Submitted:
21 November 2023
Posted:
22 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Na+ uptake and accumulation under salt stress
2.1. The hydraulic conductivity (Lp) affects ion transport
2.2. Uptake of Na+ and Cl- at whole plant level
2.3. Ion uptake across a membrane
2.4. Cellular uptake of Na+
2.4.1. Cytosolic uptake of Na+ in wheat and rice by NSCCs.
2.4.2. Cytosolic uptake of Na+ in wheat and rice by CCCs, HKTs and AKT
2.4.3. Cytosolic Na+ uptake in Arabidopsis
2.5. Long-distance translocation of sodium
2.5.1. Sodium transport in rice by HKTs
2.5.2. Sodium transport in barley by HKTs
2.5.3. Sodium transport in Arabidopsis by HKTs
2.5.4. The CCCs, cation-chloride cotransporters
2.6. Salt tolerance
2.6.1. Plants tolerate salt stress by different mechanisms
2.6.2. Halophytes and glycophytes.
2.6.3. Regulation of Na+ transport at the at xylem/parenchyma cell border
2.6.4. Different barley cultivars differ in salt tolerance
2.6.5. Tolerant rice cultivars have different salt-tolerance mechanisms
2.6.6. SOS1 role in salt tolerance
2.6.7. Na+ and K+ transport into the vacuole
2.7. Measurements of cytosolic ion changes in different species/cultivars under salinity
2.7.1. Cytosolic Na+ influx and efflux from salt tolerant and sensitive species, quince, sugar beet and wheat, differ
2.7.2. Cytosolic Na+ and pH changes are different in the halophyte quinoa and the glycophyte pea
2.7.3. Cytosolic Na+ influx and efflux in tolerant and sensitive rice
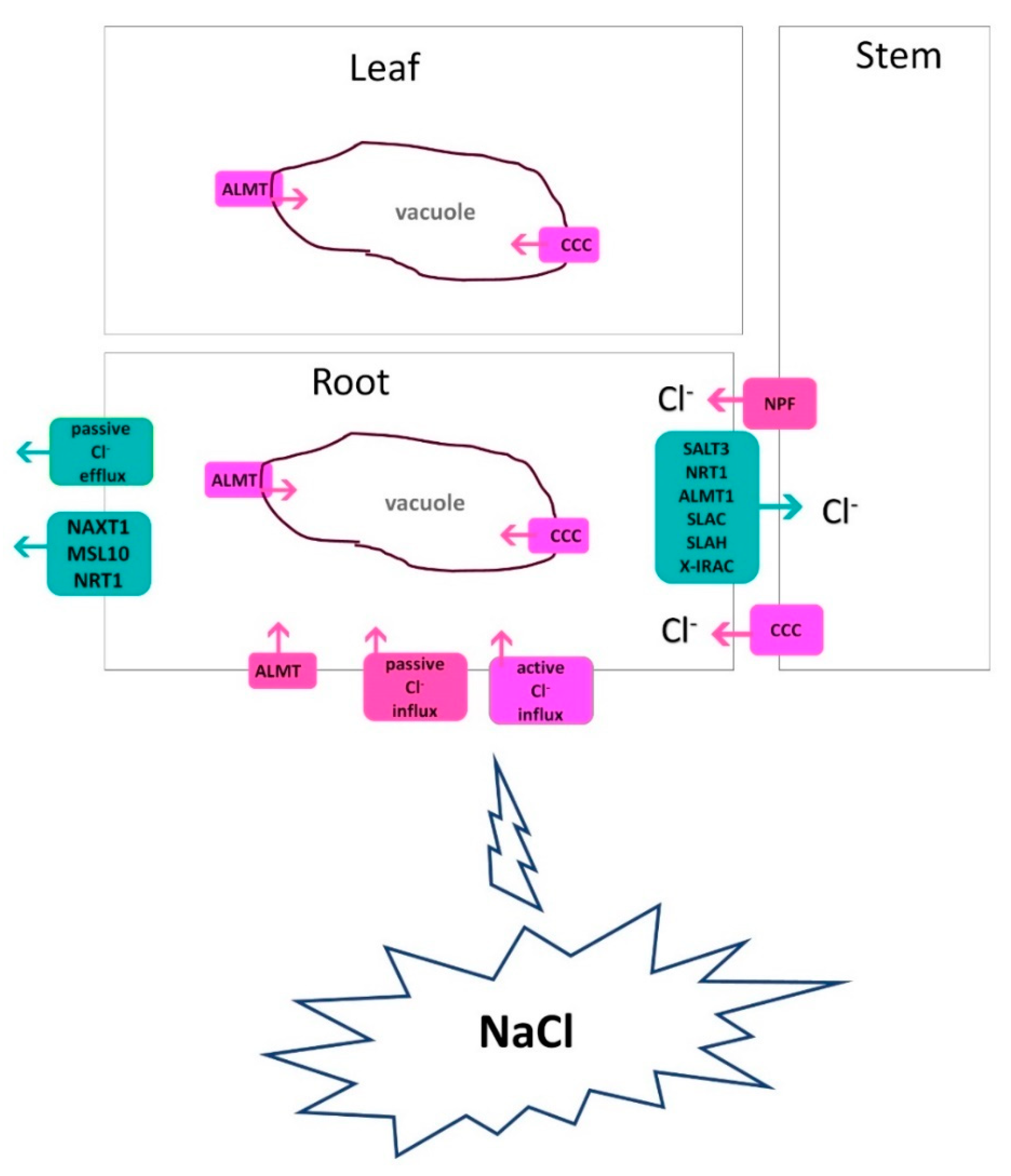
3. Cl- uptake and transport under salinity
3.1. Antagonism between Cl- and other anions in wheat and other cereals, and in tomatoes and rose plants
3.2. Wheat leaves might accumulate less Na+ and Cl− than leaves of barley, canola, and chickpea
3.3. Chloride channels and -transporters under salinity
3.3.1. Voltage-dependent chloride channels CLCs
Uptake of Na+ and Cl- and their translocation from root to shoot may differ in different wheat species and cultivars
Cl- influx channels in rice by CLCs
CLC- channels in tonoplast of soybean and cotton decreases Cl-/NO3- ratio
Voltage-dependent influx channels in barley and maize
Voltage-dependent SLAC/SLAH channels
The involvement of SLAC/SLAH in chloride efflux from barley and Arabidopsis
Calcium-activated Cl- efflux channel in sorghum
Intracellular chloride-channels in Arabidopsis
Chloride-efflux channels in guard cells
3.3.2. Stretch-activated Cl- efflux channels in guard cells and pollen tubes
3.3.3. Ion channels in xylem parenchyma cells of the root
3.3.4. ALMT channels
Calcium, boron, malate and aluminium affect the accumulation of Cl-.in wheat
3.5. Cl- transporters under salinity
3.5.1. CLCs transporting Cl- in antiport with protons
CLCs in maize, soybean and Arabidopsis
Subcellular CLCs transporters in Arabidopsis
3.5.2. Nitrate Transporter 1/Peptide Transporter Family (NFP)
Accumulation of Cl− in wheat is inhibited by silicon
3.6. Cl- Compartmentalizing transporters under salinity
3.6.1. Cation chloride cotransporters (CCCs)
CCCs in rice, soybean, grapevine and Arabidopsis
4. K+ concentrations and signaling under salinity
4.1. Cytosolic K+ retention is higher in salt-tolerant plants
4.2. K+ channels under salinity
4.2.1. Shaker K+ channels under salinity
Shaker K+ channels in Arabidopsis
Shaker K+ channels in rice and soybean
4.2.3. Tandem-pore K+ channels
4.2.4. Non-selective cation channels (NSCCs) under salinity
4.2.5. Cyclic nucleotide-gated channels (CNGCs) and glutamate-like receptors (GLRs)
4.2.6. Two-pore K+ channels under salinity
4.2.6.1. TPKs in rice
4.3. K+ transporters under salinity
4.3.1. HAK transport systems under salinity
HAKs in rice, maize, Medicago and pepper
KUP-transport systems under salinity
4.3.1. HKT-transport systems under salinity
HKTs in wheat, rice, barley, soybean and tomato
4.3. K++exchangers and antiporters under salinity
4.3.1. CPA1 transporters in transgenic Arabidopsis, sugar beet, rice and cotton with increased salt tolerance
4.4.2. K+ efflux antiporters, KEAs (CPA2) mediate both K+ influx and efflux
4.4.3. CHX transporters in Arabidopsis
4.4. K+ signaling under salinity
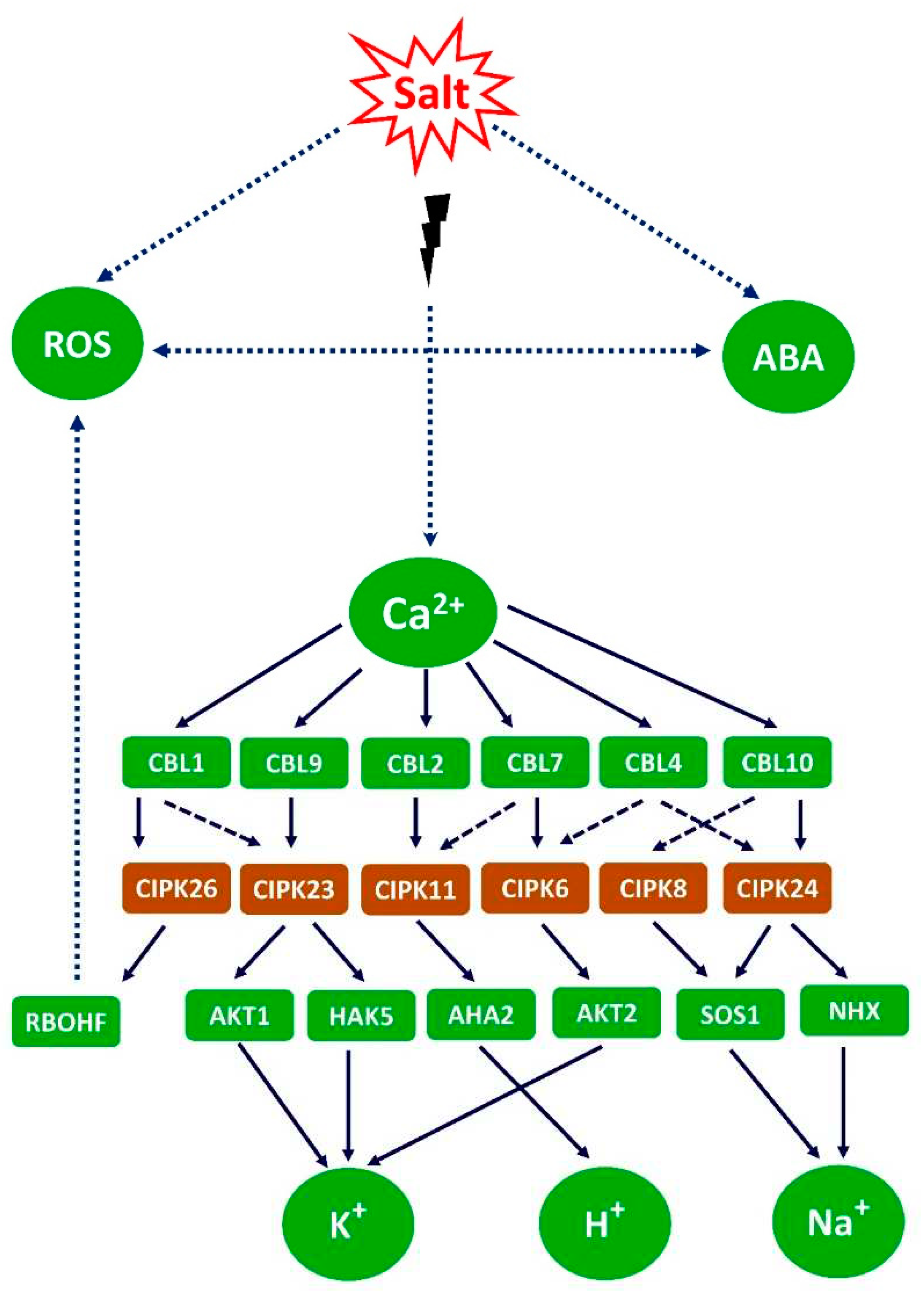
5. cytosolic calcium signaling
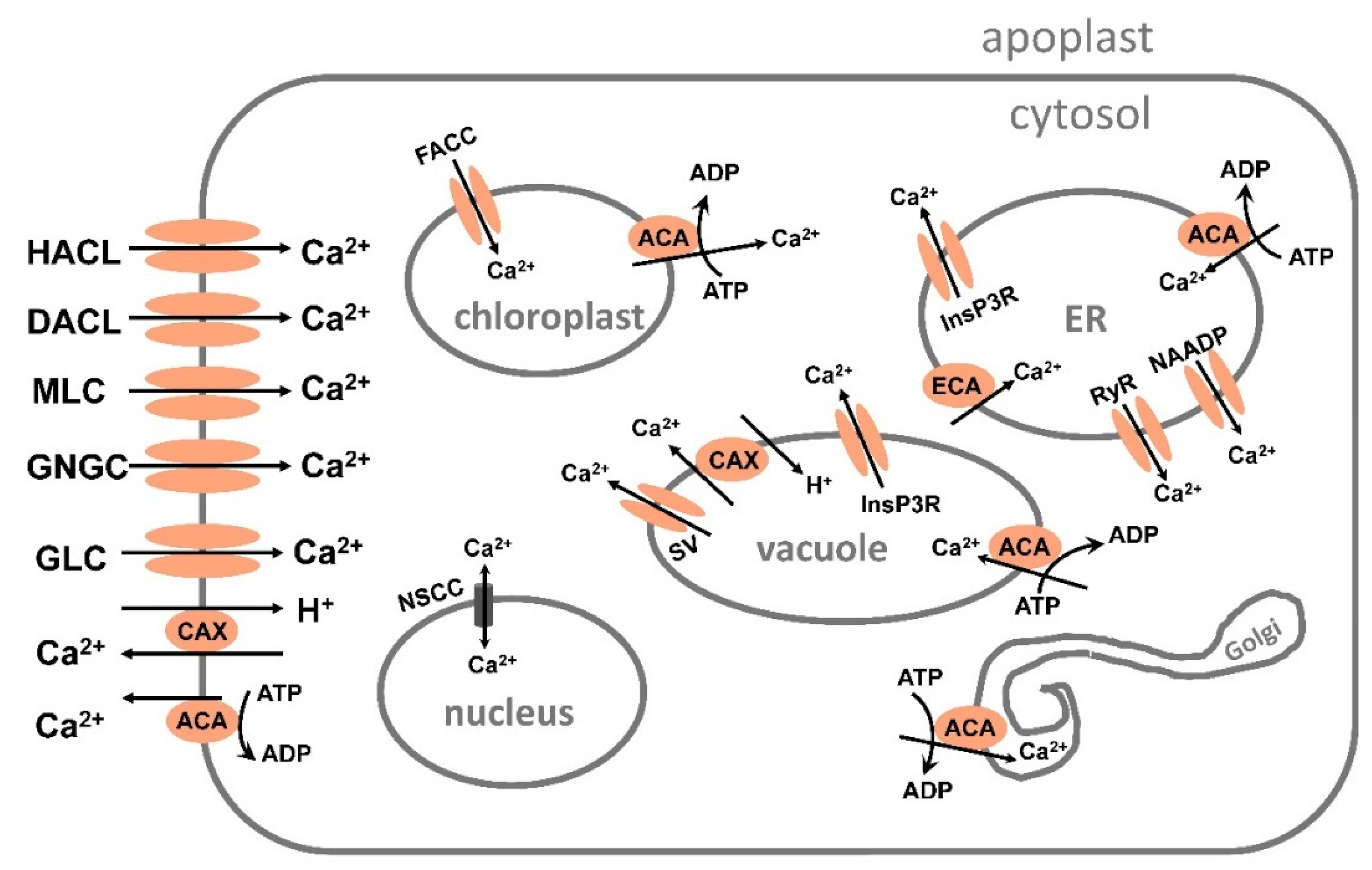
5.1. Calcium transport system
5.1.1. Calcium transport by channels.
5.1.2. Calcium transport from the cytosol and chloroplast and into ER, Golgi and vacuole
5.2. Calcium signals depends on type of stress, transporter location and type, and duration of stress.
5.2.1. Dynamics of the cytosolic calcium signals
5.3. Possible Na+ Sensors
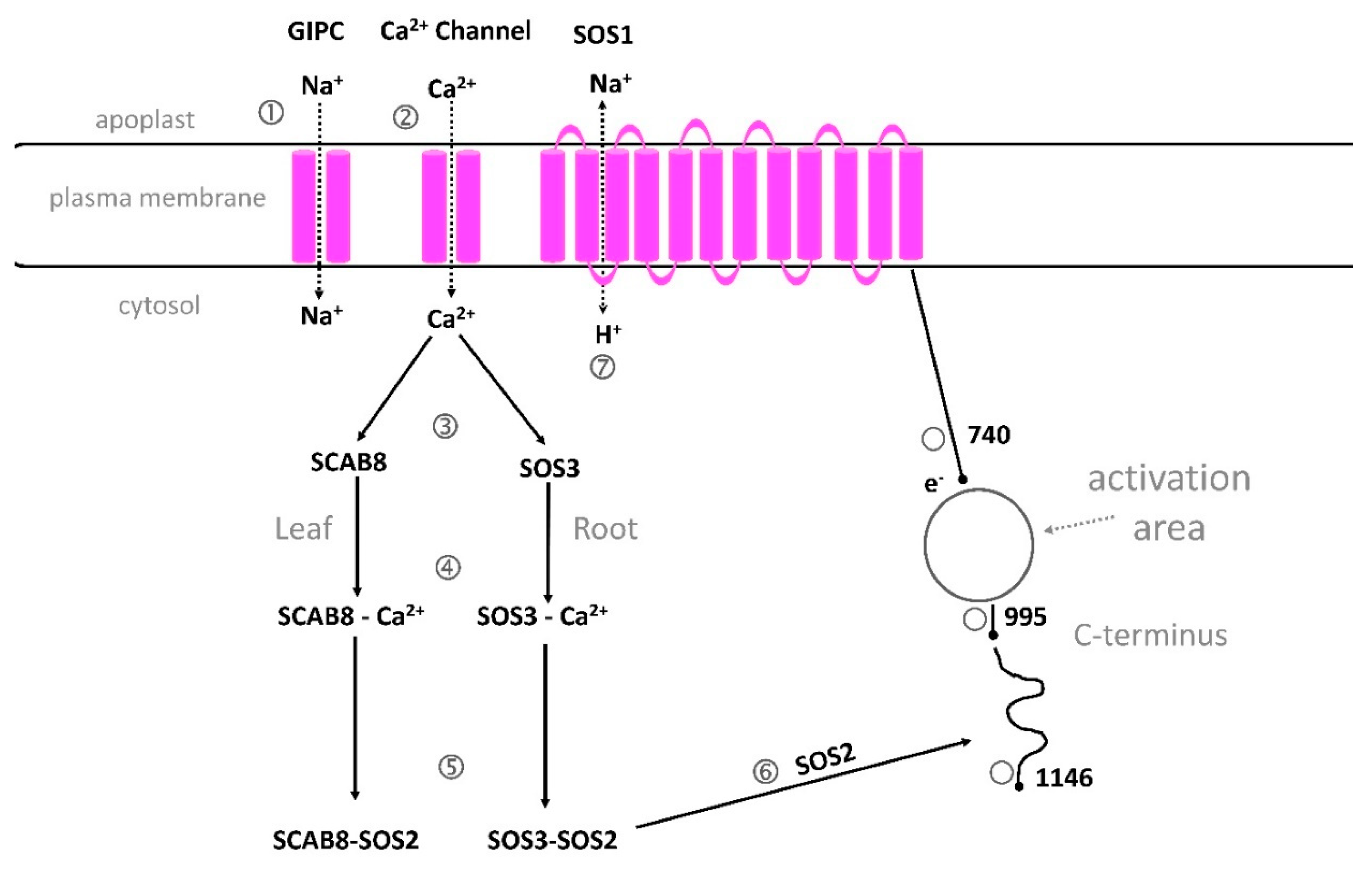
5.3.1. The Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 is critical for cytosolic calcium elevation, as shown in Arabidopsis, soybean and rice
5.3.2. GIPC can bind Na+
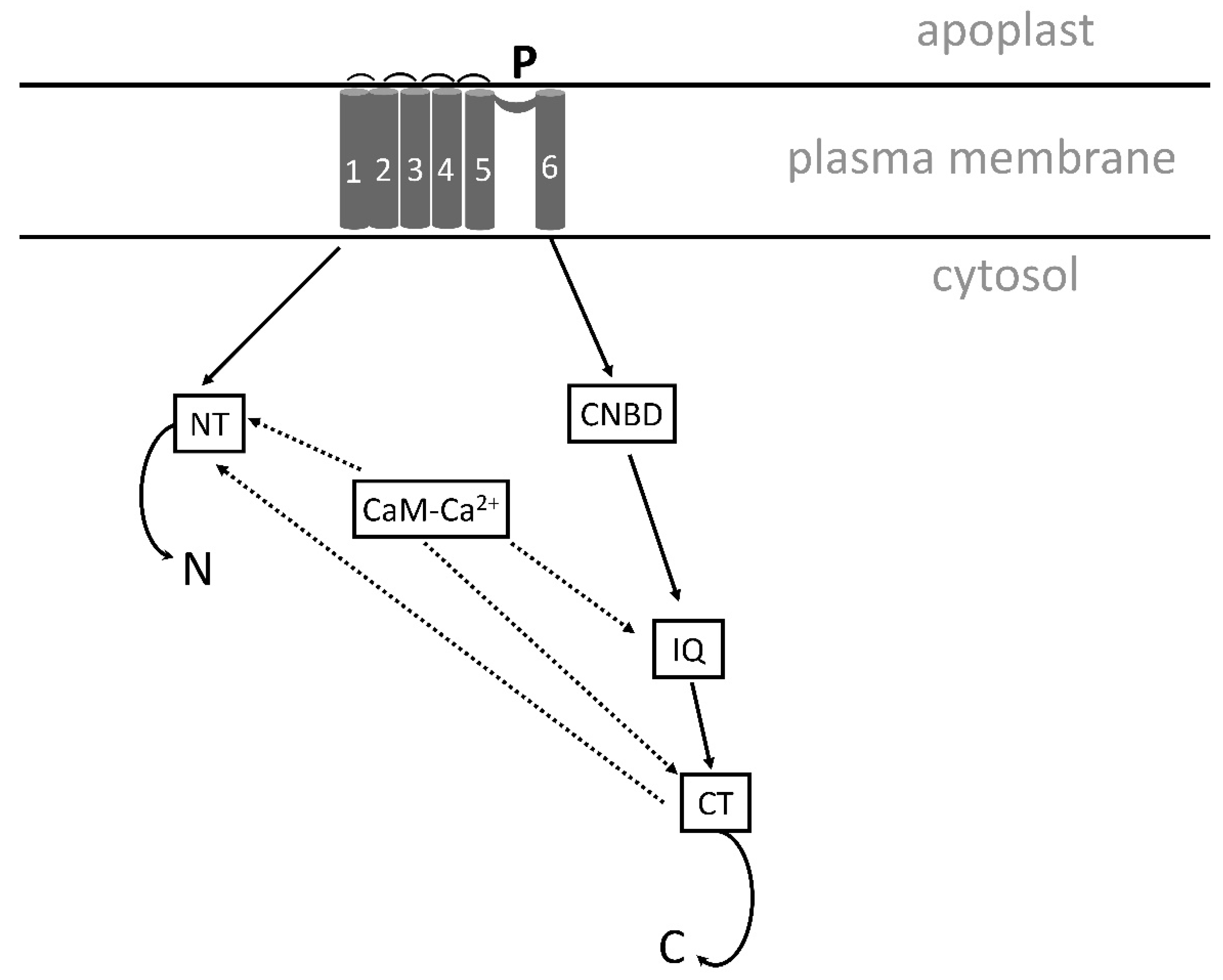
5.3.3. A proposed structure and function of SOS1.
5.3.4. ANN1, KEAs and FERONIA and other calcium transporters
6. Calcium signal transmission into intracellular downstream reactions
7. pH changes and signaling under salinity
7.2. Salinity induces different cytosolic and vacuolar pH changes in salt- sensitive and salt-tolerant species or cultivars.
7.3. Extra addition of calcium or potassium under cultivation of wheat and field beans in saline medium affects the cellular pH and H+ATPase activity.
8. Systemic calcium signaling
8.1. Electrical signals were first proposed in Mimosa pudica
8.2. Translocation of amino acids by diffusion and bulk flow activates calcium channels
8.3. Electrical signals and glutamate may be involved
8.4. Ca2+-ROS interactions
9. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data available
Conflict of interest
References
- Munns, R.; Gilliham, M. Salinity tolerance of crops – What is the cost? New Phytol. 2015, 208, 668-673. [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A.; Läuchli, A. Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1025-1043. [CrossRef]
- Maathuis, F.J.M. Sodium in plants: perception, signaling and regulation of sodium fluxes. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 849-858. [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Hou, X.; Liang, X. Response mechanisms of plants under saline-alkali stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12.667458. Sec. Plant Abiotic Stress. [CrossRef]
- Maathuis, F.J.M. Physiological functions of mineral macronutrients. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 250-258. [CrossRef]
- Colmeneros-Flores, J.M.; Franco-Navarro, J.D.; Cubero-Font, P.; Peindo-Torrubia, P.; Rosales, M.A. Chloride as a beneficial macronutrient in higher plants: New Roles and regulation. Inter. J. of Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4686. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z. Vacuolar Cl- sequestration: Revisiting the role of Cl- transport in plant salt tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1418. [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli, E.; Rengasamy, P.; McDonald, G.K. High concentration of Na+ and Cl- ions in soil solution has simultaneous detrimental effects on growth of faba bean under salinity stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 4449-4459. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 66-71. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Unraveling salt stress signaling in plants. J. Integrat. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 796-804. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Pei, Z-M. Plant cell-surface GIPC sphingolipids sense salt to trigger Ca2+ influx. Nature 2019, 572, 341-346. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fricke, W. Changes in root hydraulic conductivity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in response to salt stress and day/night can best be explained through altered activity of aquaporins. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 747-763. [CrossRef]
- Maurel, C.; Boursiac, Y.; Luu, D.-T.; Santoni, V.; Shahzad, Z.; Verdoucq, L. Aquaporins in plants. Physiol. Res. 2015, 95, 1321-1358. [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.; Yeo, A. The driving force for water and solute movement. In Yeo, A. and Flowers, T. Eds. Plant Solute Transport, 1992, pp. 29-45.
- Kronzucker, H.J.; Britto, D.T. Sodium transport in plants: a critical review. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 54-81. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Flowers, T.J.; Gong, H. Silicon decreases chloride transport in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 847-853. [CrossRef]
- Amtmann, A.; Sanders, D. Mechanisms of Na+ uptake by plant roots. Adv. Bot. Res. 1999, 29, 75-112. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Flowers, T.J.;Wang, S.M. Mechanisms of sodium uptake by roots of higher plants. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 45-60. [CrossRef]
- Haro, R.; Banuelos, M.A.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A. High affinity uptake of sodium in land plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 68-79. [CrossRef]
- Davenport, R.J.; Tester, M. A weakly voltage-dependent, nonselective cation channel mediates toxic sodium influx in wheat. Plant Physiol. 2000, 12, 823-834. [CrossRef]
- Demidschik, V.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Physiological roles of nonselective cation channels in plants: from salt stress to signaling and development. New Phytol. 2007, 175, 387-404. [CrossRef]
- Leng, Q.; Mercier, R.W.; Hua, B.; Fromm, H.; Berkowitz, G.A. Electrophysiological analysis of cloned cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 400-410. [CrossRef]
- Keisham, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhatla, S. Mechanisms of sodium transport in plants - progresses and challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 647. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, J.-K.; Shabala, S. Mechanism of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Inno. 2020, 1, 100017. [CrossRef]
- Golldack, D.; Su, H.; Quigley, F.; Kamasani, U.R.; Munoz-Garay, C.; Balderas, E.; Popova, O.V.; Bennett, J.; Hans J. Bohnert, H.J.; Pantoja, O. Characterization of an HKT-type transporter in rice as a general alkali cation transporter. Plant J. 2002, 31, 529-542. [CrossRef]
- Tester, M.; Davenport, R.J. Na+ transport and Na+ tolerance in higher plants. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 503-527. [CrossRef]
- Greger, M.; Ahmad H. Kabir, A.H.; Landberg, T.; Maity, P.J.; Lindberg, S. Silicate reduces cadmium uptake into cells of wheat. Environ. Poll. 2016, 211, 90-97. [CrossRef]
- Mian, A.; Oomen, R.J.; Isayenkov, S.; Sentenac, H.; Maathuis, F.J.; Véry, A.A. Over-expression of a Na+ and K+ permeable HKT transporter in barley improves salt tolerance. Plant J. 2011, 68, 468-479. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yin, S.; Huang, l.; Wu, X.; Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; Qiu, L.; Munns, R.; Chen, Z-H.; Zhang, G. A sodium transporter HvHKT1 confers salt tolerance in barley via regulating tissue cell ion homeostasis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1976-1989. [CrossRef]
- Essah, P.A.; Davenport, R.; Tester, M. Sodium influx and accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 307-318. [CrossRef]
- Isayenkov, S.V.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Plant salinity stress: Many unanswered questions remain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 80. [CrossRef]
- Byrt, C.S.; Zhao, M.; Koughi, M.; Bose, J.; Henderson, S.W.; Qiu, J.; et al. Non-selective cation channel activity of aquaporin AtPIP2;1 regulated by Ca2+ and pH. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 802-815. [CrossRef]
- Kader, Md.A.; Seidel, T.; Golldack, D.; Lindberg, S. Expressions of OsHKT1, OsHKT2 and OsVHA are differently regulated under NaCl stress in salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 4257-4268. [CrossRef]
- Horie, T.; Yoshida, K.; Nakayama, H.; Yamada, K.; Oiki, S.; Shinmyo, A. Two types of HKT transporters with different properties of Na+ and K+ transport in Oryza sativa. Plant J. 2001, 27, 129-138. [CrossRef]
- Rubio, F.; Nieves-Cordones, M.; Horie, T.; Shabala, S. Doing ‘business as usual’ comes with a cost: evaluating energy cost of maintaining plant intracellular K+ homeostasis under saline conditions. New Phytol. 2019, 225, 1097-1104. [CrossRef]
- Berthomieu, P.; Cone, G.; Nublat, A.; Brackenbury, W.J.; Lambert, C.; Savio, C.; Uozumi, N.; Oiki, S.; Yamada, K.; Cellier, F.; et al. Functional analysis of AtHKT1 in Arabidopsis shows that Na recirculation by the phloem is crucial for salt tolerance. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2004-2014. [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Gao, J.P.; Li, L.G. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat. Gen. 2005, 37, 1141-1146. [CrossRef]
- Brini, F.; Masmoudi, K. Ion transporters and abiotic stress tolerant plants. ISRN Mol. Biol. 2012, 927436. [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Kuang, L.; Wu, L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, G. Comparison in functions of HKT1;5 transporters between Hordeum marinum and Hordeum vulgare in responses to salt stress. Plant Growth Reg. 2019a, 89, 309-319. [CrossRef]
- Møller, I.S.; Gilliham, M.; Jha, D.; Mayo, G.M.; Roy, S.J.; Coates, J.C.; Haseloff, J.; Tester, M. Shoot Na+ exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na+ transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2163-2178. [CrossRef]
- Davenport, R.; Munoz-Mayer, A.; Jha, D., Essah, P.A.; Rus, A.; Tester, M. The Na+ transporter AtHKT1;1 controls retrieval of Na+ from the xylem in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 497-507. [CrossRef]
- Colmeneros-Flores, J.M.; Martinez, G.; Gamba, G.; Vazquez, N.; Iglesias, D.J.; Brumos, J.; Talon, M. Identification and functional characterization of cation-chloride cotransporters in plants. Plant J. 2007, 50, 278-292. [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.W.; Wege, S.; Gilliham, M. Plant cation-chloride cotransporters (CCC): Evolutionary origin and functional insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 492. [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651-681. [CrossRef]
- Isayenkov, S.V.; Dabravolski, S.A.; Pan, T.; Shabala, S. Phylogenetic diversity and physiological roles of plant monovalent cation/H+ antiporters. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 573564. [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.; Demidchik, V.; Shabala, L.; Cuin, T.A.; Smith, S.J.; Miller, A.J.; Davies, J.M.; Newman, I.A. Extracellular Ca2+ ameliorates NaCl induced K+ loss from Arabidopsis root and leaf cells by controlling plasma membrane K+-permeable channels. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1653-1665. [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Munns, R.; Colmer, T.D. Sodium chloride toxicity and the cellular basis of salt tolerance in halophytes. Ann. Bot. 2014, 115, 419-431. [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol. 2008. 179, 945-963. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Zhang, J.L.; Liu, X.S.; Li, Z.; Wu, G.Q.; Cai, J.Y.; Wang, S.M. Puccinellia tenuiflora maintains a low Na+ level under salinity by limiting unidirectional Na+ influx resulting in a high selectivity for K+ over Na+. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 486-496. [CrossRef]
- Schachtman, D.P.; Schroeder, J.I. Structure and transport mechanism of a high-affinity potassium uptake transporter from higher plants. Nature 1994, 370, 655-658. [CrossRef]
- Schachtman, D.P.; Liu, W.H. Molecular pieces to the puzzle of the interaction between potassium and sodium uptake in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 1999, 4, 281-287. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Zhang, J.L.; Flowers, T.J. Low-affinity Na+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 559-571. [CrossRef]
- Zepeda-Jazo, I.; Shabala, S.; Chen, Z.; Pottosin, I.I. Na+-K+ transport. in roots under salt stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 2008, 3, 401-403. [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.K.; Tester, M. Permeation of Ca2+ and monovalent cations through an outwardly rectifying channel in maize root stelar cells. J Exp. Bot. 1997, 48, 839-846. [CrossRef]
- Adem, G.D.; Chen, G.; Shabala, L.; Chen, Z.H. GORK channel: A master switch of plant metabolism. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 434- 445. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lindberg, S.; Shabala, L.; Morgan, S.; Shabala, S.; Jacobsen, S. E. A comparative analysis of cytosolic Na+ changes under salinity between halophyte quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) and glycophyte pea (Pisum sativum). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 141, 154-160. [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.; Shabala, L.; Cuin, T.A.; Pang, J.; Percey, W.; Chen, Z.; Wegner, L.H. Xylem ionic relations and salinity tolerance in barley. Plant J. 2010, 61, 839-853. [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S. (2017). Signaling by potassium: another second messenger to add to the list? J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 4003-4007. [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.; Hariadi, Y.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Genotypic difference in salinity tolerance in quinoa is determined by differential control of xylem Na+ loading and stomatal density. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 906-914. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2013.01. 014.
- Jia, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Salt-stress-induced ABA accumulation is more sensitively triggered in roots than in shoots. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 2201-2206. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erf079.
- Shi, H.Z.; Quintero, F.J.; Pardo, J.M.; Zhu, J.K. The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 465-477. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1105/tpc.010371.
- Zhu, M.; Zhou, M.; Shabala, L.; Shabala, S. Physiological and molecular mechanisms mediating xylem Na+ loading in the context of salinity stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 1-12. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/pce.12727.
- Huang, L.; Kuang, L.; Li, X.; Wu, L.;Wu, D.; Zhang, G. (2018). Metabolomics and transcriptomic analyses reveal the reason why Hordeum marinum has higher salt tolerance than Hordeum vulgare. Env. Exp. Bot. 2018, 156, 48-61. [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, N.T.; Tri, P.N.; Le Hong, T.; Quoc, C.D. Biomolecular evaluation of three contrasting rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) in salt stress response at seedling stage. Plant Sci. Today 2022, 9, 491-503. [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.J.; Miklavcic, S.J. A comprehensive biophysical model of ion and water transport in plant roots. II. Clarifying the rules of SOS1 in the salt-stress response Arabibopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1121. [CrossRef]
- Halperin, S.J.; Lynch, J.P. Effect of salinity on cytosolic Na+ and K+ in root hairs of Arabidopsis thaliana: in vivo measurement using the fluorescent dyes SBFI and PBFI. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 2035-2043. [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.H.; Kader, Md.A.; Lindberg, S. Cytosolic sodium influx in mesophyll protoplasts of Arabidopsis thaliana, Wt, sos1;1, and nhx1 differs and induces different calcium changes. Plants 2022, 11, 3439. [CrossRef]
- Bassil, E.B.; Zhang, S.; Gong, H.; Tajima, H.; Blumwald, E. Cation specificity of vacuolar NHX type Cation/H+ antiporters. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 616-629. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Di, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, G. AtCCX1 transports Na+ and K+ in Pitch pastoris. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 9743-9750. [DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.455.
- Zhu, X.; Pan, T.; Zhang, X.; Fan, L.; Quintero, F.J.; Zhao, H.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Villalta, I.; Mendoza ,I.; et al. (2018). K+ efflux antiporters 4, 5, and 6 mediate pH and K+ homeostasis in endomembrane compartments. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 1657-1678. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, W.; Guo, X.; Chen, P.; Cheng, Y.; Mao, K.; Ma, F. Cation/Ca2+ exchanger1 (MdCCX1), a plasma membrane-localized Na+ transporter, enhances plant salt tolerance by inhibiting excessive accumulation of Na+ and reactive oxygen species. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 746189. [CrossRef]
- D'Onofrio, C.; Kader, A.; Lindberg, S. Uptake of sodium in quince, wheat and sugar beet protoplasts determined by the fluorescent sodium-binding benzofuran isophthalate dye. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 421-428. [CrossRef]
- Kader, A.; Lindberg, S. Uptake of sodium in protoplasts of salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant cultivars of rice, Oryza sativa L. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 3149-3158. [CrossRef]
- Negulescu, P.A.; Harootunian, A.; Tsien, R.Y.; and Machen, T.E. Fluorescence measurement of cytosolic free Na concentration influx and efflux in gastri cells. Cell Regul. 1990, 1, 259-268. [CrossRef]
- Demidschik, V.; Tester, M. Sodium fluxes through nonselective cation channels in plasma membrane of protoplasts from Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 379-387. [CrossRef]
- Bose, J.; Rodrigo-Moreno, A.; Lai, D.; Xie, Y.; Shen, W.; Shabala, S. Rapid regulation of plasma membrane H+ATPase activity is essential to salinity tolerance in two halophyte species, Atriplex lentiformis and Chenopodium quinoa. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 481-494. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, K.B.; Biondi, S.; Martínez, E.A.; Orsini, F.; Antognoni, F., Jacobsen, S.E. Quinoa − a model crop for understanding salt tolerance mechanisms in halophytes. Plant Biosyst. 2016, 150, 357-371. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2015.1027317.
- Anil, V.S.; Krishnamurthy, H.; Mathew, M. Limiting cytosolic Na confers salt tolerance in rice cell in culture: a two-photon microscopy study of SBFI-loaded cells. Physiol. Plant. 2007, 129, 607-621. [CrossRef]
- Blumwald, E.; Poole, R.J. The Na+/H+ antiport in isolated tonoplast vesicles from storage tissue of Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1985, 78, 163-167. [CrossRef]
- Hassidim, M.; Braun, Y.; Lerner, H.R.; Reinhold, L. Na+/H+ and K+/H+ antiport in root membrane vesicles isolated from the halophyte Atriplex and the glycophyte cotton. Plant Physiol. 1990, 94, 1795-1801. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 441-445. [CrossRef]
- Perez-Hormaeche, J.; Villalta, I.; Espartero, J.M.; Gámez-Arjona, F.M. A critical role of sodium flux via the plasma membrane Na+/H+ Exchanger SOS1 in the salt tolerance of rice. Plant Physiol. 2018, 180, 1046-1065. [CrossRef]
- Sze, H.; Schumacher, K.; Muller, M.; Padmanaban, S.; Taiz, L. A simple nomenclature for a complex proton pump: VHA genes encode the vacuolar H+ATPase. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 157-161. [CrossRef]
- Teakle, N.L.; Tyerman, S.D. Mechanisms of Cl- transport contributing to salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 566-589. [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, I.; Aberle, T.; Plieth, C. Salt stress-induced chloride flux: a study using transgenic Arabidopsis expressing a fluorescent anion probe. Plant J. 2004, 38, 539-544. [CrossRef]
- Geilfus, C.M. Review on the significance of chlorine for crop yield and quality. Plant Sci. 2018, 270, 114-122. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Song, H.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, C. Advances in deciphering salt tolerance mechanism in maize. Crop J. 2023, 11, 1001-1010. [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Tester, M.; Roy, S.J. Quantifying the three main components of salinity tolerance in cereals. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 237-249. [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Liu, Z.; Fang, W.; Tang, J. Comparison of stress effect of NaCl, Na+ and Cl- on two Chrysanthemum species. Acta Hortic. 2012, 937, 369-375. [CrossRef]
- Abdelgadir, E. M.; Oka, M.; Fujiyama, H. Characteristics of nitrate uptake by plants under salinity. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 28, 33-46. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Schmidhalter, U. Spatial distribution sand net deposition rates of mineral elements in the elongating wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) leaf under saline soil conditions. Planta 1998, 204, 212-219. [CrossRef]
- Massa, D.; Mattson, N. S.; Lieth, H. J. Effects of saline root environment (NaCl) on nitrate and potassium uptake kinetics for rose plants: a Michaelis–Menten modelling approach. Plant Soil 2009, 318, 101-115. [CrossRef]
- Grewal, H. S. Water uptake, water use efficiency, plant growth and ionic balance of wheat, barley, canola and chickpea plants on a sodic vertosol with variable subsoil NaCl salinity. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 148-156. [CrossRef]
- Tregeagle, J.M.; Tisdall, J.M.; Tester, M.; Walker, R.R. Cl- uptake, transport and accumulation in grapevine rootstocks of differing capacity for Cl- exclusion. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 665-673. [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Kasai, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Matsumoto, H. Stimulation of plasma membrane H+-transport activity in barley roots by salt stress. Possible role of increase in chloride permeability. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1994, 40, 555-563. [CrossRef]
- Skerrett, M.; Tyerman, S.D. A channel that allows inwardly-directed fluxes of anions in protoplasts derived from wheat roots. Planta. 1994, 192, 295-305. [CrossRef]
- Wegner, L.H.; Raschke, K. Ion channels in the xylem parenchyma of barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1994, 105, 799-813. [CrossRef]
- White, P.J. Separation of K+ and Cl−-selective ion channels from rye roots on a continuous sucrose density gradient. J. Exp. Bot. 1995, 46, 361-376. [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.R.; Skerrett, M.; Findlay, G.P.; Tyerman, S.D. Aluminum activates an anion channel in the apical cells of wheat roots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6547-6552. [CrossRef]
- Kiegle, E.; Gilliham, M.; Haseloff, J.; Tester, M. Hyperpolarisation-activated calcium currents found only in cells from the elongation zone of Arabidopsis thaliana roots. Plant J. 2000, 21, 225-229. [CrossRef]
- Diatloff, E.; Roberts, M.; Sanders, D.; Roberts, S.K. Characterization of anion channels in the plasma membrane of Arabidopsis epidermal root cells and the identification of a citrate permeable channel induced by phosphate starvation. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 4136-4149. [CrossRef]
- Ouerghi, Z.; Cornic, G.; Roudani, M.; Ayadi, A.; Brulfert, J. Effect of NaCI on photosynthesis of two wheat species (Triticum durum and T. aestivum) differing in their sensitivity to salt stress. Plant Physiol. 2000, 156, 335-340. [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A. Screening methods for salinity tolerance: A case study with tetraploid wheat. Plant Soil, 2003, 253, 201-218. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/A:1024553303144.
- Skerrett, M.; Tyerman, S.D. (1994). A channel that allows inwardly directed fluxes of anions in protoplasts derived from wheat roots. Planta 1994, 192, 295-305. [CrossRef]
- Tyerman, S.D.; Skerrett, M.; Garrill, A.; Findlay, G.P.; Leigh, R.A. Pathways for the permeation of Na+ and Cl− into protoplasts derived from the cortex of wheat roots. J. Exp. Bot. 1997, 48, 459-480. [CrossRef]
- Diédhiou, C.J.; Golldack, D. Salt-dependent regulation of chloride channel transcripts in rice. Plant Sci. 2006, 170, 793-800. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Fukuda, A.; Sakai, S.; Tanaka, Y. Molecular cloning, functional expression and subcellular localization of two putative vacuolar voltage-gated chloride channels in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 32- 42. [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Che, B.; Shen, L.; Cui, Y.; Wu, S.; Cheng, C.; Liu, F.; Li, M.A.; Bingjun Yu, B.; Lam, H.M. Identification and functional characterization of the chloride channel gene, GsCLC-c2 from wild soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 121. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Agorio, A.; Jossier, M.; Depré, S.; Thomine, S.; Filleur, S. Characterization of the chloride channel-like, AtCLCg, involved in chloride tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 764-775. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Feng, J.; Ma, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Z. GhCLCg-1, a vacuolar chloride channel, contributes to salt tolerance by regulating ion accumulation in upland cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 765173. [CrossRef]
- Jossier, M.; Kroniewicz, L.; Dalmas, F.; Le Thiec, D.; Ephritikhine, G.; Thomine, S.; Barbier-Brygoo, H.; Vavasseur, A.; Filleur, S.; Leonhardt, N. The Arabidopsis vacuolar anion transporter, AtCLCc, is involved in the regulation of stomatal movements and contributes to salt tolerance. Plant J. 2010, 64, 563-576. [CrossRef]
- Kohler, B.; Raschke, K. The delivery of salts to the xylem. Three types of anion conductance in the plasmalemma of the xylem parenchyma of roots of barley. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 243-254. [CrossRef]
- Gilliham, M.; Tester, M. The regulation of anion loading to the maize root xylem. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 819-828. [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.K. Plasma membrane anion channels in higher plants and their putative functions in roots. New Phytol. 2006, 169, 647-66. [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, R.; Becker, D. Green circuits - The potential of plant specific ion channels. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 26, 1637-1650. [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, P.; Hedrich, R. Anions permeate and gate GCAC1, a voltage-dependent guard cell anion channel. 1998, Plant J. 15, 479-487. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z. The importance of Cl- exclusion and vacuolar Cl- sequestration: Revisiting the role of Cl- transport in plant salt tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 418. [CrossRef]
- Negi, J.; Matsuda, O.; Nagasawa, T.; Oba, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kawai-Yamada, M.; Uchimiya, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Iba, K. CO2 regulator SLAC1 and its homologues are essential for anion homeostasis in plant cells. Nature 2008, 452, 483-486. [CrossRef]
- Vahisalu, T.; Kollist, H.; Wang, Y.F.; Nishimura, N.; Chan, W.Y.; Valerio, G.; amminmäki, A.; Brosché, M.; Moldau, H.; Desikan, R.; Schroeder, J.I.; Kangasjärvi, J. SLAC1 is required for plant guard cell S-type anion channel function in stomatal signalling. Nature 2008, 452, 487-491. [CrossRef]
- Planes, M.D.; Niñoles, R.; Rubio, L.; Bissoli, G.; Bueso, E; García-Sánchez, M.J.; Alejandro, S.; Gonzalez-Guzmán, M.; Hedrich, R.; Rodriguez, P.L.; et al. A mechanism of growth inhibition by abscisic acid in germinating seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana based on inhibition of plasma membrane H+-ATPase and decreased cytosolic pH, K+, and anions. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 813-825. [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Font, P.; Maierhofer, T.; Jaslan, J.; Rosales, M.A.; Espartero, J.; Díaz-Rueda, P., Müller, H.M.; Hürter, A.L.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.; Marten, I.; et al. Silent S-type anion channel subunit SLAH1 gates SLAH3 open for chloride root-to-shoot translocation. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2213-2220. [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Hajibagheri, M.A. Salinity tolerance in Hordeum vulgare: ion concentrations in root cells of cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Plant Soil 2001, 231, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Brumos, J.; Talon, M.; Bouhal, R.; Colmenero-Flores, J.M. Cl- homeostasis in includer and excluder citrus rootstocks: transport mechanisms and identification of candidate genes. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 2012-2027. [CrossRef]
- Boursier, P.; Läuchli, A. Mechanisms of chloride partitioning in the leaves of salt-stressed Sorghum bicolor L. Physiol. Plant. 1989,77, 537-544. [CrossRef]
- Thomine, S.; Zimmermann, S.; Guern, J.; Barbier-Brygoo, H. ATP-dependent regulation of an anion channel at the plasma membrane of epidermal cells of Arabidopsis hypocotyls. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 2091-2100. [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.J.; Sanders, D. The Plant Vacuole. In: Advances in Botanical Research. Vol. 25, Edited by Leigh, R.A. and Sanders, D. 1997, pp. 218–252. Academic Press London, New York. [CrossRef]
- Herdean, A.; Teardo, E.; Nilsson, A.; Pfeil, B.E.; Johansson, O.N.; Ünnep, R.; Nagy, G.; Zsiros, O.; Dana, S.; Solymosi, K.; et al. A voltage-dependent chloride channel fine-tunes photosynthesis in plants. Nat Comm. 2016, 7, 11654. [CrossRef]
- Keller, B.; Hedrich, R.; Raschke, K. Voltage-dependent anion channels in the plasma membrane of guard cells. Nature 1989, 341, 450-453. [CrossRef]
- Speer, M.; Kaiser, W.M. Ionic relations of symplastic and apoplastic space in leaves from Spinacia oleracea L. and Pisum sativum L. under salinity. Plant Physiol. 1991, 97, 990-997. [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.J.; Hedrich, R. Stretch-activated Cl-, K+ and Ca2+ channels coexisting in plasma membrane of guard cells of Vicia faba L. Planta 1991, 186, 143-153. [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.M.; Maser, P.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant ion channels: gene families, physiology, and functional genomics analyses. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2009, 71, 59-82. [CrossRef]
- Veley, K.M.; Haswell, E.S. Plastids and pathogens: mechanosensitive channels and survival in a hypoosmotic world. Plant Signal Behav. 2012, 7, 668-671. [CrossRef]
- Maksaev, G.; Haswell, E.S. MscS-Like10 is a stretch-activated ion channel from Arabidopsis thaliana with a preference for anions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19015-19020. [CrossRef]
- Deger, A.G.; Scherzer, S.; Nuhkat, M.; Kedzierska, J.; Kollist, H.; Brosch, M.; Unyayar, S.; Boudsocq, M.; Hedrich, R.; Roelfsema M.R.G. Guard cell SLAC1-type anion channels mediate flagellin-induced stomatal closure. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 162-173. [CrossRef]
- Michard, E.; Simon, A.A.; Tavares, B.; Wudick, M.M.; Feijó, J.A. Signaling with ions: The keystone for apical cell growth and morphogenesis in pollen tubes. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 91-111. [CrossRef]
- De Angeli, A.; Zhang, J.; Meyer, S.; Martinoia, E. AtALMT9 is a malate-activated vacuolar chloride channel required for stomatal opening in Arabidopsis. Nat Comm. 2013, 4, 1804. [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Susanne von Caemmerer, S.V.; Munns, R. Control of salt transport from roots to shoots of wheat in saline soil. Funct. Plant Biol. 2004, 31, 1115-1126. [CrossRef]
- Yermiyahu, U.; Ben-Gal, A.; Keren, R.; Reid, R.J. Combined effect of salinity and excess boron on plant growth and yield. Plant Soil 2008, 304, 73-87. [CrossRef]
- Masood, S.; Wimmer, M.A.; Witzel, K.; Zörb, C.; Mühling, K.H. Interactive effects of high boron and NaCl stresses on subcellular localization of chloride and boron in wheat leaves. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2012, 198, 227-235. [CrossRef]
- Pineros, M.A.; Cancado, G.M.A.; Kochian, L.V. Novel properties of the wheat aluminum tolerance organic acid transporter (TaALMT1) revealed by electrophysiological characterization in Xenopus oocytes: functional and structural implications. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 2131-2146. [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qiu, J.; Jayakannan, M.; Xu, B.; Li, Y.; Mayo, G.M.; et al. AtNPF2.5 modulates chloride (Cl-) efflux from roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 02013. [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Byrt, C.; Qiu, J.; Baumann, U.; Hrmova, M.; Evrard, A.; Johnson, A.A.T.; Birnbaum, K.D.; Mayo, G.M.; Jha, D.; et al. Identification of a stelar-localized transport protein that facilitates root-to-shoot transfer of chloride in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1014-1029. [CrossRef]
- Baetz, U.; Eisenach, C.; Tohge, T.; Martinoia, E.; Angeli, A.D. Vacuolar chloride fluxes impact ion content and distribution during early salinity stress. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 1167-1181. [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tester, M.; Gilliham, M. Chloride on the Move. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 236-248. [CrossRef]
- Wege, S.; Gilliham, M.; Henderson, S.W. Chloride: Not simply a ‘cheap osmoticum’, but a beneficial plant macronutrient. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 3057-3069. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Su, S. Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, S. P.; Shan, X. H.; Liu, H. K.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Y.P. Overexpression of maize chloride channel gene ZmCLC-d in Arabidopsis thaliana improved its stress resistance. Biol. Plant. 2015, 59, 55-64. [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, K.; Song, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Lu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. Molecular dissection of maize seedling salt tolerance using a genome-wide association analysis method. Plant Biotech. 2021, 19, 1937-1951. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.F.; Wong, F.L.; Tsai, S.N.; Phang T.H.; Shao, G.H.; Lam, H.M. Tonoplast-located GmCLC1 and GmNHX1 from soybean enhance NaCl tolerance in transgenic bright yellow (BY)-2 cells. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 1122-1137. [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.H.; Li, M.W.; Yao, X.Q.; Lam, H.M. The GmCLC1 protein from soybean functions as a chloride ion transporter. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 101-104. [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, A. Yu, B.; Lam, H.M. GmCLC1 confers enhanced salt tolerance through regulating chloride accumulation in soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1082. [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Qu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, G.; Tian, L.; et al. Salinity tolerance in soybean is modulated by natural variation in GmSALT3. Plant J. 2014, 80, 937-950. [CrossRef]
- Do, T.D.; Chen, H.; Hien, V.T.T.; Hamwieh, A.; Yamada, T.; Sato, T.; Yan, Y.; Cong, H.; Shono, M.; Suenaga, K.; Xu, D. Ncl synchronously regulates Na+, K+ and Cl− in soybean and greatly increases the grain yield in saline field conditions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19147. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Qu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Hong, H.; Liu, Z.; Chang, R.; Gilliham, M.; Qiu, L.; Guan, R.. GmSALT3, which confers improved soybean salt tolerance in the field, increases leaf Cl- exclusion prior to Na+ exclusion but does not improve early vigor under salinity. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1485. [CrossRef]
- Zifarelli, G.; Pusch, M. CLC transport proteins in plants. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2122-2127. [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Tang, R.; Liu, H.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, H. Cloning and molecular analyses of the Arabidopsis thaliana chloride channel gene family. Plant Sci. 2009, 176, 650-661. [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Hajibagheri, M.A.; Yeo, A.R. Ion accumulation in the cell-walls of rice plants growing under saline conditions: evidence for the Oertli hypothesis. Plant Cell Environ. 1991, 14, 319-325. [CrossRef]
- Maathuis, F.J.M. Sodium in plants: perception, signalling and regulation of sodium fluxes. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 849-858. [CrossRef]
- Corratgé-Faillie, C.; Jabnoune, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Véry, A.A.; Fizames, C.; Sentenac, H. Potassium and sodium transport in non-animal cells: the Trk/Ktr/HKT transporter family. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2511-2532. [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Tyerman, S.D.; Dechorgnat, J.; Ovchinnikova, E.; Dhugga, K.S.; Kaiser, B.N. Maize NPF6 proteins are homologs of Arabidopsis CHL1 that are selective for both nitrate and chloride. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2581-2596. [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, A.; Javed, M.T.; Pawlowski, K.; Lindberg, S.M. Silicate inhibits the cytosolic influx of chloride in protoplasts of wheat and affects the chloride transporters, TaCLC1 and TaNPF2.4/2.5. Plants 2022, 11, 1162 . [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.C.; Yamaji, N.; Fujii-Kashino, M.; Ma, J.F. A cation-chloride cotransporter gene is required for cell elongation and osmoregulation in rice. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 494-507. [CrossRef]
- Nikolovski, N.; Rubtsov, D.; Segura, M.P.; Miles, G.P.; Stevens, T.J.; Dunkley, T.P.J.; Munro, S.; Lilley, K.S.; Dupree, P. Putative glycosyltransferases and other plant Golgi apparatus proteins are revealed by LOPIT proteomics. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1037-1051. [CrossRef]
- Groen, A.J.; Sancho-Andrés, G.; Breckels, L.M.; Gatto, L.; Aniento, F.; Lilley, K.S. Identification of trans-golgi network proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana root tissue. J. Prote. Res. 2014, 13, 763-776. [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.W.; Wege, S.; Qiu, J.; Blackmore, D.H.; Walker, A.R.; Tyerman, S.D. Walker, R.R.; Gilliham, M. Grapevine and Arabidopsis cation-chloride cotransporters localise to the golgi and trans-golgi network and indirectly influence long-distance ion transport and plant salt tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2215-2229. [CrossRef]
- Hauser, F.; Horie, T. A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: a mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K+/Na+ ratio in leaves during salinity stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 552-565. [CrossRef]
- Smethurst, C.F.; Rix, K.; Garnett, T.; Auricht, G.; Bayart, A.; Lane, P.; Wilson, S.J.; Shabala, S. Multiple traits associated with salt tolerance in lucerne: revealing the underlying cellular mechanisms. Funct. Plant Biol. 2008, 35, 640-650. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, X,; Giraldo, J.P.; and Shabala, S. It is not all about sodium: revealing tissue specificity and signalling roles of potassium in plant responses to salt stress. Plant Soil 2018, 431, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Potassium control of plant functions: ecological and agricultural implications. Plants 2021, 10, 419. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Shankar, A.; Chandran, A.K.N.; Sharma, M.; Jung, K.H.; Suprasanna, P.; Pandey, G.K. Emerging concepts of potassium homeostasis in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 608-619. [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Anuragi, H.; Chandra, K.; Tarte, S.H.; Dhaka, S.R.; Jatav, H.S.; Hingonia, K. Molecular basis of plant nutrient use efficiency - concepts and challenges for its improvement. In Sustainable Plant Nutrition: Molecular Interventions and Advancements for Crop Improvement. 2023, 107-151. [CrossRef]
- Britto, D.T.; Coskun, D.; Kronzucker, H.J. Potassium physiology from Archean to Holocene: A higher-plant perspective. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 262, 153432. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Dreyer, I.; Riedelsberger, J.; The role of K+ channels in uptake and redistribution of potassium in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 224. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Barrena, M.J.; Chaves-Sanjuan, A.; Raddatz, N.; Mendoza, I.; Cortés, Á.; Gago, F.; González-Rubio, J.M.; Benavente, J.L.; Quintero, F.J.; Pardo, J.M.; Albert, A. Recognition and activation of the plant AKT1 potassium channel by the kinase CIPK23. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 2143-2153. [CrossRef]
- Durdagi, S.; Noskov, S.Y. Mechanism of K+/Na+ selectivity in potassium channels from the perspective of the non-selective bacterial channel NaK. Channels 2011, 5, 198-200. [CrossRef]
- Obata, T.; Kitamoto, H.K.; Nakamura, A.; Fukuda, A.; Tanaka, Y. Rice shaker potassium channel OsKAT1 confers tolerance to salinity stress on yeast and rice cells. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 1978-1985. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Shen, L.; Luan, J.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, D.; Shen, Y.; Jing, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, W. Rice shaker potassium channel OsAKT2 positively regulates salt tolerance and grain yield by mediating K+ redistribution. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 2951-2965. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Fang, Q.; Chang, X.; Sun, M.; Li, W.; Li, Y. GmAKT1 is involved in K+ uptake and Na+/K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis and soybean plants. Plant Sci. 2021, 304, 110736. [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; He, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Carther K.F.I.; et al. Genome-wide identification of soybean Shaker K+ channel gene family and functional characterization of GmAKT1 in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana under salt and drought stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 266, 153529. [CrossRef]
- Demidchik, V.; Cuin, T.A.; Svistunenko, D.; Smith, S.J.; Miller, A.J.; Shabala, S.; Sokolik, A.; Yurin, V. Arabidopsis root K+-efflux conductance activated by hydroxyl radicals: single-channel properties, genetic basis and involvement in stress-induced cell death. J Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1468-1479. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ni, L.; Cui, Z.; Jiang, J.; Chen, C.; Jiang M. The NADPH oxidase OsRbohA increases salt tolerance by modulating K+ homeostasis in rice. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1611-1622. [CrossRef]
- Gobert, A.; Isayenkov, S.; Voelker, C.; Maathuis, F.J.M. The two-pore channel TPK1 gene encodes the vacuolar K+ conductance and plays a role in K+ homeostasis. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, 104, 10726-10731. [CrossRef]
- Maathuis, F. J. M.; Flowers, T.J. Sodium chloride compartmentation leaf vacuoles of the halophyte Suaeda maritima (L.) Dum. and its relation to tonoplast permeability. J. Exp. Bot. 1992, 43, 1219-1223, . [CrossRef]
- Bonales-Alatorre, E.; Pottosin, I.; Shabala, L.; Chen, Z.H.; Zeng F.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Shabala, S. Differential activity of plasma and vacuolar membrane transporters contributes to genotypic differences in salinity tolerance in a halophyte species, Chenopodium quinoa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9267-9285. [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.G.; Toyota, M.; Kim, S.H.; Gilroy, S. Salt stress-induced Ca2+ waves are associated with rapid, long-distance root-to-shoot signaling in plants. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6497-6502. [CrossRef]
- Pottosin, I.; Dobrovinskaya, O. Non-selective cation channels in plasma and vacuolar membranes and their contribution to K+ transport. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 732-742. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shabala, L.; Zhou, M.; Shabala, S. Durum and bread wheat differ in their ability to retain potassium in leaf mesophyll: implications for salinity stress tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 1749-1762. [CrossRef]
- Apsea, M.P.; Blumwaldb, E. Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2247-2254. [CrossRef]
- Hamam, A.M.; Coskun, D.; Britto D.; Plett, D.T.; Kronzucker, H.J. Plasma-membrane electrical responses to salt and osmotic gradients contradict radiotracer kinetics, and reveal Na+-transport dynamics in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 2019, 249, 1037-1051. [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Shabala, L.; Mithöfer, A.; Wang, H.; Qu, M.; Yu, M.; Cui, J.; Shabala, S. GABA operates upstream of H+-ATPase and improves salinity tolerance in Arabidopsis by enabling cytosolic K+ retention and Na+ exclusion. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 6349-6361. [CrossRef]
- Bose, J.; Shabala, L.; Pottosin, I.; Zeng, F.; Velarde-Buendi, A.; Massart, A.; Poschenrieder, C.; Haridi, Y.; Shabala, S. Kinetics of xylem loading, membrane potential maintenance, and sensitivity of K+-permeable channels to reactive oxygen species: physiological traits that differentiate salinity tolerance between pea and barley. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 589-600. [CrossRef]
- Rubio, F.; Nieves-Cordones, M.; Horie, T.; Shabala, S. Doing ‘business as usual’ comes with a cost: evaluating energy cost of maintaining plant intracellular K+ homeostasis under saline conditions. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1097-1104. [CrossRef]
- Bridges, D.; Fraser, M.E.; Moorhead, G.B. Cyclic nucleotide binding proteins in the Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa genomes. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 6. [CrossRef]
- Gobert, A.; Park, G.; Amtmann, A.; Sanders, D.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Arabidopsis thaliana cyclic nucleotide gated channel 3 forms a non-selective ion transporter involved in germination and cation transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 791-800. [CrossRef]
- Senadheera, P.; Singh, R.K.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Differentially expressed membrane transporters in rice roots may contribute to cultivar dependent salt tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 2553-2563. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.K.; Jing, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.H. Cyclic nucleotide gated channel 10 negatively regulates salt tolerance by mediating Na+ transport in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 211-220. [CrossRef]
- Lecourieux, D.; Mazars, C.; Pauly, N.; Ranjeva, R.; Pugin, A. Analysis and effects of cytosolic free calcium increases in response to elicitors in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia cells. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2627-2641. [CrossRef]
- Chiu, J.C.; Brenner, E.D.; DeSalle, R.; Nitabach, M.N.; Holmes, T.C.; Coruzzi, G.M. Phylogenetic and expression analysis of the glutamate-receptor-like gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1066-1082. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Lee, C.E.; Lin, Y.S.; Lee, M.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Chang, H.C.; Chang, I.F. The glutamate receptor-like protein GLR3.7 interacts with 14-3-3ω and participates in salt stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1169. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang X.; Sun, T.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, W.H. Glutamate receptor homolog 3.4 is involved in regulation of Seed germination under salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 978-988. [CrossRef]
- Maathuis, F.J.M. Vacuolar two-pore K+ channels act as vacuolar osmosensors. New Phytol. 2011, 191, 84-91. [CrossRef]
- Pottosin, I. I.; Martínez-Estévez, M.; Dobrovinskaya, O. R.; Muñiz, J. Potassium-selective channel in the red beet vacuolar membrane. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 663-667. [CrossRef]
- Isner, J.C.; Begum, A.; Nuehse, T.; Hetherington, A.M.; Maathuis, F.J.M. KIN7 kinase regulates the vacuolar TPK1 K+ channel during stomatal closure. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 466-472. [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, S.; Marui, J.; Matsuoka, K.; Maeshima, M.; Yabe, I.; Uozumi, N. Characterization of a tobacco TPK-type K+ channel as a novel tonoplast K+ channel using yeast tonoplasts. Mem. Trans. Stru. Funct. Biogen. 2008, 283, 1911-1920. [CrossRef]
- Latz, A.; Mehlmer, N.; Zapf, S.; Mueller, T.D.; Wurzinger, B.; Pfister, B.; Csaszar, E.; Hedrich, R., Teige, M.; Becker, D. Salt stress triggers phosphorylation of the Arabidopsis vacuolar K+ channel TPK1 by calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs). Mol. Plant. 2013, 6, 274-1289. [CrossRef]
- Isayenkov, S.; Isner, J.C.; Maathuis, F.J. Membrane localisation diversity of TPK channels and their physiological role. Plant Signal Behav. 2011, 6, 1201-1204. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Devonshire, J.; Mohamed, R.; Schultze, M.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Overexpression of the potassium channel TPKb in small vacuoles confers osmotic and drought tolerance to rice. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 1040-1048. [CrossRef]
- Demidchik, V.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Physiological roles of nonselective cation channels in plants: from salt stress to signaling and development. New Phytol. 2007, 175, 387-404. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Weim J.Genome-wide analysis and identification of HAK potassium transporter gene family in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 8465-8473. [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, A.J.; Peralta, M.L.; Santa-Maria, G.E. Expression of potassium-transporter coding genes, and kinetics of rubidium uptake, along a longitudinal root axis. Plant, Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 850-886. [CrossRef]
- Bañuelos, M.A..; Garciadeblas, B.; Cubero, B.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A. Inventory and functional characterization of the HAK potassium transporters of rice. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 784-795. [CrossRef]
- Hyun, T.K.; Rim, Y.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.S. Genome-wide and molecular evolution analyses of the KT/HAK/KUP family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Genes Genom. 2014, 36, 365-374. [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Z.; Ma, R.J., Yu, M.L. Genome-wide analysis and identification of KT/HAK/KUP potassium transporter gene family in peach (Prunus persica). Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 774-787. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, L.; Xie, C.; Shi, X.; Dong, C.; Shen, Q.; Xu, Y. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analyses of the HAK/KUP/KT potassium transporter gene family reveals their involvement in K+ deficient and abiotic stress responses in pear rootstock seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 85, 187-198. [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Jiang, W.; Yan, M. Zhang, A.; Liu, M.; Zhao, P.; Chen, X.; Tang, Z. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of HAK K+ transport family in Ipomoea. Biotech. 2021, 11, 3. [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y. et al. HAK/KUP/KT family potassium transporter genes are involved in potassium deficiency and stress responses in tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.): expression and functional analysis. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 556 . [CrossRef]
- Horie, T.; Sugawara, M.; Okada, T.; Taira, T.; Kaothien-Nakayama, P.; Katsuhara, M.; Shinmyo, A.; Nakayama, H. Rice sodium-insensitive potassium transporter, OsHAK5, confers increased salt tolerance in tobacco BY2 cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 346-356. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shen, L.; Shen, Z.; Jing, W.; Ge, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W. The potassium transporter OsHAK21 functions in the maintenance of ion homeostasis and tolerance to salt stress in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 2766-2779. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, B.; Qin, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, R.; Liu, H.; Yang, H. Progress in understanding the physiological and molecular responses of Populus to salt stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Shi, Y.; Shen, L.; Cao, C.; Shen, Y.; Jing, W.; Tian, Q.; Lin, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. An endoplasmic reticulum-localized cytochrome b5 regulates high-affinity K+ transport in response to salt stress in rice. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 2021, 118, e2114347118. [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Liu, A.; Wu, S.; Qu, K, Hu, H.; Yang, J.; Shrestha, N.; Liu, J.; Ren, G. Comparison of structural variants in the whole genome sequences of two Medicago truncatula ecotypes: Jemalong A17 and R108. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 77. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z; Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23,104-119. [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.R.; Sandhu, D.; Dueñas, C.; Dueñas, M.; Pudussery, M., Kaundal, A.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Suarez, D.L.; Skaggs, T.H. Morphological, physiological, biochemical, and transcriptome studies reveal the importance of transporters and stress signaling pathways during salinity stress in Prunus. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 274. [CrossRef]
- Santa-María, G.E.; Rubio, F.; Dubcovsky, J.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A. The HAK1 gene of barley is a member of a large gene family and encodes a high-affinity potassium transporter. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 2281-2289. [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Golldack, D.; Katsuhara, M.; Zhao, C.S.; Bohnert, H.J. Expression and stress-dependent induction of potassium channel transcripts in the common ice plant. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 604-614. [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, R.P.; Nagpal, P.; Reed, J. A mutation in the Arabidopsis KT2/KUP2 potassium transporter gene affects shoot cell expansion. Plant Cell. 2002, 14, 119-131. [CrossRef]
- Frans, J.M.; Maathuis, F.J.M. The role of monovalent cation transporters in plant responses to salinity. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1137-1147. [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wu, W.; Wu, W.H.; Wang, Y. Potassium transporter KUP7 is involved in K+ acquisition and translocation in Arabidopsis root under K+-limited conditions. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 437-446. [CrossRef]
- Ródenas, R.; García-Legaz, M.F.; López-Gómez, E.; Martínez, V.; Rubio, F.; Botella, M.A. NO3-, PO43− and SO42− deprivation reduced LKT1-mediated low-affinity K+ uptake and SKOR-mediated K+ translocation in tomato and Arabidopsis plants. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 160, 410-424. [CrossRef]
- Schachtman, D.P.; Schroeder, J.I. Structure and transport mechanism of a high-affinity potassium uptake transporter from higher plants. Nature 1994, 370, 655-658. [CrossRef]
- Horie, Y.; Hauser, F.; Schroeder, J.I. HKT transporter-mediated salinity resistance mechanisms in Arabidopsis and monocot crop plants. Trends in Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 660-668. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, C.; Shabalak, S.; Lv, C.; Guo, B.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Z. Genome wide association study and haplotype analysis reveals the role of HvHKT1;5 in potassium retention but not Na+ exclusion in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 201, 104973. [CrossRef]
- Asins, M.J.; Villalta, I.; Aly, M.M.; Olías, R.; Morales P.A.; Huertas, R.; Belver, A. Two closely linked tomato HKT coding genes are positional candidates for the major tomato QTL involved in Na+/K+ homeostasis. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 1171-1191. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, X; Gu, H.; Wu, B.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, X.; Cui, X. GmHKT1;4, a novel soybean gene regulating Na+/K+ ratio in roots enhances salt tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 73, 299-308 . [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, V.; Shabala, S.; Véry, A.A.; Hariharan, G.N.; Somasundaram, S.; Pulipati, S.; Sellamuthu, G.; Harikrishnan, M.; Kumari, K.; Shabala, L.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Z, To exclude or to accumulate? Revealing the role of the sodium HKT1;5 transporter in plant adaptive responses to varying soil salinity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 169, 333-342. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Costa, A.; Nakayama, H.; Katsuhara, M.; Shinmyo, A.; Horie, T. OsHKT2;2/1-mediated Na+ influx over K+ uptake in roots potentially increases toxic Na+ accumulation in a salt-tolerant landrace of rice Nona Bokra upon salinity stress. J. Plant Res. 2016, 129, 67-77. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.I.; Yamaji; N.; Yamamoto H.; Okubo, K.; Ueno, H.; Costa, A.; Tanoi, K.; Matsumura, H.; Fujii-Kashino, M.; Horiuchi, T.; et al. OsHKT1;5 mediates Na+ exclusion in the vasculature to protect leaf blades and reproductive tissues from salt toxicity in rice. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 91, 657-670. [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Chakraborty, K.; Mondal, S.; Jena, P.; Panda, R.K.; Samal, K.C.; Chattopadhyay, K. Relative contribution of ion exclusion and tissue tolerance traits govern the differential response of rice towards salt stress at seedling and reproductive stages. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 206, 105131. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nan, N.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T. J.; Hwang, I.; Liu, B.; Xu Z.Y. A DNA methylation reader-chaperone regulator-transcription factor complex activates OsHKT1;5 expression during salinity stress. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 3535-3558. [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Nazir, M.M.; Xu, J. Loss-of-function mutations of OsbHLH044 transcription factor lead to salinity sensitivity and a greater chalkiness in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 193, 110-123. [CrossRef]
- Hazzouri, K.M.; Khraiwesh, B.; Amiri, K.M.A.; Pauli, D.; Blake, T.; Shahid, M.; Mullath, S.K.; Nelson, D.; Mansour, A.L.; Salehi-Ashtiani, K.; Purugganan, M.; Masmoudi, K. Mapping of HKT1;5 Gene in barley using GWAS approach and its implication in salt tolerance mechanism. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 156. [CrossRef]
- Hmidi, D.; Messedi, D.; Corratgé-Faillie, C.; Marhuenda, T.; Fizames, C.; Zorrig, W.; Abdelly, C.; Sentenac, H.; Véry, A. Investigation of Na+ and K+ transport in halophytes: Functional analysis of the HmHKT2;1 transporter from Hordeum maritimum and expression under saline conditions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 2423-2435. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liang, X.; Yin, P.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, C. A domestication-associated reduction in K+ -preferring HKT transporter activity underlies maize shoot K+ accumulation and salt tolerance. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 301-317. [CrossRef]
- Leidi, E.O.; Barragánm V.; Rubio, L.; El-Hamdaoui, A.; Ruiz, M.T.; Cubero, B.; Fernández, J.A.; Bressan, R.A.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Quintero, F.J.; Pardo, J.M. The AtNHX1 exchanger mediates potassium compartmentation in vacuoles of transgenic tomato. Plant J. 2010, 61, 495-506. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.H.; Kumar, S.A.; Sivan, P.; Katam, R.; Suravajhala, P.; Rao, K.S.; Varshney, R.K.; Kishor, P.B.K. Overexpression of a plasma membrane bound Na+/H+ antiporter-like protein (SbNHXLP) confers salt tolerance and improves fruit yield in tomato by maintaining ion homeostasis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Al-Harrasi, I.; Jana, G.A.; Patankar, H.V.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Rajappa, S.; Kumar, P.P.; Yaish, M.W. A novel tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter gene from date palm (PdNHX6) confers enhanced salt tolerance response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 1079-1093. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, D.; Jin, T.; Chang, Q.; Yin, D.; Xu, S.; Liu, B.; Liu, L. The vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene SsNHX1 from the halophyte Salsola soda confers salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 29, 278-290. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Kaur, K.; Khare, T.; Srivastava, A.K.; Suprasanna, P.; Kumar, V. Genome-wide identification, characterization and transcriptional profiling of NHX-type (Na+/H+) antiporters under salinity stress in soybean. Biotech. 2021, 11, 16. [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.E.; Kim, D.; Ali, S.; Fedoroff, N.V.; Al-Babili, S. The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica enhances Arabidopsis thaliana growth and modulates Na+/K+ homeostasis under salt stress conditions. Plant Sci. 2017, 263, 107-115. [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, A.; Nakamura, A.; Hara, N.; Toki, S.; Tanaka, Y. Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes. Planta 2011, 233, 175-188. [CrossRef]
- Stephan, A.B.; Kunz, H.; Yang, E.; Schroeder, J. I. Rapid hyperosmotic-induced Ca2+ responses in Arabidopsis thaliana exhibit sensory potentiation and involvement of plastidial KEA transporters. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018, 113, E5242-E5249. [CrossRef]
- Tsujii, M.; Kera, K.; Hamamoto, S.; Kuromori, T.; Shikanai, T.; Uozumi, N. Evidence for potassium transport activity of Arabidopsis KEA1-KEA6. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10040. [CrossRef]
- Cellier, F.; Conéjéro, G.; Ricaud, L.; Luu, D.T.; Lepetit, M.; Gosti, F.; Casse, F. Characterization of AtCHX17, a member of the cation/H+ exchangers, CHX family, from Arabidopsis thaliana suggests a role in K+ homeostasis. Plant J. 2004, 39, 834-846. [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Sun, M.; Duan-Mu, H.; Ding, X.; Liu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, X. GsCHX19.3, a member of cation/H+ exchanger superfamily from wild soybean contributes to high salinity and carbonate alkaline tolerance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9423. [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S. Signaling by potassium: another second messenger to add to the list? J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 4003-4007. [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Day, D.A.; Fricke, W.; Watt, M.; Arsova, B.; Barkla, B.J.; Bose, J.; Byrt, C.S.; Chen, Z.; Foster, K.J. et al. Energy costs of salt tolerance in crop plants. New Phytol. 2019, 225, 1072-1090. [CrossRef]
- Kudla, J.; Becker, D.; Grill, E.; Hedrich, R.; Hippler, M.; Kummer, U.; Ramiske, M.; Romeis, T.; Schumacher, K. Advances and current challenges in calcium signaling. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 414-431. [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, A.; Xiang, Y.; Yan, M. The Arabidopsis AtUNC-93 acts as a positive regulator of abiotic stress tolerance and plant growth via modulation of ABA signaling and K+ homeostasis. Front Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, X.; Guo, Z.; Lu, S. CBL4-CIPK5 pathway confers salt but not drought and chilling tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 179, 104230. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lv, F.; Han, X.; Xia, X.; Yin, W. The calcium sensor PeCBL1, interacting with PeCIPK24/25 and PeCIPK26, regulates Na+/K+ homeostasis in Populus euphratica. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 611-621. [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Yang, X.X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Du, B.; Yao, L.; Li, X.T.; Guo, C. Alfalfa MsCBL4 enhances calcium metabolism but not sodium transport in transgenic tobacco under salt and saline-alkali stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 997-1011. [CrossRef]
- Amjad, M.; Akhtar, J.; Murtaza, B.; Abbas, G.; Jawad, H. Differential accumulation of potassium results in varied salt-tolerance response in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) cultivars. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 57, 248-258. [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Yao, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, G.; Zhang, H. Potassium ion regulates hormone, Ca2+ and H2O2 signal transduction and antioxidant activities to improve salt stress resistance in tobacco. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 186, 40-51. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wei, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; He, Y.; Zhou, S.; Feng, J.; Yang, G.; He, G. BdCIPK31, a calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase, regulates plant response to drought and salt stress. Front Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1184. [CrossRef]
- Khan, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Yaseen, T.; Hui, T. Expression and roles of GRAS gene family in plant growth, signal transduction, biotic and abiotic stress resistance and symbiosis formation. Plant Biol. 2021, 24, 404-416. [CrossRef]
- Kudla, J.; Batistic, O.; Hashimoto, K. Calcium signals: The lead currency of plant information processing. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 541-563. [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, Q-H.; Yu, Y.N.; Qiao, Y-M.; ul Haq, S.; Gong, Z.-H. The CBL-CIPK pathway in plant response to stress signals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5668. [CrossRef]
- Tomar, R. S.; Katarina, S.; Jajoo, A. Behind the scene: critical role of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species in salt stress tolerance. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2021, 207, 577-588. [CrossRef]
- Bose, J.; Pottosin, I.I.; Shabala, S.S.; Palmgren, M.G.; Shabala, S. Calcium efflux system in signaling and adaptation in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2011, 2, 85. [CrossRef]
- Demidchik, V.; Shabala,S.; Isayenkov, S.; Cuin, T.A.; Pottosin, I. Calcium transport across plant membranes: mechanisms and functions. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 49-69. [CrossRef]
- White, P.J.; Broadley, M.R. Calcium in Plants. Ann. Bot. 2003, 92, 487-511. [CrossRef]
- Dodd, A.N., Kudla, J. and Sanders, D. The language of calcium signalling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 593-620. [CrossRef]
- Park, C.J.; Shin, R. Calcium channels and transporters: Roles in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. Sec. Plant Membrane Traffic and Transport. 2022, 13, 964059. [CrossRef]
- Pirayesh, N.; Giridhar, M.; Khedher, A.B.; Vothknecht, U.C.; Chigri, F. Organellar calcium signaling in plants: An update. BBA Mol. Cell Res. 2021. 4, 118948. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Tong, T.; Chen, X.; Deng, F.; Zeng, F.; Pan, R.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.H. Molecular response and evolution of plant anion transport systems to abiotic stress. Plant Mol. Biol. 2022, 110, 397-412. [CrossRef]
- Shigaki, T.; Hirschi, K.D. Diverse functions and molecular properties emerging for CAX cation/H+ exchangers in plants. Plant Biol. 2006, 8, 419-429. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shigaki,T.; Mei, H., Guo, X.G.; Cheng, N-H.; Hirschi, K.D. Interaction between Arabidopsis Ca2+/H+ exchanger CAX1 and CAX3. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4605-4615. [CrossRef]
- Schulz, P.; Herde, M.; Romeis, T. Calcium-dependent protein kinases: Hubs in plant stress signaling and development. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 523-530. [CrossRef]
- Yemelyanov, V.; Shishova, M.; Chirkova, T.V.; Lindberg, S. Anoxia-induced elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in rice and wheat protoplasts. Planta 2011, 234, 271-280. [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.H.; Lindberg, S.; Maity, P.J.; Geilfus, C.M.; Plieth, C.; Mühling, K.H. Apoplastic and cytosolic Ca2+ and pH dynamics in salt-stressed Vicia faba leaves change in response to calcium. Func. Plant Biol. 2017, 44, 515-524. [CrossRef]
- Knight, H.; Trewavas, A.J.; Knight, M.R. Calcium signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana responsing to drought and salinity. Plant J. 1997, 12, 1067-1078. [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Knight, M.R.; Trewavas, A.J.; Sattelmacher, B.; Plieth, C. Self-reporting Arabidopsis expressing pH and [Ca2+] indicators unveil ion dynamics in the cytoplasm and in the apoplast under abiotic stress. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 898-908. [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, A.; Lindberg, S.; Lager, I., Rasmussen, U.; Schulz, A. Phospholipases D with C2-domains are involved in hypoxia signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2018, 167, 90-110. [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, L.; Lindberg, S.; Vitagliano, C. Cytoplasmic free Ca2+ dynamics in single tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) protoplasts subjected to chilling temperatures. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 105, 239-245. [CrossRef]
- Mahi, H. E.; Pérez-Hormaec he, J.; Luca, A. D.; Villalta, I.; Espartero, J.; Gámez-Arjona, F.; Fernández, J.L; Bundó, M.; Mendoza, I.; Mieulet, D.; et al. A critical role of sodium flux via the plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger SOS1 in the salt tolerance of rice. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1046-1065. [CrossRef]
- Lamers, J.; Van Der Meer, T.; Testerink, C. How plants sense and respond to stressful environments. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1624-1635. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X. Structure, function, and regulation of the plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter Salt Overly Sensitive 1 in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 866265. [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.A.; Lindberg, S.; Seidel, T.; Golldack, D.; Yemelyanov, V. Sodium sensing induces different changes in free cytosolic calcium concentration and pH in salt-tolerant and -sensitive rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars. Physiol. Plant. 2007, 130, 99-111. [CrossRef]
- Laohavisit, A.; Richards, S.L.; Shabala, L.; Chen, C.; Colaço, R.D.D.A.; Swarbreck, S.M.; Shaw, E.; Dark, A.; Shabala, S.; Shang, Z. et al. Salinity-induced calcium signaling and root adaptation in Arabidopsis require the calcium regulatory protein annexin1. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 253-262. [CrossRef]
- Konopka-Postupolka, D.; Clark, G. Annexins overlooked regulators of membrane trafficking in plant cells. Int. J. Sci. 2017, 18, 863. [CrossRef]
- Demidschik, V.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of cytosolic calcium elevation in plants: the role of ion channels, calcium extrusion systems and NADPH oxidase-mediated ‘ROS-Ca2+ Hub’. Func. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 9-27.
- Seifikalhor, M.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Shomali, A.; Azad, N.; Hassani, B.; Lastochkina, O.; Li, T. Calcium signaling and salt tolerance are diversely entwined in plants. Plant Sig. Behav. 2019, 14, 1665455. [CrossRef]
- McCarty, D.R.; Chory, J. Conservation and innovation in plant signaling pathways. Cell 2000, 3, 201-209. [CrossRef]
- Rubio, F.; Fon, M.; Ródenas, R.; Nieves-Cordones, M.; Alemán, F.; Rivero, R.M.; Martínez, V. A low K+ signal is required for functional high-affinity K+ uptake through HAK5 transporters. Physiol Plant. 2014, 152, 558-570. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.K. Emergence of a novel calcium-signaling pathway in plants: CBL-CIPK signaling network. Phys. Mol. Biol. Plants 2008, 14, 51-68. [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.; Xu, Z.; Luoni, L.; Bonza, M.G.; Doccula, F.G.; De Michelis, M.I.; Morris, R.J.; Schwarzländer, M. Cellular Ca2+ signals generate defined pH signatures in plants. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 2704-2719. [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.M.; Schroeder, J.I. Roles of ion channels in initiation of signal transduction in higher plants. In: Aducci, P. (eds) Signal Transduction in Plants. 1997, MCBU Molecular and Cell Biology Updates. Birkhäuser Basel. [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Kikuyama, M.; Hiramoto, Y.; Iwasaki, N. Short-term regulation of cytosolic Ca2+, cytosolic pH and vacuolar pH under NaCl stress in the charophyte alga Nitellopsis obtuse. Plant Cell Environ. 1996, 19, 569-576. [CrossRef]
- Taiz, L.; Zeiger, E. Plant Physiol. Fourth Ed., Sinauer Associates, Inc., Publisher, Sunderland, Massachusetts, 2006, p. 694.
- McKay, D.W.; McFarlane, H.E.; Qu, Y.; Situmorang, A.; Gilliham, M.; Wege, S. Plant trans-Golgi network/early endosome pH regulation requires cation chloride cotransporter (CCC1). Life 2022, 11, e70701. [CrossRef]
- Kader, Md.A.; Lindberg, S. Cytosolic calcium and pH signaling in plants under salinity stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 3, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; Geros, H. Regulation by salt of vacuolar H+ATPase and H+pyrophosphatase activities and Na+/H+ exchange. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 718-726. [CrossRef]
- Pecherina, A.; Grinberg, M.; Ageyeva, M.; Zanegina, D.; Akinchits, E.; Brilkina, A.; Vodeneev, V. Salt-induced changes in cytosolic pH and photosynthesis in tobacco and potato leaves. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 491. [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Mader, C.; Schmitz, J.; Atladottir, J.; Fitchev, P.; Cornwell, M.L.; Koleske, A.J.; Crawford, S.E.; Gorelick, F. The vacuolar-ATPase modulates matrix metalloproteinase isoforms in human pancreatic cancer. Lab Invest. 2011, 91, 732-743. [CrossRef]
- Hager, A. Role of plasma membrane H+-ATPase in auxin-induced elongation growth: historical and new aspects. J. Plant Res. 2003, 116, 4483-505. [CrossRef]
- Pitann, B.; Schubert, S.; Mühling, K.H. Decline in leaf growth under salt stress due to an inhibition of H+-pumping activity and increase in apoplastic pH of maize leaves. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 535-543. [CrossRef]
- Buch-Pedersen, M.J.; Rudashevskaya, E.L.; Berner, T.S.; Venema K, Palmgren MG. Potassium as an intrinsic uncoupler of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 15, 38285-38292. [CrossRef]
- Ekberg, K.; Pedersen, B.P.; Sørensen, D.M.; Pedersen, M.J. Structural identification of cation binding pockets in the plasma membrane proton pump. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 107, 21400-21405. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.S.; Ali, G.S.; Celesnik, H.; Day, I.S. Coping with stresses. Role of calcium and calcium/calmodulin-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2010-2032. [CrossRef]
- Hauwink, A.L. The conduction of exitation in Mimosa pudica. Rcueil des travaux neerlandais 1935, 32, 51-91. https://natuurtijdschriften.nl/pub/552269.
- Ricca, U. Transmission of stimuli in plants. Nature 1926, 117, 654-655. [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.G.; Miller, G.; Wallace, I.; Harper, J.; Mittler, R.; Gilroy, S. Orchestrating rapid long-distance signaling in plants with Ca2+, ROS and electrical signals. Plant J. 2017, 90, 698-707. [CrossRef]
- Fichman, Y.; Mittler, R. Integration of electric, calcium, reactive oxygen species and hydraulic signals during rapyid sstemic signaling in plants. Plant J. 2021, 107, 7-20. [CrossRef]
- Felle, H.H.; Zimmermann, M.R. Systemic signalling in barley through action potentials. Planta 2007, 226, 203-214. [CrossRef]
- Bellandi, A.; Papp, D.; Breakspear, A.; Joyce, A.J.; Johnston, M.G.; de Keljzer, J.; Raven, E.C.; Ohtsu, M.; Vincent, T.R.; Miller, A.J.; Sanders, D.; Hogenhout, S.A.; Morris, R.J.; Faulkner, C. Diffusion and bulk flow of amino acids mediate calcium waves in plants. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo6693. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abo6693.
- Shao, Q.; Gao, Q.; Lhamo, D.; Zhang, H., Luan, S. The glutamate- and pH-regulated Ca2+ channels are required for systemic wound signaling in Arabidopsis. Sci. Signal, 2020, 14, 453. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scisignal.aba1453.
- Miller, G.; Schlauch, K.; Tam, R.; Cortes, D.; Torres, M.A.; Shulaev, V.; Dang, J.L.; Mittler, R. The plant NADPH oxidase RBOHD mediates rapid systemic signaling in response to diverse stimuli. Sci Signal. 2009, 18, 45. [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.J.; Choi, W.G.; Gilroy, S.; Morris, R.J. A ROS-assisted calcium wave dependent on the AtRBOHD NADPH oxidase and TPC1 cation channel propagates the systemic response to salt stress. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1771-1784. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 441-445. [CrossRef]

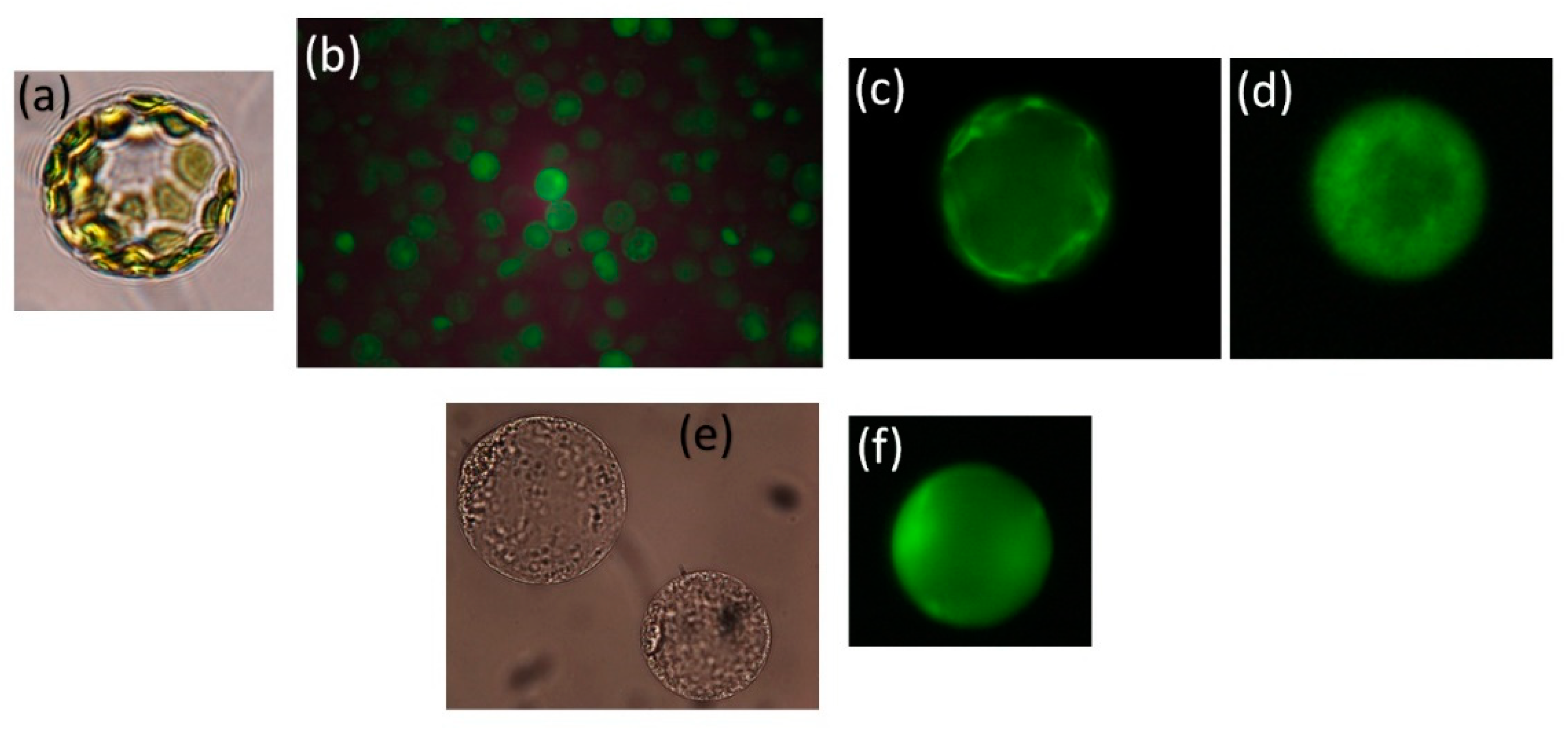
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




