Introduction
Signalized intersections represent key nodes within transportation networks where vehicles interact, and potential conflicts may arise [
1,
2,
3]. As urbanization continues to surge, the need for a deeper understanding of the dynamics governing vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) conflicts at these intersections becomes increasingly critical [
4]. This research study aims to contribute to the existing body of knowledge by focusing on a nuanced aspect often underexplored in traffic safety research—the angles of approach during V2V conflicts at signalized intersections. While past studies have primarily concentrated on factors such as traffic signal phasing, geometric design, and driver behavior [
4,
5,
6], the specific influence of angles of approach on conflict severity remains less explored. By investigating this intricate relationship, the research endeavors to unravel patterns, identify risk factors, and propose targeted interventions to enhance safety at signalized intersections.
The motivation for this study stems from the imperative to bridge existing gaps in understanding the complexities associated with V2V conflicts at signalized intersections. The ubiquity of these intersections in urban environments and their role in facilitating efficient traffic flow necessitate a comprehensive examination of the contributing factors to conflicts [
7,
8,
9,
10]. The investigation extends beyond traditional safety analyses and explores how the angles at which vehicles approach the intersection impact the severity of conflicts [
11,
12]. By undertaking this exploration, the research aims to inform evidence-based countermeasures and policy recommendations for mitigating conflict severity and fostering safer interactions among vehicles at signalized intersections. Hereupon, this study builds upon existing literature by incorporating LiDAR sensor technology [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17], a cutting-edge and precise measurement tool, to analyze the angles of approach during V2V conflicts at signalized intersections. While past research has predominantly relied on traditional methods, this research pioneers the integration of LiDAR technology to provide a more granular examination of vehicle interactions, offering insights into the spatial and temporal dimensions of conflicts. By leveraging the capabilities of LiDAR sensors, this research aims to uncover patterns, and assess risks, for enhancing safety at signalized intersection.
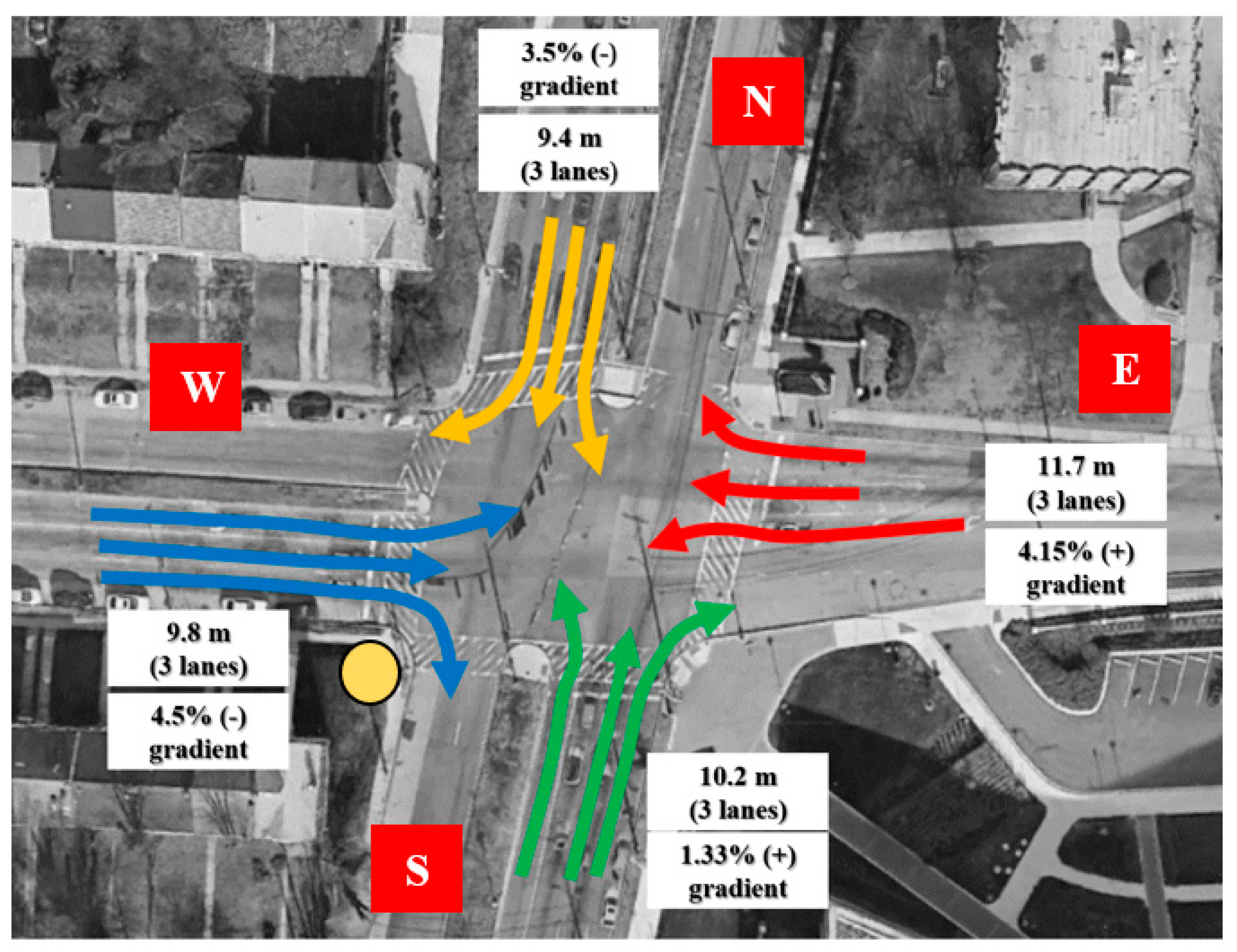
The intersection of E Cold Spring Ln and Hillen Rd in Baltimore City, MD, USA was considered for the case study. V2V conflicts were analyzed on September 13
th, a day when the traffic signal stopped working due to an electrical issue [
15]. The traffic signal stopped working from 05:30 AM to 10:23 AM. This research aims to evaluate the effect of conflict's angle on severity of V2V conflicts in traffic signal failures condition.
Methodology
Assessing the impact of traffic signal failures on traffic volume, congestion, and delays at signalized intersections using LiDAR sensor technology can be taken into account as the key aspect of intelligent mobility. The LiDAR sensor at E Cold Spring Ln – Hillen Rd intersection was installed in April 2022 to collect real-time traffic data with an efficient accuracy [
3,
4,
10,
16]. LiDAR sensors can capture high-resolution, three-dimensional data of the intersection and its surroundings. The machine learning algorithms were utilized as explained in author’s previous studies [
17,
18] to clean and preprocess LiDAR data to remove noise and outliers, and align it with signal failure timestamps.
The research concentrated on failures in traffic signal operation and delved into driver behavior at a signalized intersection known for a high frequency of collisions. Utilizing data recorded by LiDAR sensor technology, the study specifically examined instances where signal-related light patterns (such as red, green, or yellow) were absent. The investigation involved a comprehensive analysis of vehicle trajectories, speeds, and lane changes during periods of signal failure, aiming to comprehend how traffic dynamics adapt in the absence of signal control. In this study, LiDAR sensor technology is strategically deployed to capture high-resolution spatial data during vehicular movements. LiDAR sensors are positioned at key locations at the intersection to ensure comprehensive coverage of the area. The author’s previous studies [
19,
20] highlighted the significant accuracy of LiDAR sensor to capture vehicle counts, pedestrian counts, and conflict’s frequency and severity. The sensor utilizes laser pulses emitted at regular intervals, measuring the time taken for the pulses to return after hitting surrounding objects. The resulting data is then processed to generate a detailed three-dimensional map of the intersection, including the positions and movements of vehicles. The LiDAR-generated three-dimensional map provides a wealth of information about the spatial coordinates of vehicles at any given point in time [
21,
22,
23]. To calculate the trajectories of individual vehicles, the study employs a mathematical model that leverages the sequential LiDAR scans. By comparing the spatial coordinates of a vehicle between consecutive scans, the study derives the displacement vectors (
) for each vehicle (i) (
Equation 1).
It is worth mentioning that (
) and (
) represent the spatial coordinates of the vehicle at two consecutive LiDAR scans. To calculate conflict’s angle, the primary focus of this study is to calculate the angles between the trajectories of vehicles involved in V2V conflicts. The angle (θ) between two displacement vectors (V1 and V2) is determined using the dot product equation as shown in
Equation 2:
Where, demonstrates the magnitudes of the vectors. Considering the trajectories of V2V conflicts in different intersection’s approaches, the angles of V2V conflicts were calculated. Understanding the angle of V2V conflicts at signalized intersections is paramount for comprehending the severity of these conflicts and, consequently, for developing effective strategies to enhance traffic safety. The angle at which vehicles approach each other during a potential conflict holds crucial implications for the severity of collision outcomes. A nuanced exploration of these angles provides insights into the dynamics of collision forces and impact vectors. For instance, a head-on collision, where vehicles approach each other at a narrow angle, is likely to result in more severe consequences than a conflict where vehicles approach at a wider angle. The importance of considering these angles lies in the fact that they significantly influence the direction and intensity of the forces involved in a collision, affecting the extent of damage and potential for injury. By investigating the role of angles in V2V conflicts at signalized intersections, this research aims to contribute valuable insights into the spatial dynamics of collisions, ultimately informing targeted interventions for mitigating the severity of these conflicts. Moreover, the study of angle-related severity in V2V conflicts is instrumental for refining traffic management strategies and intersection design. Traffic signals play a pivotal role in regulating the flow of vehicles and minimizing the potential for conflicts. Understanding how the angle of approach correlates with conflict severity enables the development of more effective signal timing algorithms and geometric designs that consider the spatial dynamics of potential collisions.
This study concentrates on E Cold Spring Ln – Hillen Rd intersection in Baltimore City, Maryland. The LiDAR data on September, 13
th 2023 was analyzed to provide a practical accurate understanding of the intersection safety conditions [
15].
Figure 1 shows the intersection’s location. The installation location of the LiDAR sensor is shown by the yellow circle.
The Research analyzed the traffic data from 05:30 AM to 10:23 AM on September 13
th. The signal controller stopped working from 05:30 AM to 10:23 AM on September 13
th. As a result of improper traffic signal performance for four hours and fifty-three minutes, the research examined the traffic condition at the intersection in a chaos condition (traffic signal failure).
Table 1 shows the vehicle counts during the chaos condition. During the chaos, 10612 vehicles passed through the intersection.
Table 2 shows the pedestrian counts during the chaos condition.
The V2V conflicts were separately examined based on the leading and following movements. In other words, in order to determine whether the leading or following movement was responsible for V2V conflicts, the angle of each movement was investigated. LiDAR sensor technology offers a sophisticated means to collect Post Encroachment Time (PET) values during V2V conflicts at signalized intersections [
24,
25,
26,
27]. The LiDAR sensor captures the elevation data by measuring the time it takes for the laser pulses to travel to an object and back. This temporal information is then converted into precise distance measurements, creating a three-dimensional representation of the surrounding environment. By continuously scanning the intersection area, LiDAR sensors generate real-time PET values, including the elevation and trajectory of each vehicle involved in V2V conflicts. The ability of LiDAR sensors to collect PET values is particularly advantageous for assessing V2V conflicts. These sensors can accurately measure the vertical separation between vehicles, offering insights into the potential for collisions based on elevation differences. The PET data can be used to quantify the severity of conflicts, considering factors such as the height of vehicles and the elevation of collision points. This information is crucial for developing targeted safety interventions and optimizing traffic signal control strategies. Basically, PET is determined by measuring the time gap between the point when a vehicle enters the intersection space after the signal turns red and the time when a conflicting vehicle approaches the intersection from an opposing direction.
When traditional signal control mechanisms falter, the temporal dynamics of vehicle movements become even more critical for assessing potential conflicts and enhancing overall safety. LiDAR sensors, equipped with the ability to precisely measure distances and capture temporal data, play a pivotal role in monitoring vehicle behavior during these periods of signal malfunction. By continuously scanning the intersection area, LiDAR sensors record the precise moment when a vehicle encroaches into the intersection space after the signal has failed, providing essential data for calculating PET values. The calculation of PET during signal failure involves determining the time gap between the unauthorized entry of a vehicle into the intersection space and the approach of a conflicting vehicle from an opposing direction.
Data Analysis
In the context of traffic safety, the angle of V2V conflicts assumes heightened importance, particularly during instances of traffic signal failure. When the conventional control mechanisms break down, the spatial dynamics and angles at which vehicles approach intersections become critical factors influencing the severity of potential conflicts. Understanding these angles is paramount as it sheds light on the potential impact vectors and collision forces involved in a V2V conflict. A head-on collision, resulting from vehicles approaching each other at a narrow angle, is more likely to lead to severe consequences than conflicts where vehicles approach at wider angles. Therefore, during signal failure, the study of these angles becomes a linchpin for evaluating the potential severity of conflicts and informing targeted interventions for mitigating associated risks.
The angle-related considerations are vital in the context of traffic safety during signal failure as they directly impact the outcomes of V2V conflicts. For instance, a conflict between vehicles approaching at a perpendicular angle may result in a glancing impact with lower collision forces, potentially leading to less severe consequences compared to a scenario where vehicles approach at a parallel angle, resulting in a more direct and forceful collision. This nuanced understanding of angles aids in assessing the degree of potential damage and injury during signal failure scenarios. Moreover, the significance of the angle of V2V conflicts during traffic signal failure is underscored by its impact on the effectiveness of traffic signal control strategies. Traditional signal-controlled intersections rely on a predictable and regulated flow of traffic, and signal failure disrupts this order. Understanding the angles at which vehicles approach the intersection during these disruptions becomes crucial for managing and mitigating potential conflicts. Traffic signals are designed to allocate right-of-way based on predetermined signal phases, and when this control is lost, vehicles may approach the intersection from unexpected angles, leading to unregulated conflicts. Furthermore, the angle of V2V conflicts during signal failure is instrumental in informing the design and placement of traffic signals and associated infrastructure. The traditional geometric layout of intersections assumes a regulated flow of traffic, and signalized intersections are configured based on these assumptions. However, during signal failure, vehicles may approach from unconventional angles, challenging the assumptions underlying the original design. By understanding the angles at which conflicts occur, it will be possible to refine intersection designs to account for these unpredictable scenarios, enhancing the overall resilience of signalized intersections. This adaptive approach ensures that the geometry of intersections aligns with the dynamic nature of traffic during signal failure, thereby contributing to improved safety outcomes.
To investigate the effect of each leading and following movement’s angle on the severity of V2V conflicts, the conflict’s angle in the near-crash timestamps for each conflicts were analyzed. It is worth mentioning that the severity of conflicts was calculated based on
values.
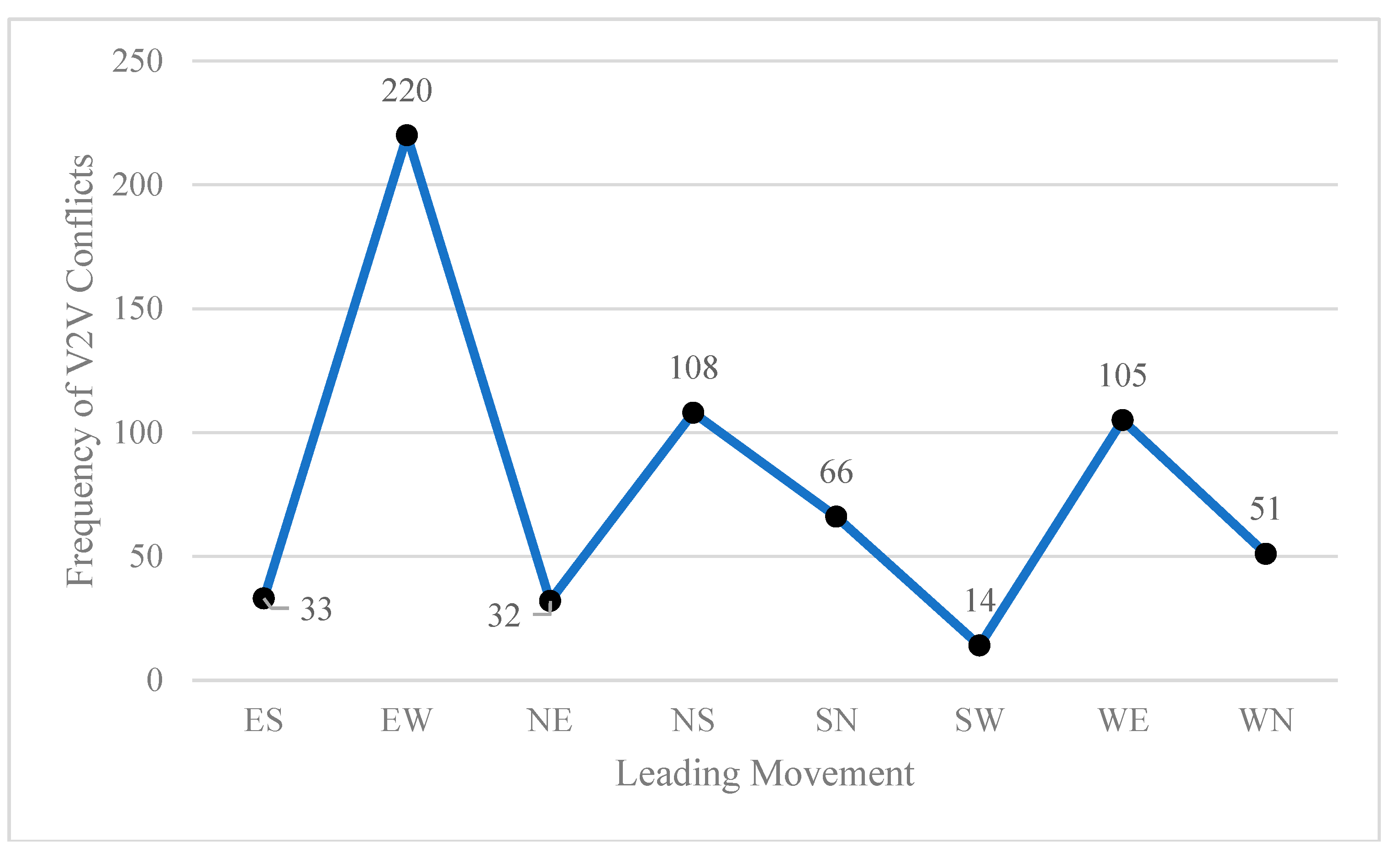
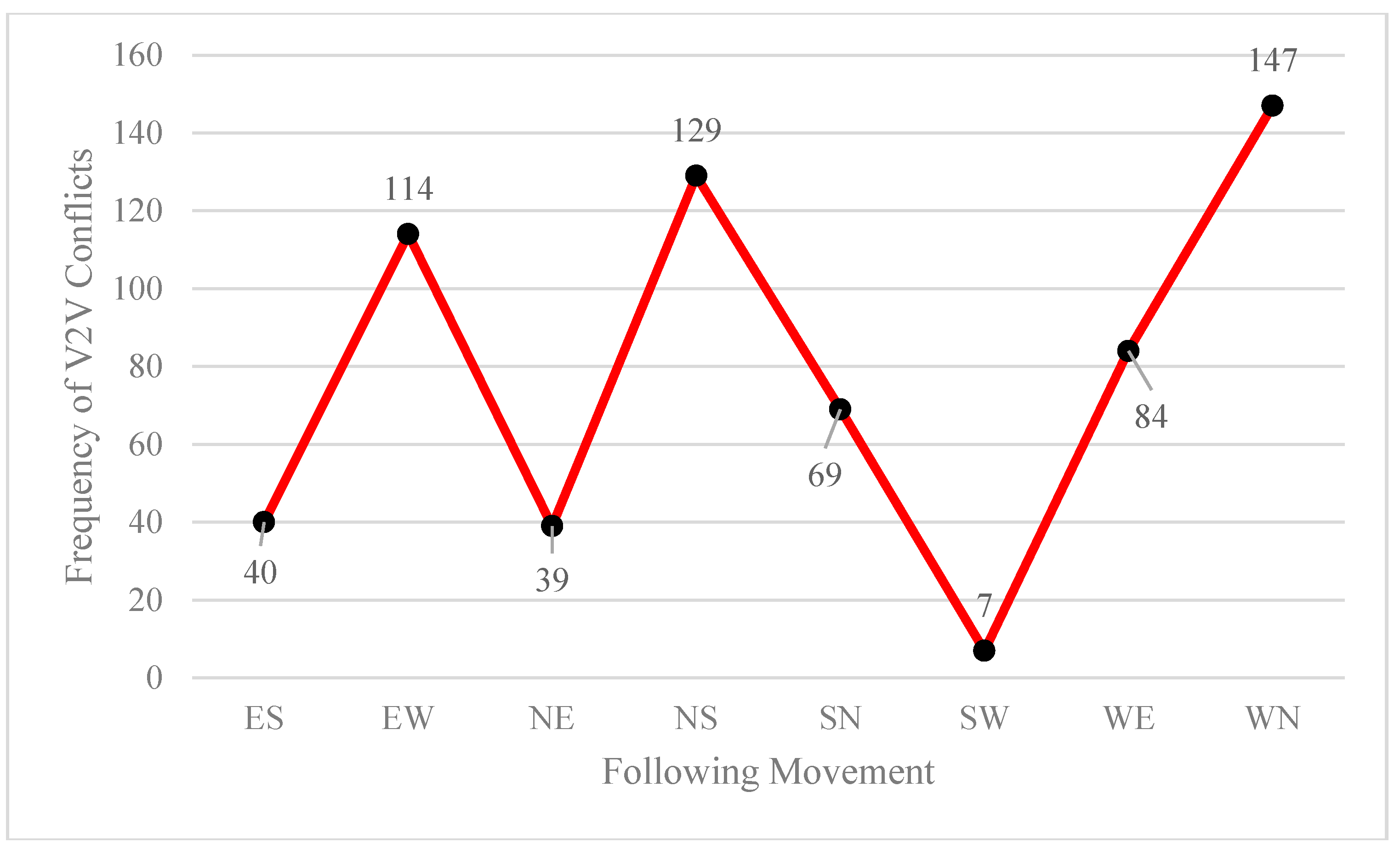
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 show the frequency of V2V conflicts based on leading and following movements during traffic signal failure interval.
As shown in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3, 35% of V2V conflicts occurred by leading movement EW (=Westbound straight through), and 23% of V2V conflicts occurred by following movement WN (=Eastbound left-turn). The leading and following movement’s conflicts were analyzed and the angle of each conflict at the conflict location at the intersection was calculated.
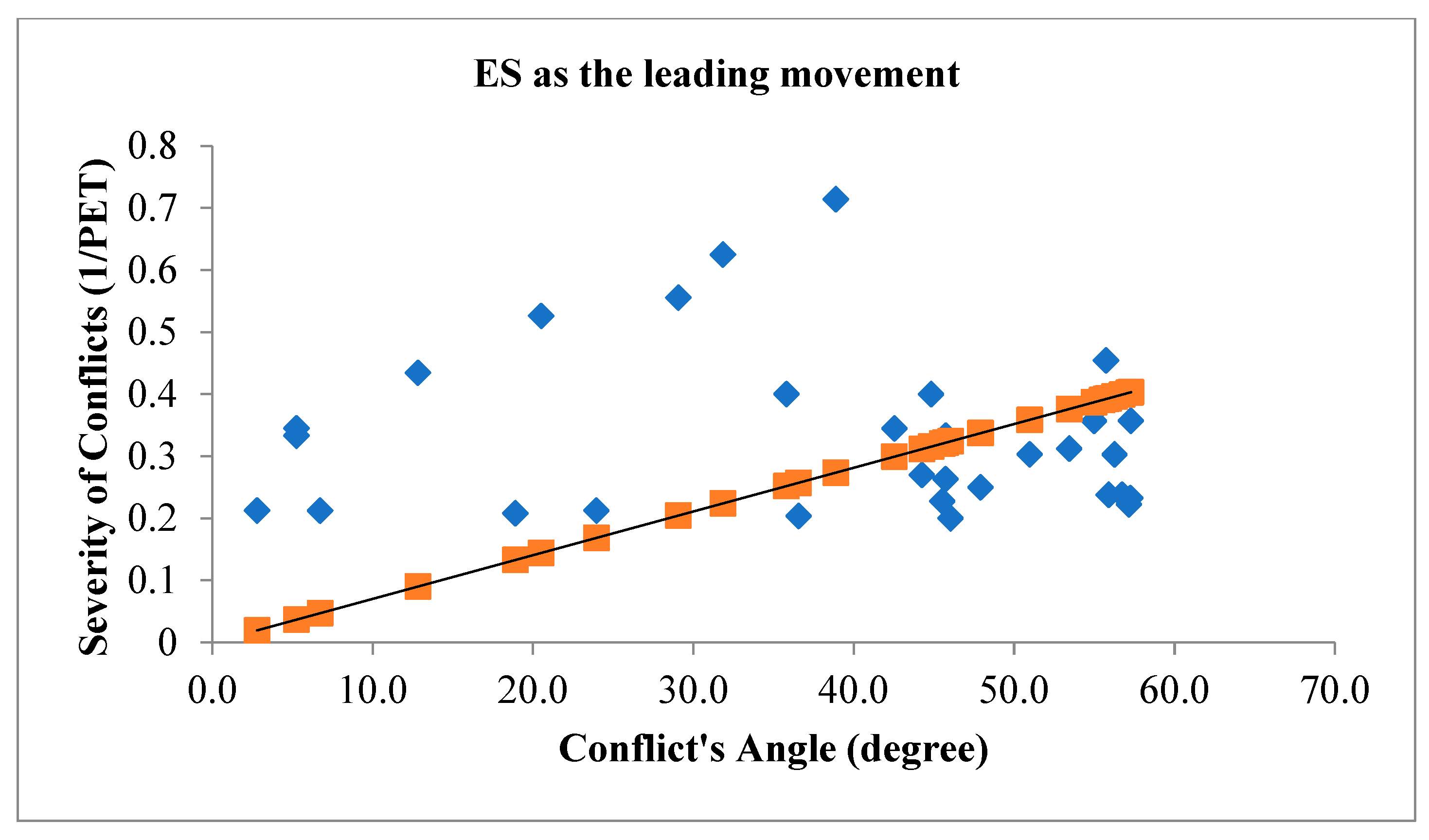
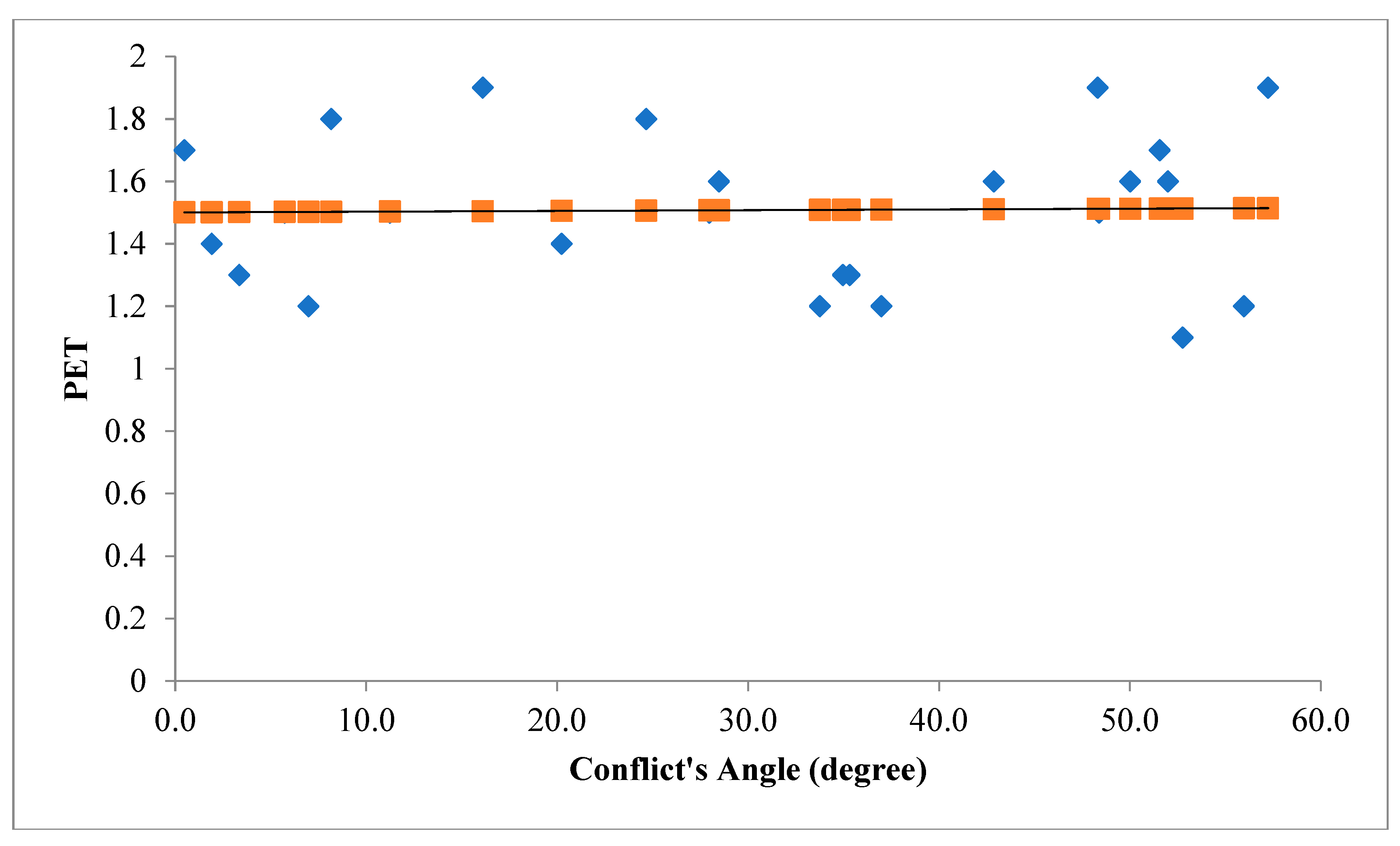
Figure 4 illustrates the angle of V2V conflicts when ES movement is the leading movement of the conflict (figure above) and when ES movement is the following movement of the conflict (figure below) with the severity of conflicts.
The orange line in
Figure 4 and the following figures shows the trend line of the conflict’s severity.
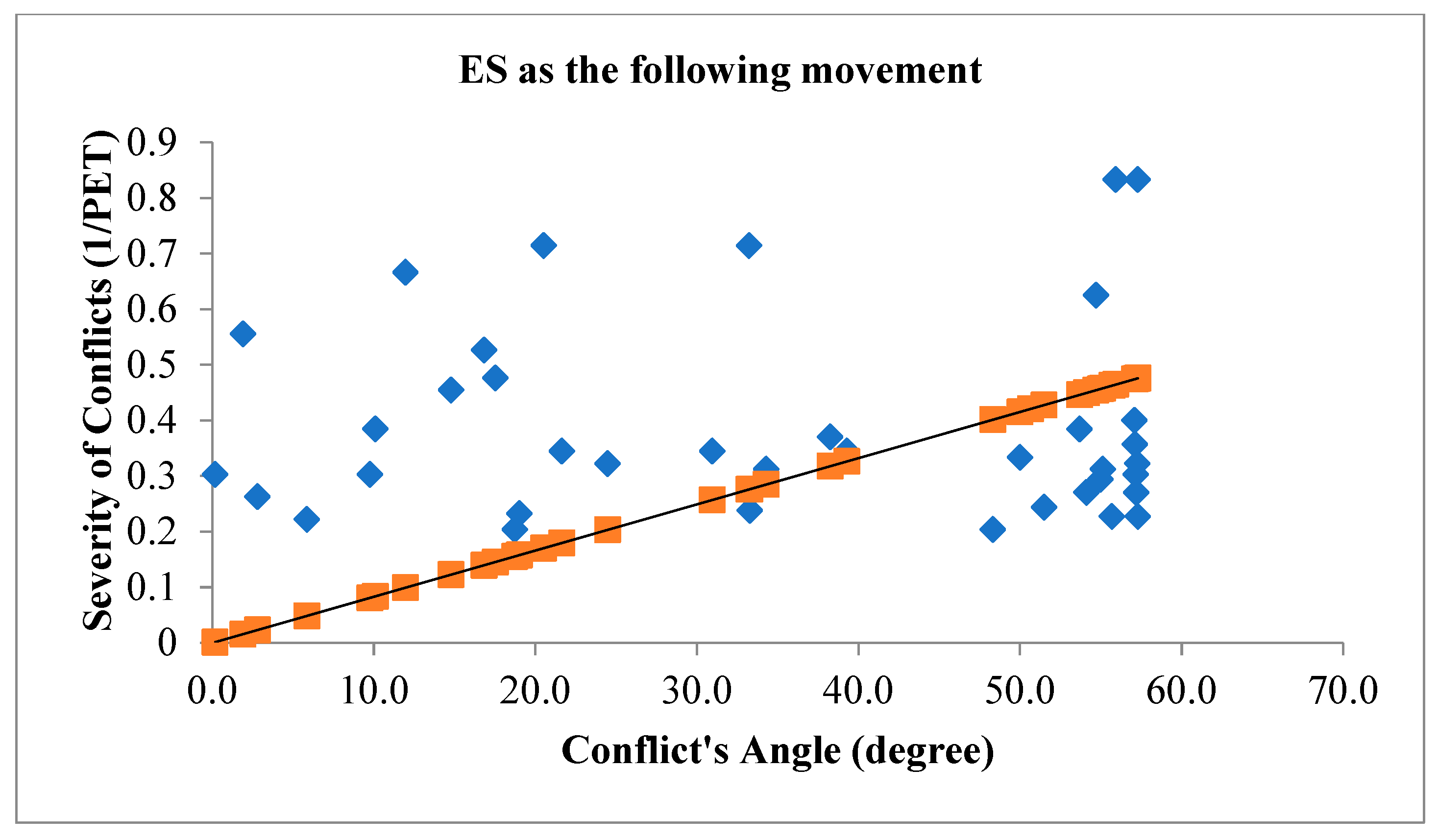
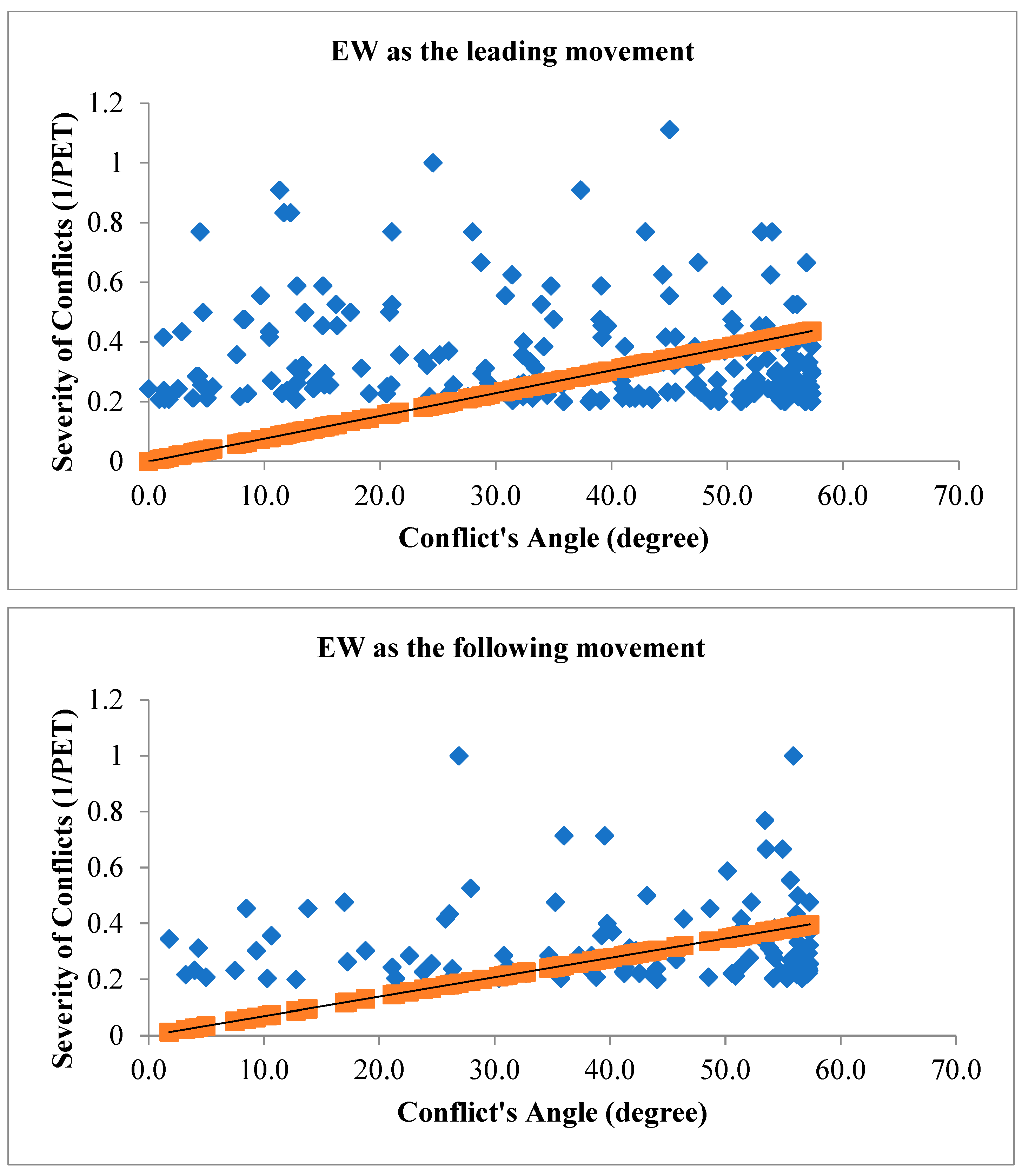
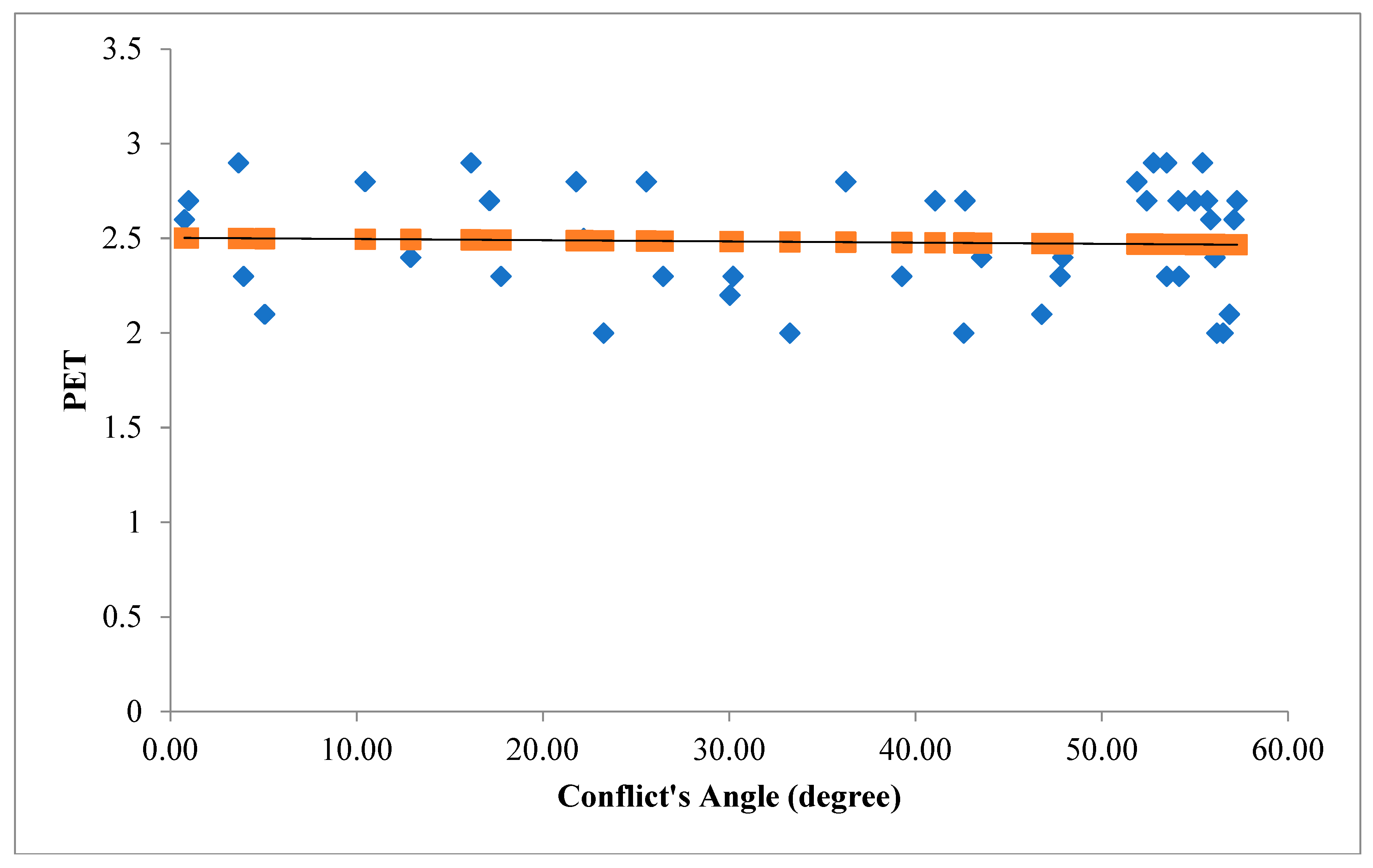
Figure 5 illustrates the angle of V2V conflicts when EW movement is the leading movement of the conflict (figure above) and when EW movement is the following movement of the conflict (figure below) with the severity of conflicts.
Figure 4.
Conflict's Angle based on ES as the leading movement (figure above) and ES as the following movement (figure below).
Figure 4.
Conflict's Angle based on ES as the leading movement (figure above) and ES as the following movement (figure below).
Figure 5.
Conflict's Angle based on EW as the leading movement (figure above) and EW as the following movement (figure below).
Figure 5.
Conflict's Angle based on EW as the leading movement (figure above) and EW as the following movement (figure below).
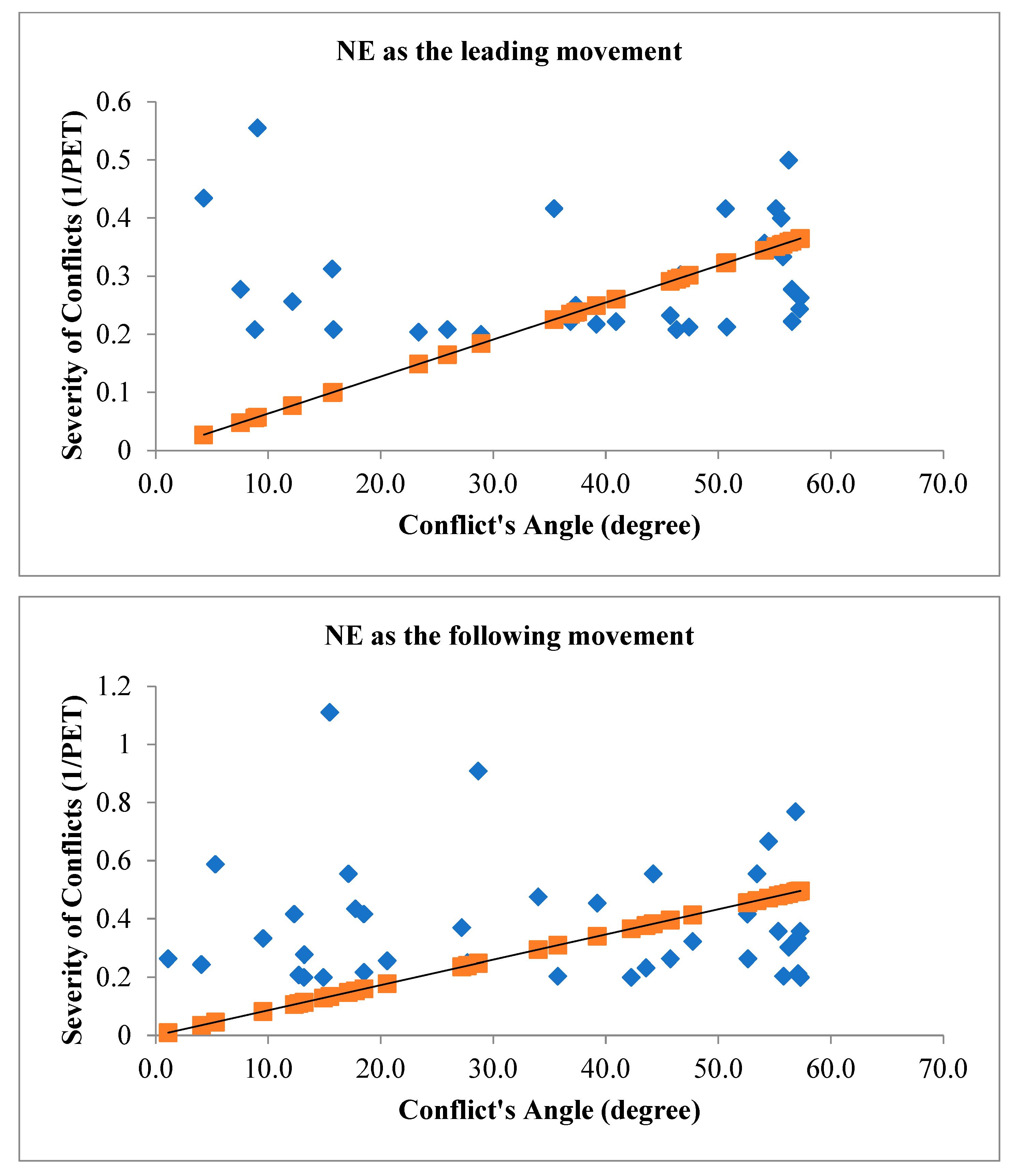
Figure 6 illustrates the angle of V2V conflicts when NE movement is the leading movement of the conflict (figure above) and when NE movement is the following movement of the conflict (figure below) with the severity of conflicts.
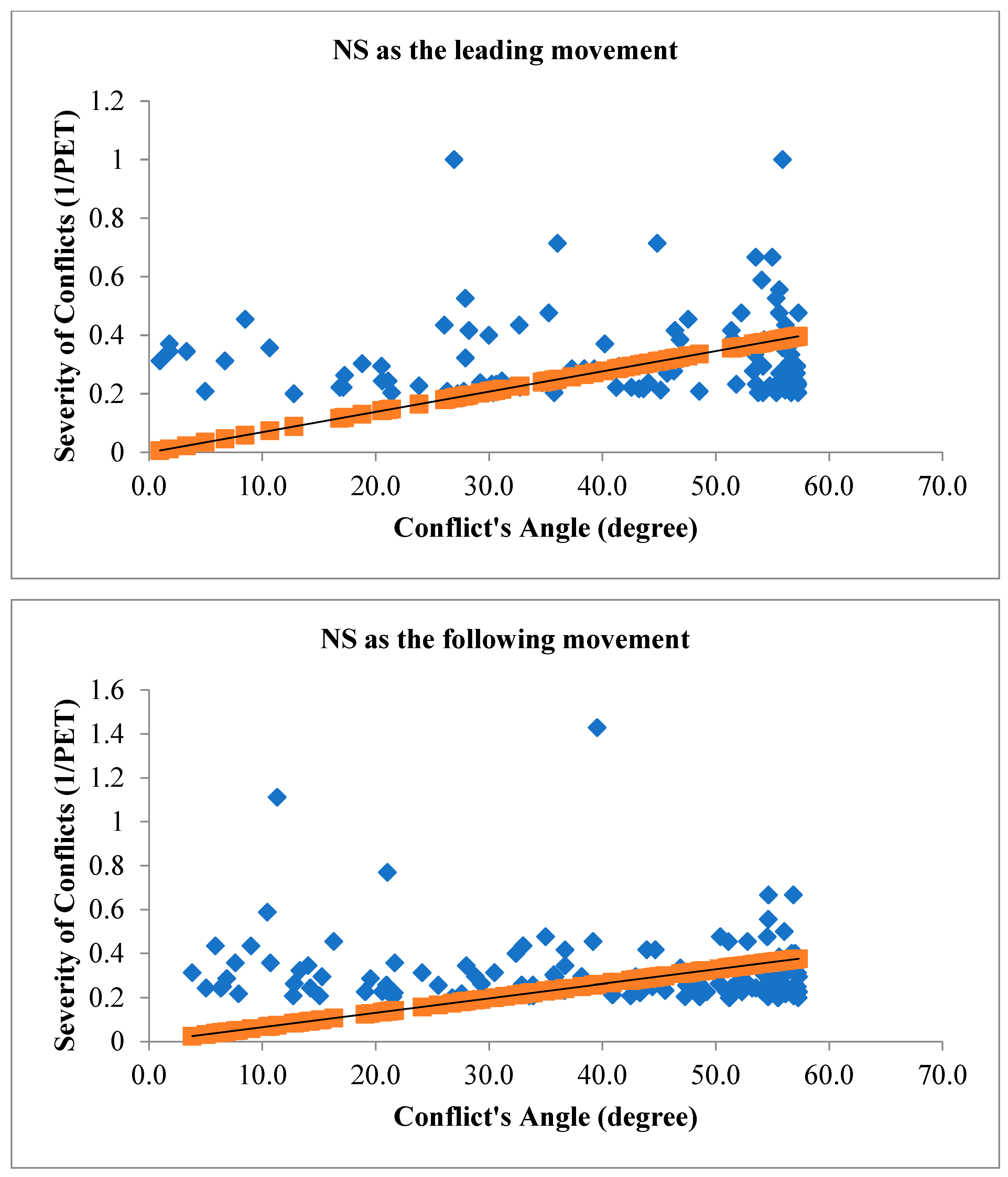
Figure 7 illustrates the angle of V2V conflicts when NS movement is the leading movement of the conflict (figure above) and when NS movement is the following movement of the conflict (figure below) with the severity of conflicts.
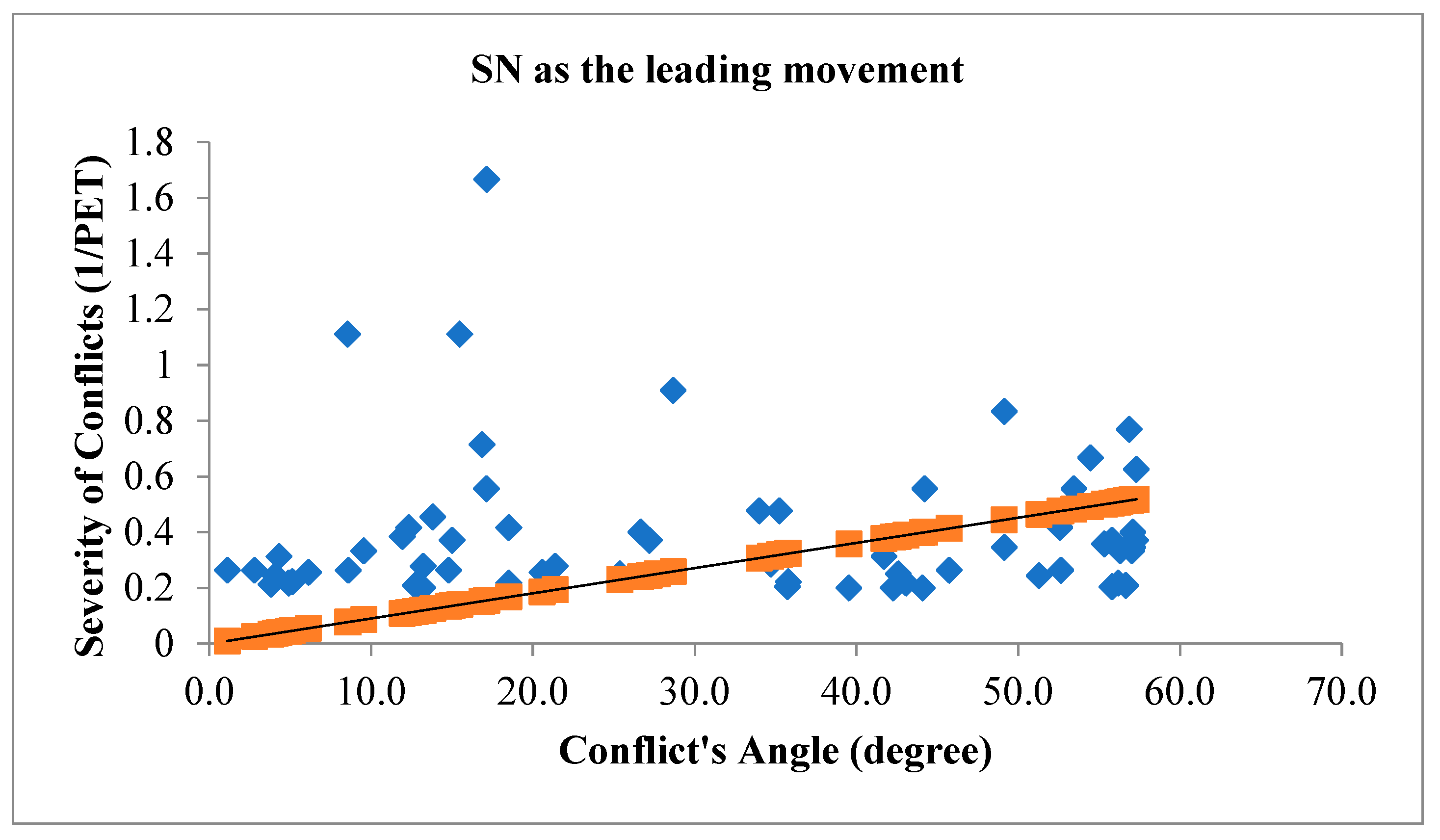
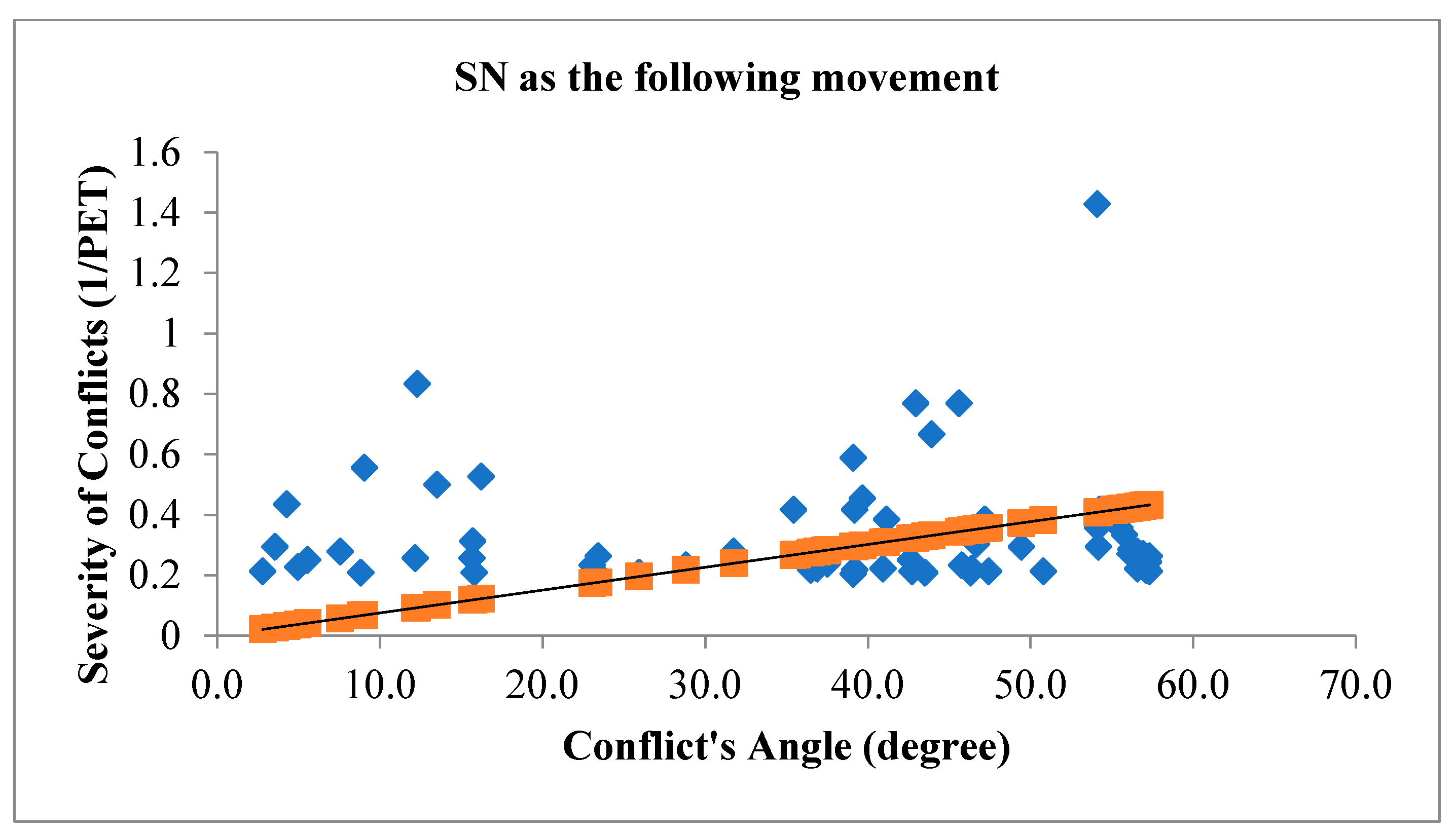
Figure 8 illustrates the angle of V2V conflicts when SN movement is the leading movement of the conflict (figure above) and when SN movement is the following movement of the conflict (figure below) with the severity of conflicts.
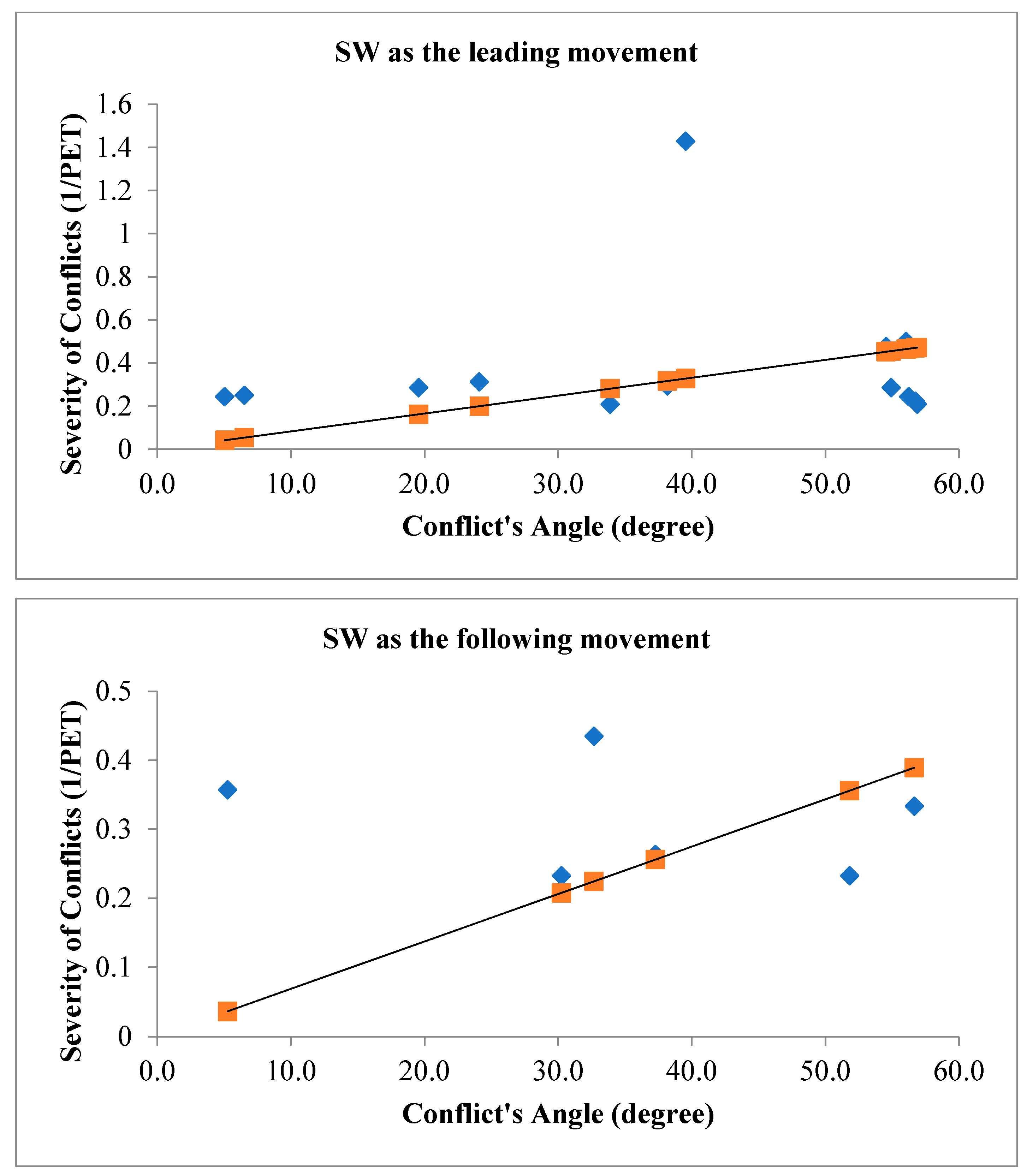
Figure 9 illustrates the angle of V2V conflicts when SW movement is the leading movement of the conflict (figure above) and when SW movement is the following movement of the conflict (figure below) with the severity of conflicts.
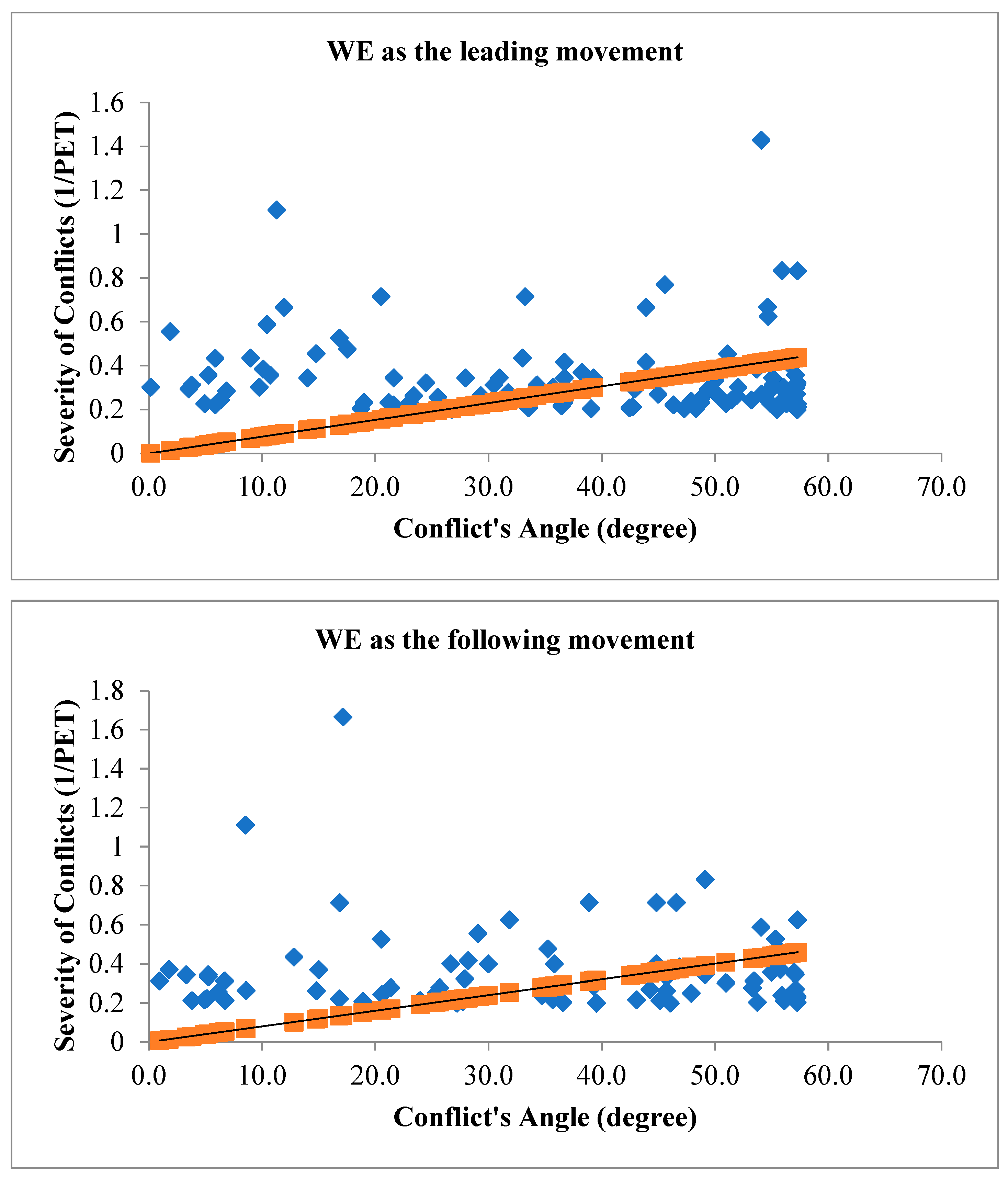
Figure 10 illustrates the angle of V2V conflicts when WE movement is the leading movement of the conflict (figure above) and when WE movement is the following movement of the conflict (figure below) with the severity of conflicts.
Finally
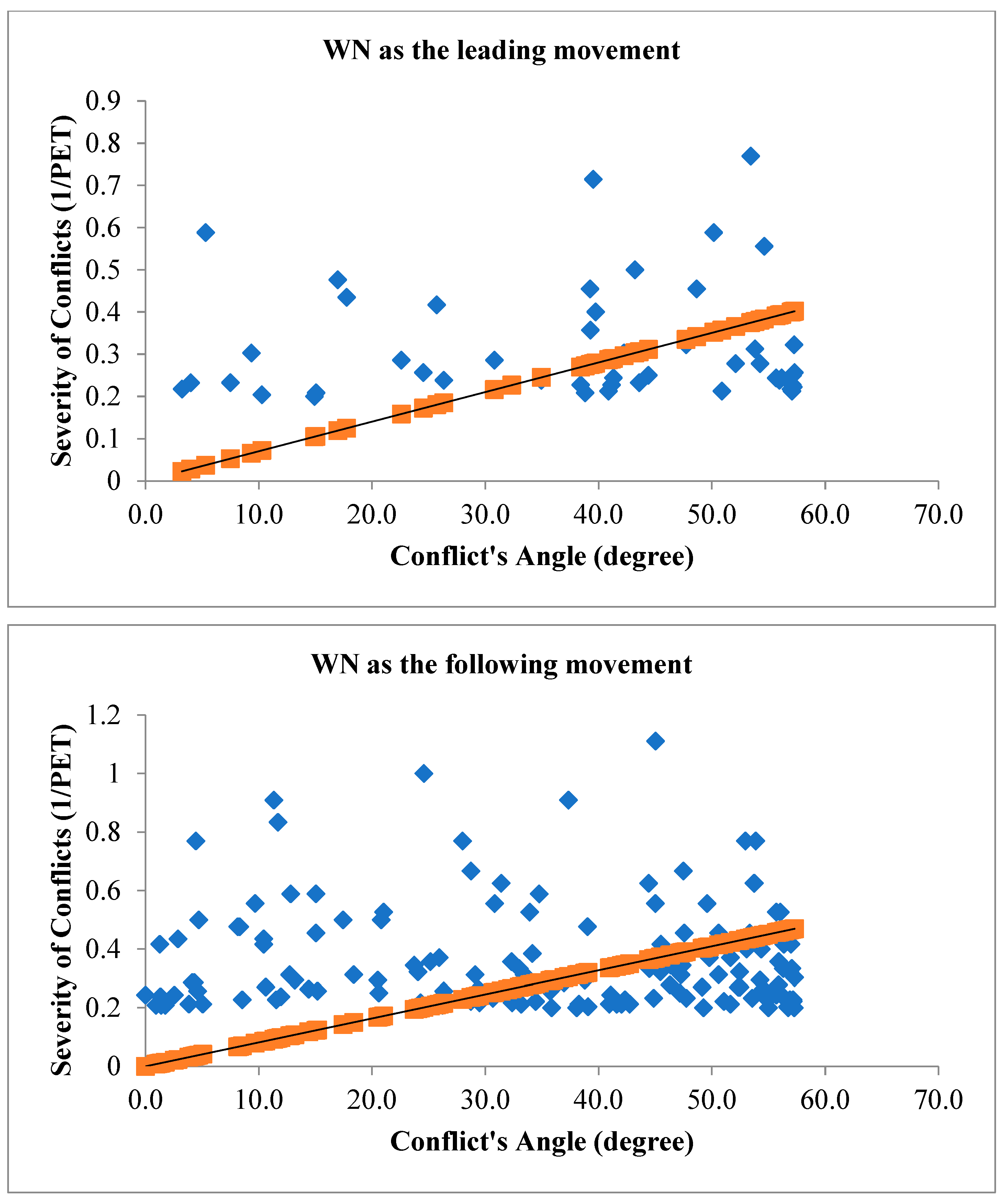
, Figure 11 illustrates the angle of V2V conflicts when WN movement is the leading movement of the conflict (figure above) and when WN movement is the following movement of the conflict (figure below) with the severity of conflicts.
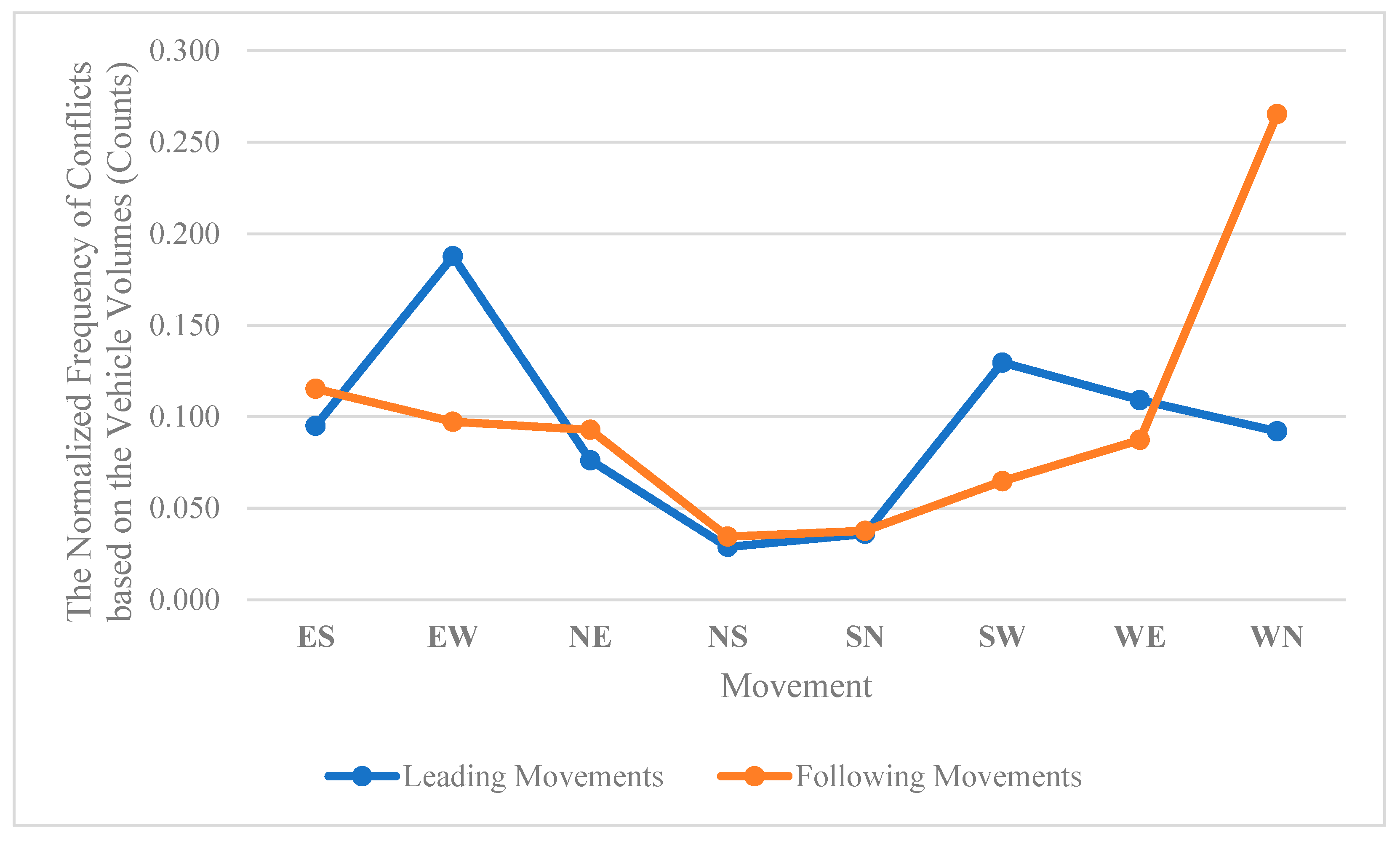
Figure 12 shows normalized conflict’s frequency calculated based on leading and following movements and the movement’s volumes (vehicle counts) during traffic signal failures.
Figure 12 demonstrates the V2V conflict’s normalized frequency based on the vehicle’s volumes passing through the intersection by different movements.
Figure 12 highlights that EW leading movement (= westbound straight through) and WN following movement (=eastbound left-turn) are critical movements of the intersection during the traffic signal failures from 05:30 AM to 10:23 AM.
Figure 11.
Conflict's Angle based on WN as the leading movement (figure above) and WN as the following movement (figure below).
Figure 11.
Conflict's Angle based on WN as the leading movement (figure above) and WN as the following movement (figure below).
Figure 12.
Normalized conflict’s frequency calculated based on leading and following movements.
Figure 12.
Normalized conflict’s frequency calculated based on leading and following movements.
The relationship between the angle of vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) conflicts and the severity of conflicts during traffic signal failures is a critical aspect of traffic safety research. The angle of conflicts plays a substantial role in influencing the outcomes of collisions, and during signal failures, when conventional traffic control mechanisms are compromised, this relationship becomes particularly significant. The study’s findings have consistently demonstrated that the angle at which vehicles approach each other during V2V conflicts correlates with the severity of the resulting collisions. A head-on collision, where vehicles approach each other at a narrow angle, tends to result in more severe consequences compared to conflicts where vehicles approach at wider angles. The spatial dynamics of these conflicts directly impact the collision forces, contributing to the potential for greater damage and increased risk of injury. During traffic signal failures, the disruption to the regulated flow of traffic introduces unpredictability into vehicle movements. The relationship between the angle of V2V conflicts and severity becomes crucial in this context, as the lack of signal control can lead to conflicts occurring at unconventional angles. Understanding how these unregulated conflicts influence severity is vital for developing effective safety interventions. For instance, a thorough analysis of collision outcomes based on conflict angles can inform the implementation of targeted measures such as improved signage, enhanced driver awareness, or adaptive traffic control systems to mitigate the impact of conflicts and reduce severity. The traditional geometric layout of signalized intersections assumes a controlled flow of traffic, and signal failures challenge these assumptions. The investigation into how conflict angles influence severity during signal failures informs the adaptation of intersection designs to better accommodate unregulated traffic movements. This might involve refining geometric configurations, adjusting signal placements, or integrating technologies that enhance intersection resilience during signal failures. To investigate the relationship between conflict’s angles with the severity of V2V conflicts,
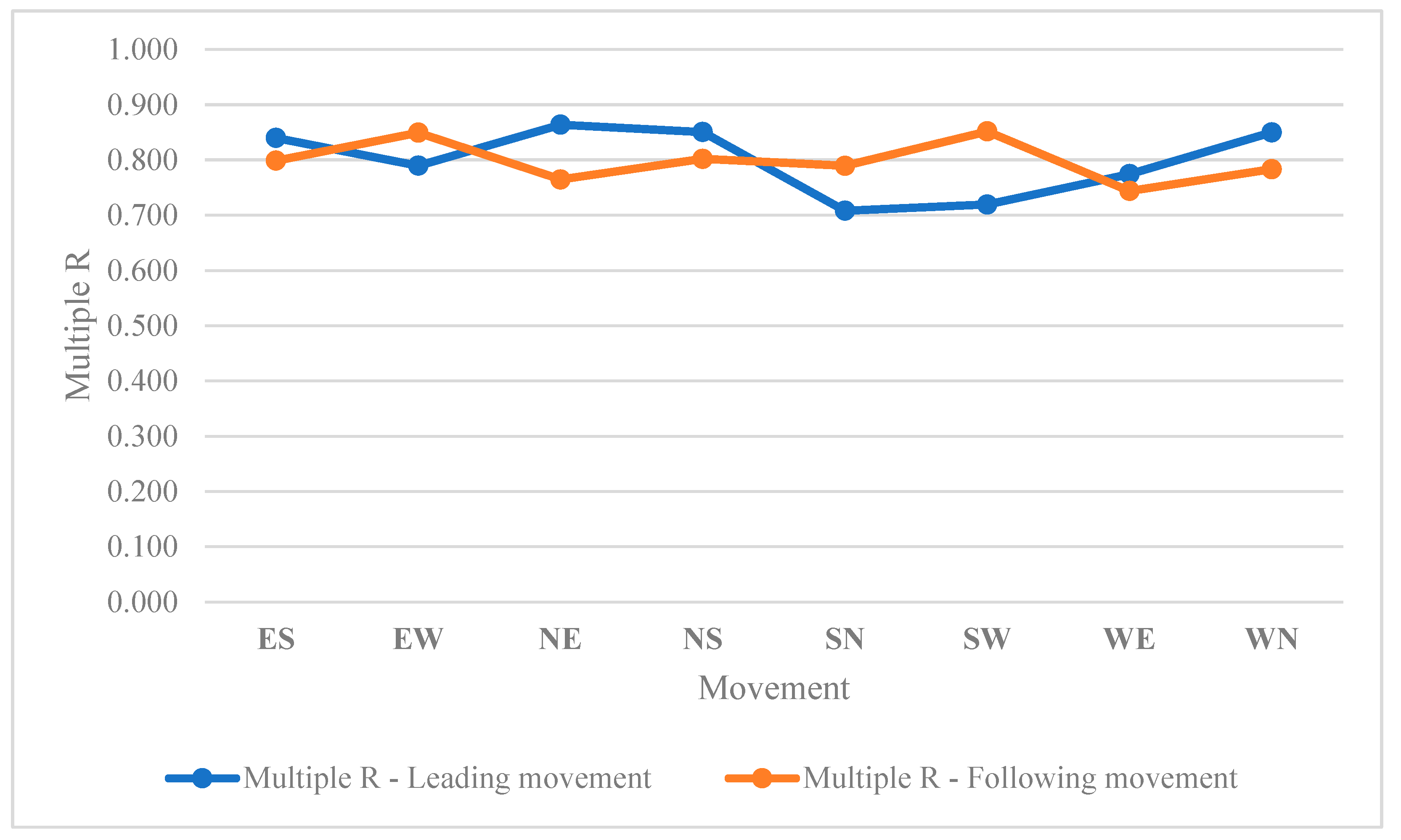
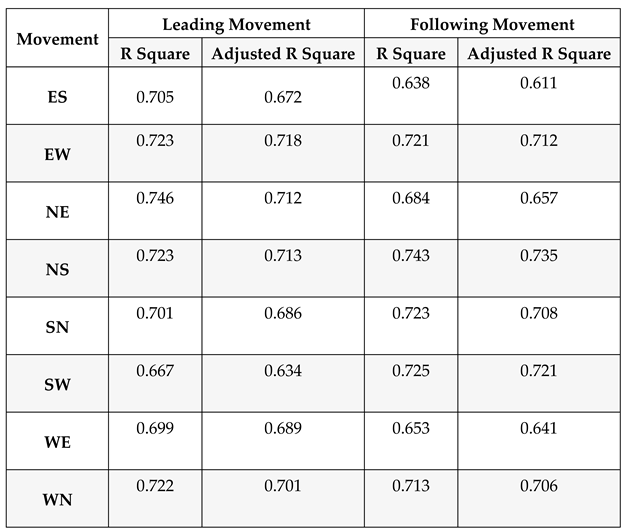
Table 3 illustrates the accuracy of calculated angles based on the LiDAR’s raw data. The linear regression relationship between conflict’s angles and severity of V2V conflicts highlighted the acceptable accuracies (R square > 0.6) of the analysis.
In linear regression models, the term "Multiple R" refers to the multiple correlation coefficient, often denoted as R or
[
28] This coefficient quantifies the strength and direction of the linear relationship between the independent variables collectively and the dependent variable in a multiple regression analysis. It provides a measure of how well the overall model predicts the dependent variable based on the independent variables. The multiple correlation coefficient is essentially the correlation between the observed and predicted values of the dependent variable [
29,
30]. It ranges from -1 to 1, where:
R=1, describes perfect positive correlation - the model perfectly predicts the dependent variable based on the independent variables.
R=0, describes no correlation - the model has no predictive power.
And R=-1, describes perfect negative correlation - the model perfectly predicts the dependent variable, but the relationship is inverse.
The square of the multiple correlation coefficient, often referred to as
or the coefficient of determination, represents the proportion of the variance in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variables. It indicates the goodness of fit of the regression model. The closer
is to 1, the better the model fits the data [
31,
32].
Figure 13 illustrates the multiple R variable for leading and following movements.
In the context of signalized intersections during traffic signal failures, the relationship between the angle of vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) conflicts and the severity of conflicts is a critical aspect of traffic safety research. The interpretation of this relationship involves understanding how changes in the angle of conflicts influence the outcomes and potential severity of collisions. As the angle of V2V conflicts increases, meaning vehicles approach each other at wider angles, the potential for severe collisions may decrease. Wider angles can result in glancing impacts rather than direct head-on collisions. In such scenarios, the forces involved in the collisions are often mitigated, leading to a reduction in the severity of the conflicts. The increased angle allows for more lateral movement during a potential collision, potentially minimizing the impact forces and decreasing the likelihood of severe consequences such as extensive vehicle damage or severe injuries. Conversely, when the angle of V2V conflicts decreases, indicating vehicles are approaching each other at narrower angles, the potential for severe collisions may increase. Narrow angles suggest a higher probability of head-on or more direct collisions, resulting in greater impact forces and, consequently, a higher likelihood of severe outcomes. Collisions occurring at smaller angles may involve more concentrated forces directed longitudinally, potentially leading to a higher risk of injury to occupants and increased damage to vehicles. This interpretation aligns with the fundamental physics of collisions, where the relative angles between vehicles influence the distribution and magnitude of forces involved. Therefore, during traffic signal failures, understanding and analyzing the relationship between the angle of V2V conflicts and the severity of conflicts provide valuable insights for developing targeted safety interventions.
Vehicle-Pedestrian (V2P) Conflicts
Signalized intersections are critical points in urban traffic management, where Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P) conflicts can significantly influence the overall safety of the intersection. This section investigates the relationship between the angle of V2P conflicts and the severity of conflicts, particularly in scenarios involving traffic signal failures. LiDAR sensor technology is employed to provide accurate and real-time data, enabling a comprehensive analysis of conflict dynamics. Understanding how variations in conflict angles correlate with conflict severity is essential for developing effective safety measures at signalized intersections. The research findings reveal a notable impact of increased conflict angles on Post-Encroachment Time (PET) during traffic signal failures. As the angle of V2P conflicts widens, PET experiences a proportional increase. A larger conflict angle signifies a more complex interaction between vehicles and pedestrians, leading to prolonged PET values. Conversely, a decrease in the angle of V2P conflicts is associated with a reduction in PET during traffic signal failures. Smaller conflict angles indicate a more streamlined interaction between vehicles and pedestrians, resulting in shorter PET values. LiDAR sensor technology proves instrumental in capturing detailed temporal information, enabling a thorough analysis of the extended PET associated with elevated conflict angles.
To provide an accurate analysis regarding the angle between vehicles and pedestrians during traffic signal failure, V2P conflicts from 05:30 AM to 10:23 AM on September 13
th (chaos condition) were analyzed. The angles between vehicles spatial vectors and pedestrian spatial vectors were assessed and four categories were investigated including (PET <1 – conflicts with more severity), (1=<PET<2 – conflicts with less severity than the first category), (2=<PET<3 – conflicts with less severity than the second category), and (3=<PET<=5 - conflicts with less severity than the third category). The result of the first category (PET <1) is can be seen in
Figure 14. The LiDAR recorded one V2P conflict with PET <1.
The angles of the V2P conflict for the second category is shown in
Figure 15 (1=<PET<2 – conflicts with less severity than the first category).
The angles of the V2P conflict for the third category is shown in
Figure 16 (2=<PET<3 – conflicts with less severity than the second category).
The angles of the V2P conflict for the fourth category is shown in
Figure 17 (3=<PET<=5 – conflicts with less severity than the third category).
In conclusion, this section underscores the significance of V2P conflict angles in shaping Post-Encroachment Time at signalized intersections during traffic signal failures. LiDAR sensor technology proves to be a valuable tool for capturing and analyzing temporal dynamics, offering insights that can inform adaptive traffic control systems. PET increases proportionally as the angle of V2P conflicts widens. As can be seen in
Figure 15 to
Figure 17, a significant number of V2P conflicts with larger angles occurs when PET increases. A larger conflict angle signifies a more complex interaction between vehicles and pedestrians, leading to prolonged PET values. PET values are shorter when conflict angles are smaller, resulting in severe V2P conflicts. The findings from this study contribute to the ongoing efforts to improve safety measures and traffic management strategies in signalized intersections under challenging conditions.
Conclusion
The use of LiDAR sensor technology in assessing the impact of traffic signal failures on traffic volume, congestion, and safety at signalized intersections represents a significant step forward in understanding and addressing the challenges posed by unexpected signal malfunctions. This study has provided valuable insights into how traffic behaves when traditional signal control systems cease to function and has shed light on potential solutions for mitigating disruptions and improving urban transportation resilience. In conclusion, the investigation into the relationship between the angle of vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) conflicts and the severity of conflicts at signalized intersections during traffic signal failures offers crucial insights into traffic safety dynamics. The findings of this study underscore the significance of considering conflict angles as a determinant of collision outcomes. As the angle increases, reflecting a wider approach between vehicles, the potential severity of conflicts tends to decrease. This is attributed to the spatial dynamics of collisions at wider angles, often resulting in glancing impacts rather than direct head-on collisions. The mitigated forces involved in collisions at increased angles contribute to a decreased likelihood of severe consequences, such as extensive vehicle damage and serious injuries to occupants.
Conversely, when the angle of V2V conflicts decreases, indicating a narrower approach between vehicles, the potential for severe collisions tends to increase. Collisions occurring at smaller angles are associated with more direct and concentrated impact forces, heightening the risk of extensive damage to vehicles and increased injury severity. This insight into the relationship between conflict angles and severity during traffic signal failures is pivotal for developing targeted safety measures. Understanding the nuances of how spatial dynamics influence collision outcomes allows for the formulation of adaptive traffic control strategies, improved signage, and enhanced driver awareness campaigns. Such interventions can effectively address the increased severity risk associated with narrower conflict angles, contributing to overall safety at signalized intersections during signal failures. The implications of these findings extend to traffic engineering and intersection design practices. The relationship between conflict angles and severity emphasizes the importance of considering unconventional traffic scenarios during signal failures in intersection layouts. The adaptability of signalized intersections to unregulated traffic movements becomes a key consideration, and incorporating this understanding into geometric designs enhances the overall resilience of the intersections. Furthermore, the study highlights the need for ongoing research and advancements in adaptive traffic control technologies to effectively manage traffic under varying conditions, including signal failures.
This study also investigated the critical interplay between the angle of Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P) conflicts and Post Encroachment Time (PET) at signalized intersections during traffic signal failures, leveraging the precision of LiDAR sensor technology. The findings underscored the nuanced dynamics that influence pedestrian safety in these scenarios. As the angle of V2P conflicts increases, a proportional extension in PET was observed, providing pedestrians with a more extended duration to complete their crossings before potential conflicts with turning vehicles arise. Conversely, a decreased conflict angle correlates with a reduction in PET, signifying a more direct and potentially challenging interaction between pedestrians and turning vehicles. These findings emphasize the need for tailored interventions based on conflict angles to mitigate the risks associated with pedestrian-vehicle interactions in the absence of functional traffic signals. Considering the obtained results in this study regarding the angle of V2P conflict, it is possible that converse results occurred in other intersections. One plausible explanation is that larger conflict angles might encourage pedestrians to underestimate the potential risks associated with turning vehicles, leading to delayed responses in initiating their crossings. In situations where the angle is large, pedestrians may perceive a larger buffer of safety, causing them to delay their movements and subsequently compressing the available PET. Additionally, larger conflict angles may introduce a false sense of security, leading pedestrians to engage in riskier behaviors, such as assuming that turning vehicles will yield in a more leisurely manner. This could result in pedestrians entering the intersection at a slower pace, contributing to stricter PET values despite the seemingly favorable conditions associated with larger angles. Moreover, the influence of traffic flow and vehicle speed cannot be ignored. Larger conflict angles may coincide with higher traffic speeds or more significant traffic volumes, reducing the effective time available for pedestrians to cross safely. In such cases, the combination of these factors can contribute to stricter PET values even when conflict angles are larger.
A key policy implication is the need for adaptive traffic control strategies that consider the spatial dynamics of conflicts under varying conditions. Specifically, during instances of signal failures, policies should prioritize the development and implementation of traffic management systems capable of adapting to unregulated traffic movements. By incorporating knowledge about the relationship between conflict angles and severity, policymakers can advocate for technologies that dynamically adjust signal timings, enhancing the predictability of traffic flow and mitigating the potential severity of conflicts. These policies should emphasize research and development initiatives to create intelligent traffic control systems that integrate real-time data on conflict angles, thereby promoting a safer and more responsive urban traffic environment. Furthermore, intersection design policies need to be informed by insights into the relationship between conflict angles and collision severity. Urban planners and traffic engineers should consider the potential for increased severity associated with narrower conflict angles during signal failures. Policies should encourage the incorporation of geometric designs that account for unconventional traffic movements during such scenarios, ensuring intersections are resilient to unregulated traffic flow. Enhanced signage and driver awareness campaigns targeting the consequences of specific conflict angles could be pivotal components of these policies, promoting safer driving behaviors and reducing the risk of severe collisions. Importantly, these policies should be adaptive and responsive to ongoing research in the field, fostering a collaborative approach between researchers, policymakers, and transportation agencies to continually refine strategies for mitigating conflict severity at signalized intersections during traffic signal failures.
Future research studies in the realm of traffic safety should delve deeper into the the exploration of additional contributing factors that may interact with conflict angles, influencing severity outcomes. Other variables such as road conditions, and driver behavior during signal failures to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the complex dynamics at play. Further studies could also focus on developing predictive models that integrate conflict angles with these additional variables, offering a robust tool for traffic engineers and policymakers to anticipate and mitigate conflict severity under various conditions.
Moreover, future research endeavors should aim to assess the long-term effectiveness of adaptive traffic control systems and intersection designs informed by the relationship between conflict angles and severity. Longitudinal studies could track the real-world impact of implemented policies and interventions, providing valuable insights into the sustainability and efficacy of such measures. Additionally, research could explore the potential role of emerging technologies, such as connected and autonomous vehicles, in influencing the relationship between conflict angles and severity during signal failures. Investigating the interplay between these technological advancements and conflict dynamics could pave the way for innovative solutions to further enhance traffic safety. Overall, the future research agenda should focus on refining our understanding of the relationship between conflict angles and severity, incorporating multidimensional analyses, and translating findings into practical applications that improve safety outcomes at signalized intersections during traffic signal failures.
References
- Arun, A.; Haque, M.M.; Bhaskar, A.; Washington, S.; Sayed, T. A systematic mapping review of surrogate safety assessment using traffic conflict techniques. Accident Analysis & Prevention 2021, 153, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, P. A review of surrogate safety measures and their applications in connected and automated vehicles safety modeling. Accident Analysis & Prevention 2021, 157, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansariyar, A. (2022). "Investigating the Car-Pedestrian Conflicts Based on an Innovative Post Encroachment Time Threshold (PET) Classification." Available at SSRN 4377745, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4377745. [CrossRef]
- Ansariyar, A.; Taherpour, A. Statistical analysis of vehicle-vehicle conflicts with a LIDAR sensor in a signalized intersection. Advances in Transportation Studies 2023, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, W. Learning V2V interactive driving patterns at signalized intersections. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2019, 108, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, M.; Wymeersch, H. (2017, December). Fine-grained vs. average reliability for V2V communications around intersections. In 2017 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
- Essa, M.; Sayed, T. Traffic conflict models to evaluate the safety of signalized intersections at the cycle level. Transportation research part C: emerging technologies 2018, 89, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Ou, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Cao, D. A review of research on traffic conflicts based on intelligent vehicles. Ieee Access 2020, 8, 24471–24483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, L. (2014). Next Generation Safety Performance Monitoring at Signalized Intersections Using Connected Vehicle Technology (Doctoral dissertation).
- Ansariyar, A.; Taherpour, A. (2023). Investigating the accuracy rate of vehicle-vehicle conflicts by LIDAR technology and microsimulation in VISSIM and AIMSUN. Advances in Transportation Studies, 61.
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Duan, K.; Xue, Q. Using a V2V-and V2I-based collision warning system to improve vehicle interaction at unsignalized intersections. Journal of safety research 2022, 83, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofolasayo, A. (2019). Evaluation of how driver’s sight lines impact available stopping distance for conflicting through and left turning vehicles at signalized intersections. In Canadian Transportation Research Forum 54th Annual Conference-Change, Disruption and Innovation in Canadian Transportation: Navigating the New Normal//Changements, perturbations et innovations dans les transports au Canada: Sur la voie de la nouvelle no.
- Ansariyar, A. Ardeshiri, A; Jeihani, M. , (2023). "Investigating the collected vehicle-pedestrian conflicts by a LIDAR sensor based on a new Post Encroachment Time Threshold (PET) classification at signalized intersections." Advances in Transportation Studies 61: 103-118. Available at: https://www.atsinternationaljournal.com/index.php/2023-issues/lxi-november-2023/1442-investigating-the-collected-vehicle-pedestrian-conflicts-by-a-lidar-sensor-based-on-a-new-post-encroachment-time-threshold-pet-classification-at-signalized-intersections. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ansariyar, A. (2023). Providing a comprehensive traffic safety analysis collected by two LiDAR sensors at a signalized intersection. [CrossRef]
- Ansariyar, A. Real-time Traffic Control and Safety Measures Analysis Using LiDAR Sensor during Traffic Signal Failures. Available at SSRN 4591914. http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.13024.25603 , https://ssrn.com/abstract=4591914. [CrossRef]
- Ansariyar, A.; Jeihani, M. (2023, June). Investigating the Vehicle-Bicyclists Conflicts using LIDAR sensor technology at signalized intersections. In ICTTE 2023: International Conference on Transportation and Traffic Engineering https://publications. waset. org/abstracts/166804/investigating-the-vehicle-bicyclists-conflicts-using-lidar-sensor-technology-at-signalized-intersections.
- Ansariyar, A. (2022). Investigating the Car-Pedestrian Conflicts Based on an Innovative Post Encroachment Time Threshold (PET) Classification. Available at SSRN 4377745, https://ssrn.com/abstract=4377745. [CrossRef]
- ANSARIYAR, A., & JEIHANI, M. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF JAYWALKING CONFLICTS BY A LIDAR SENSOR. Scientific Journal of Silesian University of Technology. Series Transport 2023, 118, 11–22.
- Ansariyar, A. (2023). Enhancing Intersection Efficiency Through Smart Green Time Allocation at a Signalized Intersection Equipped with two LiDAR Sensors. [CrossRef]
- Ansariyar, A. (2023). Evaluating Sensor Accuracy: A Comparative Study of LiDAR and CCTV Technologies performance at Signalized Intersections. A: Evaluating Sensor Accuracy. [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.; Bashir, A.K.; Alyamani, H.J.; Amin, F.; Doh, J.; Chen, J. Lidar point cloud compression, processing and learning for autonomous driving. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2022, 24, 962–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Yoo, A.; Moon, C. Design and implementation of edge-fog-cloud system through HD map generation from LiDAR data of autonomous vehicles. Electronics 2020, 9, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Sun, H., Zhang, F., Zhang, B., Tao, S., Li, H., ... & Mu, Y. Real-Time Localization and Colorful Three-Dimensional Mapping of Orchards Based on Multi-Sensor Fusion Using Extended Kalman Filter. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2158. [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.S.; Ferreira, L.; Hoque, M.S.; Tavassoli, A. Application of proximal surrogate indicators for safety evaluation: A review of recent developments and research needs. IATSS research 2017, 41, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Zhang, X.; Nakamura, H.; Alhajyaseen, W. Investigating the efficiency and safety of signalized intersections under mixed flow conditions of autonomous and human-driven vehicles. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering 2020, 45, 8607–8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Wu, Y. A multi-vehicle communication system to assess the safety and mobility of connected and automated vehicles. Transportation research part C: emerging technologies 2021, 124, 102887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Lee, J.; Rahman, M.H. Safety benefits of arterials’ crash risk under connected and automated vehicles. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2019, 100, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, N.L.; Gliner, J.A.; Morgan, G.A.; Harmon, R.J. Use and interpretation of multiple regression. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 2003, 42, 738–740. [Google Scholar]
- Nimon, K.F.; Oswald, F.L. Understanding the results of multiple linear regression: Beyond standardized regression coefficients. Organizational Research Methods 2013, 16, 650–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J. P. (2021). Linear regression models: applications in R. Crc Press.
- Alexander, D.L.; Tropsha, A.; Winkler, D.A. Beware of R 2: simple, unambiguous assessment of the prediction accuracy of QSAR and QSPR models. Journal of chemical information and modeling 2015, 55, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veall, M.R.; Zimmermann, K.F. Pseudo-R2 measures for some common limited dependent variable models. Journal of Economic surveys 1996, 10, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).