Submitted:
14 November 2023
Posted:
16 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The basic science of retinoids
2.1. Discovery of vitamin A and its utility as a cancer treatment
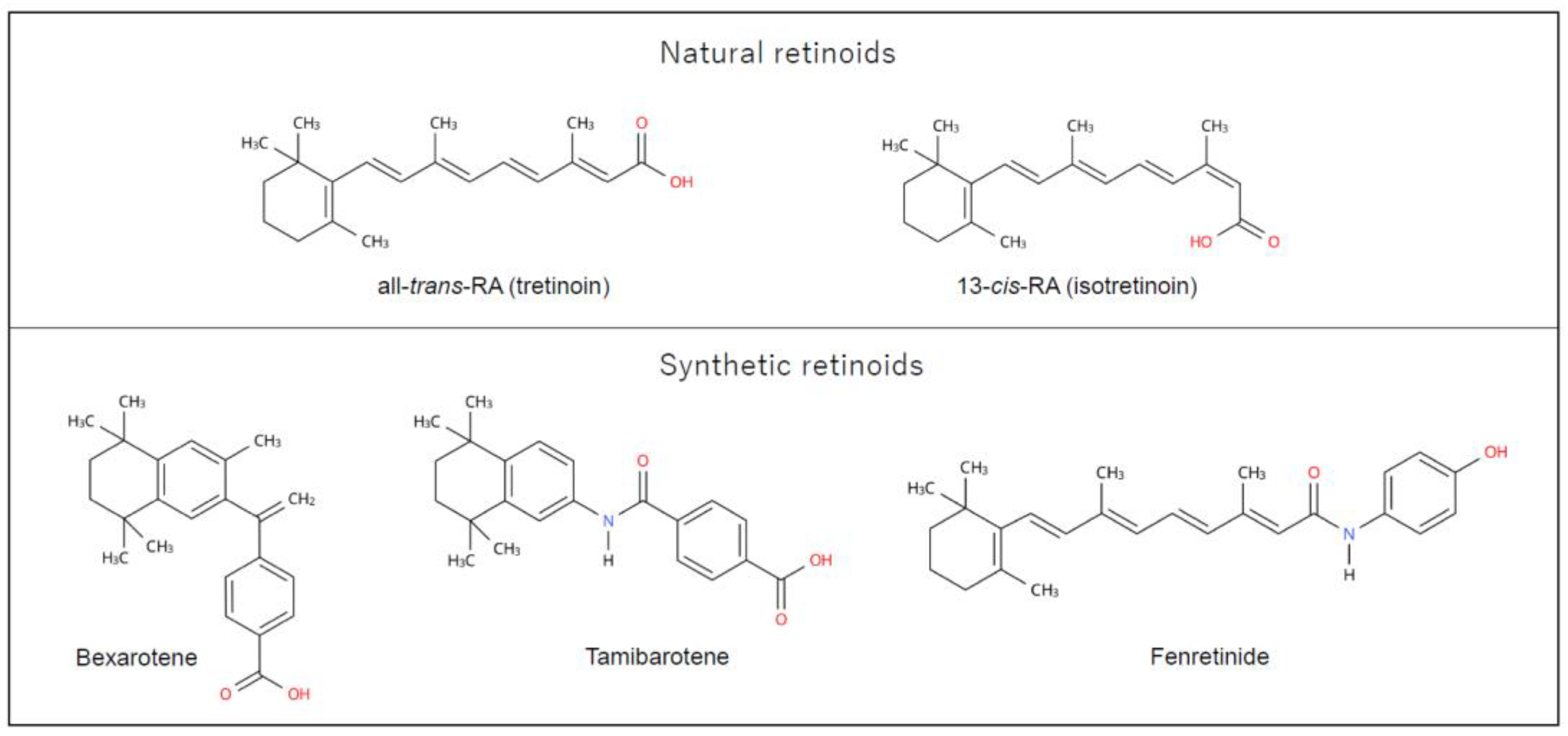
2.2. Retinoid chemistry
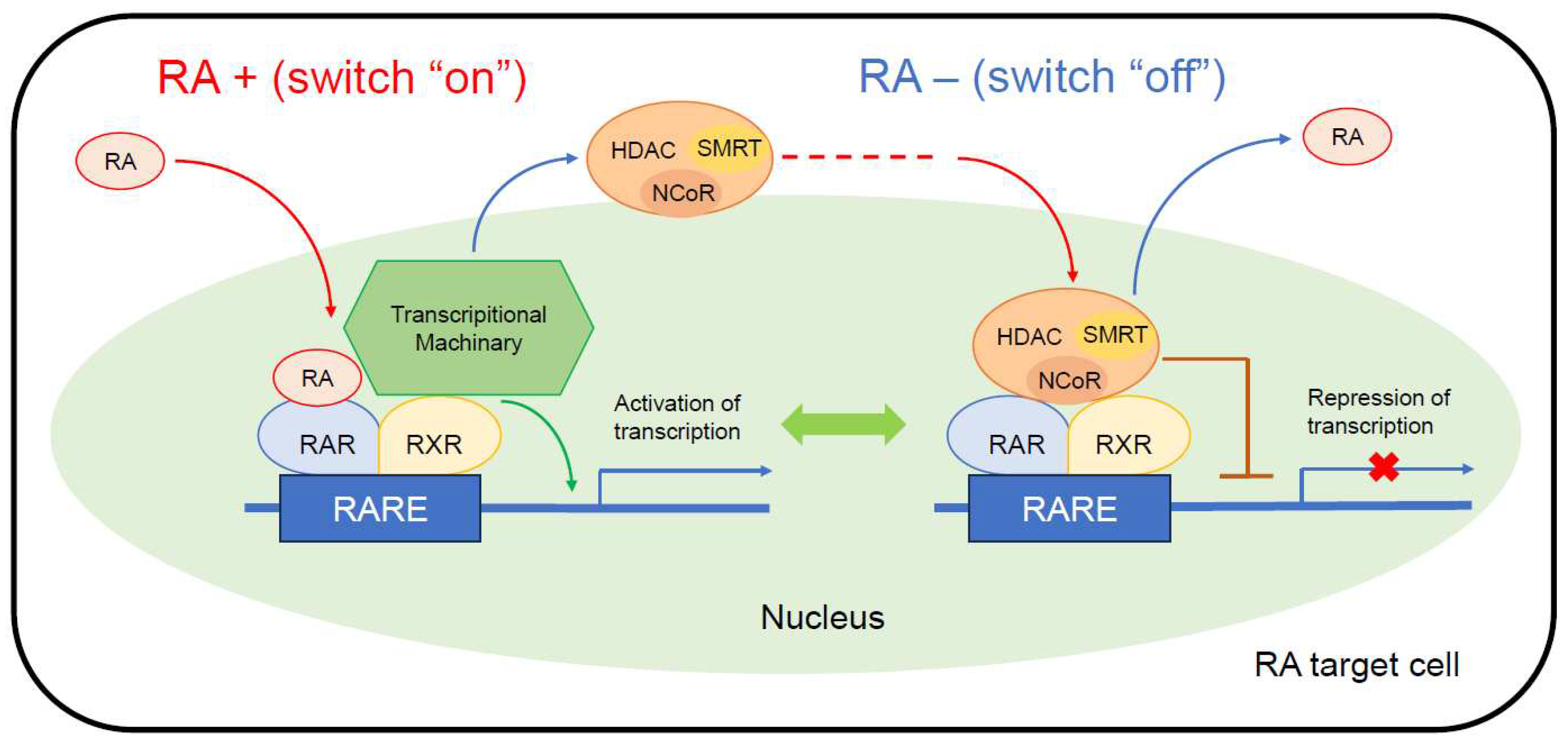
2.3. Retinoid receptors and their signal pathways
3. Preclinical evaluation of retinoids for neuroblastoma treatment
4. Clinical development of isotretinoin for neuroblastoma
5. Pharmacokinetic issues and countermeasures
6. Pediatric off-label use and countermeasures
7. Prospects for retinoid therapy
8. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ward, E.; DeSantis, C.; Robbins, A.; Kohler, B.; Jemal, A. Childhood and Adolescent Cancer Statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 83–103. [CrossRef]
- Okawa, S.; Saika, K. International Variations in Neuroblastoma Incidence in Children and Adolescents. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 52, 656–658. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.R.; Hogarty; Bagatell, R.; Schleiermacher, G.; Mosse, Y.P.; Maris; J M Neuroblastoma. In Pizzo and Poplack’s Pediatric Oncology; Blaney, S.M., Adamson, P.C., Helman, L.J., Ed.; Wolters Kluwer, 2021; pp. 647–672.
- Cohn, S.L.; Pearson, A.D.J.; London, W.B.; Monclair, T.; Ambros, P.F.; Brodeur, G.M.; Faldum, A.; Hero, B.; Iehara, T.; Machin, D.; et al. The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) Classification System: An INRG Task Force Report. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 289–297. [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.L.; Gilman, A.L.; Ozkaynak, M.F.; London, W.B.; Kreissman, S.G.; Chen, H.X.; Smith, M.; Anderson, B.; Villablanca, J.G.; Matthay, K.K.; et al. Anti-GD2 Antibody with GM-CSF, Interleukin-2, and Isotretinoin for Neuroblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1324–1334. [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.L.; Gilman, A.L.; Ozkaynak, M.F.; Naranjo, A.; Diccianni, M.B.; Gan, J.; Hank, J.A.; Batova, A.; London, W.B.; Tenney, S.C.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of a Phase III Study of Ch14.18 (Dinutuximab) + Cytokine Immunotherapy in Children with High-Risk Neuroblastoma: COG Study ANBL0032. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2179–2189. [CrossRef]
- Sidell, N. Retinoic Acid-Induced Growth Inhibition and Morphologic Differentiation of Human Neuroblastoma Cells in Vitro. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1982, 68, 589–596. [CrossRef]
- Sidell, N.; Altman, A.; Haussler, M.R.; Seeger, R.C. Effects of Retinoic Acid (RA) on the Growth and Phenotypic Expression of Several Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Exp. Cell Res. 1983, 148, 21–30. [CrossRef]
- Haussler, M.; Sidell, N.; Kelly, M.; Donaldson, C.; Altman, A.; Mangelsdorf, D. Specific High-Affinity Binding and Biologic Action of Retinoic Acid in Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1983, 80, 5525–5529. [CrossRef]
- Thiele, C.J.; Reynolds, C.P.; Israel, M.A. Decreased Expression of N-Myc Precedes Retinoic Acid-Induced Morphological Differentiation of Human Neuroblastoma. Nature 1985, 313, 404–406. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.P.; Kane, D.J.; Einhorn, P.A.; Matthay, K.K.; Crouse, V.L.; Wilbur, J.R.; Shurin, S.B.; Seeger, R.C. Response of Neuroblastoma to Retinoic Acid in Vitro and in Vivo. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1991, 366, 203–211.
- Reynolds, C.P.; Schindler, P.F.; Jones, D.M.; Gentile, J.L.; Proffitt, R.T.; Einhorn, P.A. Comparison of 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid to Trans-Retinoic Acid Using Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1994, 385, 237–244.
- Finklestein, J.Z.; Krailo, M.D.; Lenarsky, C.; Ladisch, S.; Blair, G.K.; Reynolds, C.P.; Sitarz, A.L.; Hammond, G.D. 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid (NSC 122758) in the Treatment of Children with Metastatic Neuroblastoma Unresponsive to Conventional Chemotherapy: Report from the Childrens Cancer Study Group. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1992, 20, 307–311. [CrossRef]
- Villablanca, J.G.; Khan, A.A.; Avramis, V.I.; Seeger, R.C.; Matthay, K.K.; Ramsay, N.K.; Reynolds, C.P. Phase I Trial of 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid in Children with Neuroblastoma Following Bone Marrow Transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 894–901. [CrossRef]
- Matthay, K.K.; Villablanca, J.G.; Seeger, R.C.; Stram, D.O.; Harris, R.E.; Ramsay, N.K.; Swift, P.; Shimada, H.; Black, C.T.; Brodeur, G.M.; et al. Treatment of High-Risk Neuroblastoma with Intensive Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy, Autologous Bone Marrow Transplantation, and 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid. Children’s Cancer Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1165–1173. [CrossRef]
- Matthay, K.K.; Reynolds, C.P.; Seeger, R.C.; Shimada, H.; Adkins, E.S.; Haas-Kogan, D.; Gerbing, R.B.; London, W.B.; Villablanca, J.G. Long-Term Results for Children with High-Risk Neuroblastoma Treated on a Randomized Trial of Myeloablative Therapy Followed by 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1007–1013. [CrossRef]
- di Masi, A.; Leboffe, L.; De Marinis, E.; Pagano, F.; Cicconi, L.; Rochette-Egly, C.; Lo-Coco, F.; Ascenzi, P.; Nervi, C. Retinoic Acid Receptors: From Molecular Mechanisms to Cancer Therapy. Mol. Aspects Med. 2015, 41, 1–115. [CrossRef]
- Karrer, P.; Morf, R. Pflanzenfarbstoffe XXXV. Zur Konstitution Des β-Carotins Und β-Dihydro-Carotins. Helv. Chim. Acta 1931, 14, 1033–1036. [CrossRef]
- Karrer, P.; Morf, R.; Schöpp, K. Zur Kenntnis Des Vitamins-A Aus Fischtranen. Helv. Chim. Acta 1931, 14, 1036–1040.
- Goodman, G.E.; Alberts, D.S.; Meyskens, F.L. Retinol, Vitamins, and Cancer Prevention: 25 Years of Learning and Relearning. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5495–5496. [CrossRef]
- Breitman, T.R.; Selonick, S.E.; Collins, S.J. Induction of Differentiation of the Human Promyelocytic Leukemia Cell Line (HL-60) by Retinoic Acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1980, 77, 2936–2940. [CrossRef]
- Breitman, T.R.; Collins, S.J.; Keene, B.R. Terminal Differentiation of Human Promyelocytic Leukemic Cells in Primary Culture in Response to Retinoic Acid. Blood 1981, 57, 1000–1004.
- Huang, M.E.; Ye, Y.C.; Chen, S.R.; Chai, J.R.; Lu, J.X.; Zhoa, L.; Gu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Y. Use of All-Trans Retinoic Acid in the Treatment of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia. Blood 1988, 72, 567–572.
- Fenaux, P.; Le Deley, M.C.; Castaigne, S.; Archimbaud, E.; Chomienne, C.; Link, H.; Guerci, A.; Duarte, M.; Daniel, M.T.; Bowen, D. Effect of All Transretinoic Acid in Newly Diagnosed Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia. Results of a Multicenter Randomized Trial. European APL 91 Group. Blood 1993, 82, 3241–3249.
- Gregory, J.; Kim, H.; Alonzo, T.; Gerbing, R.; Woods, W.; Weinstein, H.; Shepherd, L.; Schiffer, C.; Appelbaum, F.; Willman, C.; et al. Treatment of Children with Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: Results of the First North American Intergroup Trial INT0129. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 1005–1010. [CrossRef]
- Testi, A.M.; Biondi, A.; Lo Coco, F.; Moleti, M.L.; Giona, F.; Vignetti, M.; Menna, G.; Locatelli, F.; Pession, A.; Barisone, E.; et al. GIMEMA-AIEOPAIDA Protocol for the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL) in Children. Blood 2005, 106, 447–453. [CrossRef]
- Kutny, M.A.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Wang, Y.-C.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.A.; Fu, C.H.; Meshinchi, S.; Gamis, A.S.; Feusner, J.H.; et al. Arsenic Trioxide Consolidation Allows Anthracycline Dose Reduction for Pediatric Patients With Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: Report From the Children’s Oncology Group Phase III Historically Controlled Trial AAML0631. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3021–3029. [CrossRef]
- Kutny, M.A.; Alonzo, T.A.; Abla, O.; Rajpurkar, M.; Gerbing, R.B.; Wang, Y.-C.; Hirsch, B.A.; Raimondi, S.; Kahwash, S.; Hardy, K.K.; et al. Assessment of Arsenic Trioxide and All-Trans Retinoic Acid for the Treatment of Pediatric Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group AAML1331 Trial. JAMA Oncol 2022, 8, 79–87. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.P.; Lemons, R.S. Retinoid Therapy of Childhood Cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2001, 15, 867–910.
- Duvic, M.; Martin, A.G.; Kim, Y.; Olsen, E.; Wood, G.S.; Crowley, C.A.; Yocum, R.C.; Worldwide Bexarotene Study Group Phase 2 and 3 Clinical Trial of Oral Bexarotene (Targretin Capsules) for the Treatment of Refractory or Persistent Early-Stage Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Arch. Dermatol. 2001, 137, 581–593.
- Garaventa, A.; Luksch, R.; Lo Piccolo, M.S.; Cavadini, E.; Montaldo, P.G.; Pizzitola, M.R.; Boni, L.; Ponzoni, M.; Decensi, A.; De Bernardi, B.; et al. Phase I Trial and Pharmacokinetics of Fenretinide in Children with Neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2032–2039.
- Children’s Oncology Group (CCG 09709); Villablanca, J.G.; Krailo, M.D.; Ames, M.M.; Reid, J.M.; Reaman, G.H.; Reynolds, C.P. Phase I Trial of Oral Fenretinide in Children with High-Risk Solid Tumors: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group (CCG 09709). J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3423–3430. [CrossRef]
- Villablanca, J.G.; London, W.B.; Naranjo, A.; McGrady, P.; Ames, M.M.; Reid, J.M.; McGovern, R.M.; Buhrow, S.A.; Jackson, H.; Stranzinger, E.; et al. Phase II Study of Oral Capsular 4-Hydroxyphenylretinamide (4-HPR/Fenretinide) in Pediatric Patients with Refractory or Recurrent Neuroblastoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6858–6866. [CrossRef]
- Maurer, B.J.; Kang, M.H.; Villablanca, J.G.; Janeba, J.; Groshen, S.; Matthay, K.K.; Sondel, P.M.; Maris, J.M.; Jackson, H.A.; Goodarzian, F.; et al. Phase I Trial of Fenretinide Delivered Orally in a Novel Organized Lipid Complex in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Neuroblastoma: A Report from the New Approaches to Neuroblastoma Therapy (NANT) Consortium. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1801–1808. [CrossRef]
- Nitani, C.; Hara, J.; Kawamoto, H.; Taguchi, T.; Kimura, T.; Yoshimura, K.; Hamada, A.; Kitano, S.; Hattori, N.; Ushijima, T.; et al. Phase I Study of Tamibarotene Monotherapy in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients with Recurrent/Refractory Solid Tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 99–107. [CrossRef]
- Germain, P.; Staels, B.; Dacquet, C.; Spedding, M.; Laudet, V. Overview of Nomenclature of Nuclear Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 685–704. [CrossRef]
- Germain, P.; Chambon, P.; Eichele, G.; Evans, R.M.; Lazar, M.A.; Leid, M.; De Lera, A.R.; Lotan, R.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Gronemeyer, H. International Union of Pharmacology. LX. Retinoic Acid Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 712–725. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.P.; Matthay, K.K.; Villablanca, J.G.; Maurer, B.J. Retinoid Therapy of High-Risk Neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2003, 197, 185–192. [CrossRef]
- Rochette-Egly, C.; Germain, P. Dynamic and Combinatorial Control of Gene Expression by Nuclear Retinoic Acid Receptors (RARs). Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2009, 7, e005. [CrossRef]
- Al Tanoury, Z.; Piskunov, A.; Rochette-Egly, C. Vitamin A and Retinoid Signaling: Genomic and Nongenomic Effects. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1761–1775. [CrossRef]
- Dilworth, F.J.; Chambon, P. Nuclear Receptors Coordinate the Activities of Chromatin Remodeling Complexes and Coactivators to Facilitate Initiation of Transcription. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3047–3054. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Einhorn, P.A.; Reynolds, C.P. Expression of Retinoic Acid Receptors Alpha, Beta, and Gamma in Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1994, 385, 221–227.
- Cheung, B.; Hocker, J.E.; Smith, S.A.; Norris, M.D.; Haber, M.; Marshall, G.M. Favorable Prognostic Significance of High-Level Retinoic Acid Receptor Beta Expression in Neuroblastoma Mediated by Effects on Cell Cycle Regulation. Oncogene 1998, 17, 751–759.
- Girardi, C.S.; Rostirolla, D.C.; Lini, F.J.M.; Brum, P.O.; Delgado, J.; Ribeiro, C.T.; Teixeira, A.A.; Peixoto, D.O.; Heimfarth, L.; Kunzler, A.; et al. Nuclear RXRα and RXRβ Receptors Exert Distinct and Opposite Effects on RA-Mediated Neuroblastoma Differentiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 317–328. [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Liao, P.L.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, L.L.; Hsu, W.M.; Chuang, J.H. Immunomodulator Polyinosinic-Polycytidylic Acid Enhances the Inhibitory Effect of 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid on Neuroblastoma through a TLR3-Related Immunogenic-Apoptotic Response. Lab. Invest. 2020, 100, 606–618.
- Meseguer, S.; Escamilla, J.M.; Barettino, D. MiRNAs as Essential Mediators of the Actions of Retinoic Acid in Neuroblastoma Cells. In Neuroblastoma; Jones, M., Ed.; Hayle Medical: New Yolk, United States, 2015; pp. 281–297 ISBN 9789535111283.
- Otsuka, K.; Sasada, M.; Iyoda, T.; Nohara, Y.; Sakai, S.; Asayama, T.; Suenaga, Y.; Yokoi, S.; Higami, Y.; Kodama, H.; et al. Combining Peptide TNIIIA2 with All-Trans Retinoic Acid Accelerates N-Myc Protein Degradation and Neuronal Differentiation in MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma Cells. American Journal of Cancer Research 2019, 9, 434–448.
- Ferreira, R.; Napoli, J.; Enver, T.; Bernardino, L.; Ferreira, L. Advances and Challenges in Retinoid Delivery Systems in Regenerative and Therapeutic Medicine. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4265. [CrossRef]
- Kreissman, S.G.; Seeger, R.C.; Matthay, K.K.; London, W.B.; Sposto, R.; Grupp, S.A.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; Laquaglia, M.P.; Yu, A.L.; Diller, L.; et al. Purged versus Non-Purged Peripheral Blood Stem-Cell Transplantation for High-Risk Neuroblastoma (COG A3973): A Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 999–1008. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.R.; Kreissman, S.G.; London, W.B.; Naranjo, A.; Cohn, S.L.; Hogarty, M.D.; Tenney, S.C.; Haas-Kogan, D.; Shaw, P.J.; Kraveka, J.M.; et al. Effect of Tandem Autologous Stem Cell Transplant vs Single Transplant on Event-Free Survival in Patients With High-Risk Neuroblastoma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 322, 746–755.
- Kohler, J.A.; Imeson, J.; Ellershaw, C.; Lie, S.O. A Randomized Trial of 13-Cis Retinoic Acid in Children with Advanced Neuroblastoma after High-Dose Therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 1124–1127. [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Villablanca, J.G.; Reynolds, C.P.; Avramis, V.I. Pharmacokinetic Studies of 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid in Pediatric Patients with Neuroblastoma Following Bone Marrow Transplantation. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1996, 39, 34–41. [CrossRef]
- Veal, G.J.; Cole, M.; Errington, J.; Pearson, A.D.J.; Foot, A.B.M.; Whyman, G.; Boddy, A.V.; UKCCSG Pharmacology Working Group Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid (Isotretinoin) in Children with High-Risk Neuroblastoma - a Study of the United Kingdom Children’s Cancer Study Group. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 424–431.
- Veal, G.J.; Errington, J.; Rowbotham, S.E.; Illingworth, N.A.; Malik, G.; Cole, M.; Daly, A.K.; Pearson, A.D.J.; Boddy, A.V. Adaptive Dosing Approaches to the Individualization of 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid (Isotretinoin) Treatment for Children with High-Risk Neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 469–479. [CrossRef]
- Webster, G.F.; Leyden, J.J.; Gross, J.A. Comparative Pharmacokinetic Profiles of a Novel Isotretinoin Formulation (Isotretinoin-Lidose) and the Innovator Isotretinoin Formulation: A Randomized, 4-Treatment, Crossover Study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 762–767. [CrossRef]
- Madan, S.; Kumar, S.; Segal, J. Comparative Pharmacokinetic Profiles of a Novel Low-Dose Micronized-Isotretinoin 32 Mg Formulation and Lidose-Isotretinoin 40 Mg in Fed and Fasted Conditions: Two Open-Label, Randomized, Crossover Studies in Healthy Adult Participants. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00049. [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, P.; Cho, H.E.; Tagde, A.; Verlekar, D.; Yu, A.L.; Reynolds, C.P.; Kang, M.H. Metabolic Characteristics of 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid (Isotretinoin) and Anti-Tumour Activity of the 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid Metabolite 4-Oxo-13-Cis-Retinoic Acid in Neuroblastoma. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 5330–5344.
- Saitou, H.; Nakatani, D.; Myoui, A.; Kubota, T.; Ozono, K. Pediatric Drug Development in Japan: Current Issues and Perspectives. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 2020, 29, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, B.; Barry, E.; Fox, E.; Karres, D.; Kieran, M.; Manlay, J.; Ludwinski, D.; Reaman, G.; Kearns, P. The Critical Role of Academic Clinical Trials in Pediatric Cancer Drug Approvals: Design, Conduct, and Fit for Purpose Data for Positive Regulatory Decisions. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3456. [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.H.; Villablanca, J.G.; Glade Bender, J.L.; Matthay, K.K.; Groshen, S.; Sposto, R.; Czarnecki, S.; Ames, M.M.; Reynolds, C.P.; Marachelian, A.; et al. Probable Fatal Drug Interaction between Intravenous Fenretinide, Ceftriaxone, and Acetaminophen: A Case Report from a New Approaches to Neuroblastoma (NANT) Phase I Study. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 256.
- Shiohira, H.; Kitaoka, A.; Shirasawa, H.; Enjoji, M.; Nakashima, M. Am80 Induces Neuronal Differentiation in a Human Neuroblastoma NH-12 Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 26, 393–399. [CrossRef]
- Shiohira, H.; Kitaoka, A.; Enjoji, M.; Uno, T.; Nakashima, M. Am80 Induces Neuronal Differentiation via Increased Tropomyosin-Related Kinase B Expression in a Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cell Line. Biomed. Res. 2012, 33, 291–297. [CrossRef]
- Coffey, D.C.; Kutko, M.C.; Glick, R.D.; Swendeman, S.L.; Butler, L.; Rifkind, R.; Marks, P.A.; Richon, V.M.; LaQuaglia, M.P. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors and Retinoic Acids Inhibit Growth of Human Neuroblastoma in Vitro. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 2000, 35, 577–581.
- Coffey, D.C.; Kutko, M.C.; Glick, R.D.; Butler, L.M.; Heller, G.; Rifkind, R.A.; Marks, P.A.; Richon, V.M.; La Quaglia, M.P. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, CBHA, Inhibits Growth of Human Neuroblastoma Xenografts in Vivo, Alone and Synergistically with All-Trans Retinoic Acid. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3591–3594.
- De los Santos, M.; Zambrano, A.; Sánchez-Pacheco, A.; Aranda, A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Regulate Retinoic Acid Receptor Beta Expression in Neuroblastoma Cells by Both Transcriptional and Posttranscriptional Mechanisms. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 2416–2426.
- Pinto, N.; DuBois, S.G.; Marachelian, A.; Diede, S.J.; Taraseviciute, A.; Glade Bender, J.L.; Tsao-Wei, D.; Groshen, S.G.; Reid, J.M.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; et al. Phase I Study of Vorinostat in Combination with Isotretinoin in Patients with Refractory/Recurrent Neuroblastoma: A New Approaches to Neuroblastoma Therapy (NANT) Trial. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27023. [CrossRef]
- Zage, P.E.; Zeng, L.; Palla, S.; Fang, W.; Nilsson, M.B.; Heymach, J.V.; Zweidler-McKay, P.A. A Novel Therapeutic Combination for Neuroblastoma: The Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/Rearranged during Transfection Inhibitor Vandetanib with 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid. Cancer 2010, 116, 2465–2475.
- Cheung, B.B.; Tan, O.; Koach, J.; Liu, B.; Shum, M.S.Y.; Carter, D.R.; Sutton, S.; Po’uha, S.T.; Chesler, L.; Haber, M.; et al. Thymosin-Β4 Is a Determinant of Drug Sensitivity for Fenretinide and Vorinostat Combination Therapy in Neuroblastoma. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1484–1500. [CrossRef]
- Orienti, I.; Nguyen, F.; Guan, P.; Kolla, V.; Calonghi, N.; Farruggia, G.; Chorny, M.; Brodeur, G.M. A Novel Nanomicellar Combination of Fenretinide and Lenalidomide Shows Marked Antitumor Activity in a Neuroblastoma Xenograft Model. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 4305–4319. [CrossRef]
- Hattori, N.; Asada, K.; Miyajima, N.; Mori, A.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kimura, K.; Wakabayashi, M.; Takeshima, H.; Nitani, C.; Hara, J.; et al. Combination of a Synthetic Retinoid and a DNA Demethylating Agent Induced Differentiation of Neuroblastoma through Retinoic Acid Signal Reprogramming. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1647–1656. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




