Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Experimental section
Material
Synthesis
Standard solutions and samples preparation
Characterization and analysis
III. Results and discussion
Synthesis
Method validation
IV. Conclusion
Acknowledgement
References
- Nguyen-Vu, L. Library of Bimetallic Three Way Catalyst. Scientific Journal of Hanoi Metropolitan University. 2023, 74, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- G. C., Bond. Platinum Metals as Hydrogenation Catalysts. Platin. Met. Rev. 1957, 1, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Novell-Leruth, G., Valcárcel. Ammonia dehydrogenation over platinum-group metal surfaces. Structure, stability, and reactivity of adsorbed NHx species. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S. K. <italic>et al.</italic>; et al. Understanding the biosynthesis and catalytic activity of Pd, Pt, and Ag nanoparticles in hydrogenation and Suzuki coupling reactions at the nano-bio interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 24623–24632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didgikar, M. R., Roy. Immobilized palladium nanoparticles catalyzed oxidative carbonylation of amines. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakap, M. Poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone)-stabilized palladium-platinum nanoparticles-catalyzed hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen generation. J. Power Sources 2015, 276, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L. <italic>et al.</italic>; et al. Promotion of CeO2-ZrO2-Al2O3 composite by selective doping with barium and its supported Pd-only three-way catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 410, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, H. D. <italic>et al.</italic>; et al. Simultaneous nondestructive analysis of palladium, rhodium, platinum, and gold nanoparticles using energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10142–10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. ISO/IEC 17025:2017.
- Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results - Part 1: General principles and definitions. ISO 5725-1:1994.
- Harris, Daniel C. Quantitative Chemical Analysis Eighth Edition (8th); W.H.Freeman and Company: New York, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results - Part 2: Basic method for the determination of repeatability and reproducibility of a standard measurement method. ISO 5725-2:1994.
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis, (2019). Appendix F: Guidlines for Standard Method Performance Requirements.
- Malvern Panalytical, (2021). Products - Product category - XRF analyzers. Available online: www.malvernpanalytical.
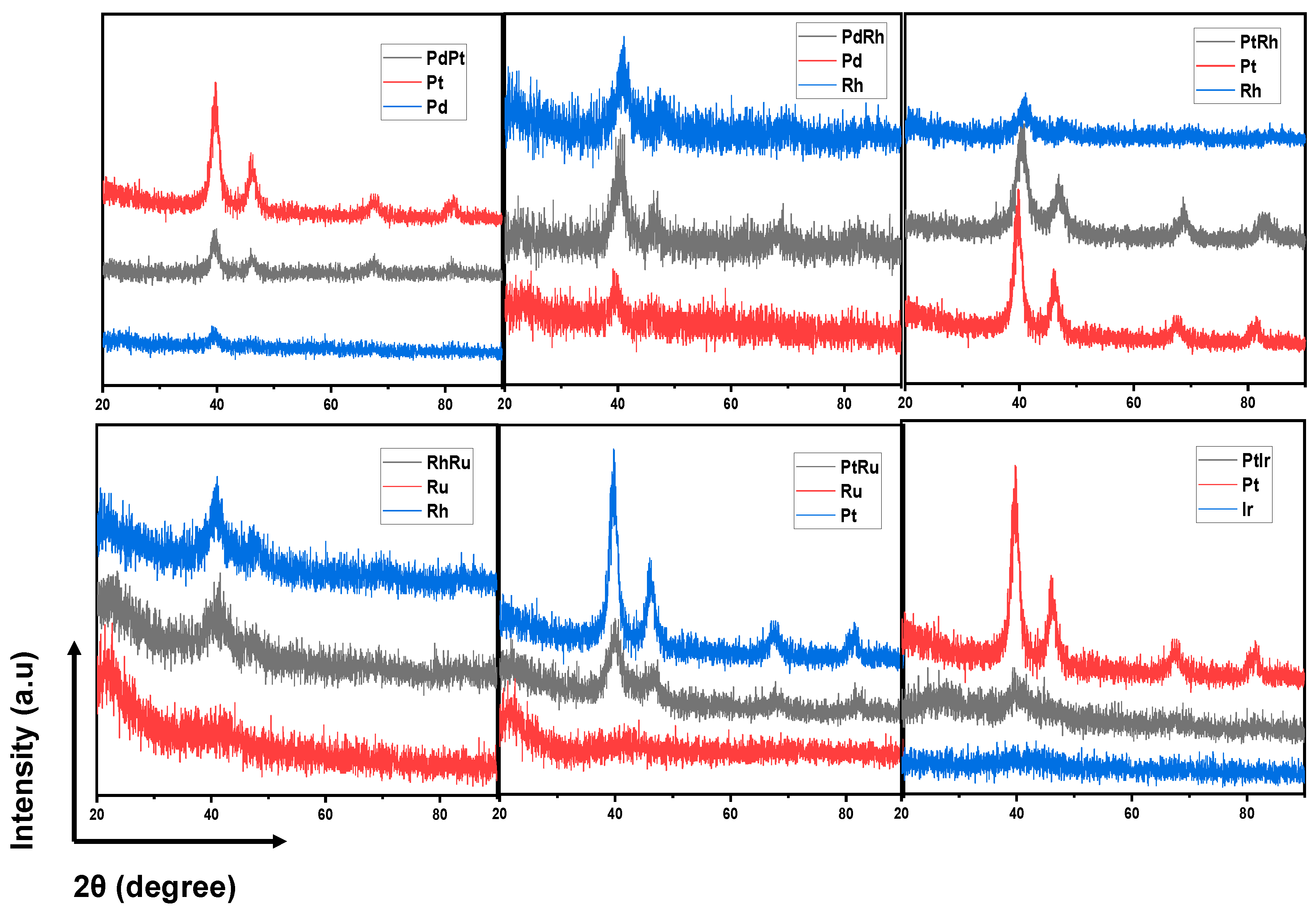
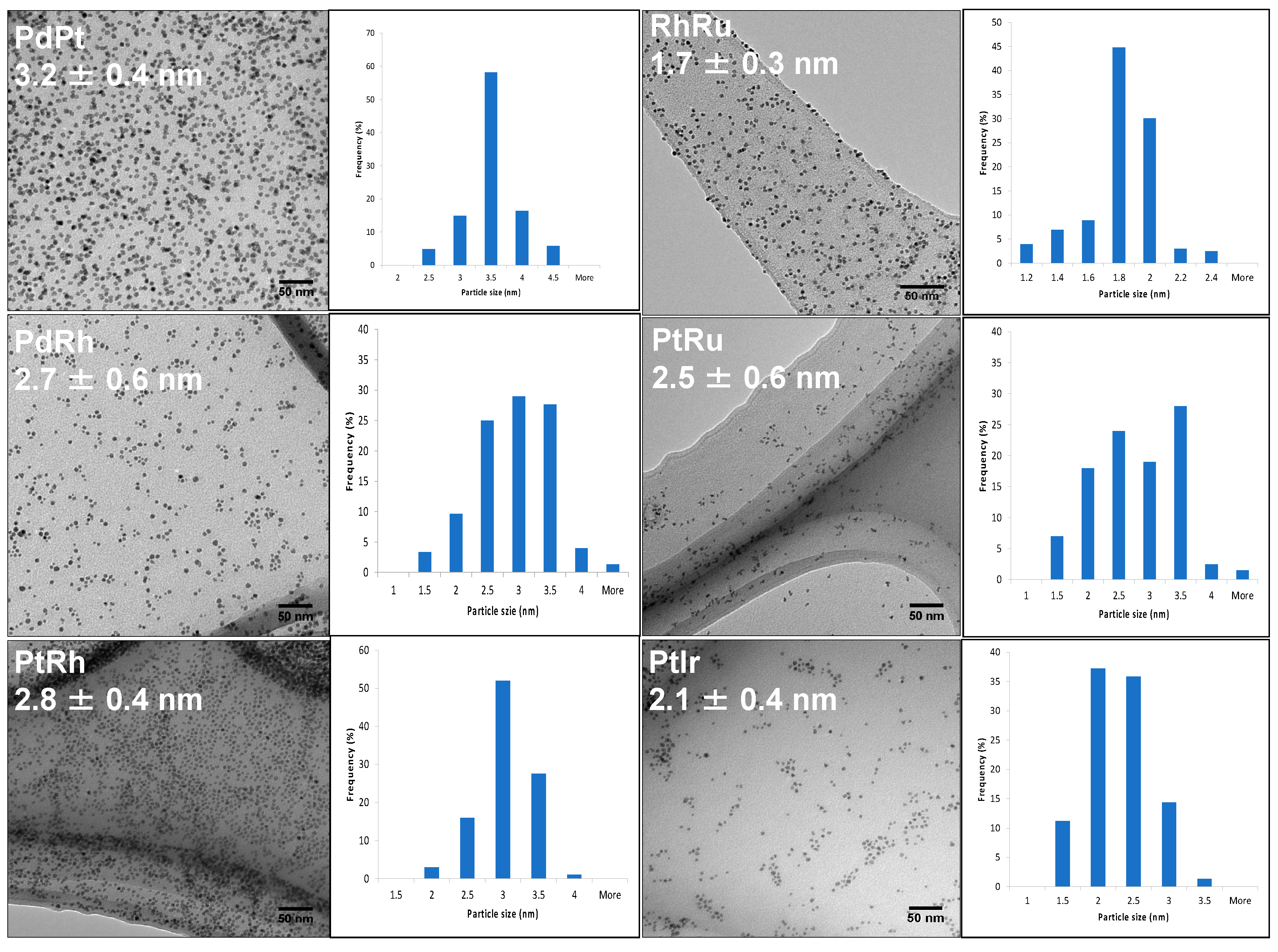
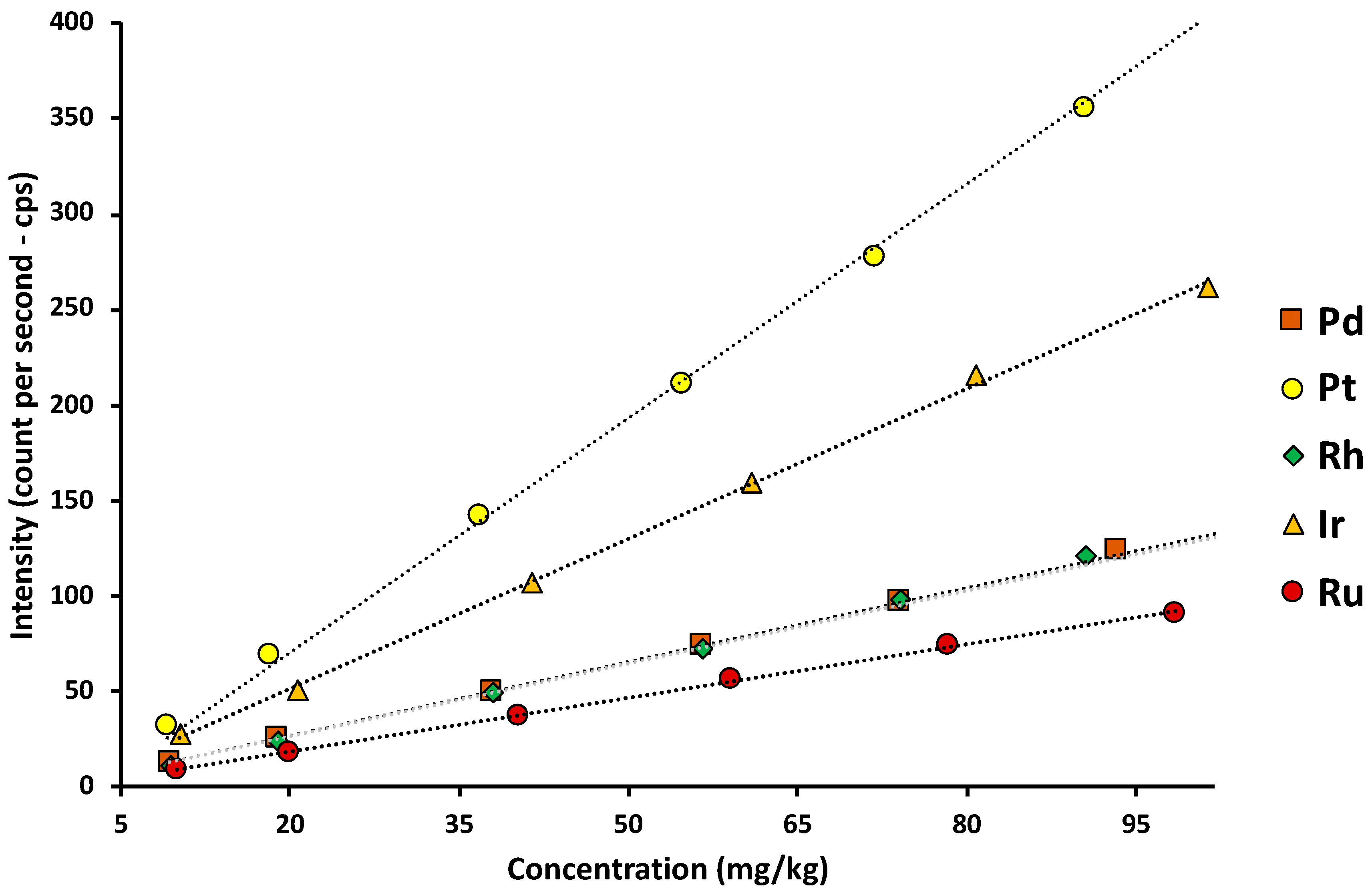
| Bimetallic particle (AB) | XRF calibration curve | SEM-EDS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conc A (mg/kg) | RSD (%) |
Conc B (mg/kg) | RSD (%) |
A : B (mol%) | A : B mol% | |
| PdPt | 58,3 ± 2,0 | 1,693 | 122,8 ± 1,2 | 0,519 | 46,5 : 53,5 ± 1,8 50,1 : 49,9 ± 2,4 52,3 : 47,7 ± 1,3 43,2 : 56,8 ± 4,2 46,4 : 53,6 ± 1,7 45,2 : 54,8 ± 1,4 |
54,6 : 45,4 ± 1,0 51,2 : 48,8 ± 0,6 47,7 : 52,3 ± 0,4 51,0 : 49,0 ± 1,5 46,5 : 53,5 ± 1,0 51,8 : 48,2 ± 0,8 |
| PdRh | 60,2 ± 1,4 | 1,160 | 58,1 ± 2,4 | 2,148 | ||
| PtRh | 142,2 ± 2,4 | 0,853 | 68,3 ± 1,2 | 0,950 | ||
| RhRu | 72,9 ± 4,4 | 2,959 | 94,2 ± 5,6 | 2,991 | ||
| PtRu | 194,4 ± 2,8 | 0,721 | 116,4 ± 3,6 | 1,561 | ||
| PtIr | 200,2 ± 2,8 | 0,681 | 239,2 ± 6,0 | 1,267 | ||
| Pd | Pt | Rh | Ir | Ru | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t caculated | 1,12308710 | 1,24474965 | 1,35082865 | 1,04573350 | 0,47278870 |
| t theory | 2,22813885 | 2,26215716 | 2,16036866 | 2,22813885 | 2,44691185 |
| Variances | Symbol | Sample 1 | Sample 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of repetition | n | 3 | 3 |
| Mean Pd content (%) | 50,1 | 50,0 | |
| Standard deviation | 1,22 | 1,13 | |
| Repeatability variance | 1,17 | ||
| 0,122 | |||
| -0,445 | |||
| Between-laboratory variance | 0,00 | ||
| General mean | 50,05 | ||
| IP variance | 1,17 | ||
| Relative IP variance (%) | 2,35 | ||
| Element | Analytical Equation | R2 | LoD (mg/kg) |
LoQ (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd | I = (1,3202 ± 0,0135)[Pd] – (0,6458 ± 0,3817) | 0.9999 | 2,1 | 7,0 |
| Pt | I = (3,9548 ± 0,0518)[Pt] – (5,1008 ± 2,8498) | 0.9998 | 4,0 | 13,2 |
| Rh | I = (1,3498 ± 0,0230)[Rh] – (2,2225 ± 1,6218) | 0.9995 | 5,6 | 18,6 |
| Ru | I = (0,9378 ± 0,0238)[Ru] – (0.6494 ± 1.4237) | 0.9994 | 4,3 | 14,3 |
| Ir | I = (2,6228 ± 0.0805)[Ir] – (1.1883 ± 4,9621) | 0.9991 | 4,5 | 15,1 |
| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 50,47 | 47,2816198 |
| Variance | 8,57904 | 11,1645337 |
| Observations | 6 | 6 |
| Pearson Correlation | -0,3341514 | |
| Hypothesized Mean Difference | 0 | |
| df | 5 | |
| t Stat | 1,52334805 | |
| P(T<=t) one-tail | 0,09408641 | |
| t Critical one-tail | 2,01504837 | |
| P(T<=t) two-tail | 0,18817282 | |
| t Critical two-tail | 2,57058184 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




