Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
0. Introduction
1. Richard Kerner agglomeration model
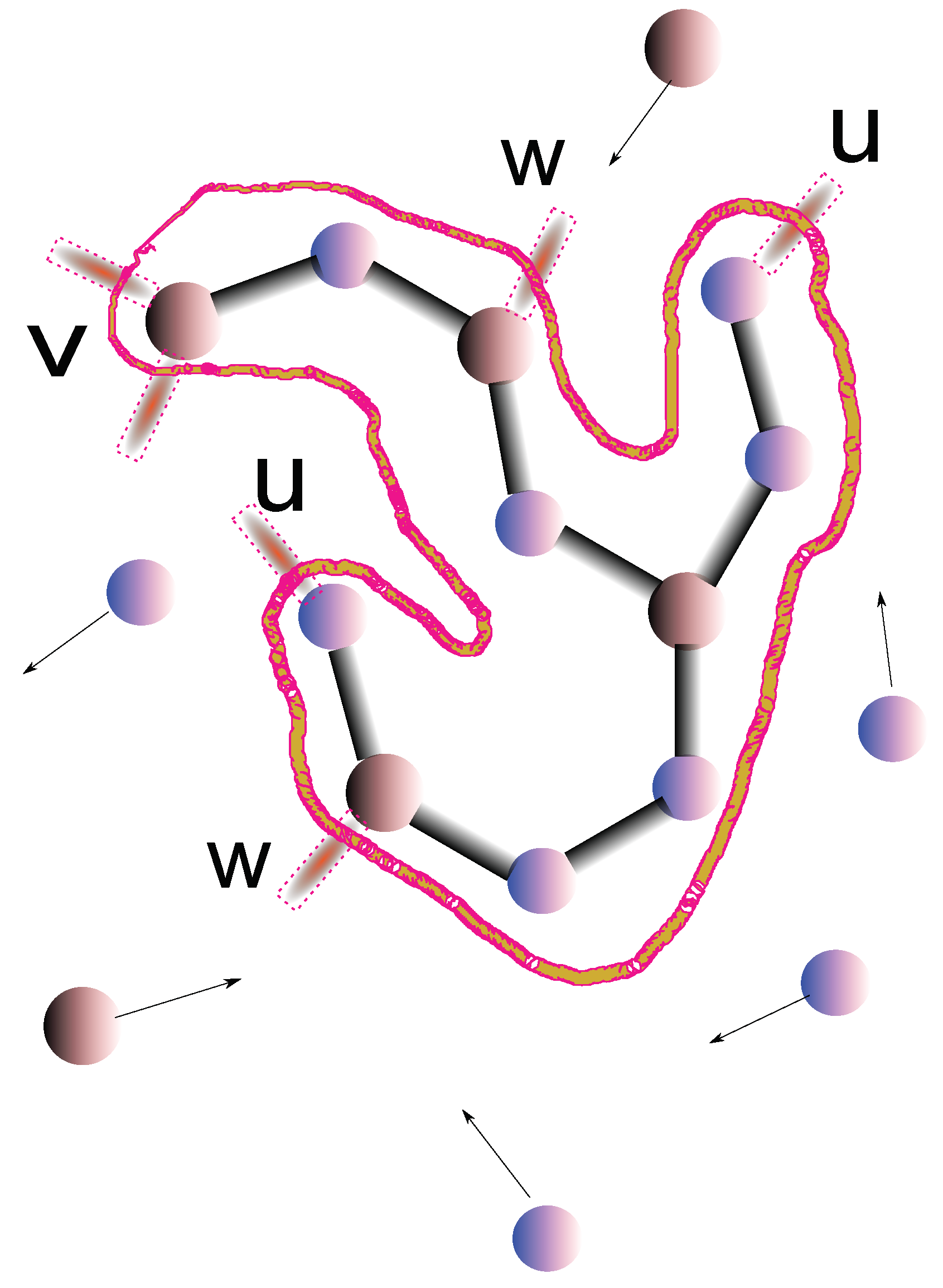
- The number of ways in which a bond can be made.
- The Bond Energy;
- The concentration of atomic species
- The temperature
- u+Se;
- u+As;
- v+Se;
- v+As;
- w+Se;
- w+As; .
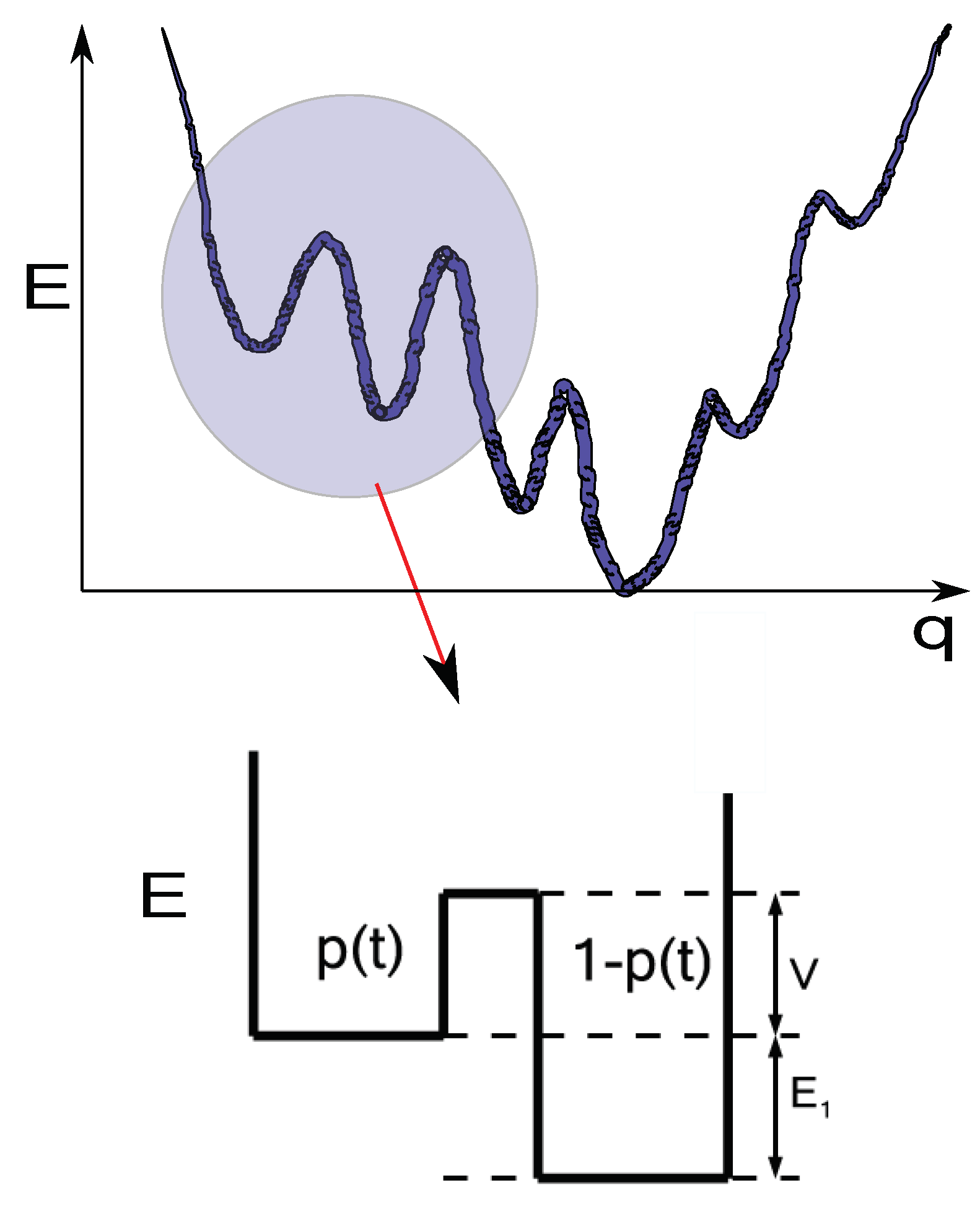
2. Translation to the energy landscape paradigm and path integrals
- The method is too simple to work.
- Topology is taken into account in a very simplistic way, just by counting the number of bonding possibilities.
- The transition elements of the stochastic matrix use Boltzmann factors, but agglomeration is usually a non-equilibrium processes.
3. Transition probabilities of the agglomeration process
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RK | Richard Kerner |
References
- Chaikin, P.; Lubensky, T. Principles of Condensed Matter Physics; Cambridge University Press, 2000.
- Kerner, R. Models of Agglomeration and Glass Transition; Imperial College Press, 2006.
- Jooss, C. Self-organization of Matter: A dialectical approach to evolution of matter in the microcosm and macrocosmos; De Gruyter STEM, De Gruyter, 2020. https://www.pnas.org/doi/pdf/10.1073/pnas.0608517103.
- Sethna, J. Statistical Mechanics: Entropy, Order Parameters and Complexity; Oxford Master Series in Physics, OUP Oxford, 2006.
- Rylance, G.J.; Johnston, R.L.; Matsunaga, Y.; Li, C.B.; Baba, A.; Komatsuzaki, T. Topographical complexity of multidimensional energy landscapes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2006, 103, 18551–18555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, G.; Urbani, P.; Zamponi, F. Theory of Simple Glasses: Exact Solutions in Infinite Dimensions; Cambridge University Press, 2020.
- Welch, R.S.; Zanotto, E.D.; Wilkinson, C.J.; Cassar, D.R.; Montazerian, M.; Mauro, J.C. Cracking the Kauzmann paradox. Acta Materialia 2023, 254, 118994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bore, S.L.; Paesani, F. Realistic phase diagram of water from first principles data-driven quantum simulations. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roder, K.; Joseph, J.A.; Husic, B.E.; Wales, D.J. Energy Landscapes for Proteins: From Single Funnels to Multifunctional Systems. Advanced Theory and Simulations 2019, 2, 1800175. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/adts.201800175. [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Rojo, R.; Mora, M.; Board, S.; Walker, J.; Boujemaa-Paterski, R.; Medalia, O.; Garcia-Manyes, S. Enhanced statistical sampling reveals microscopic complexity in the talin mechanosensor folding energy landscape. Nature Physics 2023, 19, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, C.M. Protein-misfolding diseases: Getting out of shape. Nature 2002, 418, 729–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinthal, C. Are there pathways for protein folding? J. Chim. Phys. 1968, 65, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, K.A.; Chan, H.S. From Levinthal to pathways to funnels. Nature Structural Biology 1997, 4, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wales, D.J. Discrete path sampling. Molecular Physics 2002, 100, 3285–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, K.; Wales, D.J. The Energy Landscape Perspective: Encoding Structure and Function for Biomolecules. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiranuma, N.; Park, H.; Baek, M.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Baker, D. Improved protein structure refinement guided by deep learning based accuracy estimation. Nature Communications 2021, 12, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susskind, L. The Cosmic Landscape: String Theory and the Illusion of Intelligent Design; Little, Brown, 2008.
- Kerner, R. Phenomenological Lagrangian for the amorphous solid state. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 28, 5756–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, R.; dos Santos, D.M.L.F. Nucleation and amorphous and crystalline growth: A dynamical model in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 3881–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerner, R.; Penson, K.A.; Bennemann, K.H. Model for the Growth of Fullerenes (C60, C70) from Carbon Vapour. Europhysics Letters 1992, 19, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, R.; Micoulaut, M. On the glass transition temperature in covalent glasses. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 1997, 210, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, R. Nucleation and growth of fullerenes. Computational Materials Science 1994, 2, 500–508, Theory of Atomic and Molecular Clusters. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, R. Geometrical approach to the glass transition problem. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 1985, 71, 19–27, Effects of Modes of Formation on the Structure of Glass. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumis, G.G.; Kerner, R. Stochastic matrix description of glass transition in ternary chalcogenide systems. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 1998, 231, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, R.; Naumis, G.G. Stochastic matrix description of the glass transition. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2000, 12, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos-Loff, D.M.; Micoulaut, M.; Kerner, R. Statistics of Boroxol Rings in Vitreous Boron Oxide. Europhysics Letters 1994, 28, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, R.A.; Kerner, R.; Micoulaut, M.; Naumis, G.G. Evaluation of the concentration of boroxol rings in vitreous by the stochastic matrix method. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 1997, 9, 9219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Kerner, R. Structure and function of window glass and Pyrex. The Journal of Chemical Physics 2008, 128, 174506. https://pubs.aip.org/aip/jcp/article-pdf/doi/10.1063/1.2805043/14841170/174506_1_online.pdf. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerner, R. Self-Assembly of Icosahedral Viral Capsids: the Combinatorial Analysis Approach. Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena 2011, 6, 136–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrovandi, R. Special Matrices of Mathematical Physics: Stochastic, Circulant, and Bell Matrices; World Scientific, 2001.
- Micoulaut, M.; Naumis, G.G. Glass transition temperature variation, cross-linking and structure in network glasses: A stochastic approach. Europhysics Letters (EPL) 1999, 47, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J. Topology of covalent non-crystalline solids I: Short-range order in chalcogenide alloys. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 1979, 34, 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, M. Continuous deformations in random networks. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 1983, 57, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Thorpe, M.F. Elastic Properties of Glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1985, 54, 2107–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boolchand, P.; Bauchy, M.; Micoulaut, M.; Yildirim, C. Topological Phases of Chalcogenide Glasses Encoded in the Melt Dynamics (Phys. Status Solidi B 6/2018). physica status solidi (b) 2018, 255, 1870122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumis, G.G.; Cocho, G. The tails of rank-size distributions due to multiplicative processes: from power laws to stretched exponentials and beta-like functions. New Journal of Physics 2007, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumis, G.; Phillips, J. Bifurcation of stretched exponential relaxation in microscopically homogeneous glasses. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 2012, 358, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, A.; Naumis, G.G. Evidence of a glass transition induced by rigidity self-organization in a network-forming fluid. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 184204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumis, G.G. Energy landscape and rigidity. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 026114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Ruiz, H.M.; Naumis, G.G. The transverse nature of the Boson peak: A rigidity theory approach. Physica B: Condensed Matter 2013, 418, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Ruiz, H.M.; Naumis, G.G.; Phillips, J.C. Heating through the glass transition: A rigidity approach to the boson peak. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 214201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Ruiz, H.M.; Naumis, G.G. Excess of low frequency vibrational modes and glass transition: A molecular dynamics study for soft spheres at constant pressure. The Journal of Chemical Physics 2009, 131, 154501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, J.C.; Yue, Y.; Ellison, A.J.; Gupta, P.K.; Allan, D.C. Viscosity of glass-forming liquids. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2009, 106, 19780–19784. https://www.pnas.org/content/106/47/19780.full.pdf. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kampen, N. Stochastic Processes in Physics and Chemistry; North-Holland Personal Library, Elsevier Science, 1992.
- Pauling, L. General Chemistry; Dover Books on Chemistry, Dover Publications, 2014.
- Huse, D.A.; Fisher, D.S. Residual Energies after Slow Cooling of Disordered Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 2203–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.F.; Frey, E. Master equations and the theory of stochastic path integrals. Reports on Progress in Physics 2017, 80, 046601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpen, M.E.; Tobias, D.J.; Brooks, C.L.I. Statistical clustering techniques for the analysis of long molecular dynamics trajectories: analysis of 2.2-ns trajectories of YPGDV. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husic, B.E.; Pande, V.S. Markov State Models: From an Art to a Science. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2018, 140, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, S.A.; Sethna, J.P. Entropy of Glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 61, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, S.A.; Sethna, J.P.; Grannan, E.R. Nonequilibrium entropy and entropy distributions. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 2261–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, F. Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics; Waveland Press, 2009.
- Huerta, A.; Naumis, G. Relationship between glass transition and rigidity in a binary associative fluid. Physics Letters A 2002, 299, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, A.; Naumis, G.G. Role of Rigidity in the Fluid-Solid Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 145701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, A.; Naumis, G.G.; Wasan, D.T.; Henderson, D.; Trokhymchuk, A. Attraction-driven disorder in a hard-core colloidal monolayer. The Journal of Chemical Physics 2004, 120, 1506–1510. https://pubs.aip.org/aip/jcp/article-pdf/120/3/1506/10857550/1506_1_online.pdf. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Ruiz, H.M.; Naumis, G.G. Boson peak as a consequence of rigidity: A perturbation theory approach. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 184204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumis, G.G. Glass transition phenomenology and flexibility: An approach using the energy landscape formalism. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 2006, 352, 4865–4870, Proceedings of the 5th International Discussion Meeting on Relaxations in Complex Systems. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Boratav, Kerner, R. Relativite; G - Reference,Information and Interdisciplinary Subjects Series, Ellipses, 1991.
- Kerner, R. Methodes classiques de physique theorique : cours et problemes resolus; Ellipses, 2014.
- Kerner, R. Our Celestial Clockwork: From Ancient Origins to Modern Astronomy of the Solar System; G - Reference,Information and Interdisciplinary Subjects Series, World Scientific Publishing Company Pte Limited, 2021.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




