Updated Data Repository of Antimicrobial Peptides. Scientific Data 2019, 6, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Dini, I.; De Biasi, M.G.; Mancusi, A. An Overview of the Potentialities of Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Natural Sources. Antibiotics 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.; Chapple, D.S. Peptide Antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1317–1323.
- Le, C.-F.; Fang, C.-M.; Sekaran, S.D. Intracellular Targeting Mechanisms by Antimicrobial Peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [CrossRef]
- Hilpert, K.; McLeod, B.; Yu, J.; Elliott, M.R.; Rautenbach, M.; Ruden, S.; Bürck, J.; Muhle-Goll, C.; Ulrich, A.S.; Keller, S.; et al. Short Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides Interact with ATP. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54. [CrossRef]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial Peptides: Pore Formers or Metabolic Inhibitors in Bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Sung, B.H.; Kim, S.C. Buforins: Histone H2A-Derived Antimicrobial Peptides from Toad Stomach. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2009, 1788, 1564–1569. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Takeshima, K.; Park, C.B.; Kim, S.C.; Matsuzaki, K. Interactions of the Novel Anfimicrobial Peptide Buforin 2 with Lipid Bilayers: Proline as a Translocation Promoting Factor. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 8648–8654. [CrossRef]
- Marchand, C.; Krajewski, K.; Lee, H.-F.; Antony, S.; Johnson, A.A.; Amin, R.; Roller, P.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Pommier, Y. Covalent Binding of the Natural Antimicrobial Peptide Indolicidin to DNA Abasic Sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5157–5165. [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, A.; Engström, P.; Palva, E.T.; Bennich, H. Attacin, an Antibacterial Protein from Hyalophora Cecropia, Inhibits Synthesis of Outer Membrane Proteins in Escherichia Coli by Interfering with Omp Gene Transcription. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 3040–3045.
- Mardirossian, M.; Sola, R.; Beckert, B.; Valencic, E.; Collis, D.W.P.; Borišek, J.; Armas, F.; Di Stasi, A.; Buchmann, J.; Syroegin, E.A.; et al. Peptide Inhibitors of Bacterial Protein Synthesis with Broad Spectrum and SbmA-Independent Bactericidal Activity against Clinical Pathogens. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 9590–9602. [CrossRef]
- Mardirossian, M.; Sola, R.; Beckert, B.; Collis, D.W.P.; Di Stasi, A.; Armas, F.; Hilpert, K.; Wilson, D.N.; Scocchi, M. Proline-Rich Peptides with Improved Antimicrobial Activity against E. Coli, K. Pneumoniae and A. Baumannii. ChemMedChem 2019. [CrossRef]
- Mardirossian, M.; Pérébaskine, N.; Benincasa, M.; Gambato, S.; Hofmann, S.; Huter, P.; Müller, C.; Hilpert, K.; Innis, C.A.; Tossi, A.; et al. The Dolphin Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptide Tur1A Inhibits Protein Synthesis by Targeting the Bacterial Ribosome. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Iavicoli, I.; Fontana, L.; Agathokleous, E.; Santocono, C.; Russo, F.; Vetrani, I.; Fedele, M.; Calabrese, E.J. Hormetic Dose Responses Induced by Antibiotics in Bacteria: A Phantom Menace to Be Thoroughly Evaluated to Address the Environmental Risk and Tackle the Antibiotic Resistance Phenomenon. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 798, 149255. [CrossRef]
- Gorr, S.U.; Brigman, H. V.; Anderson, J.C.; Hirsch, E.B. The Antimicrobial Peptide DGL13K Is Active against Drug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria and Sub-Inhibitory Concentrations Stimulate Bacterial Growth without Causing Resistance. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273504. [CrossRef]
- Hilpert, K.; Munshi, T.; López-Pérez, P.M.; Sequeira-Garcia, J.; Hofmann, S.; Bull, T.J. Discovery of Antimicrobial Peptides That Can Accelerate Culture Diagnostics of Slow-Growing Mycobacteria Including Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Microorganisms 2023, Vol. 11, Page 2225 2023, 11, 2225. [CrossRef]
- Ramón-García, S.; Mikut, R.; Ng, C.; Ruden, S.; Volkmer, R.; Reischl, M.; Hilpert, K.; Thompson, C.J. Targeting Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Other Microbial Pathogens Using Improved Synthetic Antibacterial Peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57. [CrossRef]
- Hilpert, K.; Winkler, D.F.H.D.F.H.; Hancock, R.E.W.R.E.W. Peptide Arrays on Cellulose Support: SPOT Synthesis, a Time and Cost Efficient Method for Synthesis of Large Numbers of Peptides in a Parallel and Addressable Fashion. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2. [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and Broth Dilution Methods to Determine the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Antimicrobial Substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3. [CrossRef]
- Frank, R. Spot-Synthesis: An Easy Technique for the Positionally Addressable, Parallel Chemical Synthesis on a Membrane Support. Tetrahedron 1992. [CrossRef]
- Schön, T.; Werngren, J.; Machado, D.; Borroni, E.; Wijkander, M.; Lina, G.; Mouton, J.; Matuschek, E.; Kahlmeter, G.; Giske, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex Isolates - the EUCAST Broth Microdilution Reference Method for MIC Determination. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1488–1492. [CrossRef]
- Banfi, E.; Scialino, G.; Monti-Bragadin, C. Development of a Microdilution Method to Evaluate Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Drug Susceptibility. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2003, 52, 796–800. [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.S.; Lee, S.S.J.; Tu, H.Z.; Huang, W.K.; Chen, Y.S.; Huang, C.K.; Wann, S.R.; Lin, H.H.; Liu, Y.C. Use of MGIT 960 for Rapid Quantitative Measurement of the Susceptibility of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex to Ciprofloxacin and Ethionamide. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 600–603. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Hannebelle, M.; Patil, V.P.; Dhar, N.; Mckinney, J.D.; Thacker Correspondence, V. V; Lle Dubois, A.; Garcia-Mouton, C.; Kirsch, G.M.; Jan, M.; et al. Mechanopathology of Biofilm-like Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Cords. Cell 2023, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Noll, H.; Bloch, H.; Asselineau, J.; Lederer, E. The Chemical Structure of the Cord Factor of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1956, 20, 299–309. [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, P.M.P.M.; Grimsey, E.; Bourne, L.; Mikut, R.; Hilpert, K. Screening and Optimizing Antimicrobial Peptides by Using SPOT-Synthesis. Front. Chem. 2017, 5. [CrossRef]
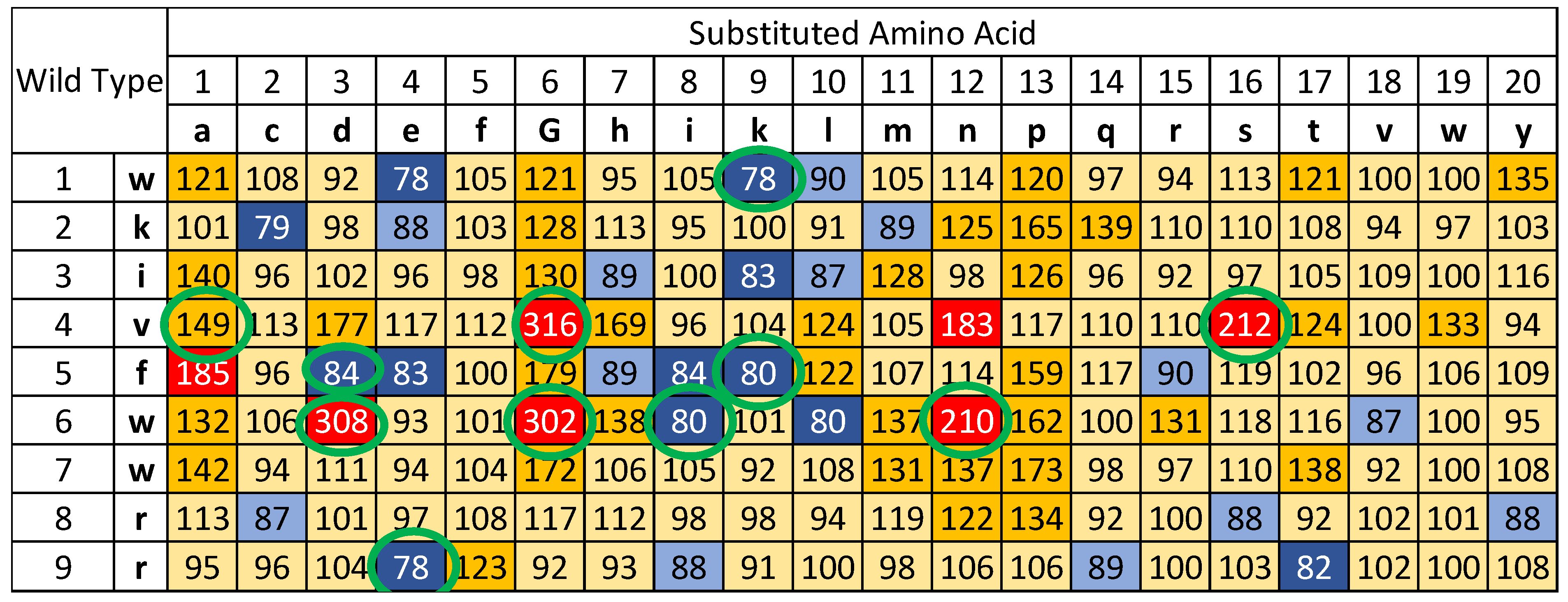
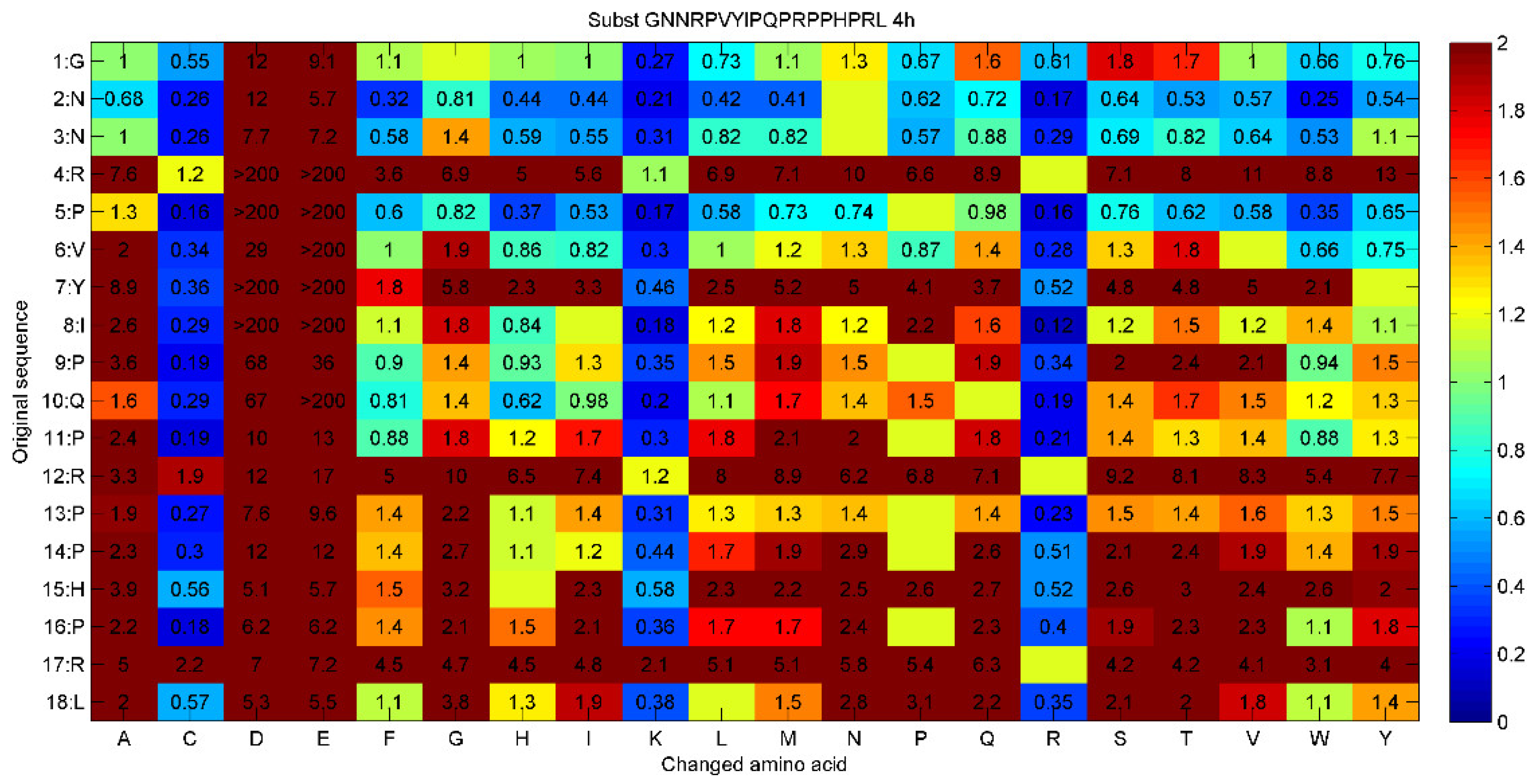
| Sequence | TTP values at different peptide concentrations | |||
| 0.3 µg/mL | 3 µg/mL | 10 µg/mL | 30 µg/mL | |
| TB alone | ||||
| 12d 4h | ||||
| Wild Type | ||||
| wkivfwwrr | 10d 17h | 10d 21h | 11d 21h | 12d 04h |
| Substitutions with potential stronger growth stimulation | ||||
| kkivfwwrr | 11d 09h | 12d 00h | 14d 00h | 46d 04h |
| wkivdwwrr | 12d 13h | 14d 12h | 16d 13h | 19d 06h |
| wkivkwwrr | 10d 08h | 10d 17h | 17d 14h | 25d 19h |
| wkivfiwrr | 10d 16h | 9d 20h | 10d 07h | 12d 21h |
| wkivfwwre | 10d 20h | 10d 00h | 11d 00h | 13d 02h |
| Substitutions with potential medium growth inhibition | ||||
| wkiafwwrr | 11d 01h | 12d 19h | 20d 16h | 47d 06h |
| Substitutions with potential strong growth inhibition | ||||
| wkiGfwwrr | 11d 19h | 15d 20h | 25d 08h | 54d 04h |
| wkisfwwrr | 10d 00h | 14d 08h | 22d 11h | 53d 20h |
| wkivfdwrr | 16d 20h | 33d 01h | 44d 02h | neg (55d) |
| wkivfGwrr | 12d 17h | 22d 08h | 46d 06h | neg (55d) |
| wkivfnwrr | 12d 21h | 15d 13h | 28d 07h | 52d 16h |
| Sequence | MIC in µg/mL | Cord formation at 10 µg/ml | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H37Rv | MDR-TB | H37Rv | MDR-TB | |
| wkivfwwrr | >50 | >50 | reduced | reduced |
| wkisfwwrr | 20 | 20 | normal | normal |
| wkivfdwrr | 20 | 20 | reduced | reduced |
| wkivfGwrr | 20 | 20 | normal | normal |
| wkivfnwrr | 20 | 20 | normal | normal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





