Submitted:
19 November 2023
Posted:
21 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
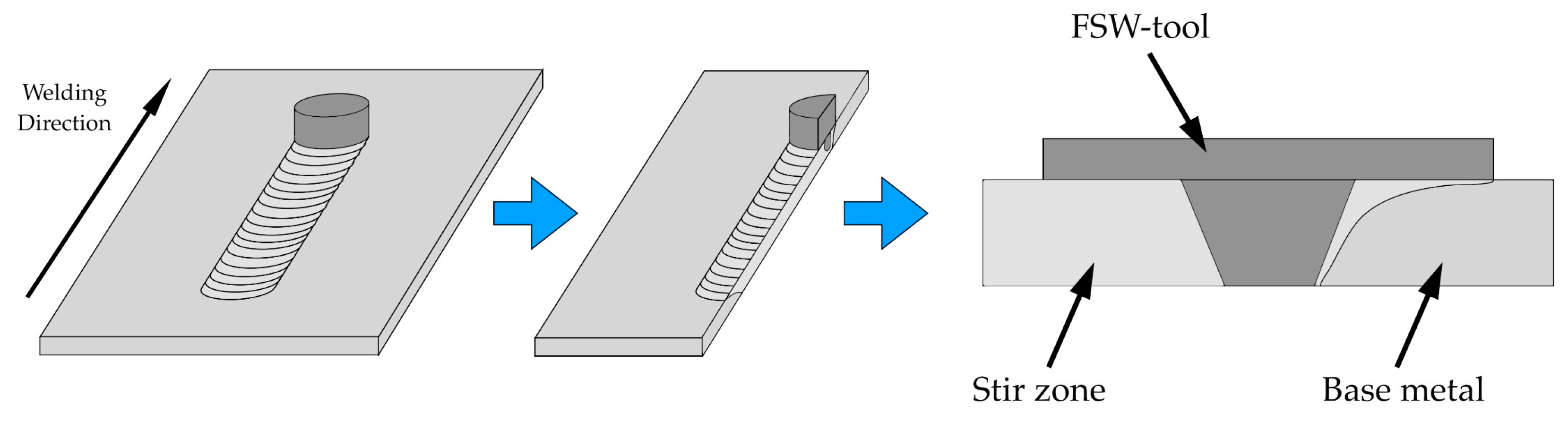
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
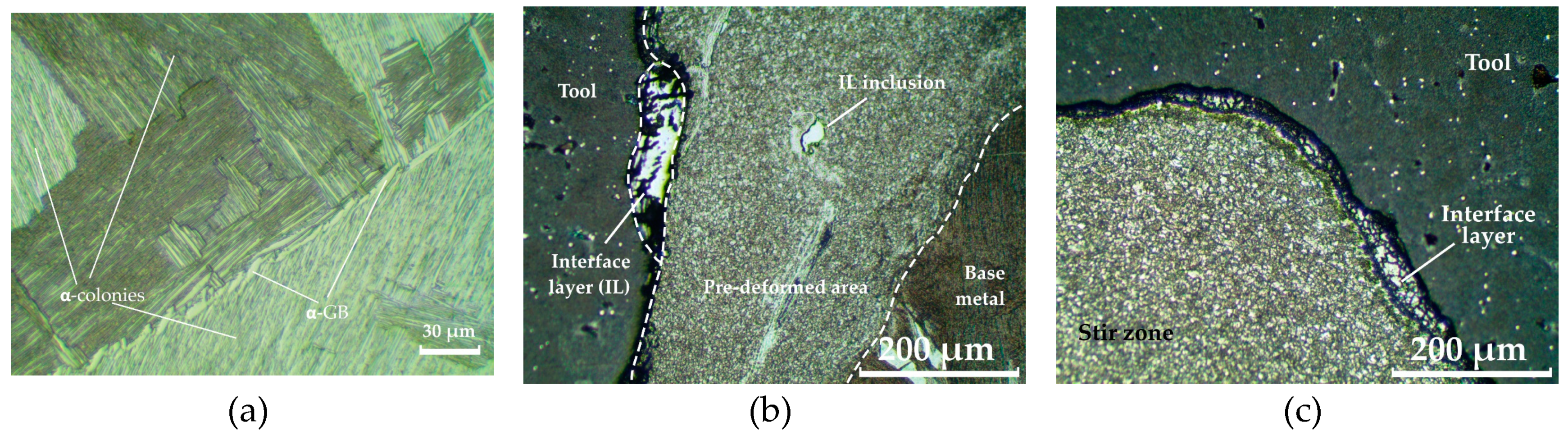
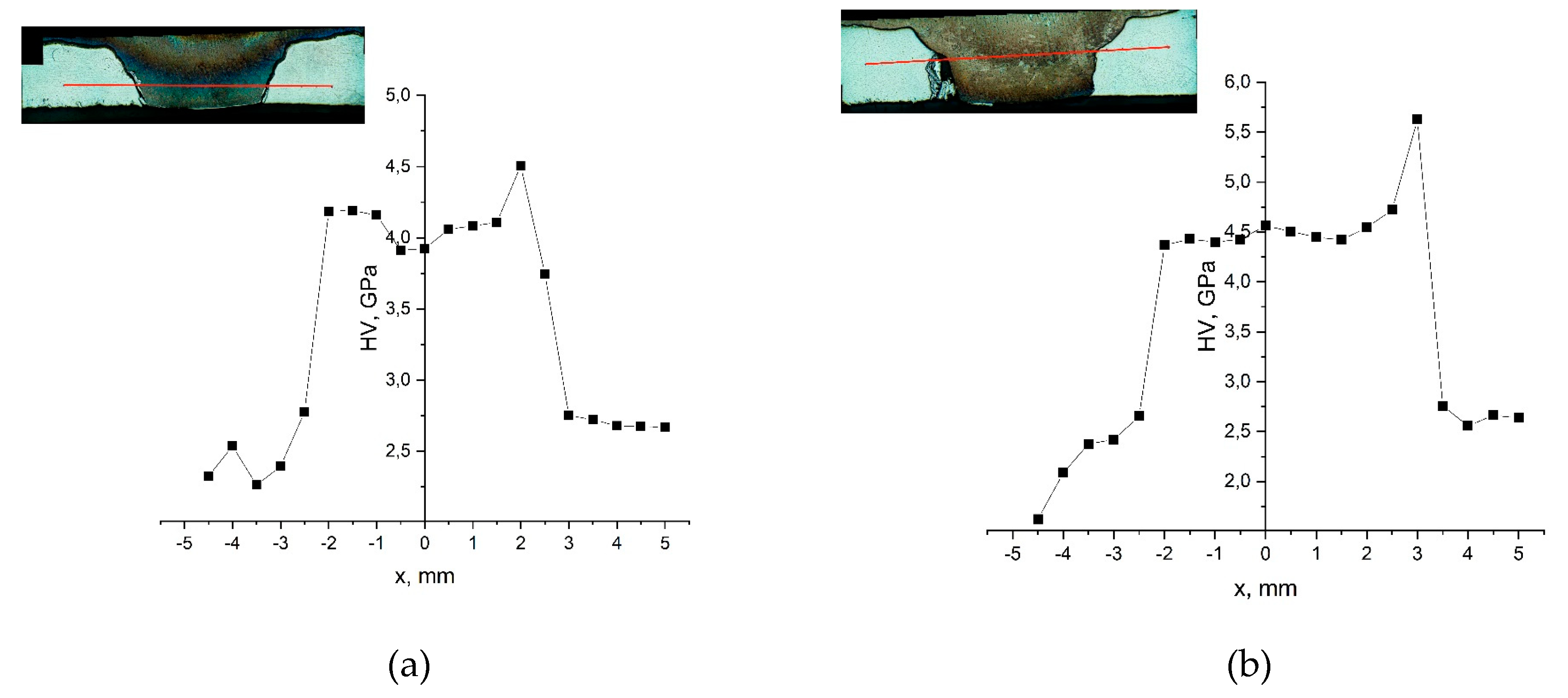
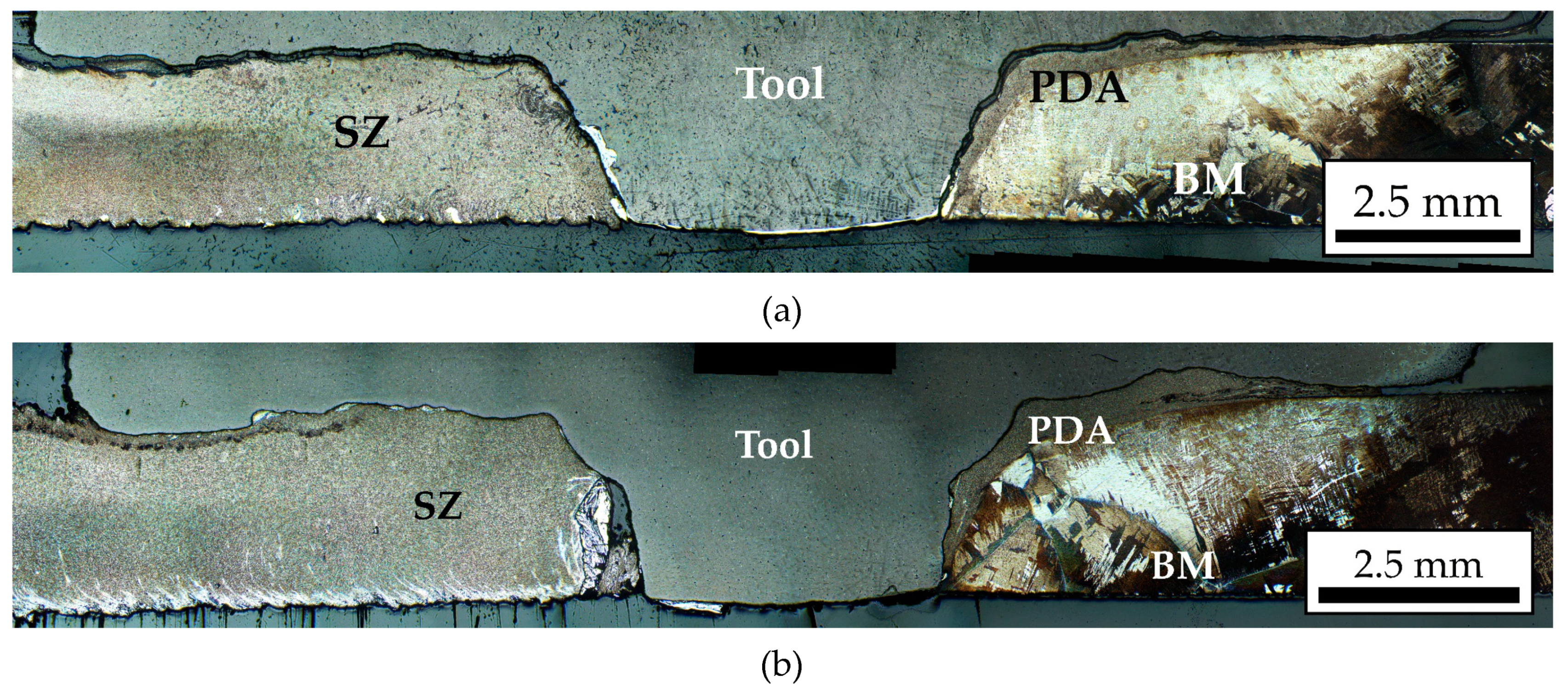
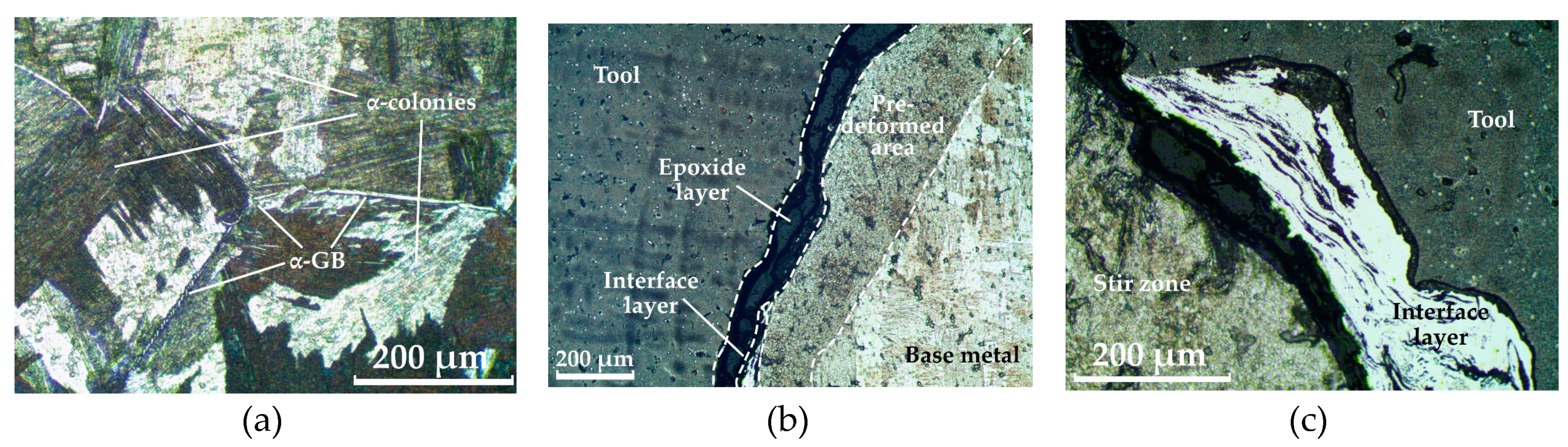
- During friction stir processing of additive Ti64 titanium alloy, a wide zone of pre-deformed material is formed in the zone in front of the tool, which is characterized by finer grains than in the stir zone. When the material is transferred behind the tool, the grain size increases due to recrystallization.
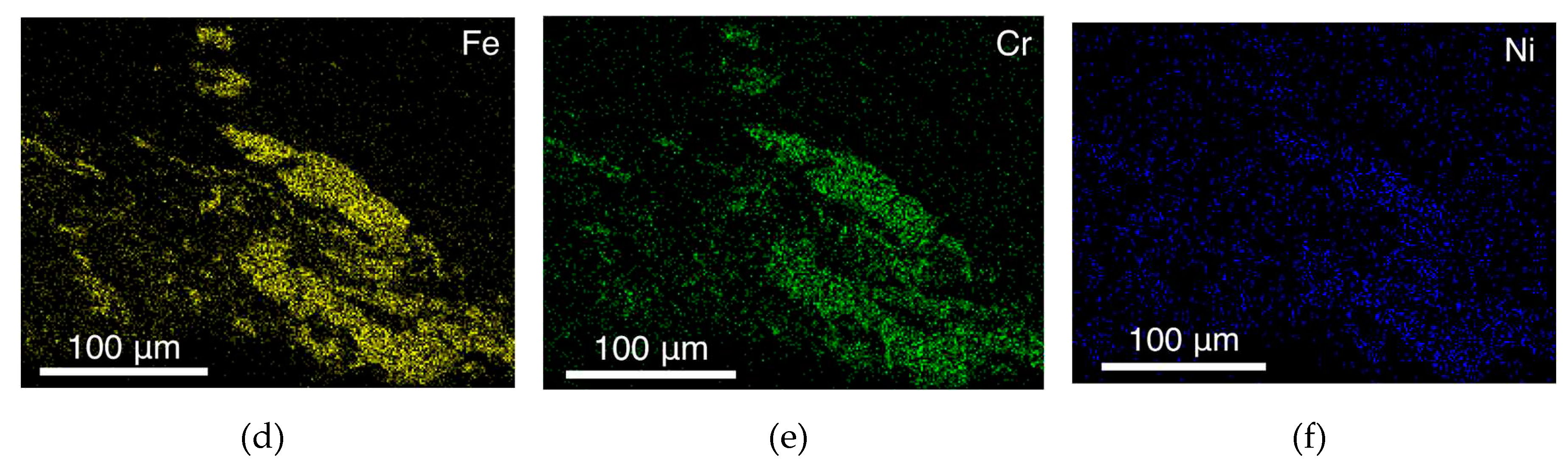
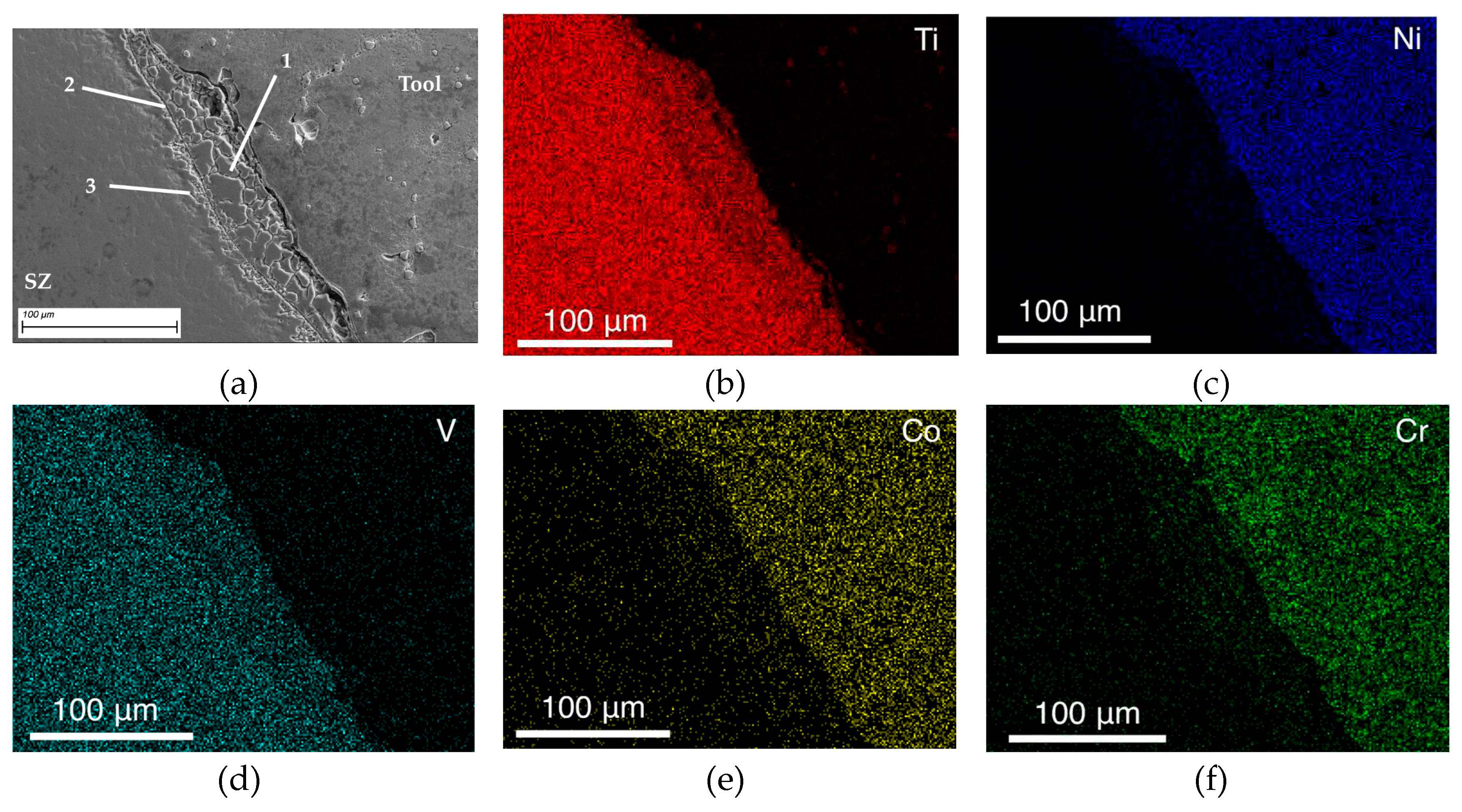
- An interface layer is formed between the tool and the workpiece, which is a layer of primary fragmented material characterized by diffusion of chemical elements of the tool material into the body of the workpiece.
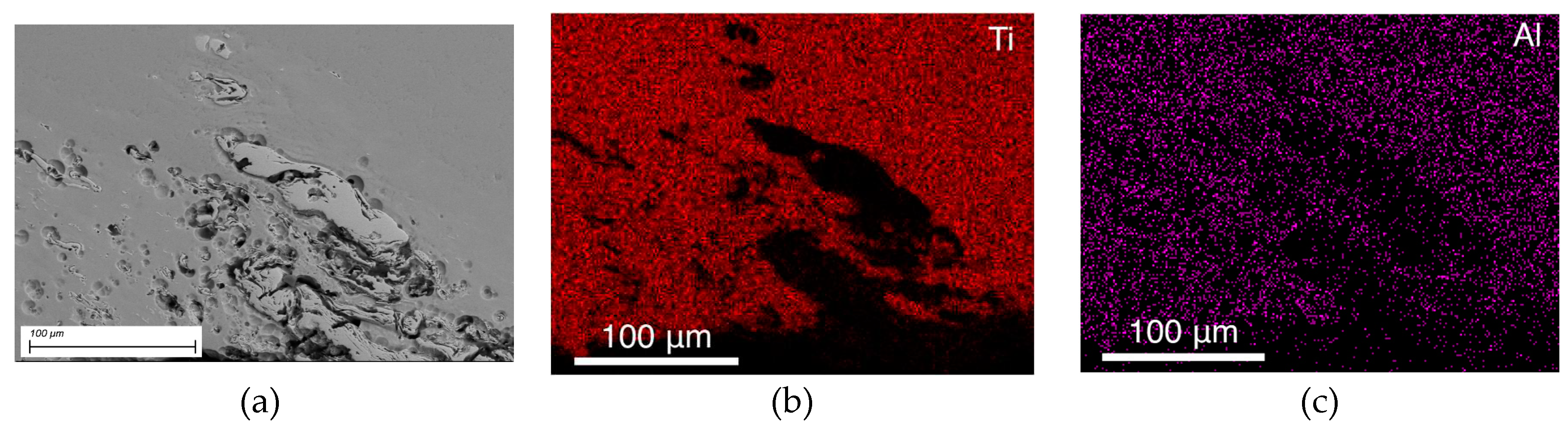
- When the tool contacts the substrate, the substrate material is transferred from the bottom to the top and mixed into the stir zone of the titanium alloy. This material forms a layer between the tool and the workpiece and increases tool wear.
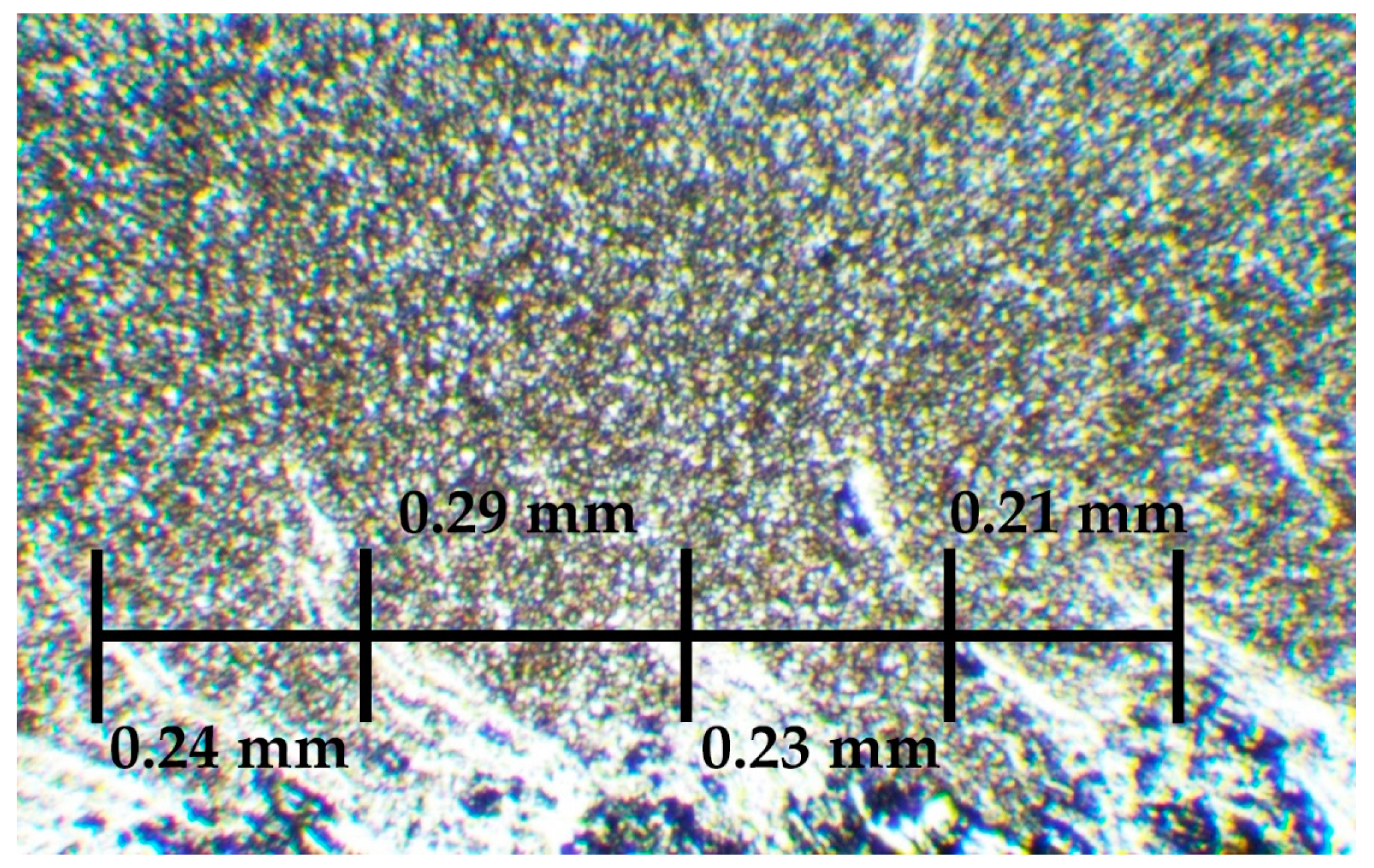
- The frequency of material transfer during friction stir processing of titanium alloy is determined by the ratio of the tool feeding speed to its rotation rate, similar to aluminum alloys.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kallee, S.W. 5—Industrial Applications of Friction Stir Welding. In Friction Stir Welding; Lohwasser, D., Chen, Z., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Welding and Other Joining Technologies; Woodhead Publishing, 2010; pp. 118–163 ISBN 978-1-84569-450-0.
- Longhurst, W.R.; Cox, C.D.; Gibson, B.T.; Cook, G.E.; Strauss, A.M.; Wilbur, I.C.; Osborne, B.E. Development of Friction Stir Welding Technologies for In-Space Manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, D.; Widener, C.; Tweedy, B. Advances in Friction Stir Welding for Aerospace Applications. In Proceedings of the 6th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration and Operations Conference (ATIO); American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, Virigina, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.X.; Liu, Q.W. Study of the Key Issues of Friction Stir Welding of Titanium Alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 638–642, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Pramanik, A.; Basak, A.K.; Dong, Y.; Prakash, C.; Debnath, S.; Shankar, S.; Jawahir, I.S.; Dixit, S.; Buddhi, D. A Critical Review on Additive Manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 4641–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabe, N.; Gnäupel-Herold, T.; Quinn, T. Fatigue Properties of a Titanium Alloy (Ti–6Al–4V) Fabricated via Electron Beam Melting (EBM): Effects of Internal Defects and Residual Stress. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 94, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, B.E.; Palmer, T.A.; Beese, A.M. Anisotropic Tensile Behavior of Ti–6Al–4V Components Fabricated with Directed Energy Deposition Additive Manufacturing. Acta Mater. 2015, 87, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Castaño, S.; Emile, P.; Archambeau, C.; Pettinari-Sturmel, F.; Douin, J. Main Microstructural Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Components Produced via Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing (EBAM) BT—TMS 2021 150th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 176–188. [Google Scholar]
- Manjunath, A.; Anandakrishnan, V.; Ramachandra, S.; Parthiban, K.; Sathish, S. Investigations on the Effect of Build Orientation on the Properties of Wire Electron Beam Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, K.N.; Chumaevskii, A. V; Kalashnikova, T.A.; Osipovich, K.S.; Kolubaev, E.A. Defect Formation in Titanium Alloy during Non-Stationary Process of Local Metallurgy. Russ. Phys. J. 2020, 63, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, K.N.; Chumaevskii, A.V.; Kalashnikova, T.A.; Kolubaev, E.A. A Substrate Material and Thickness Influence on the 3D-Printing of Ti–6Al–4V Components via Wire-Feed Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefer, K.; Nitsche, A.; Haelsig, A.; Mayr, P. Manufacturing of Titanium Components with 3DPMD. Metals (Basel). 2019, 9, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baufeld, B.; Brandl, E.; van der Biest, O. Wire Based Additive Layer Manufacturing: Comparison of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti–6Al–4V Components Fabricated by Laser-Beam Deposition and Shaped Metal Deposition. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieazad, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Gerlich, A.; Nasiri, A. Enhancing the Corrosion Properties of Additively Manufactured AlSi10Mg Using Friction Stir Processing. Corros. Sci. 2021, 178, 109073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Peng, P.; Huang, L.; Qiao, K.; Jin, Y. Effect of Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlSi10Mg Aluminum Alloy Produced by Selective Laser Melting. JOM 2019, 71, 1737–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikova, T.; Cheremnov, A.; Eliseev, A.; Gurianov, D.; Knyazhev, E.; Moskvichev, E.; Beloborodov, V.; Chumaevskii, A.; Zykova, A.; Kalashnikov, K. Structural Changes in Block-Shaped WEBAM’ed Ti6Al4V Samples after Friction Stir Processing. Lubricants 2022, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, K.; Chumaevskii, A.; Kalashnikova, T.; Cheremnov, A.; Moskvichev, E.; Amirov, A.; Krasnoveikin, V.; Kolubaev, E. Friction Stir Processing of Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy: Structure Modification and Mechanical Properties. Metals (Basel). 2021, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinenko, A.; Dolzhenko, P.; Malopheyev, S.; Shishov, I.; Mishin, V.; Mironov, S.; Kaibyshev, R. Microstructural Evolution and Material Flow during Friction Stir Welding of 6013 Aluminum Alloy Studied by the Stop-Action Technique. Metals (Basel). 2023, 13, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, C.; Weinberger, T.; Schröttner, H.; Mitsche, S.; Enzinger, N. Investigation of Friction Stir Welding of Stainless Steel Using a Stop-Action-Technique. In Proceedings of the THERMEC 2011 Supplement; Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2012; Volume 409, pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Kalashnikova, T.; Chumaevskii, A.; Kalashnikov, K.; Fortuna, S.; Kolubaev, E.; Tarasov, S. Microstructural Analysis of Friction Stir Butt Welded Al-Mg-Sc-Zr Alloy Heavy Gauge Sheets. Metals (Basel). 2020, 10, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, S.Y.; Rubtsov, V.E.; Kolubaev, E.A. A Proposed Diffusion-Controlled Wear Mechanism of Alloy Steel Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Tools Used on an Aluminum Alloy. Wear 2014, 318, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, S.Y.; Filippov, A. V; Kolubaev, E.A.; Kalashnikova, T.A. Adhesion Transfer in Sliding a Steel Ball against an Aluminum Alloy. Tribol. Int. 2017, 115, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseev, A.A.; Kalashnikova, T.A.; Filippov, A. V; Kolubaev, E.A. Material Transfer by Friction Stir Processing. In Multiscale Biomechanics and Tribology of Inorganic and Organic Systems: In memory of Professor Sergey Psakhie; Ostermeyer, G.-P., Popov, V.L., Shilko, E. V, Vasiljeva, O.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 169–188. ISBN 978-3-030-60124-9. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




