Submitted:
20 November 2023
Posted:
20 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
INTRODUCTION
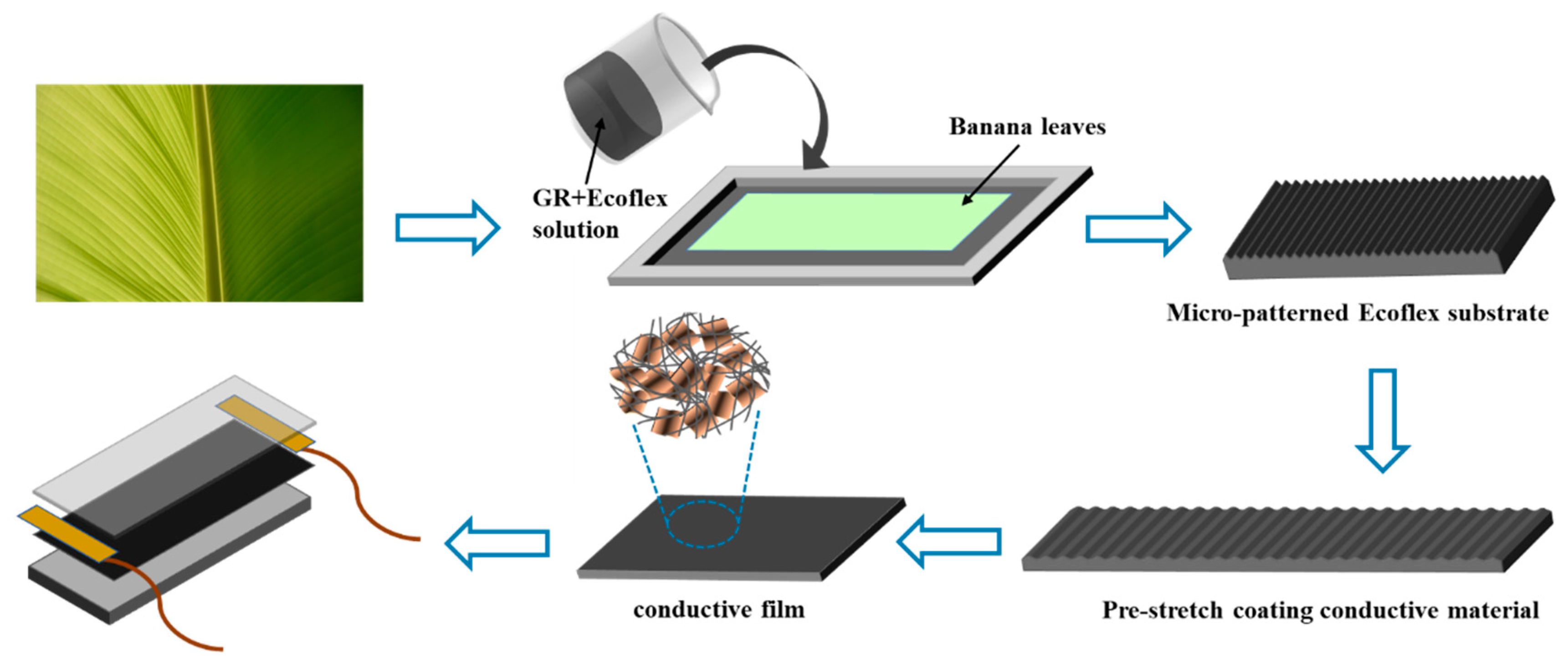
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Surface microstructure characterisation
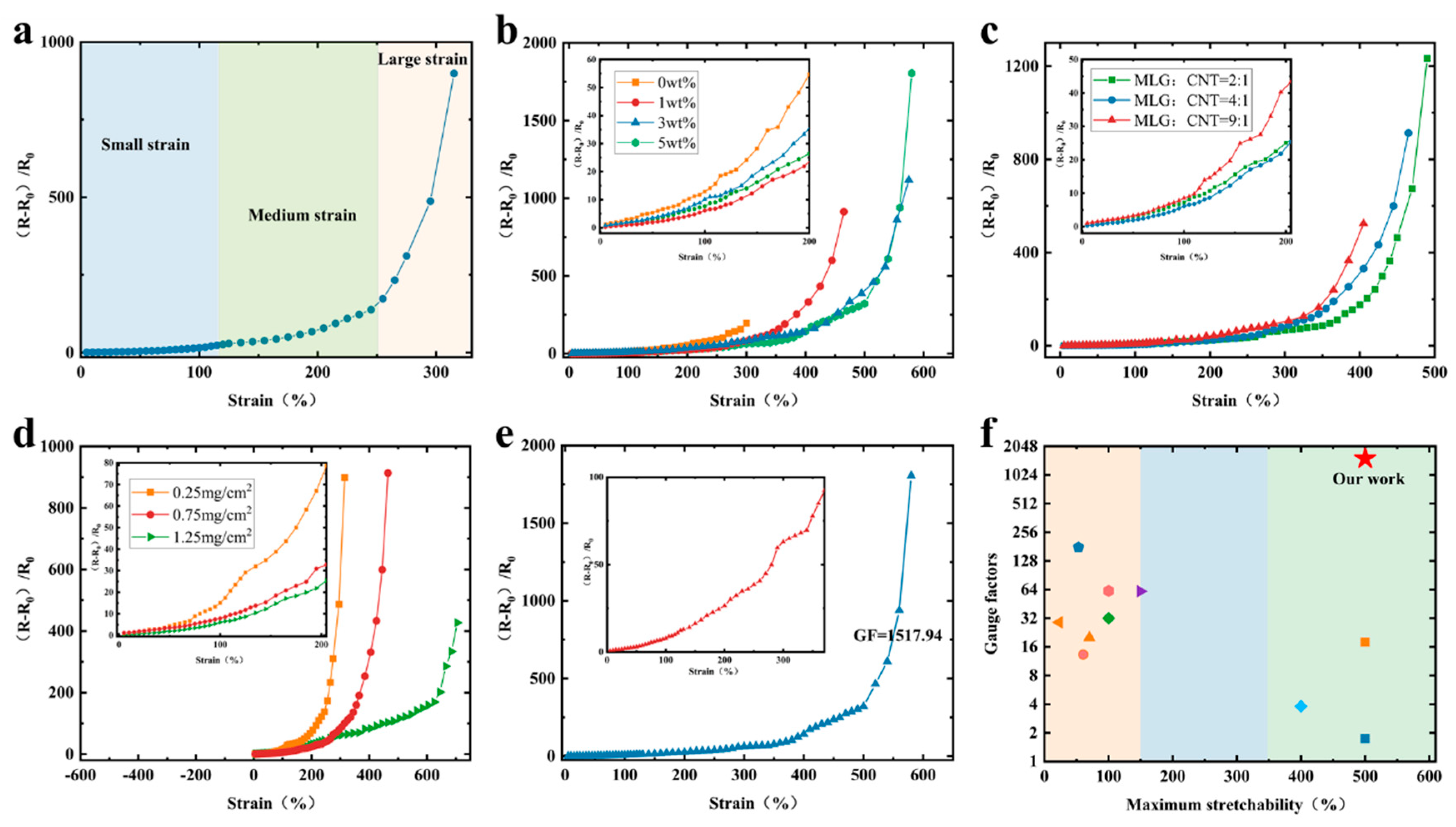
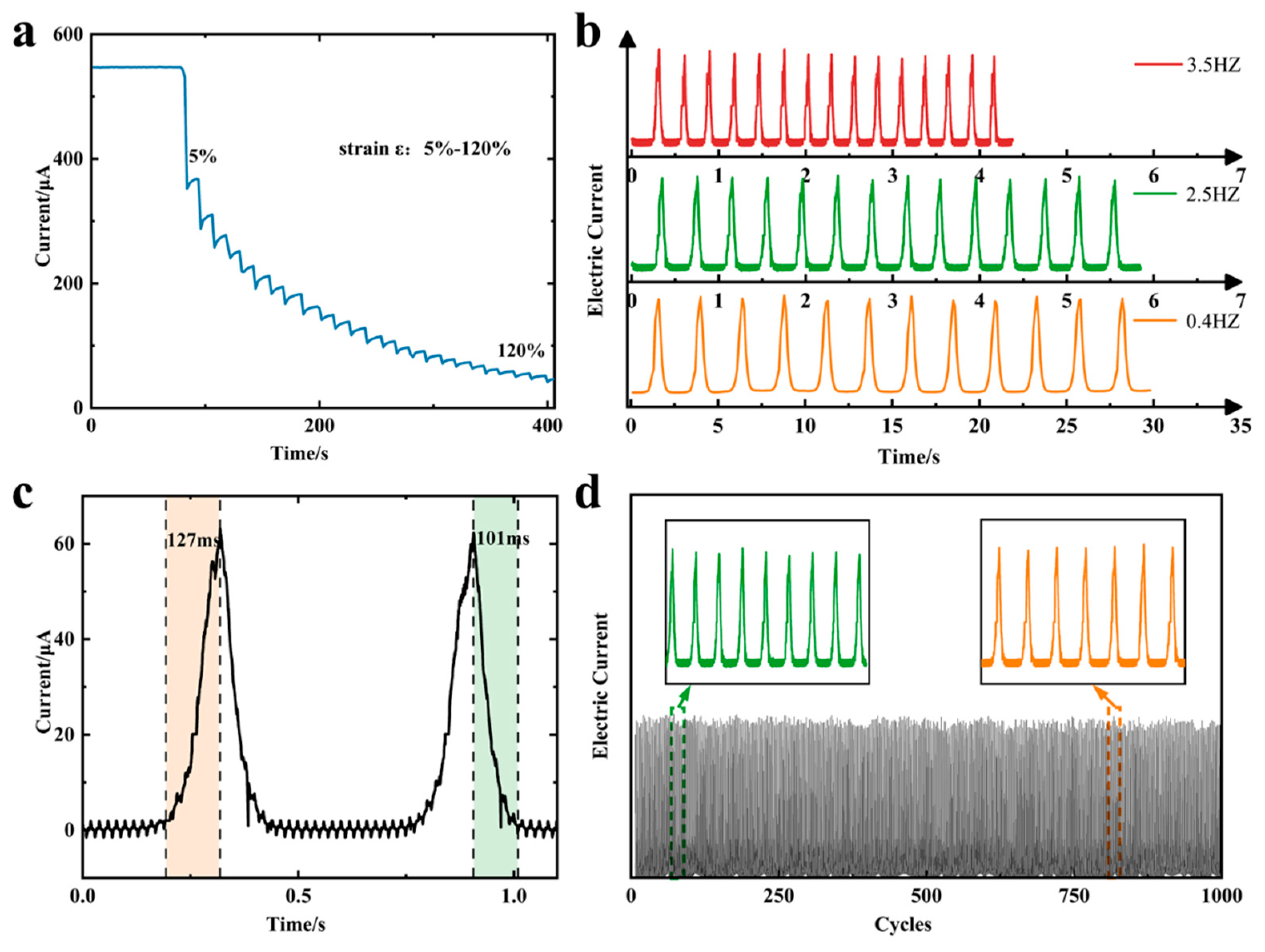
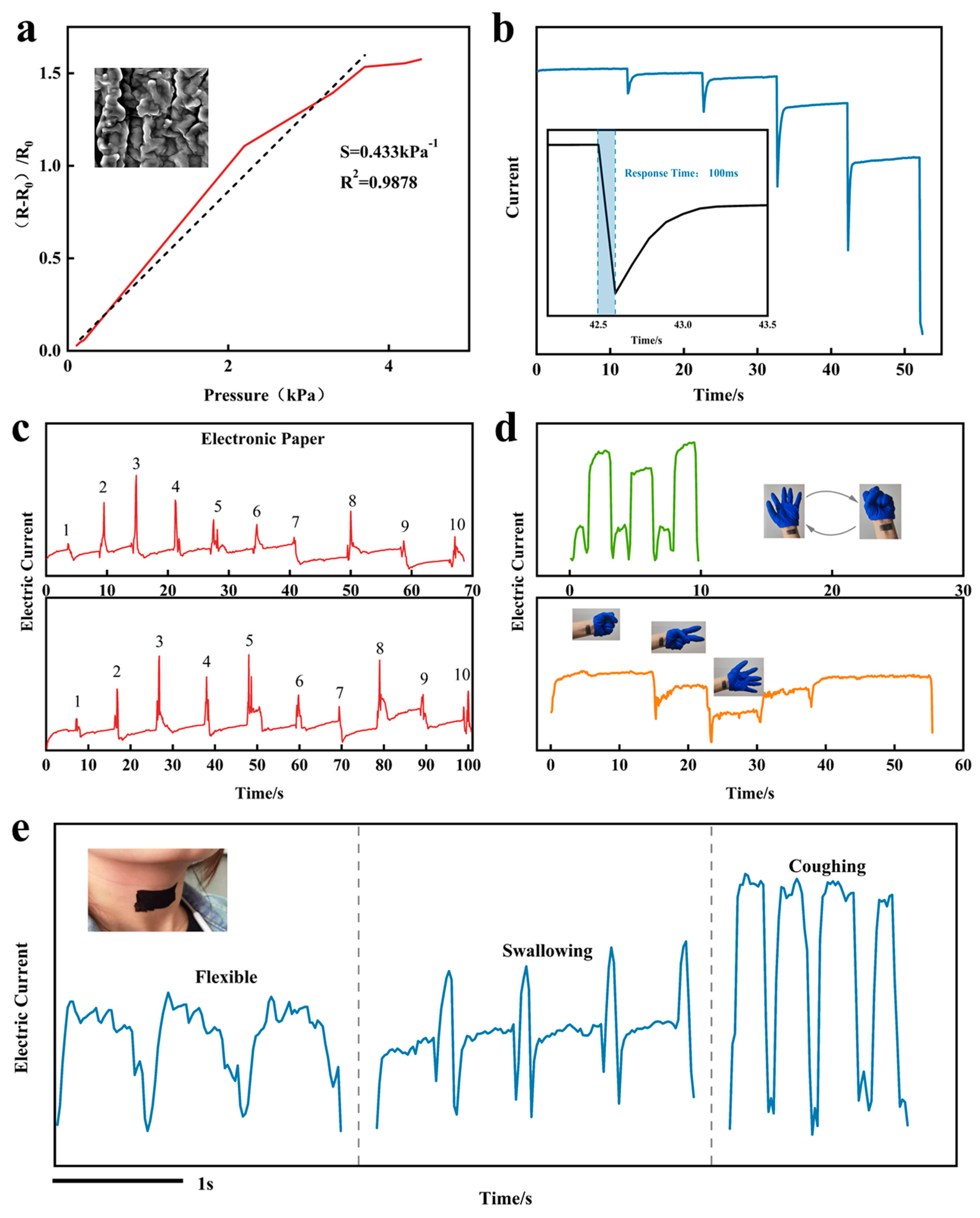
Sensing performance analysis
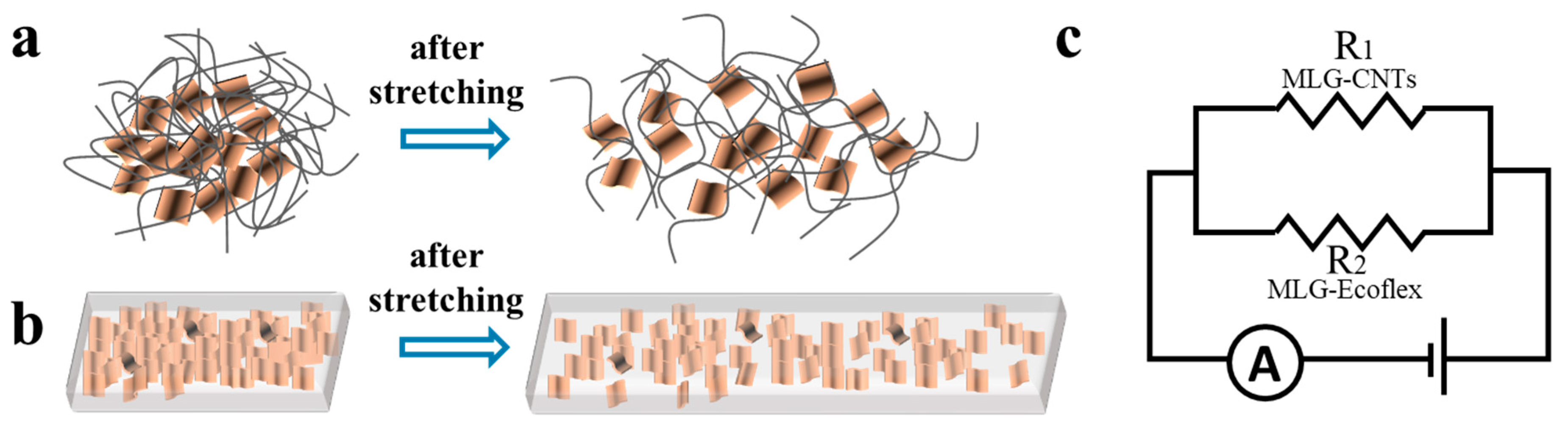
Sensing Mechanism Analysis
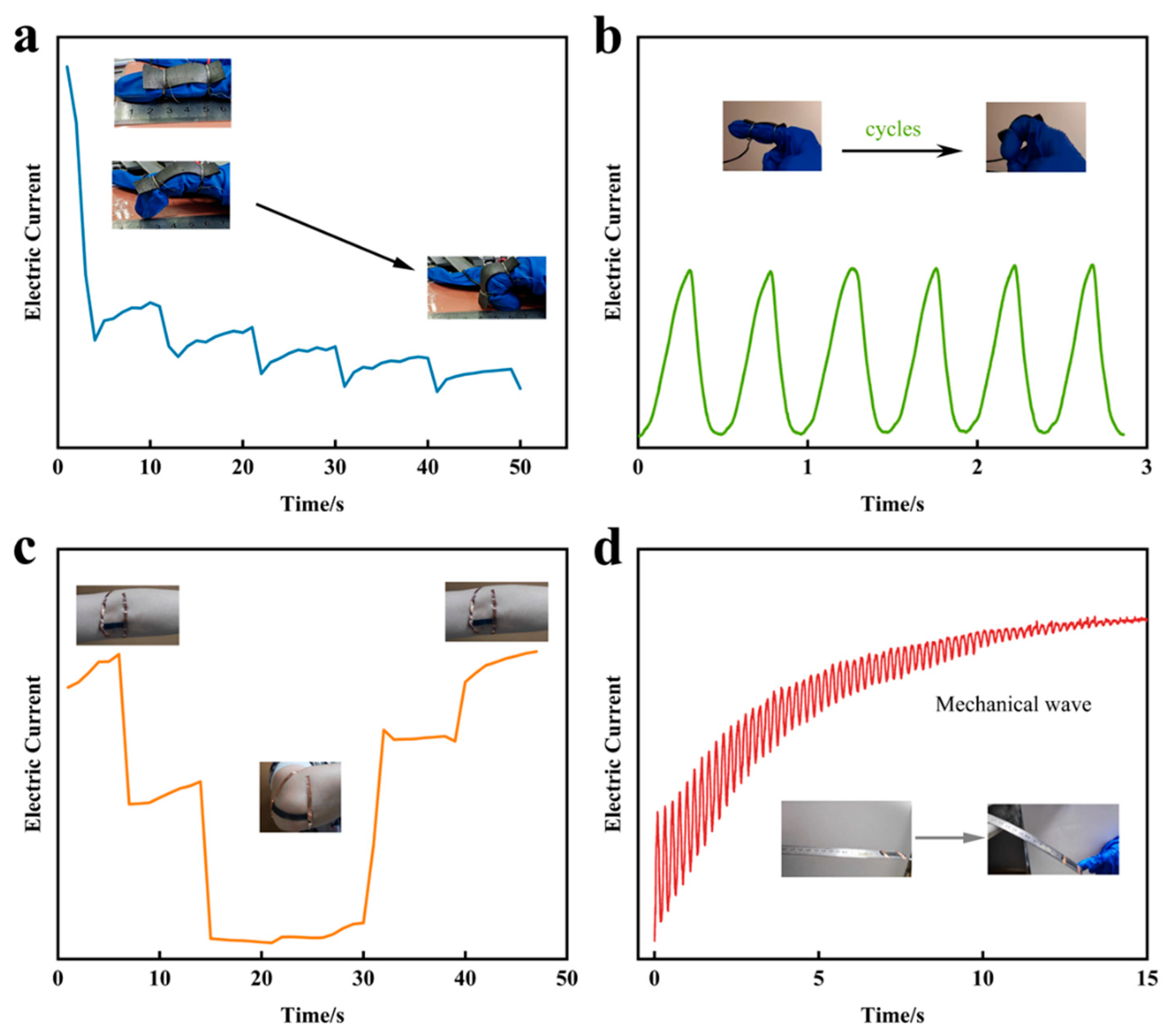
Application of human motions monitoring
CONCLUSION
References
- Boutry, C.M., et al., Biodegradable and flexible arterial-pulse sensor for the wireless monitoring of blood flow. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2019. 3(1): p. 47-57. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S., et al., Wearable Capacitive Pressure Sensor Based on MXene Composite Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Reliable Human Physiological Signal Acquisition. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020. 12(19): p. 22212-22224. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., et al., Flexible piezoelectric pressure sensor based on polydopamine-modified BaTiO<sub>3</sub>/PVDF composite film for human motion monitoring. Sensors and Actuators a-Physical, 2020. 301. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.A., et al., Graphene K-Tape Meshes for Densely Distributed Human Motion Monitoring. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2021. 6(1). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z., et al., Multifunctional conductive hydrogels and their applications as smart wearable devices. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2021. 9(11): p. 2561-2583. [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.S., et al., Research progress of multifunctional flexible proximity sensors. Sensors and Actuators a-Physical, 2023. 360. [CrossRef]
- Moussaoui, S.C., et al., Spatial Calibration of Humanoid Robot Flexible Tactile Skin for Human-Robot Interaction. Sensors, 2023. 23(9). [CrossRef]
- Takei, K., et al., Nanowire active-matrix circuitry for low-voltage macroscale artificial skin. Nature Materials, 2010. 9(10): p. 821-826. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M., et al., Fabrication and characterization of nano-ZnO/CNTs/PDMS flexible pressure sensor. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 2023. 34(21). [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, H., et al., A Flexible Pressure Sensor Based on PDMS-CNTs Film for Multiple Applications. Ieee Sensors Journal, 2022. 22(4): p. 3033-3039. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J., A. Thukral, and C.J. Yu, Highly Sensitive and Very Stretchable Strain Sensor Based on a Rubbery Semiconductor. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018. 10(5): p. 5000-5006. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L., et al., Ultra-Stretchable Monofilament Flexible Sensor with Low Hysteresis and Linearity based on MWCNTs/Ecoflex Composite Materials. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2021. 306(8). [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.R., et al., Highly Stretchable and Sensitive Strain Sensors Using Fragmentized Graphene Foam. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015. 25(27): p. 4228-4236. [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.J., et al., Dipentaerythritol-Derived Hyperbranched Polyurethane Elastomers and Their Applications in Flexible Strain Sensors. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2022. 307(7). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W., et al., Flexible and wearable strain sensors based on conductive hydrogels. Journal of Polymer Science, 2022. 60(18): p. 2663-2678. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z., et al., Flexible and high-performance piezoresistive strain sensors based on carbon nanoparticles@polyurethane sponges. Composites Science and Technology, 2020. 200. [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M., et al., Highly Stretchable and Sensitive Strain Sensor Based on Silver Nanowire-Elastomer Nanocomposite. Acs Nano, 2014. 8(5): p. 5154-5163. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J., et al., Crack-induced Ag nanowire networks for transparent, stretchable, and highly sensitive strain sensors. Scientific Reports, 2017. 7. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., et al., Review-Recent Advances in the Development of Carbon Nanotubes Based Flexible Sensors. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020. 167(4). [CrossRef]
- Wang, R., et al., A Bi-Sheath Fiber Sensor for Giant Tensile and Torsional Displacements. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017. 27(35). [CrossRef]
- Kong, M., et al., Graphene-based flexible wearable sensors: mechanisms, challenges, and future directions. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.Q., et al., Simultaneous Detection of Static and Dynamic Signals by a Flexible Sensor Based on 3D Graphene. Sensors, 2017. 17(5). [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y., et al., High performance flexible strain sensor based on self-locked overlapping graphene sheets. Nanoscale, 2016. 8(48): p. 20090-20095. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.N., et al., Strain Sensors with a High Sensitivity and a Wide Sensing Range Based on a Ti<sub>3</sub>C<sub>2</sub>T<i><sub>x</sub></i> (MXene) Nanoparticle-Nanosheet Hybrid Network. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019. 29(14). [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W., et al., Wearable CNT/Ti<sub>3</sub>C<sub>2</sub>T<i><sub>x</sub></i> MXene/PDMS composite strain sensor with enhanced stability for real-time human healthcare monitoring. Nano Research, 2021. 14(8): p. 2875-2883. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.L., et al., Pyramid microstructure with single walled carbon nanotubes for flexible and transparent micro-pressure sensor with ultra-high sensitivity. Sensors and Actuators a-Physical, 2017. 266: p. 345-351. [CrossRef]
- Park, J., et al., Tactile-Direction-Sensitive and Stretchable Electronic Skins Based on Human-Skin-Inspired Interlocked Microstructures. Acs Nano, 2014. 8(12): p. 12020-12029. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., Y. Wei, and Y.Y. Qiu, Advanced Flexible Skin-Like Pressure and Strain Sensors for Human Health Monitoring. Micromachines, 2021. 12(6). [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.S., et al., Highly Sensitive Skin-Mountable Strain Gauges Based Entirely on Elastomers. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012. 22(19): p. 4044-4050. [CrossRef]
- Muth, J.T., et al., Embedded 3D Printing of Strain Sensors within Highly Stretchable Elastomers. Advanced Materials, 2014. 26(36): p. 6307-6312. [CrossRef]
- Gong, S., et al., Tattoo like Polyaniline Microparticle-Doped Gold Nanowire Patches as Highly Durable Wearable Sensors. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015. 7(35): p. 19700-19708. [CrossRef]
- Roh, E., et al., Stretchable, Transparent, Ultrasensitive, and Patchable Strain Sensor for Human-Machine Interfaces Comprising a Nanohybrid of Carbon Nanotubes and Conductive Elastomers. Acs Nano, 2015. 9(6): p. 6252-6261. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S., et al., Vertical CNT-Ecoflex nanofins for highly linear broad-range-detection wearable strain sensors. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018. 6(19): p. 5132-5139. [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M., Y.J. Yoon, and I. Park, Ultra-stretchable and skin-mountable strain sensors using carbon nanotubes-Ecoflex nanocomposites. Nanotechnology, 2015. 26(37). [CrossRef]
- Lin, L., et al., Modified resistivity-strain behavior through the incorporation of metallic particles in conductive polymer composite fibers containing carbon nanotubes. Polymer International, 2013. 62(1): p. 134-140. [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.Y., et al., The resistivity-strain behavior of conductive polymer composites: stability and sensitivity. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014. 2(40): p. 17085-17098. [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.Y., et al., Enhanced Solid Particle Erosion Properties of Thermoplastic Polyurethane-Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2019. 304(5). [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., et al., A Facile Realization Scheme for Tactile Sensing with a Structured Silver Nanowire㏄DMS Composite. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019. 4(3). [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.Q., et al., Flexible and Highly Sensitive Pressure Sensors Based on Bionic Hierarchical Structures. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017. 27(9). [CrossRef]
- Mannsfeld, S.C.B., et al., Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers. Nature Materials, 2010. 9(10): p. 859-864. [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




