1. Introduction
Geopolymer is one of the most viable candidates for a sustainable replacement of traditional Ordinary Portland Cement -OPC- (>50% less CO
2 than OPC by a produced tonne [
1]). Geopolymer is an inorganic polymer with excellent mechanical and physical properties. They are formed by the reaction of a low-calcium aluminosilicate precursor with a high amorphous content and an alkaline activator (mainly Na or K silicates) in a reaction called geopolymerization.
Geopolymers, besides being a cementitious material with great potential to replace OPC in the construction sector, could also be used in environmental applications. Some of the most innovative uses in this field include solar energy storage [
2,
3], radioactive waste management [
4,
5], and water or wastewater treatments. In this latter application, a larger number of investigations have been carried out, including the use of geopolymers as adsorbents [
6,
7], as membrane materials [
8], as photocatalysts [
9], as buffer materials [
10], or as functional materials [
11], among others. In most of these uses, the promising results are a consequence of the ion exchange capacity through the porous structure of the material. Ion exchange ability is due to the geopolymer structure consisting of a three-dimensional network called sialate and composed by tetrahedral AlO
4- and SiO
4 alternatively bonded by O atoms. The presence of cations such as Na
+ and K
+ balances the negative charge of the AlO
4- groups and can be completely hydrated and mobilized
[12]. This gives a lower bonding strength in comparison with zeolites and an ease to be ion exchanged when they are in contact with solutions of a desired cation. The geopolymer structure will not be modified when the exchangeable ion is replaced with another atom.
The possibility to change the stoichiometry and composition (Si/Al or Na/Al ratios, alkaline activator nature, among others…), even with the addition of functional fillers, makes these materials extremely versatile. Another industrially advantageous aspect is the possibility of modulating the geopolymer porosity and giving complex shapes, conferring new properties to the material.
The most common synthesis route to produce porous geopolymers is the incorporation of a foaming agent in the admixture (e.g., hydrogen peroxide, fine metal powders…) [
14,
15,
16,
17]. This process generates gas bubbles due to the reaction with the alkaline species which are trapped inside the binding matrix during setting, resulting in the production of air voids in the hardened body. In case of hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) the porosity generation is given by reactions a and b. H
2O
2 decomposes in the alkaline medium at a very slow rate to form water and oxygen gas and the oxygen gas enables the generation of voids while geopolymer is being cured.
- a)
H2O2 + OH- → HO2- + H2O
- b)
H2O2 + HO2- → O2 + OH- + H2O
Geopolymers can be modified to increase their porosity and thus their physical adsorption capacity, assimilating pollutants on their surface due to physical forces such as Van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interactions, polarity and space forces. In addition, increasing porosity and surface area also increases the active sites to promote ion exchange as well [
13].
On the other hand, ammonium (NH4+) is the most dominant form of nitrogen pollution in the aquatic environment. Elevated NH4+ concentrations in untreated waterways contribute to eutrophication and dissolved oxygen depletion, which cause severe degradation of water quality. Untreated wastewater containing high organic and nitrogen contents poses serious environmental problems if those pollutants are improperly managed. Anaerobic treatment technology is commonly adopted to treat piggery wastewater, especially in developing countries, with an emphasis on removing organic matter. However, NH4+ removal in anaerobic systems is limited.
The methods that are commonly used for NH
4+ removal include microbial nitrification-denitrification reactions, which is the most widely used, breakpoint chlorination, air extraction, reverse osmosis, and ionic exchange [
18,
19]. However, the nitrification rate drops sharply as the temperature of wastewater decreases in case of the nitrification-denitrification method [
18,
20] and adsorption and/or ion-exchange-based approaches offer a more robust alternative method for NH
4+ removal. Previous studies demonstrated by simulation that anaerobic digestion followed by zeolite-based ion exchange had lower operational costs and better nitrogen removal [
18,
21]. However, one of the main problems with zeolites is their synthesis, which requires high temperatures (50°C-150ºC). Therefore, geopolymers have emerged as a promising alternative with a zeolite-like structure formed by a network of aluminosilicates with a negative charge on the AlO
4-. The geopolymer, unlike zeolites, can be synthesized at room temperature, resulting in lower energy consumption. Additionally, these materials can be produced from industrial by-products (commonly fly ashes, steel slags, etc…) to reduce the consumption of non-renewable resources in line with the circular economy principle.
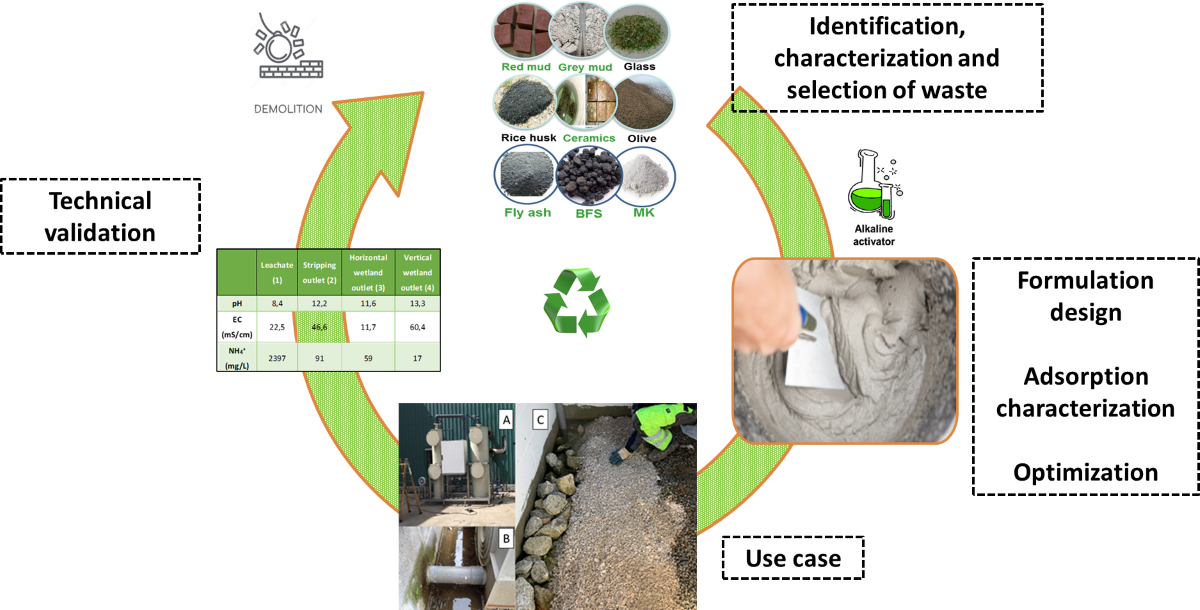
In the present study, a porous metakaolin-based geopolymer was synthetized and characterized at laboratory scale to evaluate the NH4+ removal capacity. Granite wastes were considered as an alternative raw material. The optimized geopolymer formulation was validated in a relevant environment, a real wastewater treatment pilot plant.
2. Materials and Methods
The geopolymers were manufactured using commercial metakaolin (MK) as main raw material, granite waste (GW) from the granite industry as filler and sodium silicate (Na
2SiO
3) as alkaline activator. The MK was provided by Arciresa S.A. (54% SiO2, 41.1% Al
2O3 and D
50=8µm). GW (66,73% SiO
2, 17,51 % Al
2O
3 and D
50=8µm) was supplied by Godoy Maceira S.L. The aim is to maximize the amount of filler in the final formulation in order to minimize the environmental impact and the cost of the material, contributing to the sustainability of the process. Commercial Na
2SiO
3 solution from Quimipur, containing 25,6% SiO
2, 7,9% Na
2O, and 66,5% H
2O, and sodium hydroxide pellets (NaOH) from Scharlau, were used as alkaline activators with different silicate modulus (SiO
2/Na
2O, Ms). H
2O
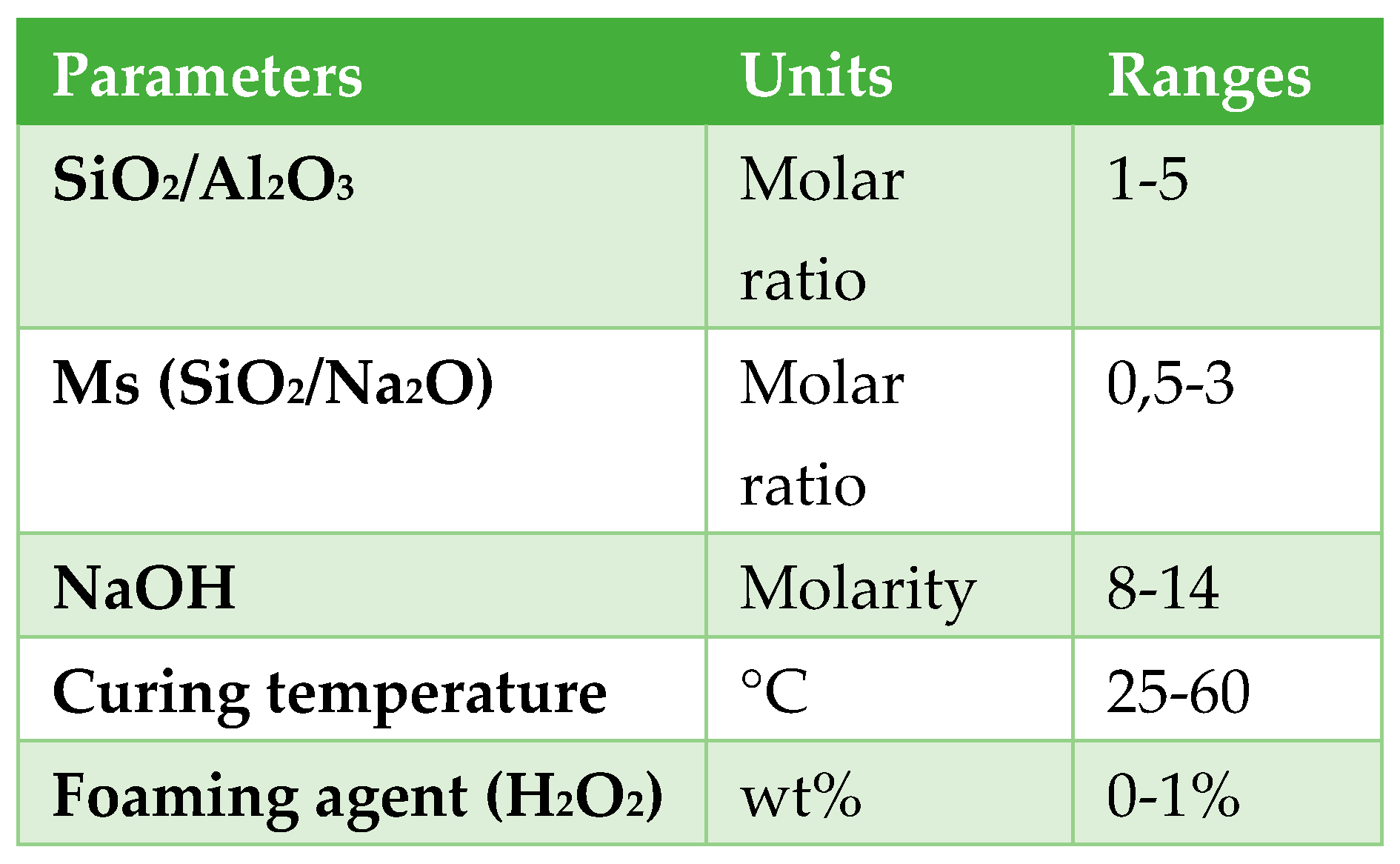
2 was added as a foaming agent. The parameters studied in the preliminary formulation design are summarized in
Table 1.
The different activating solutions were prepared 24 hours before the geopolymer mixing. The mixing process was carried out in a concrete laboratory mixer, adding firstly the solid components, metakaolin and granite powder, to achieve an intimate mixture for 5 minutes mixing. The alkaline activator was then added and stirred for 15 minutes to promote the complete dissolution of species. Finally, the corresponding amount of H2O2 was added to generate the porosity of the material. The admixtures were molded to obtained samples with OPC standard dimensions (4x4x16 cm3) for testing (UNE-196-1). The specimens were covered with plastic to avoid abrupt water losses and demolded after 24 h. Subsequently, the specimens were cured in a humidity chamber (room temperature, 99% humidity) for 28 days.
The selection of the optimal geopolymer formulation was based on the analysis of the results obtained from tests of microstructure (DRX, SEM), mechanical strength (flexural and compression tests), physical properties (e.g. bulk and true density, and total porosity) and chemical integrity in water.
The selected formulation was crushed in a jaw crusher and sieved to obtain particle sizes ranging from 4 to 12 mm to be used in batch and continuous tests with the aim to assess the optimal adsorption conditions. On one hand, batch experiments were carried out in 250 mL erlenmeyer flasks using deionized water with the following fixed conditions: contact time of 24 h, pH = 6, [NH4+] = 50 mg/L and 5 g/L of geopolymer gravel. The effect of the variables in the adsorption process was measured, including the initial water pH, adsorbent dose, contact time and initial adsorbate concentration. The experimental data were fitted to different isotherm models and kinetic equations. On the other hand, column tests were carried out under a continuous flow of 6mL/min, [NH4+] = 250 mg/L and 160 h long to determine the NH4+ adsorption capacity on the produced material.
As a final validation, the selected formulation and conditions obtained from the laboratory measurements were scaled-up following the same manufacturing procedures and applied in a pilot plant for wastewater treatment located at Xiloga Landfill site (As Somozas, Galicia, Spain). The plant consists of 4 key locations, including 2 wetlands where the geopolymers were disposed. The high amount of NH4+ contained in the initial leachates made it necessary the use of a stripping column to eliminate an initial fraction of this NH4+ and avoid the degradation of the wetland’s plants. Then, 125L of the selected geopolymer formulation were disposed in two wetlands (horizontal and vertical) specifically designed for the wastewater pilot plant. Data of NH4+ concentration variation, pH and conductivity were collected from this demo-site.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization and selection of geopolymer adsorbent formulation
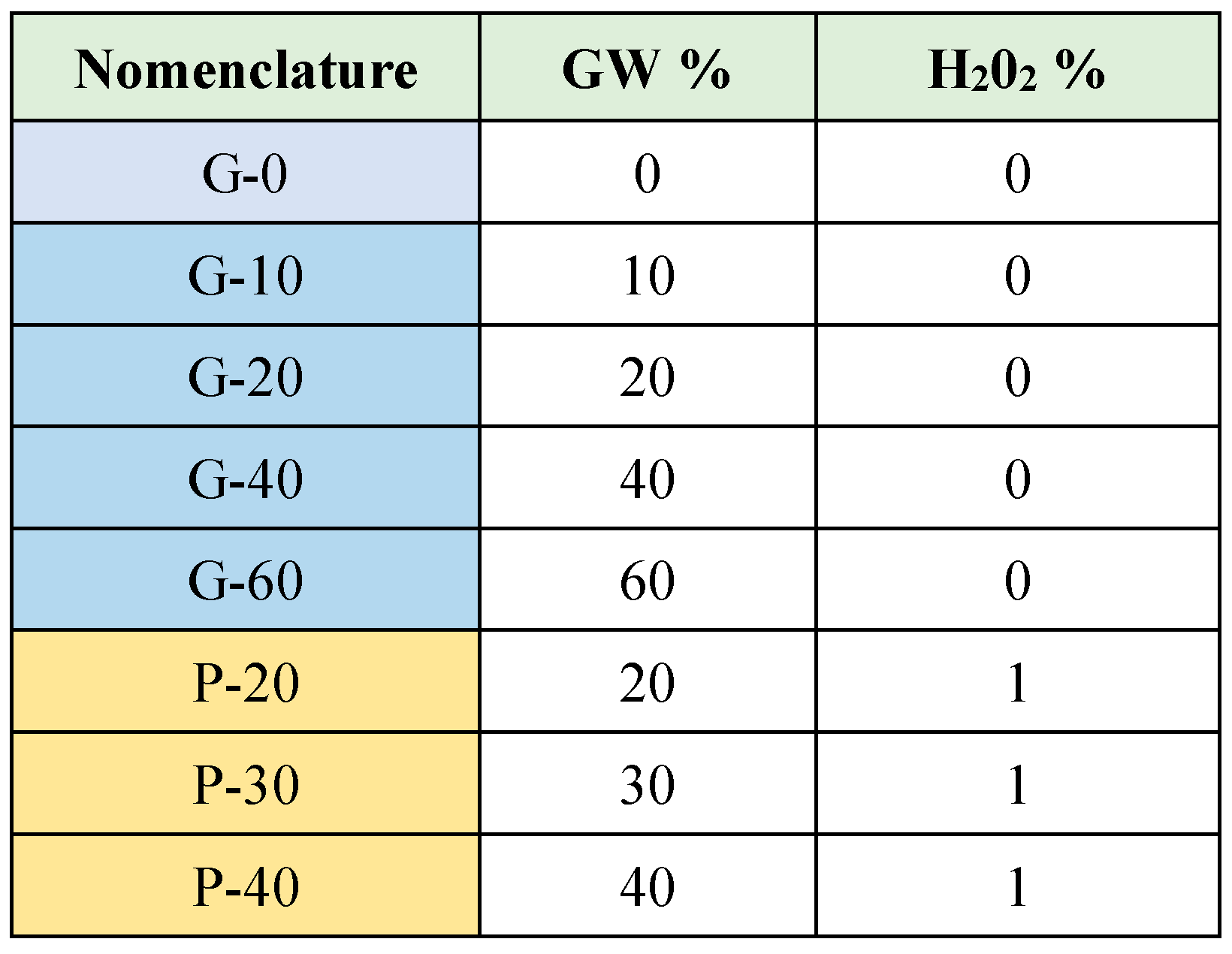
The different formulations evaluated in this studied are summarized in
Table 2. Some of the parameters were fixed after preliminary tests (not shown in this paper) as SiO
2/Al
2O
3=3, Ms=1.5 and curing process at room temperature.
With these optimized parameters, the formulations obtained are named G (without H
2O
2 addition) and P (with 1% H
2O
2 addition). Partial substitution of MK by GW is considered in certain formulations as shown in
Table 2.
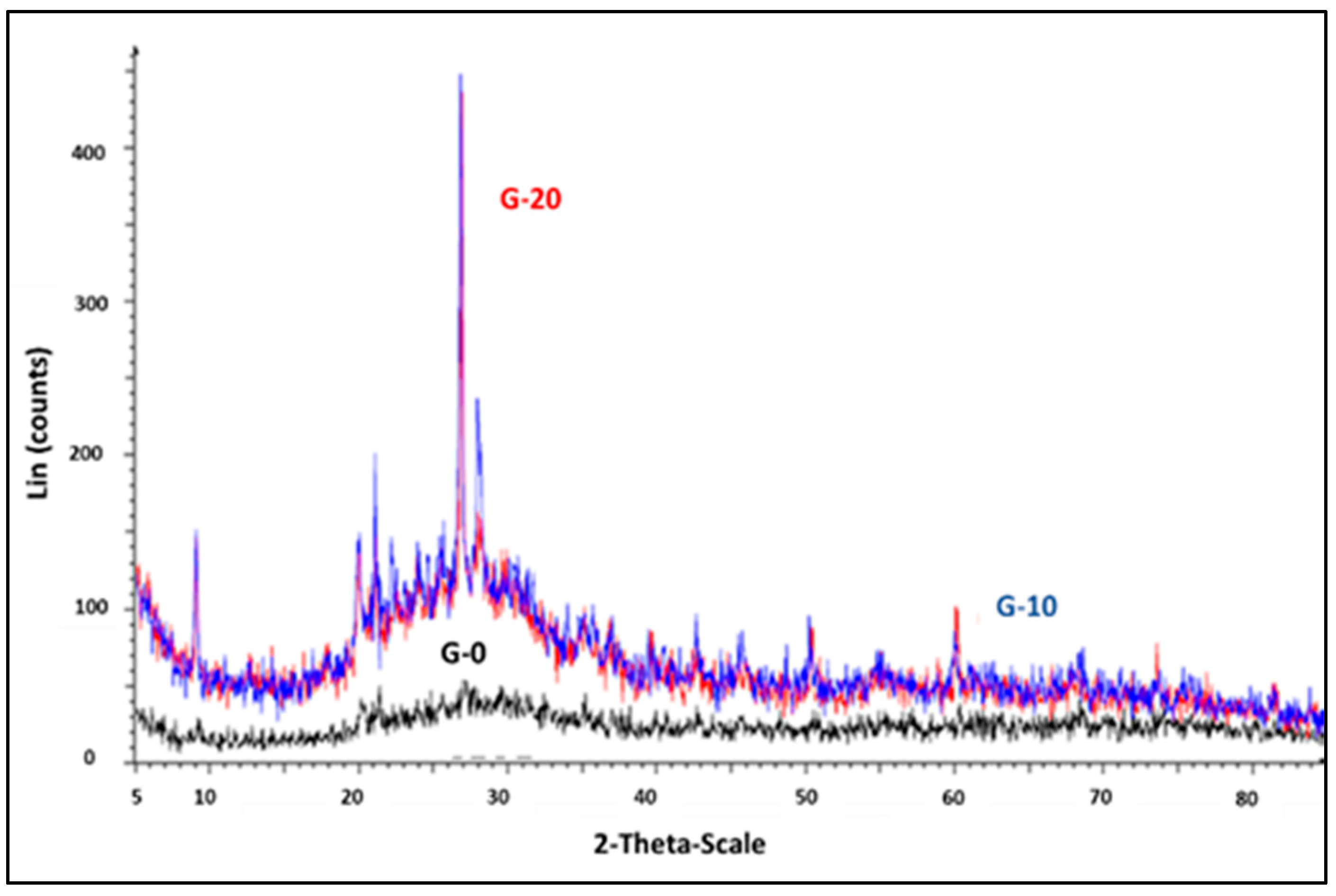
X-ray analyses were carried out in the samples as an indicator of the geopolymer gel formation. X-ray diffraction patterns of G-0, G-10 and G-20 are depicted in
Figure 1. The microstructure of the MK-based geopolymer is mainly amorphous, presenting typical amorphous humps located between 20º-30º 2Ɵ which corresponds to the aluminosilicate gel that forms the fundamental binding phase of the geopolymer matrix, responsible of the mechanical strength. Likewise, a crystalline peak is clearly observed when GW is introduced in the mixture at a 26º 2Ɵ. This sharp peak is the main signal of quartz which increases with the addition of GW suggesting the presence of crystalline SiO
2 and, affecting the geopolymer gel microstructure and, in consequence, the mechanical strength as will be seen in the following sections.
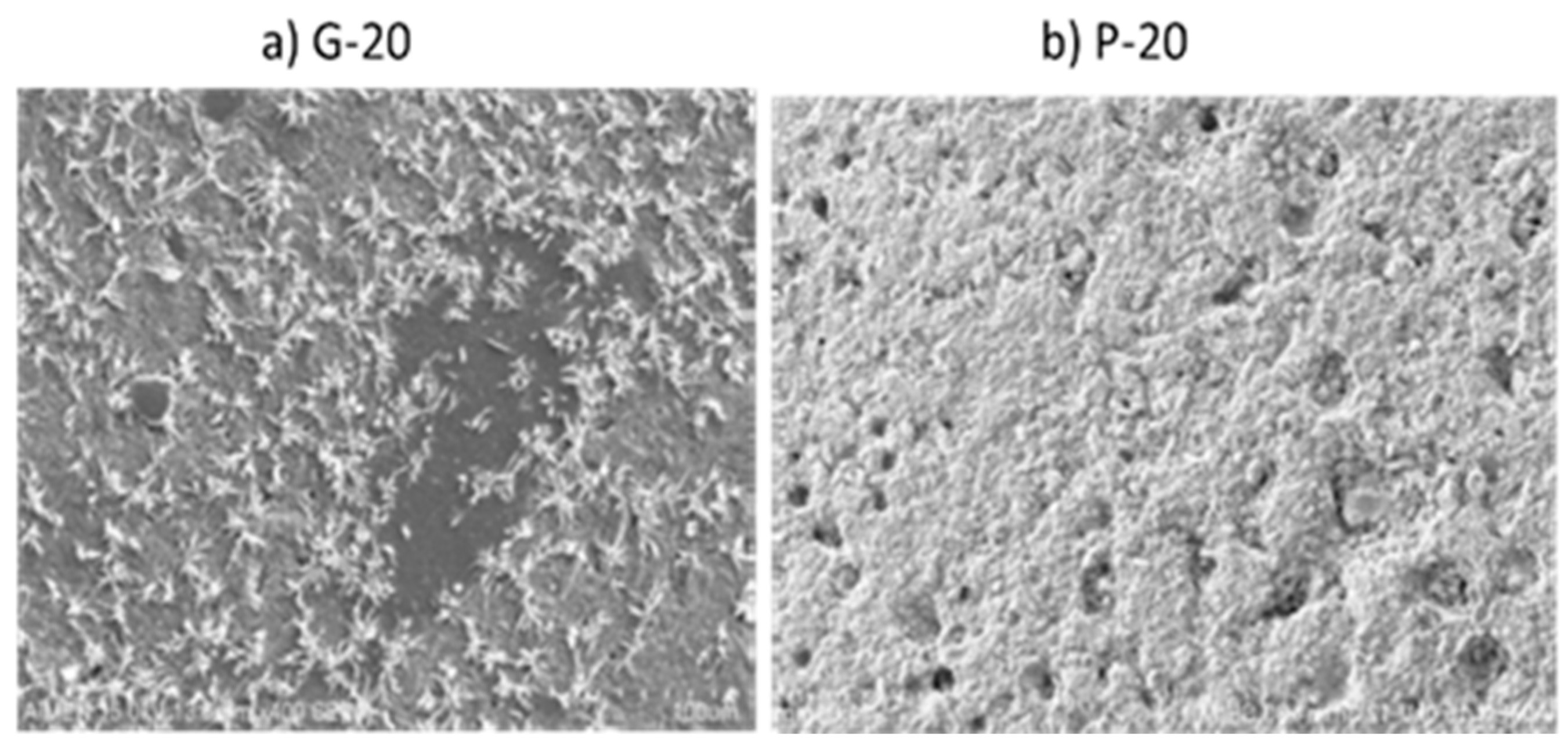
Figure 2 shows the SEM images for G-20 and P-20. Lamellar particles in gel phase corresponding to unreacted metakaolin are observed in sample G-20. As expected, a higher fraction of pores is confirmed in the images of P-20.
The porous structure of the geopolymer induced by H2O2 is very heterogeneous, with a broad pore size distribution from the micron range up to 2 mm diameter.
Mechanical strength was determined on normalized samples following the standard UNE-196-1 for OPC.
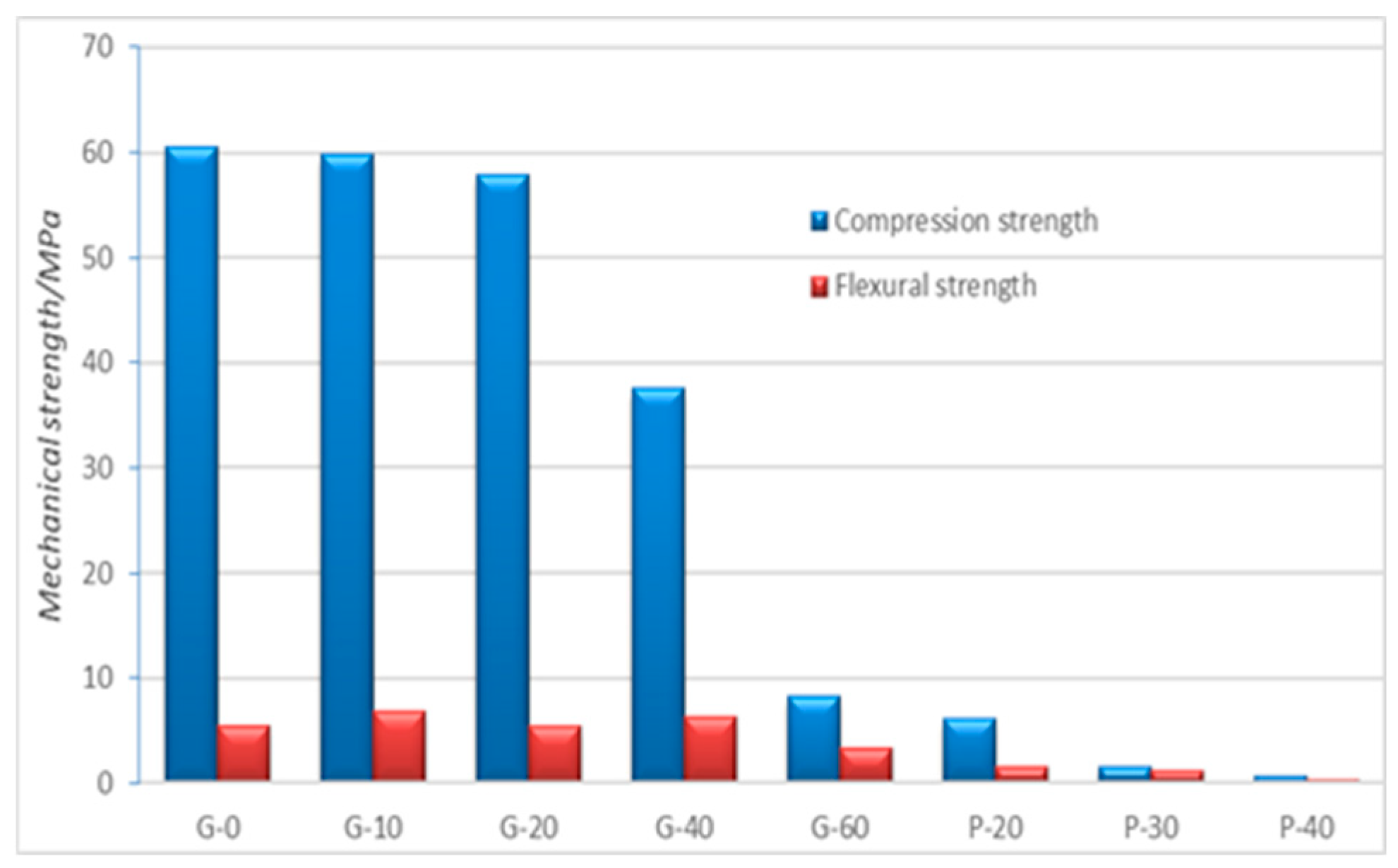
Figure 3 shows the compression and flexural strengths obtained for the different geopolymers after 28 days-age. The results suggested that GW additions do not affect the mechanical strength up to 20%, decreasing significantly at 40% and 60% of MK substitution due to the reduction of the amorphous gel fraction. Particularly noteworthy is the value reached with 20% of GW (58MPa) for the compression strength.
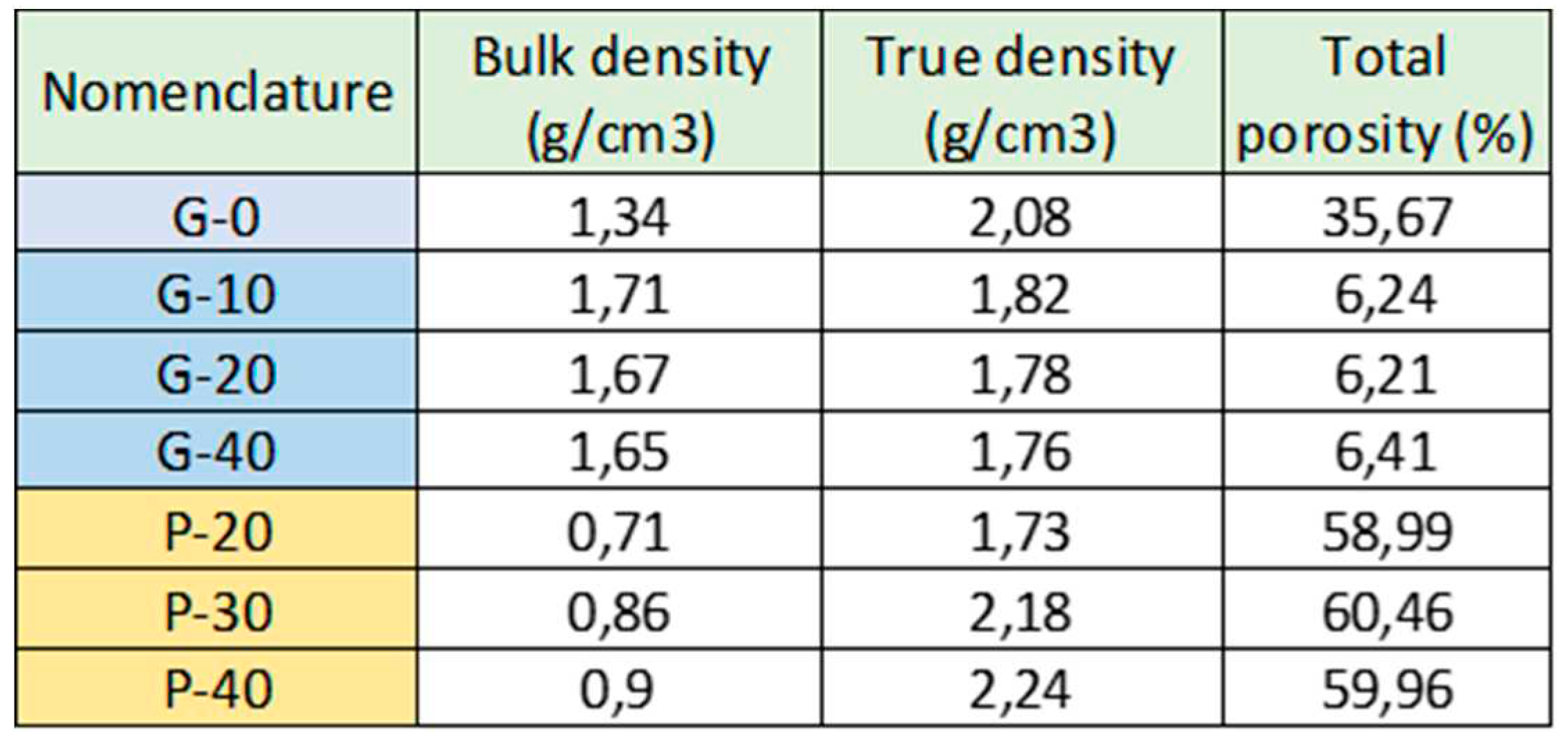
These mechanical results are closely linked to the density and porosity of the developed materials, shown in
Table 3. As expected, the foaming agent addition promotes a dramatic drop of the mechanical values. For the particular case of 20% of GW, the compressive strength decreases down to 6.7MPa (P-20), a 93% lower than the non-porous G-20 (with 0% H
2O
2).
The results showed the differences between pure geopolymers (G-0), hybrid GW-geopolymers (G-10, G-20 and G-30) and the porous ones (P-20, P30 and P-40).
The lowest value of bulk density, which considers both the solids and the pores spaces, is obtained for G-0, and grows with GW additions. This means than with GW substitutions, the filler occupies the empty voids, increasing the density values. On the contrary, the true density value for G-0 is the highest, since neither open nor closed pores are considered for this measurement. As expected, the results indicate that the intrinsic porosity of the MK-based geopolymers decreases by the addition of GW.
In contrast, with the 1% introduction H2O2, the porosity % is increased by a factor of 10 and the bulk density decreased due to the air voids formation obtaining a lighter material.
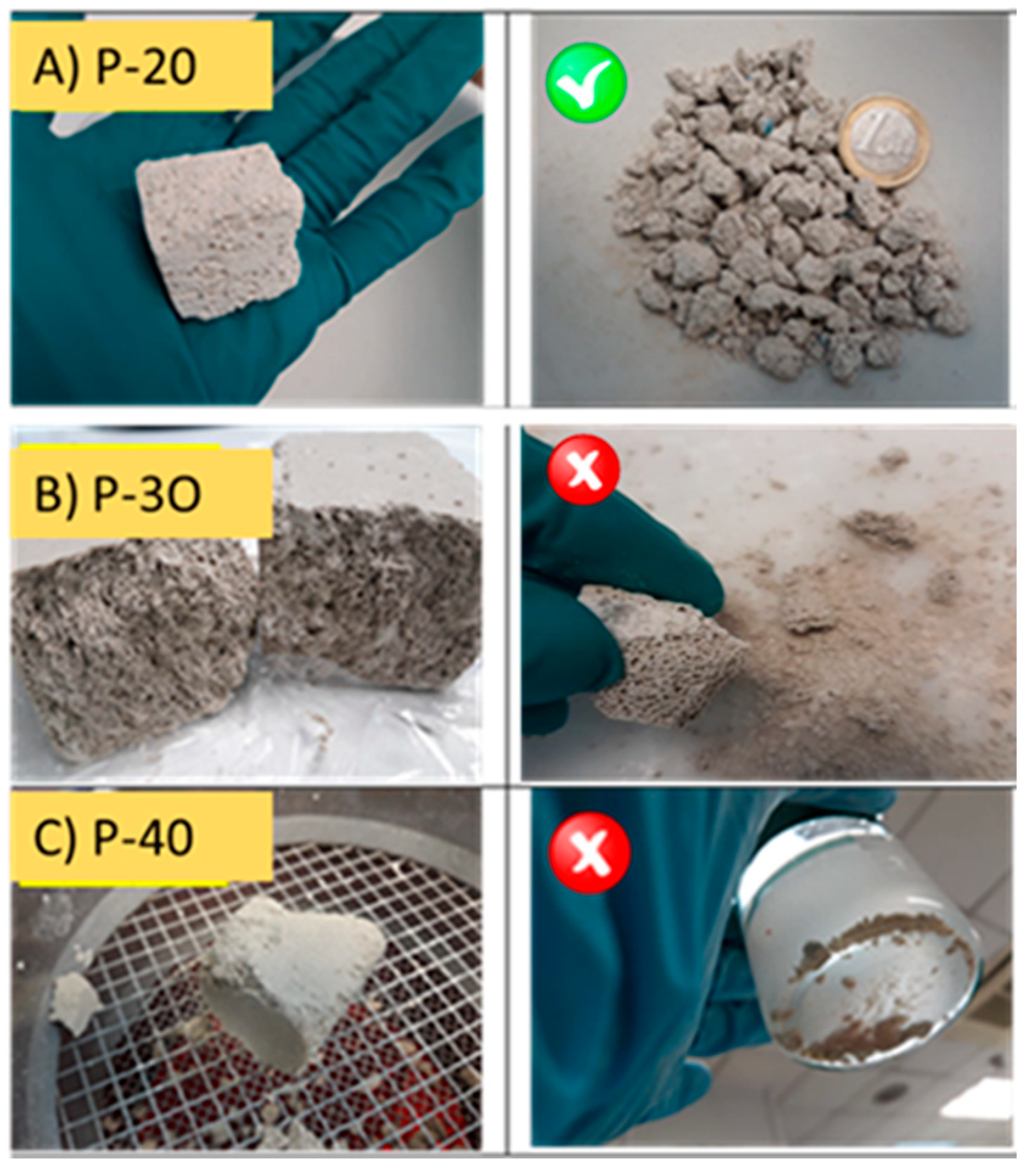
Additionally, porous geopolymers with different GW substitution were immersed in water for 24 h to validate the chemical integrity of the formed gel matrix. The appearances of the resulting materials are shown in
Figure 4. It was confirmed that GW substitutions up to 20% showed good integrity, obtaining 4-12 mm gravel after crushing without generating much dust during processing. Nevertheless, geopolymers with GW substitutions above this percentage (>20%) were turned into dust after manipulation, suggesting a non- acceptable geopolymer gel reaction, probably due to high crystalline fraction of the raw material (GW) and thus, they were discarded for the adsorption studies.
3.2. Characterization and selection of geopolymer adsorbent formulation.
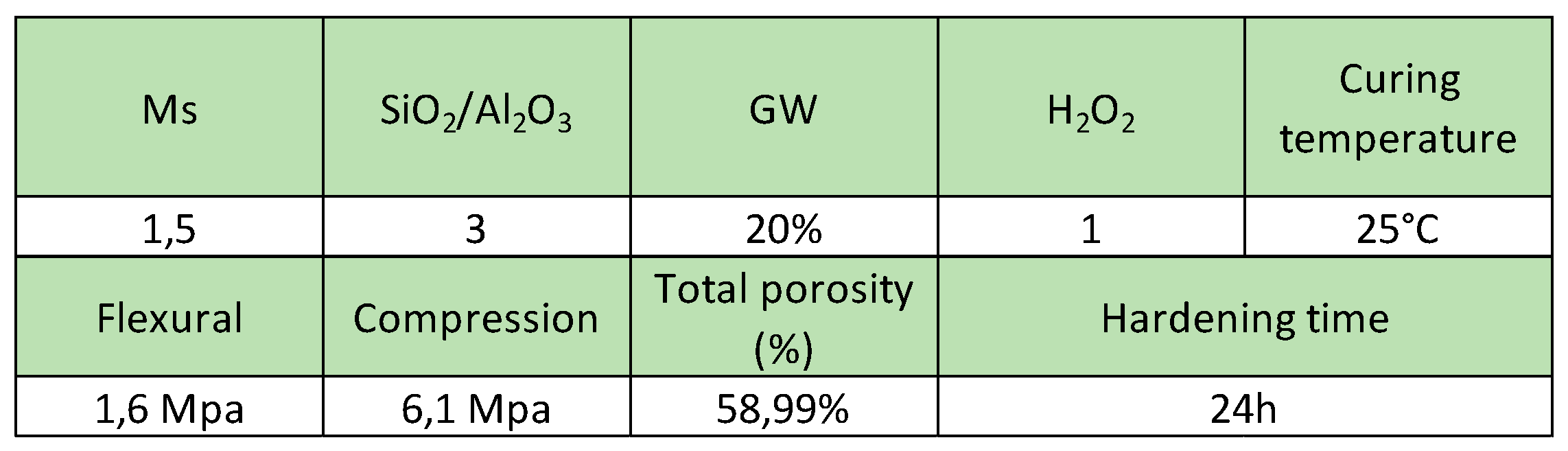
Considering the previous results, geopolymer P-20 was selected as the most promising formulation for the application as adsorbent material. The synthesis parameters and their properties are detailed in
Table 4. P-20 samples were crushed and sieved to obtain particle sizes of 4 - 12 mm to carry out adsorption tests.
3.2.1. Lab-scale ammonium removal experiments
The effect of different conditions on ammonium adsorption was studied through discontinuous or batch tests.
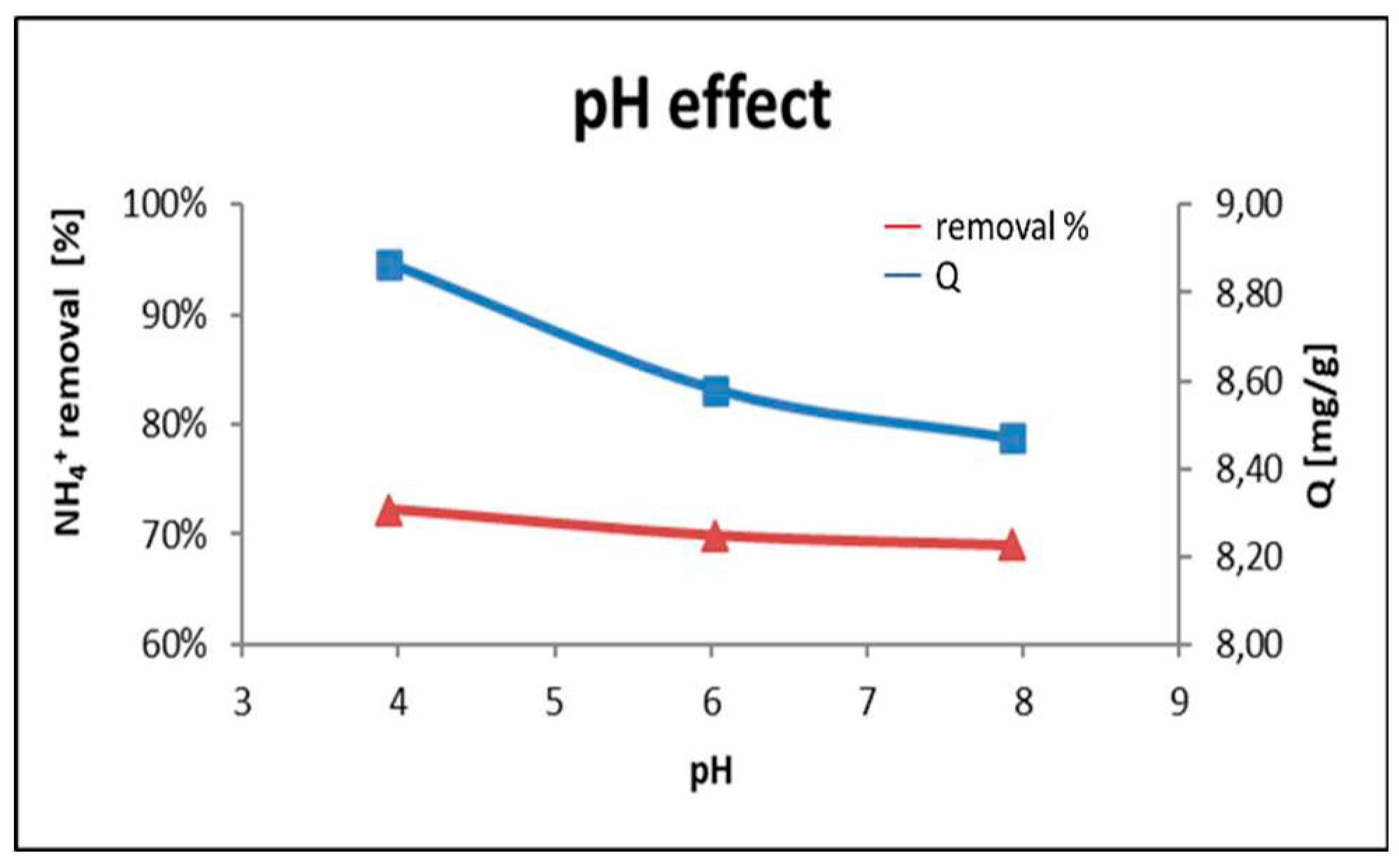
Figure 5 shows the pH effect on the adsorption capacity of P-20 geopolymer. There are no significant differences between the range of study (pH4 to pH8), however the more acid media suggest a slight improvement in the adsorption capacity (Q) and NH
4+ removal. This could be due to the equilibrium ammonium-ammonia which is affected by the pH18. An increase in pH causes a displacement of the equilibrium favoring ammonium production and therefore more adsorbate available for the adsorption process.
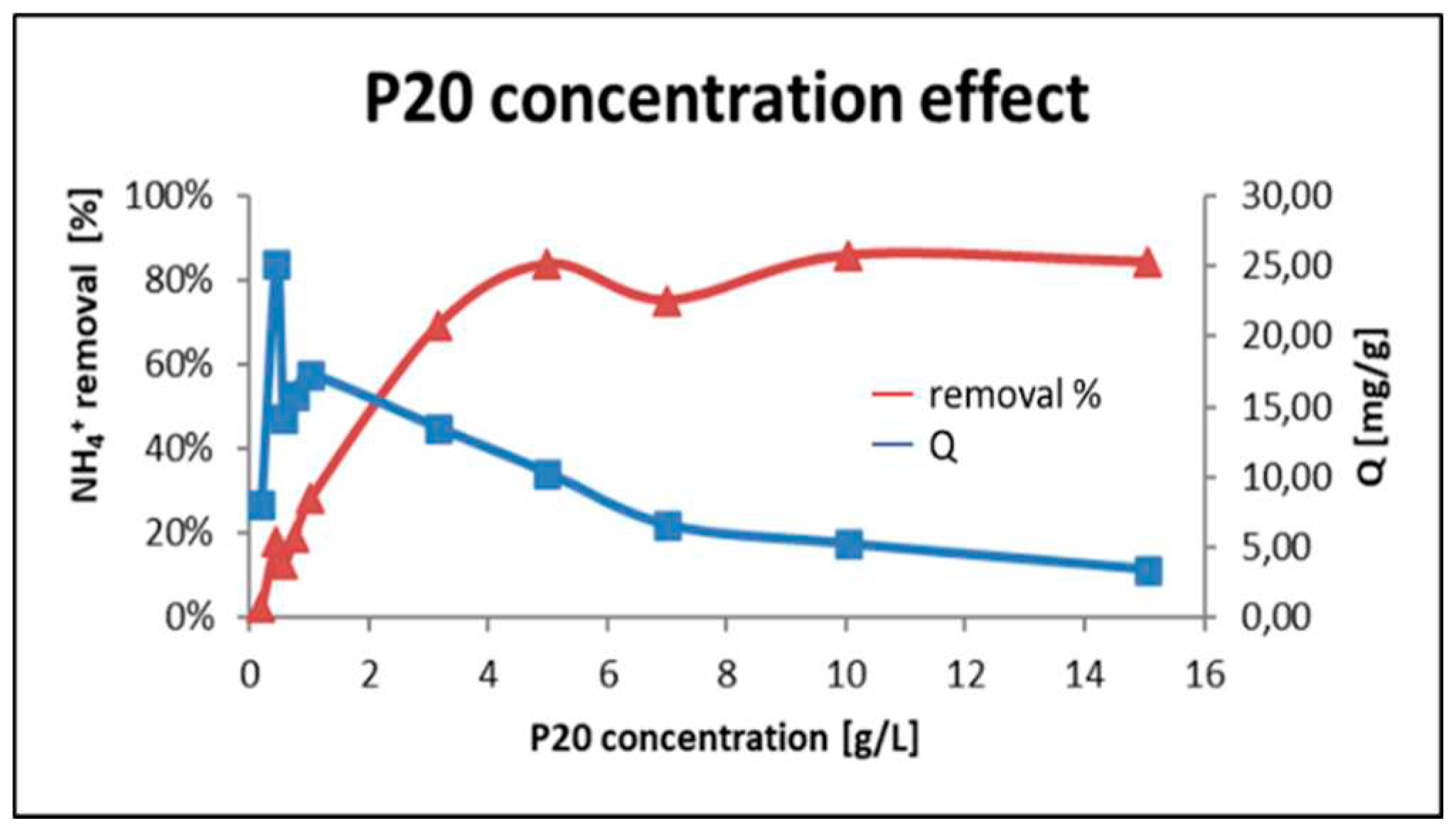
The optimal adsorbent dose (g P-20/ L) was also evaluated.
Figure 6 shows that the increase of the adsorbent dose up to 5g/L promotes an increment of the NH
4+ removal up to 80%. From this point, at higher geopolymer dose, the removal levels keep similar. Q reaches a maximum of 25,17 mg/g at 0.44 g/L and then tends to decrease.
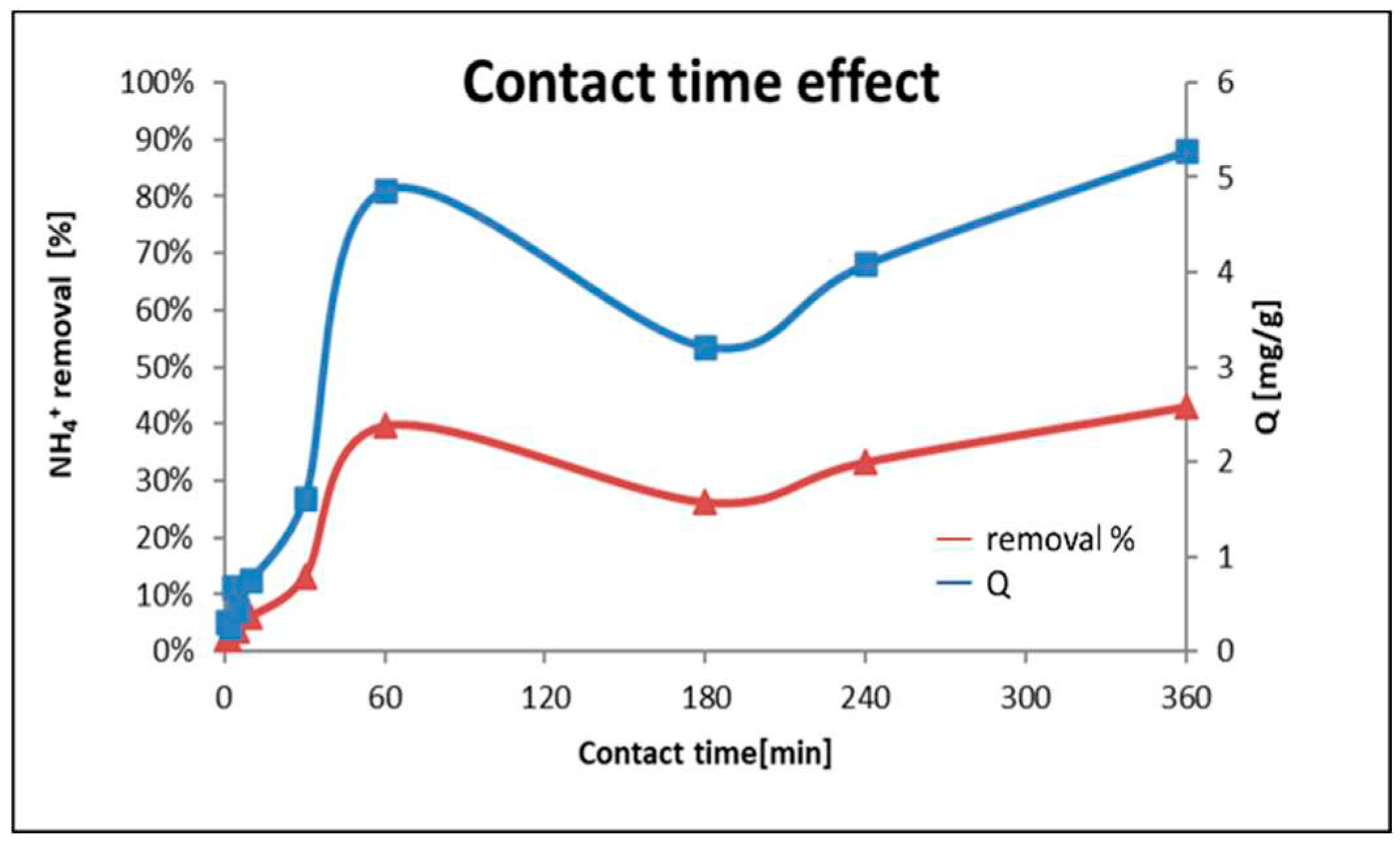
The effect of the contact time between the adsorbent and the adsorbate is depicted in
Figure 7. The graph demonstrated that after 1 h of immersion, the NH
4+ removal is 40% with a Q of 6 mg/g and the adsorption increases (in a general trend) progressively as the contact time increases. Therefore, the general trend is growing, being faster at the beginning of the procedure.
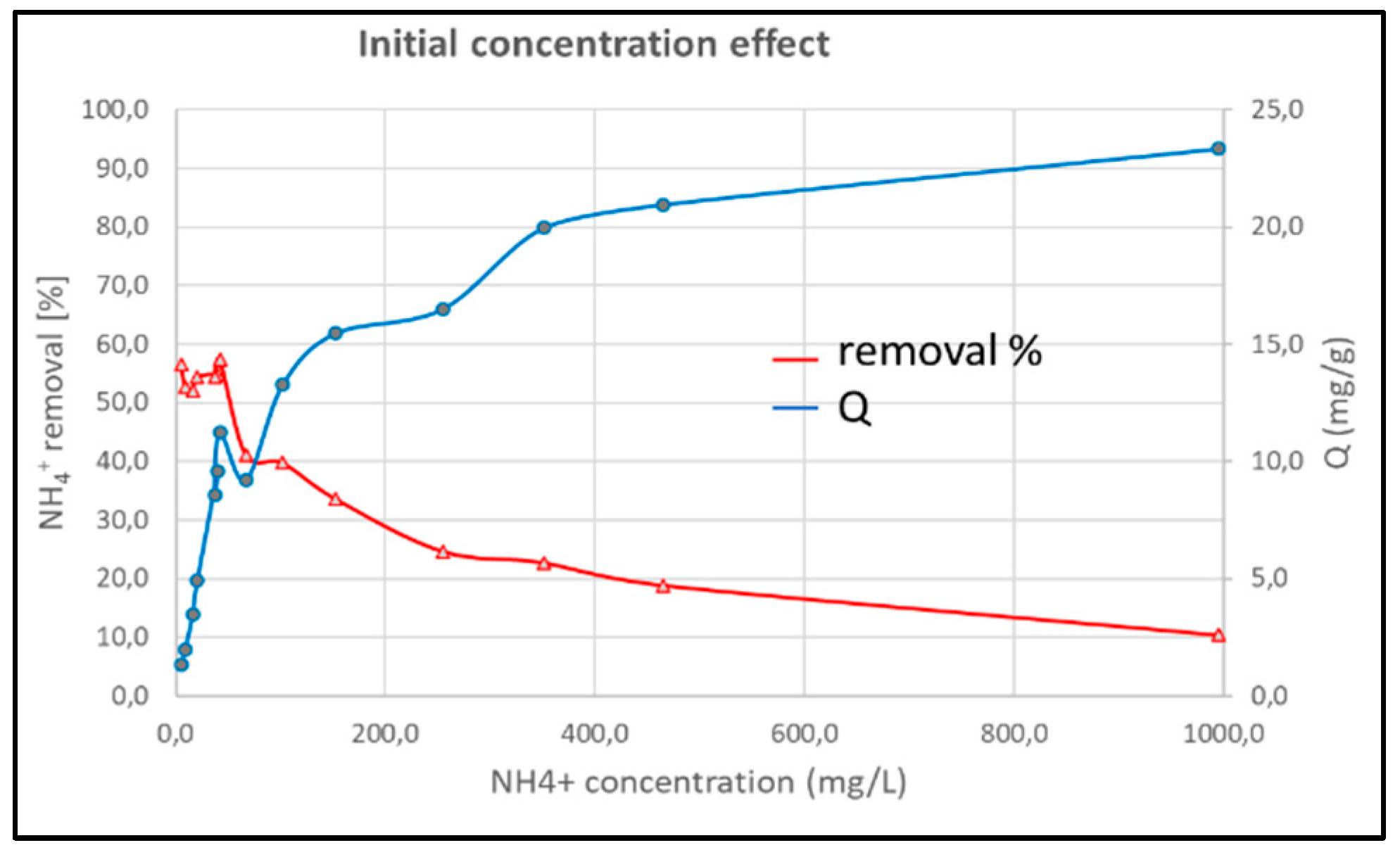
Adsorbent characteristics of P-20 are measured by varying the initial ammonium concentration from 10 mg/L to 1000 mg/L.
Figure 8 shows a rapid Q increase until it reaches 9 mg/g. Then, it continues to grow at a slower rate (lower slope) until it reaches 23 mg/g with an initial NH
4+ concentration of 1000 mg/L. This behaviour suggests part of the adsorbent mechanism: as the voids of the P20 geopolymer are being occupied, its adsorption capacity decreases, until it reaches a point where it becomes saturated and does not accept any more NH
4+ ions. The maximum capacity determined for P-20 is 23 mg/g, however, very high contaminant concentrations are required.
These experimental data were used to carry out the adsorption mechanism characterization (isotherm and kinetics).
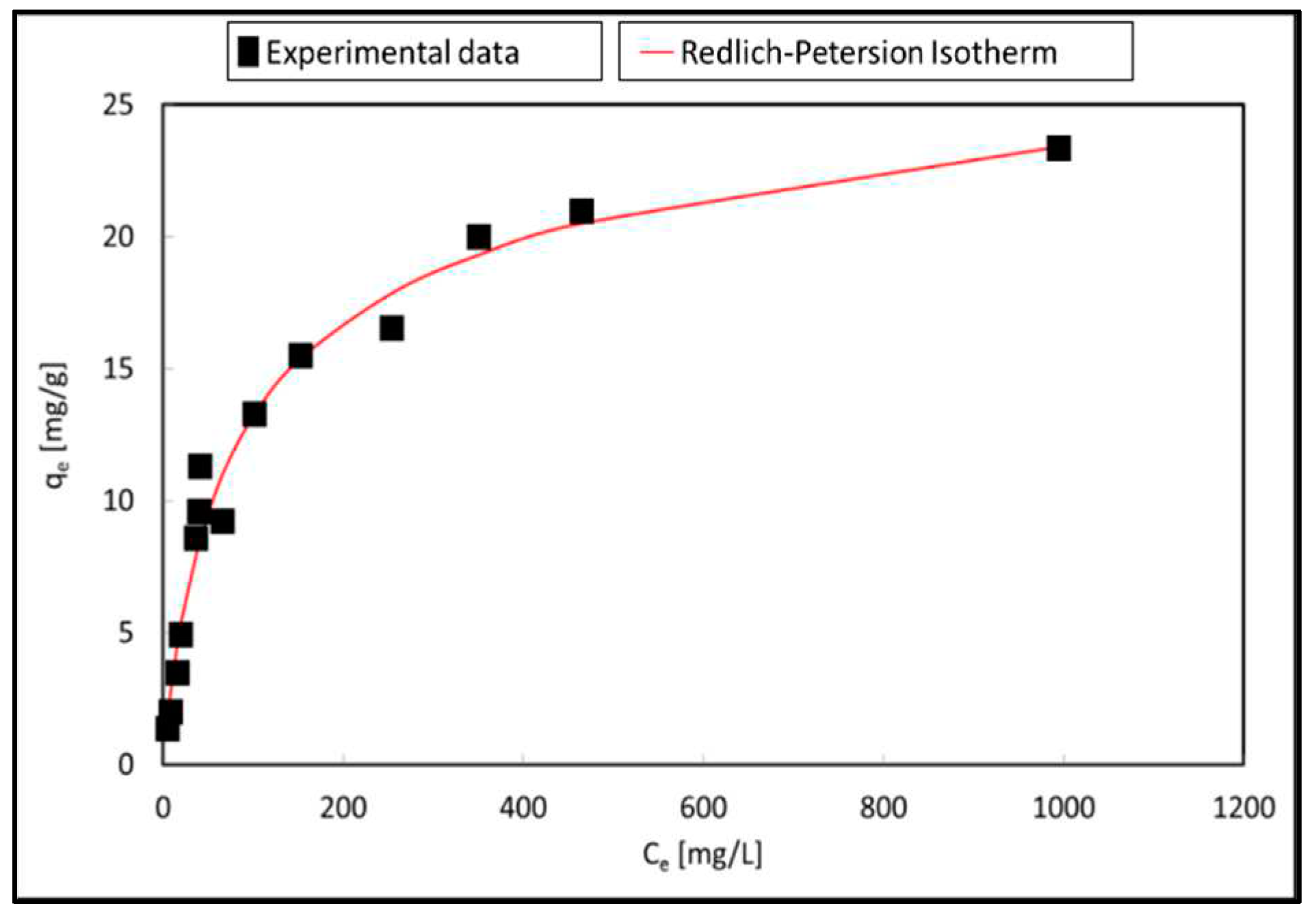
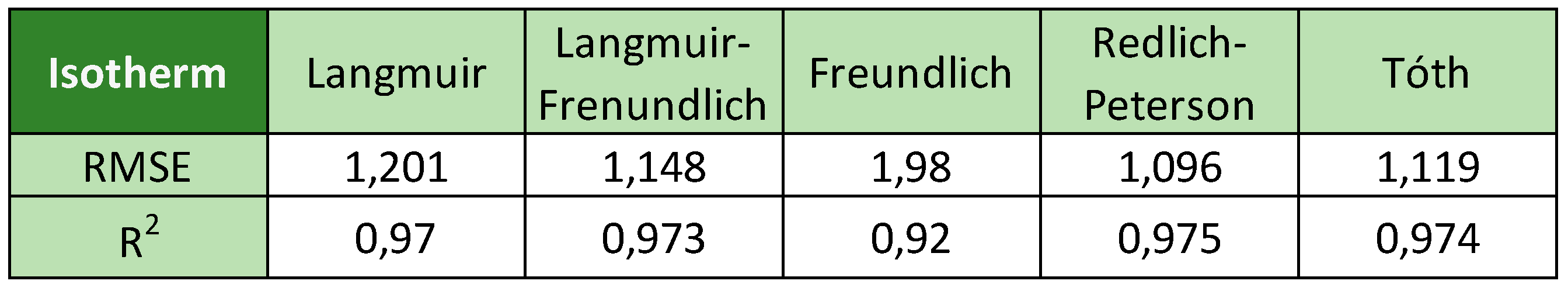
Adsorption processes can be studied from equilibrium equations. These equations allow to know, at equilibrium, the amount of adsorbed ion, as a function of temperature and ion concentration. For convenience in representation and use, the temperature is considered constant, giving them the name of adsorption isotherms. The data from the initial contaminant concentration effect test will be used to fit the different isothermal models. Five isotherm models (Langmuir, Langmuir-Freundlich, Freundlich, Redlich- Peterson and Tóth) were tested for modelling the adsorption mechanisms of the geopolymers. The parameters shown in these isotherms are common to the different models. These parameters are: a) the maximum capacity (Qm), b) the dimensionless parameter b, indicative of the adsorption energy and c) the dimensionless parameter n which represents the heterogeneity of the adsorbent surface.
The different isotherms models were evaluated by RSME (error measure) and by R
2 (goodness). The best fit was achieved with the Redlich-Peterson equation according to the high value of correlation coefficient as detailed in
Figure 9 and
Table 5.
This isotherm model is an empirical isotherm incorporating three parameters and combines elements from both Langmuir and Freundlich equations; therefore, the mechanism of adsorption is a mix and does not follow ideal monolayer adsorption. With this model, equation number 1 is obtained with the following values for the parameters: Qm=18.35 mg/g, b= 0.02, indicative of the affinity of the binding sites, and n=0,9 (this value, close to 1, indicates that the adsorption on the surface is homogeneous). The value of Qm is 27% higher than of the reference natural clinoptilolite-heulandite zeolite (14.42 mg/g) [
22].
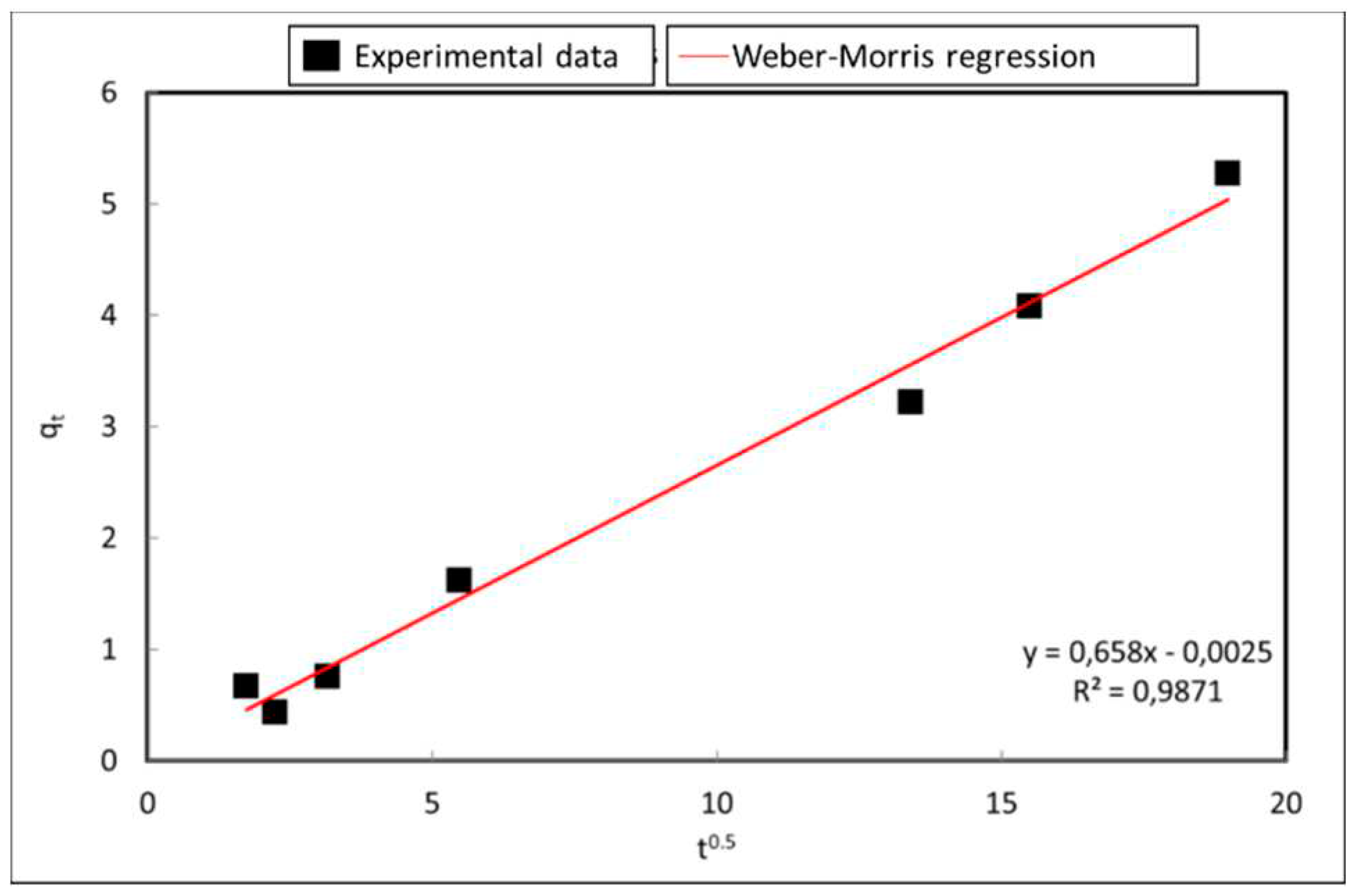
The equilibrium obtained with the above isotherm requires some time to be reached. The ions go through a series of processes until they reach the adsorbent surface, and the slowest ones determine the kinetics of the reaction. Adsorption kinetics provides insight into the reaction rate and the sorption mechanism involving mass transfer, diffusion, and reaction on the adsorbent surface during adsorption.
Various adsorption kinetic models [
23], such as the pseudo-first-order model, the pseudo-second-order model, the Elovich model and Weber-Morris model were tested in this case.
Figure 10 and
Table 6 detail the R
2 of the fit with the Weber Morris equation being the one that presents the best results.
The Webber-Morris equation is the following:
According to the data of this study, the equation 3 is obtained:
The value of C (value of the equation for t=0) close to 0 revealed that the limiting process was intraparticle diffusion. Furthermore, the fit of the data did not present multilinearity and the divergence of the slope of the curve with 0.5 indicates that the intraparticle diffusion process is the limiting factor.
The adsorption kinetics includes 3 mass transfer processes [
24]: the external diffusion (or film diffusion): the transfer of adsorbate in the liquid film around the adsorbent; the internal diffusion (or intraparticle diffusion): the transfer of adsorbate (NH
4+) through the pores of the adsorbent; and the adsorption onto the active sites. Considering the high porosity of identified in P-20 material, it can be confirmed that internal diffusion through porosity is the limiting process.
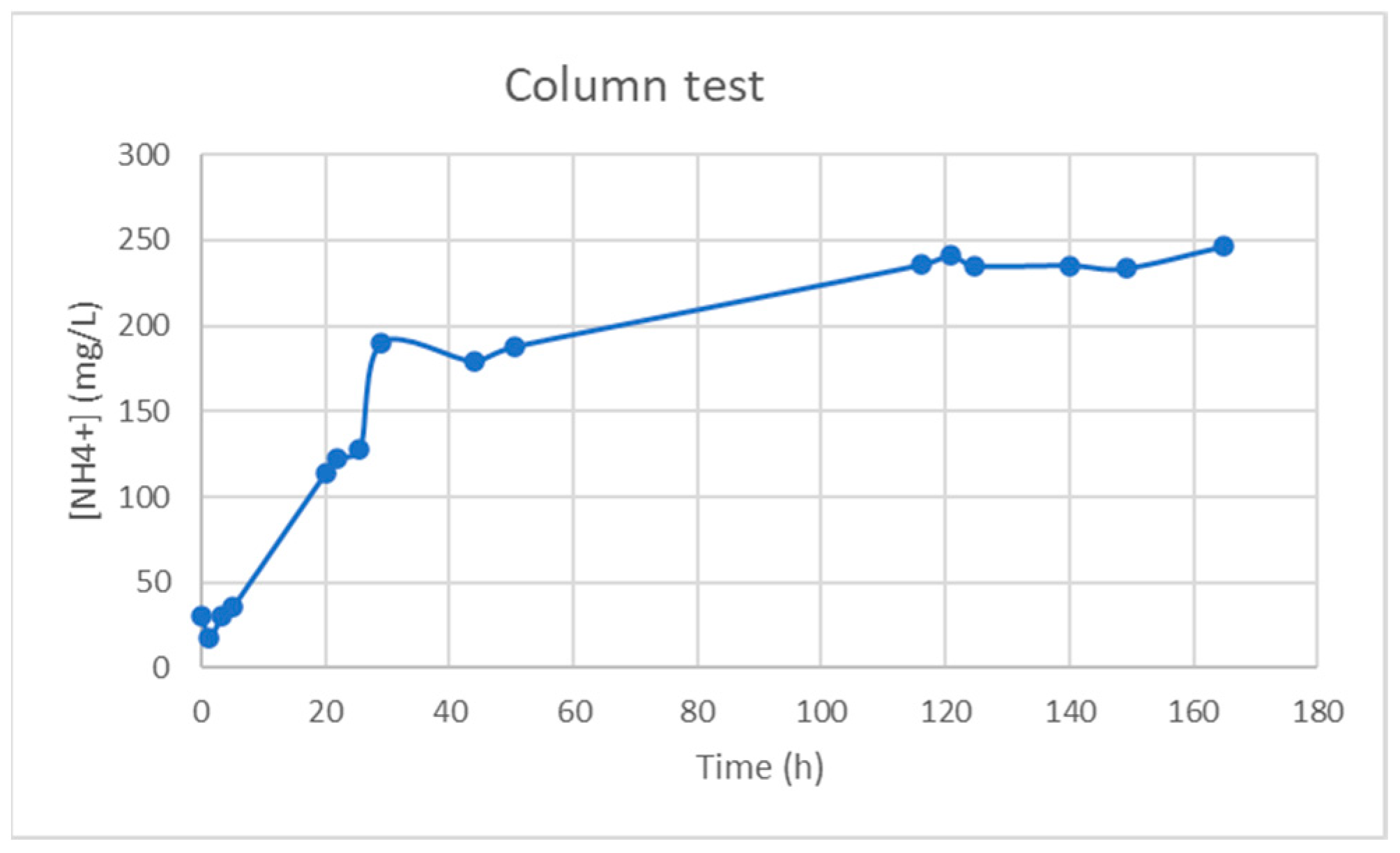
3.2.2. Continuous tests
Figure 11 shows the results obtained of the column test carried out for 160 h with an initial concentration of 250mg/L of NH
4+. It can be observed that the concentration of NH
4+ ions dropped sharply at the beginning of the test, around 17mg/L, obtaining an outstanding NH
4+ removal of 93% during the first hours. However, this value grows up to 123 mg/L at 25 h, being 50% the NH
4+ removal. From then on, the output solution has an increasing concentration of contaminant, reaching almost an asymptote at 110 h, i.e., the geopolymer hardly retains NH
4+ from the solution, becoming saturated. Therefore, a regeneration process of P-20 for reuse should be considered after 110 hours of adsorption treatment.
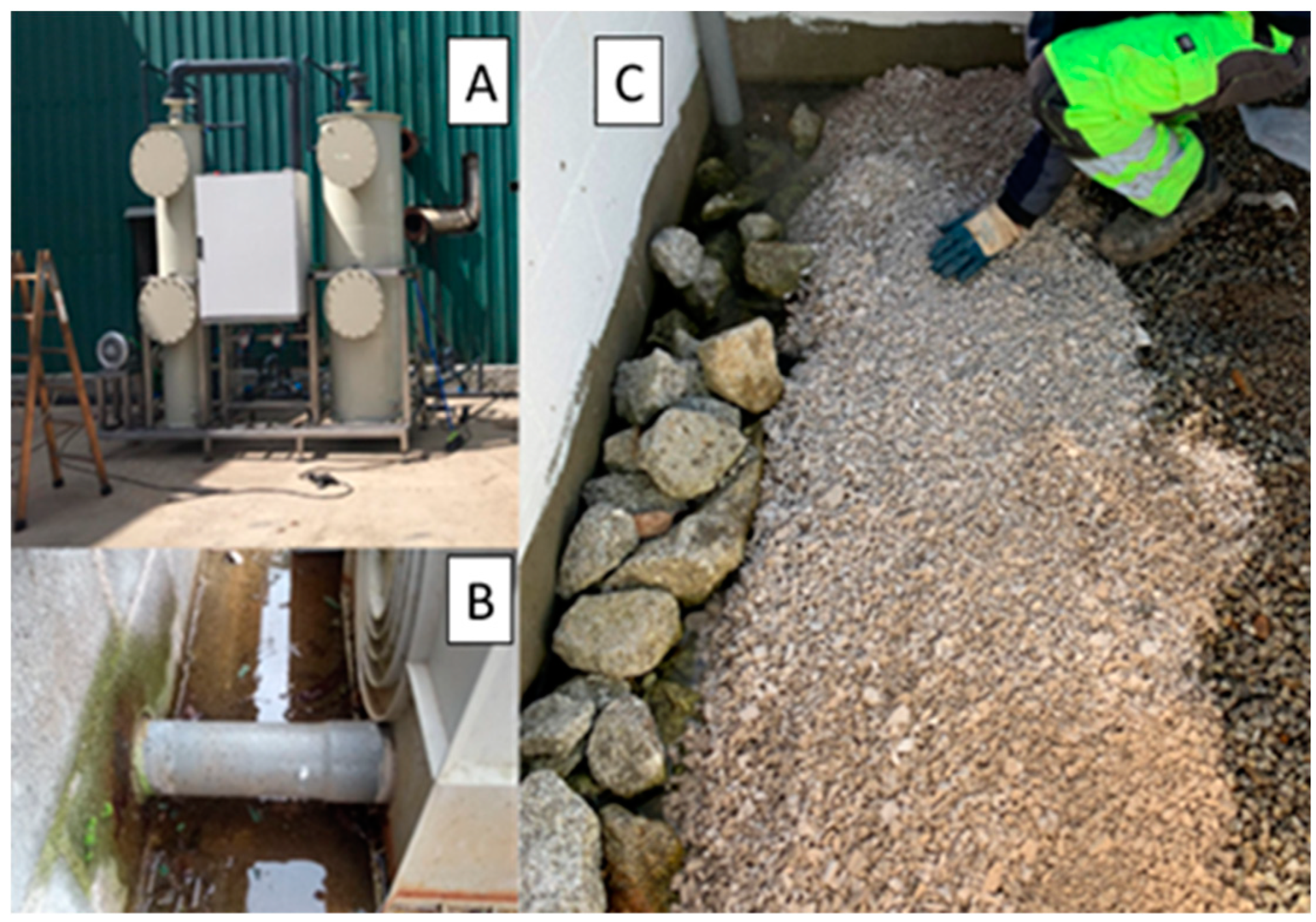
3.3. Validation of material through a pilot plant at a real wastewater treatment plant..
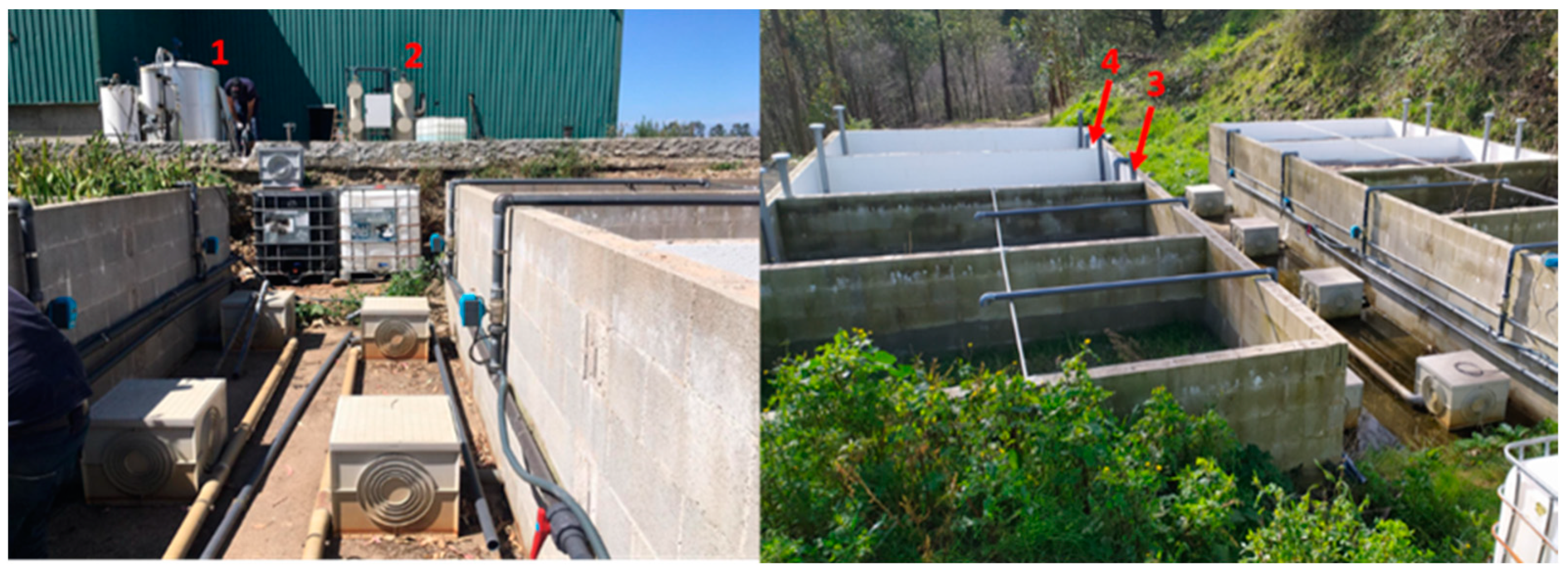
The pilot plant for wastewater treatment was designed at Xiloga Landfill. The plant consists of 3 filters as it can be seen in
Figure 12.
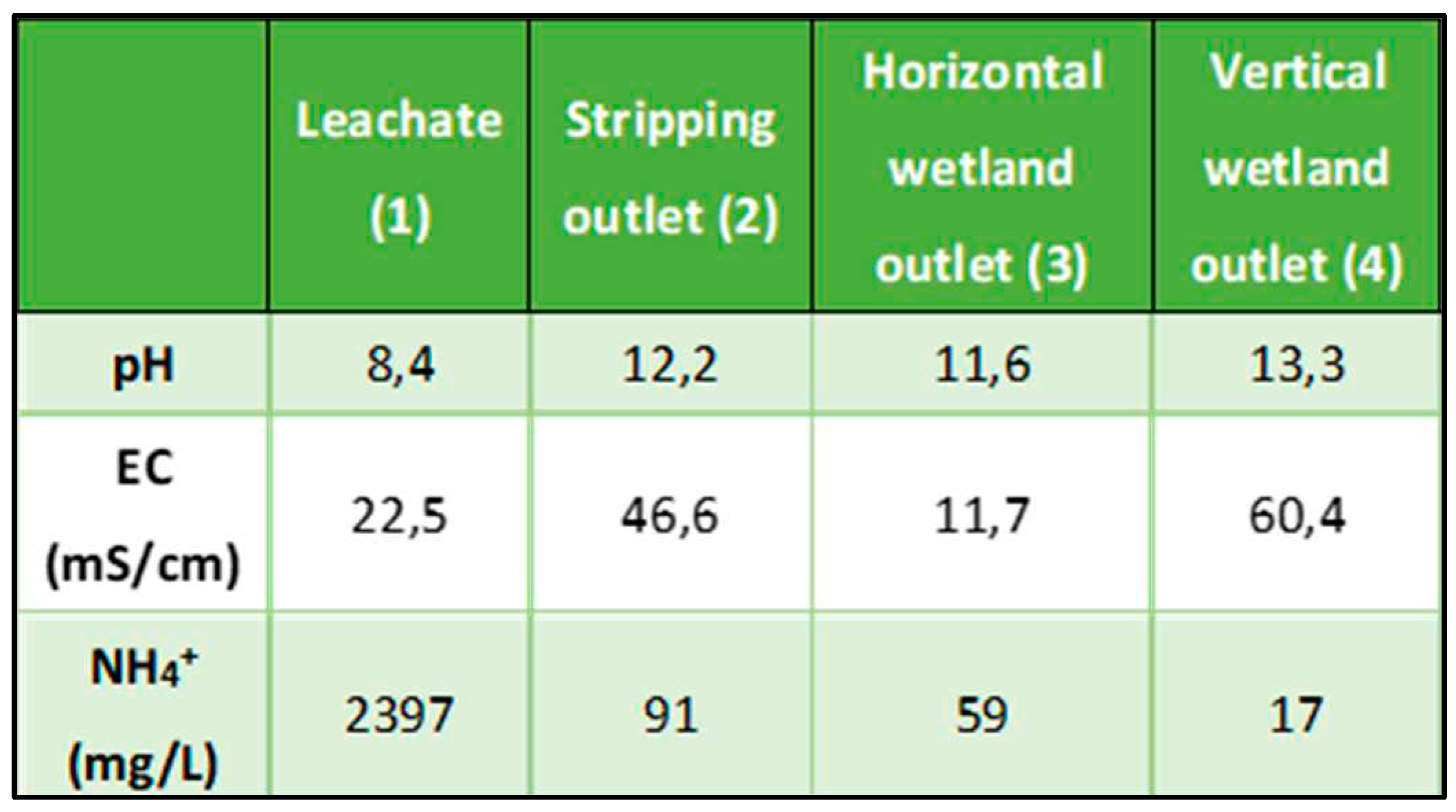
Figure 13 shows a global view of the pilot plant. Four key locations were identified for the NH
4+ removal monitoring. The first tank (1) with the raw leachate and the three abovementioned filters (2,3,4).
The results were monitored during 24 h at those four fluid outlets points. The monitored parameters were the pH, electric conductivity (EC) and [NH
4+] indicated in
Table 7.
The obtained values showed that the stripping system removed a very high amount of NH
4+ but promoted a significant increment in the pH values. This system requires high pH levels for high ammonium removal efficiency 25,26. Ammonia reacts with water to form ammonium hydroxide. Thus, in ammonia stripping, lime or caustic is added to the wastewater until the pH reaches to 11.5 -12.0 standard units which converts ammonium hydroxide ions to ammonia gas (NH
4OH → NH
3 + H
2O). When the leachate passes through the horizontal wetland, NH
4+ concentration decreased from 91 mg/L to 59 mg/L, which supposes a 35% of pollutant diminution. The decrease in the vertical wetland was even higher, 71%. resulting in a final elimination of 81% of NH
4+, similar to that obtained for commercial zeolites [
22]. It is worth to note the increment in the electrical conductivity (from 46,6 to 60,4ms/cm) and pH (from 12,2 to 13,3) during the treatment. This is probably due to the leaching of alkali species from the geopolymer to the liquid fluid.
4. Discussion
A porous geopolymer material (P-20) based on metakaolin was developed, characterized and evaluated as potential adsorbent material. The introduction of 20 % of GW minimizes the impact and the cost of the final product, contributing to the sustainability of the process. High porosity (59%) was established by the addition of H2O2 (1%) as a foaming agent. The produced material is resistant in water and presents a compressive strength of 6.7MPa at 28 days-age.
The adsorption characteristics were also determined obtaining a Qm of 18.95 being 27% higher than reference zeolites. The kinetics followed the Weber-Morris equation rate indicating that the intraparticle diffusion through the pores is the limiting mass transfer mechanism. Continuous laboratory experiments indicated an outstanding 93% of NH4+ removal during the first hours. This value decreases up to 50% after 25h. Finally, it is confirmed that P-20 tends to be completely saturated at 110h.
The material is validated in a relevant pilot plant designed with P-20 disposed in two wetlands for wastewater treatment. The material shows encouraging results of adsorption capacitance reaching up to 80% overall NH4+ removal, similar to the traditional zeolites.
These preliminary studies suggest that this sustainable, low-cost and easy-to-install material could be effectively used for NH4+ treatments.
However, future investigations will be focused on overcoming challenges as the pH and electrical conductivity increments due to alkalis leaching. Treatments such as acid/neutral pre-washing may reduce this leaching. On the other side, early saturation of the material could be alleviated by regeneration techniques. Finally, the advantages of additive manufacturing of geopolymers should be studied in this application. With 3D printing it is possible to manufacture parts with complex designs creating tortuous channels and increasing the porosity obtaining a greater efficiency in the process.
Author Contributions
Material design and development, methodology, analysis and validation, draft writing, M. Otero. Adsorption characterization, methodology, formal analysis and validation, S. Gómez-Cuervo and C. Ávila. Funding acquisition, project management, review and editing, investigation and supervision, L. Freire. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Axencia Galega de Innovación and FEDER under the project GEOPOLAR of Conecta Peme Program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest and the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- R. Carreño-Gallardo et al. In the CO2 emission remediation by means of alternative geopolymers as substitutes for cements. J. Env. Chemical Eng. 2018, 6 4878. [CrossRef]
- R. Jacob, N. Trout, A. Solé, S. Clarke, A.I. Fernández, L. Cabeza, W. Saman, F. Bruno, Novel geopolymer for use as a sensible storage option in high temperature thermal energy storage systems, AIP Conference Proceedings, 2020, 2303, 190019.
- M. Rahjoo et al, Geopolymer Concrete Performance Study for High-Temperature Thermal Energy Storage (TES) Applications. Sustainability, 2022, 14, 1937. [CrossRef]
- D. Perera et al, Characterisation of Geopolymers for the Immobilisation of Intermediate Level Waste, Proceedings of the International Conference on Radioactive Waste Management and Environmental Remediation, 2003, ICEM 3, 1807–1814.
- J.L. Provis, In Geopolymers: Structures, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications, 2009,421–440.
- P. Duan, C. Yan, W. Zhou, D. Ren, Development of fly ash and iron ore tailing based porous geopolymer for removal of Cu(II) from wastewater, Ceram Int. 2016, 42, 13507- 13518. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ge, X. Cui, Y. Kong, Z. Li, Y. He, Q.J. Zhou, Hazard Mater, 2015, 283, 244-251.
- Y. Ge, Y. Yuan, K. Wang, Y. He, X. Cui , Hazard Mater. 2015, 299, 711-718.
- J.R. Gasca-Tirado, A. Manzano-Ramírez, P.A. Vazquez-Landaverde, E. I. Herrera-Díaz, M. E. Rodríguez-Ugarte, J. C. Rubio-Ávalos, V. Amigó-Borrás, M. Chávez-Páez, Ion-exchanged geopolymer for photocatalytic degradation of a volatile organic Compound, Mater Lett. 2014, 134, 222-224. [CrossRef]
- R.M. Novais, M.P. Seabra, J.A. Labrincha, Porous geopolymer spheres as novel pH buffering materials, Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 143, 1114-1122. [CrossRef]
- M. Alshaaer et al., Development of functional geopolymers for water purification, and construction purposes, J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2016, 20, S85-S92. [CrossRef]
- J.R. Gasca-Tirado, A. Manzano-Ramírez, E. Rivera Muñoz, R. Velázquez-Castillo, M. Apátiga-Castro, R. Nava and A. Rodríguez-López, Ion Exchange in Geopolymers, New Trends in Ion Exchange Studies, 2018, 5.
- T.H. Tan, K.H. Mo, T. Ling, S.H. Lai, Current development of geopolymer as alternative adsorbent for heavy metal removal, Environmental Technology & Innovation. 2020, 20, 100684. [CrossRef]
- JL Bell, WM. Kriven. Preparation of Ceramic foams from metakaolin-based geopolymer gels. Ceram Eng Sci Proc. 2008, 29, 97–112.
- E. Kränzlein, H. Pöllmann, W. Krcmar. Metal powders as foaming agents in fly ash based geopolymer synthesis and their impact on the structure depending on the Na/Al ratio. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 8, 90-161. [CrossRef]
- E. Prud’homme, P. Michaud, E. Joussein, C. Peyratout, A. Smith, S. Rossignol. In situ inorganic foams prepared from various clays at low temperature. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 51, 15-22. [CrossRef]
- J. Henon, A. Alzina, J. Absi, DS. Smith, S. Rossignol. Potassium geopolymer foams made with silica fume pore forming agent for thermal insulation. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 37–46. [CrossRef]
- T Luukkonen, K. Věžníková, E.T. Tolonen, H. Runtti, J. Yliniemi, T. Hu, K. Kemppainen, U. Lassi, Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater with powdered and granulated metakaolin geopolymer, Environm.Technol. 2017, 4, 414-423. [CrossRef]
- G. Tchobanoglous, FL. Burton, HD. Stensel. Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. 4th ed. New York (NY): Mc Graw Hill, 2004.
- J.H. Hwang, J.A. Oleszkiewicz, Effect of Cold -Temperature Shock on Nitrification, Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 964 –968. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lin, M. Guo, N. Shah, D.C. Stuckey, Economic and environmental evaluation of nitrogen removal and recovery methods from wastewater, Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 227 –238. [CrossRef]
- T. Luukkonen, M. Sarkkine, K. Kemppainen, J. Rämö, U. Lassi, Metakaolin geopolymer characterization and application for ammonium removal from model solutions and landfill leachate, Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, Part 2:266-276. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, X. Guo, Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods, Journal of Hazardous materials, 2020, 390, 122156. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, X. Guo, Rethinking of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption kinetics model: Interpretation, solving methods and applications, Chemosphere, 2022, 309, 136732. [CrossRef]
- EPA, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet Ammonia Stripping, online at https://www3.epa.gov/npdes/pubs/ammonia_stripping.pdf (accessed on 18/10/2023).
- C.Q. Wu et al, Ammonia removal mechanism by the combination of air stripping and ultrasound as the function of pH, IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 344, 012051. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of G-0, G-10 and G-20.
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of G-0, G-10 and G-20.
Figure 2.
SEM images for a) G-20 and b) P-20 at 400x.
Figure 2.
SEM images for a) G-20 and b) P-20 at 400x.
Figure 3.
Mechanical strengths obtained for G and P geopolymers with different GW substitution.
Figure 3.
Mechanical strengths obtained for G and P geopolymers with different GW substitution.
Figure 4.
appearance after 1 day immersion in water of: a) P-20 b) P-30 and c) P-40.
Figure 4.
appearance after 1 day immersion in water of: a) P-20 b) P-30 and c) P-40.
Figure 5.
Effect of pH on the adsorption process.
Figure 5.
Effect of pH on the adsorption process.
Figure 6.
Effect of adsorbent dose on the adsorption process.
Figure 6.
Effect of adsorbent dose on the adsorption process.
Figure 7.
Effect of contact time on the adsorption process.
Figure 7.
Effect of contact time on the adsorption process.
Figure 8.
Effect of NH4+ initial concentration on the adsorption process.
Figure 8.
Effect of NH4+ initial concentration on the adsorption process.
Figure 9.
Redlich Peterson isotherm.
Figure 9.
Redlich Peterson isotherm.
Figure 10.
Adjustment of the data by Webber Morris regression.
Figure 10.
Adjustment of the data by Webber Morris regression.
Figure 11.
P-20 column test.
Figure 11.
P-20 column test.
Figure 12.
A) Air stripping system B) horizontal wetland C) vertical wetland.
Figure 12.
A) Air stripping system B) horizontal wetland C) vertical wetland.
Figure 13.
Key locations of the pilot plant: 1) tank 2) stripping system 3) horizontal wetland 4) vertical wetland.
Figure 13.
Key locations of the pilot plant: 1) tank 2) stripping system 3) horizontal wetland 4) vertical wetland.
Table 1.
Studied parameters for formulation optimization at laboratory scale.
Table 1.
Studied parameters for formulation optimization at laboratory scale.
Table 2.
Formulations studied in this work.
Table 2.
Formulations studied in this work.
Table 3.
Bulk density, true density and total porosity of G and P formulations with different GW content.
Table 3.
Bulk density, true density and total porosity of G and P formulations with different GW content.
Table 4.
P-20 synthesis parameters and properties.
Table 4.
P-20 synthesis parameters and properties.
Table 5.
RSME and R2 of the different isotherm models.
Table 5.
RSME and R2 of the different isotherm models.
Table 6.
Goodness of the different kinetic models.
Table 6.
Goodness of the different kinetic models.
Table 7.
Values of pH, EC and [NH4+].
Table 7.
Values of pH, EC and [NH4+].
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).