Submitted:
10 November 2023
Posted:
10 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials & Methods
Results
Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global nutrition targets 2025: low birth weight policy brief. World Health Organization; 2014 [cited 2023 Aug 12]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-NMH-NHD-14.5.
- Rechia IC, Oliveira LD, Crestani AH, Biaggio EPV, de Souza APR. Efeitos da prematuridade na aquisição da linguagem e na maturação auditiva: revisão sistemática. CoDAS. 2016;28:843–54. https://doi.org/10.1590/2317-1782/20162015218. [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Caderno de Atenção Básica - Atenção ao pré-natal de baixo risco [Internet]. Departamento de Atenção Básica, Brasília. Editora do Ministério da Saúde. 2012 [cited 2023 Aug 12]; 32. Available from: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/cadernos_atencao_basica_32_prenatal.pdf.
- World Health Organization. Um em cada sete bebês em todo o mundo nascem com baixo peso. Perspectiva Global Reportagens Humanas. 2019 [cited 2023 Aug 12]. Available from: https://news.un.org/pt/story/2019/05/1672441.
- Pessoa TAO, de Godoy Martins CB, Aguiar Lima FC, Munhoz Gaíva MA. O crescimento e desenvolvimento frente à prematuridade e baixo peso ao nascer. Av. Enferm. 2015;33(401).
- Kuhn-Santos RC, Suano-Souza FI, Puccini RF, Strufaldi MWL. Fatores associados ao excesso de peso e baixa estatura em escolares nascidos com baixo peso. Cien Saude Colet. 2019;24(2). https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-81232018242.30702016. [CrossRef]
- Pescador MVB, Streher AAF, da Silva JMF, Valente GCC, Nakagiri M, Boguszewski MCS. Aspectos Endocrinológicos das Crianças e Adultos Nascidos Pequenos para a Idade Gestacional. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2001;45:361–70. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0004-27302001000100004. [CrossRef]
- Bismarck-Nasr EM, Frutuoso MFP, Gamabardella AMD. Efeitos tardios do baixo peso ao nascer. Rev Bras Desenvolv Hum. 2008;1:98–103. https://doi.org/10.7322/jhgd.19871. [CrossRef]
- Lobato JCP, Costal AJL, Kele PL, Cavalcanti MLT, Kuschnir MCC, Velard LGC, et al. Programação fetal e alterações metabólicas em escolares: metodologia de um estudo caso-controle, Rev bras epidemiol. 2016;19:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5497201600010005. [CrossRef]
- Heijmans BT, Tobi EW, Stein AD, Putter H, Blauw GJ, Susser ES, et al. Persistent epigenetic differences associated with prenatal exposure to famine in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:17046–9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0806560105. [CrossRef]
- Noor N, Cardenas A, Rifas-Shiman SL, Pan H, Dreyfuss JM, Oken E, et al. Association of Periconception Paternal Body Mass Index With Persistent Changes in DNA Methylation of Offspring in Childhood. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e1916777. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.16777. [CrossRef]
- Osborne-Majnik A, Fu Q, Lane RH. Epigenetic mechanisms in fetal origins of health and disease. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2013; 56:622–32. https://doi.org/10.1097/grf.0b013e31829cb99a. [CrossRef]
- Fu Q, Yu X, Callaway CW, Lane RH, McKnight RA. Epigenetics: intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) modifies the histone code along the rat hepatic IGF–1 gene. FASEB J. 2009;23:2438–49. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.08-124768. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro AM, Lima MC, de Lira PIC, da Silva GAP. Baixo peso ao nascer e obesidade: associação causal ou casual?. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2015;33:340–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpped.2014.09.007. [CrossRef]
- Wilcox A. On the importance—and the unimportance—of birthweight. Int J Epidemiol. 2001;30:1233–41. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/30.6.1233. [CrossRef]
- Pico C, Palou A. Perinatal programming of obesity: an introduction to the topic. Front Physiol. 2013;4:255. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2013.00255. [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard PF, Hansen M, Frystyk J, Espelund U, Christiansen JS, Jorgensen JOL, et al. Serum levels of bioactive IGF1 and physiological markers of ageing in healthy adults. Eur J Endocrinol. 2013;170:229–36. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje-13-0661. [CrossRef]
- Lupu F, Terwilliger JD, Lee K, Segre GV, Efstratiadis A. Roles of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 in mouse postnatal growth. Dev Biol. 2001;229:141–62. https://doi.org/10.1006/dbio.2000.9975. [CrossRef]
- Brooks AJ, Waters MJ. The growth hormone receptor: mechanism of activation and clinical implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010;6:515–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2010.123. [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg N, Barkan A. Factors regulating growth hormone secretion in humans. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2007;36:37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2006.11.003. [CrossRef]
- Mullis PE. Genetics of growth hormone deficiency. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2007;36:17–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2006.11.010. [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Saúde (BR), Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde. Atenção à saúde do recém-nascido: guia para os profissionais de saúde. Brasília (DF); 2014.
- Fávero LP. Métodos Quantitativos com Stata ebook. Barueri: Grupo GEN; 2013.
- de Barros MVG, Hallal PC, Florindo AA, de Farias Júnior JD. Análise de dados em saúde, first edition. Londrina: Midiograf; 2012.
- Vieira S. Introdução à bioestatística, sixth edition. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier; 2011.
- Aline BVC, Andréa R. Prematuridade e baixo peso ao nascimento e sua associação com fatores de risco cardiovascular em adolescentes [doctoral thesis]. Rio de Janeiro: Universidade Regional do Rio de Janeiro; 2016.
- Remmers F, Delemarre-van de Wall HA. Developmental programming of energy balance and its hypothalamic regulation. Endocrine Reviews. 2011;32:272–311. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2009-0028. [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Low birthweight; 2023 [cited 2023 Aug 12]. https://data.unicef.org/topic/nutrition/low-birthweight.
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight; 2021 [cited 2023 Aug 12]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
- Reynolds RM, Phillips DIW. Long-term consequences of intrauterine growth retardation. Horm Res. 1998;49(suppl 2):28–31. https://doi.org/10.1159/000053084. [CrossRef]
- Halfon N, Larson K, Lu M, Tullis E, Russ S. Lifecourse health development: past, present and future. Matern Child Health J. 2014;18:344–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-013-1346-2. [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Solís R, Matos RJB, Guzmán-Quevedo O, de Souza SL, Bihouée A, Houlgatte R, et al. Nutritional Programming in the Rat Is Linked to Long-Lasting Changes in Nutrient Sensing and Energy Homeostasis in the Hypothalamus, PLoS One. 2010;5:e13537. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013537. [CrossRef]
- Langley-Evans SC. Developmental programming of health and disease. Proc Nutr Soc. 2006;65:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1079/pns2005478. [CrossRef]
- Labayen I, Ruiz JR, Huybrechts I, Ortega FB, Rodríguez G, DeHenauw S, et al. Sexual Dimorphism in the Early Life Programming of Serum Leptin Levels in European Adolescents: The HELENA Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:E1330–4. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2011-1036. [CrossRef]
- Bouret SG, Simerly RB. Developmental programming of hypothalamic feeding circuits. Clin Genet. 2006;70:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00684.x. [CrossRef]
- Newnham JP, Pennell CE, Lye SJ, Rampono J, Challis JRG. Early life origins of obesity. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2009;36:227–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ogc.2009.03.004. [CrossRef]
- Uthaya S, Thomas EL. Hamilton G, Doré CJ, Bell J, Modi N. Altered adiposity after extremely preterm birth. Pediatr Res. 2005;57:211–5. https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000148284.58934.1C. [CrossRef]
- Elmrayed, S., Ye, X. Y., Zhu, J., & Hanley, J. A. (2021). Are small-for-gestational-age preterm infants at increased risk of overweight? Statistical pitfalls in overadjustment for body size. Journal of Perinatology, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-021-01050-5. [CrossRef]
- Hofman PL, Regan F, Jackson WE, Jefferies C, Knight DB, Robinson EM. Premature birth and later insulin resistance, N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:2179–86. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa042275. [CrossRef]
- Casteels K, Ong K, Phillips D, Bendall H, Pembrey M. Mitochondrial 16189 variant, thinness at birth, and type-2 diabetes. ALSPAC study team. Avon Longitudinal Study of Pregnancy and Childhood. Lancet. 1999;353:1499–1500.. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(98)05817-6. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira CRP, Salvatori R, Meneguz-Moreno RA, Aguiar-Oliveira MH, Pereira RMC, Valença EHA, et al. Adipokine profile and urinary albumin excretion in isolated growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:693–8. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-1919. [CrossRef]
- Møller N, Gjedsted J, Gormsen L, Fuglsang J, Djurhuus C. Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism in humans. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2003;13 Suppl A:S18-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1096-6374(03)00048-0. [CrossRef]
- Sakharova AA, Horowitz JF, Surya S, Goldenberg N, Harber MP, Symons K, et al. Role of growth hormone in regulating lipolysis, proteolysis, and hepatic glucose production during fasting. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:2755–9. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-0079. [CrossRef]
- da Silveira VMF, Horta BL. Peso ao nascer e síndrome metabólica em adultos: meta-análise. Rev Saude Publica. 2008;42. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-89102008000100002. [CrossRef]
- Soto INM, Mericq GV. Restricción del crecimiento fetal e insulinorresistencia: nuevos hallazgos y revisión de la literatura. Rev Med Chil. 2005;133:97–104. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0034-98872005000100013. [CrossRef]
- Hypponen E, Power C, Smith GD. Prenatal growth, BMI, and risk of type 2 diabetes by early midlife. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2512–7. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.9.2512. [CrossRef]
- Hales CN, Barker DJ, Clark PM, Cox LJ, Fall C, et al. Fetal and infant growth and impaired glucose tolerance at age 64. BMJ. 1991;303:1019–22. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.303.6809.1019. [CrossRef]
- Barker DJ, Bull AR, Osmond C, Simmonds SJ. Fetal and placental size and risk of hypertension in adult life. BMJ. 1990;301:259–62. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.301.6746.259. [CrossRef]
- Gluckman PD, Hanson MA, Spencer HG, Bateson P. Environmental influences during development and their later consequences for health and disease: implications for the interpretation of empirical studies. Proc Biol Sci. 2005; 272:671–7. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2004.3001. [CrossRef]
- Ong KK, Loos RJF. Rapid infancy weight gain and subsequent obesity: systematic reviews and hopeful suggestions. Acta Pediatr. 2006;95:904–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/08035250600719754. [CrossRef]
- Parlee SD, MacDougald OA. Maternal nutrition and risk of obesity in offspring: the Trojan horse of developmental plasticity. Biochim Bophysica Acta. 2014;1842:495–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.07.007. [CrossRef]
- Desai M, Ross MG. Fetal programming of adipose tissue: effects of intrauterine growth restriction and maternal obesity/high-fat diet. Semin Reprod Med. 2011;29(3):237–45. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1275517. [CrossRef]
| All newborns | Newborns with normal birth weight | Newborns with low birth weight | P value | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | Standard deviation | Minimum | Maximum | N | Mean | Standard deviation | Minimum | Maximum | n | Mean | Standard deviation | Minimum | Maximum | ||||
| Approximate gestational age | 30 | 37 | 3 | 27 | 41 | 15 | 39 | 1 | 37 | 41 | 15 | 35 | 3 | 27 | 36 | 0.000* | ||
| Birth weight | 30 | 2616 | 830 | 965 | 3985 | 15 | 3324 | 466 | 2520 | 3985 | 15 | 1908 | 368 | 965 | 2465 | 0.000** | ||
| Weight at 3 months | 25 | 6744 | 757 | 5400 | 8000 | 12 | 6704 | 805 | 5700 | 8000 | 13 | 6780 | 740 | 5400 | 7900 | 0.808** | ||
| Weight at 6 months | 25 | 9298 | 1420 | 7100 | 13000 | 12 | 9038 | 1447 | 7495 | 13000 | 13 | 9538 | 1407 | 7100 | 11300 | 0.390** | ||
| Weight gain at 3 months | 25 | 4116 | 1080 | 2370 | 5915 | 12 | 3374 | 880 | 2370 | 5290 | 13 | 4800 | 752 | 3615 | 5915 | 0.000** | ||
| Weight gain from the third to the sixth month | 25 | 2555 | 1252 | 120 | 6100 | 12 | 2334 | 1562 | 120 | 6100 | 13 | 2758 | 898 | 1400 | 4200 | 0.408** | ||
| Total weight gain (from birth to the sixth month) | 25 | 6670 | 1627 | 4370 | 9315 | 12 | 5708 | 1250 | 4370 | 9015 | 13 | 7559 | 1443 | 5315 | 9315 | 0.004* | ||
| Length of hospital stay, days | 30 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 22 | 15 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 5 | 9 | 0 | 22 | 0.622* | ||
| All newborns | Newborns with normal birth weight | Newborns with low birth weight | P value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Gestational age classification | |||||||
| Preterm (< 37 weeks) | 16 | 53.3 | 1 | 6.7 | 15 | 100.0 | 0.000* |
| Term (37 to 41 weeks) | 14 | 46.7 | 14 | 93.3 | - | ||
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 15 | 50.0 | 7 | 46.7 | 8 | 53.3 | 0.715* |
| Female | 15 | 50.0 | 8 | 53.3 | 7 | 46.7 | |
| Classification of weight at 3 months | |||||||
| Normal weight | 18 | 75.0 | 8 | 72.7 | 10 | 76.9 | 1.000** |
| Overweight | 6 | 25.0 | 3 | 27.3 | 3 | 23.1 | |
| Classification of weight at 6 months | |||||||
| Normal weight | 14 | 56.0 | 8 | 66.7 | 6 | 46.2 | 0.233** |
| Overweight | 5 | 20.0 | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 15.4 | |
| Obesity | 6 | 24.0 | 1 | 8.3 | 5 | 38.5 | |
| Classification of birth weight | |||||||
| Normal weight | 15 | 50.0 | 15 | 100.0 | - | 0.000* | |
| Low weight | 15 | 50.0 | - | 15 | 100.0 | ||
| Type of delivery | |||||||
| Vaginal | 24 | 80.0 | 15 | 100.0 | 9 | 60.0 | 0.017** |
| Cesarean | 6 | 20.0 | - | 6 | 40.0 | ||
| Complications during delivery | |||||||
| No | 23 | 76.7 | 15 | 100.0 | 8 | 53.3 | 0.006** |
| Yes | 7 | 23.3 | - | 7 | 46.7 | ||
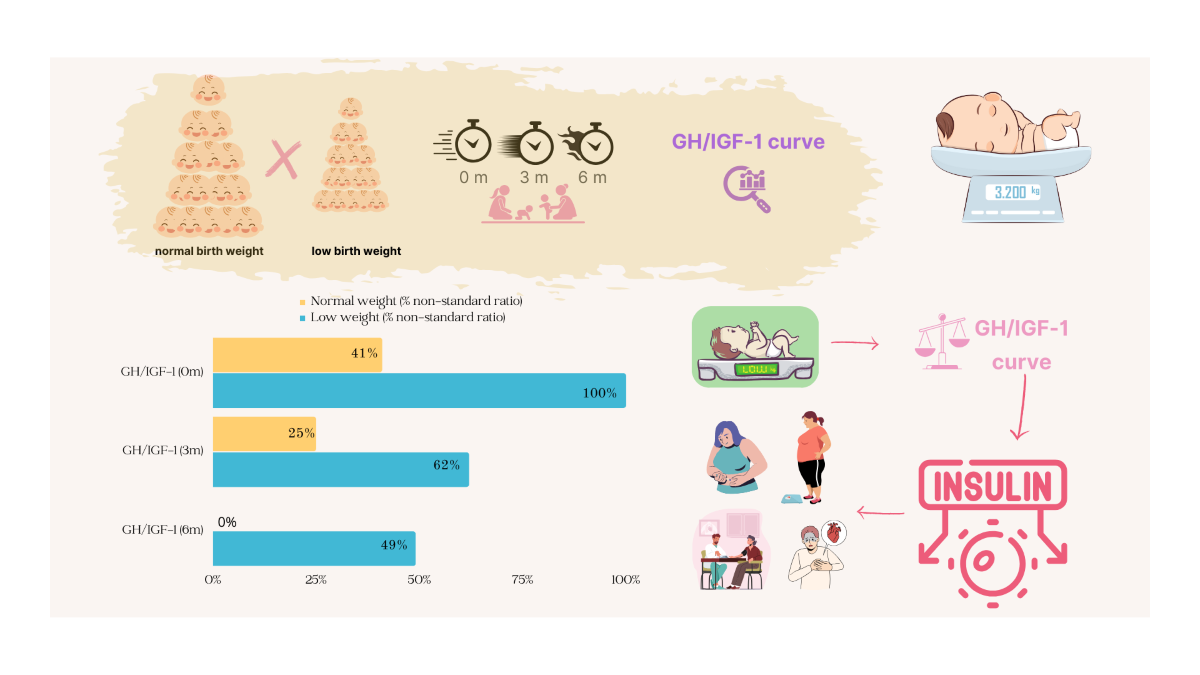
| GH/IGF-1 curve, at birth | |||||||
| Normal | 7 | 28.0 | 7 | 58.3 | - | 0.002** | |
| Altered | 18 | 72.0 | 5 | 41.7 | 13 | 100.0 | |
| GH/IGF-1 curve, at 3 months | |||||||
| Normal | 13 | 52.0 | 9 | 75.0 | 4 | 30.8 | 0.027* |
| Altered | 12 | 48.0 | 3 | 25.0 | 9 | 69.2 | |
| GH/IGF-1 curve, at 6 months | |||||||
| Normal | 20 | 76.9 | 12 | 100.0 | 8 | 57.1 | 0.017** |
| Altered | 6 | 23.1 | - | 6 | 42.9 | ||
| Postpartum referral | |||||||
| Rooming-in | 20 | 66.7 | 15 | 100.0 | 5 | 33.3 | 0.000** |
| Internal nursery | 8 | 26.7 | 8 | 53.3 | |||
| Intensive care unit | 2 | 6.7 | 2 | 13.3 | |||
| Breastfed within the first hour of life | |||||||
| No | 17 | 56.7 | 3 | 20.0 | 14 | 93.3 | 0.000* |
| Yes | 13 | 43.3 | 12 | 80.0 | 1 | 6.7 | |
| Reason for not breastfeeding with the first hour | |||||||
| Mother not producing milk | 1 | 5.9 | 1 | 33.3 | 0.010** | ||
| Respiratory distress | 10 | 58.8 | 10 | 71.4 | |||
| Mother referred to the intensive care unit and respiratory distress | 2 | 11.8 | 2 | 14.3 | |||
| Newborn dyspnea | 1 | 5.9 | 1 | 7.1 | |||
| Lethargic newborn | 2 | 11.8 | 2 | 66.7 | |||
| Ventilatory support | 1 | 5.9 | 1 | 7.1 | |||
| All newborns | Normal weight | Low weight | P value | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | SD | Min | Max | N | Mean | SD | Min | Max | n | Mean | SD | Min | Max | ||||
| GH& result, at birth | 30 | 15.6 | 9.4 | 1.4 | 37.8 | 15 | 11.9 | 9.4 | 1.4 | 37.8 | 15 | 19.4 | 7.9 | 6.6 | 34.8 | 0.011* | ||
| IGF-1& result, at birth | 30 | 43.0 | 19.0 | 14.0 | 78.0 | 15 | 44.9 | 20.8 | 18.0 | 78.0 | 15 | 41.1 | 17.6 | 14.0 | 76.0 | 0.593** | ||
| GH& result, third month | 25 | 5.5 | 3.5 | 0.6 | 12.0 | 12 | 4.3 | 3.8 | 0.6 | 12.0 | 13 | 6.7 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 11.5 | 0.083** | ||
| IGF-1& result, third month | 25 | 50.9 | 19.8 | 20.0 | 91.0 | 12 | 45.9 | 18.9 | 20.0 | 71.0 | 13 | 55.5 | 20.2 | 28.0 | 91.0 | 0.236** | ||
| GH& result, sixth month | 25 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 0.2 | 18.0 | 12 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 4.0 | 13 | 5.3 | 4.8 | 0.3 | 18.0 | 0.008* | ||
| IGF-1& result, sixth month | 25 | 44.0 | 28.9 | 15.0 | 126.0 | 12 | 44.8 | 28.6 | 20.0 | 126.0 | 13 | 43.2 | 30.3 | 15.0 | 97.0 | 0.479* | ||
| GH& at birth | IGF-1& at birth | GH& at 3 months | IGF-1& at 3 months | GH& at 6 months | IGF-1& at 6 months | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | P value | Coef. | P value | Coef. | P value | Coef. | P value | Coef. | P value | Coef. | P value | |
| All newborns | ||||||||||||
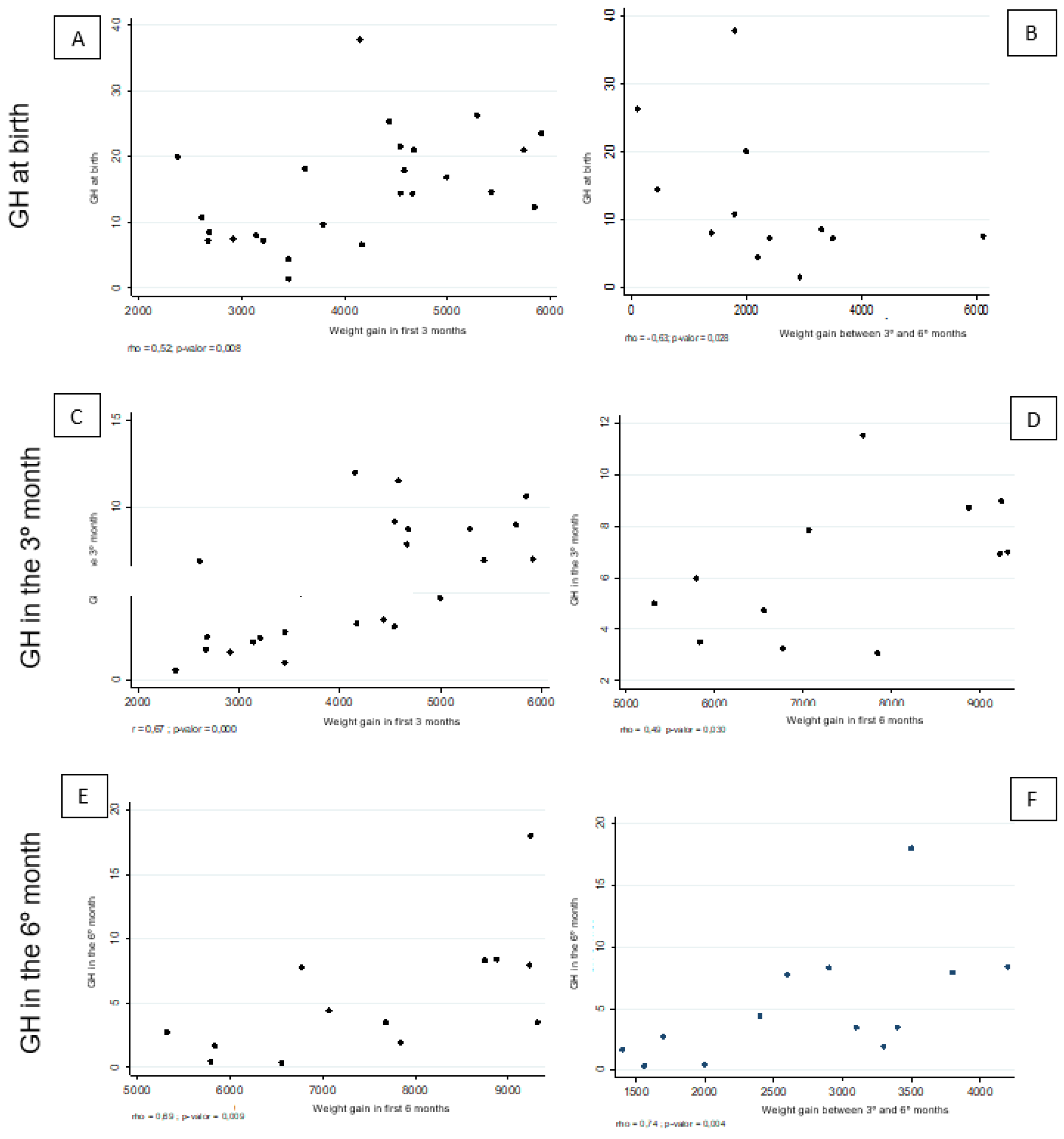
| Weight gain during the first 3 months | 0.52 | 0.008** | −0.21 | 0.323* | 0.67 | 0.000* | 0.09 | 0.686* | ||||
| Weight gain between the third and sixth month | −0.16 | 0.431** | 0.10 | 0.627* | −0.15 | 0.472* | 0.47 | 0.018* | 0.53 | 0.007** | −0.02 | 0.913** |
| Weight gain during the first 6 months | 0.14 | 0.514** | −0.06 | 0.782* | 0.29 | 0.154** | 0.39 | 0.054** | 0.58 | 0.002** | −0.07 | 0.732** |
| Newborns with low birth weight | ||||||||||||
| Weight gain during the first 3 months | 0.16 | 0.591** | −0.01 | 0.972* | 0.48 | 0.099* | 0.40 | 0.171* | ||||
| Weight gain between the third and sixth month | 0.17 | 0.578** | −0.02 | 0.946* | 0.48 | 0.093* | 0.34 | 0.253* | 0.74 | 0.004** | 0.09 | 0.760** |
| Weight gain during the first 6 months | 0.27 | 0.364** | −0.02 | 0.952* | 0.49 | 0.030** | 0.39 | 0.187** | 0.69 | 0.009** | 0.10 | 0.753** |
| Newborns with normal birth weight | ||||||||||||
| Weight gain during the first 3 months | 0.15 | 0.640** | −0.45 | 0.144* | 0.72 | 0.009* | −0.63 | 0.029* | ||||
| Weight gain between the third and sixth month | −0.63 | 0.028** | 0.18 | 0.586* | −0.56 | 0.060* | 0.55 | 0.061* | 0.22 | 0.485** | −0.27 | 0.397** |
| Weight gain during the first 6 months | −0.52 | 0.085** | −0.10 | 0.766* | −0.04 | 0.897* | 0.17 | 0.587** | 0.01 | 0.983** | −0.31 | 0.330** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





