1. Introduction
Public health promotion is becoming increasingly crucial, as physical-mental health and well-being are part of a feedback system that affects all aspects of human activity [
1,
2]. The COVID-19 pandemic, combined with ongoing lockdowns and limited economic, professional, and social activity, have tested public health [
3]. The pandemic outbreak [
4], in addition to its high toll in human lives, the extraordinary struggle of health professionals, and the environmental, economic, and social impact [
5], which is yet to be fully realized, has also put forward essential defects of public health systems in communal, national, and global level [
6]. Additionally, efforts are being made in order to evaluate the personal and social psychological repercussions of this ongoing distress [
7].
Psychological resilience, a concept in psychology that refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and cope effectively with stress, adversity, and life challenges, is considered an important factor that could improve people’s health and well-being [
8]. Beyond the psychological factor, nutrition can also affect mental health and well-being [
9]. One of the dietary patterns that has been extensively researched and recognized for enhancing health is the Mediterranean diet. Mediterranean diet is a dietary pattern characterized by a high phenolic-rich foods intake and is based on the traditional eating habits of the people living in the Mediterranean region [
10]. A structure that combines both psychology and nutrition is mindful eating. Mindful eating is a practice that involves bringing one’s full attention and awareness to the experience of eating. It is based on the principles of mindfulness, which is a type of meditation that involves paying attention to the present moment with a non-judgmental and accepting attitude [
11]. Both Mindful eating and the Mediterranean diet are not a specific diet plan or a weight-loss program, but rather a general pattern of eating that is part of a healthful diet [
12,
13].
The choice of a healthful diet presupposes knowledge but also experience, which Aristotle in the 4th century BC defined as phronesis. Aristotle valued phronesis as the highest spiritual virtue. In his work, Nichomachean Ethics, book VI, bekker page 1141b, in order to explain its importance, he gives an example of the application of phronesis to diet, writing that: "if a man knows that light meat is easily digested and therefore salubrious, but does not know what kinds of meat are light, he will not be so likely to restore you to health as a man who merely knows that chicken is wholesome" [
14].
Phronesis, one of the basic principles of Aristotelian Eudaemonia, is a word that has no common English translation. According to McEvilley [
15], a scholar of ancient Greek philosophy, the most accurate translation of phronesis into English is mindfulness. Although mindfulness has been associated with Buddhism, the exchange of philosophical views between ancient Greece and Eastern civilization may have contributed to the formation of its philosophy [
16]. Weiss [
16], accepting the definition of phronesis as mindfulness, states that the connecting link between phronesis and mindfulness is eudaemonia. Eudaemonia, which is a reference point in the present study, is one of the important components of well-being. The theoretical framework of well-being and its separation into hedonistic and eudaemonic components has contributed to a better understanding of the mechanisms that mediate its promotion. Both hedonistic and eudaemonic well-being seem to be associated with psychological resilience [
8,
13].
Mindfulness, which is inspired by the values of eudaemonia, seems to have positive effects on psychological resilience and the adherence to a healthy diet [
11,
17]. The Mediterranean lifestyle, as epitomized by adherence to the Mediterranean diet and active-natural living, appears to have a positive effect on health and well-being [
10]. Although these concepts share common values and mechanisms at their core, their connection has not been thoroughly examined.
Mindful eating, an evolving scientific trend, could be the connecting link between these concepts. The hypotheses of this study were that mindful eating, and the Mediterranean lifestyle are associated to psychological resilience and maintaining a healthy body weight, and that all three of them were inspired by Aristotelian eudaemonia values. The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between mindful eating and the Mediterranean diet and lifestyle with psychological resilience, body weight, and eating behavior.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Procedure
The type of study chosen was that of a cross-sectional study [
18]. An online questionnaire was used for data collection, which was designed and implemented using Sogolytics cloud survey software [
19].
The questionnaire was offered both in Greek and English. The first three survey questions served as inclusion/exclusion criteria. The first question concerned acceptance of the terms and conditions of research participation regarding data protection, confidentiality and anonymity of the participants, with those who did not accept them being excluded. The second and third questions concerned age and occupation, respectively. People under the age of 25 or over the age of 65, as well as pupils/students or pensioners, were barred from participating in the study's continuation. The exclusion of specific groups was chosen for the research participants to come from the workforce. This decision was made because psychological resilience is a factor that is frequently researched on the workplace, as it contributes significantly to the well-being and performance at work [
20]. Derived from the Greek population, the total sample size necessary, with a 95% confidence level and a 5% confidence interval, was established at 384 individuals [
21].
Participants were recruited through social media invitations in Greek domains. Transparency, a non-exceptionalist methodology, privacy respect, and adherence to the terms of use of social media platforms were all part of the recruiting process [
22]. A pilot study with a sample of 40 people was conducted before the survey was officially distributed to check for potential ambiguities [
23]. Data structure, distribution, collection, and analysis were all flawless. The data from the pilot study was incorporated into the final sample. The survey's official distribution began in September 2021 and ended in November 2021. Before collecting data, the analytic plan and hypotheses of this study were specified.
2.2. Ethics and deontology issues
The conduct of this research was in full compliance with the prescribed codes of ethics and deontology, according to the Declaration of Helsinki. Acceptance of the research's terms and conditions was a requirement for participation. The research application no. 17715 / 09.09.2021 was approved by the University of the Aegean's ethics and deontology committee because it was deemed to comply with the ethical, deontological, and legal framework of research as defined in the University's Code of Ethics and Deontology of Research. There was no funding for this study, and there was no conflict of interest.
2.3. Scales
The MES-16 is an abbreviated version of the 28-item Mindful Eating Scale (MES-28). MES-28 was developed by Hulbert-Williams et al., [
24] to address the need for a robust and theoretically conscious alignment measure specifically for the food sector [
25]. Hulbert-Williams et al., [
26] identified some inadequate psychometric properties in the data and a sub-scale in MES-28. To improve their original scale, they proceeded to remove them. The final form of the new abbreviated scale consists of 16 elements divided into 5 sub-scales. The five sub-scales are self-acceptance, awareness, inaction, or routine, and conscious action. The MES-16 is rated on a Likert scale. The Likert scale is a scale for evaluating opinions or behavior, where the examinee is asked to answer closed-ended questions, choosing answers in the form of scales that indicate a different degree of agreement [
27]. A typical question of the MES-16 scale is: “I eat something without really being aware of it.” The MES-16 answer options are divided into 4 levels (never, rarely, sometimes, always) and the answers are graded from 1 to 4 points. The final score of MES-16 ranges from 16 to 64 points. A higher score indicates increased mindful eating.
This scale was chosen because its abbreviated version is the scale that best reflects the characteristics and principles of mindfulness as they apply to nutrition (26). In the current study, the internal consistency index (Cronbach's) of the MES-16 scale was α = 0.75. Cronbach’s a between 0.7 and 0.8 is described by George and Mallery (2003) as "acceptable". The Cronbachs of the MES-16 sub-scale were α = 0.846 for acceptance, α = 0.841 for awareness, α = 0.790 for non-reactivity, α = 0.734 for routine, α = 0.799 for acting with awareness, and they correspond to those of the original scale of Hulbert-Williams et al., (26).
The 14-MEDAS scale, a creation of Schroeder et al. [
28] within the PREDIMED study framework, is a 14-item tool designed to assess adherence to the Mediterranean diet. A sample question from the 14-MEDAS is: "Is olive oil your primary culinary fat?" Each query is rated on a scale from 0 to 1, with a final 14-MEDAS score ranging from 0 to 14 points. Scores between 0 and 5 reflect low adherence, 6 to 9 indicate moderate adherence, and 10 to 14 demonstrate high adherence [
28]. Validated in various countries and languages, including Greek, the Greek version of 14-MEDAS displayed a significant concordance (81.2 ± 10.7%) with the Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) in a study by García-Conesa et al. [
29], affirming its validity and reliability as a research instrument for evaluating adherence to the Mediterranean diet within the Greek population.
The CD-RISC-10 is a brief version of the Connor and Davidson resilience scale [
30]. It is one of the most widely used scales for measuring psychological resilience, containing ten of the original scale's twenty-five items. Each answer is worth 0 to 4 points on a Likert scale. A typical question of CD-RISC-10 is: “I am able to adapt when changes occur.” Scores on the scale can fall within the 0-to-40-point range, with a higher score serving as an indicator of increased resilience. CD-RISC-10's validation in Greek by Tsigkaropoulou et al. [
31] was established through a case-control study involving a total sample of 546 individuals, leading the authors to affirm the Greek translation's reliability and validity for measuring psychological resilience within the Greek population. In this study, the internal consistency index (Cronbach's α) for the CD-RISC-10 scale was α= 0.856.
It was decided to include questions about the respondents' lifestyle in order to investigate the relationships between mindful eating, adherence to the Mediterranean lifestyle, and resilience with their eating behaviors, health, and well-being. The two most used factors associated with the Mediterranean lifestyle, according to previous studies, are increased physical activity and contact with nature [
32]. The weekly threshold for increased physical activity was set at 3 hours [
33]. Increased contact with nature was defined as spending more than 2 hours per week in its presence [
34]. Questions that separated happiness as joy (hedonistic well-being or SWB) from happiness as meaning in life (eudaemonic or PWB) were included. Joy is at the heart of hedonistic well-being principles, while meaning is at the heart of eudaemonic well-being principles [
35].
To minimize survey dropout rates [
36], questions pertaining to demographic and somatometric data were positioned at the survey's conclusion. Demographic inquiries encompassed aspects such as education, employment status, marital status, and gender. Participants were requested to provide their height and weight for the computation of their BMI. While relying on self-reported height and weight may not yield the most accurate data regarding respondents' body composition, it remains a valid approach for calculating BMI in adult populations across diverse socio-demographic groups [
37]. Moreover, to delve deeper into participants' dietary habits, the survey assessed whether they had previously engaged in weight loss diets and the enduring impacts on their body weight. Based on established guidelines [
38], individuals' BMIs were classified into subcategories, including underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obesity.
2.4. Statistical analysis
A thorough review of the data was conducted to identify any potential omissions. Instances where participants abruptly discontinued the questionnaire (Missing Completely at Random) resulted in the exclusion of the respective data from the analysis [
39]. In the event of accidental oversights (Missing at Random), the missing data points were substituted with the mean value derived from all respondents' answers.
The data was exported in a format compatible with import and processing in SPSS v26 and R-Statistics. Analysis and visualization of the data were carried out using the statistical analysis software SPSS v26 and R-Statistics. Prior to subjecting the data to statistical tests, a regularity check was performed to ensure their distribution met established criteria. The literature recommends conducting the regularity test before engaging in statistical analyses. To ensure the most accurate and reliable assessment of regularity, a combination of visual examination and the Shapiro-Wilk test was employed [
40]. The primary research variables underwent thorough regularity testing. The predetermined statistical significance level was established at p<0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Sample
A total of 430 people participated in the survey. After excluding 125 people who did not meet the survey's inclusion criteria and 17 incomplete (less than 50% of total questions were answered) or random responses (questions answered in less than 3 minutes), the final sample consisted of 288 employed and unemployed people aged 25 to 65.
The independent-sample Kruskal-Wallis test revealed a statistically significant (p<0.05) lower MES-16 score in women and a lower 14-MEDAS score in private sector employees. The CD-RISC-10 score was higher in the self-employed and lower in the unemployed. People in relationships had lower BMIs.
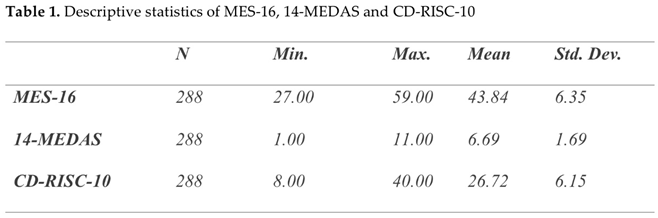
The descriptive statistics of mindful eating (MES-16), adherence to the Mediterranean diet (14-MEDAS) and resilience (CD-RISC-10) measurement scales in the final sample were calculated (Table 1). The MES-16, 14-MEDAS, and CD-RISC-10 scales in the present study follow a normal distribution while BMI does not.
3.2. Correlations among mindful eating, the Mediterranean diet, psychological resilience and BMI
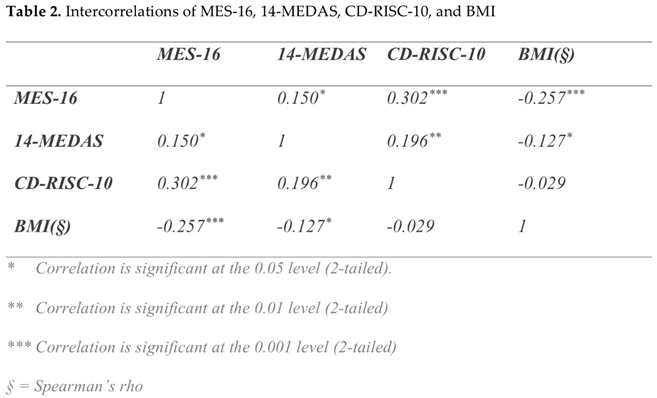
In order to test the correlation between MES-16, 14-MEDAS, CD-RISC-10, and BMI, the Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients were calculated. It was discovered that there was a statistically significant correlation between the scores MES-16 and 14-MEDAS, as well as the score CD-RISC-10.BMI had a statistically significant negative correlation with the MES-16 and 14-MEDAS scores. No correlation was found between CD-RISC-10 and BMI (Table 2).
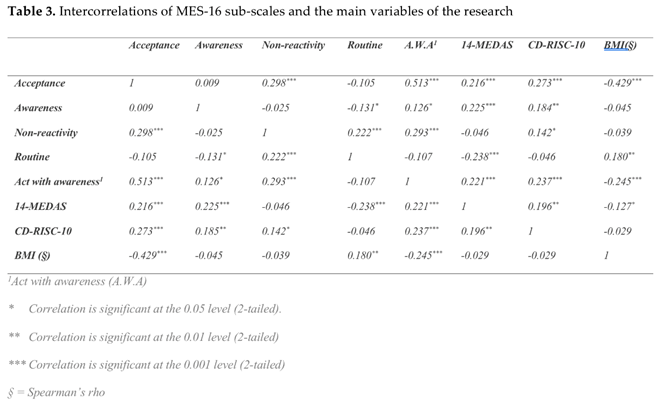
The 5 sub-scales of MES-16 were tested for any correlations with each other but also with the scores of the 14-MEDAS, CD-RISC-10, and BMI. A statistically significant positive correlation was found between the sub-scales of acceptance, awareness, and acting with awareness with 14-MEDAS. On the contrary, there was a statistically significant negative correlation between routine and 14-MEDAS. All sub-scales of MES-16 had a statistically significant positive correlation with CD-RISC-1O except for routine. Regarding BMI, acceptance and acting with awareness had a statistically significant positive correlation, whereas routine had a statistically significant negative correlation (Table 3).
3.3. Mindful eating, the Mediterranean diet-lifestyle, and psychological resilience
The statistical test of multiple linear regression showed that the score of MES-16 (p<0.0001) and the score of 14-MEDAS (p = 0.007) were statistically significant predictors of psychological resilience as they explained 11.5% of its variance. With the same test MES-16 and 14-MEDAS score along with physical activity and proximity to nature explained 17.4% of psychological resilience’s variance (p<0.001)
After applying a one-way anova test, it was found that there was a statistically significant difference between the means of CD-RISC-10 in different adherence categories to the Mediterranean diet (p<0.05). Application of the LSD post hoc test showed a statistically significant difference in the mean scores of CD-RISC-10 between poor and moderate adherence to the Mediterranean diet (p=0.002).
3.4. Mindful Eating, the Mediterranean diet, and weight
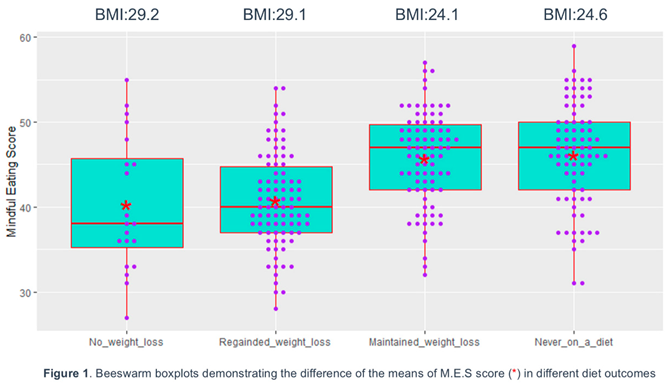
Following the implementation of the independent-samples Kruskal-Wallis Test, results indicated a significant difference among the MES-16 score means across different BMI categories (p = 0.001). The Independent-Samples Kruskal-Wallis Test also revealed a variance in the means of 14-MEDAS scores within various BMI categories, nearly reaching statistical significance (p = 0.082). Subsequent analysis through the post hoc LSD test unveiled a significant difference in the 14-MEDAS means between individuals with normal weight and those who were overweight (p=0.031). After conducting an independent-Samples Kruskal-Wallis Test and a post hoc LSD test, it was found that there was a statistically significant difference in the mean scores of MES-16, between those who maintained the weight they lost after dieting and those who regained the same or even greater weight or failed to achieve weight loss (p<0.0001). A statistically significant difference (p<0.0001) was also found between the BMI averages of the participants and the groups with different dietary outcomes (Figure 1). Multinomial logistic regression analysis identified MES-16 as a prognostic factor in maintaining weight loss after diet (OR: 1,142, 95% CI: 1,084, 1,204, p<0.0001, compared to recovery to the same or greater weight). In addition, the MES-16 score predicted the participants' normal BMI category (OR: 1.113, 95% CI: 1.057, 1.172, p<0.01, compared to the obesity BMI category).
3.5. Mindful eating, the Mediterranean diet, psychological resilience, and overall well-being
On a Likert scale from 1 to 5, the weighted score of all respondents was 3.43 on a question related to their happiness, and 3.94 on a question related to their meaning in life. When one-way anova was applied to the question "how happy have you been in the last 12 months," it revealed a statistically significant difference in the CD-RISC-10 score averages for the 5 different answers (p<0.0001). In contrast, no statistically significant difference was found between the means of MES-16 and 14-MEDAS between the different levels of happiness. A one-way anova analysis of the responses to the question "How meaningful do you feel your life has been in the last 12 months" revealed a statistically significant difference in the mean scores of MES-16 (p=0.005) and CD-RISC-10 (p<0.0001). At the limits of statistical significance (p = 0.072), there was also a difference in the mean of the 14-MEDAS score in the 5 different answers.
3.6. Active-natural living as a part of the Mediterranean lifestyle
The independent-samples T-test showed statistically significant higher 14-MEDAS scores in people with active-natural living as expressed by high physical activity and proximity to nature (p<0.05). The same test revealed that people who had high physical activity and were close to nature had statistically significant higher MES-16, and CD-RISC-10 scores. Independent-samples Kruskal-Wallis Test demonstrated that people with active-natural lifestyle had statistically significant lower BMI (p<0.05).
4. Discussion
Although the number of articles on mindful eating has increased significantly over the last decade, it appears that its research has been limited to the treatment of emotional eating and binge eating disorders [
41]. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between mindful eating and factors that contribute to mental-physical health and well-being, such as the Mediterranean lifestyle, psychological resilience, and weight management.
One of the hypotheses of this study was that mindful eating, the Mediterranean lifestyle, and psychological resilience are all inspired by Aristotelian eudaemonia values. This hypothesis appeared to be supported by the results of the study which underline the link between happiness with mindful eating and psychological resilience, as expressed by the existence of meaning in life. The absence of a link between mindful eating and the Mediterranean diet with hedonistic well-being as expressed by joy, validated the authors’ choice of dividing well-being into hedonistic (joy) and eudaemonic (meaning). On the other hand, and in line with previous research [
42], there was a strong link between psychological resilience and both hedonistic and eudaemonic well-being.
In terms of the sample's demographics, employment status was linked to adherence to the Mediterranean diet and psychological resilience. Working in the private sector appeared to have a negative impact on Mediterranean diet adherence. Other studies have already suggested that long working hours have a negative impact on following a prudent diet [
43,
44], something that seems to apply on the Mediterranean diet adherence as well. This study also indicated a difference in psychological resilience levels between the unemployed and the self-employed. Lower levels of psychological resilience in the unemployed and higher levels in the self-employed could indicate the importance of "ergon" -work for a purpose, according to Aristotle- in withstanding life adversities [
45].
The findings of this research supported the hypothesis that mindful eating and adherence to the Mediterranean lifestyle are associated with psychological resilience and maintaining a healthy weight. There was a link between psychological resilience and both mindful eating and Mediterranean lifestyle adherence. Furthermore, the combination of mindful eating and the Mediterranean lifestyle appeared to work in addition to the psychological resilience prognosis. Low psychological resilience was associated with poor adherence to the Mediterranean diet and lifestyle.
The results of mindful eating's sub-scales, particularly the "routine" sub-scale, were intriguing. The negative correlation of "routine" with the Mediterranean diet, non-correlation with psychological resilience, and positive correlation with BMI contrasts with the results of almost all other MES-16 sub-scales. For instance, a question on this sub-scale was: "I have a routine when I eat". So, it appears that the lack of routine in when and what we eat is negatively related to the Mediterranean diet and a normal BMI. The available research on the relationship between dietary routine and body weight is relatively scares, particularly in Greece. It would be interesting to investigate this relationship further. It is worth noting that the "routine" sub-scale of the MES-16 is the only one that is not conceptually related to mindfulness [
24].
In contrast to the "routine" sub-scale, the overall score of mindful eating and adherence to the Mediterranean diet were negatively correlated with BMI. The high MES-16 and 14-MEDAS scores in healthy weight individuals supported this negative correlation. Similar findings have been reported by other researchers [
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51]. It is worth noting that mindful eating had a stronger negative correlation with BMI than the Mediterranean diet, underlining the importance of how we eat as well as the diet we follow. Mediterranean lifestyle factors like active-natural living were associated with higher mindful eating, psychological resilience, and lower BMI, emphasizing the significance of lifestyle. Additionally, an active-natural lifestyle was directly associated with 14-MEDAS, confirming previous research [
32] on the association of physical activity and proximity to nature with the Mediterranean lifestyle.
The relationship between mindful eating and following a weight loss diet and long-term weight maintenance was also studied. People who did not have to diet and those who maintained the weight they lost after a weight loss diet, had a higher MES-16 score than those who regained the same or greater body weight or failed to lose weight after dieting. The average BMI of each category also contributes to the validity of the results. Both groups with a high MES-16 score had normal BMIs, whereas the two groups with a low mindful eating score had BMIs bordering on obesity. Furthermore, the mindful eating score appeared to be a predictor of weight loss maintenance after dieting.
These results hold significance as they represent the first instance in the literature where mindful eating has been associated with the sustained maintenance of weight loss over the long term, addressing the persistent issue of the yo-yo dieting phenomenon. This phenomenon has not been adequately tackled and is a contributing factor to the widespread prevalence of obesity. This phenomenon was attributed to hormonal factors by Sumithran et al., [
52]. According to Contreras et al., [
53], current treatment for weight variation is inadequate and is limited to either bariatric surgery or an attempt to modify the epigenetic mechanisms associated with obesity. This study could serve as the foundation for designing randomized controlled trials to investigate the relationship between mindful eating and weight variation, with the goal of developing future intervention programs to address the yo-yo dieting phenomenon and, as a result, obesity.
Limitations
The study's cross-sectional design makes it impossible to determine the direction of the causal correlation. It is not impossible that psychological resilience influences mindful eating and the Mediterranean diet. Nonetheless, previous research has shown that mindfulness interventions can increase psychological resilience [
11,
12], and studies have also linked Mediterranean diet and lifestyle adherence to psychological resilience [
9,
54]. The findings of these studies support the current study hypothesis' causal direction.
Another constraint involves employing an online questionnaire for data collection (non-probability sampling). To mitigate the limitations inherent in an online survey, such as compromised data quality resulting from bots, haphazard responses, and superficial engagement, this survey incorporated various strategies. These included incorporating open-ended questions (e.g., entering height, weight), implementing timing checks (excluding surveys completed under 4 minutes), and integrating consistency checks (including follow-up questions). Non-probability sampling results and conclusions are difficult to generalize to the general population. To address this limitation, purposive sampling and quota sampling were used, which resulted in sample homogenization. Homogenization of the sample has been proposed as a method of overcoming the limitations of non-probability sampling [
55]. The demographic characteristics of the total sample of 430 people and the final sample of 288 people were comparable to those of the general population and the sector of interest (workforce in Greece).
5. Conclusions
To our knowledge, this study represents the inaugural attempt to explore the synergic association of mindful eating and the Mediterranean lifestyle with resilience and wellness. The results of this study suggest that meaning in life appears to be the connecting link between Mindful Eating, the Mediterranean lifestyle, and psychological resilience. Employment status is related to Mediterranean diet adherence and psychological resilience, while a meal routine is associated with the Mediterranean diet and a normal BMI. In conclusion, mindful eating and adherence to the Mediterranean lifestyle may have a positive effect on psychological resilience and could be the key to achieving and maintaining weight loss on a weight-reduction diet. To confirm the findings of this cross-sectional study, randomized control trials should be conducted.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Efstratios Christodoulou and Antonios Koutelidakis; Data curation, Efstratios Christodoulou; Formal analysis, Efstratios Christodoulou; Investigation, Efstratios Christodoulou, Georgia-Eirini Deligiannidou, Christos Kontogiorgis and Constantinos Giaginis; Methodology, Efstratios Christodoulou, Georgia-Eirini Deligiannidou, Christos Kontogiorgis and Constantinos Giaginis; Project administration, Antonios Koutelidakis; Resources, Efstratios Christodoulou, Georgia-Eirini Deligiannidou, Christos Kontogiorgis, Constantinos Giaginis and Antonios Koutelidakis; Software, Efstratios Christodoulou; Supervision, Antonios Koutelidakis; Validation, Efstratios Christodoulou; Visualization, Antonios Koutelidakis; Writing – original draft, Efstratios Christodoulou; Writing – review & editing, Antonios Koutelidakis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
“The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the ethics and deontology committee of the University of the Aegean (protocol no. 17715 / 09.09.2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
New data is not available.
Acknowledgments
Authors thanks a lot all the participants of the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kumar S, Preetha G. Health promotion: an effective tool for global health. Indian J Community Med. 2012;37(1):5-12. [CrossRef]
- Søvold LE, Naslund JA, Kousoulis AA, et al. Prioritizing the Mental Health and Well-Being of Healthcare Workers: An Urgent Global Public Health Priority. Front Public Health. 2021;9:679397. Published 2021 May 7. [CrossRef]
- Colbourn, T. COVID-19: extending or relaxing distancing control measures. Lancet Public Health. 2020;5(5):e236-e237. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury MA, Shuvho MBA, Shahid MA, et al. Prospect of biobased antiviral face mask to limit the coronavirus outbreak. Environ Res. 2021;192:110294. [CrossRef]
- Mofijur M, Fattah IMR, Alam MA, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on the social, economic, environmental and energy domains: Lessons learnt from a global pandemic. Sustain Prod Consum. 2021;26:343-359. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Challenges and Approaches of the Global Governance of Public Health Under COVID-19. Front Public Health. 2021;9:727214. Published 2021 Nov 8. [CrossRef]
- Dong F, Liu HL, Dai N, Yang M, Liu JP. A living systematic review of the psychological problems in people suffering from COVID-19. J Affect Disord. 2021;292:172-188. [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou E, Meca A, Koutelidakis AE. Herbal Infusions as a Part of the Mediterranean Diet and Their Association with Psychological Resilience: The Paradigm of Greek Mountain Tea. Nutraceuticals. 2023; 3(3):438-450. [CrossRef]
- Muscaritoli, M. The Impact of Nutrients on Mental Health and Well-Being: Insights From the Literature. Front Nutr. 2021;8:656290. Published 2021 Mar 8. [CrossRef]
- Martini, D. Health Benefits of Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients. 2019;11(8):1802. Published 2019 Aug 5. [CrossRef]
- Mantzios, M. Mindful eating: A conceptual critical review of the literature, measurement and intervention development [published online ahead of print, 2023 Jan 26]. Nutr Health. 2023;2601060231153427. [CrossRef]
- Finicelli M, Di Salle A, Galderisi U, Peluso G. The Mediterranean Diet: An Update of the Clinical Trials. Nutrients. 2022;14(14):2956. Published 2022 Jul 19. [CrossRef]
- Mantzios, M. (Re)defining mindful eating into mindful eating behaviour to advance scientific enquiry. Nutr Health. 2021;27(4):367-371. [CrossRef]
- Rackham, H. Aristotle the Nichomachean Ethics with an English translation by H. Rackham (book). Harvard University Press, Boston. Published 1926.
- McEvilley, T. The Shape of Ancient Thought (book), Allworth Press, New York, NY, 2002, p. 609.
- Weiss, N. Philosophical Mindfulness an essay about the art of philosophizing. Revista Internacional de Filosofía Aplicada, no 8, pp.91-123. Published 2017.
- Mantzios M, Wilson JC. Mindfulness, Eating Behaviours, and Obesity: A Review and Reflection on Current Findings. Curr Obes Rep. 2015;4(1):141-146. [CrossRef]
- Garg, R. Methodology for research I. Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):640-645. [CrossRef]
- Regmi PR, Waithaka E, Paudyal A, Simkhada P, van Teijlingen E. Guide to the design and application of online questionnaire surveys. Nepal J Epidemiol. 2016;6(4):640-644. Published 2016 Dec 31. [CrossRef]
- Rees CS, Breen LJ, Cusack L, Hegney D. Understanding individual resilience in the workplace: the international collaboration of workforce resilience model. Front Psychol. 2015;6:73. Published 2015 Feb 4. [CrossRef]
- Charan J, Biswas T. How to calculate sample size for different study designs in medical research?. Indian J Psychol Med. 2013;35(2):121-126. [CrossRef]
- Gelinas L, Pierce R, Winkler S, Cohen IG, Lynch HF, Bierer BE. Using Social Media as a Research Recruitment Tool: Ethical Issues and Recommendations. Am J Bioeth. 2017;17(3):3-14. [CrossRef]
- In, J. Introduction of a pilot study. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2017;70(6):601-605. [CrossRef]
- Hulbert-Williams L, Nicholls W, Joy J, Hulbert-Williams N. Initial validation of the Mindful Eating Scale. Mindfulness, 2014;5(6):719–729. [CrossRef]
- Michail Mantzios. Development and initial validation of the Trait and State Mindful Eating Behaviour scales, 29 November 2022, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square.
- Hulbert-Williams L, Nichols W, Flynn S, Hulbert-Williams N. Further development and validation of a novel measure of trait mindful eating (Poster). Retrieved from University of Chester website: https://www.chester.ac.uk/sites/files/chester/Mindful%20eating%20scale%20CFA%20poster.pdf.
- Arnold WE, McCroskey JC, Prichard SVO. The Likert-type scale. Today's Speech, 15/2: 31-33. Published 1967.
- Schröder H, Fitó M, Estruch R, et al. A short screener is valid for assessing Mediterranean diet adherence among older Spanish men and women. J Nutr. 2011;141(6):1140-1145. [CrossRef]
- García-Conesa MT, Philippou E, Pafilas C, et al. Exploring the Validity of the 14-Item Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS): A Cross-National Study in Seven European Countries around the Mediterranean Region. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):2960. Published 2020 Sep 27. [CrossRef]
- Connor KM, Davidson JR. Development of a new resilience scale: the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC). Depress Anxiety. 2003;18(2):76-82. [CrossRef]
- Tsigkaropoulou E, Douzenis A, Tsitas N, Ferentinos P, Liappas I, Michopoulos I. Greek Version of the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale: Psychometric Properties in a Sample of 546 Subjects. In Vivo. 2018;32(6):1629-1634. [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou E, Deligiannidou G-E, Kontogiorgis C, Giaginis C, Koutelidakis AE. Natural Functional Foods as a Part of the Mediterranean Lifestyle and Their Association with Psychological Resilience and Other Health-Related Parameters. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(7):4076. [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Cuberos R, Castro-Sánchez M, Pérez-Turpin JA, Olmedo-Moreno EM, Zurita Ortega F. Levels of Physical Activity Are Associated With the Motivational Climate and Resilience in University Students of Physical Education From Andalucía: An Explanatory Model. Front Psychol. 2019;10:1821. Published 2019 Aug 6. [CrossRef]
- White MP, Alcock I, Grellier J, et al. Spending at least 120 minutes a week in nature is associated with good health and wellbeing. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):7730. Published 2019 Jun 13. [CrossRef]
- Ryff, C D, Singer B. The contours of positive human health. Psychological Inquiry, 9(1), 1–28. Published 1998. [CrossRef]
- Jones TL, Baxter MA, Khanduja V. A quick guide to survey research. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2013;95(1):5-7. [CrossRef]
- Hodge JM, Shah R, McCullough ML, Gapstur SM, Patel AV. Validation of self-reported height and weight in a large, nationwide cohort of U.S. adults. PLoS One. 2020;15(4):e0231229. Published 2020 Apr 13. [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, FQ. Body Mass Index: Obesity, BMI, and Health: A Critical Review. Nutr Today. 2015;50(3):117-128. [CrossRef]
- Kwak SK, Kim JH. Statistical data preparation: management of missing values and outliers. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2017;70(4):407-411. [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi A, Zahediasl S. Normality tests for statistical analysis: a guide for non-statisticians. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2012;10(2):486-489. [CrossRef]
- Warren JM, Smith N, Ashwell M. A structured literature review on the role of mindfulness, mindful eating and intuitive eating in changing eating behaviours: effectiveness and associated potential mechanisms. Nutr Res Rev. 2017;30(2):272-283. [CrossRef]
- Di Fabio A, Palazzeschi L. Hedonic and eudaimonic well-being: the role of resilience beyond fluid intelligence and personality traits. Front Psychol. 2015;6:1367. Published 2015 Sep 11. [CrossRef]
- Escoto KH, Laska MN, Larson N, Neumark-Sztainer D, Hannan PJ. Work hours and perceived time barriers to healthful eating among young adults. Am J Health Behav. 2012;36(6):786-796. [CrossRef]
- Min J, Lee DW, Kang MY, Myong JP, Kim HR, Lee J. Working for Long Hours Is Associated With Dietary Fiber Insufficiency. Front Nutr. 2022;9:786569. Published 2022 Feb 18. [CrossRef]
- Angier, T. Aristotle on work. Revue internationale de philosophie, 278,435-449. Published 2016. [CrossRef]
- Fuentes Artiles R, Staub K, Aldakak L, Eppenberger P, Rühli F, Bender N. Mindful eating and common diet programs lower body weight similarly: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2019;20(11):1619-1627. [CrossRef]
- Demirbas N, Kutlu R, Kurnaz A. The Relationship between Mindful Eating and Body Mass Index and Body Compositions in Adults. Ann Nutr Metab. 2021;77(5):262-270. [CrossRef]
- Buckland G, Bach A, Serra-Majem L. Obesity and the Mediterranean diet: a systematic review of observational and intervention studies. Obes Rev. 2008;9(6):582-593. [CrossRef]
- Estruch R, Martínez-González MA, Corella D, et al. Effect of a high-fat Mediterranean diet on bodyweight and waist circumference: a prespecified secondary outcomes analysis of the PREDIMED randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(5):e6-e17. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González MA, García-Arellano A, Toledo E, et al. A 14-item Mediterranean diet assessment tool and obesity indexes among high-risk subjects: the PREDIMED trial. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43134. [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos DB, Chrysohoou C, Pitsavos C, Stefanadis C. Association between the prevalence of obesity and adherence to the Mediterranean diet: the ATTICA study. Nutrition. 2006;22(5):449-456. [CrossRef]
- Sumithran P, Prendergast LA, Delbridge E, et al. Long-term persistence of hormonal adaptations to weight loss. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(17):1597-1604. [CrossRef]
- Contreras RE, Schriever SC, Pfluger PT. Physiological and Epigenetic Features of Yoyo Dieting and Weight Control. Front Genet. 2019;10:1015. Published 2019 Dec 11. [CrossRef]
- Sotos-Prieto M, Ortolá R, López-García E, Rodríguez-Artalejo F, García-Esquinas E. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Resilience in Older Adults: The Seniors-ENRICA Cohort. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2021;76(3):505-512. [CrossRef]
- Jager J, Putnick DL, Bornstein MH. II. MORE THAN JUST CONVENIENT: THE SCIENTIFIC MERITS OF HOMOGENEOUS CONVENIENCE SAMPLES. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 2017;82(2):13-30. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).








