Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
26 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Breastfeeding
2.1. General
2.2. Immune and gut microbiota maturation
3. Breastfeeding and risk of IBD
3.1. IBD presentation
3.2. Milk components and gut inflammation: what do experimental model of colitis tell us?
3.3. The role of breastfeeding in the development of human IBDs: clinical evidence
| Design | Place | Sample size | Breastfeeding was associated with IBD |
Specific comments | Breastfeeding duration |
Main outcome | Publication date | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case control study | UK | 57 CD and 114 controls, 51 UC and 102 controls | Yes/No | Adults Never breast-fed was a risk factor for UC, not for CD |
No association when breastfeeding far at least 2 weeks | CD, UC | 1979 | Whorwell et al. [143] |
| Case control study | Sweden | 308 matched pairs patients and controls | Yes | Adults There were more individuals with no or very short periods of breast-feeding among patients with Crohn’s disease than among the controls. CD overrepresented among those with no or very short periods of breast-feeding. The mean length of the breast-feeding period was 4.59 months among patients and 5.76 months among controls. |
Lenght of breastfeeding collected | CD | 1983 | Bergstrand et al. [129] |
| Case control study | International (USA, Canada, UK, Sweden, Denmark, The Netherland, France, Italy, Israel) | 302 CD, 197 UC, 998 sex- and age-matched (within 1 year) controls were studied for each patient | No | Patients whose disease started before 20 years and under study < 25 years olds | Not reported | CD, UC | 1987 | Gilat et al. [147] |
| Case control study | Canada | 114 families included with one child with CD, 180 unafected siblings as controls | Yes | Adolescent Lack of breastfeeding was a risk factor associated with development of CD during childhood and adolescence |
No effect of length of breastfeeding | CD | 1989 | Koletzko et al. [118] |
| Case control study | Sweden | 93 CD, 164 UC and 514 controls | No | Adults. Exclusive breastfeeding (Breast-fed only) or not. The comparison between cases and control could be somewhat misleading in that study as subsequent changes in breast feeding status after leaving the maternity ward were not recorded. |
Not reported | CD, UC | 1990 | Ekbom et al. [127] |
| Case control study | Canada | 93 families included with one child with UC and 138 unaffected siblings | No | Adolescent The lack of breastfeeding and formula feeding were not identified as risk factors during childhood |
No influence of breastfeeding duration | UC | 1991 | Koletzko et al. [117] |
| Case control study | Sweden | 167 UC and 167 controls | No | Adults No difference as how soon the patients were weaned |
Weaning < 14 days | UC | 1991 | Samuelsson et al. [130] |
| Case control study | Sweden | 152 CD, 135 UC, 305 controls | No | Adolescent and adults Analysis did not support increased risk of IBD among individuals with no or only a short duration of breastfeeding |
< 2 months | CD, UC | 1993 | Persson et al. [131] |
| Case control study | USA | 68 CD, 39 UC and 202 controls | Yes | Children and adolescents Breastfeeding has been negatively associated with CD and UC with evidence of duration-dependent trends |
≤ 5 months 6-11 months ≥ 12 months |
CD, UC | 1993 | Rigas et al. [119] |
| Case control study | USA | 54 CD and 90 controls | No | <22 years | Not reported | CD | 1996 | Gruber et al. [120] |
| Case control study | Italy | 225 CD and 594 UC with age-sex matched paired controls | Yes | Adults Lack of breastfeeding was associated with an increased risk of CD and UC |
<4 months | CD, UC | 1998 | Corrao et al. [132] |
| Case control study | Israel | 33 CD and 55 UC patients, in matched 76 population and 68 clinic controls | No | Adults | Not reported | CD, UC | 1998 | Klein et al. [145] |
| Case control study | The Netherlands | 290 CD, 398 UC and 616 controls | No | Adults Breastfeeding was not associated with IBD in adults, however a positive association was observed with pancolitis |
Not reported | CD, UC | 1998 | Russel et al. [135] |
| Case control study | Japan | 42 CD with 126 controls and 133 UC with 266 controls | Yes | < 15 years Comparison between the group fed exclusively by breast milk or mixed, and the group fed by artificial (bottle) feeding alone for the development of inflammatory bowel disease. Breast feeding during infancy until postnatal 4 months might decrease the development of chronic inflammatory bowel disease |
Not reported | CD | 1999 | Urashima et al. [109] |
| Case control study | UK | 26 CD and 29 UC and matched controls (8 controls for each case) | Yes | Adults A trend for breastfed infants to have a lower risk of having developed CD but a higher risk to develop UC |
Not reported | CD, UC | 2000 | Thompson et al. [133] |
| Case control study | France | 222 CD and 60 UC patients matched with controls | Yes | Before 17 years of age Increased risk of CD development when exclusive or partial breastfeeding during infancy. Data not reported for UC in relation with breastfeeding |
Not reported | CD, UC | 2005 | Baron et al. [136] |
| Case control study | Canada | 194 CD patients and 194 controls | No | Less than 20 years The proportion of case mothers who breastfed their children was similar to that of the control group |
Breasfeeding < 6months between 7 and 12 months, >1 year |
CD | 2006 | Amre et al. [121] |
| Case control study | China | 177 UC and 177 age-matched and sex-matched controls | No | Adults | Not reported | UC | 2007 | Jiang et al. [111] |
| Case control study | Germany | 444 CD, 304 UC and 1481 controls | No | Adolescents (median age: 11 years old) Association between nutrition other than breast milk at 5 m and reduced risk of both CD and UC |
Exclusive breastfeeding <5 months versus ≥ 5 months | CD, UC | 2007 | Radon et al. [140] |
| Case control study | Germany | 1096 CD and 763 UC patients, 878 healthy controls | No | Adults | 1 month 1–3 months 3–6 months 6 months |
CD, UC | 2007 | Sonntag et al. [139] |
| Case control study | Germany | 374 CD and 169 UC, 743 controls | Yes | Children and young adolescent Time of breastfeeding was not associated with CD or UC. Significantly shorter time of breastfeeding as compared with the control group was found in patients with UC and CD |
The duration of breastfeeding was recorded. Average duration was 4.8 months | CD, UC | 2010 | Decker et al. [137] |
| Case control study | New Zealand | 638 CD and 653 UC, 600 matched controls | Yes | Adults Breastfeeding was protecting when >3 months |
0-2 months 3-6 months 6-12 months More than 12 months |
CD, UC | 2010 | Gearry et al. [110] |
| Case control study | New Zealand | 197 CD patients and 290 controls (Informed for breastfed during infancy) | No | Age range between 5 and 86 years for the complete cohort Breastfed in infancy was not associated with an increased or a decreased risk of having CD |
Not reported | CD | 2010 | Han et al. [112] |
| Case control study | Spain | 124 CD and 235 matched controls, 146 UC and 278 matched controls | Yes/no | Adults Breastfeeding, either partial or exclusive, was protective factor for CD, but not for UC in the univariate analysis |
Not reported | CD, UC | 2010 | Lopez-Serrano et al. [134] |
| Case control study | Denmark | 123 CD and 144 UC, 267 controls | Yes | Adults Breastfeeding more than 6 months decreased the odds for IBD whereas no effect of ever breastfed was observed |
Ever breastfed or > 6 months | CD, UC | 2011 | Hansen et al. [138] |
| Prospective cohort | UK | 114 CD and 66 UC, 248 479 controls | No | Children and early adulthood. Artificial versus breastfed |
Not reported | UC, CD | 2011 | Roberts et al. [63] |
| Case control study | Iran | 95 CD and 163 UC patients, 285 and 489 age (and sex)-matched controls, respectively | No | Adults No difference bewtten breastfed infants and not-breasfed No difference in mean duration of breasfeeding between IBD patiens eand controls (children were breasfed almost 18 months in all groups) |
Mean duration of breastfeeding reported | CD, UC | 2011 | Vahedi et al. [113] |
| Case control study | Italy | 567 CD and 428 UC patients, 562 healthy controls | No | Adults | Not reported | CD, UC | 2012 | Castiglione et al. [142] |
| Case control study | USA | 89 IBD cases and 3,080 age-and membership-matched control | No | Pediatric (< 18 years) Neither exposure was associated with pediatric-onset IBD in the fully adjusted model (formula versus exclusive breast feeding or missing) |
exclusive breast-feeding, formula feeding with or without breast feeding or missing recorded | CD, UC | 2012 | Hutfless et al. [123] |
| Case control study | Slovakia | 129 CD, 96 UC, 293 controls | No | Adults Risk of CD and UC associated with breastfeeding < 6 months |
0 – 5 months 6 – 12 months More than 12 months |
CD, UC | 2013 | Hlavaty et al. [144] |
| Case control study | Denmark | 59 CD and 56 UC patients, 477 healthy controls | Yes | Children<15 years Breastfeeding more than 3 months was associated with a reduced risk of IBD |
>3 months as a variable in a multivariate analysis | CD, UC | 2013 | Jakobsen et al. [141] |
| Prospective cohort | USA | 146 681 248 incident cases of CD and 304 incident cases of UC |
No | Adult women No association with breastfeeding duration |
≤ 3 months 4-8 months ≥ 9 months |
UC, CD | 2013 | Khalili et al. [99] |
| Case control study | China | 1308 UC and matched controls | No | Adults | Not reported | UC | 2013 | Wang et al. [115] |
| Prospective cohort | USA | 333 CD and 270 UC patients | Yes/No | Adult patients Breastfeeding was statistically significant in its inverse relationships with CD-related surgery, no association with UC-related surgery |
Not reported | UC, CD (IBD-related surgery) | 2014 | Guo et al. [98] |
| Case control study | Australia | 154 MEM (middle Eastern Migrants in Australia) cases (75 CD; 79 UC), 153 MEM controls, 162Caucasian cases (85 CD; 77 UC), 173 Caucasian controls, 153 controls in Lebanon | Yes | Adults Declined risk of CD if breastfeeding ≥3 months and decreased risk of UC if breastfeeding ≥6 months |
Breastfeeding duration effects investigated | CD, UC | 2015 | Ko et al. [116] |
| Case control study | Asia-Pacific (China, HongKong, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Macau, Malaysia, Singapore,Thailand and Australia) | 442 cases and 940 controls | Yes | Childhood. Breastfeeding > 12 months reduced the risk of IBD |
0-6 months 7-12 months More than 12 months |
CD, UC | 2015 | Ng et al. [114] |
| Case control study | Canada | 973 CD and 698 UC, 10 488 controls | No | Childhood and adolescence between 0 and 20 years old No association between initiating breastfeeding at the time of birth or, alternatively, not initiating breastfeeding and being diagnosed with IBD later in life. The authors could not know how long breastfeeding was maintained after discharge. |
Not reported | CD, UC | 2016 | Bernstein et al. [122] |
| Prospective cohort | Australia | 81 CD and 51 UC patients, 103 controls | No | Adults |
Not reported | CD, UC | 2016 | Niewiadomski et al. [100] |
| Case control study | Brazil | 145 CD patients and 163 controls | No | Adults | Not reported | CD | 2017 | Salgado et al. [124] |
| Case control study | Italy | 102 CD and 162 UC, 103 controls | Yes/No | From early childhood to adolescence (between 1 and 18 years) No association reported between breastfeeding and UC Breastfeeding >3 months was associated with higher risk of developing CD |
Breastfeeding >3 months (as a variable in the multivariate analysis) | CD, UC | 2017 | Strisciuglio et al. [128] |
| Prospective cohort | North American (USA and Canada) | 1 119 | Yes | Pediatric cohort Exclusive breastfeeding inversely correlated with complicated pediatric CD. No difference according to exclusive breastfeeding duration (dichotomized <3 months to >3 months) |
Breastfeeding exposure was initially analyzed as any duration of exclusive breastfeeding (of these breastfed patients, 104 (13.4%) were exclusively breastfed for less than 1 month, 170 (21.8%) for 1–3 months, 170 (21.8%) for 3–6 months, and 302 (38.8%)). Subsquent analysis stratified by duration of breastfeeding and compared never, those with 1–3 months of exclusive breastfeeding, and children with >3 months of exclusive breastfeeding | Complicated CD, need for CD-related hospitalization, and surgery | 2018 | Lindoso et al. [97] |
| Case control study | Swiss | 617 CD, 494 UC and 352 controls | Yes/No | Adults Neither association with the risk of IBD or CD. A shorter duration (<6 months) was protective for UC |
<6 months vs 6 months | CD, UC | 2020 | Lautenschlager et al. [125] |
| Case control study | The Netherlands | 323 CD and 321 UC, 1348 controls | Yes/no | Adults. A protective effect was described when breastfeeding <3 months for CD, not for UC. |
<3 months vs > 3 months | CD, UC | 2020 | Van der Sloot et al. [151] |
| Case control study | Southeast Asian (Malaysia) | 38 CD and 32 UC patients, 140 healthy controls matched by gender, age and ethnicity | Yes/No | Children/Adolescents (<18 years) Breastfed ≥ 6 months was protective for UC but not CD |
Duration of breastfeeding considered | CD, UC | 2022 | Lee et al. [108] |
| Case control study | Israel | 405 CD and 341 UC, 2043 controls | No | Adults in a population with a follow-up of 50 years | Not reported | CD, UC | 2022 | Velosa et al. [146] |
| Design | Place | Sample size | Breastfeeding was associated with IBD |
Specific comments | Breastfeeding duration |
Main outcome | Publication date | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meta-analysis | International | 17 published-studies, five were graded to be of high quality | Yes | This meta-analysis demonstrates that breastfeeding has a statistically significant protective role against UC and an even greater role against CD. | Duration of breast-feeding was sought and documented | UC, CD | 2004 | Klement et al. [106] |
| Systematic review | International | Seven studies that included patients with early onset IBD | Yes | Breast milk exposure had a significant protective effect developing early-onset IBD. A non-significant difference was demonstrated for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease individually | Not reported | IBD | 2009 | Barclay et al. [105] |
| Meta-analysis | International | 35 studies including 7536 patients with CD, 7353 patients with UC, 330 222 controls | Yes | Magnitude of protection higher in Asian population. Similar magnitude of lower susceptibility in pediatric and adult-onset disease |
Stronger decreased risk when breastfeeding > 12 months as compared with 3 or 6 months | UC, CD | 2017 | Xu et al. [104] |
| Systematic review | China | Eight full-text with epidemiological data, 25 with risk factor data in Chinese and 7 full-text with epidemiological data, 12 with risk factor data in English were included for analysis | Yes | Two references underlined a protective effect in China for UC. Not reported for CD. | Not reported | IBD | 2018 | Cui et al. [103] |
| Systematic review | International | Two of the 17 articles included for the infant milk-feeding practices and IBD examined shorter versus longer durations of exclusive human milk feeding and none examined the intensity, proportion, or amount of human milk fed to mixed-fed infants. Thirteen articles examined the relationship between never versus ever feeding human milk and IBD. Nine articles examined the relationship between shorter versus longer durations of any human milk feeding and IBD | Yes/No | The relationship between never versus ever feeding human milk and IBD risk was inconclusive. This review includes 2 articles, which provided insufficient evidence to draw any conclusions about the relationship between the duration of exclusive breastfeeding and IBD. Feeding human milk for short durations or not at all associates with higher risk of diagnosed IBD | Shorter versus longer duration of any human milk feeding are associated with higher risk of IBD | IBD | 2019 | Güngor et al. [102] |
| Umbrella review of Meta-analysis | International | 53 eligible publication included with 71 reported trisk factors for IBD | Yes | Longer exposures were associated with decreased risk. The protective effect was greater in Asian than white individuals (and in studies conducted before 2000) | Discussed | UC, CD | 2019 | Piovani et al. [148] |
| Meta-analysis | International | Two cohort studies and 40 case-control studies | Yes | Breastfeeding, especially of longer duration, was protective against IBD development | Discussed | UC, CD | 2021 | Agrawal et al. [101] |
| Mendelian Randomization analysis | European | 418 109 | Yes | Relationships between colitis, and both physical activity and breastfeeding; breastfeeding decreased the risk of CD (in the univariate models) and UC (in the multivariate model). Genetically predicted breastfeeding was associated with lower risk of UC and CD | Not reported | UC, CD | 2023 | Saadh et al. [107] |
4. Early determinants of microbiota and colitis trajectories
4.1. General
4.2. Maternal IBD and gut microbiota
4.3. Gut microbiota and IBD: a possible intervention?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barker, D.J.; Winter, P.D.; Osmond, C.; Margetts, B.; Simmonds, S.J. Weight in infancy and death from ischaemic heart disease. Lancet 1989, 2, 577–580, doi:S0140-6736(89)90710-1 [pii]. [Google Scholar]
- Delpierre, C.; Lepeule, J.; Cordier, S.; Slama, R.; Heude, B.; Charles, M.A. [DOHaD: epidemiological researches]. Med Sci (Paris) 2016, 32, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A.; Cooper, C.; Thornburg, K.L. Effect of in utero and early-life conditions on adult health and disease. N Engl J Med 2008, 359, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, C.; Mazzantini, S.; Zuccotti, G.V. Nutrition in the First 1000 Days: The Origin of Childhood Obesity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.D.; Diaz-Castillo, C.; Chamorro-Garcia, R. Multigenerational metabolic disruption: Developmental origins and mechanisms of propagation across generations. Front Toxicol 2022, 4, 902201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, L.M.; Morrison, J.L.; Rattanatray, L.; Zhang, S.; Ozanne, S.E.; McMillen, I.C. The early origins of obesity and insulin resistance: timing, programming and mechanisms. Int J Obes (Lond) 2016, 40, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roseboom, T.; de Rooij, S.; Painter, R. The Dutch famine and its long-term consequences for adult health. Early Hum Dev 2006, 82, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Painter, R.C.; Osmond, C.; Gluckman, P.; Hanson, M.; Phillips, D.I.; Roseboom, T.J. Transgenerational effects of prenatal exposure to the Dutch famine on neonatal adiposity and health in later life. BJOG 2008, 115, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooij, S.R.; Bleker, L.S.; Painter, R.C.; Ravelli, A.C.; Roseboom, T.J. Lessons learned from 25 Years of Research into Long term Consequences of Prenatal Exposure to the Dutch famine 1944-45: The Dutch famine Birth Cohort. Int J Environ Health Res 2022, 32, 1432–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klooker, T.K.; Braak, B.; Painter, R.C.; de Rooij, S.R.; van Elburg, R.M.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; Roseboom, T.J.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. Exposure to severe wartime conditions in early life is associated with an increased risk of irritable bowel syndrome: a population-based cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol 2009, 104, 2250–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, M.A.; Delpierre, C.; Breant, B. [Developmental origin of health and adult diseases (DOHaD): evolution of a concept over three decades]. Med Sci (Paris) 2016, 32, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.D.; Heaton, T.L.; Goates, M.C.; Packer, J.M. Intersystem Implications of the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease: Advancing Health Promotion in the 21st Century. Healthcare (Basel) 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junien, C.; Panchenko, P.; Fneich, S.; Pirola, L.; Chriett, S.; Amarger, V.; Kaeffer, B.; Parnet, P.; Torrisani, J.; Bolanos Jimenez, F.; et al. [Epigenetics in transgenerational responses to environmental impacts: from facts and gaps]. Med Sci (Paris) 2016, 32, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marousez, L.; Lesage, J.; Eberle, D. Epigenetics: Linking Early Postnatal Nutrition to Obesity Programming? Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Bottacini, F.; Casey, E.; Turroni, F.; Mahony, J.; Belzer, C.; Delgado Palacio, S.; Arboleya Montes, S.; Mancabelli, L.; et al. The First Microbial Colonizers of the Human Gut: Composition, Activities, and Health Implications of the Infant Gut Microbiota. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2017, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautkramer, K.A.; Kreznar, J.H.; Romano, K.A.; Vivas, E.I.; Barrett-Wilt, G.A.; Rabaglia, M.E.; Keller, M.P.; Attie, A.D.; Rey, F.E.; Denu, J.M. Diet-Microbiota Interactions Mediate Global Epigenetic Programming in Multiple Host Tissues. Mol Cell 2016, 64, 982–992, doi:S1097-2765(16)30670-0[pii] 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.10.025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Loret de Mola, C.; Davies, N.M.; Victora, C.G.; Relton, C.L. Breastfeeding effects on DNA methylation in the offspring: A systematic literature review. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0173070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrio, F.; Martini, S.; Francavilla, R.; Corvaglia, L.; Cristofori, F.; Mastrolia, S.A.; Neu, J.; Rautava, S.; Russo Spena, G.; Raimondi, F.; et al. Epigenetic Matters: The Link between Early Nutrition, Microbiome, and Long-term Health Development. Front Pediatr 2017, 5, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Esch, B.; Porbahaie, M.; Abbring, S.; Garssen, J.; Potaczek, D.P.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; van Neerven, R.J.J. The Impact of Milk and Its Components on Epigenetic Programming of Immune Function in Early Life and Beyond: Implications for Allergy and Asthma. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, E.L.; Larson, L.M.; Cox, K.; Bettencourt, K.; Kubes, J.N.; Shankar, A.H. Do effects of early life interventions on linear growth correspond to effects on neurobehavioural development? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health 2019, 7, e1398–e1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, J.Y.; Armand, M.; Peyre, H.; Garcia, C.; Forhan, A.; De Agostini, M.; Charles, M.A.; Heude, B.; Group, E.M.-C.C.S. Breastfeeding, Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Levels in Colostrum and Child Intelligence Quotient at Age 5-6 Years. J Pediatr 2017, 183, 43–50 e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, E.; Ibanez, C.; Martinez-Samayoa, P.M.; Lomas-Soria, C.; Durand-Carbajal, M.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, G.L. Maternal Obesity: Lifelong Metabolic Outcomes for Offspring from Poor Developmental Trajectories During the Perinatal Period. Arch Med Res 2016, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.J.; Fowden, A.L.; Thornburg, K.L. Placental Origins of Chronic Disease. Physiol Rev 2016, 96, 1509–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastorci, F.; Linzalone, N.; Ait-Ali, L.; Pingitore, A. Environment in Children’s Health: A New Challenge for Risk Assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, D.; Desseyn, J.L.; Mischke, M.; Knol, J.; Turck, D.; Gottrand, F. Early-life origin of intestinal inflammatory disorders. Nutr Rev 2017, 75, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- https://apps.who.int/nutrition/topics/exclusive_breastfeeding/en/index.html. Breastfeeding. Availabe online: (accessed on 2021).
- Ames, S.R.; Lotoski, L.C.; Azad, M.B. Comparing early life nutritional sources and human milk feeding practices: personalized and dynamic nutrition supports infant gut microbiome development and immune system maturation. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2190305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.Y.; Tan, L.T.; Law, J.W.; Hong, K.W.; Ratnasingam, V.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Lee, L.H.; Letchumanan, V. Exploring the Potential of Human Milk and Formula Milk on Infants’ Gut and Health. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Huerou-Luron, I.; Blat, S.; Boudry, G. Breast- v. formula-feeding: impacts on the digestive tract and immediate and long-term health effects. Nutr Res Rev 2010, 23, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roze, J.C.; Darmaun, D.; Boquien, C.Y.; Flamant, C.; Picaud, J.C.; Savagner, C.; Claris, O.; Lapillonne, A.; Mitanchez, D.; Branger, B.; et al. The apparent breastfeeding paradox in very preterm infants: relationship between breast feeding, early weight gain and neurodevelopment based on results from two cohorts, EPIPAGE and LIFT. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e000834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.; Franca, G.V.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, L.S.; Parks, O.B.; Good, M. A Review of the Immunomodulating Components of Maternal Breast Milk and Protection Against Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Nutrients 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.S.; Chalmers, B.; Hodnett, E.D.; Sevkovskaya, Z.; Dzikovich, I.; Shapiro, S.; Collet, J.P.; Vanilovich, I.; Mezen, I.; Ducruet, T.; et al. Promotion of Breastfeeding Intervention Trial (PROBIT): a randomized trial in the Republic of Belarus. JAMA 2001, 285, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J. The adiposity rebound in the 21st century children: meaning for what? Korean J Pediatr 2018, 61, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Carpen, N.; Helve, O.; de Vos, W.M.; Korpela, K.; Salonen, A. Early-life gut microbiota and its connection to metabolic health in children: Perspective on ecological drivers and need for quantitative approach. EBioMedicine 2021, 69, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotiby, A.A. The role of breastfeeding as a protective factor against the development of the immune-mediated diseases: A systematic review. Front Pediatr 2023, 11, 1086999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.M.; Gao, Y.; de Groot, N.; Vonk, M.M.; Ulfman, L.; van Neerven, R.J.J. Babies, Bugs, and Barriers: Dietary Modulation of Intestinal Barrier Function in Early Life. Annu Rev Nutr 2022, 42, 165–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrick, B.M.; Rodriguez, L.; Lakshmikanth, T.; Pou, C.; Henckel, E.; Arzoomand, A.; Olin, A.; Wang, J.; Mikes, J.; Tan, Z.; et al. Bifidobacteria-mediated immune system imprinting early in life. Cell 2021, 184, 3884–3898 e3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olin, A.; Henckel, E.; Chen, Y.; Lakshmikanth, T.; Pou, C.; Mikes, J.; Gustafsson, A.; Bernhardsson, A.K.; Zhang, C.; Bohlin, K.; et al. Stereotypic Immune System Development in Newborn Children. Cell 2018, 174, 1277–1292 e1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Morales, A.; Caba, M.; Garcia-Juarez, M.; Caba-Flores, M.D.; Viveros-Contreras, R.; Martinez-Valenzuela, C. Breastfeeding Contributes to Physiological Immune Programming in the Newborn. Front Pediatr 2021, 9, 744104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgman, S.L.; Konya, T.; Azad, M.B.; Sears, M.R.; Becker, A.B.; Turvey, S.E.; Mandhane, P.J.; Subbarao, P.; Scott, J.A.; Field, C.J.; et al. Infant gut immunity: a preliminary study of IgA associations with breastfeeding. J Dev Orig Health Dis 2016, 7, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Hida, M.; Kohgo, T.; Fukunaga, Y. Changes in salivary and fecal secretory IgA in infants under different feeding regimens. Pediatr Int 2009, 51, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Secretory IgA: Designed for Anti-Microbial Defense. Front Immunol 2013, 4, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Ren, C.; Han, X.; Huang, W.; You, Y.; Zhan, J. Role of IgA in the early-life establishment of the gut microbiota and immunity: Implications for constructing a healthy start. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, C.; Baldridge, M.T.; Wallace, M.A.; D, C.A.; Burnham; Virgin, H. W.; Stappenbeck, T.S. Vertically transmitted faecal IgA levels determine extra-chromosomal phenotypic variation. Nature 2015, 521, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Profio, E.; Magenes, V.C.; Fiore, G.; Agostinelli, M.; La Mendola, A.; Acunzo, M.; Francavilla, R.; Indrio, F.; Bosetti, A.; D’Auria, E.; et al. Special Diets in Infants and Children and Impact on Gut Microbioma. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, M.C.; Stiemsma, L.T.; Amenyogbe, N.; Brown, E.M.; Finlay, B. The intestinal microbiome in early life: health and disease. Front Immunol 2014, 5, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brink, L.R.; Mercer, K.E.; Piccolo, B.D.; Chintapalli, S.V.; Elolimy, A.; Bowlin, A.K.; Matazel, K.S.; Pack, L.; Adams, S.H.; Shankar, K.; et al. Neonatal diet alters fecal microbiota and metabolome profiles at different ages in infants fed breast milk or formula. Am J Clin Nutr 2020, 111, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Differding, M.K.; Benjamin-Neelon, S.E.; Hoyo, C.; Ostbye, T.; Mueller, N.T. Timing of complementary feeding is associated with gut microbiota diversity and composition and short chain fatty acid concentrations over the first year of life. BMC Microbiol 2020, 20, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhed, F.; Roswall, J.; Peng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jia, H.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhong, H.; et al. Dynamics and Stabilization of the Human Gut Microbiome during the First Year of Life. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
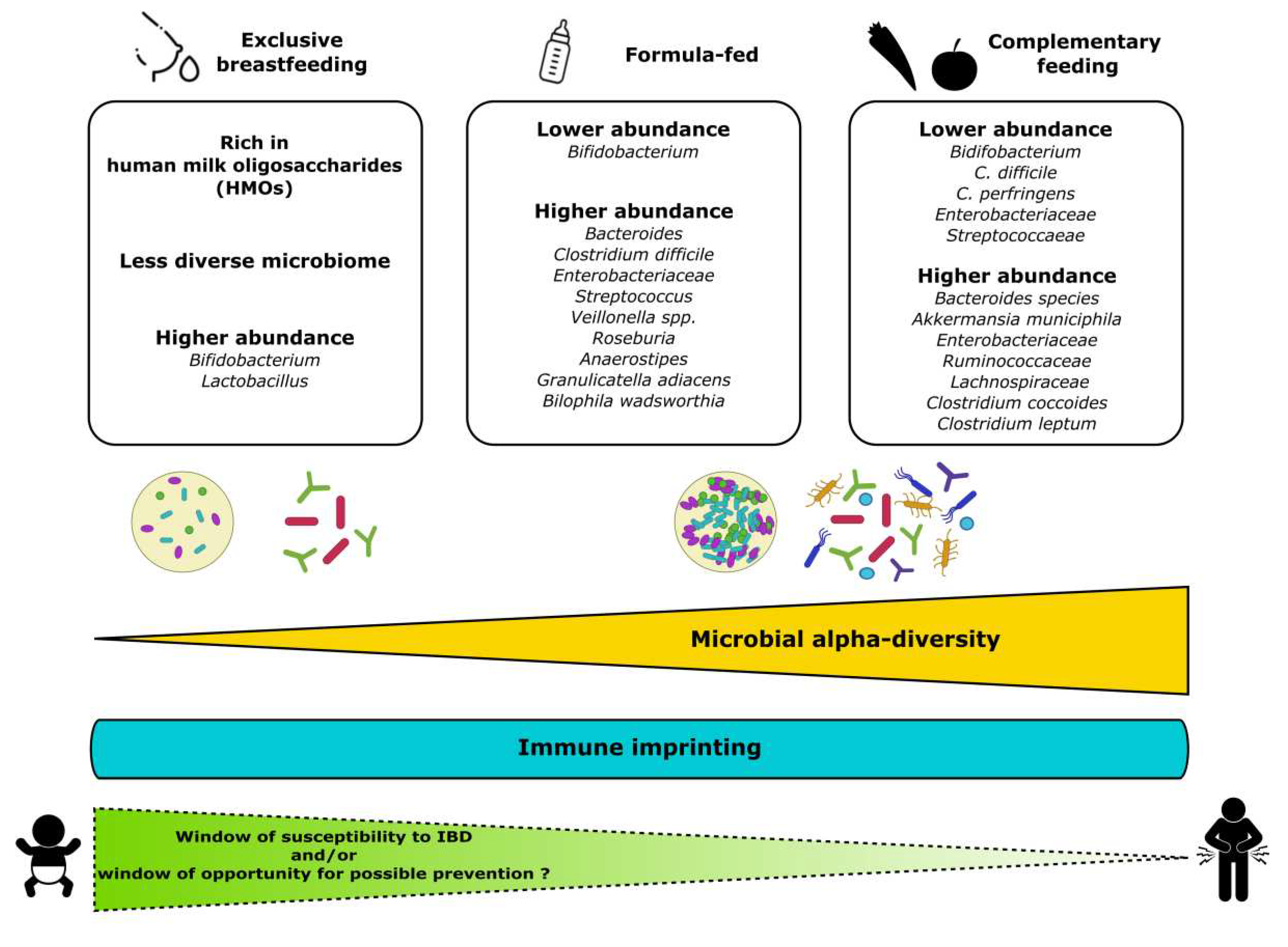
- Chichlowski, M.; van Diepen, J.A.; Prodan, A.; Olga, L.; Ong, K.K.; Kortman, G.A.M.; Dunger, D.B.; Gross, G. Early development of infant gut microbiota in relation to breastfeeding and human milk oligosaccharides. Front Nutr 2023, 10, 1003032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, H.; Zhuo, N.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, D. Comparison of gut microbiota in exclusively breast-fed and formula-fed babies: a study of 91 term infants. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 15792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbermatter, C.; Fernandez Trigo, N.; Christensen, S.; Ganal-Vonarburg, S.C. Maternal Microbiota, Early Life Colonization and Breast Milk Drive Immune Development in the Newborn. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 683022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lif Holgerson, P.; Esberg, A.; West, C.E.; Johansson, I. The breast milk and childhood gastrointestinal microbiotas and disease outcomes: a longitudinal study. Pediatr Res 2023, 93, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nabhani, Z.; Eberl, G. Imprinting of the immune system by the microbiota early in life. Mucosal Immunol 2020, 13, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinleyici, M.; Barbieur, J.; Dinleyici, E.C.; Vandenplas, Y. Functional effects of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs). Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2186115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chleilat, F.; Klancic, T.; Ma, K.; Schick, A.; Nettleton, J.E.; Reimer, R.A. Human Milk Oligosaccharide Supplementation Affects Intestinal Barrier Function and Microbial Composition in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Young Sprague Dawley Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gart, E.; Salic, K.; Morrison, M.C.; Giera, M.; Attema, J.; de Ruiter, C.; Caspers, M.; Schuren, F.; Bobeldijk-Pastorova, I.; Heer, M.; et al. The Human Milk Oligosaccharide 2’-Fucosyllactose Alleviates Liver Steatosis, ER Stress and Insulin Resistance by Reducing Hepatic Diacylglycerols and Improved Gut Permeability in Obese Ldlr-/-.Leiden Mice. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 904740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivak, I.; Fluhr, L.; Elinav, E. Local and systemic effects of microbiome-derived metabolites. EMBO Rep 2022, 23, e55664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, L.F.; Geddes, D.T. Microbial metabolites: the next frontier in human milk. Trends Microbiol 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; He, C.; Fu, C.; Wei, Q. The role of the gut microbiota in health and cardiovascular diseases. Mol Biomed 2022, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.E.; Wotton, C.J.; Williams, J.G.; Griffith, M.; Goldacre, M.J. Perinatal and early life risk factors for inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2011, 17, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, A.J.; Nowak, J.K.; Adams, A.T.; Uhlig, H.H.; Satsangi, J. Defining Interactions Between the Genome, Epigenome, and the Environment in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Progress and Prospects. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 44–60 e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleynen, I.; Boucher, G.; Jostins, L.; Schumm, L.P.; Zeissig, S.; Ahmad, T.; Andersen, V.; Andrews, J.M.; Annese, V.; Brand, S.; et al. Inherited determinants of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis phenotypes: a genetic association study. Lancet 2016, 387, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, S.; Zielinska, M.; Sokal, A.; Filip, R. Genetic and Epigenetic Etiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Update. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, D.R.; Russell, R.K.; Nimmo, E.R.; Satsangi, J. New genes in inflammatory bowel disease: lessons for complex diseases? Lancet 2006, 367, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montbarbon, M.; Pichavant, M.; Langlois, A.; Erdual, E.; Maggiotto, F.; Neut, C.; Mallevaey, T.; Dharancy, S.; Dubuquoy, L.; Trottein, F.; et al. Colonic inflammation in mice is improved by cigarette smoke through iNKT cells recruitment. PLoS One 2013, 8, e62208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzig, M.E.; Fung, S.G.; Marderfeld, L.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Kaplan, G.G.; Ng, S.C.; Wilson, D.C.; Cameron, F.; Henderson, P.; Kotze, P.G.; et al. Twenty-first Century Trends in the Global Epidemiology of Pediatric-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1147–1159 e1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, J.; Pomahacova, R.; Kreslova, M.; Cvalinova, D.; Stych, P.; Schwarz, J. Current global trends in the incidence of pediatric-onset inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2018, 24, 2741–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubatan, J.; Kulkarni, C.V.; Talamantes, S.M.; Temby, M.; Fardeen, T.; Sinha, S.R. Dietary Exposures and Interventions in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Evidence and Emerging Concepts. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Albenberg, L.; Compher, C.; Baldassano, R.; Piccoli, D.; Lewis, J.D.; Wu, G.D. Diet in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albenberg, L. The Role of Diet in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2023, 52, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Impact of Diet on Risk of IBD. Crohns Colitis 360 2020, 2, otz054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsandegwaza, B.; Horsnell, W.; Smith, K. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review of Pre-Clinical Murine Models of Human Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, E.; Margonis, G.A.; Angelou, A.; Pikouli, A.; Argiri, P.; Karavokyros, I.; Papalois, A.; Pikoulis, E. The TNBS-induced colitis animal model: An overview. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2016, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Aitken, J.D.; Malleshappa, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Curr Protoc Immunol 2014, 104, 15 25 11–15 25 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesler, P.; Fuss, I.J.; Strober, W. Experimental Models of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015, 1, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, K.L.; Fedorak, R.N.; Tavernini, M.M.; Doyle, J.S. Normal Breast Milk Limits the Development of Colitis in IL-10-Deficient Mice. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2002, 8, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Villoslada, F.; Debras, E.; Nieto, A.; Concha, A.; Galvez, J.; Lopez-Huertas, E.; Boza, J.; Obled, C.; Xaus, J. Oligosaccharides isolated from goat milk reduce intestinal inflammation in a rat model of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Clin Nutr 2006, 25, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daddaoua, A.; Puerta, V.; Requena, P.; Martinez-Ferez, A.; Guadix, E.; de Medina, F.S.; Zarzuelo, A.; Suarez, M.D.; Boza, J.J.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Goat milk oligosaccharides are anti-inflammatory in rats with hapten-induced colitis. J Nutr 2006, 136, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrer, A.; Sprenger, N.; Kurakevich, E.; Borsig, L.; Chassard, C.; Hennet, T. Milk sialyllactose influences colitis in mice through selective intestinal bacterial colonization. J Exp Med 2010, 207, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurl, S.; Munzert, M.; Boehm, G.; Matthews, C.; Stahl, B. Systematic review of the concentrations of oligosaccharides in human milk. Nutr Rev 2017, 75, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.A.; Mukerji, P.; Kelder, B.; Erney, R.; Gonzalez, D.; Yun, J.S.; Smith, D.F.; Moremen, K.W.; Nardelli, C.; Pierce, M.; et al. Remodeling of mouse milk glycoconjugates by transgenic expression of a human glycosyltransferase. J Biol Chem 1995, 270, 29515–29519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabinger, T.; Glaus Garzon, J.F.; Hausmann, M.; Geirnaert, A.; Lacroix, C.; Hennet, T. Alleviation of Intestinal Inflammation by Oral Supplementation With 2-Fucosyllactose in Mice. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai-li Li, W.-w.N. , Ying Li, Xin Zhang, Jia-jie Yang, Xiang-yang Ma, Xin-dong Jia, Chun Li, Li-bo Liu. Effect of 2′-fucosyllactose supplementation on intestinal flora in mice with intestinal inflammatory diseases. International Dairy Journal 2020, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Yin, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Differential responses on gut microbiota and microbial metabolome of 2’-fucosyllactose and galactooligosaccharide against DSS-induced colitis. Food Res Int 2022, 162, 112072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Fan, L.; Zheng, N.; Blecker, C.; Delcenserie, V.; Li, H.; Wang, J. 2’-Fucosyllactose Ameliorates Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Promoting MUC2 Expression. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 822020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.H.; Shin, C.S.; Yoon, J.W.; Jeon, S.M.; Song, Y.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, K. 2’-Fucosyllactose and 3-Fucosyllactose Alleviates Interleukin-6-Induced Barrier Dysfunction and Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis by Improving Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulating the Intestinal Microbiome. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmoussa, A.; Diallo, I.; Salem, M.; Michel, S.; Gilbert, C.; Sevigny, J.; Provost, P. Concentrates of two subsets of extracellular vesicles from cow’s milk modulate symptoms and inflammation in experimental colitis. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, S.; Elbaum-Shiff, Y.; Koroukhov, N.; Shilo, I.; Musseri, M.; Golan-Gerstl, R. Cow and Human Milk-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Colitis in DSS Murine Model. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Paz, H.A.; Sadri, M.; Cui, J.; Kachman, S.D.; Fernando, S.C.; Zempleni, J. Dietary bovine milk exosomes elicit changes in bacterial communities in C57BL/6 mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2019, 317, G618–G624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Hao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yi, H. Oral Administration of Bovine Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Alters the Gut Microbiota and Enhances Intestinal Immunity in Mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 2020, 64, e1901251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, T.; Gong, P.; Zhang, L.; Cao, F.; et al. Milk-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate ulcerative colitis by regulating the gut immunity and reshaping the gut microbiota. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8570–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C.; Hao, H.; Tan, M.S.; Yu, X.; Lou, C.K.L.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Milk-derived extracellular vesicles protect intestinal barrier integrity in the gut-liver axis. Sci Adv 2023, 9, eade5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindoso, L.; Mondal, K.; Venkateswaran, S.; Somineni, H.K.; Ballengee, C.; Walters, T.D.; Griffiths, A.; Noe, J.D.; Crandall, W.; Snapper, S.; et al. The Effect of Early-Life Environmental Exposures on Disease Phenotype and Clinical Course of Crohn’s Disease in Children. Am J Gastroenterol 2018, 113, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.Y.; Stevens, B.W.; Wilson, R.G.; Russell, C.N.; Cohen, M.A.; Sturgeon, H.C.; Thornton, A.; Giallourakis, C.; Khalili, H.; Nguyen, D.D.; et al. Early life environment and natural history of inflammatory bowel diseases. BMC Gastroenterol 2014, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili, H.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Higuchi, L.M.; Richter, J.M.; Fuchs, C.S.; Chan, A.T. Early life factors and risk of inflammatory bowel disease in adulthood. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2013, 19, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiadomski, O.; Studd, C.; Wilson, J.; Williams, J.; Hair, C.; Knight, R.; Prewett, E.; Dabkowski, P.; Alexander, S.; Allen, B.; et al. Influence of food and lifestyle on the risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease. Intern Med J 2016, 46, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Sabino, J.; Frias-Gomes, C.; Hillenbrand, C.M.; Soudant, C.; Axelrad, J.E.; Shah, S.C.; Ribeiro-Mourao, F.; Lambin, T.; Peter, I.; et al. Early life exposures and the risk of inflammatory bowel disease: Systematic review and meta-analyses. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 36, 100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, D.; Nadaud, P.; Dreibelbis, C.; LaPergola, C.C.; Wong, Y.P.; Terry, N.; Abrams, S.A.; Beker, L.; Jacobovits, T.; Jarvinen, K.M.; et al. Infant milk-feeding practices and diagnosed celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease in offspring: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr 2019, 109, 838S–851S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Yuan, A. A Systematic Review of Epidemiology and Risk Factors Associated With Chinese Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Med (Lausanne) 2018, 5, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Lochhead, P.; Ko, Y.; Claggett, B.; Leong, R.W.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Systematic review with meta-analysis: breastfeeding and the risk of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2017, 46, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, A.R.; Russell, R.K.; Wilson, M.L.; Gilmour, W.H.; Satsangi, J.; Wilson, D.C. Systematic review: the role of breastfeeding in the development of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr 2009, 155, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klement, E.; Cohen, R.V.; Boxman, J.; Joseph, A.; Reif, S. Breastfeeding and risk of inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 2004, 80, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadh, M.J.; Pal, R.S.; Arias-Gonzales, J.L.; Orosco Gavilan, J.C.; Jc, D.; Mohany, M.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Bahrami, A.; Kadham, M.J.; Amin, A.H.; et al. A Mendelian Randomization Analysis Investigates Causal Associations between Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Variable Risk Factors. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Song, Z.L.; Wong, S.Y.; Gan, C.W.; Koay, Z.L.; Em, J.M.; Chong, S.Y.; Lim, C.B.; Wong, S.Y.; Chew, K.S.; et al. Environmental risk factors for inflammatory bowel disease: A case control study in Southeast Asian children. J Paediatr Child Health 2022, 58, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urashima, H. , Ohmori, I., Shiraki, K. Epidemiological Survey on Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease Developed during Childhood in Japan, and a Case-Control Study on Nutrition during Infancy. Yonago Acta medica 1999, 42, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Gearry, R.B.; Richardson, A.K.; Frampton, C.M.; Dodgshun, A.J.; Barclay, M.L. Population-based cases control study of inflammatory bowel disease risk factors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010, 25, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xia, B.; Li, J.; Ye, M.; Deng, C.; Ding, Y.; Luo, H.; Ren, H.; Hou, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Risk factors for ulcerative colitis in a Chinese population: an age-matched and sex-matched case-control study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2007, 41, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.Y.; Fraser, A.G.; Dryland, P.; Ferguson, L.R. Environmental factors in the development of chronic inflammation: a case-control study on risk factors for Crohn’s disease within New Zealand. Mutat Res 2010, 690, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, H. , Chaharmahali, M., Momtahen, Sh., Kolahdoozan, Sh., Khademi, H., Olfati, G., Tabrizian, T., Rashtak, S., Khaleghnejad, R., Naserimoghadam, S., Malekzadeh, F., Malekzadeh, R. A Case-Control study on the risk factors of IBD in 258 Iranian patients. Govaresh 2011, 16, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, S.C.; Tang, W.; Leong, R.W.; Chen, M.; Ko, Y.; Studd, C.; Niewiadomski, O.; Bell, S.; Kamm, M.A.; de Silva, H.J.; et al. Environmental risk factors in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based case-control study in Asia-Pacific. Gut 2015, 64, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Ou-Yang, Q.; Xia, B.; Liu, L.N.; Gu, F.; Zhou, K.F.; Mei, Q.; Shi, R.H.; Ran, Z.H.; Wang, X.D.; et al. Multicenter case-control study of the risk factors for ulcerative colitis in China. World J Gastroenterol 2013, 19, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Kariyawasam, V.; Karnib, M.; Butcher, R.; Samuel, D.; Alrubaie, A.; Rahme, N.; McDonald, C.; Cowlishaw, J.; Katelaris, P.; et al. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Environmental Risk Factors: A Population-Based Case-Control Study of Middle Eastern Migration to Australia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015, 13, 1453–1463 e1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, S.; Griffiths, A.; Corey, M.; Smith, C.; Sherman, P. Infant feeding practices and ulcerative colitis in childhood. BMJ 1991, 302, 1580–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, S.; Sherman, P.; Corey, M.; Griffiths, A.; Smith, C. Role of infant feeding practices in development of Crohn’s disease in childhood. BMJ 1989, 298, 1617–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigas, A.; Rigas, B.; Glassman, M.; Yen, Y.Y.; Lan, S.J.; Petridou, E.; Hsieh, C.C.; Trichopoulos, D. Breast-feeding and maternal smoking in the etiology of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in childhood. Ann Epidemiol 1993, 3, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, M.; Marshall, J.R.; Zielezny, M.; Lance, P. A case-control study to examine the influence of maternal perinatal behaviors on the incidence of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterol Nurs 1996, 19, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amre, D.K.; Lambrette, P.; Law, L.; Krupoves, A.; Chotard, V.; Costea, F.; Grimard, G.; Israel, D.; Mack, D.; Seidman, E.G. Investigating the hygiene hypothesis as a risk factor in pediatric onset Crohn’s disease: a case-control study. Am J Gastroenterol 2006, 101, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, C.N.; Banerjee, A.; Targownik, L.E.; Singh, H.; Ghia, J.E.; Burchill, C.; Chateau, D.; Roos, L.L. Cesarean Section Delivery Is Not a Risk Factor for Development of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Population-based Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016, 14, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutfless, S.; Li, D.K.; Heyman, M.B.; Bayless, T.M.; Abramson, O.; Herrinton, L.J. Prenatal and perinatal characteristics associated with pediatric-onset inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 2012, 57, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, V.C.L.; Luiz, R.R.; Boechat, N.; Schorr, B.C.; Leao, I.S.; Nunes, T.; Zaltman, C. Crohn’s disease environmental factors in the developing world: A case-control study in a statewide catchment area in Brazil. World J Gastroenterol 2017, 23, 5549–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautenschlager, S.A.; Fournier, N.; Biedermann, L.; Pittet, V.; Schreiner, P.; Misselwitz, B.; Scharl, M.; Rogler, G.; Siebenhuner, A.R. The Influence of Breastfeeding, Cesarean Section, Pet Animals, and Urbanization on the Development of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Data from the Swiss IBD Cohort Study. Inflamm Intest Dis 2020, 5, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Sloot, K.W.J.; Weersma, R.K.; Alizadeh, B.Z.; Dijkstra, G. Identification of Environmental Risk Factors Associated With the Development of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekbom, A.; Adami, H.O.; Helmick, C.G.; Jonzon, A.; Zack, M.M. Perinatal risk factors for inflammatory bowel disease: a case-control study. Am J Epidemiol 1990, 132, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strisciuglio, C.; Giugliano, F.; Martinelli, M.; Cenni, S.; Greco, L.; Staiano, A.; Miele, E. Impact of Environmental and Familial Factors in a Cohort of Pediatric Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2017, 64, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstrand, O.; Hellers, G. Breast-feeding during infancy in patients who later develop Crohn’s disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 1983, 18, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelsson, S.M.; Ekbom, A.; Zack, M.; Helmick, C.G.; Adami, H.O. Risk factors for extensive ulcerative colitis and ulcerative proctitis: a population based case-control study. Gut 1991, 32, 1526–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, P.G.; Leijonmarck, C.E.; Bernell, O.; Hellers, G.; Ahlbom, A. Risk indicators for inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Epidemiol 1993, 22, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Tragnone, A.; Caprilli, R.; Trallori, G.; Papi, C.; Andreoli, A.; Di Paolo, M.; Riegler, G.; Rigo, G.P.; Ferrau, O.; et al. Risk of inflammatory bowel disease attributable to smoking, oral contraception and breastfeeding in Italy: a nationwide case-control study. Cooperative Investigators of the Italian Group for the Study of the Colon and the Rectum (GISC). Int J Epidemiol 1998, 27, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, N.P.; Montgomery, S.M.; Wadsworth, M.E.; Pounder, R.E.; Wakefield, A.J. Early determinants of inflammatory bowel disease: use of two national longitudinal birth cohorts. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2000, 12, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Serrano, P.; Perez-Calle, J.L.; Perez-Fernandez, M.T.; Fernandez-Font, J.M.; Boixeda de Miguel, D.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, C.M. Environmental risk factors in inflammatory bowel diseases. Investigating the hygiene hypothesis: a Spanish case-control study. Scand J Gastroenterol 2010, 45, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russel, M.G.; Engels, L.G.; Muris, J.W.; Limonard, C.B.; Volovics, A.; Brummer, R.J.; Stockbrugger, R.W. Modern life’ in the epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: a case-control study with special emphasis on nutritional factors. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1998, 10, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, S.; Turck, D.; Leplat, C.; Merle, V.; Gower-Rousseau, C.; Marti, R.; Yzet, T.; Lerebours, E.; Dupas, J.L.; Debeugny, S.; et al. Environmental risk factors in paediatric inflammatory bowel diseases: a population based case control study. Gut 2005, 54, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, E.; Engelmann, G.; Findeisen, A.; Gerner, P.; Laass, M.; Ney, D.; Posovszky, C.; Hoy, L.; Hornef, M.W. Cesarean delivery is associated with celiac disease but not inflammatory bowel disease in children. Pediatrics 2010, 125, e1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.S.; Jess, T.; Vind, I.; Elkjaer, M.; Nielsen, M.F.; Gamborg, M.; Munkholm, P. Environmental factors in inflammatory bowel disease: a case-control study based on a Danish inception cohort. J Crohns Colitis 2011, 5, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonntag, B.; Stolze, B.; Heinecke, A.; Luegering, A.; Heidemann, J.; Lebiedz, P.; Rijcken, E.; Kiesel, L.; Domschke, W.; Kucharzik, T.; et al. Preterm birth but not mode of delivery is associated with an increased risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease later in life. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2007, 13, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radon, K.; Windstetter, D.; Poluda, A.L.; Mueller, B.; von Mutius, E.; Koletzko, S.; Chronische Autoimmunerkrankungen und Kontakt zu Tieren Study, G. Contact with farm animals in early life and juvenile inflammatory bowel disease: a case-control study. Pediatrics 2007, 120, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, C.; Paerregaard, A.; Munkholm, P.; Wewer, V. Environmental factors and risk of developing paediatric inflammatory bowel disease -- a population based study 2007-2009. J Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, F.; Diaferia, M.; Morace, F.; Labianca, O.; Meucci, C.; Cuomo, A.; Panarese, A.; Romano, M.; Sorrentini, I.; D’Onofrio, C.; et al. Risk factors for inflammatory bowel diseases according to the “hygiene hypothesis”: a case-control, multi-centre, prospective study in Southern Italy. J Crohns Colitis 2012, 6, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whorwell, P.J.; Holdstock, G.; Whorwell, G.M.; Wright, R. Bottle feeding, early gastroenteritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Br Med J 1979, 1, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavaty, T.; Toth, J.; Koller, T.; Krajcovicova, A.; Oravcova, S.; Zelinkova, Z.; Huorka, M. Smoking, breastfeeding, physical inactivity, contact with animals, and size of the family influence the risk of inflammatory bowel disease: A Slovak case-control study. United European Gastroenterol J 2013, 1, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, I.; Reif, S.; Farbstein, H.; Halak, A.; Gilat, T. Preillness non dietary factors and habits in inflammatory bowel disease. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1998, 30, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Velosa, M.; Hochner, H.; Yerushalmi, B.; Harel, S.; Friss, C.; Calderon-Margalit, R.; Paltiel, O.; Manor, O.; Balicer, R.D.; Greenfeld, S.; et al. Pre- and Perinatal Factors Predicting Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Population-Based Study with Fifty Years of Follow-Up. J Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilat, T.; Hacohen, D.; Lilos, P.; Langman, M.J. Childhood factors in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. An international cooperative study. Scand J Gastroenterol 1987, 22, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovani, D.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Nikolopoulos, G.K.; Lytras, T.; Bonovas, S. Environmental Risk Factors for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 647–659 e644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Epidemiology and risk factors for IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015, 12, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolph, T.E.; Zhang, J. Diet fuelling inflammatory bowel diseases: preclinical and clinical concepts. Gut 2022, 71, 2574–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sloot, K.W.J.; Amini, M.; Peters, V.; Dijkstra, G.; Alizadeh, B.Z. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Review of Known Environmental Protective and Risk Factors Involved. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2017, 23, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raygoza Garay, J.A.; Turpin, W.; Lee, S.H.; Smith, M.I.; Goethel, A.; Griffiths, A.M.; Moayyedi, P.; Espin-Garcia, O.; Abreu, M.; Aumais, G.L.; et al. Gut Microbiome Composition Is Associated With Future Onset of Crohn’s Disease in Healthy First-Degree Relatives. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliland, A.; Chan, J.; De Wolfe, T.J.; Yang, H.; Vallance, B.A. Pathobionts in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Origins, Underlying Mechanisms, and Implications for Clinical Care. Gastroenterology, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Estelle, J.; Tambosco, K.; Chadi, S.; Maillard, F.; Gallopin, M.; Planchais, J.; Chain, F.; Kropp, C.; et al. Gut barrier-microbiota imbalances in early life lead to higher sensitivity to inflammation in a murine model of C-section delivery. Microbiome 2023, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Hu, J.; Seki, A.; Eisele, C.; Nair, N.; Huang, R.; Tarassishin, L.; Jharap, B.; Cote-Daigneault, J.; Mao, Q.; et al. Infants born to mothers with IBD present with altered gut microbiome that transfers abnormalities of the adaptive immune system to germ-free mice. Gut 2020, 69, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.S.; Tarassishin, L.; Eisele, C.; Barre, A.; Nair, N.; Rendon, A.; Hawkins, K.; Debebe, A.; White, S.; Thjomoe, A.; et al. Longitudinal Changes in Fecal Calprotectin Levels Among Pregnant Women With and Without Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Their Babies. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1118–1130 e1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quin, C.; Gibson, D.L. Human behavior, not race or geography, is the strongest predictor of microbial succession in the gut bacteriome of infants. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1143–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voreades, N.; Kozil, A.; Weir, T.L. Diet and the development of the human intestinal microbiome. Front Microbiol 2014, 5, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roswall, J.; Olsson, L.M.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Nilsson, S.; Tremaroli, V.; Simon, M.C.; Kiilerich, P.; Akrami, R.; Kramer, M.; Uhlen, M.; et al. Developmental trajectory of the healthy human gut microbiota during the first 5 years of life. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 765–776 e763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmela, C.; Chevarin, C.; Xu, Z.; Torres, J.; Sevrin, G.; Hirten, R.; Barnich, N.; Ng, S.C.; Colombel, J.F. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2018, 67, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.P.; Longhi, C.; Marazzato, M.; Conte, A.L.; Aleandri, M.; Lepanto, M.S.; Zagaglia, C.; Nicoletti, M.; Aloi, M.; Totino, V.; et al. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC) in pediatric Crohn’s disease patients: phenotypic and genetic pathogenic features. BMC Res Notes 2014, 7, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wymore Brand, M.; Proctor, A.L.; Hostetter, J.M.; Zhou, N.; Friedberg, I.; Jergens, A.E.; Phillips, G.J.; Wannemuehler, M.J. Vertical transmission of attaching and invasive E. coli from the dam to neonatal mice predisposes to more severe colitis following exposure to a colitic insult later in life. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0266005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.P.; Rochat, F.; Chassard, C. Vertical mother-neonate transfer of maternal gut bacteria via breastfeeding. Environ Microbiol 2014, 16, 2891–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, H.; Martin, R.; Ishikawa, E.; Gawad, A.; Kubota, H.; Sakai, T.; Oishi, K.; Tanaka, R.; Ben-Amor, K.; Knol, J.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing of bifidobacterial strains from infant’s faeces and human milk: are bifidobacteria being sustainably shared during breastfeeding? Benef Microbes 2015, 6, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Ma, X. Dietary Inulin Regulated Gut Microbiota and Improved Neonatal Health in a Pregnant Sow Model. Front Nutr 2021, 8, 716723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatelais, L.; Jamin, A.; Gras-Le Guen, C.; Lalles, J.P.; Le Huerou-Luron, I.; Boudry, G. The level of protein in milk formula modifies ileal sensitivity to LPS later in life in a piglet model. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudry, G.; Jamin, A.; Chatelais, L.; Gras-Le Guen, C.; Michel, C.; Le Huerou-Luron, I. Dietary protein excess during neonatal life alters colonic microbiota and mucosal response to inflammatory mediators later in life in female pigs. J Nutr 2013, 143, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.V.; Naidu, K.A. Maternal and neonatal dietary intake of balanced n-6/n-3 fatty acids modulates experimental colitis in young adult rats. Eur J Nutr 2016, 55, 1875–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, A.; Mantel, M.; Marchix, J.; Bodinier, M.; Jan, G.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M. Inflammatory bowel disease therapeutic strategies by modulation of the microbiota: how and when to introduce pre-, pro-, syn-, or postbiotics? Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2022, 323, G523–G553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskey, N.; Dahl, W.J. Synbiotic therapy: a promising new adjunctive therapy for ulcerative colitis. Nutr Rev 2006, 64, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Cordisco, L.; Tarasco, V.; Palumeri, E.; Calabrese, R.; Oggero, R.; Roos, S.; Matteuzzi, D. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 in infantile colic: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatrics 2010, 126, e526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Cai, D.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Qu, H.; Zong, Q.; Bao, W.; Chen, A.; Liu, H.Y. How Early-Life Gut Microbiota Alteration Sets Trajectories for Health and Inflammatory Bowel Disease? Front Nutr 2021, 8, 690073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nabhani, Z.; Dulauroy, S.; Marques, R.; Cousu, C.; Al Bounny, S.; Dejardin, F.; Sparwasser, T.; Berard, M.; Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Eberl, G. A Weaning Reaction to Microbiota Is Required for Resistance to Immunopathologies in the Adult. Immunity 2019, 50, 1276–1288 e1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiemsma, L.T.; Michels, K.B. The Role of the Microbiome in the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease. Pediatrics 2018, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronman, M.P.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Haynes, K.; Feng, R.; Coffin, S.E. Antibiotic exposure and IBD development among children: a population-based cohort study. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theochari, N.A.; Stefanopoulos, A.; Mylonas, K.S.; Economopoulos, K.P. Antibiotics exposure and risk of inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review. Scand J Gastroenterol 2018, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchimol, E.I.; Kaplan, G.G.; Otley, A.R.; Nguyen, G.C.; Underwood, F.E.; Guttmann, A.; Jones, J.L.; Potter, B.K.; Catley, C.A.; Nugent, Z.J.; et al. Rural and Urban Residence During Early Life is Associated with Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Population-Based Inception and Birth Cohort Study. Am J Gastroenterol 2017, 112, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Dunsmore, G.; Koleva, P.; Elloumi, Y.; Wu, R.Y.; Sutton, R.T.; Ambrosio, L.; Hotte, N.; Nguyen, V.; Madsen, K.L.; et al. The Profile of Human Milk Metabolome, Cytokines, and Antibodies in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Versus Healthy Mothers, and Potential Impact on the Newborn. J Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





