Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
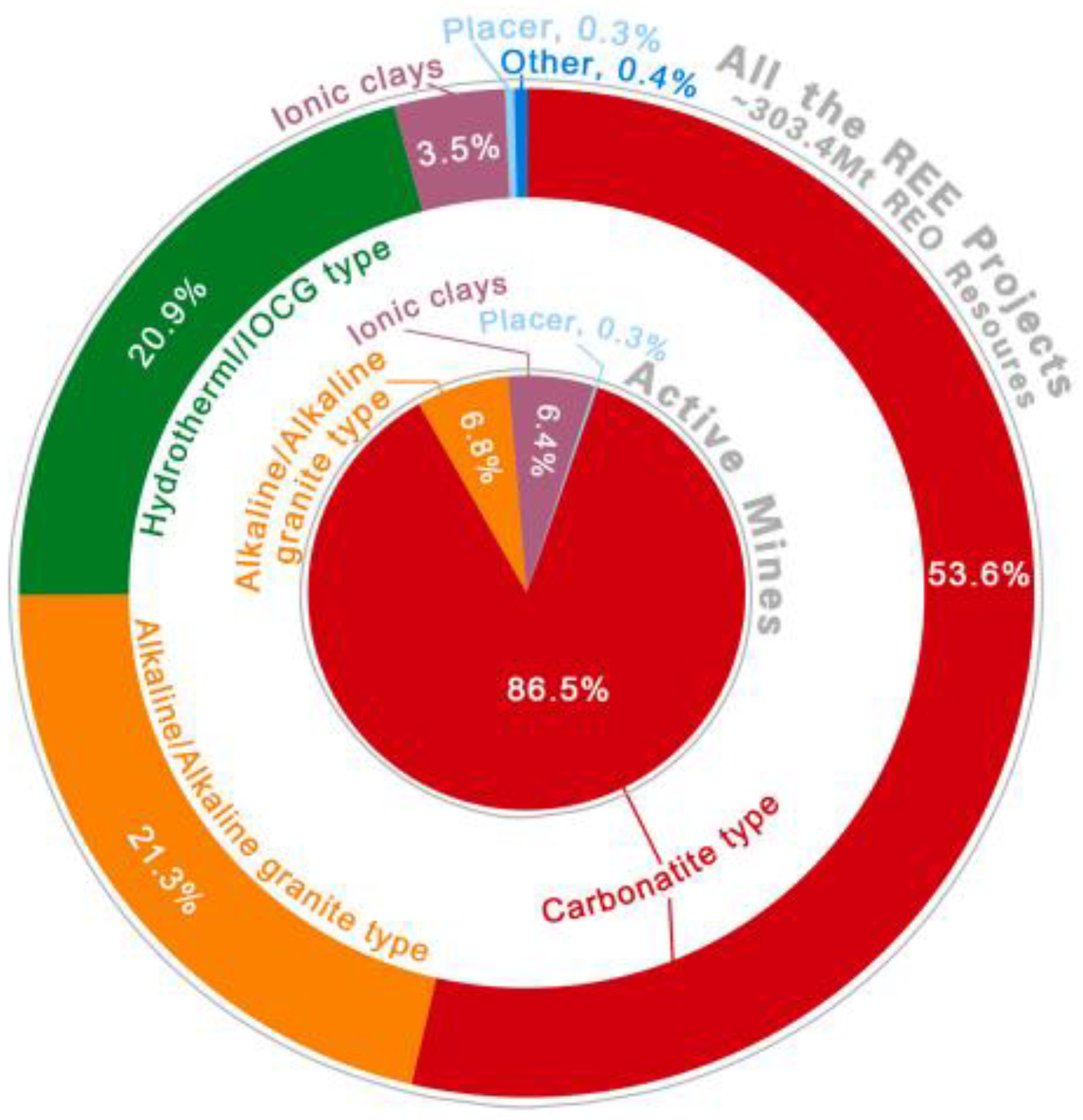
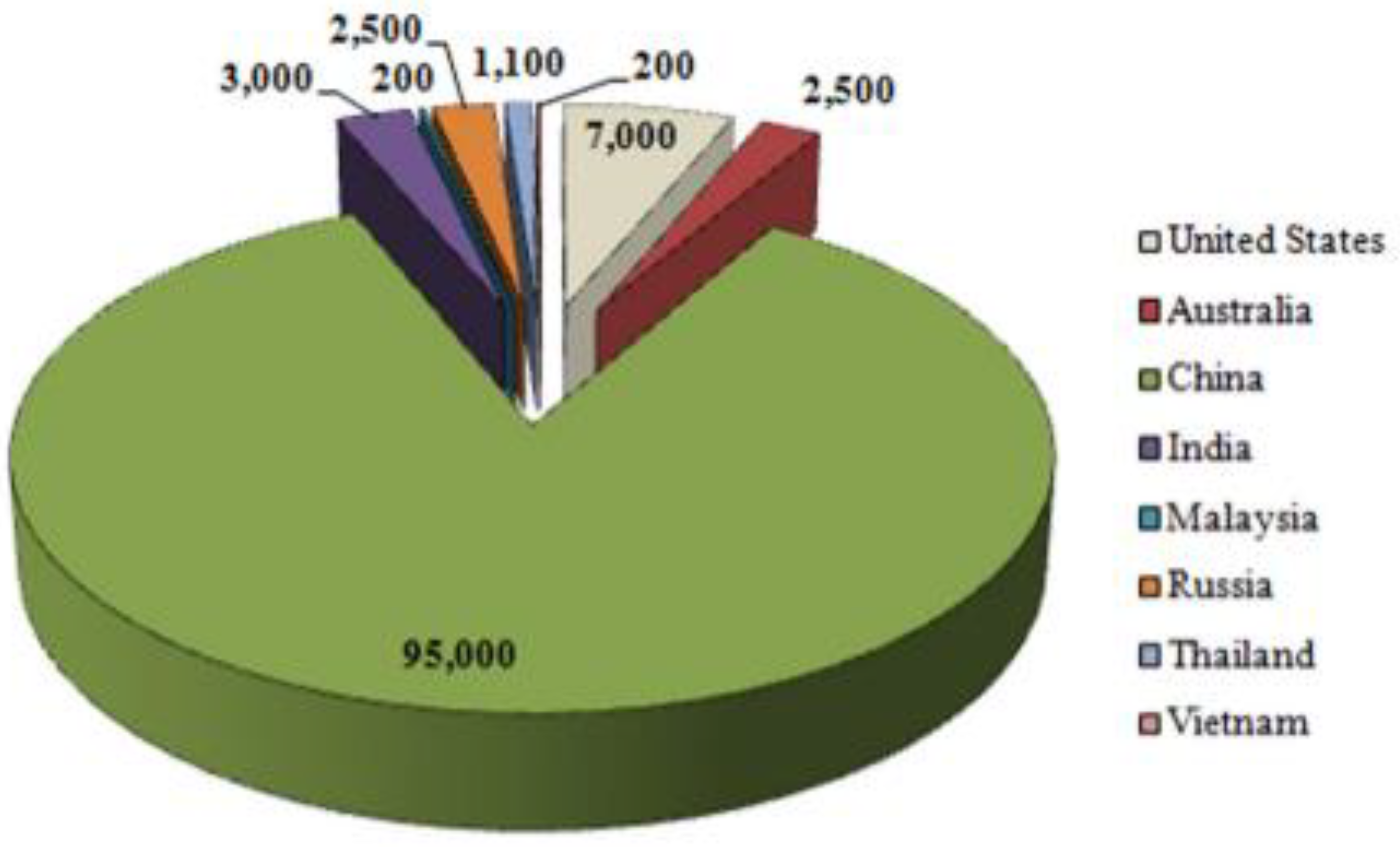
2. Geological Resources of Rare Earth Elements
2.1. Regolith Hosted Deposits
2.2. Rare Earth Elements from Carbonatites
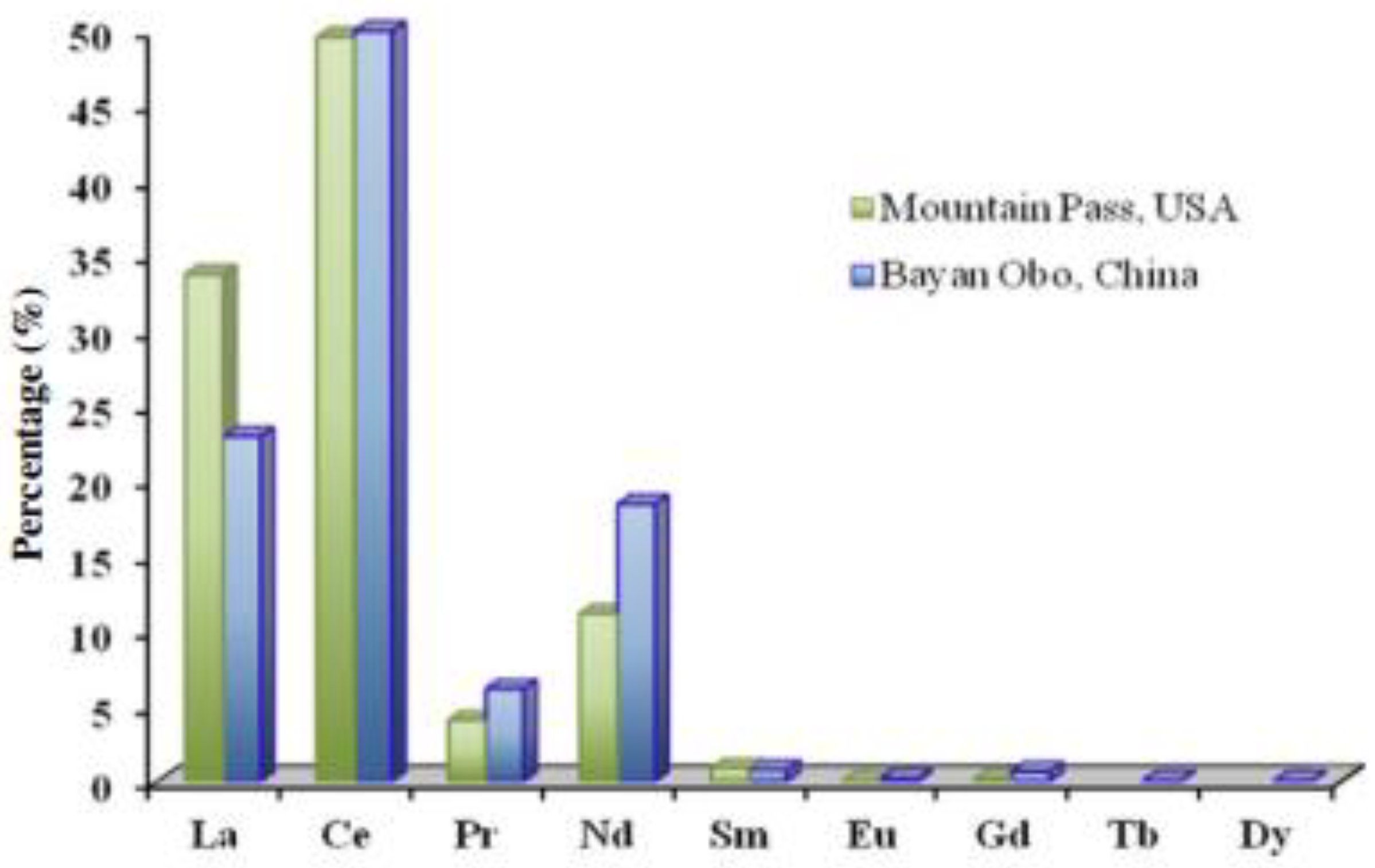
2.3. Primary sources of REEs in Geologic Systems
2.3.1. Bastnasite
2.3.2. Monazite
2.3.3. Xenotime
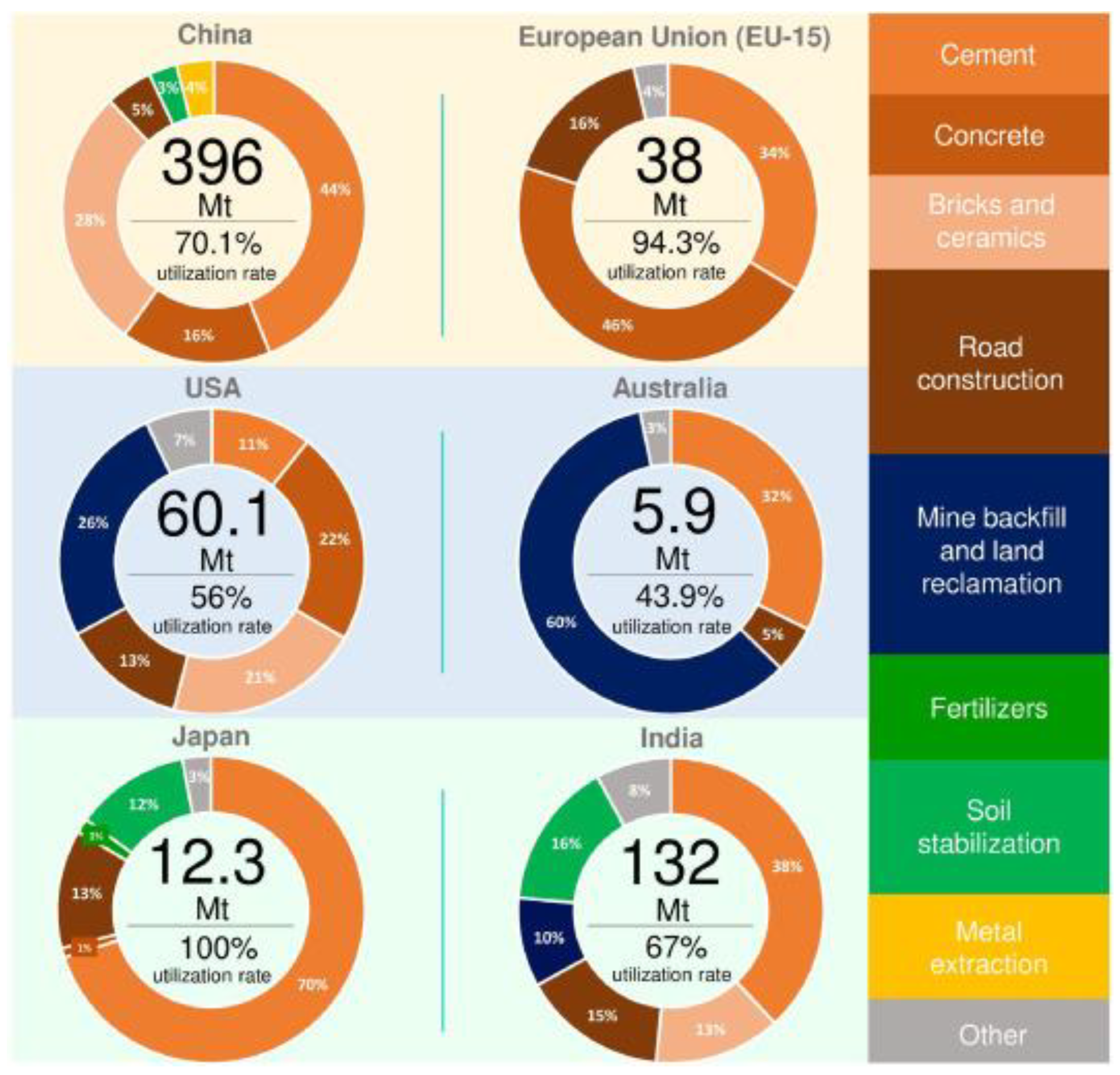
3.4. REEs Resources of Coal Derived Ashes
3.5. The Chemistry of Coal Ash
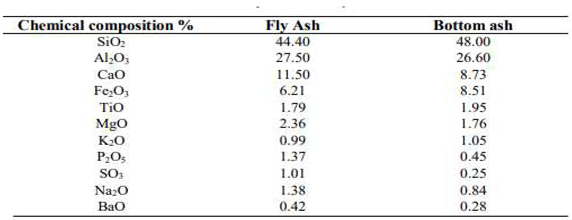
3.5.1. Major Oxides of Coal Ash
3.5.2. Trace Elements of Coal Ash
3.6. Natural Evidence of REEs Leaching from Waste
3.7. Hydrometallurgical Profiles of Conventional Mineral Acids
- Its less corrosive nature gives flexibility in the choice of materials for the building of process units.
- The use of sulfuric acid comes with no concern for odor and volatility of toxic gases. Moreover, electrowinning processes based on sulfuric acid electrolytes have the advantage that oxygen gas is formed at the anode.
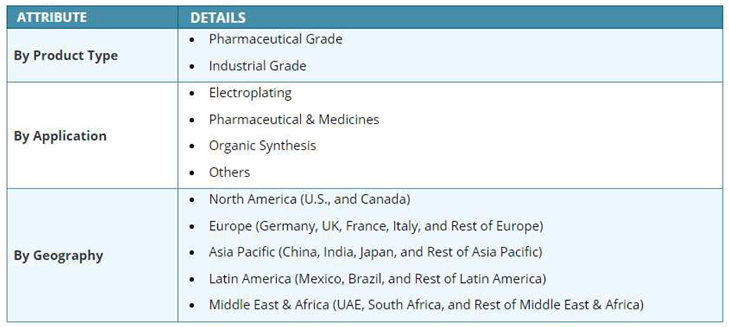
3.8. The Potential of Organosulfonic Acid
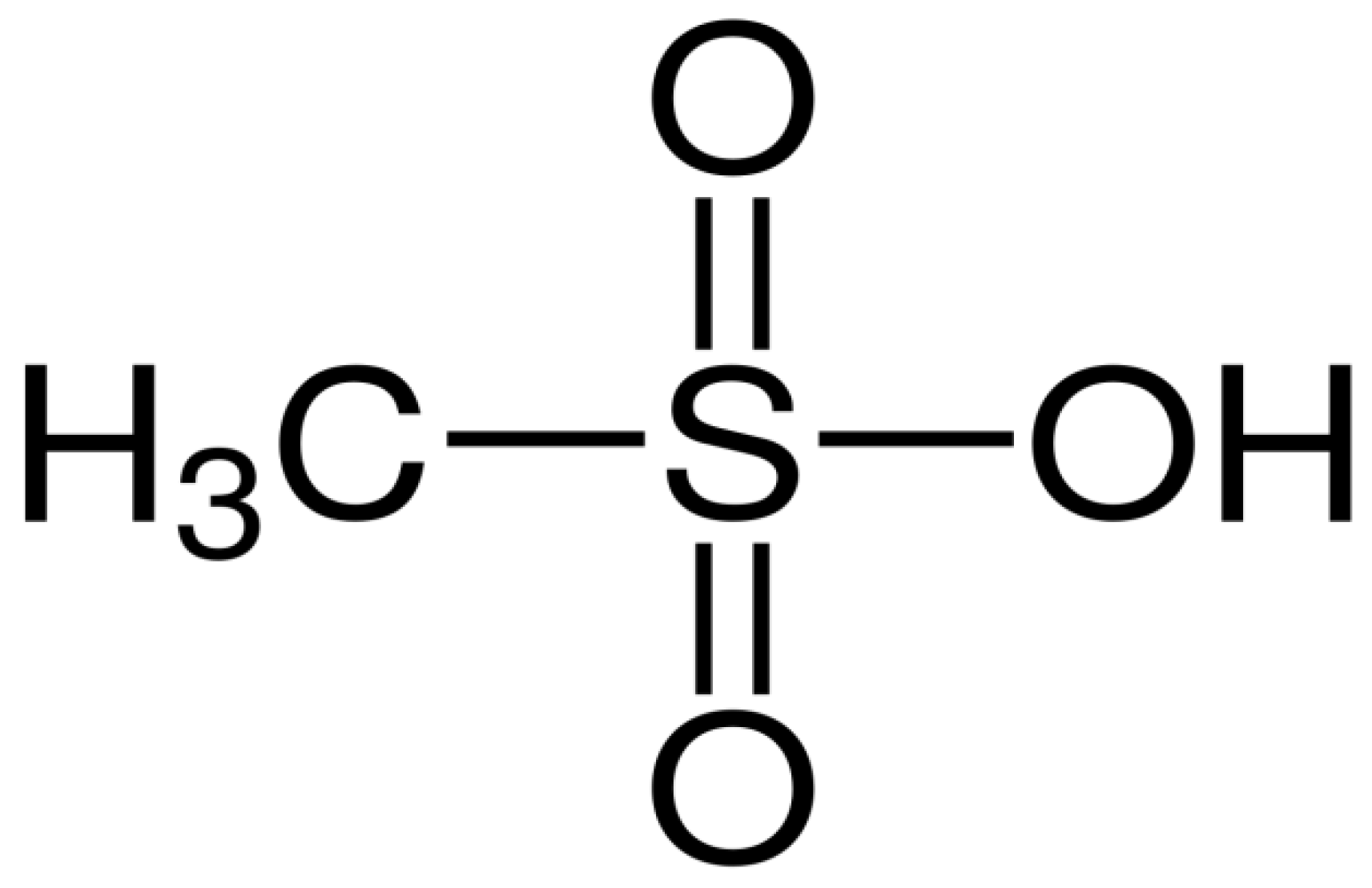
3.9. Properties of Methane Sulfonic Acid
4. Use of Organosulfonic Acid Derivatives in Extractuve Metallurgy
4.1. Solubility of REEs Organosulfonate Salts and the Potential for Their Recovery by Electrolysis
5. Process Optimization
5.1. Hydrometallurgical Aspects
5.2. Recovery Using Methane Sulfonic Acid (MSA)
- Usung 1 M MSA, close to 70% of REEs can be leached from coal at 90 °C in one hour. With minimal (<10%) prominat coal ash minerals being leached.
- Using optimum experimental conditions PTSA showed only 60% leaching efficiency with 0.5 M concentration.
5.3. Optimization of Coal Ash Leaching Uisng Oxidative Assisted Leaching Methodology
5.4. Potential for Oxidative Dissolution of RREs in Hydrogenated Hydrothermal Solutions
5.5. Optimization of Leaching Process: Microwave Assisted Option
5.6. Enhance Lixiviant Diffusion due to Microwave Assisted
5.7. Optimization of Acid Leaching Process by Reducing Acid Consumption
5.7.1. Tribolelectrical Technology Option
5.7.2. Thermal Decarbonization Option
5.8. Advantages of REEs Leaching from Coal Ash Uising Organosulfonic Acids
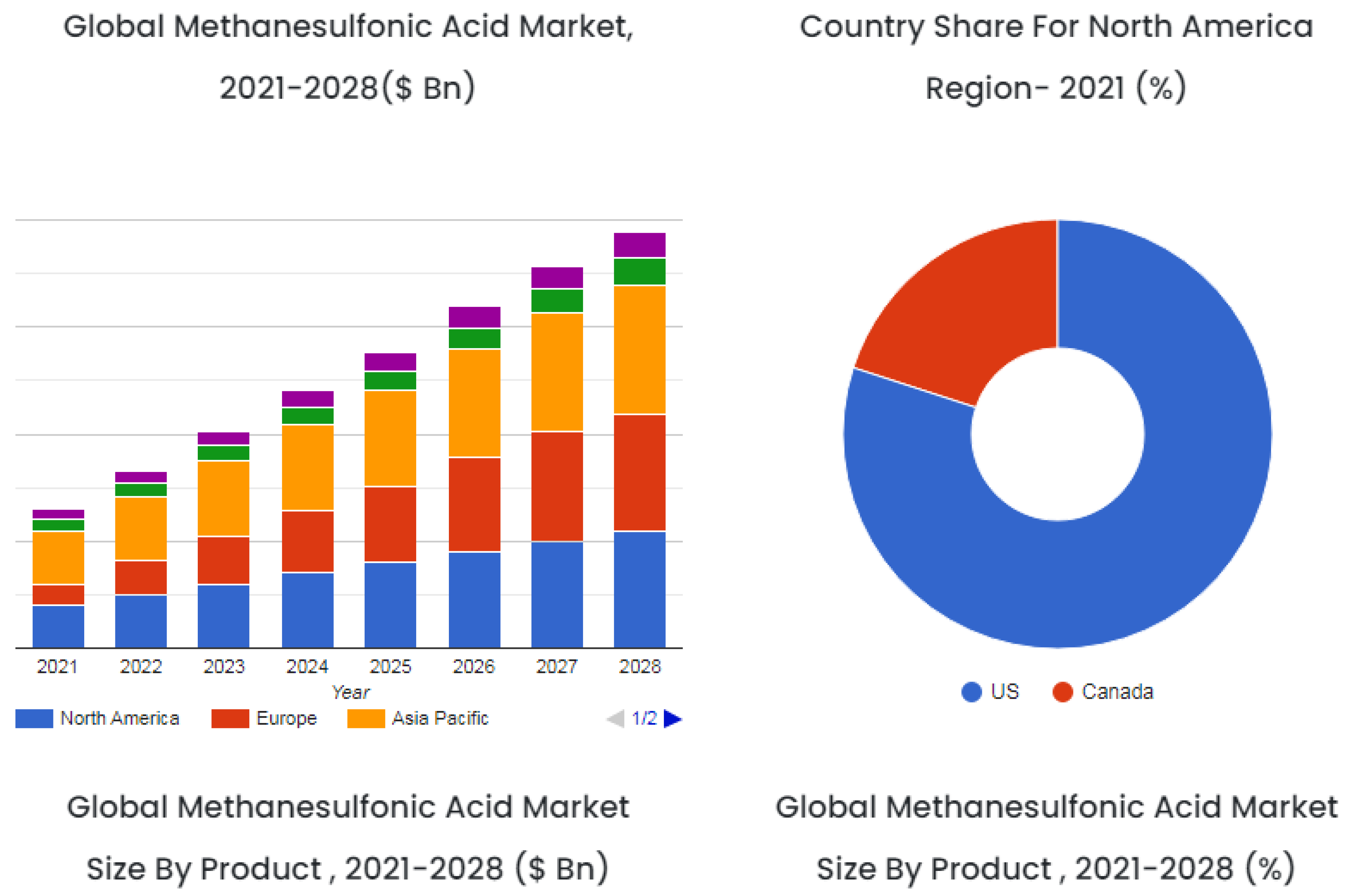
5.9. Global Market Trends of Organosulfonic Acids
5.9.1. Methane Sulfonic Acid
5.9.2. P-Toluene Sulfonic Acid (PTSA)
6. Prospects of Organosulfonic Acids for in REEs Hydrometallurgy
7. Summary and Conclusion
- Coal ash deposits are potential sources of RREs due to their combustion induced concentration, this concetration being dependent on the source of coal and the operational parameters of coal cumbustion chambers,
- Organosulfonic acids hold the potential for optimized RREs extration from coal ash due to the enhanced solubility of their salts,
- While the use of conventional minerals acid as lixiviants lead to REEs extraction with reported efficiencies in the literature, their uses will render leached coal ash residues unsuitable for the construction industry because they destroy the aluminosilicate strucure of amorphous phases of coal ash, which prompt their use as concrete aggregate,
- The use of Organsosulfonic acids as lixiviants will preserve the amorphous aluminosilicate structure to maintain the geotechnically important aspect of coal ash for concrete aggregate,
- The use of organosulfonic acids for REEs extraction from coal ash has the same potentrial to optimize the leaching process due to the rival nature of its pKa value as reported in the literature compared to those of conventional minerals acids,
- The global market production of organosulfonic acids is poised to grow, given their increasd uses for diversed industrial process , which will give impetus for their use as lixiviants for REEs extration from coal ash,
- The high solubility of Organsosulfonic acids coupled with their high pKa values are indicators for the potential use in hydrometallurgical processes involving RREs extraction from coal ash.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adebayo, A., & Olasehinde, E. (2015). Leaching kinetics of lead from galena with acified hydrogen peroxide and sodium chloride solution. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. Sect. C, 124, 137-142. [CrossRef]
- Alaba, P. A., Sani, Y. M., & Daud, W. M. (2016). Efficient biodiesel production via solid superacid catalysis: a critical review on recent breakthrough. RSC Adv, 6, 78351-78368. [CrossRef]
- Alex, P., Suri, A., & Gupta, C. (1998). Processing of xenotime concentrate. Hydrometallurgy, 50(3), 331-338. [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M., & Kingman, S. (2004). Microwave-assisted leaching-a review. Hydrometallurgy, 73(3-4), 189-203. [CrossRef]
- Amjad, R. S., Asadollahzadeh, M., Torkaman, R., & Torab-Mostaedi, M. (2022). An efficiency strategy for cobalt recovery from simulated wastewater by biphasic system with polyethylene glycol and ammonium sulfate. Scientific Reports, 12, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Amli, R. (1975). Mineralogy_and-Rare Earth Geochemistry of Apatite and Xenotime from the Gloserheia Granite Pegmatite, Froland, Southern Norway. American Mineralogist, 60, 607-620.
- Anderson, J. M., Johnson, R. L., Schmidt-Rohr, K., & Shanks, B. H. (2014). Hydrothermal degradation of model sulfonic acid compounds: Probing the relative sulfur-carbon bond strength in water. Catalysis Communications, 51, 33-36. [CrossRef]
- Anggara, F., Besari, D. A., Mursalin, A., Amijaya, D. H., & Petrus, H. T. (2020). Coal and coal ash characteristics to understand mineral transformation : A case study from Senakin coal field Indonesia. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Volume 789, International Conference on the Ocean and Earth Sciences 18-20 November 2020, Jakarta Selatan, Indonesia. 789, pp. 1-10. Jakarta Selatan: Earth Environ. Sci. [CrossRef]
- Argumedo, D., Johnson, K., Heinrichs, M., Peterson, R., Winburn, R., & Brewer, J. (2020). Recovery of High Purity Rare Earth Elements (REE) from Coal Ash via a Novel Electrowinning Process (Final Report). Washington: USDOE Office of Fossil Energy (FE). [CrossRef]
- Aricó, E., Zinnera, L., Apostolidis, C., Dornbergerb, E., Kanellakopulosb, B., & Rebizant, J. (1997). Structures of the anhydrous Yb(II1) and the hydrated Ce(III), Sm(II1) and Tb (III) methanesulfonates. J. Alloy. Compd, 249, . 111-115. [CrossRef]
- ASTM. (2017). Standard Specification for Coal Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete.
- Atia, T. A., Wouters, W., Monforte, G., & Spooren, J. (2021). Microwave chloride leaching of valuable elements from spent automotive catalysts : Understanding the role of hydrogen peroxide. Resour. Conserv. Recycl., 166, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Backer, L. D., & Baron, G. (1993). Effective diffusivity and tortuosity in a porous glass immobilization matrix. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 39, 281-284. [CrossRef]
- Badenhorst, C. J., Wagner, N. J., Valentim, B. R., Viljoen, K. S., & Santos, A. C. (2019). Separation of Unburned Carbon from Coal Conversion Ash: Development and. Coal Combustion and Gasification Products, 11, 89-96.
- Baker, L., Gupta, A., Gasiorowski, S., & Hrach, F. (2022). Triboelectrostatic beneficiation of landfilledand ponded flyash. Retrieved from https://worldofcoalash.org/.
- Baker, M. C. (1964). CBD-56. Thermal and Moisture Deformations in Building Materials. Retrieved from National Research Council of Canada: http://web.mit.edu/parmstr/Public/NRCan/CanBldgDigests/cbd056_e.html.
- Baker, S. C., . Kelly, D. P., & Murrell, J. C. (1991). Nature, 350, 627 -628. [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. (2019). Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geoscience Frontiers, 10(4), 1285-1303. [CrossRef]
- Balaz, P., & Ebert, I. (1991). Oxidative leaching of mechanically activated sphalerite. Hydrometallurgy, 27, 141-150. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R., Chakladar, S., Chattopadhyay, S. K., & Chakravarty, S. (2023). Leaching of rare earth elements from coal ash using low molecular weight organocarboxylic acids: Complexation overview and kinetic evaluation. International Journal of Cghemical Kinetics, 55(10), 606-618. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R., Chakladar, S., Mohanty, A., Chattopadhyay, S. K., & Chakravart, S. (2022). Leaching characteristics of rare earth elements from coal ash using organosulphonic acids. Minerals Engineering, 185, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R., Chakladar, S., Mohanty, A., Chattopadhyay, S. K., & Chakravarty, S. (2022). Leaching characteristics of rare earth elements from coal ash using organosulphonic acids. Minerals Engineering, 185, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R., Chakladar, S., Mohanty, A., Chattopadhyay, S. K., & Chakravarty, S. (2022). Leaching characteristics of rare earth elements from coal ash using organosulphonic acids. Minerals Engineering, 185, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Barker, C. (1972). Aquathermal Pressuring-Role of Temperature in Development of Abnormal-Pressure Zones: GEOLOGICAL NOTES. AAPG Bulletin, 56(10), 2068-2071. [CrossRef]
- Belfqueh, S., Seron, A., Chapron, S., Arrachar, G., & Menad, N. (2023). Evaluating organic acids as alternative leaching reagents for rare earth elements recovery from NdFeB magnets. Journal of Rare Earths, 41(4), 621-631. [CrossRef]
- Bertkau, W., Hatscher, S., Frenzel, S., & Ossmer, U. (2015). Patent No. US Patent US20150175872.
- Binnemans, K., & Jones, P. (2023a). Methanesulfonic Acid (MSA) in Hydrometallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall., 9, 26-45. [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K., & Jones, P. (2023b). The Twelve Principles of Circular Hydrometallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall., 1-25. [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K., & Jones, P. T. (2022). Methanesulfonic Acid (MSA) in Hydrometallurgy Hydrometallurgy. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 9, 26-45. [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K., Pontikes, Y., Jones, P. T., & Gerven, T. V. (2016). Recovery of rare earths from industrial waste residues: a concise review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 99, 17-38. [CrossRef]
- Birk, D., & White, J. C. (1991). Rare earth elements in bituminous coals and underclays of the Sydney Basin, Nova Scotia: Element sites, distribution, mineralogy. International Journal of Coal Geology, 19(1-4), 219-251. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, B. A., Shivakumar, K. R., Alessi, D. S., & Robbins, L. J. (2023). Insights into the rare earth element potential of coal combustion by-products from western Canada. Environ. Sci.: Adv., 2, 529-542. [CrossRef]
- Bititannica. (2023). Abundance, occurrence, and reserves. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/science/rare-earth-element/Elastic-properties.
- Borst, A. M., Smith, M. P., Finch, A. A., Estrade, G., Cristina Villanova-de-Benavent 2, P. N., Goodenough, K. M., et al. (2020). Adsorption of rare earth elements in regolith-hosted clay deposits. Nature communications, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Borst, A. M., Smith, M. P., Finch, A. A., Estrade, G., Villanova-de-Benavent, C., Nason, P., et al. (2020). Adsorption of rare earth elements in regolith-hosted clay deposits clay deposits. Nature Communications volume, 11, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, B. P. (1996). The di usive tortuosity of ne-grained unlithi ed sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60(16), Boudreau, B. P. (1996). The di usive tortuosity of ne-grained unlithi ed sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60(16):3139 3142. [CrossRef]
- Brahim, J. A., Merroune, A., Boulif, R., Mounirb, E. M., & Beniazza, R. (2022). Efficient leaching process of rare earth, alkali and alkaline earth metals from phosphogypsum based on methanesulfonic acid (MSA) as green & eco-friendly lixiviant†. RCS Adv, 12, 302639-20649. [CrossRef]
- Buchill, P., Howarth, O., Richards, D., & Sword, B. (1990). Solid-state Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Phosphorus and Boron in Coals and Combustion Residues. Fuels, 69, 4ZI-428. [CrossRef]
- Bwchill, P., How&h, O., Richards, D., & Sword, B. (1990). Solid-state Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Phosphorus and Boron in Coals and Combustion Residues. Fuels, 69, 4ZI-428. [CrossRef]
- Cai, J., Wei, W., Hu, X., & Wood, D. A. (2017). Electrical conductivity models in saturated porous media: A review. Earth-Science Reviews, 171, 419-433. [CrossRef]
- Cambridge-University. (2022). New approach to 'cosmic magnet' manufacturing could reduce reliance on rare earths in low-carbon technologies. Retrieved from University of CAambridge: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/10/221024193256.htm.
- Canada. (2014). The rare earth elements industry in canada ─ summary of evidence :Standing Committee on:. 41st PARLIAMENT, SECOND SESSION , Hose of Commons.
- Canada, E. (2022). History of Electricity. Retrieved from https://www.electricity.ca/knowledge-centre/about-the-electricity-sector/history-of-electricity/.
- Canada.ca. (2023). Coal facts. Retrieved from https://natural-resources.canada.ca/our-natural-resources/minerals-mining/mining-data-statistics-and-analysis/minerals-metals-facts/coal-facts/20071.
- Carlson, C., & Adriano, D. (1993). Environmental impacts of coal combustion residues. Journal of Environmental Quality, 22(2), 227-247. [CrossRef]
- Castro, L., Blázquez, M. L., González, F., & Muñoz, J. Á. (2021). Biohydrometallurgy for Rare Earth Elements Recovery from Industrial Wastes. 26(20), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E., Watt, & George. (1941). THE IDENTIFICATION OF SULFONIC ACIDS. J. Org. Chem., 06(3), 376-383. [CrossRef]
- Chen, G., Sun, Q., Xu, J., Zheng, L., Junfeng, R., & Zong, B. (2021). Sulfonic Derivatives as Recyclable Acid Catalysts in the Dehydration of Fructose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Biphasic Solvent Systems. ACS Omega, 16(10), 6798-6809. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. (2011). Global rare earth resources and scenarios of future rare earth industry. Journal of Rare Earths, 29(1), 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Chikanda, F., Otake, T., Ohtomo, Y., Ito, A., Yokoyama, T. D., & Sato, T. (2019). Minerals. Magmatic-Hydrothermal Processes Associated with Rare Earth Element Enrichment in the Kangankunde Carbonatite Complex, Malawi, 9(7), 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Chong, S., Hawker, W., & Vaughan, J. (2013). Selective reductive leaching of oxidised cobalt containing residue. Miner. Eng., 12, 82-87. [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A. K., Kumar, S., Sharma, R. V., Satyanarayanan, M., & Maity, S. (2023). Targeting ash generated from coal combustion as secondary source of rare earth elements. Nternational journal of coal preparation and utilization, 1-17.
- Cotton, S. (2006). Lanthanide and Actinide Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. [CrossRef]
- Dahan, A. M., Alorro, R. D., Pacaña, M. L., Baute, R. M., Silva, L. C., Tabelin, C. B., et al. (2022). Hydrochloric Acid Leaching of Philippine Coal Fly Ash: Investigation and Optimisation of Leaching Parameters by Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Sustain. Chem., 3, -90. [CrossRef]
- Das, S., Gustav, G., Sekar, A., & Williams, E. (2018). Techno-Economic analysis of supercritical extraction of rare earth elements from coal ash. Journal of Cleaner Production, 189 , 539-551. [CrossRef]
- Demopoulos, G., Li, Z., Becze, L., Moldoveanu, G., Cheng, T., & Harris, B. (2008). 2New technologies for HCl regeneration in chloride hydrometallurgy. World Metall-ERZMETALL, 61(2), 89-98.
- Dinh, T., Dobo, Z., & Kovacs, H. (2022). Phytomining of rare earth elements - A review. Chemosphere, 279, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Dmitry, V., Petr, B., Nikita, O., Konstantin, V., & Cristian, S. C. (2022). A review of the alumina production from coal fly ash, with a focus in Russia. Journal of Cleaner Production, 363, 1-23. [CrossRef]
- Dostal, J. (2017). Rare earth element deposits of alkaline igneous rocks. Resources, 6(34), 1-2. [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, J. P., & Masliyah, J. H. (1991). Flow through isotropic granular porous media. Transport in porous media, 6(3), 207-221. [CrossRef]
- Dugin, S. V., Sorokin, A. P., & Konyushok, A. A. (2022). Potentially Economic Concentrations of Rare Earth Elements and Gold in Power Plant Coal Combustion Products (Far East, Russia). Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 40(4), 1236-1251. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, E., Abdollahi, H., Shafaei, S. Z., Ghanbarzad, M., & Talebi, E. (2023). Green extraction of pure ferromagnetic nickel from spent hydroprocessing catalysts via deep eutectic solvents. Separation and Purification Technology, 313, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Ekmann, J. (2012). Rare Earth Elements in Coal Deposits - a Prospectivity Analysis. Retrieved from AAPG: https://www.searchanddiscovery.com/documents/2012/80270ekmann/ndx_ekmann.pdf.
- EL-Bar, D., & Barket, D. (2018). Leaching of metals from hydrometallurgical residue by Sulfuric Acid. Aspects in Mining & Mineral Science, 1(4). [CrossRef]
- Elbashier, E., Mussa, A., Hafiz, M., & Hawari, A. H. (2021). Recovery of rare earth elements from waste streams using membrane processes: An overview. Hydrometallurgy, 204, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Epstein, N. (1989.). On tortuosity and the tortuosity factor in ow and di usion through porous media. Chemical Engineering Science, 44(3), 777-779. [CrossRef]
- Eterigho-Ikelegbe, O., Harrar, H., & Bada, S. (2021). Rare earth elements from coal and coal discard - A review. Minerals Engineering, 173, 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Ewe, T., & Scheible, W. (2017). Der Griff zum Heiligen Gral. Bild der Wiss.
- FEECO. (2023). Heap Leaching: A Growing Technology in Beneficiation. Retrieved from https://feeco.com/heap-leaching-a-growing-technology-in-beneficiation/.
- FENG, Q., WEN, S., ZHAO, W., LV, C., & BA, X. (2015). Leaching of Copper from Malachite with Methane-sulfonic Acid. Solvent Extraction Research and Developmen, 22(2), 159 - 168. [CrossRef]
- Ferron, C. (2008). Sulfur Dioxide:A versatile reagent for the processing of cobaltic oxide minerals. JOM, 60, 50-54. [CrossRef]
- Fibers. (2023). Retrieved from Coal Ash at a Glance: https://www.gcsfibers.com/toxic-coal-ash.
- Finkelman, R. (1993). Trace and minor elements in coals, In: Engel, M.H. and Macko,S.A. (Eds.),. Organic Geochemistry. New York: Plenum, 593-607. [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R. B. (1980). Modes of Occwrence of Trace Elements in Coal. (U. o. Mayrland, Producer) Retrieved from https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1981/0099/report.pdf.
- 75. [CrossRef]
- Florence, F., Nisha, S. R., Srinivasan, K. N., & John, S. (2011). Int. J. ChemTech Res., 3, F. Florence , S. R. Nisha , K. N. Srinivasan and S. John.
- Fortune. (2020). Methanesulfonic Acid Market report summaries detailed information by top playesr as Arkema Group, Oxon Italia S.p.A., Shinya Chem, Yanuo Chemical, Xingchi Science and Technology, BASF SE among others... Read More at:- https://www.fortunebusinessinsights. Retrieved from Business Insights: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/methanesulfonic-acid-market-103963.
- Franus, W., Wiatros-Motyka, M., & Wdowin, M. (2015). Coal fly ash as a resource for rare earth elements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res, 22, 9464-9474. [CrossRef]
- Free, M. (2013). Hydrometallurgy: fundamentals and applications. New York: Wiley. [CrossRef]
- Fu, B., Hower, J. C., Zhang, W., Luo, G., Hu, H., & Yao, H. (2022). A review of rare earth elements and yttrium in coal ash: Content, modes of occurrences, combustion behavior, and extraction methods. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 88, 1-47. [CrossRef]
- Fuchida, S., Yokoyama, A., Fukuchi, R., Ishibashi, J.-i., Kawagucci∥⊥, S., Kawachi, M., et al. (2017). Leaching of Metals and Metalloids from Hydrothermal Ore Particulates and Their Effects on Marine Phytoplankton. ACS Omega, 2(7), 3175-3182. [CrossRef]
- Generalic, E. (2012). RARE EARTH ELEMENTS. Retrieved from https://www.periodni.com/rare_earth_elements.html#:~:text=The%20unsaturated%204f%20electronic%20structure,it%20has%20no%20known%20substitute.
- Gernon, M., Wu, M., Buszta, T., & Janney, P. (1999). Green Chem., 1, 127-140. [CrossRef]
- Gijsemans, L., Forte, F., Onghena, B., & Binnemans, K. (2018). Recovery of rare earths from the green lamp phosphor LaPO4:Ce3+, Tb3+ (LAP) by dissolution in concentrated methanesulphonic acid. RSC Adv., 8, 26349-26355. [CrossRef]
- Gluskoter, H. J., Ruch, R. R., Miller, W. G., R.A.Cahill, Dreher, G. B., & Kuhn, J. K. (1997). Trace elements in coal occurrence and distribution. illinois : illinois state geological surveY.
- Goldfarb, R., & Marsh, E. T. (2010). A review of silver-rich mineral deposits and their metallogeny. In The Challenge of Finding New Mineral Resources: Global Metallogeny, Innovative Exploration, and New Discoveries (pp. 85-117). USGS. [CrossRef]
- Gosch, R., Cruz, R., & Lazaro, I. (2008). Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration . Hydrometallurgy 2008, 1110-1118.
- Gulliani, S., Volpe, M., Messineo, A., & Volpe, R. (2023). Recovery of metals and valuable chemicals from waste electric and electronic materials: a critical review of existing technologies. RSC Sustain., 1, 1085-1108. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C., & Krishnamurthy, N. (1992). Extractive metallurgy of rare earths. Int. Mater. Rev., 37(5), 197-248. [CrossRef]
- Halbach, P., Pracejus, B., & Maerten. (1993). Geology and mineralogy ofmassive sulfide ores from the central Okinawa Trough. Japan.Econ.Geol, 88, 210−2225. [CrossRef]
- Han, C.-C., Zhang, X.-B., Wu, S.-S., & Liu, Y.-T. (2022). The Magmatic-Hydrothermal Ore-Forming Processes of the Tonggou Cu-Zn Deposit, NW China: Constraints from Magnetite Chemistry and Fluid Inclusions. Minerals, 12(4), 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Hauashdh, A., Mohamed, R. M., Jailani, J., & Rahman, J. A. (2020). Stabilization of Peat Soil Using Fly Ash, Bottom Ash and Portland Cement: Soil Improvement and Coal Ash Waste Reduction Approach. IConCEES, 498, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Hedenquist, J. W., & Lowenstern, J. B. (1994). The role of magmas in the formation of hydrothermal ore deposits. Nature, 370, 519-527. [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, J. (1992). Rare earths. Min. Eng (Colorado) (USA), 44(6), 571-576.
- Honaker, R. Q., Zhang, W., & Werner, J. (2019). Acid Leaching of Rare Earth Elements from Coal and Coal Ash: Implications for Using Fluidized Bed Combustion To Assist in the Recovery of Critical Materials. Energy Fuels, 32(7), 5971-5980. [CrossRef]
- Honaker, R. Q., Zhang, W., & Werner, J. (2019). Acid Leaching of Rare Earth Elements from Coal and Coal Ash: Implications for Using Fluidized Bed Combustion To Assist in the Recovery of Critical Materials. Energy Fuels, 33(7), 5971-5980. [CrossRef]
- Honaker, R., Zhang, W., & Werner, J. (2019). Acid Leaching of Rare Earth Elements from Coal and Coal Ash: Implications for Using Fluidized Bed Combustion To Assist in the Recovery of Critical Materials. 2019Energy & Fuels, 33(7), 5971-5980. [CrossRef]
- Hopf, J., Weigelt, A., Bombach, H., Stelter, M., & Charitos, A. (2021). Refining of Precious Metal Bearing Materials from Secondary Sources-Methanesulfonic Acid Leaching of Raw Silver Granules as a Promising Approach towards a Green Way of Silver Refining. Materials (Basel), 14(20), 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z., Liu, Y., Tian, S., Yang, Z., & Xie, Y. (2015). Formation of carbonatite-related giant rare-earth-element deposits by the recycling of marine sediments. Scientific Reports, 5, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Hower, J., Ruppert, L., & Eble, C. (1999). Lanthanide, yttrium, and zirconium anomalies in the Fire Clay coal bed, eastern Kentucky. International Journal of Coal Geology, 39(1-3), 141-153. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C., Wang, Y., Huang, B., Dong, Y., & Sun, X. (2019). The recovery of rare earth elements from coal combustion products by ionic liquids. Minerals Engineering, 130, 142-147. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X., Long, Z., Li, H., Ying, W., Zhang, G., & Xue, X. (2005). Development of rare earth hydrometallurgy in China. J. Rare Earths 23 (1),, 23(1), 1-4.
- IEA. (2023). World Energy Balances: Overview. Retrieved from https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-balances-overview/world.
- Ilankoon, I., Dushyantha, N., Mancheri, N., Edirisinghe, P., Neethling, S., Ratnayake, N., et al. (2022). Constraints to rare earth elements supply diversification: Evidence from an industry survey. Journal of Cleaner Production, 331(10), 1-16. [CrossRef]
- IRENA. (2022). Critical materials for the energy transition: rare earth elements.
- Ishibashi, J.-i., Ikegami, F., Tsuji, T., & Urabe, T. (2015). Hydrothermalactivity in the Okinawa Trough back-arc basin: geological backgroundand hydrothermal mineralization. InSubseafloor Biosphere Linked toHydrothermal Systems. In TAIGA Concept; Ishibashi, J.-i., Okino, K.,Sunamura, M. (p. 337−359). Springer. [CrossRef]
- Ives, B. M. (2013). Boom in Mining Rare Earths Poses Mounting Toxic Risks. Retrieved from https://e360.yale.edu/features/boom_in_mining_rare_earths_poses_mounting_toxic_risks.
- Jankowski, J., Ward, C., French, D., & Groves, S. (2006). Mobility of trace elements from selected Australian fly ashes and its potential impact on aquatic ecosystems. Fuel, 85(2), 243-256. [CrossRef]
- Joo, M. H., Park, S. J., Hong, S. M., Rhee, C. K., & Sohn, Y. (2020). Electrochemical Recovery and Behaviors of Rare Earth (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, and Yb) Ions on Ni Sheets. Materials, 13(23), 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Jordens, A., Cheng, Y. P., & Waters, K. E. (2013). A review of the beneficiation of rare earth element bearing minerals. Minerals Engineering, 41, 97-114. [CrossRef]
- Jordens, A., Cheng, Y., & Waters, K. (2013). 2013. A review of the beneficiation of rare earth element bearing minerals. Miner. Eng. , 41, 97-114. [CrossRef]
- Jordens, A., Cheng, Y., & Waters, K. (2013). A review of the beneficiation of rare earth element bearing minerals. Miner. Eng., 41, 97-114. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J., Mishra, M., & Srinivasarao, M. (2011). Silica-supported methanesulfonic acid - An efficient solid Brønsted acid catalyst for the Pechmann reaction in the presence of higher n-alkanes. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 89(6). [CrossRef]
- Jowitt, S. M., Wong, V. N., Wilson, S. A., & Gore, O. (2017). Critical metals in the critical zone: controls, resources and future prospectivity of regolith-hosted rare earth elements. AU. Aust. J. Earth Sci., 64, 1045-1054. [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, K., & Kamitani, M. (2005). Rare earth minerals and resources in the world. J. Alloys Compd., 408-412 , 1339-1343. [CrossRef]
- Kappenthuler, S., Olveira, S., Wehrli, J., & Seeger, S. (2018). Environmental assessment of alternative methanesulfonic acid production using direct activation of methane. Journal of Cleaner Production, 202, 1179-1191. [CrossRef]
- Karalar, M., Bilir, T., Çavuşlu, M., Özkili, Y. O., & Sabri, M. M. (2022). Use of recycled coal bottom ash in reinforced concrete beams as replacement for aggregate. Front. Mater., 9, 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Kim, R., Cho, H., Han, K. N., Kim, K., & Mun, M. (2016). Optimization of Acid Leaching of Rare-Earth Elements from Mongolian Apatite-Based Ore. Minerals, 6(3), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y., Kim, S., & Lee, J. (2019). Economic Evaluation of Rare Earth Elements Contained in Coal Ash. Resources Recycling, 28(6), 26-35. [CrossRef]
- Kopecky, J., Martinek, K., & Hinterholzinger, O. (1986). Method of neutralizing residual acid in leaching ores which are difficult to leach. Zpusob neutralizace zbytkove kyseliny pri louzeni tezce louzitelnych rud.
- Kozakiewicz, R., Grzesik, K., Bieda, B., & Kossakowska, K. (2019). Environmental and Sustainable Development indicators for a preliminary strategic assessment of REE recovery from mine tailings. IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science 214 (pp. 1-10). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, N., & Gupta, G. (2015). Extractive Metallurgy of Rare Earths:2nd ed. CRC Press. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P. (2015). Methane Sulphonic Acid is Green Catalyst in Organic Synthesis. Oriental Journal Of Chemistry, 31(1), 447-451. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P. (2015). Methane Sulphonic Acid is Green Catalyst in Organic Synthesis. Oriental Journal of Chemistry, 31(1), 447-451. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A., Panda, R., Jha, M. K., & Kumar, J. (2015). Process development to recover rare earth metals from monazite mineral: A review. Minerals Engineering, 79, 103-115. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A., Panda, R., Jha, M. K., Kumar, J. R., & Lee, J. Y. (2015). Process development to recover rare earth metals from monazite mineral: A review. Minerals Engineering, 79, 102-115. [CrossRef]
- KYTE-RESEARH. (2023). P-Toluenesulfonic Acid Market Size 2023 - 2030 Global Industrial Analysis, Key Geographical Regions, Market Share, Top Key Players, Product Types and. Retrieved from P-Toluenesulfonic Acid Market Size 2023 - 2030 Global Industrial Analysis, Key Geographical Regions, Market Share, Top Key Players, Product Types and: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/p-toluenesulfonic-acid-market-size-2023-2030-global-industrial/.
- Lafitte, J., & Monguillon, B. (2013). Patent No. US patent 8,574,370. United States.
- Law, D. W., Gunasekara, C., & Setunge, S. (2022). Use of Brown Coal Ash as a Replacement of Cement in Concrete Masonry Bricks. Proceedings of NICOM7, 31 October-02 November, 2022, Melbourne, Australia (pp. 23-25). Melbourne, Australia: Springer. [CrossRef]
- Li, G. K., Fischer, W. W., & Ji, J. (2021). Coal fly ash is a major carbon flux in the Chang Jiang (Yangtze River) basin Chang Jiang (Yangtze River) basin. PNAS, 118(21), 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., Fu, Y., Liang, J., Li, C., Wang, J., Yan, H., et al. (2021). Electrochemical Mechanism of Recovery of Nickel Metal from Waste Lithium Ion Batteries by Molten Salt Electrolysis. Materials (Basel)., 14, 1-18. [CrossRef]
- LI, L. Z., & YANG, X. (2014). China's rare earth ore deposits and beneficiation. ERES2014: 1st European Rare Earth Resources Conference|Milos|04-07/09/2014 (pp. 26-36). ERES.
- Li, M., Liu, C., Ding, A., & Cgaenggliang. (2023). A review on the extraction and recovery of critical metals using molten salt electrolysis. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11, 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Lia, D., Tang, Y., Denga, T., Chena, K., & Liua, D. (2008). Geochemistry of rare earth elements in coal-A case study from Chongqing, southwestern China. Energy exploration & exploitation, 26(6), 355-362. [CrossRef]
- Liang, X., Gao, S., Gong, G., Wang, Y., & Yang, J.-G. (2008). Synthesis of a Novel Heterogeneous Strong Acid Catalyst from p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA) and its Catalytic Activities. Catalysis Letters volume, 352-356. [CrossRef]
- Limaz, A. T., & Ottosen, L. M. (2022). Rare Earth Elements Partition and Recovery During Electrodialytic Treatment of Coal Fly Ash. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 169, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B., Robertson, G. P., Kim, D.-S., Guiver, M. D., Hu, W., & Jiang, Z. (2007). Aromatic Poly(ether ketone)s with Pendant Sulfonic Acid Phenyl Groups Prepared by a Mild Sulfonation Method for Proton Exchange Membranes. Macromolecules , 40, Macromolecules. [CrossRef]
- Liu, P., Zhao, S., Xie, N., Yang, L., Wang, Q., Wen, Y., et al. (2023 ). Green Approach for Rare Earth Element (REE) Recovery from Coal Fly Ash. Environ Sci Technol., 57(13), 5414-5423. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-L., Fan, H.-R., Liu, X., Meng, J., Butcher, A. R., Yann, L., et al. (2023). Global rare earth elements projects: New developments and supply chains. Ore Geology Reviews, 157, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-L., Fan, H.-R., Liu, X., Meng, J., Butcher, A. R., Yann, L., et al. (2023,). Global rare earth elements projects: New developments and supply chains. Ore Geology Reviews, 157, 1-11.
- Long, K. R., Gosen, B. S., Foley, N. K., & Cordier, D. (2010). The Geology of Rare Earth Elements. Retrieved from Geology.com: https://geology.com/usgs/ree-geology/.
- Long, K., Van Gosen, B., Foley, N., & Cordier, D. (2013). The Principal Rare Earth Elements Deposits of the United States-A Summary of Domestic Deposits and a Global Perspective. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report . http:/. [CrossRef]
- Looney, J. R., & McDougall, L. A. (1984). Patent No. US 4442014. USA.
- Lottermoser, B. (2010). Mine Wastes: Characterization, Treatment and Environmental Impacts, 3 rd Edition. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. [CrossRef]
- Lu, J., & Dreisinger, D. (2021). Lead electrowinning from methane sulfonic acid. Hydrometallurgy, 203, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Luís, A. T., Córdoba, F., Antunes, C., Loayza-Muro, R., Grande, J. A., Silva, B., et al. (2022). Extremely Acidic Eukaryotic (Micro) Organisms: Life in Acid Mine Drainage Polluted Environments-Mini-Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health., 19(1), 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Luong, B., Petre, A., Hoelderich, W., Commarieu, A., Laffitte, J., Espeillac, M., et al. (2004). Use of methanesulfonic acid as catalyst for the production of linear alkylbenzenes. Journal of Catalysis, 2262, 301-307. [CrossRef]
- Mahindaratne, M. P., & Wimalasena, K. (1998). Detailed Characterization of p-Toluenesulfonic Acid Monohydrate as a Convenient, Recoverable, Safe, and Selective Catalyst for Alkylation of the Aromatic Nucleus. Org. Chem., 6(9), 2858-2866. [CrossRef]
- Maity, S., Choudhary, A. K., Kumar, S., & Gupta, P. K. (2022). Partitioning of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from Coal to Coal Fly Ash in Different Thermal Power Stations (TPSs) of India. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 98, 460-466 (2022. [CrossRef]
- Maliki, A. I., Shahidan, S., Ali, N., Hannan, N. I., Zuki, S. S., Ibrahim, M. H., et al. (2017). Compressive and tensile strength for concrete containing coal. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 271 , pp. 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Mangi, S. A., Ibrahim, M. H., Jamaluddin, N., Arshad, M. F., & Mudjanarko, S. W. (2019). Recycling of Coal Ash in Concrete as a Partial Cementitious Resource. Resources , 8(2). [CrossRef]
- Martyak, N., & Ricou, P. (2004). Mater. Chem. Phys., 84, 87-98. [CrossRef]
- Mbaraka, I. K., Radu, D. R., Lin, V. S.-Y., & Shanks, B. H. (2003). Organosulfonic acid-functionalized mesoporous silicas for the esterification of fatty acid. Journal of Catalysis, 219(2), 329-336. [CrossRef]
- MEI. (2018). Comminution '18 Conference Diary. Comminution '18 Conference Diary. Cape Town: MEI.
- Metaxas, A., & Meredith, R. (1998). handbook of industrial microwave heating. No. 25. Iet. Meredith, Roger J. Engineers.
- Michigan-State-University. (2023, September 06). Perchloric Acid. Retrieved from https://ehs.msu.edu/lab-clinic/chem/perchloric.html.
- Miranda, M. M., Bielicki, J. M., Chun, S., & Cheng, C.-M. (2022). Recovering Rare Earth Elements from Coal Mine Drainage Using Industrial Byproducts: Environmental and Economic Consequences. Environmental Engineering Science, 39(9), 770-783. [CrossRef]
- Mission-2016. (2016). The Future of Strategic Natural Resources. Retrieved from Rare Earth Elements: https://web.mit.edu/12.000/www/m2016/finalwebsite/elements/ree.html#:~:text=Rare%20earth%20elements%20occur%20in,use%2C%20such%20as%20Cu%20or.
- Moncur, M. C. (2023, September 13). Acid mine drainage: past, present...future. Retrieved from University of Waterloo: https://uwaterloo.ca/wat-on-earth/news/acid-mine-drainage-past-presentfuture.
- Moncur, M., Ptacek, C., Blowes, D., & Jambor, J. ( 2005). Release, transport and attenuation of metals from an old tailings impoundment. Applied Geochemistry, 20, 639-659. [CrossRef]
- National-Cancer-Institute. (2022). Strong Inorganic Acid Mists Containing Sulfuric Acid. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/substances/inorganic-acid.
- NETL. (2020). Acid digestion and electrowinning processes demonstrate recovery of rare earth elements from coal fly ASH . Retrieved from National Energy Technology Laboratory: https://netl.doe.gov/node/9792.
- Newsted, J., & Jones, P. (2005). Surfactants, Perfluorinated. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Second Edition) (pp. 121-123). [CrossRef]
- Ngo, S.-H., Huynh, T.-P., Le, T.-T. T., & Mai, N.-H. T. (2018). Effect of High Loss on Ignition-Fly Ash on Properties of Concrete Fully Immersed in Sulfate Solution. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Volume 371, 2018 3rd International Conference on Building Materials and Construction (ICBMC 2018) (pp. 1-8). Nha Trang,Vietnam: IOP. [CrossRef]
- Nicol, M. J. (2020). The role and use of hydrogen peroxide as an oxidant in the leaching of minerals. 1. acid solutions. Hydrometallurgy, 193, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, T., Ito, H., Horiba, K., & Toyoda, N. (2022). Synthesis of Water-Soluble Polymeric Surfactants Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups and the Effects of Hydrophilic Components on the Rheology and Dispersive Properties of Dye Dispersions. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater., 4(11), 8556-8563. [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, T., Ito, H., Horiba, K., & Toyoda, N. (2022). Synthesis of Water-Soluble Polymeric Surfactants Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups and the Effects of Hydrophilic Components on the Rheology and Dispersive Properties of Dye Dispersions. ACS Appl. Polym., 4(11), 8556-8563. [CrossRef]
- Oishi, T., Konishi, H., Nohira, T., & Tanaka, M. (2010). Separation and Recovery of Rare Earth Metals by Molten Salt Electrolysis using Alloy Diaphragm. Kagaku Kōgaku Ronbunshū 36(4):299-303, 36(4), 299-303. [CrossRef]
- Ozbayoglu, G. U. (2000). Beneficiation of bastnaesite by a multi-gravity separator. J. Alloys Compd., 303-304, 520-523. [CrossRef]
- Palden, T., Onghena, B., Regadío, M., & Binnemans, K. (2019). Methanesulfonic acid: a sustainable acidic solvent for recovering metals from the jarosite residue of the zinc. Industry Green Chem., 21, 5394-5404. [CrossRef]
- Palden, T., Onghena, B., Regadío, M., & Binnemans, K. (2019). Methanesulfonic acid: a sustainable acidic solvent for recovering metals from the jarosite residue of the zinc industry. Green Chem., 19(21), 5394-5404. [CrossRef]
- Palma, M. N., Rocha, G. C., Valadares Filho, S. C., & Detmann, E. (2015). Evaluation of Acid Digestion Procedures to Estimate Mineral Contents in Materials from Animal Trials. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci., 28(11), 1624-1628. [CrossRef]
- Pan, J., Hassas, B. V., Rezaee, M., Zhou, C., & Pisupat, S. V. (2021). Recovery of rare earth elements from coal fly ash through sequential chemical roasting, water leaching, and acid leaching processes. Journal of Cleaner Production, 284, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Pan, J., Nie, T., Hassas, B. V., Rezaee, M., Wen, Z., & Zhou, C. (2020). Recovery of rare earth elements from coal fly ash by integrated physical separation and acid leaching. Chemosphere. [CrossRef]
- Pan, J., Zhou, C., Liu, C., Tang, M., Cao, S., Hu, T., et al. (2018). Modes of Occurrence of Rare Earth Elements in Coal Fly Ash: A Case Study. Energy Fuels, 32, 9738-9743. [CrossRef]
- Parac-Vogt, T., & Binnemans, K. (2004). Lanthanide(III) nosylates as new nitration catalysts. Tetrahedron Lett., 45(15), 3137-3139. [CrossRef]
- Park, S., Kim, M., Lim, Y., Yu, J., Chen, S., Woo, S. W., et al. (2021). Characterization of rare earth elements present in coal ash by sequential extraction. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 402, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Park, S., Kim, M., Yejee Lim, J. Y., Chen, S., Woo, S. W., Yoon, S., et al. (2021). Characterization of rare earth elements present in coal ash by sequential extraction. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 4020(15), 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Pecharsky, V. K., & Gschneidner, K. A. (2023). Rare earth Elements. Retrieved from The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica: https://www.britannica.com/science/rare-earth-element.
- Pecina, T., Franco, T., Castillo, P., & Orrantia, E. (2008). Leaching of a zinc concentrate in H2SO4 solutions containing H2O2 and complexing agents. Min. Eng., 21, 23-30. [CrossRef]
- Peiravi, M., Ackah, L., Guru, R., Mohanty, M., J. Liu, B. X., Zhu, X., et al. (2017). Chemical extraction of rare earth elements from coal ash. Miner. Metall. Process., 34(4), 170-177. [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, A. F., Soliman, M. M., Pinto, T. V., Silva, S. M., Costa, P., Alegria, E. C., et al. (2021). Highly active organosulfonic aryl-silica nanoparticles as efficient catalysts for biomass derived biodiesel and fuel additives. Biomass and Bioenergy, 145, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Peng, S., Hu, Q., & Hamamoto, S. (2012). Diffusivity of rocks : Gas diffusion measurements and correlation to porosity and pore size distribution. Water resources research, 48, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Prihutami, P., Prasetya, A., Sediawan, W. B., Petrus, H. T., & Anggara, F. (2021). Study on Rare Earth Elements Leaching from Magnetic Coal Fly Ash by Citric Acid. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 1241-1253(7), 1241-1253. [CrossRef]
- Pritzker, M. D. (1996). Shrinking-core model for systems with facile heterogeneous and homogeneous reactions. Chemical Engineering Science, 51(14), 3631-3645. [CrossRef]
- Raask, E. (1985). The mode of occurrence and concentration of trace elements in coal. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 11(2), 97-118. [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, G., Rastegar, S. O., Chianeh, F. R., & Gu, T. (2020). Ultrasound-assisted leaching of vanadium from fly ash using lemon juice organic acids. RSC Advances, 10(3), 1685-1696. [CrossRef]
- Rappoport, Z., & Patai, S. (1991). The Chemistry of Sulphonic Acids, Esters and their Derivatives (Vol. 251). New York: John Wiley and Sons.
- Razieh Sobhi Amjad, M. A.-M. (n.d.). An efficiency strategy for cobalt recovery from simulated wastewater by biphasic system with polyethylene glycol and ammonium sulfate. Scientific Reports, 12, 1-12.
- Reinhardt, H. (1998). Hazardous wastE: Sources, Effects and Management. International Conference on Hazardous waste: Sources, Effects and Management. Cairo: Hazardous wast.
- Resende, L. V., & Morais, C. A. (2015). Process development for the recovery of europium and yttrium from computer monitor screens. Minerals Engineering, 70, 217-221. [CrossRef]
- Reuters. (2021). Factbox: Automakers cutting back on rare earth magnets. Retrieved from https://www.reuters.com/business/autos-transportation/automakers-cutting-back-rare-earth-magnets-2021-07-19/.
- Riddell, J. (2020). Evaluation of coal ash chemistry indices for predicting CSR (coke strength after reaction with CO2 British Columbia. Ministry of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources Mines and Mineral Resources Division British Columbia Geological Survey. Ministry of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources.
- Rodriguez, N. R., Onghena, B., & Binnemans, K. (2019). Recovery of Lead and Silver from Zinc Leaching Residue Using Methanesulfonic Acid. CS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 7(24), 19807-19815. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N., Grymonprez, & Binnemans, K. (2021). Integrated Process for Recovery of Rare-Earth Elements from Lamp Phosphor Waste Using Methanesulfonic Acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 60(28), 10319-10326. [CrossRef]
- Roitman, D., McAlister, J., & Oaks, F. (1004). Composition characterization of methanesulfonic-acid. J Chem Eng Data, 39, :56-60. [CrossRef]
- Saha, B., Eliason, K., Golui, D., Masud, J., Bezbaruah, A., & Iskander, S. (2023). Rare earth elements in sands collected from Southern California sea beaches. Chemosphere, 344. [CrossRef]
- Sanematsu, K., & Watanabe, Y. (2016). Characteristics and genesis of ion adsorptiontype rare earth element deposits. Rev. Econ. Geol., 18, 55-79. [CrossRef]
- Sangsiri, P., Laosiripojana, N., & Daorattanachai, P. (2022). Synthesis of sulfonated carbon-based catalysts from organosolv lignin and methanesulfonic acid: Its activity toward esterification of stearic acid. Renewable Energy, 193, 113-127. [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, M., King, M., Sole, K., & Davenport, W. (2011). Extractive metallurgy of copper. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
- Schoonheydt, R. A., & Johnston, C. T. (2013). Chapter 5 - Surface and Interface Chemistry of Clay Minerals. In: Developments in Clay Science. Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Schure, M. R., Soltys, P. A., Natusch, D. F., & Mauney, T. (1985). Surface Area and Porosity of Coal Fly Ash. Environ. Sci. Technol., 19, 82-86. [CrossRef]
- Scientific, F. (2023, 09 06). Organic sulfonic acids and derivatives. Retrieved from https://www.fishersci.ca/ca/en/browse/80013802/organic-sulfonic-acids-and-derivatives.
- Seferinoğlu, M., Paul, M., Sandström, Å., Köker, A., Toprak, S., & Paul, J. (2003). Acid leaching of coal and coal-ashes. Fuel, 82(14), 1721-1734. [CrossRef]
- Seligman, L. (2022). China Dominates the Rare Earths Market. This U.S. Mine Is Trying to Change That. Retrieved from Politica: https://www.politico.com/news/magazine/2022/12/14/rare-earth-mines-00071102#:~:text=As%20of%20today%2C%20China%20accounts,firearms%2C%20radars%20and%20stealth%20aircraft.
- Seredin, V. (1996). Rare earth element-bearing coals from the Russian Far East deposits. International Journal of Coal Geology, 30(1-2), 101-129. [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V., & Dai, S. (2012). Coal deposits as potential alternative sources for lanthanides and yttrium. Int. J. Coal Geol., 94 (2012), pp. 67-93, Int. J. Coal Geol. [CrossRef]
- Shen, L., & Zeng, Q. (2021). Investigation of the kinetics of spontaneous combustion of the major coal seam in Dahuangshan mining area of the Southern Junggar coalfield, Xinjiang, China. Scientific Reports, 876, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Shena, L., Shen, L., & Chen, Z. (2007). Critical review of the impact of tortuosity on diffusion. Chemical Engineering Science (Pergamon), 62(14), 748-3755. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y., & Wang, C.-Y. (1986). Pore pressure generation in sedimentary basins: Overloading versus aquathermal. 91(B2), 2153-2162. [CrossRef]
- Shopper, A., Valeev, D., Napol'skikh, J., Loginova, I., Pan, J., Chen, H., et al. (2023). Rare-Earth Elements Extraction from Low-Alkali Desilicated Coal Fly Ash by (NH4)2SO4 + H2SO4. Bessel, 16(1), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Shunda Yuan, J. P., Bi, X., Qi, L., Li, Z., Li, X., & Shuang, Y. (2008). Characteristics of rare-earth elements (REE), strontium and neodymium isotopes in hydrothermal fluorites from the Bailashui tin deposit in the Furong ore field, southern Hunan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 27, 342-350. [CrossRef]
- Silva, S. M., Peixoto, A. F., & Freire, C. (2020). Organosulfonic acid functionalized montmorillonites as solid catalysts for (trans) esterification of free fatty acids and (waste) oils. Renewable Energy, 146(C), 2416-2429. [CrossRef]
- Silyanov, S. A., Sazonov, A. M., Naumov, E. A., Lobastov, B. M., Zvyagina, Y. A., Artemyev, D. A., et al. (2022). Mineral Paragenesis, formation stages and trace elements in sulfides of the Olympiada gold deposit (Yenisei Ridge, Russia). Ore Geology Reviews, 143, 1-19. [CrossRef]
- SkyQuest. (2022). Global Methane Sulfonic Acid Market Insights. Retrieved from https://www.skyquestt.com/report/methanesulfonic-acid-market#:~:text=Global%20Methanesulfonic%20Acid%20Market%20Insights,period%20(2023%2D2030).
- Smith, M., Moore, K., Kavecsánszki, D., Finch, A., Kynicky, J., & Wall, F. (2016). From mantle to critical zone: a review of large and giant sized deposits of the rare earth elements. Geosci. Front., 7, 315-334. [CrossRef]
- Smolka-Danielowska, D. (2010). 2010. Rare earth elements in fly ashes created during the coal burning process in certain coal-fired power plants operating in Poland-Upper Silesian Industrial Region. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 101, 965-968. [CrossRef]
- Sobri, N., Yunus, M., & Harun, N. (2023). A review of ion adsorption clay as a high potential source of rare earth minerals in Malaysia. Materials Today: Proceedings, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, A. P., Konyushok, A. A., Ageev, O. A., Zarubina, N. V., Ivanov, V. V., & Wang, J. (2019). Distribution of rare earth and selected trace elements in combustion products of Yerkovetskoe brown coal deposit (Amur Region, Russia). Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 37(6), 1721-1736. [CrossRef]
- Sowerbutts, L. (2013). Rare Earth Element Deposits. Retrieved from Geology for Inventors.
- Speight, J. G. (2017). Chapter Three - Industrial Inorganic Chemistry. In Environmental Inorganic Chemistry for Engineers (pp. 111-169). Science Direct. [CrossRef]
- Springborn-Laboratories. (1997). An Acute Oral Toxicity Study in Rats with 70% Methane Sulfonic Acid. SLI Study No. 3255.
- Suoranta, T., Zugazu, O., & Niemel, M. (2015). Recovery of palladium, platinum, rhodium and ruthenium from catalyst materials using microwave assisted leaching and cloud point extraction. Hydrometallurgy, 154 , 56-62. [CrossRef]
- Swaine, D. (1977). Trace Elements in Coak in Traw Substances in Environmental Health-XI. In D. E. Hemphill (Ed.).
- Taggart, R. K., Hower, J. C., Dwyer, G. S., & Hsu-Kim, H. (2016). Trends in the Rare Earth Element Content of U.S.-Based Coal. Environ. Sci. Technol., 50, 5919−5926. [CrossRef]
- Tang, M., Zhou, C., Pan, J., Zhang, N., Liu, C., Cao, S., et al. (2019). Study on extraction of rare earth elements from coal fly ash through alkali fusion - Acid leaching. Minerals Engineering, 136, 36-42. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P., Choi, Y., & Vidal, E. (2003). Hydrometallurgy 2003, 1, Society for Mining, metallurgy and exploration, Littleton, Colorado . Fluosilicic acid leaching of galena, 461-473.
- Thakkar, R., & Chudasama, U. (2008). Synthesis of mono and diesters using eco-friendly solid acid catalyst - zirconium titanium phosphate. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 2(2), 61-69. [CrossRef]
- Thenepalli, T., Chilakala, R., Tuan, L. Q., & Kim, C. S. (2019). A Brief Note on the Heap Leaching Technologies for the Recovery of Valuable Metals. Sustainability (11). [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A. S., OWENS, N. J., & MURRELL, C. J. (1995). Isolation and Characterization of Methanesulfonic AcidDegrading Bacteria from the Marine Environment. Applied and environmental microbiologY, 61(6), 2388-2393. [CrossRef]
- Thonstad, J. (1990). Some Recent Trends in Molten Salt Electrolysis of Titanium, Magnesium, and Aluminium. High Temperature Materials and Processes, 9(2-4), 135-146. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y., Meng, X., Duan, J.-y., & Shi, L. (2012). A Novel Application of Methanesulfonic Acid as Catalyst for the Alkylation of Olefins with Aromatics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 51(42), 13627-13631. [CrossRef]
- Tjaden, B., Lane, J., Withers, P. J., Bradley, R. S., Brett, D. J., & Shearing, P. R. (2016). The application of 3d imaging techniques, simulation and di usion experiments to explore transport properties in porous oxygen transport membrane support materials. Solid State Ionics, 288, 31-321. [CrossRef]
- USDE. (2020). Recovery of High Purity Rare Earth Elements (REE) from Coal Ash via a Novel Electrowinning Process: Final Report. U.S. Department of Energy.
- USDT. (2016). User Guidelines for Waste and Byproduct Materials in Pavement Construction. Federal Highway Administration Research and Technology.
- USGS. (2014). The Rare-Earth Elements-Vital to Modern Technologies and Lifestyles. USGS.
- USGS. (2017). Rare Earth Elements in Coal and Coal Fly Ash. Retrieved from Science for Cahnaging World: https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2019/3048/fs20193048.pdf.
- USGS. (2015). Mineral Commodity Summaries. U.S. Geological Survey .
- Valkovic, V. (1983). Trace Elements in coal, Boca Raton. CRC Press.
- Vandenberghe, R., Resende, V. d., Costa, G. d., & Grave, E. D. (2010). Study of loss-on-ignition anomalies found in ashes from combustion of iron-rich coal. Fuel, 89, 2405-2410. [CrossRef]
- Verplanck, P. L., Mariano, A. N., & Marianov Jr., A. (2016). Rare earth element ore geology of carbonatites. Littleton, CO: Society of Economic Geologists, Inc. [CrossRef]
- VDH. (2023). Hydro Chloric Acid. Retrieved from https://www.vdh.virginia.gov/environmental-health/public-health-toxicology/hydrochloric-acid/.
- Wall, F., Rollat, A., & Pell, R. S. (2017). Responsible sourcing of critical metals Elements. 313-318, 13, 313-318. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B., Tian, W., Fu, B., & Fang, J.-Q. (2021). Channelized CO2-Rich Fluid Activity along a Subduction Interface in the Paleoproterozoic Wutai Complex, North China Craton. Minerals, 11(748), 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S., Li, J., Narita, H., & Tanaka, M. (2018). Equilibrium Modeling for Solvent Extraction of Nickel and Ammonia from Alkaline Media with the Extractant LIX84-I. Materials transactions, 59(4). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., Dai, S., Zou, J., French, D., & Graham, I. (2019). Rare earth elements and yttrium in coal ash from the Luzhou power plant in Sichuan, Southwest China: Concentration, characterization and optimized extraction. Int. J. Coal Geol., 203, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y., Fan, H.-R., Zhou, L., K.-F. Y., & She, H.-D. (2020). Carbonatite-Related REE Deposits: An Overview. Hai-Dong She, 10(965), 1-26. [CrossRef]
- Ward, C., & French, D. (2005). Relation between coal and fly ash mineralogy, based on quantitative X-ray diffraction methods. World Coal Ash (WOCA), 11, 1-14.
- Weng, Z., Jowitt, S. M., Mudd, G. M., & Haque, N. (2015). A detailed assessment of global rare earth element resources: opportunities and challenges. Econ. Geol., 110, 1925-1952. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Lin, Z., Liang, X., et al. (2023). Review of rare earth element (REE) adsorption on and desorption from clay minerals: Application to formation and mining of ion-adsorption REE deposits. Ore Geology Reviews. [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.-l., Feng, M., Zhang, L.-w., & Nie, Z.-r. (2020). Applications of molten salt and progress of molten salt electrolysis in secondary metal resource recovery. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 27, 1599-1617. [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.-l., Feng, M., Zhang, L.-w., & Nie, Z.-r. (2020). Applications of molten salt and progress of molten salt electrolysis in secondary metal resource recovery. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 27(12), 1599-1617. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L., Cheng, X., Zhang, T., Guo, M., & Zhang, M. (2022). Efficient Inorganic/Organic Acid Leaching for the Remediation of Protogenetic Lead-Contaminated Soil. Appl. Sci., 12(8), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, Q., Geng, X., Liang, C., Zhang, P., et al. (2023). Failure and regeneration of hydroxyoxime in copper solvent extraction process: A review. Hydrometallurgy, 221, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Xin, C., Xia, H., Jiang, G., Zhang, Q., Zhang, L., & Xu, Y. (2022). Studies on Recovery of Valuable Metals by Leaching Lead-Zinc Smelting Waste with Sulfuric Acid. Minerals, 12, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Yan, H., Pi, D.-H., Jiang, S.-Y., Mao, J., Xu, L., Yang, X., et al. (2022). Mineral paragenesis in Paleozoic manganese ore deposits: Depositional versus post-depositional formation processes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 325, 65-86. [CrossRef]
- Yan, X. Y., & Fray, D. J. (2010). Molten salt electrolysis for sustainable metals extraction and materials processing - A REVIEW. In In: Electrolysis: Theory, Types and Applications-Chapter 6 (pp. 1-49). Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
- Yang, X. J., Lin, A., b, X.-L. L., Wu, Y., Zhou, W., & Chen, Z. (2013). China's ion-adsorption rare earth resources, mining consequences and preservation. Environ. Dev., 8, 131-136. [CrossRef]
- Yin, X. Y., Martineau, C., Demers, I., Basiliko, N., & J., N. (2021). The potential environmental risks associated with the development of rare earth element production in Canada. Environmental ReviewsVolume, 29(3). [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y., Lou, X., Li, S., Yang, C., & Yin, X. (2014). Direct simulation of the influence of the pore structure on the diffusion process in porous media. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 67(2), 412-423. [CrossRef]
- Zapp, P., Schreiber, A., Marx, J., & Kuckshinrichs, W. (2022). Environmental impacts of rare earth production. MRS Bulletin volume, 47, 267-275. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S., Zhang, W., Zhang, G., Bai, Y., Chen, S., Xu, J., et al. (2018). p-Toluenesulfonic acid catalytic polymerization of EDOT without oxidants. Materials Letters, 222, 105-108. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W., Yang, X., & Honaker, R. Q. (2018). Association characteristic study and preliminary recovery investigation of rare earth elements from Fire Clay seam coal middlings. Fuel, 215, 551-560. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. e. (2020). . "Alkaline electrochemical leaching of Sn and Pb from the surface of waste printed circuit board and the stripping of gold by methanesulfonic acid. " Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 39(2). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Guan, & al, G. Y. (2017). Effective dismantling of waste printed circuit board assembly with methanesulfonic acid containing hydrogen peroxide. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 36:873-878, 36, 873-878. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C., Jiang, K., Cao, Z., Northwood, D. O., Waters, K. E., Wang, H., et al. (2023). Agitation Leaching Behavior of Copper-Cobalt Oxide Ores from the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Minerals, 13, 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Zhifeng, G., Zhen, L., Peng, L., & Wanchun, L. (2016). Experimental analysis of aquathermal pressuring under high temperature conditions and its geological implications. Petroleum geology & experiment, 2016, 38(6): 836-841, 38(6), 836-841.
- Zhou, B., Li, Z., & Chen, C. (2017). Global Potential of Rare Earth Resources and Rare Earth Demand from Clean. Technologies. Minerals, 7(203), 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C. H., & Keeling, J. (2013). Fundamental and applied research on clay minerals:from climate and environment to nanotechnology. Appl. Clay Sci., 74, 3-9. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J., Meng, X., Zhang, R., Liu, H., & Liu, ·. Z. (2021). Progress on Electrodeposition of Rare Earth Metals and Their Alloys. Electrocatalysis, 12, 628-640. [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, R., Foster, A., Meeker, G., & Brownfield, I. (2007). Mode of occurrence of arsenic in feed coal and its derivative fly ash, Black Warrior Basin, Alabama. Fuel, 86(4), 560-572. [CrossRef]
- Ziemniak, S. E., Guilmette, P. A., Turcotte, R. A., & Tunison, H. M. (2007). Oxidative Dissolution of Nickel Metal in Hydrogenated Hydrothermal Solutions. Lockheed Martin Corporation. [CrossRef]
- Ziyan Yang a b, F. X., Sun, S., Zhong, H., & Tu, G. (2023). REEs recovery from molten salt electrolytic slag: Challenges and opportunities for environmentally friendly techniques. Journal of Rare Earths. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





