Submitted:
27 November 2023
Posted:
29 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of [18F]IDIF
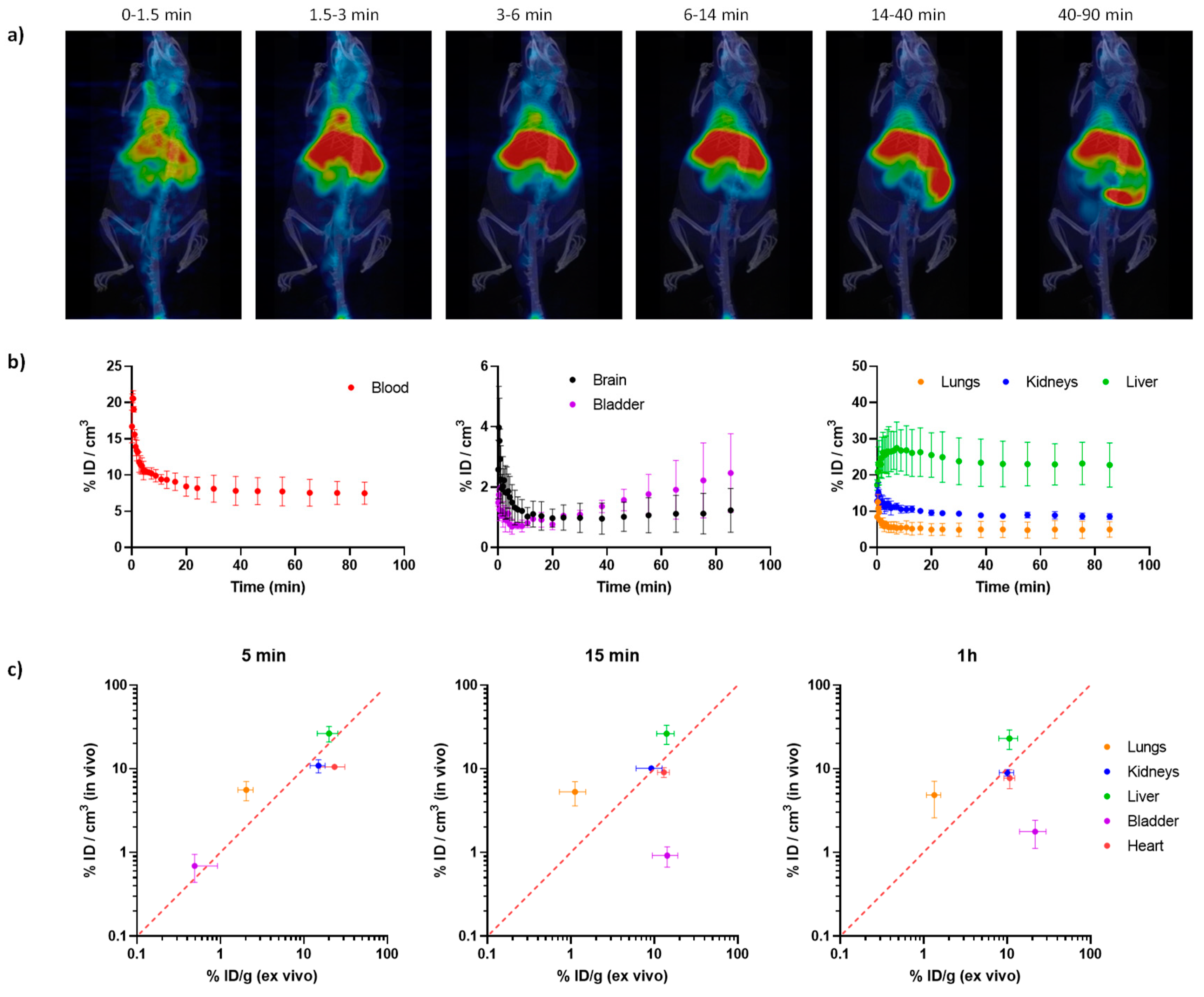
2.3. In vivo imaging
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durst, F.; Tropea, C. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. Available online: https://www.alz.org/media/documents/alzheimers-facts-and-figures.pdf. [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Cairns, N.J.; Crowther, R.A. Tau proteins of Alzheimer paired helical filaments: abnormal phosphorylation of all six brain isoforms. Neuron 1992, 8, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, S.; Baglietto-Vargas, D.; Martini, A.C.; Trujillo-Estrada, L.; LaFerla, F.M. Synaptic Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Dysregulated Symphony. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, A.; Phillips, E.; Zheng, R.; Biju, M.; Kuruvilla, T. Evidence for neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neurol. Psychiatry 2016, 20, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, K.; Wang, G.; Park, L. Endothelial Dysfunction and Amyloid-β-Induced Neurovascular Alterations. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 155–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M.; Saraiva, M.J. Transthyretin: a multifaceted protein. Biomol. Concepts. 2014, 5, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloeckner, S.F.; Meyne, F.; Wagner, F.; Heinemann, U.; Krasnianski, A.; Meissner, B.; Zerr, I. Quantitative analysis of transthyretin, tau and amyloid-beta in patients with dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2008, 14, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serot, J.M.; Christmann, D.; Dubost, T. , Couturier, M. Cerebrospinal fluid transthyretin: Aging and late onset Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 1997, 63, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Jung, E.S.; Sohn, J.H.; Hong, H.J.; Hong, H.S.; Kim, J.W.; Na, D.L.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.; Ha, H.J.; et al. Human serum transthyretin levels correlate inversely with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 25, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.A.; Santana, I.; Oliveira, C.; Baldeiras, I.; Moreira, J.; Saraiva, M.J.; Cardoso, I. Transthyretin Decrease in Plasma of MCI and AD Patients: Investigation of Mechanisms for Disease Modulation. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayudhan, L.; Killick, R.; Hye, A.; Kinsey, A.; Güntert, A.; Lynham, S.; Ward, M.; Leung, R.; Lourdusamy, A.; To, A.W.; Powell, J.; Lovestone, S. Plasma transthyretin as a candidate marker for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 28, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.M.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Cardoso, I.; Saraiva, M.J. Gender-dependent transthyretin modulation of brain amyloid-β levels: evidence from a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 27, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxbaum, J.N.; Ye, Z.; Reixach, N.; Friske, L.; Levy, C.; Das, P.; Golde, T.; Masliah, E.; Roberts, A.R.; Bartfai, T. Transthyretin protects Alzheimer’s mice from the behavioral and biochemical effects of Abeta toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008, 105, 2681–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gião, T.; Saavedra, J.; Cotrina, E.; Quintana, J.; Llop, J.; Arsequell, G.; Cardoso, I. Undiscovered Roles for Transthyretin: From a Transporter Protein to a New Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadami, S.A.; Chia, S.; Ruggeri, F.S.; Meisl, G.; Bemporad, F.; Habchi, J.; Cascella, R.; Dobson, C.M.; Vendruscolo M, Knowles TPJ, Chiti, F. Transthyretin Inhibits Primary and Secondary Nucleations of Amyloid-β Peptide Aggregation and Reduces the Toxicity of Its Oligomers. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1112–1125. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzman, A.L.; Gregori, L.; Vitek, M.P.; Lyubski, S.; Strittmatter, W.J.; Enghilde, J.J.; Bhasin, R.; Silverman, J.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Coyle, P.K.; Zagorski, M.G.; Talafous, J.; Eisenberg, M.; Saunders, A.M.; Rose, A.D.; Goldgaber, D. Transthyretin sequesters amyloid β-protein and prevents amyloid formation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1994, 91, 8368–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Gonçalves, A.; Saraiva, M.J.; Cardoso, I. Transthyretin binding to A-Beta peptide--impact on A-Beta fibrillogenesis and toxicity. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemi, M.; Gaiteiro, C.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Santos, L.M.; Gomes, J.R.; Oliveira, S.M.; Couraud, P.O.; Weksler, B.; Romero, I.; Saraiva, M.J.; Cardoso, I. Transthyretin participates in beta-amyloid transport from the brain to the liver--involvement of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1? Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 20164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, M.; Tachibana, M.; Kanekiyo, T.; Bu, G. Role of LRP1 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from clinical and preclinical studies. J Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gião, T.; Saavedra, J.; Vieira, J.R.; Pinto, M.T.; Arsequell, G.; Cardoso, I. Neuroprotection in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease is promoted by transthyretin angiogenic properties. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.R.; Nogueira, R.S.; Vieira, M.; Santos, S.D.; Ferraz-Nogueira, J.P.; Relvas, J.B.; Saraiva, M.J. Transthyretin provides trophic support via megalin by promoting neurite outgrowth and neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1749–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, C.E.; Mar, F.M.; Franquinho, F.; Saraiva, M.J.; Sousa, M.M. Transthyretin internalization by sensory neurons is megalin mediated and necessary for its neuritogenic activity. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3220–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morfino, P.; Aimo, A.; Vergaro, G.; Sanguinetti, C.; Castiglione, V.; Franzini, M.; Perrone, M.A.; Emdin, M. Transthyretin Stabilizers and Seeding Inhibitors as Therapies for Amyloid Transthyretin Cardiomyopathy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Mizuguchi, M. Transthyretin Amyloidogenesis Inhibitors: From Discovery to Current Developments. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 3, 14228–14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Anna, R.; Gallego, P.; Robinson, L.Z.; Pereira-Henriques, A.; Ferreira, N.; Pinheiro, F.; Esperante, S.; Pallares, I.; Huertas, O.; Almeida, M.R.; Reixach, N.; Insa, R.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Reverter, D.; Reig, N.; Ventura, S. Repositioning tolcapone as a potent inhibitor of transthyretin amyloidogenesis and associated cellular toxicity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10787, Erratum in: Nat. Commun. 2023 Feb 3;14(1):582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencetti, S.; Rossello, A.; Orlandini, E. Tafamidis (Vyndaqel): A Light for FAP Patients. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 1617–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, J.L.; Suhr, O.B.; Obici, L.; Sekijima, Y.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Yamashita, T.; Heneghan, M.A.; Gorevic, P.D.; Litchy, W.J.; Wiesman, J.F.; Nordh, E.; Corato, M.; Lozza, A.; Cortese, A.; Robinson-Papp, J.; Colton, T.; Rybin, D.V.; Bisbee, A.B.; Ando, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Seldin, D. .C.; Merlini, G.; Skinner, M.; Kelly, J.W.; Dyck, P.J. Diflunisal Trial Consortium. Repurposing diflunisal for familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. J. A. M. A. 2013, 310, 2658–2667. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mairal, T.; Nieto, J.; Pinto, M.; Almeida, M.R.; Gales, L.; Ballesteros, A.; Barluenga, J.; Pérez, J.J.; Vázquez, J.T.; Centeno, N.B.; Saraiva, M.J.; Damas, A.M.; Planas, A.; Arsequell, G.; Valencia, G. Iodine atoms: a new molecular feature for the design of potent transthyretin fibrillogenesis inhibitors. PLoS One 2009, 4, e4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejc, L.; Gómez-Vallejo, V.; Rios, X.; Cossío, U.; Baz, Z.; Mujica, E.; Gião, T.; Cotrina, E.Y.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Quintana, J.; Arsequell, G.; Cardoso, I.; Llop, J. Oral Treatment with Iododiflunisal Delays Hippocampal Amyloid-β Formation in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Longitudinal in vivo Molecular Imaging Study1. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 77, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.A.; Oliveira, S.M.; Guido, L.F.; Magalhães, A.; Valencia, G.; Arsequell, G.; Saraiva, M.J.; Cardoso, I. Transthyretin stabilization by iododiflunisal promotes amyloid-β peptide clearance, decreases its deposition, and ameliorates cognitive deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 39, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrina, E.Y.; Santos, L.M.; Rivas, J.; Blasi, D.; Leite, J.P.; Liz, M.A.; Busquets, M.A.; Planas, A.; Prohens, R.; Gimeno, A.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Gales, L.; Llop, J.; Quintana, J.; Cardoso, I.; Arsequell, G. Targeting transthyretin in Alzheimer’s disease: Drug discovery of small-molecule chaperones as disease-modifying drug candidates for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 226, 113847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, X.; Gómez-Vallejo, V.; Martín, A.; Cossío, U.; Morcillo, M.Á.; Alemi, M.; Cardoso, I.; Quintana, J.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Cotrina, E.Y.; Valencia, G.; Arsequell, G.; Llop, J. Radiochemical examination of transthyretin (TTR) brain penetration assisted by iododiflunisal, a TTR tetramer stabilizer and a new candidate drug for AD. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 13672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, S.A.; Yusubov, M.S.; Beloglazkina, E.K.; Nenajdenko, V.G. Synthesis of Radioiodinated Compounds. Classical Approaches and Achievements of Recent Years. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubost, E.; McErlain, H.; Babin, V.; Sutherland, A.; Cailly, T. Recent Advances in Synthetic Methods for Radioiodination. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 8300–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacace, F.; Speranza, M.; Wolf, A.P.; Macgregor, R.R. Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution; Kinetics of Fluorine-18 Substitution Reactions in Polyfluorobenzenes. Isotopic Exchange between 18F- and Polyfluorobenzenes in Dimethylsulfoxide. A Kinetic Study. J. Fluor. Chem 1982, 21, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, N.E.S.; Chen, W.; Levens, A.; Pistritto, V.A.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Nicewicz, D.A. 19F- and 18F-Arene Deoxyfluorination via Organic Photoredox-Catalysed Polarity-Reversed Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaró, M.; Nieto, J.; La Parra, J.R.; Almeida, M.R.; Ballesteros, A.; Planas, A.; Arsequell, G.; Valencia, G. Tuning transthyretin amyloidosis inhibition properties of iododiflunisal by combinatorial engineering of the nonsalicylic ring substitutions. ACS Comb Sci. 2015, 17, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
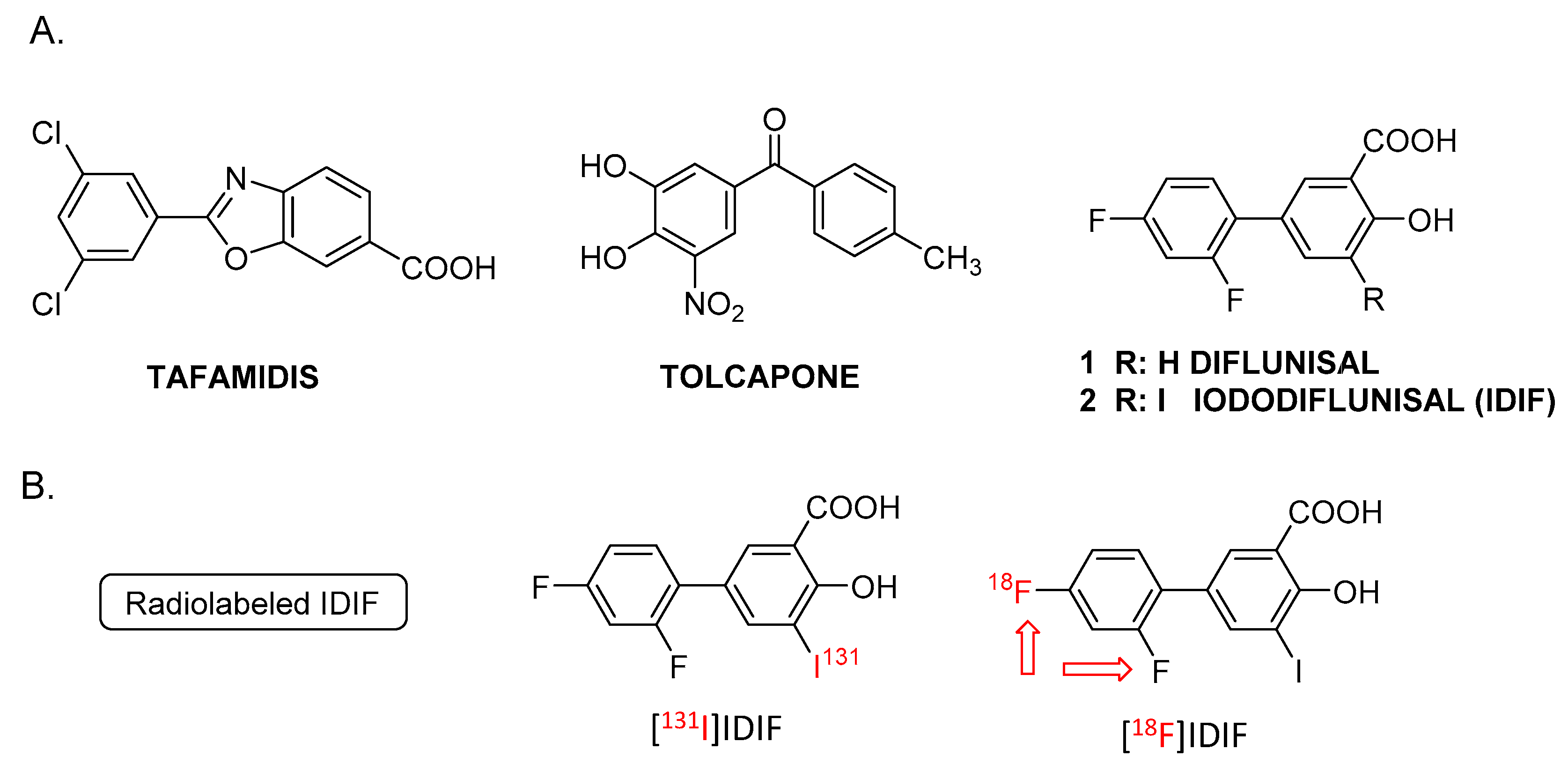
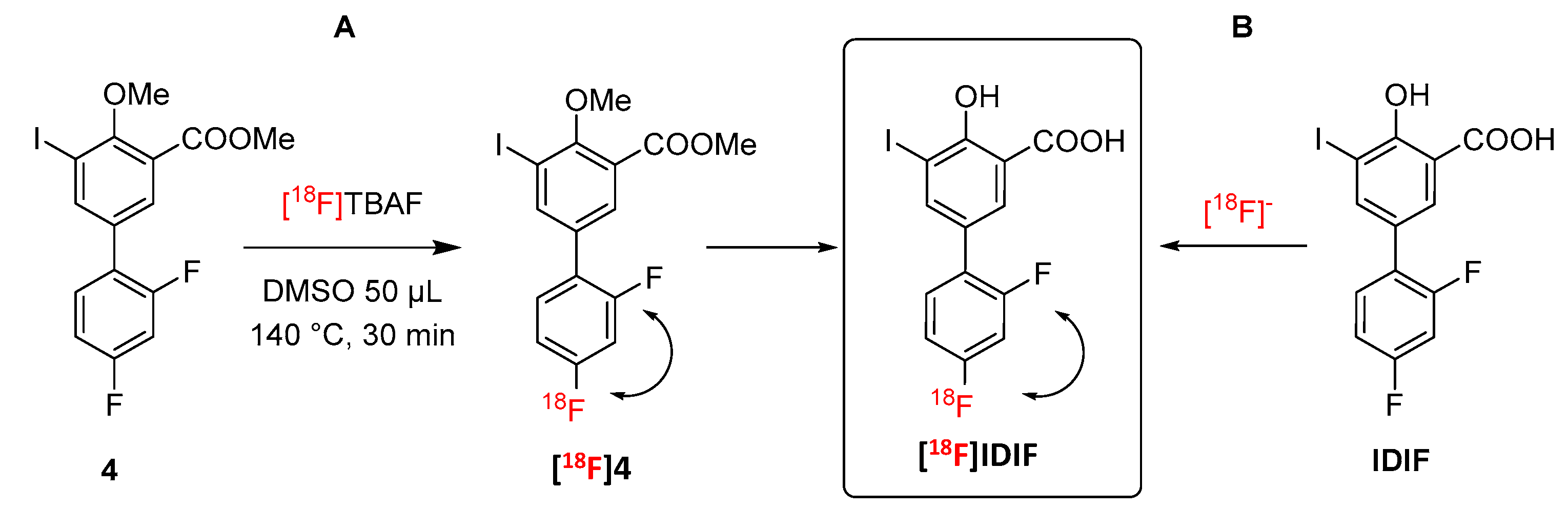
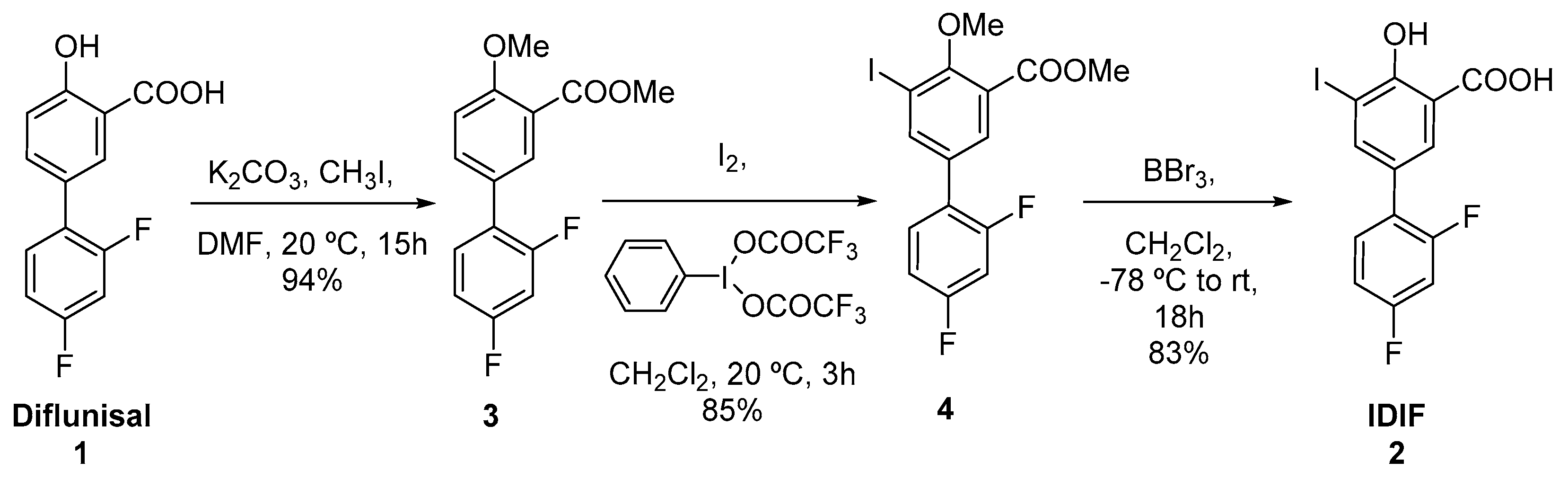
| Entry 1 | Solvent | IDIF (mg) | Temperature (°C) | RCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DMSO | 1 | 80 | 0 |
| 2 | DMSO | 4 | 80 | 0 |
| 3 | DMSO | 4 | 120 | 0.8±0.4 |
| 4 | DMSO | 1 | 160 | 12.4±2.9 |
| 5 | DMSO | 4 | 160 | 20.6±3.7 |
| 6 | DMF | 4 | 150 | 2.2±1.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





