Submitted:
18 November 2023
Posted:
20 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
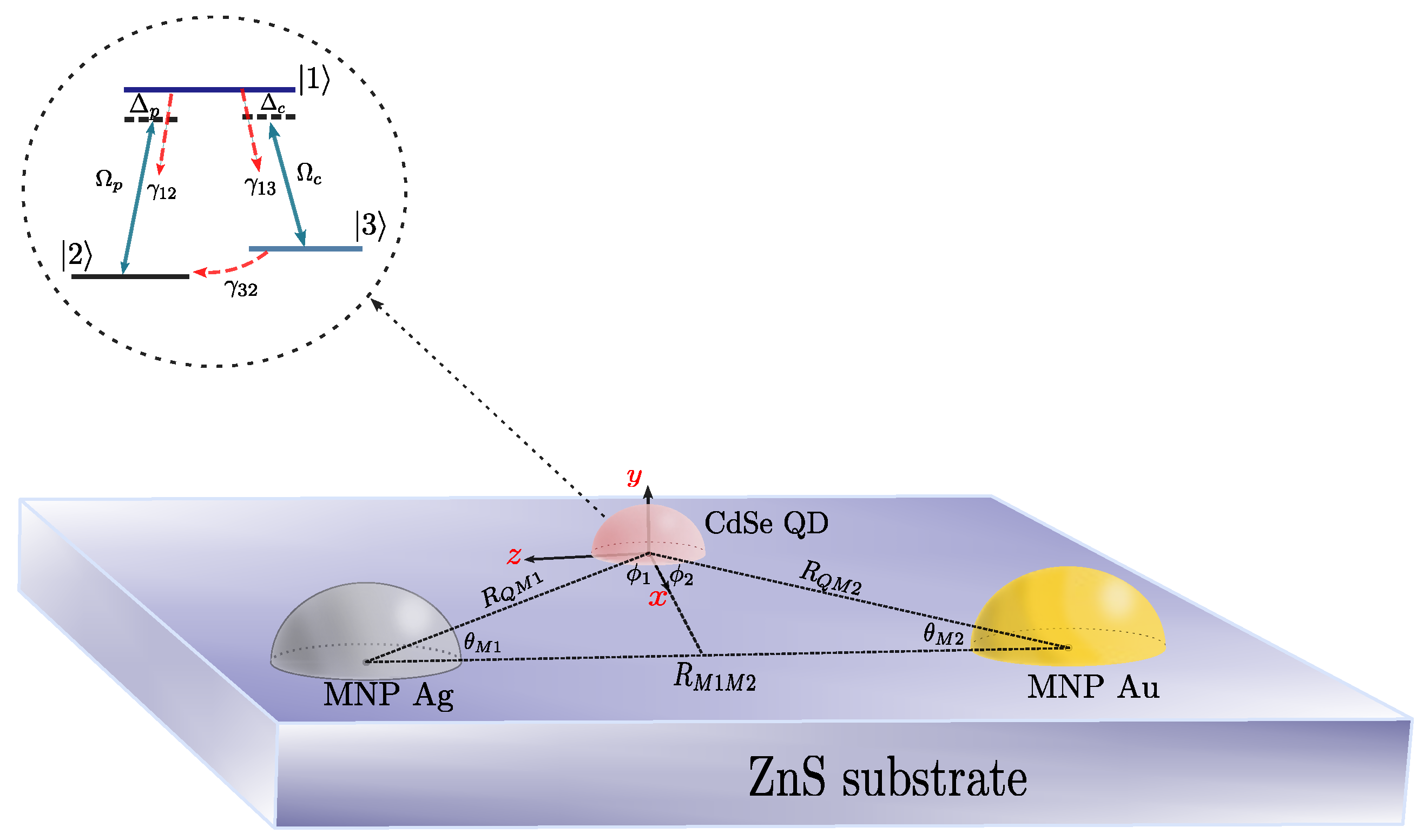
2. Theoretical Formalism
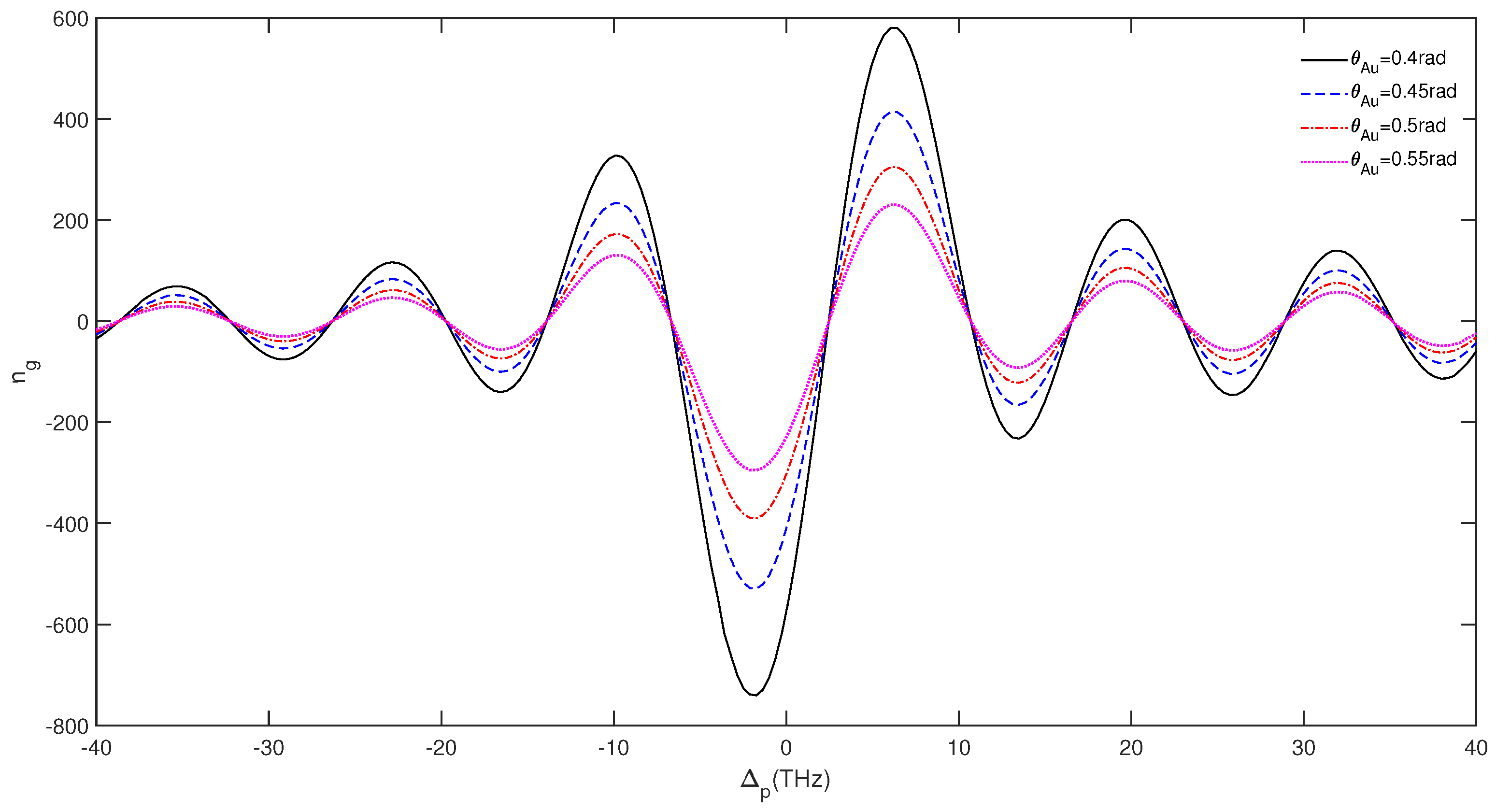
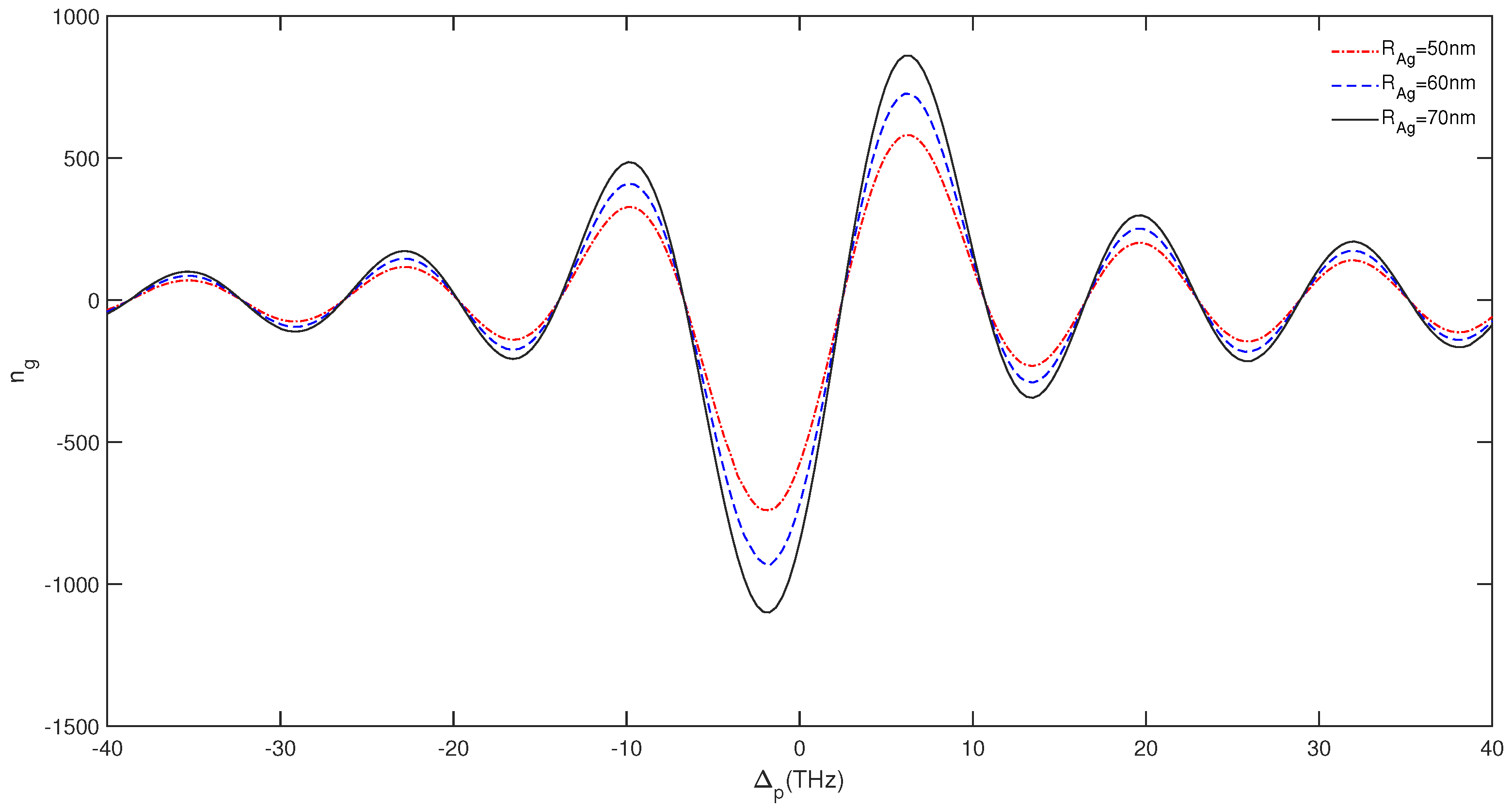
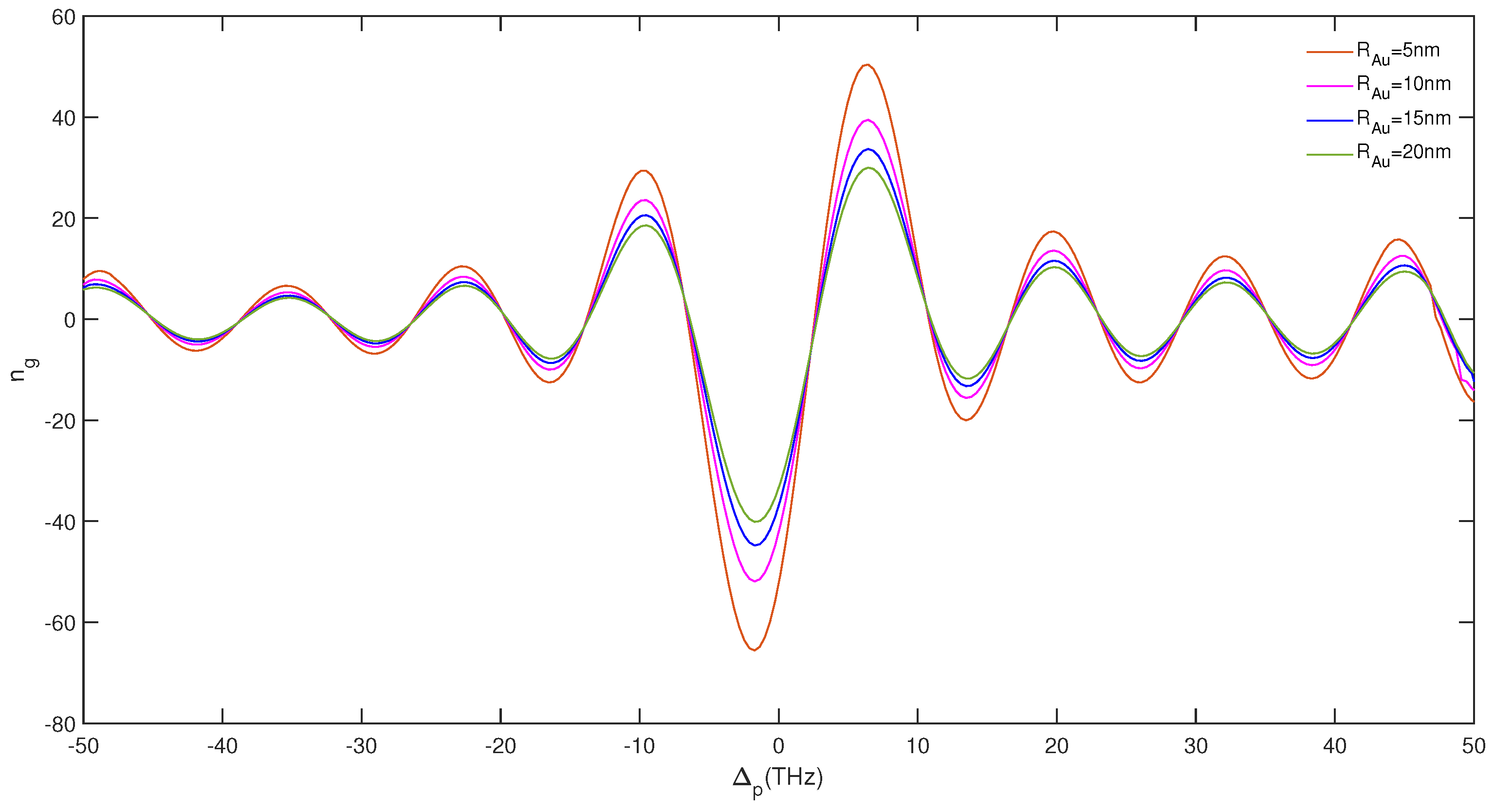
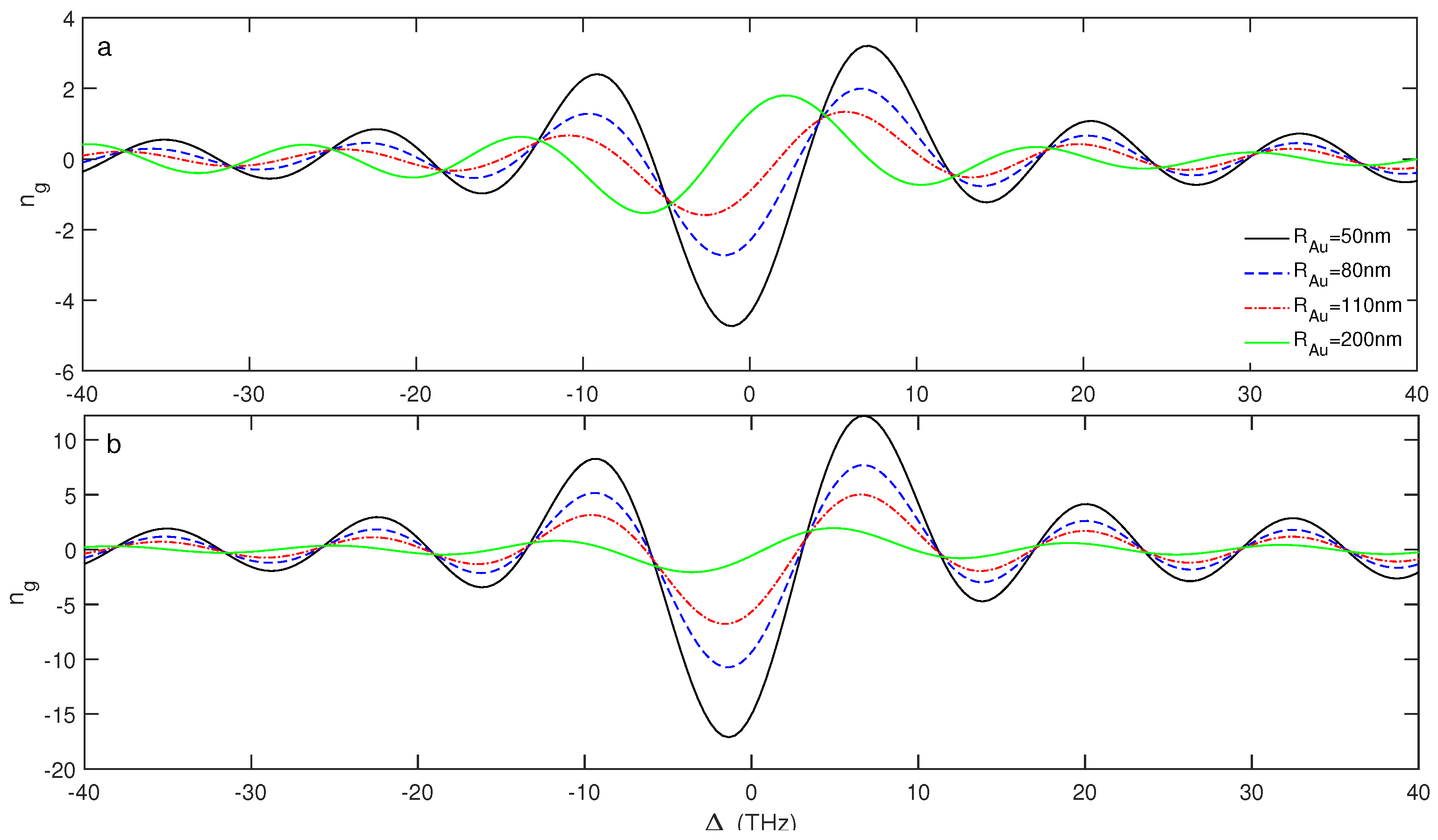
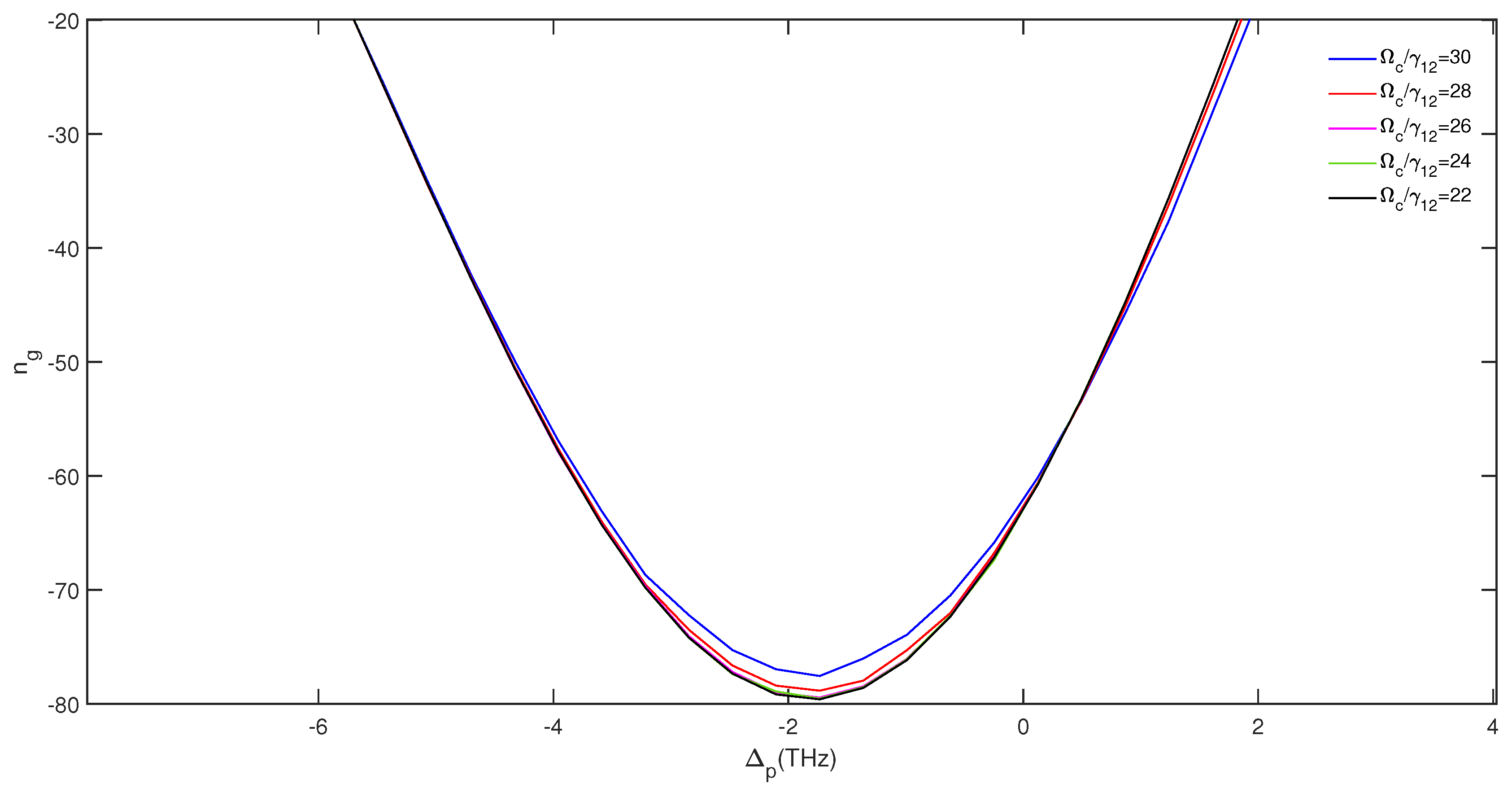
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mauriz, E.; Dey, P.; Lechuga, L.M. Advances in nanoplasmonic biosensors for clinical applications. Analyst 2019, 144, 7105–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, H.; Pishva, P.; Pehlivan, Z.S.; Arsoy, E.G.; Saleem, Q.; Bayazıt, M.K.; Yüce, M. Nanoplasmonic biosensors: Theory, structure, design, and review of recent applications. Analytica Chimica Acta 2021, 1185, 338842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cennamo, N.; Bossi, A.M.; Arcadio, F.; Maniglio, D.; Zeni, L. On the Effect of Soft Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles Receptors Combined to Nanoplasmonic Probes for Biomedical Applications. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2021, 9, 801489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi, S.M.; Örtegren, J.; Bayati, M.S.; Ram, S.B. A multipurpose and highly-compact plasmonic filter based on metal-insulator-metal waveguides. IEEE Photonics Journal 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.; Kumar, A.; Adhikari, R.; Saini, R.K.; Chang, S.H.; Dwivedi, R.P. High performance vanadium dioxide based active nano plasmonic filter and switch. Optik 2021, 225, 165672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaat, S.K.; Musleh, H.; Asad, J.; Shurrab, N.; Issa, A.; AlKahlout, A.; Al Dahoudi, N. Nanoplasmonic for Solar Energy Conversion Devices. In Solar Cells; IntechOpen, 2019.
- Wang, M.; Ye, M.; Iocozzia, J.; Lin, C.; Lin, Z. Plasmon-mediated solar energy conversion via photocatalysis in noble metal/semiconductor composites. Advanced Science 2016, 3, 1600024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, K.M.; Hafner, J.H. Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chemical reviews 2011, 111, 3828–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Williams, R.T. Excitonic and photonic processes in materials; Springer, 2015.
- Yu, H.; Peng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.Y. Plasmon-enhanced light–matter interactions and applications. npj Computational Materials 2019, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaponenko, S.V. Introduction to nanophotonics; Cambridge University Press, 2010.
- Remesh, V. Spectral phase control of nanoscale nonlinear optical responses 2020.
- Khurgin, J.B.; Boltasseva, A. Reflecting upon the losses in plasmonics and metamaterials. MRS bulletin 2012, 37, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, H.S. Quantum dots and nanocomposites. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology 2010, 2, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riel, B. An introduction to self-assembled quantum dots. American Journal of Physics 2008, 76, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koole, R.; Groeneveld, E.; Vanmaekelbergh, D.; Meijerink, A.; de Mello Donegá, C. Size effects on semiconductor nanoparticles. Nanoparticles: Workhorses of Nanoscience 2014, pp. 13–51.
- Singh, M.R.; Schindel, D.G.; Hatef, A. Dipole-dipole interaction in a quantum dot and metallic nanorod hybrid system. Applied Physics Letters 2011, 99, 181106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, T. Electromagnetically induced grating in semiconductor quantum dot and metal nanoparticle hybrid system by considering nonlocality effects. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Physics 2020, 14, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J. Fano resonance induced fast to slow light in a hybrid semiconductor quantum dot and metal nanoparticle system. Laser Physics Letters 2020, 17, 025201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasa, P. Exciton-surface plasmon polariton interactions. Advances in Physics: X 2020, 5, 1749884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapuarachchi, H.; Premaratne, M.; Bao, Q.; Cheng, W.; Gunapala, S.D.; Agrawal, G.P. Cavity QED analysis of an exciton-plasmon hybrid molecule via the generalized nonlocal optical response method. Physical Review B 2017, 95, 245419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.C.; Kim, N.C.; Choe, S.I.; So, G.H.; Jang, P.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, I.G.; Li, J.B. Plasmonic effect on the optical properties in a hybrid V-Type three-level quantum dot-metallic nanoparticle nanosystem. Plasmonics 2018, 13, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Insights into Fano-type resonance fluorescence from quantum-dot–metal-nanoparticle molecules with a squeezed vacuum. Physical Review A 2021, 104, 013717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Nisika, N.; Kumar, M. Modified absorption and emission properties leading to intriguing applications in plasmonic–excitonic nanostructures. Advanced Optical Materials 2021, 9, 2001150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, A.; Bashir, A.I.; Khan, N.; Hayat, S.S. Quantum coherence-enhanced optical properties and drag of photons and SPPs in semiconducting quantum dots and resonantly-coupled dot–nanoparticle plasmonic interfaces. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 2023, 172, 111088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Qi, Y.; Niu, Y.; Gong, S. Surface plasmon-assisted optical bistability in the quantum dot-metal nanoparticle hybrid system. Journal of Modern Optics 2016, 63, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buk, V.; Pemble, M.E.; Twomey, K. Fabrication and evaluation of a carbon quantum dot/gold nanoparticle nanohybrid material integrated onto planar micro gold electrodes for potential bioelectrochemical sensing applications. Electrochimica Acta 2019, 293, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajender, G.; Choudhury, B.; Giri, P. In situ decoration of plasmonic Au nanoparticles on graphene quantum dots-graphitic carbon nitride hybrid and evaluation of its visible light photocatalytic performance. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 395703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapuarachchi, H.; Mallawaarachchi, S.; Hattori, H.T.; Zhu, W.; Premaratne, M. Optoelectronic figure of merit of a metal nanoparticle—quantum dot (mnp-qd) hybrid molecule for assessing its suitability for sensing applications. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2018, 30, 054006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Yadav, R.; Verma, S.; Kaur, M.; Singh, B.P.; Husale, S. Au-Nanoislands and Quantum Dots growth on Flexible Light weight MWCNTs paper exhibiting SEM resolution and NIR photodetecting capabilities. Carbon Trends 2023, 10, 100241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, M.A.; Abdoos, H. A critical review on quantum dots: From synthesis toward applications in electrochemical biosensors for determination of disease-related biomolecules. Talanta 2021, 224, 121828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohari, M.M.; Lyras, A.; AlSalhi, M.S. Giant Self-Kerr Nonlinearity in the Metal Nanoparticles-Graphene Nanodisks-Quantum Dots Hybrid Systems Under Low-Intensity Light Irradiance. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohari, M.M. Near-infrared switching between slow and fast light in the metal nanoparticles-graphene nanodisks-quantum dots hybrid systems. Physica Scripta 2022, 97, 045808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.A.; Scherer, N.F.; Pelton, M.; Gray, S.K. Ultrafast reversal of a Fano resonance in a plasmon-exciton system. Physical Review B 2013, 88, 075411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W. Sub-Poissonian photon statistics in quantum dot-metal nanoparticles hybrid system with gain media. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 10088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, M.J. The Study of Nano-Optics in Hybrid Systems. PhD thesis, The University of Western Ontario (Canada), 2016.
- Bitton, O.; Gupta, S.N.; Haran, G. Quantum dot plasmonics: from weak to strong coupling. Nanophotonics 2019, 8, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambropoulos, P. Fundamentals of quantum optics and quantum information; Springer, 2007.
- Rioux, D.; Vallières, S.; Besner, S.; Muñoz, P.; Mazur, E.; Meunier, M. An analytic model for the dielectric function of Au, Ag, and their alloys. Advanced Optical Materials 2014, 2, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Pons, T.; Medintz, I.L.; Mattoussi, H. Biosensing with luminescent semiconductor quantum dots. Sensors 2006, 6, 925–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.K.; Thyrrestrup, H.; Mørk, J.; Tromborg, B. Numerical investigation of electromagnetically induced transparency in a quantum dot structure. Optics express 2007, 15, 6396–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.S.; Chiu, K.P.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.H.; Yuan, C.T. Modification of spontaneous emission rates of self-assembled CdSe quantum dots by coupling to hybrid optical nanoantennas. Plasmonics 2017, 12, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.C.; Luo, Y.L.; Hsu, H.Y. 7 Redox-Triggered, Biocompatible, Inorganic Nanoplatforms for Cancer Theranostics. Biological and Pharmaceutical Applications of Nanomaterials 2015, p. 171.
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.Y. Near-infrared-responsive cancer photothermal and photodynamic therapy using gold nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohari, M.M.; Alqahtani, M.M. Gain without population inversion and superluminal propagation in the metal nanoparticles-graphene nanodisks-quantum dots hybrid systems. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2021, 33, 325302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



