1. Introduction
Roundup Ready crops, defined as crop plants modified to withstand glyphosate, entered the US market in 1990’s. Growers spray glyphosate-based herbicides on Roundup Ready crops, killing weeds without damaging the crops. The use of these genetically modified crops drove agriculture toward a paradigm shift. Commercial agriculture now uses zero tillage and direct-seed planting [
1,
2,
3], and Roundup herbicides are currently the most frequently used pesticide in the agricultural sector [
4]. Glyphosate, glyphosate-based formulations, and their degradants are regularly released into our environment because of this shift in our agricultural practices, because of our practice of applying glyphosate-based herbicides to crops shortly before harvest (e.g. green burndown) [
1], and because increased weed resistance leads to heavier applications of glyphosate-based herbicides [
5]. To establish meaningful and sustainable policy directives for sustainable pesticide use in agriculture, baseline knowledge of basic impacts of agrochemicals such as glyphosate and its associated metabolites on non-target organisms is required.
The toxicity of glyphosate and some of its formulations on non-target animals is well studied (e.g. [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]), but the same is not true for the chemicals that glyphosate creates as it mineralizes. Glyphosate’s main metabolite is AMPA, aminomethylphosphonic acid. It occurs in significant amounts as glyphosate degrades [
12], but its impacts on many classes of non-target organisms are not well studied (but see [
13]).
Because of glyphosate’s popularity, AMPA has been detected in various global fresh-waterways, including ditches and drains, precipitation, rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, wetlands, and groundwater [
4,
14,
15]. In the US, one study found AMPA in 90% of stream samples [
4]. Another study that focused on US ecosystems found AMPA in 14.3% of sampled groundwater samples, 71.6% of sampled streams, 80.7% of sampled ditches and drains, and 29.8% of sampled lakes and ponds [
4]. AMPA is very water soluble and has an aquatic half-life that ranges from 2 to 91 days [
16,
17]. Concentrations of AMPA in freshwater environments for Mississippi and Iowa are reported at 0.02–5.7 μg/L [
18]. Median AMPA concentrations in US waterways range from 0.02 μg/L (groundwater, lakes, ponds and wetlands) to 0.43 μg/L (ditches and drains) [
4]. Median AMPA concentrations are 0.15 μg/L in waterways, with a median maximum of 5.6 μg/L [
14].
Because of the ubiquity of AMPA in freshwater, it has the potential to impact non-target water-dwelling invertebrates, and this means that our current method of harvesting crops and controlling weeds can reverberate through freshwater ecosystems. Concurrently, several highly diverse taxa of aquatic invertebrates are still poorly described and are poorly considered in protection programs, despite the fact they provide a fundamental component of biodiversity [
19]. This means that if aquatic invertebrates are negatively impacted by agricultural practices, the results might be both poorly predicted and poorly described.
Freshwater invertebrates play significant roles in their ecosystems. Planarians, for example are small, free-living flatworms that provide ecosystem services in part by consuming small living invertebrates and decaying organisms [
20,
21]. They can control population growth in species such as mosquitos and snails [
21,
22]. They serve as a food source for higher trophic levels, such as fish, and contribute to sediment formation and sediment dwelling microbial communities through bioturbation.
Water-dwelling planarian species are sensitive to organic matter pollution and water quality [
19,
20], and therefore serve as optimal bioindicators for freshwater ecosystems [
23]. Additionally, planarians display an array of sensitive and reliable responses to environmental stressors, making them ideal as ecotoxicological model species [
24]. Their utility in ecotoxicology studies additionally benefits from the fact that they have startling developmental plasticity and regenerative capacity in response to variable nutrient conditions or injury [
25,
26], allowing researchers to assess the effects of potential toxins on regenerative processes.
In summary, the widespread presence of AMPA in aquatic ecosystems raises significant concerns for current agricultural methods. Our study seeks to bridge the existing gap in understanding the ecological repercussions of AMPA exposure on freshwater ecosystems. The lack of comprehensive data on the diverse taxa of aquatic invertebrates underscores the urgency for a more nuanced approach to conservation. This research addresses this gap by exploring the nuanced responses of water-dwelling planarians, shedding light on their intricate roles in maintaining ecological balance and serving as sentinel species in assessing the broader impacts of evolving agricultural practices on freshwater biodiversity. We conducted a series of experiments to determine the impact of both chronic and acute AMPA exposure on the health of a common freshwater invertebrate: the brown planarian (Girardia tigrina), a freshwater planarian native to the Americas.
2. Materials and Methods
As an overview, in order to understand the impact of current agricultural methods on freshwater invertebrates, we measured the impact of both acute and chronic exposure to AMPA on the survivorship, regenerative abilities from head segments, regenerative abilities from the tail segments, regenerative abilities of the eyespots, and locomotion after regeneration in the planarian. The following information details how we executed each of the experiments.
2.1. Planarian
Brown planarian,
Girardia tigrina, were purchased from Carolina Biological Supply and housed collectively in glass jars (45 x 28 x 17 cm) filled with water from our greenhouse pond. They were fed approximately 0.2 g ground earthworm (
Eisenia fetida) once per week. Following [
27], we maintained them in Conviron Growth Chambers for 24-hour darkness at 23
oC. We habituated them to this housing environment for two weeks before experimentation.
2.2. Contamination
AMPA (99% pure) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich® Solutions. We mixed AMPA with greenhouse pond water to create two concentrations, 0.02 µg/L (low dose) and 3.1 µg/L (high dose). We selected these doses because they represent low and high ends of the range observed in existing US water systems [
4,
14].
2.3. Swimming Speed
We built an apparatus to measure the speed at which individuals swam away from a bright light source. The apparatus consisted of an opaque plastic chamber (200 x 140 x 60 mm) covered with a one-way tint film. We cut a hole through the film and shone a 1000-lumen flashlight through it, creating a ring of light with a diameter of 31.65 mm. We centered a 90 mm Petri dish beneath the light and placed a sheet of graph paper beneath the dish. With the flashlight clamped 152 mm above the chamber, we set a planarian in the center of the Petri dish using a dropper and measured the time in seconds used by the planarian to leave the ring of light. Each square on the graph paper measured 2.5 mm, allowing us to measure distance per second.
2.4. Body Measurements
We used ImageJ, open-source software that processes images, to assess 1) eyespot distance (mm), defined the distance between the center of the two pupils, and 2) body length, defined as the distance from the tip of the head to the end of the tail.
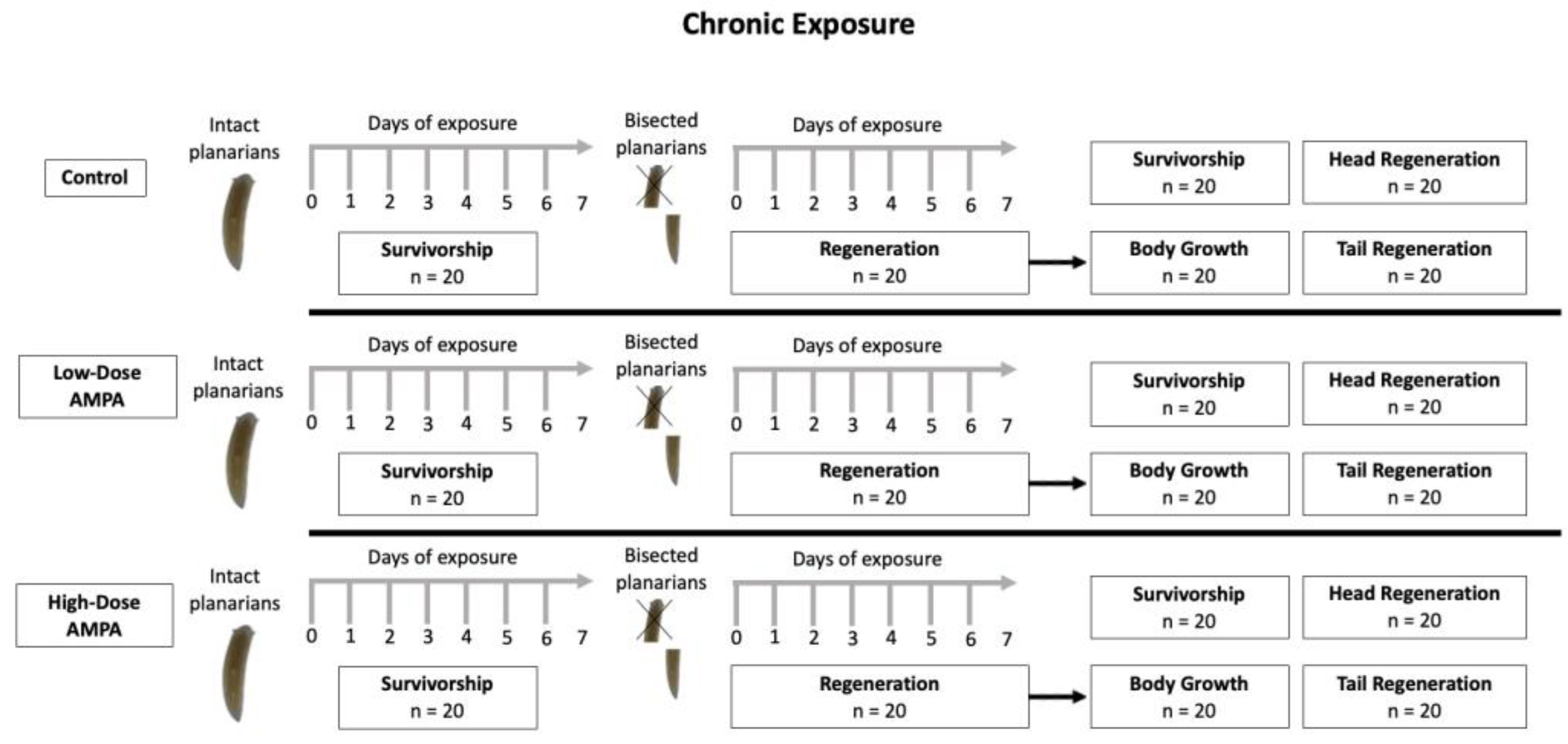
2.5. Chronic Exposure
Experiment that measured the impact of chronic exposure ran for 14 days. We prepared twenty replicates within three treatments: control, low-dose AMPA, and high-dose AMPA. Jars for the control treatment (N = 20) received only 503.2 mL pond water; jars for the low-dose experimental treatment (N = 20) received 503.2 mL of AMPA solution at the low-dose concentration; jars for the high-dose experimental treatment (N = 20) received 503.2 mL of AMPA solution at the high dose concentration.
Before we began the experiments, we allowed 60 group-living subjects to consume 0.2 g of shredded earthworm (Eisenia fetida) for one hour. We then extracted individuals one at a time, placed each into its own Petri dish using a dropper, and measured its body length using imageJ, ensuring that mean body lengths were similar across treatments.
This process yielded the following distribution of body lengths: individuals in the control treatment (N = 20) measured 9.40 + 2.39 mm; individuals in the low-dose treatment (N = 20) measured 10.36 + 4.79 mm, and individuals in the high-dose treatment (N = 20) measured 8.43 mm + 1.62 mm. An ANOVA detected no significant difference in initial mean body lengths across treatments (DF = 2, 57; F = 1.80; P = 0.18).
We did not feed the planarians for the duration of this experiment, and after seven days of exposure to their treatments, we bisected them transversely at approximately 50% of its length, measured the resulting segments, and placed the resulting segments into jars containing uncontaminated pondwater or AMPA solutions matching their original treatment. The segments were allowed to regenerated in their appropriate solutions for an additional seven days. See
Figure 1.
Via this bisection process, we produced heads with following means and standard deviation: 3.85 + 1.24 mm for the control (N = 20); 3.47 + 1.13 mm for the low-dose treatment (N = 20), and 3.70 + 1.24 mm for the high-dose treatment (N = 20). These lengths were did not significantly differ from each other (DF = 2, 57; F = 0.51; P = 0.60). Via bisection, we produced tails with the following means and standard deviations: 2.80 + 1.14 mm for the control (N = 20), 2.70 + 0.70 mm for the low-dose treatment (N = 20), and 3.17 + 1.35 mm for the high-dose treatment (N = 20). According to an ANOVA, these lengths were not significantly different from each other (DF = 2, 57; F = 1.02; P = 0.37).
As endpoints, we measured survivorship, body growth, degree of head regeneration, and degree of tail regeneration after chronic exposure. To assess survivorship, we counted the number of survivors after the first week of exposure. Additionally, we counted the number of head segments and tail segments that survived regeneration after the second week of exposure. To assess growth, we compared the initial body size to the body size measured after seven days of exposure, just prior to bisection. Lastly, to measure head regeneration, we subtracted the final regenerated size from the original size, and to measure tail regeneration, we subtracted final regenerated tail size from the original.
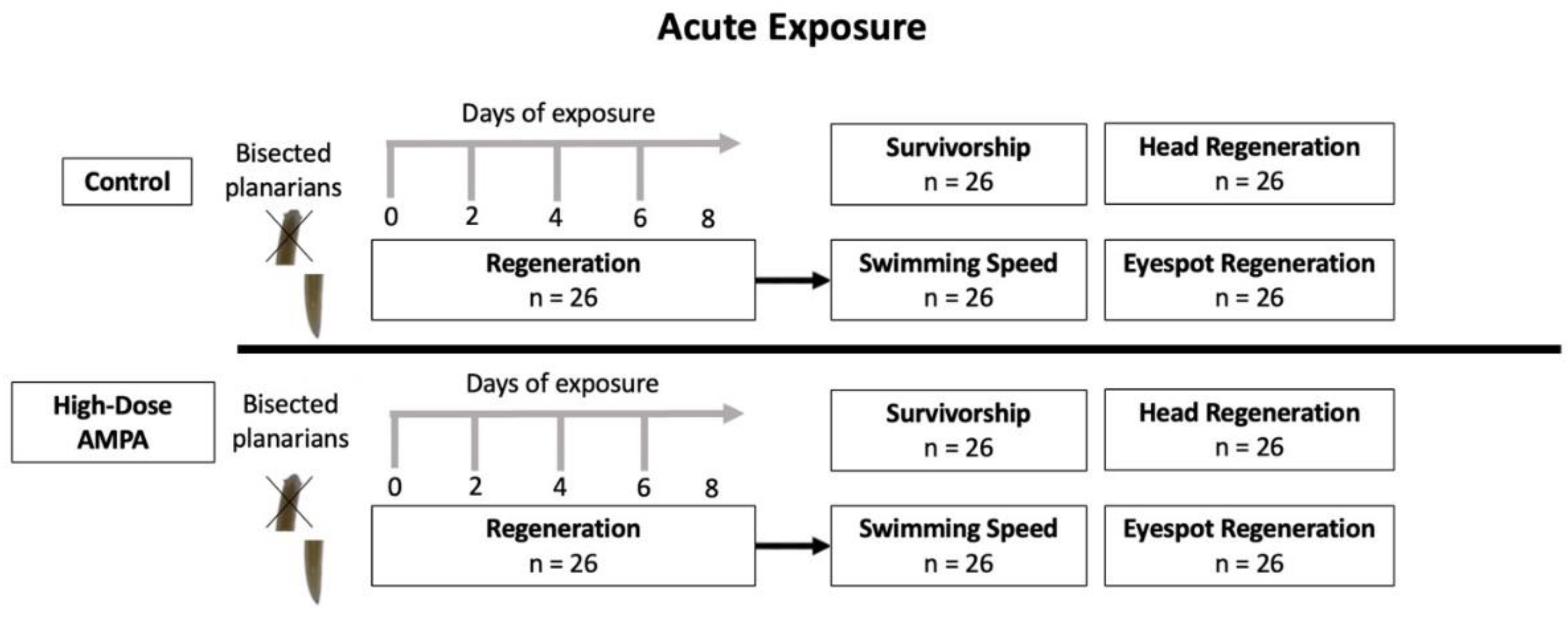
2.6. Acute AMPA Exposure
The experiments to examine the impact of acute AMPA exposure on planarians ran for seven days. We created 26 replicates within two treatments: control and AMPA. Jars for the control treatment (N = 26) received 300.7 mL uncontaminated pond water; jars in the second treatment (N = 26) received 300.7 mL of high-dose AMPA solution.
We began by allowing 52 group-living subjects to consume 0.2 g of shredded earthworm (Eisenia fetida) for one hour. We then extracted individuals one at a time, placed each into its own Petri dish with a dropper, and measured body length (mm), ensuring that mean body lengths were similar across treatments. Individuals slated for the uncontaminated water (N = 26) had a mean and standard deviation in body length of 10.61 mm + 1.94, and individuals slated for the AMPA-contaminated water had a mean and standard deviation in body length of 10.71 mm + 1.93. A one-way ANOVA detected no significant difference (DF = 1, 50, F = 0.04, P = 0.84).
After planarians were assigned to treatment groups, we bisected each organism transversely at approximately 50% of its length, discarded the head segment, and allowed the tail segment to regenerate in its treatment for seven days. See
Figure 2.
We assessed survivorship by counting how many tail segments within each treatment survived the seven-day exposure period. To assess proportion of body length regeneration, we divided the length of the regenerated tail segment by its length before bisection. To assess eyespot regeneration, we compared the average distance between eyespots across the two treatments. To assess swimming speed (mm-s), we measured speed of light avoidance for all individuals after seven days of exposure and compared means.
2.7. Data Analysis
All data were recorded into Microsoft Excel. After determining that variables were distributed normally using a Kolmogorov-Smirnov/Lilliefor test, we examined differences between means using one-way ANOVAs significant at the 0.05 level. When we detected a difference in means, we followed up with post-hoc Scheffe tests, which are designed for unplanned comparisons, to determine where the differences lay. We ran all analyses in StatPlus v6. Samples size (N), means, and standard deviations are reported throughout. Error bars in graphs represent the standard error of the means.
3. Results
3.1. Survivorship while Regenerating during Chronic Exposure
We measured survivorship of both intact and bisected planarians. All intact planarians demonstrated 100% survivorship (20/20), surviving the initial 7-day exposure period, regardless of treatment.
After we bisected those planarians and let them regenerate for one week, mortality occurred only in the treatments with contamination. This was true for both head and tail segments. Specifically, for the planarians regenerating in uncontamianted water, survivorship of the head segments was 100% (20/20). Survivorship of the head segments regenerating in the low-dose AMPA treatment demonstrated a 95% (19/20) survivorship, and the head segments regenerating in the high-dose AMPA treatment demonstrated a 90% (18/20) survivorship.
Similarly, the tail segments regenerating in the uncontaminated pond water demonstrated a 100% (20/20) survivorship; those regenerating in the low-dose AMPA treatment demonstrated 85% (17/20) survivorship; and for the planarians regenerating in the high-dose AMAPA treatment, the tail segments demonstrated 85% (17/20) survivorship.
3.2. Growth during Chronic Exposure
After seven days of exposure but before bisection, all planarians demonstrated reduced body length, likely because they received no food. Planarians living in uncontaminated water (N = 20) decreased 1.32 mm + 2.07 in length. Planarians living in low-dose AMPA (N = 20) decreased 3.16 mm + 5.03, and planarians exposed to high-dose AMPA (N = 20) decreased 1.64 mm + 1.49. While planarians living in uncontaminated water decreased in body length the least, an ANOVA detected no significant difference (DF = 2, 57; F = 1.83; P = 0.17).
3.3. Head Regeneration after Chronic Exposure
After bisection and seven more days of exposure, head-segment lengths increased in all treatments. The head segments in the control group increasing the most, demonstrating a mean and standard deviation increase of 1.34 mm + 1.08 (N = 20). The head segments regenerating in the low-dose AMPA water increased 1.01 mm + 1.08 (N =19), and the head segments regenerating in high-dose AMPA water increased 0.83 mm + 1.31. While the control group had the greatest recovery, an ANOVA detected no significant difference in head-segment regeneration (DF = 2, 54; F = 0.96; P = 0.39).
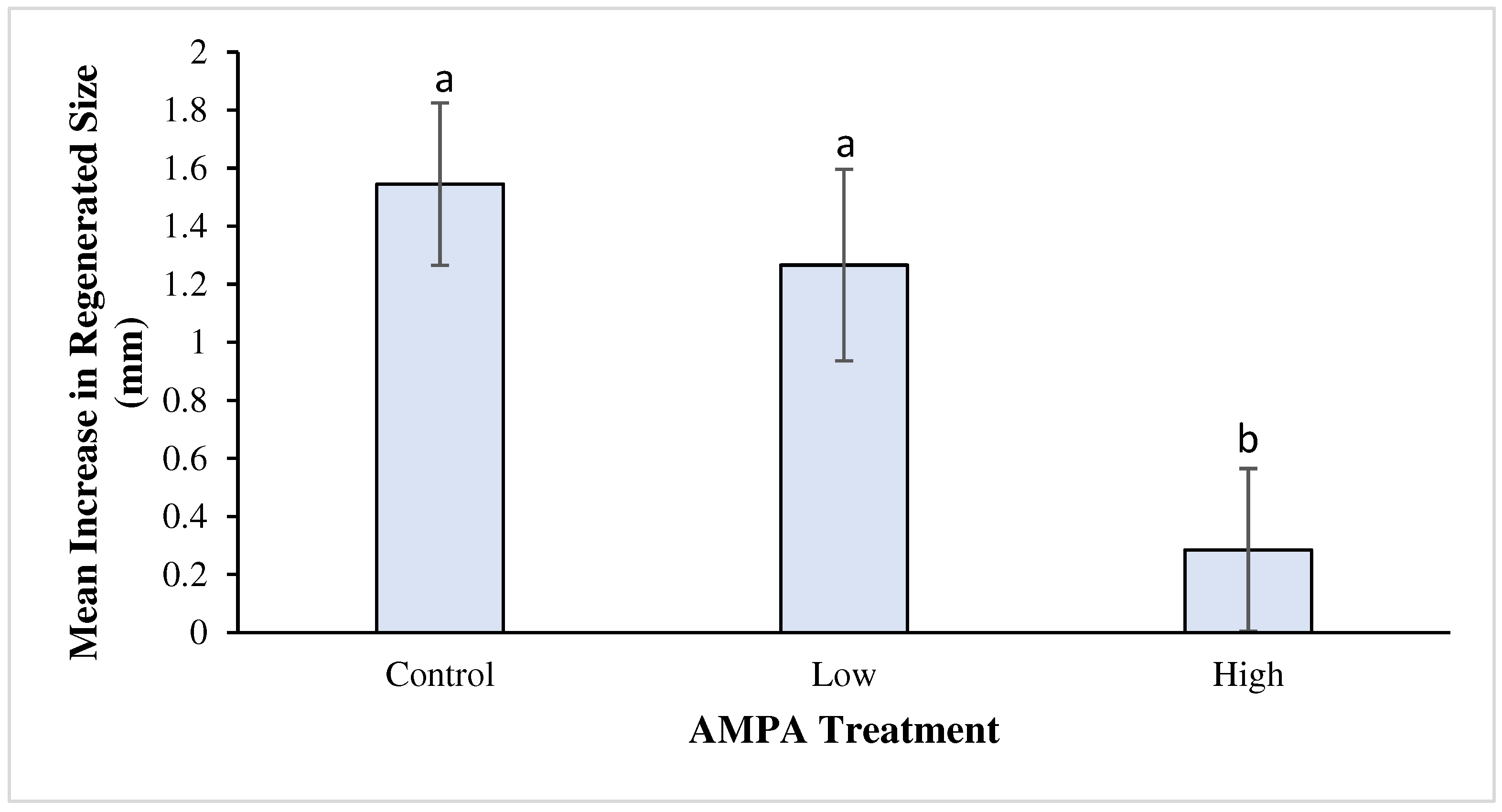
3.4. Tail Regeneration after Chronic Exposure
Chronic AMPA exposure significantly slowed tail segment regeneration (ANOVA: DF = 2, 51; F = 4.89; P = 0.01), particularly at the high-dose level. Tail segment length increased in all treatments, with the control group demonstrating a mean and standard deviation increase of 1.55 mm
+ 1.27 (N = 20). Individual tail segments within the low-dose treatment demonstrated a mean body length increase of 1.27 mm
+ 1.38 (N =17), and tail segments regenerating in the high-dose AMPA water increased a mean of 0.29 mm
+ 1.14 (N = 17). A Sheffe post hoc test identified a significant difference (P = 0.02) between the mean for the control and the high-dose treatment; the difference between the means for low and high approach significance (P = 0.08). See
Figure 3.
3.5. Survivorship after Acute Exposure
During an acute-exposure event, regenerating in contaminated water did not impact survivorship. Tail segments that regenerated in uncontaminated pondwater demonstrated 92.3% (24/26) survivorship while those that regenerated in AMPA-contaminated water demonstrated 96.2% (25/26) survivorship.
3.6. Body Regeneration after Acute Exposure
Acute exposure to AMPA during regeneration did not slow regeneration. After bisection and exposure, tail segments in the control group (N = 24) regained a mean 65.0% + 9.4 of their initial body size and those in the AMPA treatment (N = 25) regained 65.7% + 10.2 of their initial size. An ANOVA found no difference (DF = 1,47; F = 0.07, P = 0.79).
3.7. Eye Spot Regeneration after Acute Exposure
Acute exposure to AMPA during regeneration did not alter regenerated head morphology, as measured by distance between eyespots. Before bisection and exposure to contamination, the mean distance and standard deviation between eyespots was 0.56 mm + 0.12 for the control group (N = 26) and 0.56 mm + 0.11 for the group exposed to AMPA (N = 26). After bisection and seven days of exposure, planarians in uncontaminated water (N = 24) regained 56.1% + 16.6 of their initial value while those regenerating in AMPA-contaminated water regained 56.5% + 13.9 of their initial value. An ANOVA found no significant difference (DF = 1, 47; F = 0.007, P = 0.93).
3.8. Swimming Speed after Acute Exposure
Acute exposure to AMPA during regeneration did not alter locomotory ability as measured by swimming speed when exposed to light. Planarians that were bisected and then returned to uncontaminated water for seven days (N = 24) demonstrated a mean swimming speed of 0.75 mm-s + 0.22. Similarly, planarians that regenerated in AMPA-contaminated water (N = 25) demonstrated a swimming speed of 0.83 mm-s + 0.22. An ANOVA detected no significant difference (DF = 1, 48; F = 1.61, P = 0.21).
4. Discussion
This series of experiments show that chronic exposure to high but realistic doses of AMPA significantly slows regeneration from tail segments and has a negative impact on planarian mortality. Acute AMPA exposure had no impact on our measured endpoints, and chronic exposure had no impact on regeneration from head segments or general body growth. Taken together, these results suggest planarias can likely recover from one short exposure, but that multiple exposures or chronic exposure to environmental AMPA will impact the ecosystem services delivered by planarians.
Given the ubiquity of environmental AMPA in freshwater systems resulting from current agricultural practices [
4], our results suggest the need to assess the response of planaria living in the wild to actual chronic field doses of AMPA. Several taxa of aquatic invertebrates, including planarians, are still poorly described [
19]. They are rarely considered in protection programs [
19]. In our laboratory experiments, chronic exposure, which lasted only two weeks, negatively impacted planarian’s ability to regenerate. In the wild, exposure lengths are likely to exceed two weeks, and exposure is likely to co-occur with glyphosate [
4]. Planarians provide a fundamental component of biodiversity [
19] and deliver critical ecosystem services. Understanding the impact of this contaminant on these invertebrates is critical.
Furthermore, our experiments used conservative doses of AMPA, with our high-dose experiments not quite reaching the highest observed AMPA levels in lakes, streams, and ponds, and our chronic exposure ran only two weeks. When planarians are exposed to AMPA for longer time periods, might endure more dramatic health impacts. Follow-up experiments might include water contaminated with both AMPA and glyphosate.
Data about AMPA toxicity in aquatic systems are scarce and contradictory [
28,
29]. A literature review concerning the impact of AMPA on aquatic organisms reported serious impacts on the European eel (
Anguilla anguilla), zebrafish (
Danio rerio), guppies (
Poecilia reticulata), Mediterranean mussels (
Mytilus galloprovincialis), and toads (
Bufo spinosus) [
13], but another study found that AMPA was the least toxic of the chemicals associated with Roundup formulations to zebrafish [
29]. AMPA exposure causes genotoxicity and immunotoxicity in fish, adverse changes in hemolymph parameters, effects on mussels’ antioxidant enzymes, and developmental delay and survival of tadpoles [
13]. Also, AMPA induced sublethal responses in mosquito (
Aedes aegypti) larvae during acute exposures [
28]. However, under environmental concentrations, AMPA was not toxic to aquatic vertebrates and invertebrates [
30,
31]. The no observed-adverse effect concentration (NOAEC) of AMPA to fathead minnow fish (
Pimephales promelas) and to
Daphnia magna was far below levels encountered in nature [
12]. Similarly, AMPA had no effect on mortality of the earthworm (
Eisenia andrei) under field-relevant concentrations [
32]. In the few studies that examined the impact of AMPA on planarians, researchers found that exposure can cause seizures in
D. dorotocephala via the inhibition of glutamate-activated ion channels [
33,
34], but both studies were aimed at understanding pharmacology rather than ecotoxicity. Our experiments add to our understanding of the impact of field-realistic doses of AMPA on an important freshwater invertebrate.
While our study suggests that the sublethal impacts of AMPA to planarians might disrupt their ability to deliver ecosystem services directly, another danger may lie in bioaccumulation. Organisms such as mussels (
Mytilus galloprovincialis) [
35], carp (
Ctenopharyngodon idellus) [
36], snails (
Helix aspersa) [
37] and earthworms (
Allolobophora chlorotica) [
38] can bioaccumulate AMPA. Via bioaccumulation, AMPA can advance up the trophic levels of the food web. If planarias survive AMPA and glyphosate exposure while storing it their tissue, they may cause damage to the organisms that prey upon them.
On a different note, our study finds that after living in AMPA-contaminated water for a week and then regenerating in it, only the tail segments regenerated significantly slower rate than those in the uncontaminated water; head segments were not similarly impacted. This finding suggests that exposure to AMPA might impact axial patterning, the process by which the anterior-posterior (head-tail) axis is established and maintained during the regeneration, within the planaria.
After bisection, position control genes (PCGs) govern the planarian patterning pathways that influence whether to grow a head or a tail. [
39]. Upon bisection, the planarian tail segment will express anterior PCGs at the anterior facing wound, and the planarian head segment will express posterior PCGs at the posterior facing wound [
40]. Regional expression of Wingless/Integrated (
Wnt) ligands (posteriorly) and
Wnt inhibitors (anteriorly) are necessary for planarians to develop head and tail segments [
41,
42]. Once a wound has been inflicted, PCGs will express
Wnt1, which leads to the expression of
ß-catenin [
41].
ß-catenin expression triggers planarians to regenerate tail segments, while
Wnt inhibitor
notum expression inhibits
ß-catenin expression, leading to head regeneration [
43]. Our findings suggest that AMPA may interfere with the expression of
Wnt inhibitors, which may lead to a slower rate of head regeneration from tail segments. Future studies can employ assays to determine the expression of PCGs to further understand the impact of AMPA on axial patterning and regeneration rate.
In summary, our set of experiments demonstrate that chronically exposing freshwater planarians to realistic field doses of AMPA alone causes sublethal impacts to their health. Given the role that planarians play in nutrient cycling, control of other invertebrate populations, providing prey for organisms higher on the trophic levels, and in bioturbation, our findings suggest that our current agricultural reliance on glyphosate to control weeds and to harvest crops may have a measurable impact on freshwater ecosystems, and as we strive towards sustainable growing methods, this cost belongs in the accounting.
Author Contributions
Sharon T. Pochron: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, resources, data curation, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration Samy Sasoun: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, data curation, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition Siddhartha Maharjan: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration Wali U. Pirzada: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration Samantha Byrne: software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing-review and editing, visualization Mary Girgis: investigation Morgan A. Jacobellis: investigation Johanna Mitra: investigation Alec Miranda: investigation Grace Van Gelder: investigation Sayeed Khan: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration. Authors Samantha Byrne, Sayeed Khan, Siddhartha Maharjan, and Wali U. Pirzada contributed equally to this project.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We thank greenhouse curators Michael Axelrod and Sean Halliwell for their technical support of this (and many other) projects. We thank Dr. Katherine Aubrecht, chair of the Sustainability Studies Program, Dr. Paul Shepson, Dean of the School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences, for their continued support of undergraduate research opportunities. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors, however, Stony Brook University’s Undergraduate Research & Creative Activities (URECA) provided summer funds for the second author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Myers, J.P.; Antoniou, M.N.; Blumberg, B.; Carroll, L.; Colborn, T.; Everett, L.G.; Hansen, M.; Landrigan, P.J.; Lanphear, B.P.; Mesnage, R.; Vandenberg, L.N. Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: a consensus statement. Environ Health 2016, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, N.C.; Marino, D.J.; Natale, G.S.; Somoza, G.M. Effects of glyphosate and its commercial formulation, Roundup® Ultramax, on liver histology of tadpoles of the neotropical frog, Leptodactylus latrans (amphibia: Anura). Chemosphere 2018, 202, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudell, E.C.; Zanrosso, B.A.; Frandaloso, D.; Giacomini, A.J.; Spadotto, D.V.; Vargas, L.; Nunes, A.L.; Santos, F.M. Integrated weed management strategies in a long-term crop rotation system. Weed Science 2023, 41, e020220053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglin, W.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Kuivila, K.M.; Dietze, J.E. Glyphosate and its degradation product AMPA occur frequently and widely in US soils, surface water, groundwater, and precipitation. JAWRA 2014, 50, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, Y.; Bobadilla, L.K.; Giacomini, D.A.; Montgomery, J.S.; Murphy, B.P.; Tranel, P.J. Evolution of glyphosate-resistant weeds. Rev Environ Contam T 2021, 255, 93–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.P.K.; Sethi, N.; Mohan, A.; Datta, S.; Girdhar, M. Glyphosate toxicity for animals. Environ Chem Lett 2018, 16, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochron, S.; Choudhury, M.; Gomez, R.; Hussaini, S.; Illuzzi, K.; Mann, M.; Mezic, M.; Nikakis, J.; Tucker, C. Temperature and body mass drive earthworm (Eisenia fetida) sensitivity to a popular glyphosate-based herbicide. Appl Soil Ecol 2019, 139, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochron, S.; Simon, L.; Mirza, A.; Littleton, A.; Sahebzada, F.; Yudell, M. 2020. Glyphosate but not Roundup® harms earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochron, S.T.; Mirza, A.; Mezic, M.; Chung, E.; Ezedum, Z.; Geraci, G.; Mari, J.; Meiselbach, C.; Shamberger, O.; Smith, R.; Tucker, W.J. Earthworms Eisenia fetida recover from Roundup exposure. Appl Soil Ecol 2021, 158, 103793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanabar, M.; Bauer, S.; Ezedum, Z.M.; Dwyer, I.P.; Moore, W.S.; Rodriguez, G.; Mall, A.; Littleton, A.T.; Yudell, M.; Kanabar, J.; Tucker, W.J. Roundup negatively impacts the behavior and nerve function of the Madagascar hissing cockroach (Gromphadorhina portentosa). Environ Sci Pollut Res 2021, 28, 32933–32944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochron, S.T.; Mezic, M.; Byrne, S.; Sasoun, S.; Casamassima, A.; Kilic, M.; Nuzzo, A.; Beaudet, C.E. Exposure to Roundup increases movement speed and decreases body mass in earthworms. Front Environ Sci 2021, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.L.; von Mérey, G.; Minderhout, T.; Manson, P.; Sutton, P. Aminomethylphosphonic acid has low chronic toxicity to Daphnia magna and Pimephales promelas. Environ Toxicol Chem 2015, 34, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tresnakova, N.; Stara, A.; Velisek, J. Effects of glyphosate and its metabolite AMPA on aquatic organisms. Appl Sci-Basel 2021, 11, 9004–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medalie, L.; Baker, N.T.; Shoda, M.E.; Stone, W.W.; Meyer, M.T.; Stets, E.G.; Wilson, M. Influence of land use and region on glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in streams in the USA. Sci Tot Environ 2020, 707, 136008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretta, L.; Masin, R.; Zanin, G. Review of studies analysing glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) occurrence in groundwater. Environ Rev 2022, 30, 88–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesy, J.P.; Dobson, S.; Solomon, K.R. Ecotoxicological risk assessment for Roundup® herbicide; Springer: New York, USA, 2000; pp. 35–120. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, L.; Börjesson, E.; Stenström, J. Laboratory and lysimeter studies of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in a sand and a clay soil. J Environ Qual 2011, 40, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupe, R.H.; Kalkhoff, S.J.; Capel, P.D.; Gregoire, C. Fate and transport of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters of agricultural basins. Pest Manag Sci 2012, 68, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, R.; Barzaghi, B.; Lana, E.; Stocchino, G.A.; Manconi, R.; Lunghi, E. The stenoendemic cave-dwelling planarians (Platyhelminthes, Tricladida) of the Italian Alps and Apennines. J Nat Conserv 2018, 45, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynoldson, T.B.; Young, J. A key to the freshwater triclads of Britain and Ireland with notes on their ecology; FBA Scientific Publishing: Cumbria, England, 2000; pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, A.S.; Andrade, C.F.S. Differential predation of the planarian Dugesia tigrina on two mosquito species under laboratory conditions. J Am Mosquito Contr 2001, 17, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tranchida, M.C.; Pelizza, S.A.; Micieli, M.V.; Maciá, A. Consequences of the introduction of the planarian Girardia anceps (Tricladida: Dugesiidae) in artificial containers with larvae of the mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae) from Argentina. Biol Contr 2014, 71, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.C.; Pipan, T. Shallow Subterranean Habitats: Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, United Kingdom, 2014; pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Pestana, J.L.T.; Ofoegbu, P.U. Ecotoxicity Assays Using Freshwater Planarians. In C. M. M. Palmeira, D. P. DeOliveira, & D. J. Dorta (Eds.), TOXICITY ASSESSMENT: Methods and Protocols 2021, (Vol. 2240, pp. 125–137).
- Sheiman, I.M.; Kreshchenko, N.D. Regeneration of planarians: Experimental object. Russ J Dev Biol 2015, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangel, M.; Bonsall, M.B.; Aboobaker, A. Feedback control in planarian stem cell systems. BMC Syst Biol 2016, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, T. Effects of ethanol on negative phototaxis and motility in brown planarians (Dugesia tigrina). Neurosci Lett 2018, 685, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.P.; dos Santos, M.P.; de Freitas, P.L.; Schafaschek, A.M.; de Barros, E.N.; Kitamura, R.S.A.; Navarro-Silva, M.A. The aquatic macrophyte Salvinia molesta mitigates herbicides (glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid) effects to aquatic invertebrates. Environ Sci Pollut R 2023, 30, 12348–12361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito Rodrigues, L., Costa, G.G., Thá, E.L., da Silva, L.R., de Oliveira, R., Leme, D.M., Cestari, M.M., Grisolia, C.K., Valadares, M.C. and de Oliveira, G.A.R., 2019. Impact of the glyphosate-based commercial herbicide, its components and its metabolite AMPA on non-target aquatic organisms. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 842, pp.94-101. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Santos, J.; da Silva Pontes, M.; Grillo, R.; Fiorucci, A.R.; de Arruda, G.J.; Santiago, E.F. Physiological mechanisms and phytoremediation potential of the macrophyte Salvinia biloba towards a commercial formulation and an analytical standard of glyphosate. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struger, J.; Thompson, D.; Staznik, B.; Martin, P.; McDaniel, T.; Marvin, C. Occurrence of glyphosate in surface waters of southern Ontario. B Environ Contamin Tox 2008, 80, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Brown, G. G.; Sautter, K. D.; Ribas de Oliveira, C. M.; de Vasconcelos, E. C.; Niva, C. C.; Bedano, J.C. Toxicity of AMPA to the earthworm Eisenia andrei Bouché, 1972 in tropical artificial soil. Sci Rep-UK 2019, 6, 19731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawls, S.M.; Thomas, T.; Adeola, M.; Patil, T.; Raymondi, N.; Poles, A.; Raffa, R.B. Topiramate antagonizes NMDA- and AMPA-induced seizure-like activity in planarians. Pharmacol Biochem Be 2009, 93, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, R.B.; Finno, K.E.; Tallarida, C.S.; Rawls, S.M. Topiramate-antagonism of L-glutamate-induced paroxysms in planarians. Eur J Pharmacol 2010, 649, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotti, R., Fiori, J., Furlanetto, S., Orlandini, S., Candela, M. and Franzellitti, S., 2022. Assessment of bioaccumulation of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in marine mussels using capillary electrophoresis with light-emitting diode-induced fluorescence detection. Journal of Chromatography A, 1681, p.463452. [CrossRef]
- Yan, B., Sun, Y., Fu, K., Zhang, Y., Lei, L., Men, J., Guo, Y., Wu, S., Han, J. and Zhou, B., 2023. Effects of glyphosate exposure on gut–liver axis: Metabolomic and mechanistic analysis in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Science of The Total Environment, 902, p.166062. [CrossRef]
- Druart, C., Millet, M., Scheifler, R., Delhomme, O., Raeppel, C. and De Vaufleury, A., 2011. Snails as indicators of pesticide drift, deposit, transfer and effects in the vineyard. Science of the total environment, 409(20), pp.4280-4288. [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, C., Bertrand, C., Bretagnolle, V., Coeurdassier, M., Delhomme, O., Deschamps, M., Gaba, S., Millet, M., Nélieu, S. and Fritsch, C., 2022. Glyphosate, AMPA and glufosinate in soils and earthworms in a French arable landscape. Chemosphere, 301, p.134672. [CrossRef]
- Witchley, J.N.; Mayer, M.; Wagner, D.E.; Owen, J.H.; Reddien, P.W. Muscle cells provide instructions for planarian regeneration. Cell Rep 2013, 4, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddien, P.W. The cellular and molecular basis for planarian regeneration. Cell 2018, 175, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, C.P.; Reddien, P.W. A wound-induced Wnt expression program controls planarian regeneration polarity. PNAS 2009, 106, 17061–17066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurley, K.A.; Elliott, S.A.; Simakov, O.; Schmidt, H.A.; Holstein, T.W.; Alvarado, A.S. Expression of secreted Wnt pathway components reveals unexpected complexity of the planarian amputation response. Dev Biol 2010, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheong, S.M.; Amado, N.G.; Reis, A.H.; MacDonald, B.T.; Zebisch, M.; Jones, E.Y.; Abreu, J.G.; He, X. Notum is required for neural and head induction via Wnt deacylation, oxidation, and inactivation. Dev Cell 2015, 32, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).