1. Introduction
With the development of modern industry, the composition of industrial wastewater has become extremely complex, making water contamination highly problematic. Inappropriate wastewater treatment incorporating dyes can directly affect regional water quality, thereby threatening environmental and human health [
1,
2,
3]. Of all the efficient treatment processes for organic colourants [
4,
5], the Fenton-type heterogeneous oxidation process involving Fe
3O
4 nanoparticles represents one of the most advanced and successful treatment technologies and has been extensively investigated for the removal of organic dyes with high efficiency coupled with the non-selective decomposition of organic pollutants [
6]. Nevertheless, neat Fe
3O
4 nanoparticles exhibit a propensity to decompose in water. At the same time, pure Fe
3O
4 nanoparticles aggregate and corrode readily at acidic pH, restricting their catalytic performance and durability, and reducing their broad application in wastewater treatment [
7].
A typical approach to deal with these disadvantages is to use support materials, including zeolite, porous silica, porous carbon, and carbon nanomaterials, to immobilise Fe
3O
4 nanoparticles [
8]. However, most supporting materials were found to be non-degradable or environmentally damaging. Moreover, their synthesis is complicated and involves the consumption of hazardous substances. Thus, it is crucial to develop a practical and straightforward approach for the production of biocompatible support catalysts with enhanced performance, stability, and recyclability over a broad pH range. This has been achieved owing to the availability of bio-based, recyclable, and environmentally compatible materials [
9].
As an emerging class of biocompatible plant-derived nanomaterials, cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) have attracted considerable attention for wastewater treatment applications because of their natural abundance, environmental compatibility, and high resistance strength [
10] when used as a scaffold for magnetite nanoparticles. This technique can assist the homogeneous distribution of Fe
3O
4 to enhance the effective cross-linked specific surface area. Therefore, the catalytic efficiency increased. Associated research indicates that the magnetite agglomeration strategy can reduce magnetite agglomeration efficiently but only marginally enhances the catalytic activity of the obtained Fe3O4/CNF nano-catalyst in comparison to bare Fe
3O
4 nanoparticles [
11]. In addition, Fe3O4 nanoparticle coating on cellulose supports is essential to prevent iron drainage during application, and they are quickly corroded in acidic media, which results in unsatisfactory catalyst durability and recoverable properties, along with a relatively limited applicable pH range. Recently, Nieto et al. described the synthesis and advanced oxidation competencies of bio-nanocomposite magnetic cellulosic fibres in indigo carmine aqueous solution decolourisation using heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation processes [
2]. In another recent report, Wang et al. developed a new mussel-inspired magnetic carboxylated cellulose nanofiber (MCNF/PDA) for efficient Fenton-like methylene blue degradation [
12].
Similarly, Multi-Component Reactions (MCRs) are accustomed to the standards of environmental chemistry aimed at reducing the generation of harmful waste [
13]. Indeed, magnetically modified cellulose derivatives are gaining increasing interest in the field of organic synthesis because of the higher odds of increasing molecular structural diversifications [
14,
15,
16]. Several recent studies have reported the use of new catalytic systems to produce a new range of molecules [
17,
18,
19]. Heterocyclic derivatives possess optical, sensing, medicinal, and biological applications, such as tetra-substituted imidazoles, which are a key class of basic organic frameworks [
20,
21].
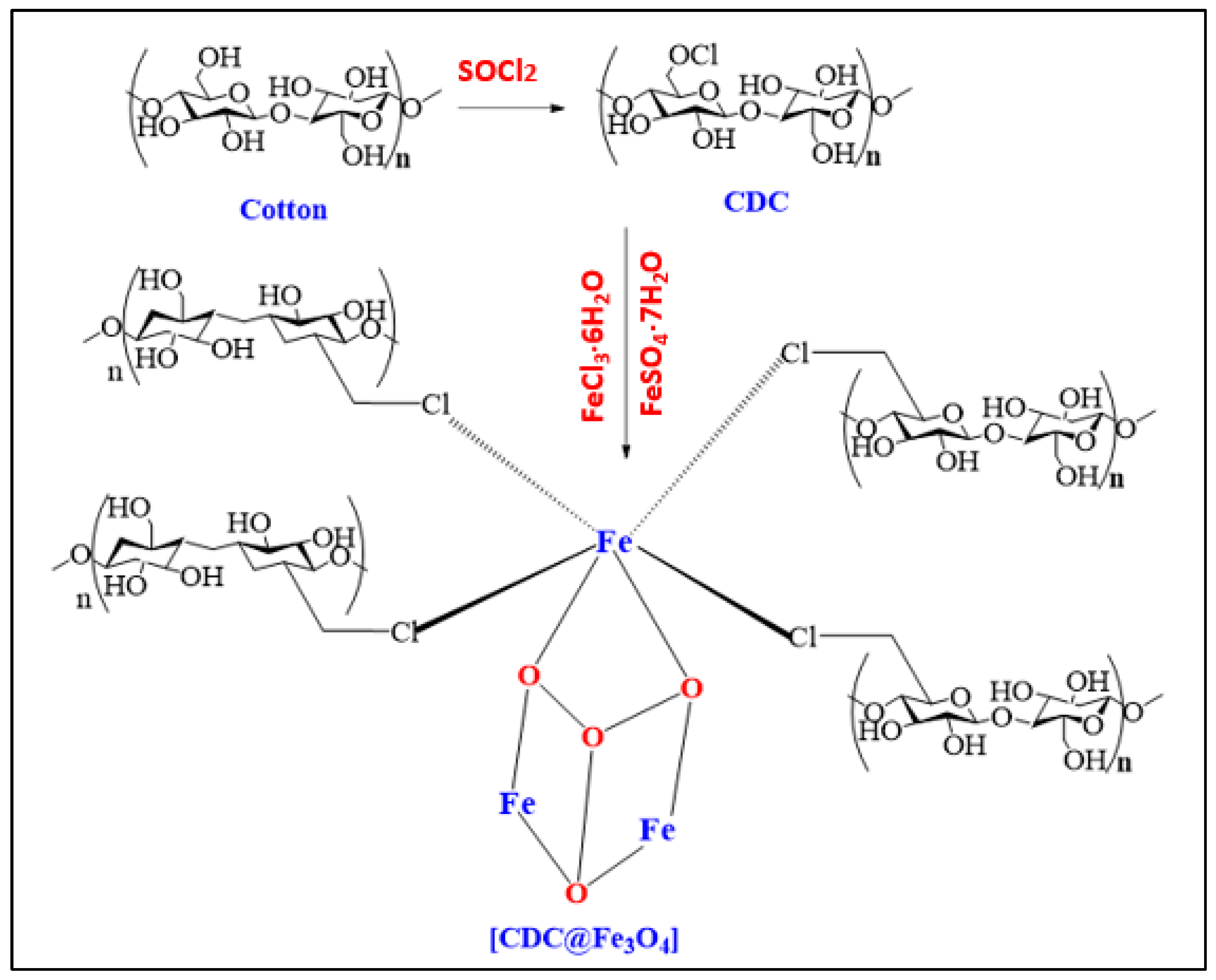
This study is the first to elucidate the design of a novel magnetic heterogeneous Fenton photocatalyst (CDC@Fe3O4) for degrading Methyl Orange (MO) organic dyes. The (CDC@Fe3O4) nanocomposites were synthesised using Fe3O4 nanoparticles embedded in chloro-deoxycellulose nanofibres. Therefore, we aimed to use (CDC@Fe3O4) nanoparticles to decompose MO under eco-friendly conditions. As a second application, (CDC@Fe3O4) will be used as a recyclable nano-catalyst for an improved synthesis protocol of tetra-substituted imidazole.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Cotton was furnished through SITEX (International Textile Society, Tunisia) and drabbed using hydrogen peroxide before magnetite nanoparticle coating. Methyl Orange, FeCl2.4H2O, FeCl3.6H2O, Thionylchloride (SOCl2) and NaOH, benzyl, 5-Chloro- salicylaldehyde, pyridin-2-amine, 5-methylpyridin-2-amine and 4-(tert-butyl) aniline are approved chemicals from Sigma-Aldrich.
2.2. Preparation of (CDC@Fe3O4)
Activated cotton (10 g) was activated at 80°C for 12 h and dispersed in 200 mL DMF. Then, 35 mL of (SOCl2) was slowly added, and mechanical stirring was maintained at the same temperature for 4 h. Next, the cooled suspension of cellulose chloride (CDC) was washed several times with a dilute ammonium hydroxide solution. The pH of the supernatant was controlled to maintain the target natural pH, followed by suspension washing using distilled water. At the end of this step, the obtained samples were separated by filtration and dried at room temperature [
22,
23]. The coating of magnetic nanoparticles on chloro-deoxy-cellulose (CDC) is as follows: 100 g of Cotton, 3.0 g of FeSO4. 4H2O and 7.5 g FeCl3.6H2O was dissolved in distilled water (200 ml of distilled water at 70°C under mechanical stirring in an inert atmosphere. Next, a NaOH solution (4 M) was added dropwise to reach a pH of 12.0. The entire coprecipitation process was performed for 40 min. The precipitated magnetic nanocomposites were magnetically removed and cleaned using distilled water to obtain a neutral pH solution. The obtained nanocomposites (CDC@Fe3O4) were dried at 70°C for 48 h.
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of magnetic functionalized cotton.
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of magnetic functionalized cotton.
2.3. Apparatus
(FTIR) spectra were recorded on a Perkin Elmer spectrometer (Nicolet FTIR 460, 4000–400 cm-1 range). (XRD) diffractograms were obtained using a Siemens diffractometer (D500, KR radiation, 15KV, 1.5405 Å). Thermogram curves (TGA) were obtained using Carl-Zeiss-Sigma (TA-SDT Q 600). (SEM) micrographs were captured using a scanning electron microscope (SEM,69, FEI Quanta-200). The magnetic properties of the catalyst were determined using a vibrating sample magnetometer (Lake Shore, 7304, France, -1.7 to +1.7 range). Sonication was performed using an Elma-Ultrasonic device (S40, 800 WL-1). Absorption spectra were recorded using a spectrophotometer (SPECORD PLUS, 190-1100 nm). Color changes in aqueous solutions were monitored in the 200−700 nm range to evaluate the removal efficiency during catalytic treatment. A 15 W Hg UV lamp was used for the preliminary Fenton photodegradation assays.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.1.1. UV-Vis absorption data
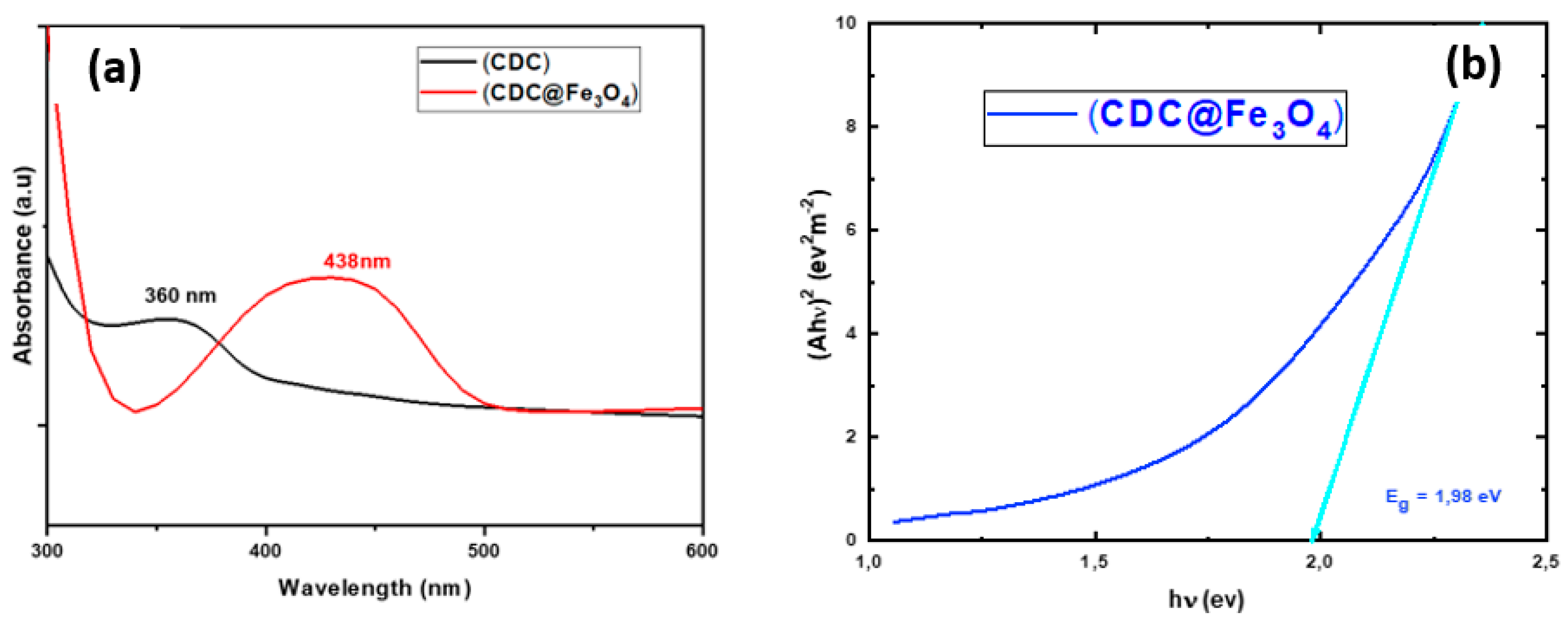
Figure 1 depicts both the absorption spectra of (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4) as well as the recorded energy gap of the synthesized catalyst.
The designed photocatalyst and its corresponding ligand (CDC) showed maximal absorptions at ~360 and 438 nm, with absorption edges in the ranges of 320 -380 and 340-500 nm respectively, indicating that both synthesised materials are photolytically active in both the UV and visible regions. The bandgap energy of the magnetic catalyst is 1.98 eV (
Figure 1b). A large range of light irradiation enhances the photocatalytic degradation performance.
3.1.2. FTIR
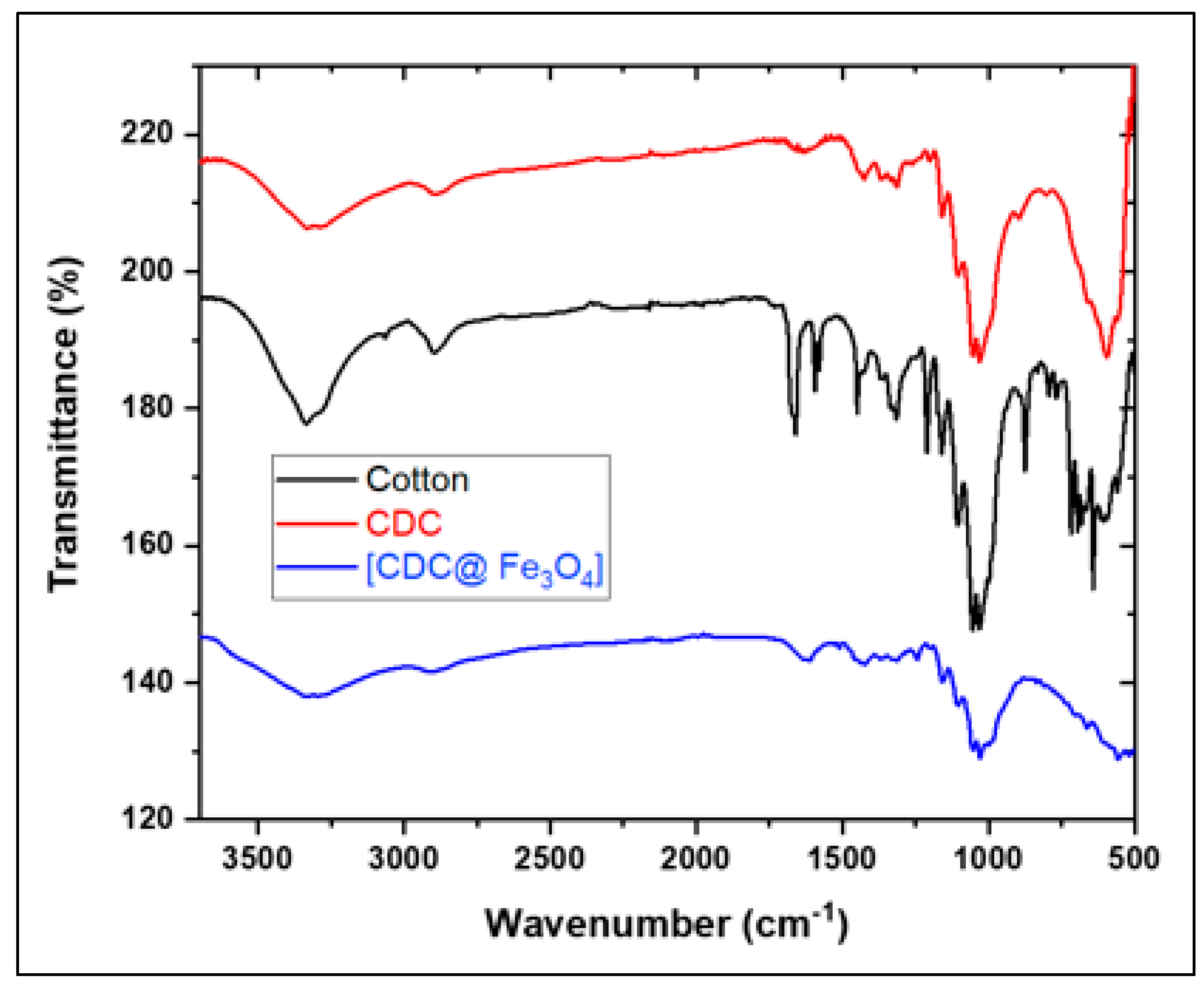
The transmittance bands in the cotton graph (
Figure 2) at 3300–3200 cm
-1, 2906 cm
-1, 1628 cm
-1, and ∼ 1020 cm
-1 refer to the stretching vibrations of hydroxyl groups, stretching vibrations of CH, bending vibrations of hydroxyl groups, and C-O-C stretching vibrations, respectively [
15].
FTIR spectroscopy was performed to analyse the corresponding target chemical structures induced by the modification of cotton fibres and coating with magnetite nanoparticles.
Figure 2 depicts the graph of cotton (a), 6-CDC, (b), and (CDC@Fe
3O
4) (c). The cotton spectrum shows the appearance of two characteristic bands around 883 and 1678 cm
-1, ascribed to the stretching and bending vibrations of C–Cl, respectively [
23]. These changes confirm the substitution of hydroxyl groups by chlorine atoms in (6-CDC) [
23]. The intense band recorded at approximately 590 cm
-1 is ascribed to the Fe-O stretching vibration [
24]. This peak proves the successful coating of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the modified cotton surface [
25].
3.1.3. TGA
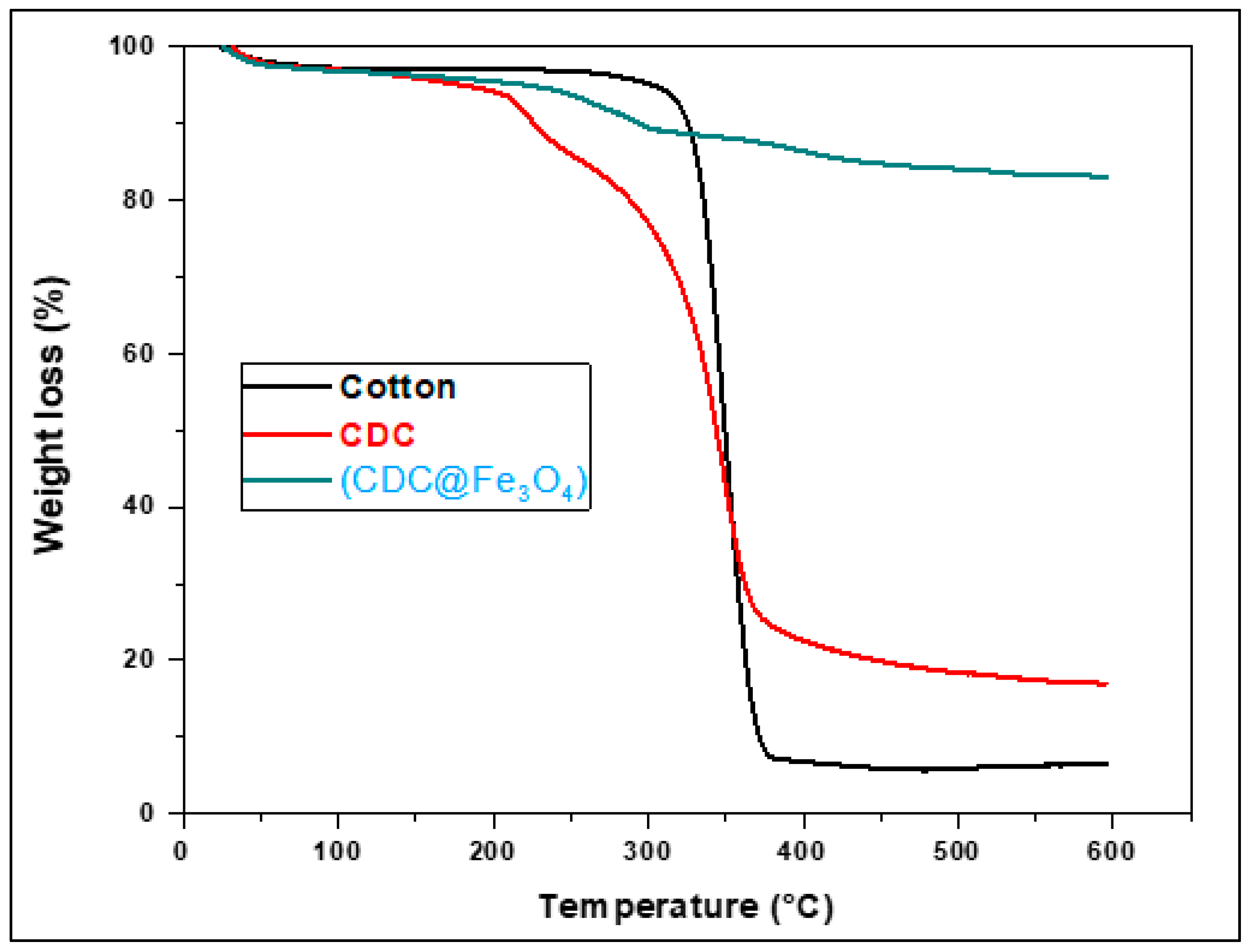
The thermal stability of the synthesised materials was quantitatively evaluated using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Indeed, TGA is often used to determine the grafting density of the organic groups. The TGA thermogram of cotton (
Figure 3) shows the first weight loss below 310 °C, corresponding to a relatively slow onset of degradation, whereas the major weight loss (93%) at approximately 320 °C may be ascribed to the degradation of glycosyl units.
Chlorine-modified cotton (6-CDC) showed relative mass stability up to 200°C. Subsequently, the mass loss began at approximately 200°C and extended to 382°C, with one sharp weight drop and 16% remaining weight. The (CDC@Fe3O4) thermogram does not show significant mass loss up to 330°C, and the remaining 83 % of the total weight at 600ºC proposes that the synthesised magnetic nanomaterial satisfies the requirements of several applications that require elevated thermostability.
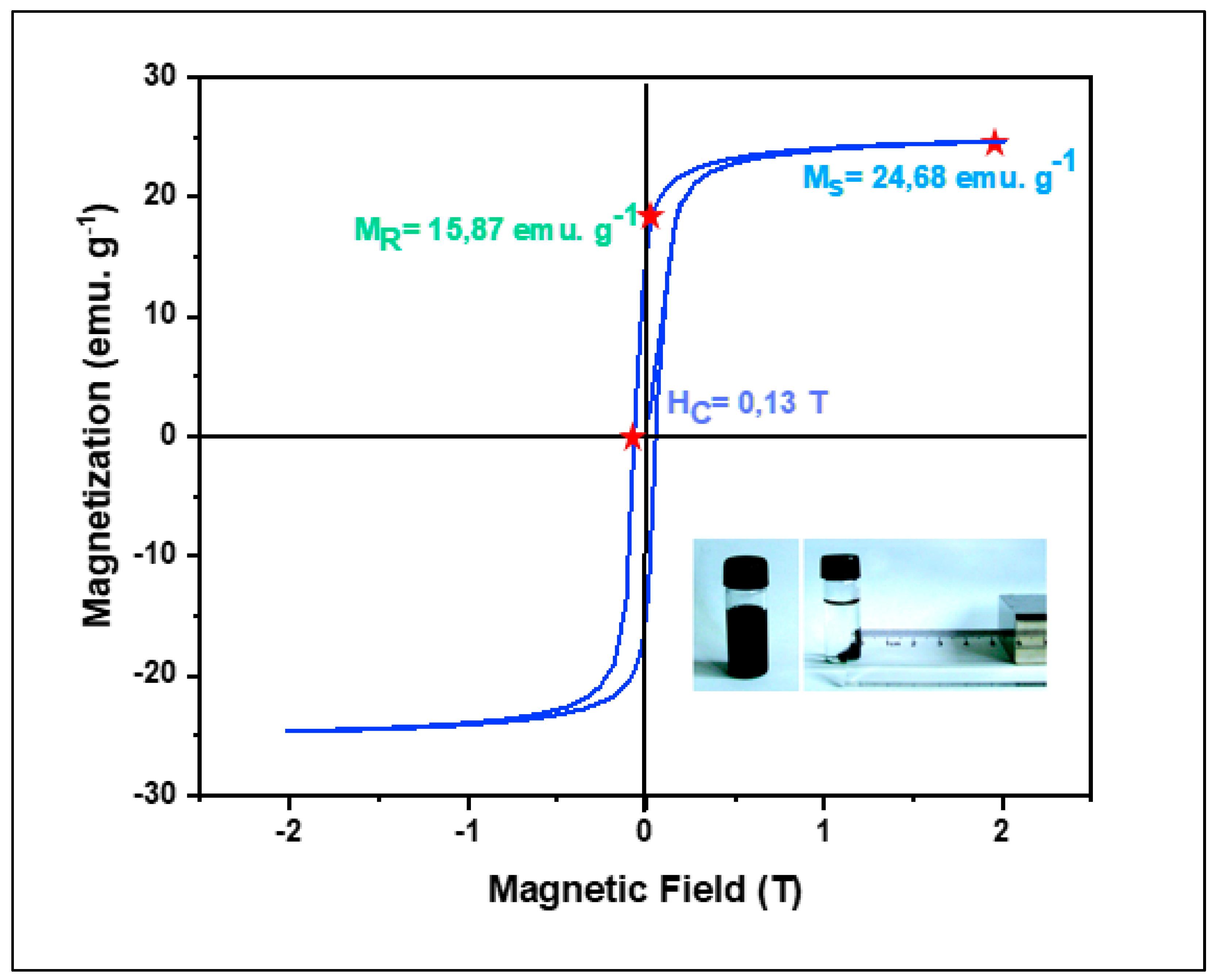
3.1.4. VSM
The magnetization characteristics of (CDC@Fe3O4) magnetically modified cotton were investigated by recording the magnetic hysteresis loop (MH) at 300 K in addition to magnetization plots (M) versus an imposed magnetic field (T), as shown in
Figure 4.
Magnetisation examination provided evidence of the ferromagnetic properties of the designed nano -catalyst. The nanocomposite saturated magnetization (MS) was 24.86 emu.g -1 while its corresponding remnant magnetization (MR) was detected at 15.87 emu.g -1 and the matched coercive field (HC) reached 0.14 T.
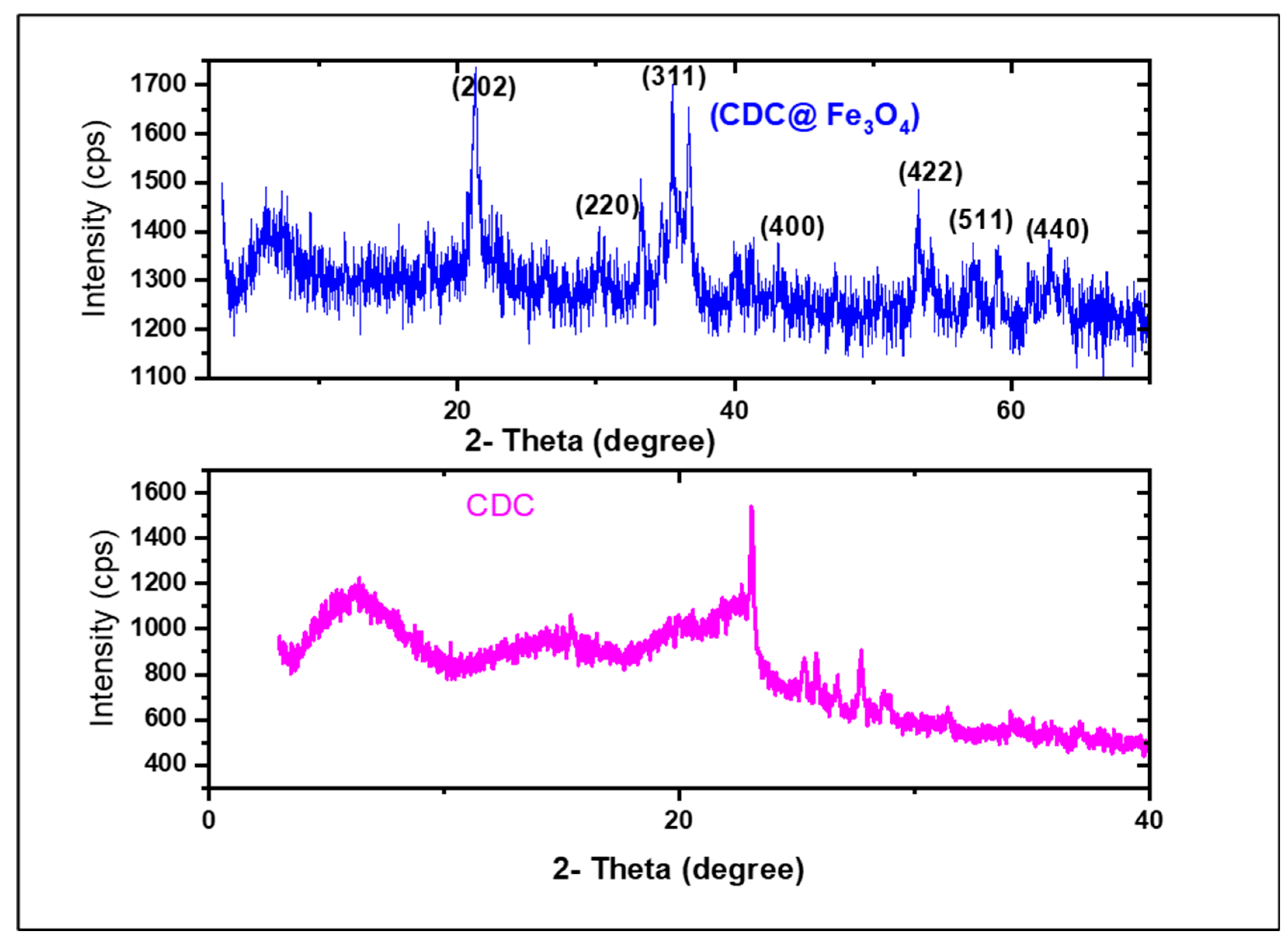
3.1.5. XRD
The crystalline structures of (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4) were registered using XRD examinations from 10 °to 50°in the 2θ scanning angle range, as depicted in
Figure 5. The X-ray diffraction pattern of (CDC) displays an obvious main peak at approximately 2 θ = 6.15°, 15.45°, 23.06° corresponding to (1 1 0), (1 10), and (0 2 0).
The heterogeneous reaction of the ToS-Cl treatment can modify the polymer surface or its internal layers, thereby reaching the corresponding amorphous regions. The reduced intensity of the peaks indicates the presence of only small crystallites owing to the involvement of chlorine atoms in hydrogen bonds [
26]. Such conduct reduces the space separating the chains, leading to peak shifting, and providing higher h values. The confinement of the linked chlorine atoms enables them to form hydrogen bonds which can be distinguished from those formed at the surface of the material [
27].
The XRD pattern of (CDC@Fe3O4) shown in
Figure 6 shows a broad peak around 2ϴ = 15°, ascribed to the cellulosic moiety of the synthesised nanomaterial. The typical diffraction peaks of magnetite nanoparticles were observed at 21.22°, 30.42°, 35.52°, 43.14°, 53.35°, 57.34°, and 60.04°, corresponding to the (202), (220), (311), (400), (422), (511), and (440) crystal planes, correspondingly [
28].
The average (CDC@Fe3O4) nanocomposite size was estimated to be 88 nm using the Scherrer equation:
where D is the crystallite size, K is the crystallite shape factor (K = 0.94), k corresponds to the X-ray incident wavelength, β denotes the adapted FWHM referring to the full width at half maximum of the corresponding highest intensity recorded diffraction, and h symbolizes the diffraction angle (2h =35.52°) [
13].
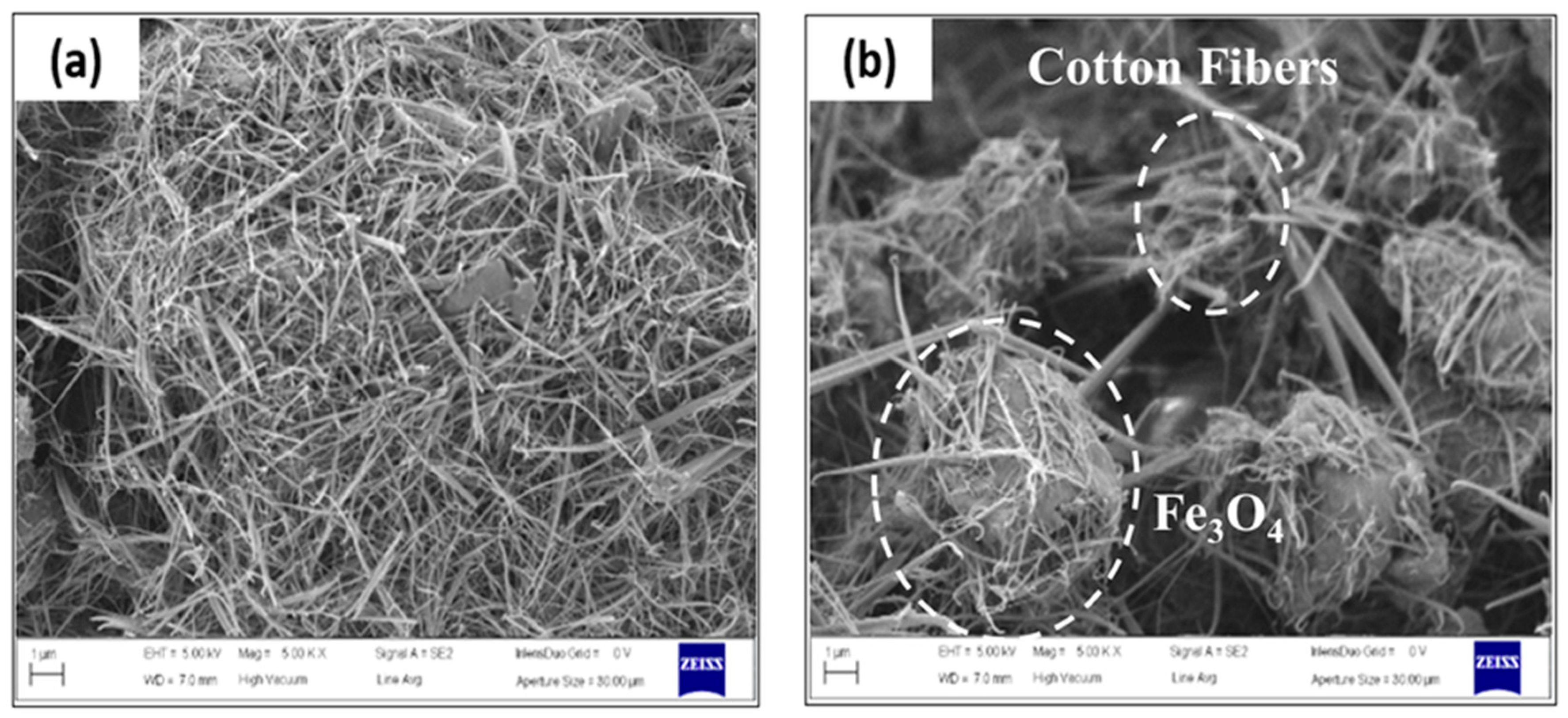
3.1.6. SEM
Figure 6a,b shows SEM images of (CDC) and (CDC@Fe
3O
4) respectively. The surface morphology of both the synthesized compounds showed a fibrous network.
The iron oxide nanoparticles appear to be packed within (CDC) 3D network. This fibrous environment may possess pore sizes that hinder the growth of magnetite nanoparticles during the coprecipitation reaction. Therefore, magnetite nanoparticles not only coat (CDC) surfaces but also fill the interfibrillar pores.
3.2. Optimisation of photocatalytic degradation parameters.
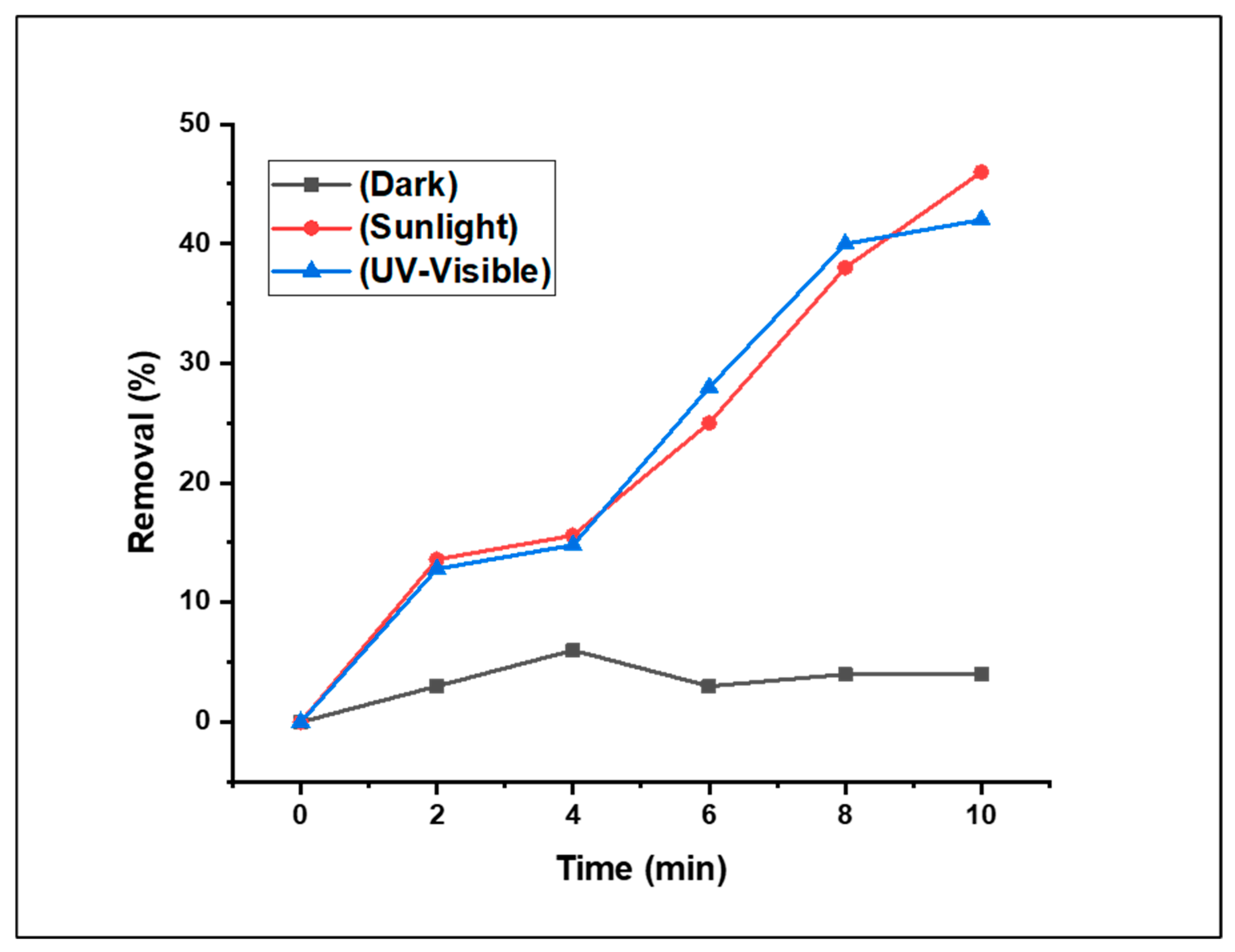
3.2.1. The Effect of the Light Source on Fenton-photodegradation process
The synthesised (CDC@Fe
3O
4) nanocomposites exhibited Fenton-photocatalytic activity in both the UV and visible ranges, as verified in the UV–Vis spectrum. In this preliminary study, we introduced 5 mg (CDC@Fe
3O
4) and 5 mM of H
2O
2 to treat an aqueous solution (5 mg/L) of Methyl Orange (MO) at neutral pH and room temperature. Preliminary investigations were performed to highlight the effects of the light source on the removal efficiency of the designed photocatalyst. Thus, the Fenton-photocatalytic degradation study of MO dye using (CDC@Fe
3O
4) was carried out under three different conditions: in the dark and under visible and UV light irradiation. The results revealed that the (CDC@Fe
3O
4) nanoparticles were dynamic under both UV and sunlight (
Figure 7).
As anticipated, the photodegradation results recorded under dark conditions may be neglected. In addition, the Fenton-photocatalytic tests performed under UV and natural light indicate that the removal of MO under natural solar light irradiation is noticeably more efficient than the treatment under UV light irradiation. Given the solar irradiation results, the synthesised (CDC@Fe3O4) photocatalyst successfully reduced 46% of MO, whereas the reduction attained under UV irradiation generated a 41% removal rate under the same degradation time (10 min), as depicted in Figure. From the above-mentioned data, it can be deduced that the degradation efficiency of MO under natural light is improved compared to the results obtained after UV irradiation. This improvement may be attributed to the concomitant existence of UV and visible light under natural solar irradiation [
29]. Therefore, it can be concluded that the (CDC@Fe3O4) photocatalyst is active under sunlight, and the subsequent optimisation analyses are assisted by natural light.
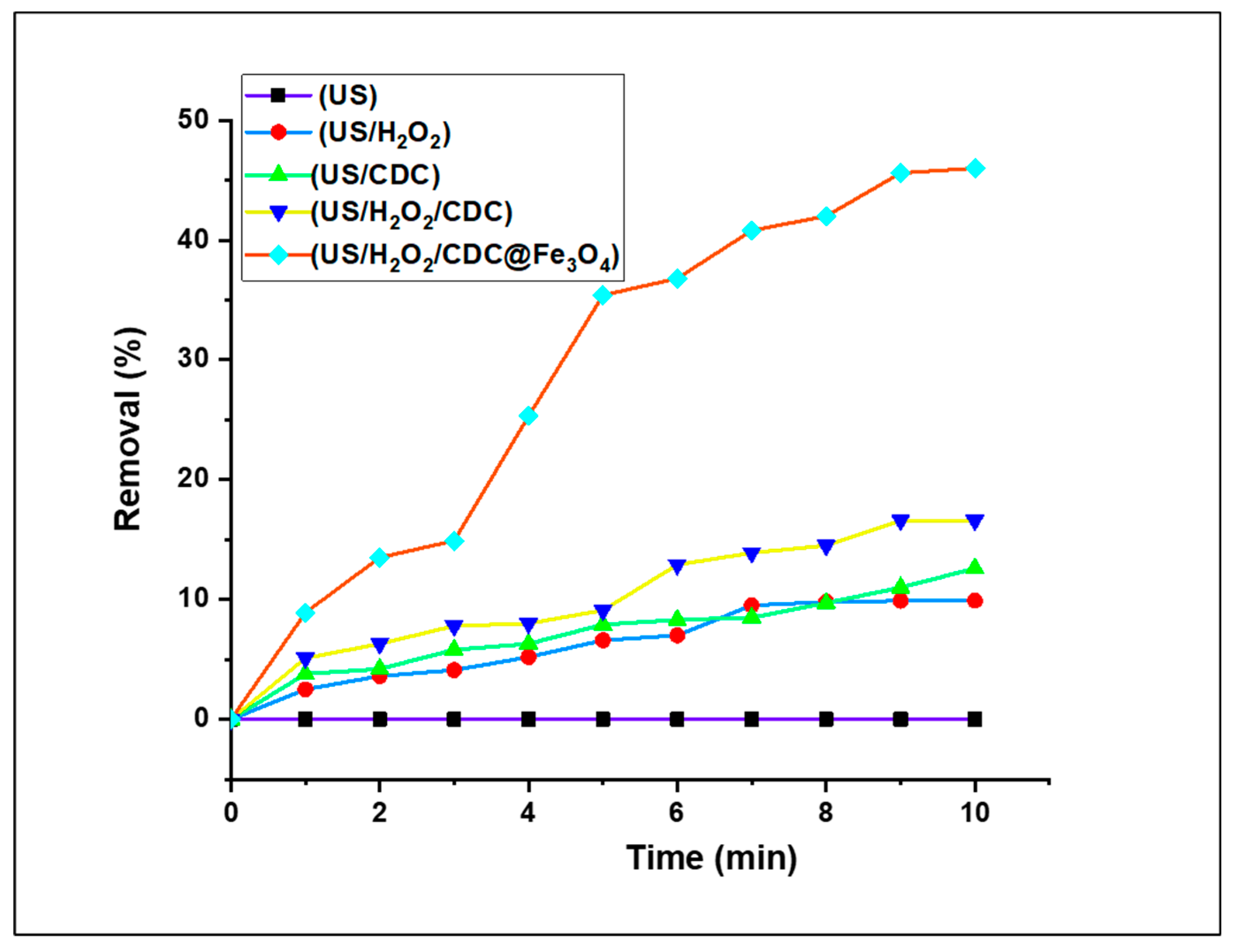
3.2.2. Preliminary Fenton-Photocatalytic Efficacity Studies of MO reduction under several catalytic systems
As mentioned, the degradation of textile dyes is critical to devote effort for addressing environmental problems. Methyl Orange dye is among most used dyes in textile industries, which have ominous impacts on the environment. In this catalytic study, we investigated the effect of the treatment of aqueous solutions of these dyes using different combinations of catalytic systems: US, US/H
2O
2, US/ (CDC), US/H
2O
2/(CDC), and US/H
2O
2/ (CDC@Fe
3O
4) For this preliminary study, and 5 mg (CDC@Fe
3O
4) and 5 mM H
2O
2 to treat an aqueous solution (5 mg/L) of Methyl Orange (MO) at neutral pH and room temperature. All reduction assays were performed for 10 min. As illustrated in
Figure 8, the aqueous solution of the studied dye solution was treated using a selected combination of catalytic systems. Apparently, the reduction of dye does not occur instantaneously and is to be monitored by referring to regular variations in the UV–Vis spectrum. An undetailed absorption study is presented in the following sections. As the exposure time of the desired reduced dye under the optimised catalytic system increases, the corresponding absorption peaks decrease. The reduction percentage and degeneration of Methyl Orange by the optimised catalytic systems progressively improved with time, thereby confirming the high reduction capability of US/H
2O
2/ (CDC@Fe
3O
4).
A sequence of tests was conducted to evaluate the catalytic performance, and the results are shown in
Figure 8. No removal rates were recorded using US alone as the catalytic system. It can be clearly observed that the decomposition rates using the US/H
2O
2 combination are very low (9.9% at 10 min), even with the assistance of H
2O
2. Using US/(6-CDC) and US/H
2O
2/(6-CDC) as Fenton-photocatalytic MO removal systems resulted in slightly improved degradation rates of 12.6 and 16.6%, respectively. The decomposition level increased to 46% upon the addition of [CDC@Fe
3O
4] to the solution. From these readings, it is evident that the (CDC@Fe
3O
4) nano-biomaterial has significantly enhanced Fenton-photocatalytic performance compared to that of (6-CDC). Accordingly, US/H
2O
2/ (CDC@Fe
3O
4) was used in combination for further catalytic assays.
The efficiency of photocatalysis depends on the surface morphology, particle size, energy gap, crystallinity, and amount of hydroxyl radicals on the catalyst surface [
30]. The generation of electrons and bores on the catalyst surface is followed by light absorption. They are then discharged or recombined to contribute to this reduction. In the case of providing an exterior surface for charge carrying, electrons and holes will displace. In this case, the generated electrons are entangled by the photocatalyst, whereas the holes are caught by hydroxyl radicals to generate HO
2 • and OH
•. The photocatalyst afforded an additional surface for the removal of charge carriers; hence, the formed hydroxyl radicals were used competently for the Fenton-photocatalytic decomposition of MO molecules. Moreover, hydroxyl radicals (OH
•) are unstable and extremely dynamic chemical species that have an important impact on the Fenton-photocatalytic reduction.
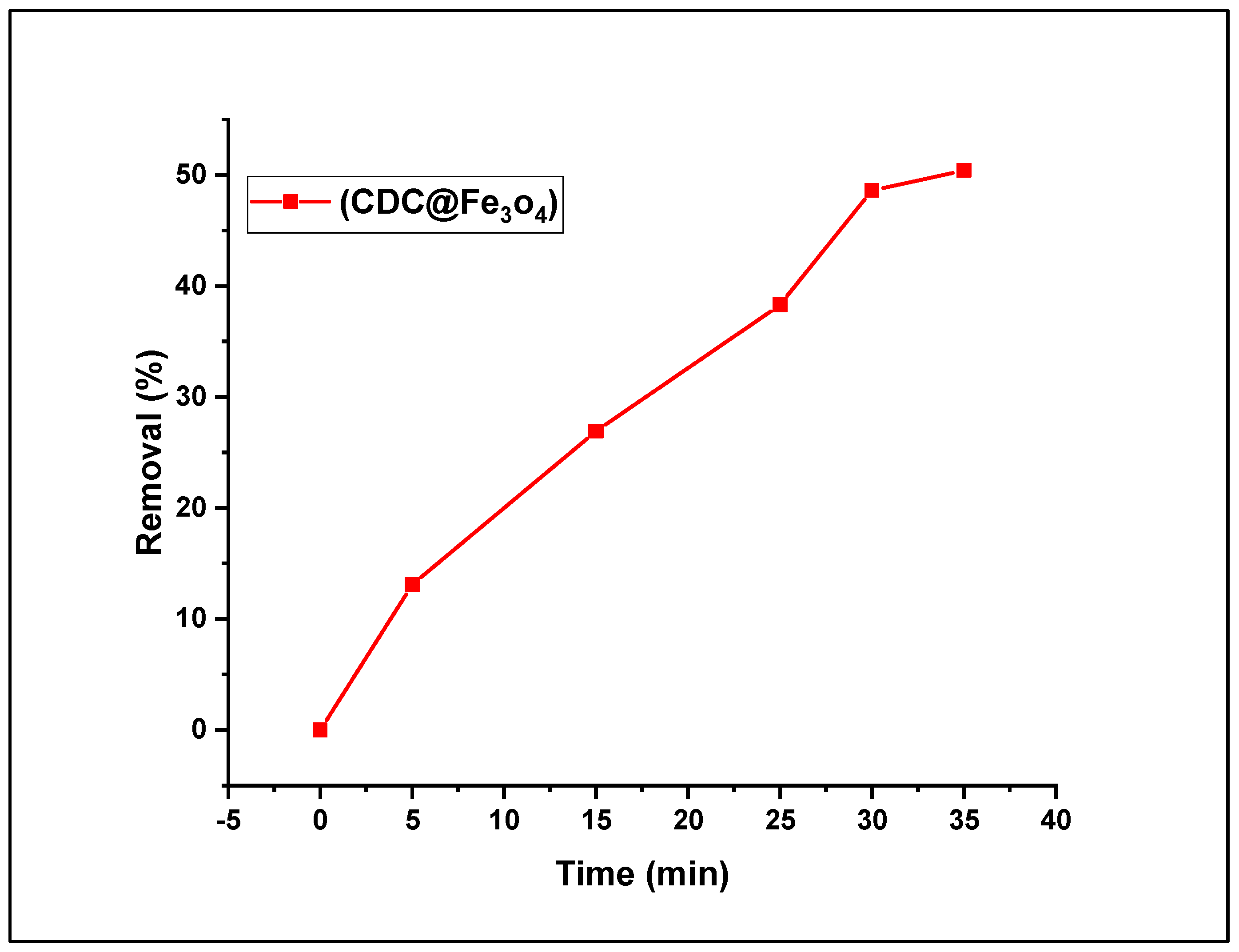
3.2.3. Effect of (CDC@Fe3O4) load on the Fenton photodegradation process
The catalyst load is a crucial factor in the dye removal process because the optimum dose of the catalyst provides more active sites and, thereby, efficient absorption of photons. To explore the impact of the magnetic photocatalyst load (CDC@Fe
3O
4) on the MO aqueous solution treatment, a series of five doses (5, 15, 25, 30, and 35 mg) was performed, and the findings are depicted in
Figure 9. To determine the impact of catalyst load on dye reduction performance, an aqueous solution of methyl orange dye (5. 10
-4 mol L
-1), was prepared and treated with the Fenton-photocatalytic system, US/H
2O
2/ (CDC@Fe3O4), maintaining an initial dose of 5 mol L
-1 of H
2O
2, neutral pH conditions, and a contact time of 10 min. It can be deduced from the figure that as the catalyst load increased, the MO degradation rate progressively increased. The degradation rate improved notably when (CDC@Fe
3O
4) amount was augmented from 5 mg to 30 mg. The highest MO removal rate (50.4%) was attained for (CDC@Fe
3O
4) (35 g), whereas a degradation rate of 48.6 % was obtained using only 30 mg of the bio-polymeric photocatalyst.
Therefore, it was important to use a catalyst dose of 30 mg as the optimal amount for the photocatalytic degradation process. Generally, increasing the catalyst load leads to an increase in the number of surface-available active sites (Fe
2+/
3+ ions), and thereby, the dynamic generation of active radicals on the catalyst surface [
31].
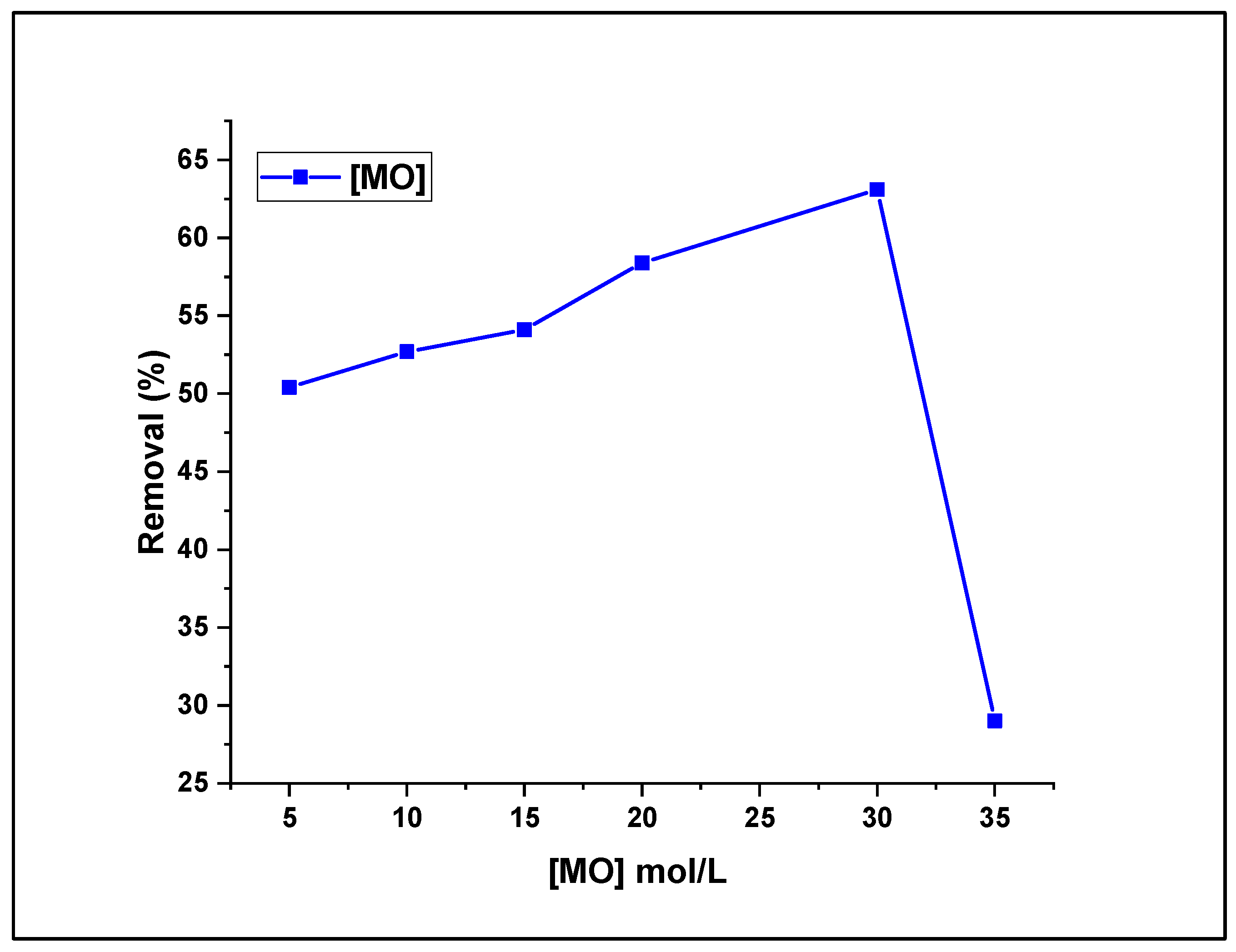
3.2.4. Effect of MO Concentration on Fenton-photodegradation process
The impact of the initial concentration of the MO dye on the removal efficiency was also studied by increasing the dye aqueous solution concentration from 5 to 35.10
-4 mol L
-1 under sunlight and US irradiation, using a solution of 5 mM H
2O
2 and maintaining 30 mg as the catalyst dose at pH 7. The Fenton-photocatalytic removal results are graphically represented in
Figure 10.
The recorded data show that the degradation efficiency of (CDC@Fe
3O
4) seems proportional to the treated dye concentration when the concentration of aqueous solutions is increased from 5 to 30 10
-4 mol L
-1, that is, the highest removal rate was 63.1% treating a 30.10
-4 mol L
-1 MO aqueous solution. In contrast, the lowest removal rate (29%) was recorded for the highest dye concentration (35. 10
-4 mol L
-1). Upon increasing the MO concentration from 30 to 35 10
-4 mol L
-1, the photodegradation efficiency of MO decreased from 63.1% to 29%, as illustrated in
Figure 10. This finding can be attributed to the fact that Fenton-photo-catalytically dynamic sites can be hidden with MO molecules which limit the light absorption and generation of radicals on the magnetic catalyst surface at increased dye amounts, thereby lowering the removal efficiency. However, photons easily reach the catalyst surface at inferior dye doses, and the formation of hydroxyl radicals is effortless [
32]. Hence, the next Fenton-photocatalytic optimisation assays will be carried out to reduce aqueous dye solutions with a concentration of which × 30.10
-4 mol L
-1.
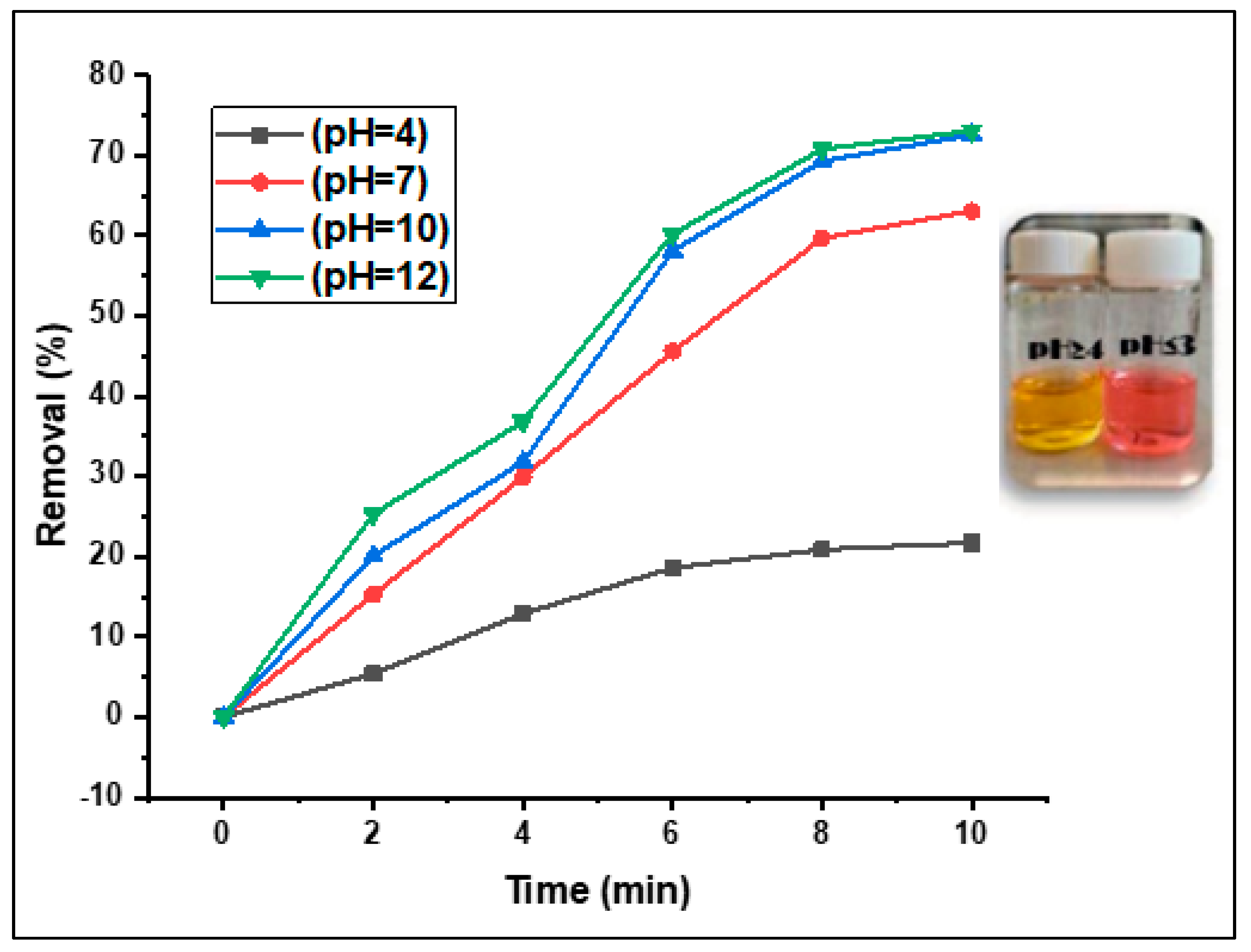
3.2.5. Effect of The Solution pH on the Fenton photodegradation process
As reported in several previous studies, the Fenton-photocatalytic performance of a catalyst is commonly associated with its capacity for the generation of hydroxyl radicals, thereby enhancing Fenton-photocatalytic removal by numerous folds at alkaline pH [
33].
Figure 11 shows the effect of pH on the removal rate of the MO dye over the US/H2O2/ (CDC@Fe3O4) Fenton-photocatalytic system.
The effect of pH on the degradation of the MO dye was studied at several pH values (4, 7, 10, and 12) while keeping the aforementioned factors unchanged (i.e., 30 mg catalyst load, 30.10-4 molL
-1 concentration of aqueous dye solution, sunlight irradiation, and after 10 min of treatment). As predicted, the lowest removal rate (21.7%) was achieved at the minimum pH value (pH= 4). In contrast, the catalytic activity increased with increasing pH, and almost 73% degradation of MO was achieved at pH 10 and 12 (
Figure 11). This result is possibly due to the increased rate of hydroxyl radical creation as well as their accumulation on the surface of the (CDC@Fe
3O
4) nanocomposites at high pH values [
33]. Correspondingly, the chosen pH value for further Fenton-photocatalytic processes was 10.
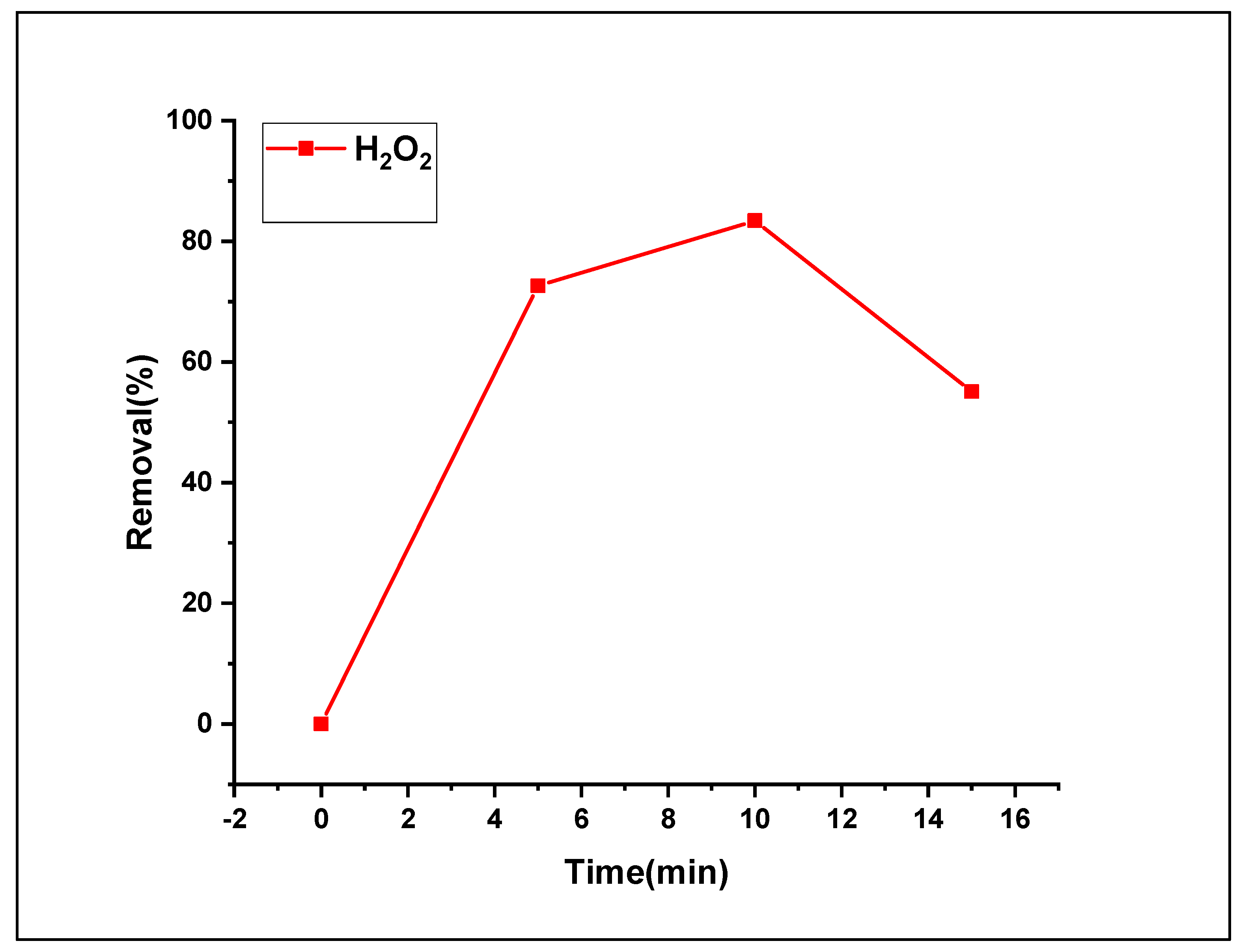
3.2.6. Effect of H2O2 loading on the Fenton photodegradation process
The concentration of H2O2 directly affected the removal efficiency of the Fenton photodegradation process. The impact of H
2O
2 dosage was investigated by estimating the oxidation process. The tested H2O2 loads were 5, 10, and 15 mmol L
-1. Based on a similar study [
34], we noticed that the use of high amounts of H
2O
2 leads to a “scavenger” impact of HO
2• radicals as well as HO
• radicals, which increases with increasing concentration. Therefore, the generation of radicals was partial [
35,
36]. In Fenton photocatalytic progression, the active radical scavenger species (HO
•), superoxide radical anions (•O
2 −), and holes (h
+) can be dissipated by hydrogen peroxide addition [
36]. In this study, pouring an amount of 10 ml of H
2O
2 was added (from the tested loads of 5 and 10 mmol L
-1) facilitates the refraining from the described scavenger impacts. The obtained findings displayed in
Figure 12 show that MO Fenton photodegradation was enhanced swiftly by multiplying the concentration of H
2O
2 (5 to 10 mmol L
-1) from 72.6 to 83.4%. The removal rate decreased to 55.1% with an increase in the concentration of H
2O
2 (10 mmol L
-1).
The decrease in the MO degradation percentage is attributed to the fact that an increased load of H2O2 results in a greater number of absorbed photons [
37]. Moreover, more Fenton-photocatalytic sites are accessible, leading to a higher degradation rate. In contrast, attention must be paid because the use of the H
2O
2 fraction during treatment progression is suppressed, and therefore, an excessive quantity is not advisable. It has been stated in the literature that the presence of H
2O
2 is hazardous to a wide range of species and will considerably reduce the general decomposition rate if Fenton-photocatalytic oxidation is applied as pretreatment for biological degradation. The detrimental effect of H
2O
2 is the scavenging of the generated hydroxyl radicals. This occurs when large volumes of hydrogen peroxide are applied [
37].
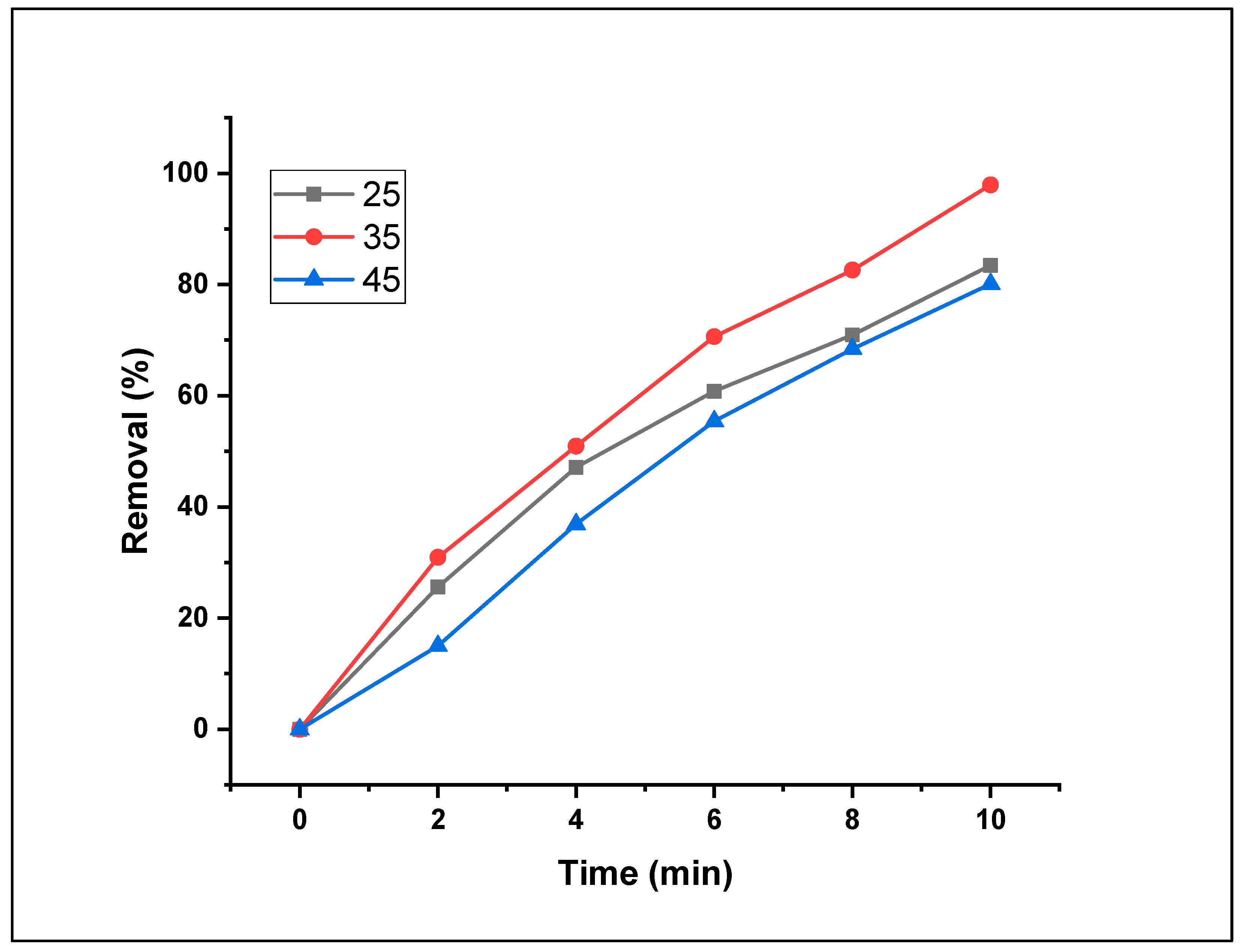
3.2.7. Effect of temperature on Fenton photodegradation
The evolution of the MO degradation level as a function of the reaction temperature was examined by incubating the aqueous dye solutions at various temperatures ranging from 25°C to 35°C to 45°C. The elimination ratio of MO increased with increasing reaction temperature, from 83.4% at 25°C to 97.9% at 35°C.
Figure 13 shows that the best temperature for the removal reaction was established when the reaction was performed at 35°C.
Indeed, increasing the temperature of the reaction mixtures led to a faster distribution rate of dye molecules in the nanomaterial. In this study, when the decomposition temperature was increased from 35°C to 45°C, the removal rate decreased to 80.1%. Comparable findings were reported by [
38,
39] when studying the impact of varying temperatures on dye-removal procedures. Nevertheless, adsorption trials are typically conducted at an adequate temperature to reduce operational costs. Thus, 35°C was selected for the adsorption procedures in the present investigation.
3.3.8. Fenton-photocatalytic degradation of Methyl Orange: a UV-Vis study and proposed Fenton-photocatalytic mechanism
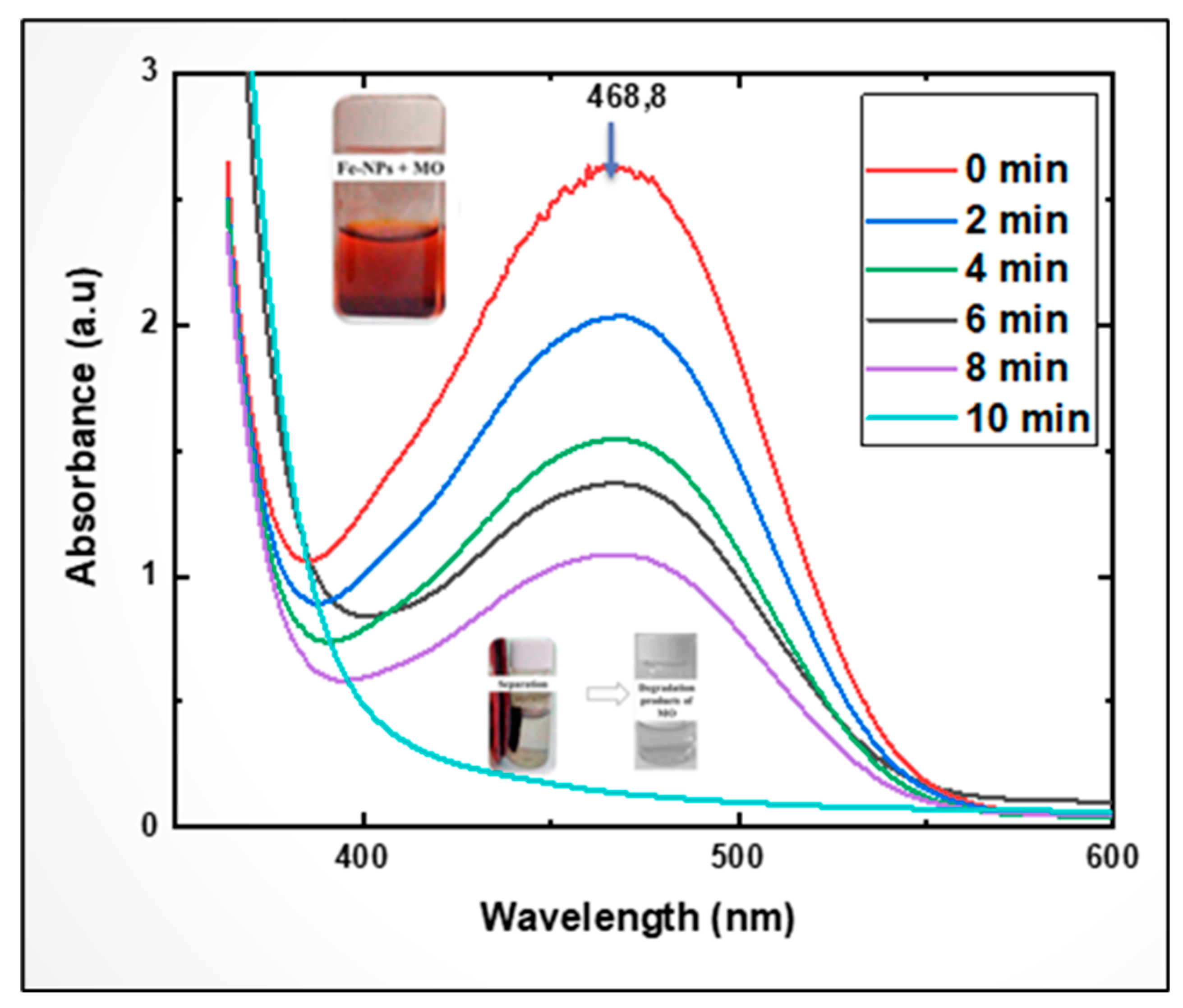
The Fenton-photocatalytic performance of the (CDC@Fe3O4) photocatalyst was studied for the Fenton-photocatalytic decomposition of MO under sunlight. The UV spectrum of MO shows two clear absorption peaks at approximately 460 and 270 nm. The first peak can be attributed to the (–N=N–) chromophore azo bond, and the second peak at 270 nm to the MO corresponding to the benzene rings [
40].
Figure 14 shows the gradual decrease in the intensity of the second absorption peak around 460 nm with increasing irradiation time. This finding shows that MO solution decolourisation by (CDC@Fe3O4) was achievable owing to the photocatalytic reactivity.
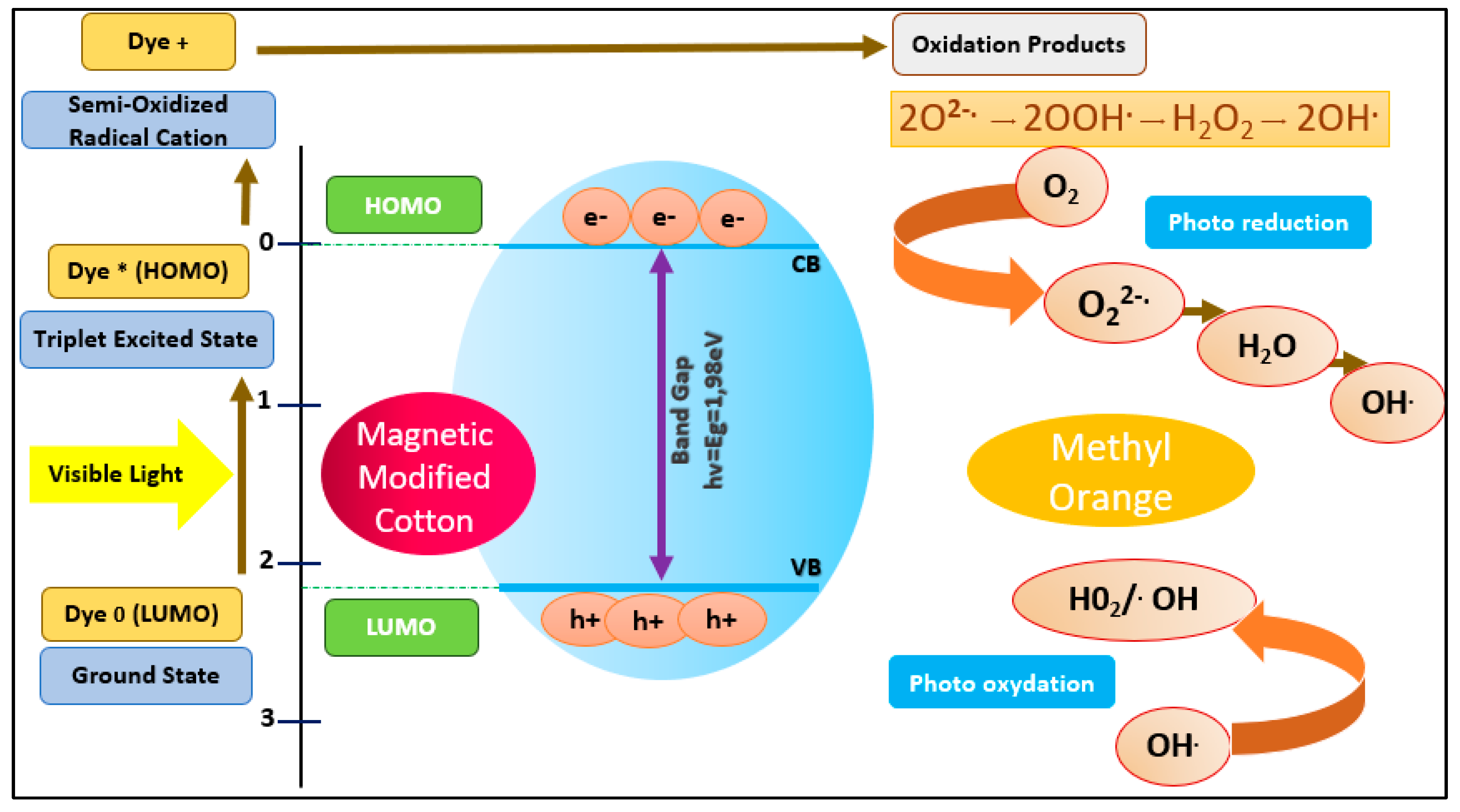
In general, the photocatalytic behaviour can be attributed to the association of both oxidation and reduction processes, where coated magnetite nanoparticles are active sites where the MO dye molecules are absorbed. The photocatalytic degradation mechanism (
Figure 16) involves MO excitation under visible light from the ground state (MO 0) to the triplet excited state (MO*). Meanwhile, (MO*) produces semi-oxidised radial cations (MO•+) caused by electron injection into the magnetite conduction band. Hence, superoxide radicals (O2•-) are generated as a result of the response of the trapped electrons to the dissolved oxygen [
41]. Consequently, these radical anions result in the generation of hydroxyl radicals (OH •) [
42], which oxidise and degrade the target dye (
Figure 15).
3.4. Reusability of Fenton-Photocatalytic Performance of (CDC@Fe3O4).
The stability of heterogeneous photocatalysts is crucial, along with their performance, from practical application and economic viewpoints. In this investigation, heterogeneous photocatalyst nanoparticles were quickly removed from the catalytic system following degradation assays using an external magnet.
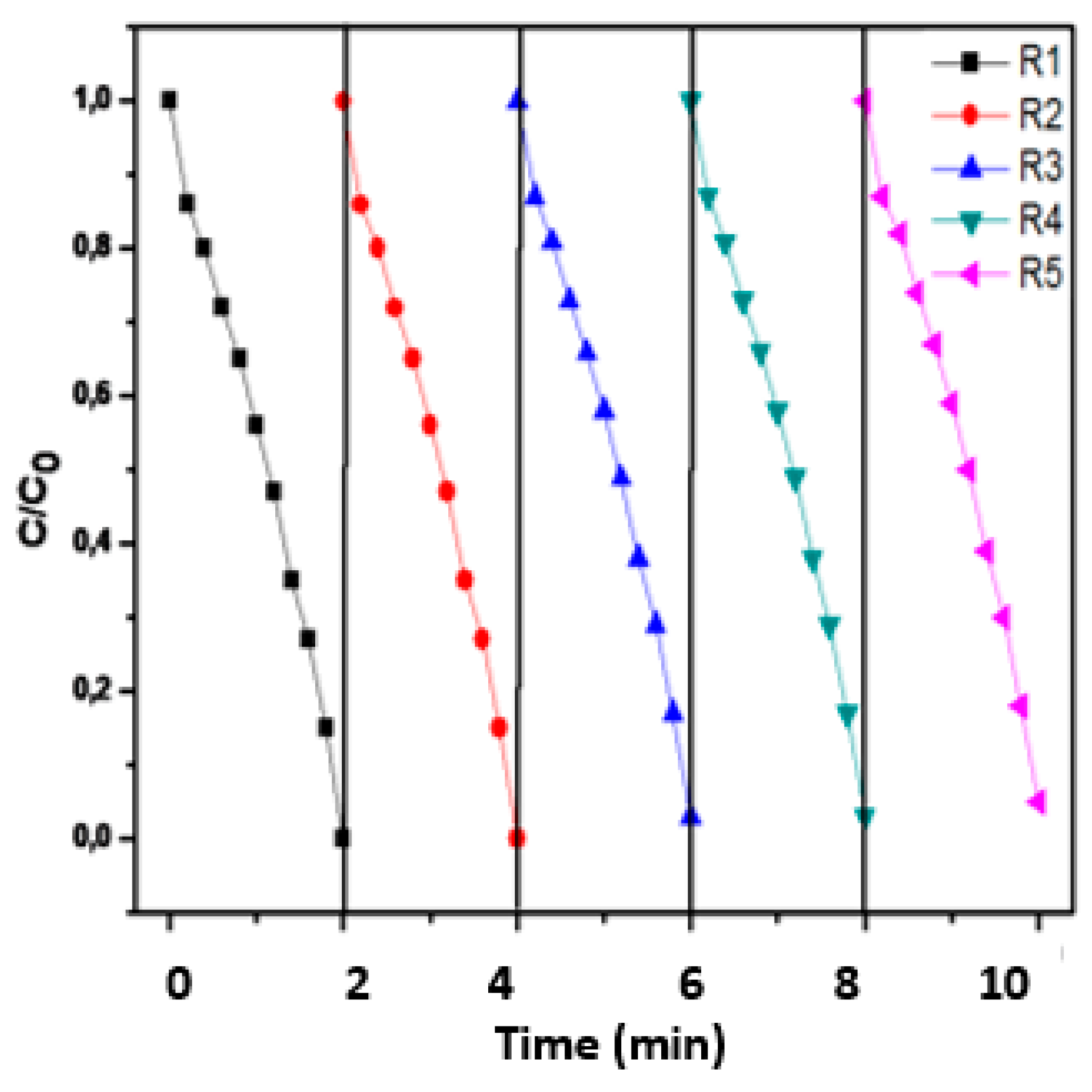
The removed catalyst was then collected and washed with distilled water. After exhaustive rinsing, the recovered photocatalyst was reused in the following run of MO removal under the optimised conditions five consecutive times. The results are shown in
Figure 16. The photocatalytic performance of (CDC@Fe3O4) nanocomposites decreased slightly in the first catalytic cycle (from 97.9% to 93.8 %) and then to 82 % in the fifth cycle (
Table 1). We noticed a drop-in catalytic activity after the sixth catalytic reuse (61.6%).
The time course of MO removal throughout the five photocatalytic cycles under the optimised conditions is shown in Figure. The values of the constant rate for the corresponding first efficient cycles were 0.0978 min-1, 0.0987 min-1, 0.0984 min-1, 0.0978 min-1, 0.0972 min-1. No major loss of catalytic activity for MO degradation was observed over (CDC@Fe3O4), proving that the synthesised magnetic nanocomposites possess good long-term stability and reusability. Thus, the synthesised magnetic photocatalyst appears to be promising for practical economic applications.
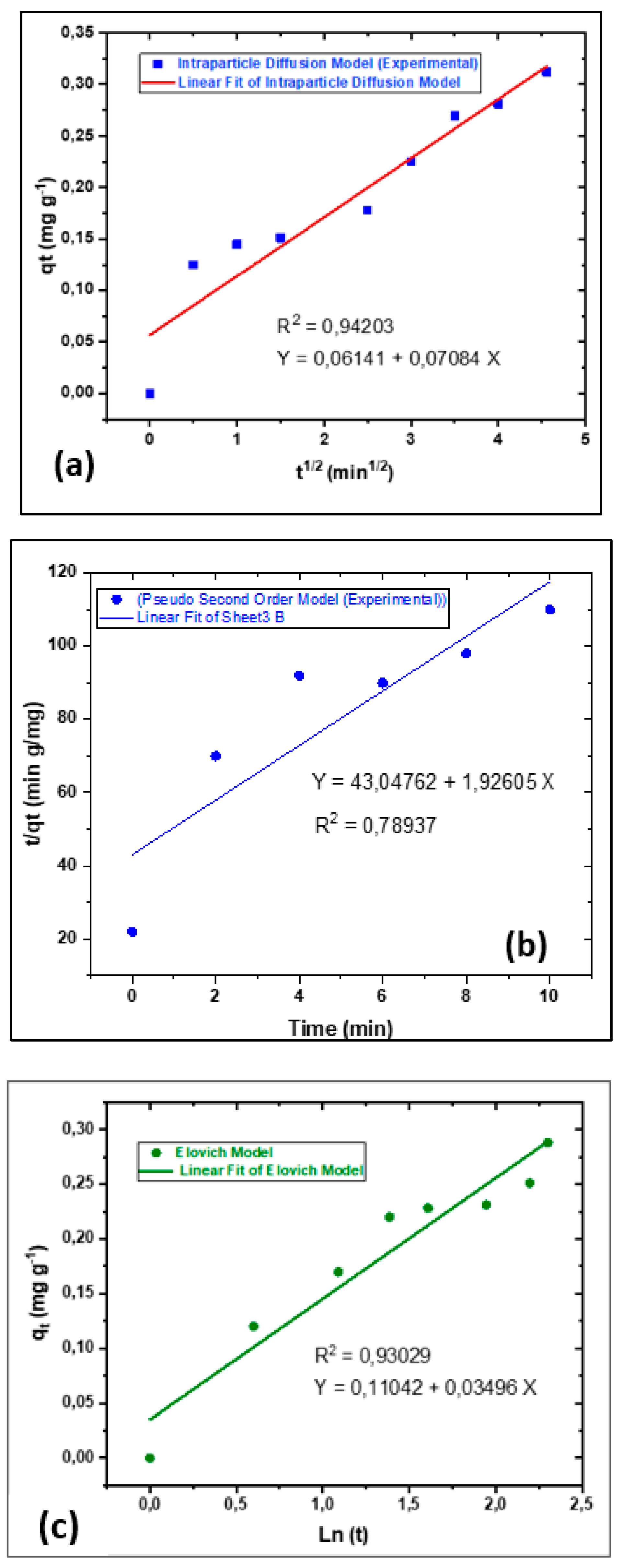
3.5. Theoretical adsorption kinetics models
Theoretical adsorption models were evaluated to characterise the kinetics of (CDC@Fe
3O
4). Therefore, three theoretical models were selected based on the experimental results of the decolourisation process. Pseudo-first and second order as well as Elovich, and Intraparticle diffusion models have been used to illustrate and adjust the parameters of kinetics adsorption. The equations governing these models, described in various reports [
43,
44,
45,
46]
Figure 17a–c show charts related to the kinetic adsorption models. as we can notice from these collected findings, the third model showed the maximal correlation rate R
2, (0.93029).
Based on this finding, it is possible to confirm that MO decolourisation treatment was performed along with intraparticle diffusion. The intraparticle diffusion model was mainly designated in three steps. First, immediate adsorption was detected because the external solution concentration was adequately elevated. Next, progressive adsorption behaviour was observed during the MO degradation process. Generally, the time required for this phase depends on the degradation parameters, including the catalyst load and its corresponding nanoparticle size, temperature, and aqueous solution concentration [
47]. Finally, the degraded MO molecules exhibited moderate adsorption performance until the target equilibrium was reached. Thus, the intraparticle diffusion model explains the MO decomposition phenomenon.
3.6. Catalytic synthesis of the tetra-substituted imidazole derivatives
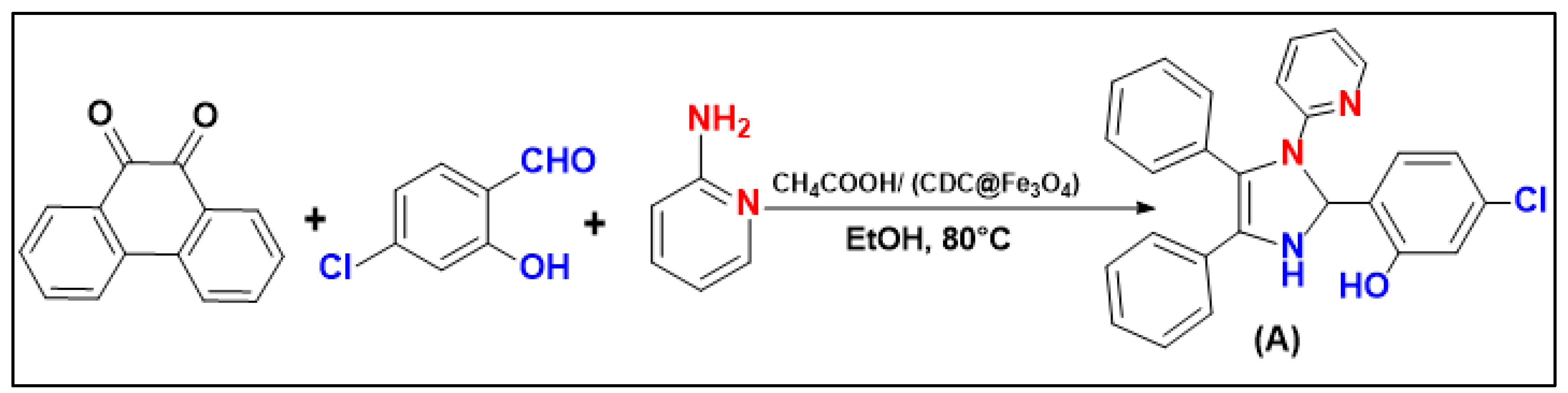
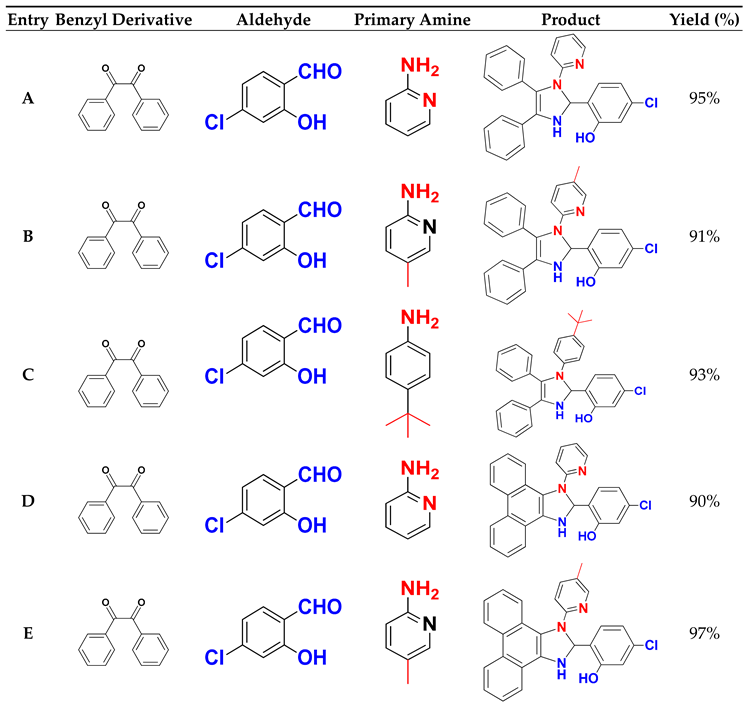
To evaluate the efficacity of (CDC@Fe3O4) for the catalytic synthesis of nine 1,2,4,5-tetrasubstituted Imidazole derivatives, the reaction of benzyl (1.00 mmol), (5-Chloro- salicylaldehyde (1.00 mmol), ammonium acetate (3 mmol) and pyridine-2-amine (1.00 mmol) was accomplished as the model reaction (
Scheme 2).
The one-pot four-component reaction was first carried out to choose a suitable catalyst amount to obtain the highest amounts of 5-chloro-2-(4,5-diphenyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-Imidazole-2-yl) phenol (A).
Table 1 presents the results. First, the rate of the chosen imidazole derivative (A) in the absence of (CDC@Fe
3O
4) after 12 h in acetic acid at 80°C was relatively low (21%). Furthermore, the impact of catalyst loading was studied in subsequent tests (entries 2–7). Indeed, a loading of 3 mg of (CDC@Fe
3O
4) improved the yield of (A) in acetic acid at 80°C for 12 h to approximately 46%. Next, the synthesis yield was tripled (63%) using 5 mg of the magnetic nano-catalyst (CDC@Fe
3O
4). However, no further improvement in the reaction yields was observed when using higher amounts of (CDC@Fe
3O
4) load (entry 7). In the next step, we aimed to eliminate the use of an acidic solvent and use a green solvent (entries 8 and 9). In addition, a similar study emphasised that solvent polarity is efficient for imidazole derivative synthesis [
48]. Ethanol and water were tested as they are the most environmentally friendly solvents. The results in
Table 2 indicate that the highest synthesis rate of (A) was attained in ethanol. Indeed, the polarity of ethanol and the high solubility of the starting reagents in this solvent, along with the generated hydrogen bonds between ethanol and water molecules issued from the synthesis reaction, are the main reasons for obtaining better yields in ethanol.
Subsequently, several experiments were performed to select the optimal energy output and reaction time (entries). As shown in
Table 2, increasing both the reaction temperature and time did not significantly increase the reaction yields. By contrast, the synthesis of (A) under ultrasound irradiation increased the synthesis yield. The obtained reaction yield of (A) was 95% in ethanol using 5 mg of (CDC@Fe3O4) and only after 30 min of continuous ultrasound irradiation.
Thus, the synthesis of the target imidazole derivatives was carried out under optimised conditions.
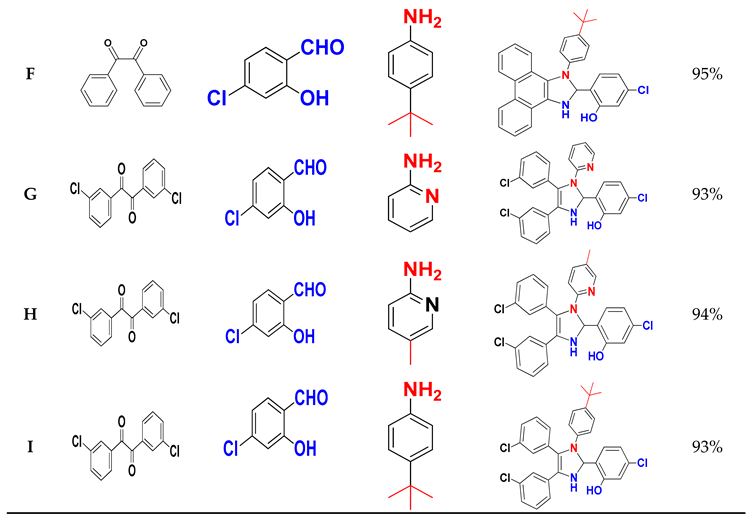
Table 3 summarises the molecular structures and yields obtained in this study.
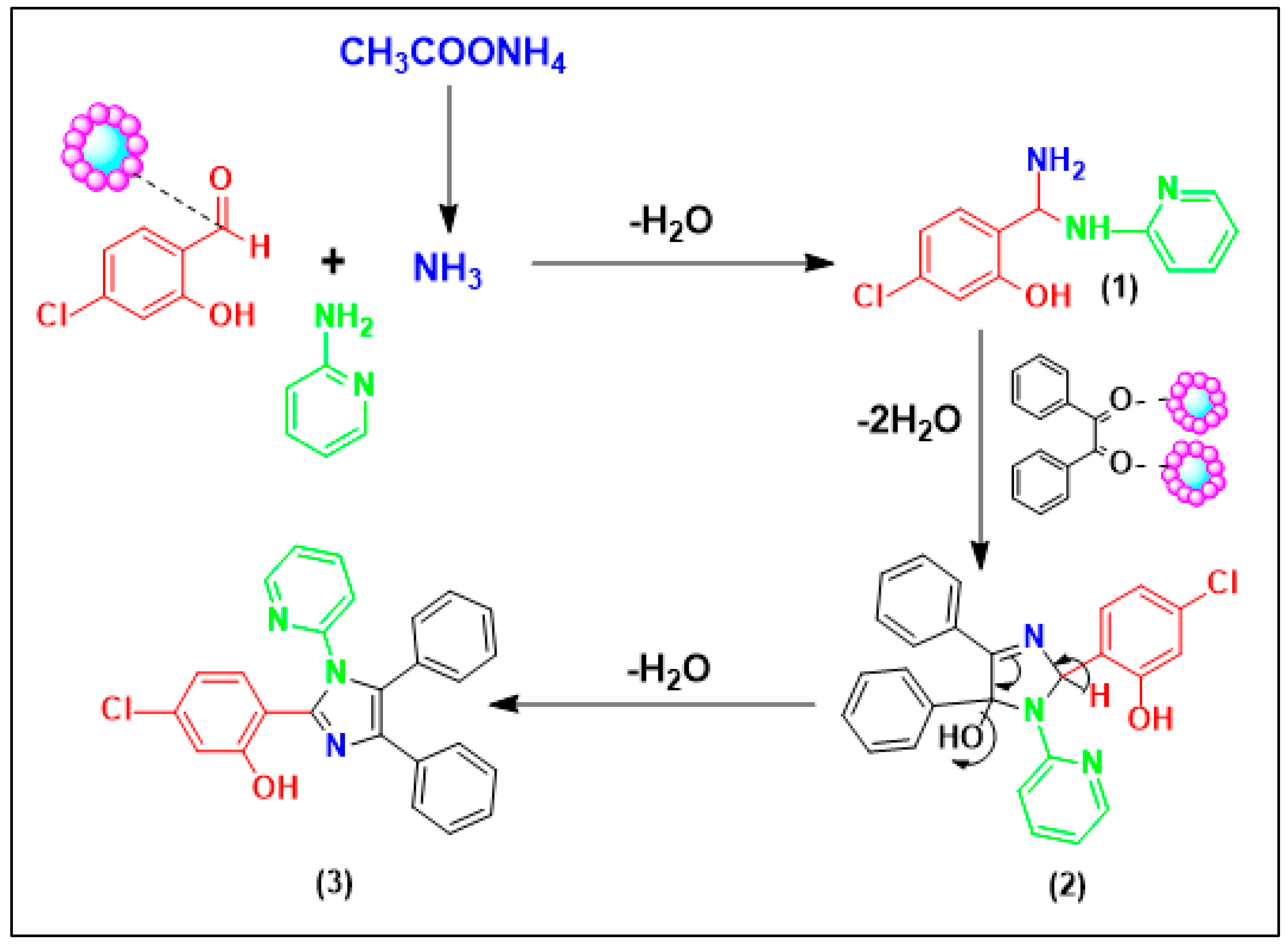
A probable catalytic mechanism is proposed for this scheme. This mechanism is consistent with that of a previous report [
49]. The scheme shows the proposed catalytic mechanism for imidazole derivative synthesis. First, intermediate (1) is generated following the nucleophilic addition of ammonia and the imine derivative to the initiated aldehyde. Afterwards, we can postulate that the embedded Fe
2O
3 groups on modified cellulose are qualified as Lewis acid sites and initiate the carbonyl moieties by activating their corresponding oxygen atoms which produce a higher amount of intermediates (2), thereby increasing the generation of imine groups. Subsequently, the imine nitrogen atom breaks down the iminium moiety, thereby affording a related cyclisation along with dehydration, followed by reorganisation by hydrogen alteration to generate the target imidazole ring (3). It is significant to emphasize that all carried out catalytic reactions showed good yields despite their achievement under oxygen atmosphere. These findings indicate the non-oxidation features of the designed catalyst.
3.6.1. Reusability
(CDC@Fe
3O
4) can be easily removed using an external magnet. Subsequently, the recyclability probability was investigated. (CDC@Fe
3O
4) was cleaned using a cold water: ethanol mixture (2:1), filtered, and used in the next catalytic run. Table X shows the good yields of (A) throughout the five repeated runs. These results are ascribed to the excellent dispersion of the coating and non-agglomerated magnetite nanoparticles on the modified cellulose support.
Table 4 shows that the developed values of both turn over number (TON) and turn over frequency (TOF) of (CDC@Fe
3O
4) were 418.27 and 836.54 h
-1 relatively.
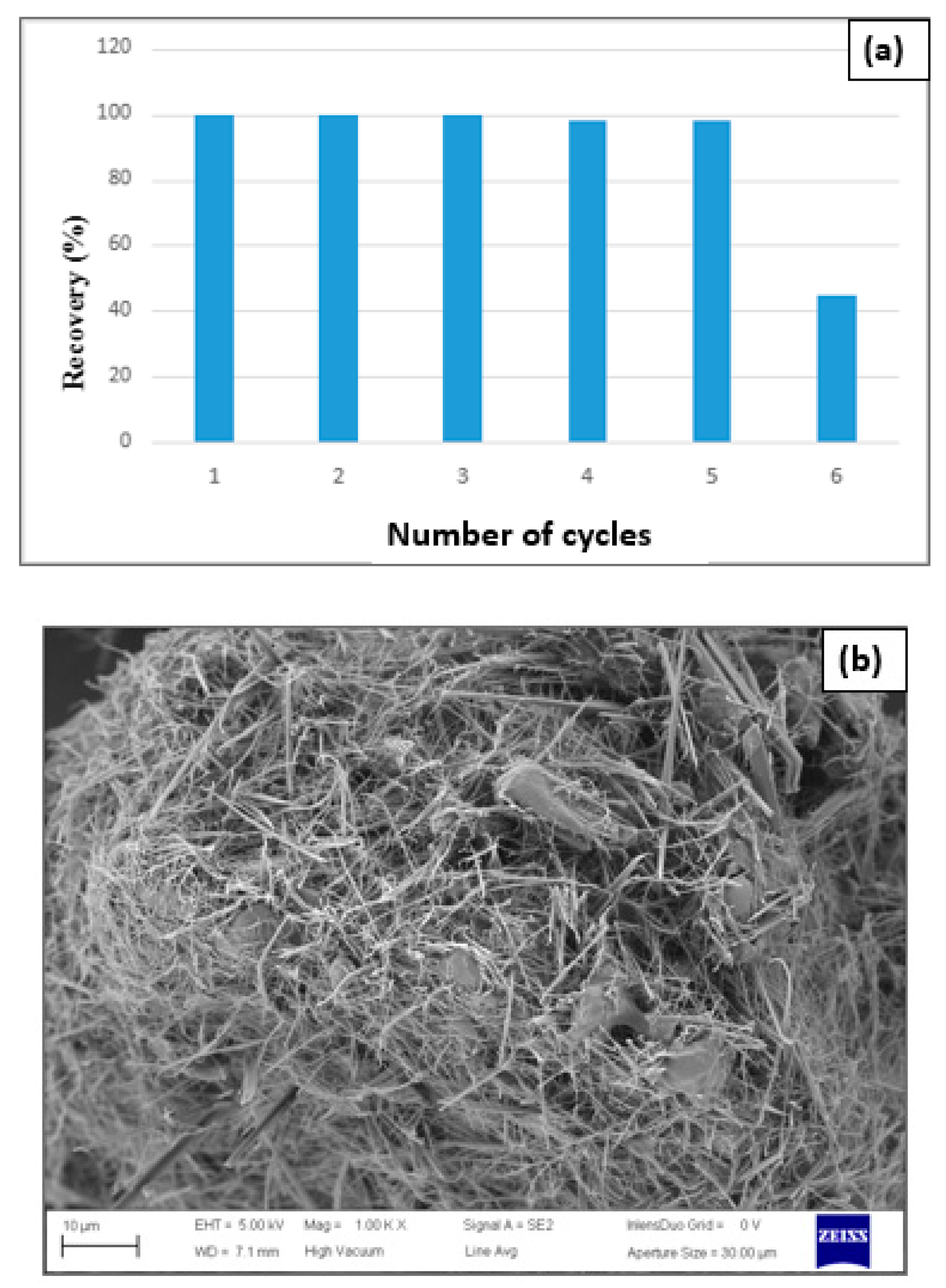
An exceptional decline in the synthesis rates was verified when carrying out the sixth catalytic run (
Figure 18a).
Figure 18b shows the discharge of most magnetite nanoparticles on the modified cellulose surface and, therefore, the decrease in catalyst efficiency starting from the sixth catalytic cycle.
4. Conclusions
In this report, we describe a simple two-step synthesis of a magnetically modified cellulose nanocomposite (CDC@Fe3O4). Characterisation of the obtained nanocomposites revealed the crystalline nature of the nanosized (CDC@Fe3O4) photocatalyst. The designed samples were used as heterogeneous catalysts for two applications. First, the designed catalyst was used for the photodegradation of Methyl Orange dye (MO). The (CDC@Fe3O4) nanocomposites were tested for Fenton-photodegradation of MO dye under dark, UV, and sunlight irradiation conditions, and it was assumed that the Fenton-photocatalytic process has a high photodegradation efficiency, which depends essentially on the variations in light sources, catalyst loads, dye concentration, treatment temperature, oxidant dose, and pH values of the treated dye aqueous solutions. The recorded kinetics of the Fenton photocatalytic process showed 97.9 % degradation of MO dye in 10 min under the optimised degradation conditions. For the catalytic organic synthesis application, a low catalyst loading (5 mg) was used for an optimised multi-component reaction of nine tetra-substituted imidazoles in ethanol under ultrasound irradiation at room temperature. All derivatives were produced in good yields (90-97%). Moreover, all Imidazole derivatives were easily isolated from the reaction mixtures. (CDC@Fe3O4) nanomaterial exhibited high catalytic activity after five consecutive runs without a remarkable decrease in yield. These findings provide new concepts for enhancing the Fenton-photodegradation catalytic efficacy of modified cellulose-based nanomaterials for improved applications in decontaminating organic dyes from water effluents and heterogeneous organic synthesis catalysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.A. and A.K.H.; methodology, M.A.A.; software, A.K.H.; validation, M.A.A, B.J. and A.K.H.; formal analysis, O.A.A; investigation, O.A.A.; M.A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.H., M.A.A; O.A.A writing—review and editing, M.A.A.; visualization, A.K.H.; supervision, B.J; funding acquisition, A.K.H.
Funding
This research was funded by University of Tabuk, grant number 0155-1444-S.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the deanship of Research and Graduate Studies at University of Tabuk for funding this work through Research no.0155-1444-S.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- O. Eskikaya, Z. Isik, C. Arslantas, E. Yabalak, D. Balakrishnan, N. Dizge, K. S. Rao, Preparation of hydrochar bio-based catalyst for fenton process in dye-containing wastewater treatment, Environ. Res, 216 (2023) 114357. [CrossRef]
- E. R. Nieto, S. A. O. Serrano, E. A. G. Pineda, C. B.Tirado, M. Y. Combariza, Textile wastewater depuration using a green cellulose based Fe3O4 bionanocomposite, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11 (2023) 109516.
- T. Islam, M. R. Repon, T. Islam, Z. Sarwar, M. M. Rahman, Impact of textile dyes on health and ecosystem: a review of structure, causes, and potential solutions, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 30 (2023) 9207–9242. [CrossRef]
- H. Kaur, N. Devi, S. S. Siwal, W. F. Alsanie, M. K.Thakur, V. K. Thaku, Metal–Organic Framework-Based Materials for Wastewater Treatment: Superior Adsorbent Materials for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants, ACS Omega, 8 (2023) 9004–9030. [CrossRef]
- S. Mohanty, S. Dash, N. Pradhan, S. K. Maji, Bio-Remediation of Organic Dyes from Wastewater by Microbial Colony—A Short Review, Nano-engineered Materials for Textile Waste Remediation, 20 (2023) 61-104.
- H. G. Quynh, H. V. Thanh, N. T. T. Phuong, N. P. T. Duy, L. H. Hung, N. V. Dung, N. T. H. Duong, N. Q. Long, Rapid removal of methylene blue by a heterogeneous photo-Fenton process using economical and simple-synthesized magnetite–zeolite composite, Environ. Technol. Innovation, 31 (2023) 103155-103168. [CrossRef]
- R. Mehdaoui, S. Agren, A. Dhahri, J. E. Haskouri, E. Beyou, M. Lahcini, M. H. V. Baouab, New sonochemical magnetite nanoparticles functionalization approach of dithiooxamide–formaldehyde developed cellulose: From easy synthesis to recyclable 4-nitrophenol reduction, Appl. Organomet. Chem, 35 (2021) 6257-6276. [CrossRef]
- A. Lourens, A. Falch, R. M. Enus, Magnetite immobilized metal nanoparticles in the treatment and removal of pollutants from wastewater: a review, J. Mater. Sci. volume 58 (2023) 2951–2970. [CrossRef]
- S. Olivera, H. B. Muralidhara, K. Venkatesh, V. K. Guna, K. Gopalakrishna, Y. Kumar K, Potential applications of cellulose and chitosan nanoparticles/composites in wastewater treatment: A review, Carbohydr. Polym., 153 (2016) 600-618. [CrossRef]
- K. Li, C. M. Clarkson, L. Wang, Y. Liu, M. Lamm, Z. Pang, Y. Zhou, J. Qian, M. Tajvidi, D. J. Gardner, H. Tekinalp, L. Hu, T. Li, A. J. Ragauskas, J. P. Youngblood, Soydan Ozcan, Alignment of Cellulose Nanofibers: Harnessing Nanoscale Properties to Macroscale Benefits, ACS Nano, 15 (2021) 3646–3673. [CrossRef]
- S. E. F. Camacho, E. J. S. Benítez, A. G. García, L. M. A. Arellano, J. F. Pérez-Robles, how to decrease the agglomeration of magnetite nanoparticles and increase their stability using surface properties, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 574 (2019) 29-35.
- G. Wang, J. Xiang, J. Lin, L. Xiang, S. Chen, B. Yan, H. Fan, S. Zhang, X. Shi, Sustainable Advanced Fenton-like Catalysts Based on Mussel-Inspired Magnetic Cellulose Nanocomposites to Effectively Remove Organic Dyes and Antibiotics, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 12 (2020) 51952-51959. [CrossRef]
- S. Agren, R. Mehdaoui, J. E. Haskouri, E. Beyou, M. Lahcini, M. H. V. Baouab, Reusable Magnetic Catalysed Synthesis of Fluorescent Imidazole Derivatives: Their Use as Chromogenic and Fluorogenic Probes for Metal Cation’s Detection, J. Mol. Struct. 1287 (2023) 135641-135656. [CrossRef]
- F. Ganjali , A. Kashtiaray , S. Zarei-Shokat , R. Taheri-Ledari, A. Maleki, Functionalized hybrid magnetic catalytic systems on micro- and nanoscale utilized in organic synthesis and degradation of dyes, Nanoscale Adv. 4 (2022) 1263-1307. [CrossRef]
- H.Veisi, M. Pirhayatib, P. Mohammadia, T. Tamoradic, S. Hemmatia, B. Karmakar, Recent advances in the application of magnetic nanocatalysts in multicomponent reactions, RSC Adv. 13 (2023) 20530-20556.
- M. Liu, Y. Ye, J. Ye, T. Gao, D. Wang, G. Chen, Z. Song, Recent Advances of Magnetite (Fe3O4)-Based Magnetic Materials in Catalytic Applications, Magnetochemistry. 10 (2023) 110-119.
- L. Pakjo, S. Rahimpour, R. T. Mofrad, Design and synthesis of ferrocene-based magnetic nanoparticle and investigation of its catalytic ability in the synthesis of novel 6-[(morpholin-4-yl)methyl] substituted pyrano [3,2-b]pyran derivatives, Appl. Organomet. Chem., 37 (2022) 6956.
- L. He, Z. Zhou, Z. Liu, X. Nan, T. Wang, X. Sun, P. Bai, Morphology design and synthesis of magnetic microspheres as highly efficient reusable catalyst for organic dyes, Colloids Surf., A, 656 (2023) 7757-7927. [CrossRef]
- M. Gholinejad, H. Bagheri, F. Zareh, J. M. Sansano, Palladium supported on hydrophilic magnetic nanoparticles as a new efficient catalyst in aqueous media, J. Mol. Struct. 1288(2023)135804. [CrossRef]
- S.Rui Li ,Y.M. Tan, L. Zhang, C.H. Zhou, Comprehensive Insights into Medicinal Research on Imidazole-Based Supramolecular Complexes, Pharm. 15 (2023) 1348-1363. [CrossRef]
- Y.D Lin, W.W. Tsai, C.W. Lu, Exploring the Electroluminescent Applications of Imidazole Derivatives, Chem. - Eur. J. 23 (2023) 3040-3069.
- T. Tashiro, Y. Shimura, Removal of mercuric ions by systems based on cellulose derivatives, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 27 (1982) 747–756. [CrossRef]
- A. E. Ghali, M. H. V. Baouabb, M. S. Roudesli, Preparation, characterization and application of a [copper (II)/ethylenediamine–cotton] complex for the removal of AB25 from aqueous solution in a laboratory scale column, Chem. Eng. J. 174 (2011) 18–26.
- L. Zanata, A. Tofanello, H. S. Martinho, J. A. Souza, D. S. Rosa, Iron oxide nanoparticles–cellulose: a comprehensive insight on nanoclusters formation, J. Mater. Sci. volume 57 (2022) 324–335. [CrossRef]
- A. E.Chirita, M. C. Marius, Highly crystalline porous magnetite and vacancy-ordered maghemite microcrystals of rhombohedral habit, J. Cryst. Growth. 380 (2013) 182-186.
- E. C. da Silva, F. Sirlane, A. A. Santana, J. C. P. Melo, F. J. V. E. Oliveira, C. Airoldi, X-ray diffraction and thermogravimetry data of cellulose, chlorodeoxycellulose and aminodeoxycellulose, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 100 (2010) 315–321.
- D. Klemm, B. Heublein, H.P. Fink, A. Bohn, Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl.44 (2005) 3358 – 3393.
- K. S.H. Musa, A. A. Salmah, I. Zamri, Use of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for enhancement of biosensor response to the herbicide 2, 4- dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, Sens. 8 (2008) 5775-5791.
- P. Kharazi, R. Rahimi, M. Rabbani, Study on porphyrin/ZnFe2O4@ polythiophene nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent and visible light driven photocatalyst for the removal of methylene blue and methyl orange, Mater. Res. Bull. 103 (2018) 133–141. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zhang, Y. Ma, X. Bu, Q.Wu, Z. Hang, Z. Dong, X. Wu, Facile one-step synthesis of TiO2/Ag/SnO2 ternary heterostructures with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity, Sci. Rep. 8 (2018) 1–11.
- R. Mehdaoui, S. Agren, J.E. Haskouri, E. Beyou, M. Lahcini, M.H.V. Baouab, An optimized sono-heterogeneous Fenton degradation of olive-oil mill wastewater organic matter by new magnetic glutarlaldehyde-crosslinked developed cellulose, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 5 (2022) 2–19. [CrossRef]
- C.H. Nguyen, C.C. Fu, R.S Juang, Degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange by palladium-doped TiO2 photocatalysis for water reuse: Efficiency and degradation pathways, J. Cleaner Prod. 202 (2018) 413–427. [CrossRef]
- M.H. Farzana, S. Meenakshi, Synergistic effect of chitosan and titanium dioxide on the removal of toxic dyes by the photodegradation technique, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53 (2014) 55–63. [CrossRef]
- J.P. Shubha, H.S. Savitha, S.F. Adil, M. Khan, M.R. Hatshan, K. Kavalli, B. Shaik, Straightforward Synthesis of Mn3O4/ZnO/Eu2O3- Based Ternary Heterostructure Nano-Photocatalyst and Its Application for the Photodegradation of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue Dyes, Mol. 26 (2021) 4661-4677.
- H. Chen, N. Chen, Y. Gao, C. Feng, Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by magnetically recoverable Fe3O4/Ag6Si2O7 under simulated visible light, Powder Technol. 326 (2018) 247–254.
- M.M.S. Sanad, M. M. Farahat, S.I. El-Hout, S.M. El-Sheikh, Preparation and characterization of magnetic photocatalyst from the banded iron formation for effective photodegradation of methylene blue under UV and visible illumination, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9 (2021) 105127-105141. [CrossRef]
- M. Golshan, M. Zare, G. Goudarzi, M. Abtahi, A.A. Babaei, Fe3O4@HAP-enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Acid Red73 in aqueous suspension: Optimization, kinetic, and mechanism studies, Mater. Res. Bull. 91 (2017) 59-67.
- X. Zhao, L. Baharinikoo, M.F. Davoodabadi, B. Mahdizadeh A.K. Farizhandi, Experimental modelling studies on the removal of dyes and heavy metal ions using ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles, Sci. Rep. 12 (2022) 1-15.
- O. A. Oyewo, A. Adeniyi, B.B. Sithole, M.S. Onyango, Sawdust-based cellulose nanocrystals incorporated with ZnO nanoparticles as efficient adsorption media in the removal of methylene blue dye, ACS omega. 30 (2020), 18798-18807. [CrossRef]
- N. Panda, H, Sahoo, S, Mohapatra, Decolourization of methyl orange using Fenton-like mesoporous Fe2O3–SiO2 composite, J. Hazard. Mater. 185 (2011) 359–365. [CrossRef]
- J. Patel,A. K. Singh, S. A. C Carabineiro, Assessing the photocatalytic degradation of fluoroquinolone norfloxacin by Mn:ZnS quantum dots: Kinetic study, degradation pathway and influencing factors, Nanomat. 2020, 10, 964. [CrossRef]
- J. P, Montañez, C. L. Heredia, E.L. Sham, E.M. Farfán Torres, Photodegradation of herbicide Metsulfuronmethyl with TiO2 supported on magnetite particles coated with SiO2, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6 (2018) 7402–7410.
- Á. D. J. Ruíz-Baltazar, N. Méndez-Lozano, D. Larrañaga-Ordáz, S. Y. Reyes-López, M. A. Z. Antuñano, R. P. Campos, Magnetic Nanoparticles of Fe3O4 Biosynthesized by Cnicus benedictus Extract: Photocatalytic Study of Organic Dye Degradation and Antibacterial Behavior, Processes. 8 (2020) 946- 977. [CrossRef]
- B. Jain, A. Hashmi, S. Sanwaria, A.K. Singh, M.A.B.H. Susan, S.A.C. Carabineiro, Catalytic Properties of Graphene Oxide Synthesized by a “Green” Process for Efficient Abatement of Auramine-O Cationic Dye, Anal. Chem. Lett. 10 (2020) 21–32. [CrossRef]
- R.Chakraborty, A. Asthana, A.K. Singh, S. Yadav, , M.A.B.H. Susan Carabineiro. Intensified elimination of aqueous heavy metal ions using chicken feathers chemically modified by a batch method, J. Mol. Liq. 312 (2020) 113475-113498.
- D. Vanhecke, F. Crippa, M. Lattuada, S. Balog, B. Rothen-Rutishauser, A. Petri-Fink, Characterization of the shape anisotropy of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles during thermal decomposition, Mat. 13 (2020) 2013- 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. Du, L.F. Zhou, Q. Zhang, L.Y. Liu, G. Li, W.B. Luo, H.K. Liu, Mesoporous structured aluminaosilicate with excellent adsorption performances for water purification, Sustainable Mater. Technol. 18 (2018), 80-111. [CrossRef]
- S. Saeedi, A. Rahmati, MNP–cellulose–OSO3H as an efficient and biodegradable heterogeneous catalyst for green synthesis of trisubstituted imidazoles, RSC Adv. 12 (2022) 11740-11749.
- T. T. Nguyen, N-P. T. Le, T. T. Nguyen, P. Hoang, An efficient multicomponent synthesis of 2,4,5-trisubstituted and 1,2,4,5-tetrasubstituted imidazoles catalyzed by a magnetic nanoparticle supported Lewis acidic deep eutectic solvent, Tran, RSC Adv. 9 (2019) 38148-38153.
Figure 1.
UV–Vis absorption of (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4) and the corresponding bandgap data of (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 1.
UV–Vis absorption of (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4) and the corresponding bandgap data of (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of Cotton, (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of Cotton, (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 3.
TGA curves of Cotton, (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 3.
TGA curves of Cotton, (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 4.
Magnetization curve of (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 4.
Magnetization curve of (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 5.
XRD patterns of (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 5.
XRD patterns of (CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 6.
SEM images of CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 6.
SEM images of CDC) and (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 7.
Variations in the MO removal rates under different light sources.
Figure 7.
Variations in the MO removal rates under different light sources.
Figure 8.
Variations in the MO removal rates under different catalytic systems.
Figure 8.
Variations in the MO removal rates under different catalytic systems.
Figure 9.
Effect of (CDC@Fe3O4) load on MO removal rate.
Figure 9.
Effect of (CDC@Fe3O4) load on MO removal rate.
Figure 10.
Effect of MO concentration on removal rates.
Figure 10.
Effect of MO concentration on removal rates.
Figure 11.
Variations of MO removal rates under different pH values.
Figure 11.
Variations of MO removal rates under different pH values.
Figure 12.
Effect of [H2O2] concentration on MO removal rate.
Figure 12.
Effect of [H2O2] concentration on MO removal rate.
Figure 13.
Effect of temperature on MO removal rate.
Figure 13.
Effect of temperature on MO removal rate.
Figure 14.
MO UV-visible spectra exhibited an absorbance decrease at 468.8 nm within 10 min. Photographs showing vanishing colour during the photocatalytic treatment.
Figure 14.
MO UV-visible spectra exhibited an absorbance decrease at 468.8 nm within 10 min. Photographs showing vanishing colour during the photocatalytic treatment.
Figure 15.
Proposed Fenton-photocatalytic degradation mechanism.
Figure 15.
Proposed Fenton-photocatalytic degradation mechanism.
Figure 16.
Five consecutive photocatalytic MO degradation processes of MO using (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 16.
Five consecutive photocatalytic MO degradation processes of MO using (CDC@Fe3O4).
Figure 17.
Investigated and simulated chosen kinetic adsorption models: (a) Intraparticle diffusion, (b) Pseudo-second order and (c) Elovich.
Figure 17.
Investigated and simulated chosen kinetic adsorption models: (a) Intraparticle diffusion, (b) Pseudo-second order and (c) Elovich.
Scheme 2.
Schematic representation of imidazole derivative (A) synthesis.
Scheme 2.
Schematic representation of imidazole derivative (A) synthesis.
Scheme 3.
Proposed catalytic mechanism.
Scheme 3.
Proposed catalytic mechanism.
Figure 18.
Efficiency of the catalytic run (a) and SEM images (CDC@Fe3O4) after six runs (b).
Figure 18.
Efficiency of the catalytic run (a) and SEM images (CDC@Fe3O4) after six runs (b).
Table 1.
Removal rate during five consecutive catalytic cycles.
Table 1.
Removal rate during five consecutive catalytic cycles.
| Cycle number |
Removal Rate |
| Cycle 1 |
97.9% |
| Cycle 2 |
93.8% |
| Cycle 3 |
90.3% |
| Cycle 4 |
85.4 % |
| Cycle 5 |
82.0% |
Table 2.
Comparison of different catalytic systems.
Table 2.
Comparison of different catalytic systems.
| Entry |
Catalyst load (mg) |
Energy output |
Time |
Solvent |
Yield (%) |
| 1 |
1 |
80°C |
12 h |
Acetic Acid |
21% |
| 2 |
2 |
80°C |
12 h |
Acetic Acid |
25% |
| 3 |
3 |
80°C |
12 h |
Acetic Acid |
46% |
| 4 |
4 |
80°C |
12 h |
Acetic Acid |
50% |
| 5 |
5 |
80°C |
12 h |
Acetic Acid |
63% |
| 6 |
6 |
80°C |
12 h |
Acetic Acid |
63% |
| 7 |
7 |
80°C |
12 h |
Acetic Acid |
63% |
| 8 |
5 |
80°C |
12 h |
Ethanol |
75% |
| 9 |
5 |
80°C |
12 h |
Water |
71% |
| 10 |
5 |
120°C |
15 h |
Acetic Acid |
63% |
| 11 |
5 |
US |
30 min |
Ethanol |
95% |
| 12 |
5 |
US/ 50°C |
30 min |
Ethanol |
95% |
Table 3.
Obtained tetra substituted Imidazole derivatives under optimized catalytic system.
Table 3.
Obtained tetra substituted Imidazole derivatives under optimized catalytic system.
Table 4.
(CDC@Fe3O4) catalytic efficacity for six catalytic runs.
Table 4.
(CDC@Fe3O4) catalytic efficacity for six catalytic runs.
| (CDC@Fe3O4)a
|
TONb |
TOF (h-1) c |
| Run 1 |
418.27 |
836.54 |
| Run 2 |
398.75 |
797.50 |
| Run 3 |
390.38 |
780.76 |
| Run 4 |
384.81 |
769.62 |
| Run 5 |
376.44 |
734.88 |
| Run 6 |
223.08 |
446.16 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).