1. Introduction
Male reproductive efficiency is an essential component of cattle’s production, biological breeding or reproduction, and economic efficiency (Ansari-Lari et al., 2010; Han & Peñagaricano, 2016; Liu et al., 2022). The elite genetic gain is made through enhanced production of sperm and selective gametes utilization from desirable sires to improve production and reproduction characteristics in dairy and beef industry on large scales. Bull fertility is an important factor in dairy farm businesses with strong influence on breeding and conception of cows (Han & Peñagaricano, 2016; Waqas et al., 2019). Selection of good breeding soundness bulls may have increase 20-40% of fertility in getting cows pregnant. Improved bulls fertility increases conception rate and calf weaning weight, reduce culling females, and reduce calving season. Artificial insemination and single-sire mating groups can also increase fertility of bulls in dairy farms and ranches. Therefore, standard breeding soundness evaluation of bulls and their testis must be considered to solve the substantial deficit of fertility with limitation to detect sub fertile bulls in a consistent manner. Variations in fertility can be suggested with combinations of laboratory tests at cellular, molecular and animal levels (Kastelic & Thundathil, 2008).The testis is the site of the spermatogenesis process performing two major functions namely, exocrine function and endocrine function. The endocrine function of testis is production of differentiated gametocytes facilitated by Sertoli cells, which then released in to the lumen of seminiferous tubules and stored in the epididymis, while the endocrine function is supported by leydig cells to produce steroids (Ge et al., 2021; Staub & Johnson, 2018).
Spermatogenesis is a long, orderly sophisticated developmental process of gametes multiplication and differentiation into spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules. Mammalian spermatogenesis is an androgen dependent process in which male germ line cells divide and differentiate (Grande et al., 2022; Sahlu et al., 2020; Smith & Walker, 2014; Zhao, Wang, et al., 2022). The undifferentiated spermatogonial germ cells starts to split and divided in to spermatocytes, spermatids and finally in to the production of mature spermatozoa, released in seminiferous tubules, at the apical pole of Sertoli cells and stored in the epididymis (Sahlu et al., 2020; Staub & Johnson, 2018). This process involves mitotic division, differentiation meiotic divisions and post meiotic divisions. Spermatogonial stem cells to produce type A spermatogonia developing in to type B spermatogonia that differentiate in to diploid primary spermatocytes (Zhao et al., 2021). The primary spermatocytes then divided into secondary spermatocytes during the meiosis I. The secondary spermatocytes also divided to produce four haploid spermatids. During spermiogenesis process, the haploid spermatids undergo morphological changes, including Chromatid reorganization, elimination of cytoplasm, flagellum development, nuclear formation and acrosomal formation to produce mature spermatozoa (Sahlu et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2021). Testosterone (T), a well-known and prominent sexual steroid hormone that functions prepubertal development for the expression of specific transcripts, in males that plays a crucial role for Sertoli cells, function in pubertal period prior to testicular maturation , largely produced by the Leydig cells in the testes (Johnston et al., 2004). At different stages during the development of the testes, Leydig, Sertoli, and Germ cells are also capable of producing estrogen. Estrogen has an important function in early testicular development and is primarily produced by Sertoli cells, which are found in the immature testis regulating Leydig cells development and number (Baker et al., 2003; Carreau et al., 2012). As their testes continue to generate estrogen and control spermatogenesis throughout this time, prepubertal animals, have a significant quantity of estradiol (E2) in their serum (Schulster et al., 2016).
MicroRNAs(miRNAs) are endogenous transcriptomic elements of small noncoding RNAs that are identified in animals, plants and viruses with 20-25 nucleotide length controlling most of the genes expression by blocking translation or inducing degradation of target messenger RNAs at posttranscriptional and transcriptional levels (Baohong et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2019; Vigneault et al., 2012). The miRNAs help to mediate coding and noncoding RNA molecules during fine-tuning crosstalk by sharing miRNA response elements (MRE) (Ala, 2020). These are responsible for RNA silencing, gene expression through targeting mRNA for post-transcriptional endonucleolytic cleavage (Wu et al., 2014), and translational repression or mRNA decay (Ala, 2020; Baohong et al., 2007).They also play regulatory and mediation functions in the cross-talks between the coding and noncoding transcriptome components by recognizing the target sites in various biological functions and physiological processes (Ala, 2020; Sun et al., 2019).The regulation of miRNAs is modulated by noncoding RNAs that are significantly expressed in many biological and cellular processes.
The high-tech sequencing technologies such as second generation sequencing technologies, micro RNA deep sequencing and Illumina-Solexa high throughput sequencing technologies speed up the identification and discovery of new miRNA species (Li et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2014).Multiple studies shown that miRNAs play an important role in the regulation of various biological processes and tissue systems that function as regulation of cellular differentiation, self-renewal and apoptosis (Niu et al., 2011), including mammalian spermatogenesis and reproductive system development (La et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2014; Yin et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022). Lots of studies indicate the involvement of miRNAs modulating gene expression in multiple cellular and biological processes, including proliferation (Kim et al., 2017), organ development, stem cell differentiation (Luo et al., 2020), hormone secretion, metabolism and reproductive regulation (Gao et al., 2020; La et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2014). Additionally, miRNAs can serve as epigenetic modulators, influencing target mRNAs' protein levels without altering gene sequences. The expression of miRNAs is influenced by the regulation of epigenetic machineries, such as DNA methylation and RNA modification (Yao et al., 2019). Su et al. reported the expression profiles of miRNAs in different tissues (bovine sera, exosomes, mammary gland, rumen and gut) (Sun et al., 2019). This study identified 639 miRNAs providing a clue to the understanding of miRNAs and their regulatory roles in tissue specific and tissue development functions that can be applied in animal production, animal health and human health research. Puberty is closely related with sexual and testicular maturity, spermatogenesis and capability of reproduction. There is increased evidence of miRNAs involvement in regulating testicular development and spermatogenesis. Zhang et al. screened out 322 novel miRNAs, 767 known miRNAs and 359 exist miRNAs regulating precocious sexual maturity traits providing new light on miRNAs role and regulation mechanisms in Land race and Hezuo boars for precocious puberty (Zhang et al., 2022). A study by Zhu et al. on Saanen Dairy Goat Testis found conserved miRNAs through Illumina high-throughput sequencing technology and miRNA sequences blasted to miRNAs of cow and sheep in miRBase 19.0 identifying 373 conserved miRNAs and 91 novel paired-miRNAs while those blasted to miRNAs of cow and mouse resulted in 128 conserved miRNA, which may reveal their involvement in meiosis and testis development in the dairy goat testis (Wu et al., 2014). An investigation by Liu et al. conducted a comprehensive sequencing analysis study using testicular tissue samples from three immature calves and three sexually mature bulls of the Wandong cattle breed identified 151 differentially expressed (DE) miRNAs and miRNA-linked genes. The miRNA-linked genes found involved in PI3KAkt signaling, TNF signaling and T cell receptor of biological pathways and functions affecting spermatogenesis and testicular development. The DE expressed miRNAs were also associated with sexual maturation and sperm production in Wandong Cattle (Bos taurus) (Liu et al., 2022).
The identification of single stranded noncoding RNA is important to determine the functional mechanisms during sexual maturation and testicular growth at transcriptional and post transcriptional levels (Liu et al., 2022).The improvement of reproductive efficiency in breeding Holstein bulls with emphasis on potential genetic resources regulating spermatogenesis and testis development at molecular level remains unexplored. Even though, the comprehensive expression profiles of miRNA in different age groups of cattle breeds and different species have been studied, the spermatogenesis related miRNAs expression in Holstein bulls has not been reported. Therefore, there is a gap on the expression of miRNAs, regulatory mechanisms and expression profiles in the developing Holstein bull testis and remains uncertain. The final goal of the study was to determine potential biomarkers related to Holstein bulls testes and find miRNA associated candidate mRNAs or target genes so as to improve Holstein bull reproductive performance for the future.
I study the insights of miRNA and its related mRNA accompanying spermatogenesis and testicular growth to further broaden the understanding of miRNA regulation of spermatogenesis and testicular development in immature and mature Holstein bull testes was briefly described.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
All animal protocols, experimental designs and procedures required for study were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Institute of Animal Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China. All the required standards with necessary measures were made to minimize and avoid suffering of the experimental animal from pain.
2.2. Experimental Animals and Testis Tissue Sample Collection
Before the start of the experiment, the experimental animals were checked for their health status and six animals selected from those healthy and free of disease. Animals were based on similar genetic background of the same breed and body condition according to their female parent’s better calving interval and categorized in to two according to their age. Three 80 weeks old mature Holstein bull (n=3; designated as D5, D6 and D7) and three 8 weeks young Holstein bulls (n=3; designated as X1, X2 and X3) were filtered and surgically castrated to obtain intact testis after being given general anesthesia (Zoletil 50, Virbac Co., France). The experimental animals were properly restrained in a clean environment before and after sedation. Then castration started following the excision of the testis with removing the lower third of the scrotum and testis cutting the spermatic cord by surgical blade in a manner of reduced or with no bleeding. The connective tissue, tunica albuginea and fat were removed using forceps under the stereomicroscope cutting the middle segments of the testis parenchymal tissue, quarter of each pair testes near the epididymis tail, incised into1-2cm3 size tissues, collected with RNAlater and snap frozen in (-196 oC) liquid nitrogen immediately for isolation. The frozen sample then transported to Institute of Animal Science, Key Laboratory of Animal Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction and stored at -80 oC until RNA extraction.
2.3. Determination of Hormonal Concentration
A total of six Holstein bulls were used, comprising three young and three mature Holstein bulls sourced from the same dairy farm in Beijing, China. These bulls were divided into two groups, with three bulls assigned to each group, namely 8 week old and 80 week old. Blood samples were collected from all six bulls through the tail vein venipuncture. Within one hour of collection, the samples were centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 5 minutes to collect serum and then stored at -20°C for further analysis for T (testosterone), E2 (estradiol), and P4 (progesterone) hormone concentrations.
To determine the concentrations of T, E2, and P4 in each bull’s serum, a radioimmunoassay system (XH6080, China) was used. The measurements were performed in triplicate as per the manufacturer's instructions. Subsequently, the serum levels of T, E2, and P4 were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) in the SPSS software.
2.4. Histological Assessment
Following the removal of the fascial tissue, tunica vaginalis, and tunica albuginea, a testicular sample was obtained by cross-cutting a slice from the middle region of the testes using precise dissection techniques. The slice was preserved in a 4% formaldehyde solution to enable subsequent histological evaluation. The testicular tissues were further processed, sectioned into sections measuring 6μm thickness, and stained with Masson's trichrome stain. The stained sections were examined under different magnification powers to assess the histomorphology of the testicular tissues. A comprehensive analysis of the structural characteristics and composition of the testis in the two groups was achieved, allowing for a detailed understanding of its intricate histological features in between the group.
2.5. RNA Extraction and Qualification
Initially, the frozen testicular tissues were pulverized into a fine powder. Subsequently, the extraction of tissue RNA was carried out using a trizol reagent kit (Thermo Fisher, 15596-026), and the quantification of total RNA was accurately performed using the qubit RNA assay br kit (Invitrogen, Q10211). The ribo-zero magnetic kit (Lucigen, MRZPL116) was employed to eliminate ribosomal RNA (rRNA) from the total RNA. The agilent RNA 6000 pico chip (Agilent, 5067-1511) was utilized for quality control of the rRNA that had been removed from the total RNA.
2.6. Quality Control of Sequence Reads
The raw data was filtered using third party software with the filtering criteria of discarding reads with 5'-end adapter contaminants, trim 3'-end adapter; reads with 3'-end adapter only, reads with length <18nt, reads with N base, reads with poly-A in 3'-end, reads with length >30nt and low quality reads (more than 70% bases with quality score <20). The FastQC was used for the quality checks on the raw data of the six testicular tissue samples resulting in high quality sequences. The adapter sequences (Adapter, Oligonucleotide sequences for TrueSeqTM Small RNA sample prep kits of RNA 5' Adapter (RA5), part# 15013205 GUUCAGAGUUCUACAGUCCGACG AUC and RNA 3' Adapter (RA3), part # 15013207 AGATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCT were used to filter out the sequence reads. The Cutadapt-1.7.1 and fastx-toolkit-0.0.14 were used to remove the adaptors or the connector sequences and low quality reads, respectively. The clean reads statistical results were used for comparisons and sequence analysis.
2.7. Reads Mapping and Sequence Analysis
The cDNA libraries were constructed from testicular tissues of three young Holstein bulls (X1, X2, X3; group YB) and three mature Holstein bulls (D5, D6, D7; group AB). The sequence reads for each sample was from the Illumina high-throughput sequencing. They compared to reference genome with HISAT22.1.0 software (Institute Pasteur, Paris, France) (Kim et al., 2015) according to the criteria. Cutadapt-1.7.1 was used to remove the adapters and fastx-toolkit-0.0.14 to eliminate the low quality reads. The reads were aligned to the Rfam database and mapped using the Blastin. The number and percentage of clean reads of pre-miRNA, rRNA, tRNA, snRNA, other ncRNAs and repeats were compared to sample species miRNA precursor sequence database (miRBase v21), Rfam database (release11.0, rRNAsequences) and the Silva database (rRNAdatabase), Rfam database (release 11.0, tRNA sequences), Rfam database (release 11.0, snRNA sequences), Rfam database (release11.0, except miRNA, tRNA, snRNA, rRNA sequences) and repeat region with the RepBase (version 20.04) database, respectively, as a base for classification statistics of high quality clean data. The filtered sequences that do not matched to those databases are not classified. Bovine rRNA, sRNA, snRNA, and snoRNA mapping reads were eliminated. The sRNAs were categorized, and readings were mapped to the bovine reference genome (ARS-UCD1.3), both in exon and intron sequences, using Bowtie v1.1.1; Boao Crytal Code Program. The retained reads that were mapped to the bovine genome and intron region were further processed for novel miRNAs prediction and quantification of known miRNAs via the miRDeep2 v2.0.0.6 module and quantifier module of the miRDeep2 software (Friedländer et al., 2012).
2.8. Predicting miRNAs
In order to predict miRNAs, the first step involved was extracting candidate precursor sequences from the reference genome by extending the sequences of Clean Reads at 20nt upstream and 70nt downstream, as well as 70nt upstream and 20nt downstream, with a total length of less than 120nt. The extracted sequences were comprehensively scored based on the thermodynamic stability of the hairpin structure and secondary structure of the candidate pre-miRNA sequences. The miRDeep2 software predicted precursor pre-miRNAs that satisfy specific conditions, including more than 60% of the bases in the mature miRNA sequence being paired with star miRNAs, a length difference between mature miRNA and star miRNA of less than 6nt, and no branching in the precursor structure. The predicted pre-miRNAs were filtered based on criteria such as the total number of Clean Reads compared to pre-miRNA being greater than or equal to 2 and the total number of Clean Reads compared to mature miRNAs and star miRNAs as a percentage of the total number of precursor Clean Reads being greater than or equal to 20%. Additionally, the starting position of Clean Reads was within 2nt overhang upstream of the 5'-end of the known miRNA sequence and the ending position of clean reads were within 2nt overhang downstream of the 3'end of the known miRNA sequence. MiRDeep2 analysis software was used and resulted in novel miRNA prediction, secondary structure, length and base distribution, and comparison display map.
2.9. Expression Normalization and Correlation Analysis of Samples
After localizing clean reads specifically to miRNAs, the numbers of localized reads in the miRNAs were utilized to determine the expression level of miRNAs. Since the number of reads is also dependent on the length and sequencing depth, normalization using TPM (Transcripts Reads Number per Million) was done before expression analysis. The denominator in the equation represents the total number of reads in a sample as compared to the reference genome, while the numerator represents the total number of reads in a specific miRNA. The normalized TPM values (TPM=1,000,000*(The miRNA Mapped Reads/Total Mapped Reads) represent the expression of miRNA in a given sample, and these values were applied in subsequent analysis. The Boao Jingdian program is the expression normalization analysis software utilized in the process to determine the expression of miRNA in the sample groups more accurately and creatively. To conduct analysis of the sample correlation utilizing the R language; the Pearson Correlation Coefficient was calculated. This value, which falls between the range of -1 and 1, was determined using the TPM values of both the samples of known miRNA and novel miRNA. The Pearson Correlation Coefficient serves as an essential indicator of biological replicate correlation, with a value closer to 1 suggest a stronger correlation between the two replicates.
2.10. Differential Expression Analysis
The expression level of miRNAs was compared by the R package edgeR/limma package for the two grouped testicular tissue samples. Differential miRNA expression analysis was performed on grouped samples to find up- and down-regulated miRNAs. Specifically, the lowly expressed miRNAs were filtered with the TPM normalization method. To screen the differentially expressed miRNAs between the two group samples, the significant P-value and fold-change (FC) were used as the criteria for differential expression: (1) Judged Up-regulated miRNAs when P-value ≤ 0.05 and FC≥ 2 (log2 (FC) ≥ 1); (2) Down-regulated miRNAs was judged when p-value ≤ 0.05 and FC ≤ 0.5 (log2(FC) ≤ -1). Larger difference multiples of FC values indicated that miRNA expression was more different in the two grouped samples. The differentially expressed miRNAs in known miRNAs and novel miRNAs were systematically clustered separately to construct differential expression profiles, and miRNAs with similar expression patterns in multiple samples would be clustered together. Volcano plot was carried out to merge common DE miRNAs between the two groups for further analysis. The differentially expressed miRNAs in known miRNAs and novel miRNAs were systematically clustered separately to construct differential expression profiles, and miRNAs with similar expression patterns in multiple samples would be clustered together.
2.11. Target Prediction and Function Annotation
With the miRNAs of the two age groups (X vs D) being filtered, miRanda was employed to predict their target genes. The threshold of the prediction software miRanda was set to Score ≥ 140 and Energy ≤ -20 kcal/mol. Finally, the target gene prediction results were taken from the top 10 of the miRanda software prediction results. The miRanda Prediction principle was used for miRanda Target Gene Prediction Software by Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Research Center (
https://www.mskcc.org/),published in 2003. miRanda predicts target genes based on the complementarity of miRNA sequences and candidate 3'UTR or mRNA sequences, as well as the thermal stability of miRNA-mRNA duplexes. The miRNAs interact with mRNAs and can regulate mRNA expression at the translational level through complementary pairing. Each miRNA can have multiple target genes, and several miRNAs can regulate the same gene. This complex regulatory network can either regulate the expression of multiple genes through a single miRNA or finely regulate the expression of a gene through a combination of several miRNAs. Thus, the 3'UTR region of mRNAs as the target gene prediction database was used for selection of the miRNAs. Therefore, the gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was performed to gain a deeper understanding on the DEGs expression patterns of miRNAs and their function extrapolating the data for profound processes and pathways.
2.12. Network Analysis of Differentially Expressed miRNA Target Genes
In order to comprehensively understand the complex relationships between functional processes and genes with their respective pathways the powerful tool of igraph R package (the network analysis package) was utilized to illustrate net plots and provide a clear depiction of the correlations among pathways. In particular, the study focused on creating diagrammatic representations of the GO to GO, gene to pathways, and pathway to pathway plots.
2.13. RT-qPCR Validation and Statistical Analysis
To validate the sequencing results, an experiment was conducted on miRNAs and target genes chosen randomly for qRT-PCR validation and U6 was used as a house keeping gene. Further experimentation was done on the selected up/down regulated miRNAs and mRNAs using specific primers and conditions. The 2-∆∆CT method was utilized for quantifying the relative expression of miRNAs and target genes. A student’s t-test was conducted using Graph Pad Prism 8 software for comparing the differences among the young and adult Holstein bull testis tissue samples. The p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant while p-value < 0.01 was considered extremely significant.
Table 1.
The information on the primers for mRNA genes used in RT-qPCR validation.
Table 1.
The information on the primers for mRNA genes used in RT-qPCR validation.
| Gene Name |
Sequence of Primers (5’- 3’) |
Product Length (bp) |
Tm (◦C) |
| THAP3 |
F: TCTGGGGAGAGAAAGGTCCTC
R: AGGGCATAGCTGTGATCGGA |
227 |
60.27 |
| FOSB |
F: GAGAAGAGAAGGGTTCGCCG
R: CTAGCTGATCTGTCTCCGCC |
106 |
60.46 |
| SLC2A5 |
F: CTAGCTGATCTGTCTCCGCC
R: GTCGACGGTGGAAACTCCTT |
203 |
60.03 |
| CCNT2 |
F: ACCCAGTTAGTAAGAGCAAGCA
R: CAGGGATCTCCCAATTGGACC |
160 |
59.36 |
| CMC1 |
F: ACCCCTCAGAGCAGCAT
R: TGGGAAGCTTCTGTAGCCTTT |
300 |
57.33 |
| GAPDH |
F: CTTCGGCATTGTGGAGGG
R: GGAGGCAGGGATGATGTTCT |
130 |
61.3 |
Table 2.
Stem-loop RT-PCR primers for real-time quantification of selected differentially expressed miRNAs in testis between Young bull and Adult bull.
Table 2.
Stem-loop RT-PCR primers for real-time quantification of selected differentially expressed miRNAs in testis between Young bull and Adult bull.
| MiRNA ID (5′-3′) |
Stem-loop RT primer (5′-3′) |
MiRNA specific forward primer |
| bta-miR-11971 |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTTCTCA --3' |
5'--CGCGTGAGGGGCAGAGAG --3' |
| bta-miR-2284c |
5'-- GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACAAAACC --3' |
5'--GCGCGAAAAAGTTCGTTTT --3' |
| bta-miR-3956 |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACCCTCTG --3' |
5'--CGACGTGGATGCTGAAGGT --3' |
| bta-miR-135b |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTCACAT --3' |
5'--CGCGTATGGCTTTTCATTCCT --3' |
| bta-miR-299-2 |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACATGGTT --3' |
5'--CGCGGTATGTGGGACGGTA --3' |
| bta-miR-433 |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACACACCG --3' |
5'--GCGATCATGATGGGCTCCT --3' |
| bta-miR-191 |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACCAGCTG --3' |
5'--CGCAACGGAATCCCAAAAG --3' |
| bta-miR-20a |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACCTACCT --3' |
5'--GCGCGTAAAGTGCTTATAGTGC --3' |
| 4_37054-5p(cli-miR-9632-3p) |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACAGTCCG --3' |
5'--GCGAACTTTTGCCCCTAGTAA --3' |
| 7_42582-5p |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTGTTAG --3' |
5'--GCGCGTGAGAGGTCTGTAATAA --3' |
| 6_40791-3p |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGTCCC --3' |
5'--GCGTGAGTGTGCATCCACG --3' |
| 21_23590-5p(mmu-miR-665-3p) |
5'--GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGCTCAT --3' |
5'-- CGCCCAGGAGAATGAGGG --3' |
3. Results
3.1. Hormonal Concentration
Hormonal profiles of the Holstein young bull and mature bull testis as the testes developed, the testosterone, estrogen and P4 (progesterone) levels underwent significant changes, with a noteworthy surge from 0.003 ± 0.001 ng/mL to 0.167 ± 0.0078 ng/mL, 62.12 ± 7.07 ng/mL to 57.22 ± 21.41 ng/mL and 0.12 ± 0.01 ng/mL to 0.16± 0.04 ng/mL, respectively, as revealed by hormone testing, indicating a crucial role of hormonal profiles in the developmental stages (
Table 3).
3.2. Testicular Tissue Morphologic Characteristics of Six Samples
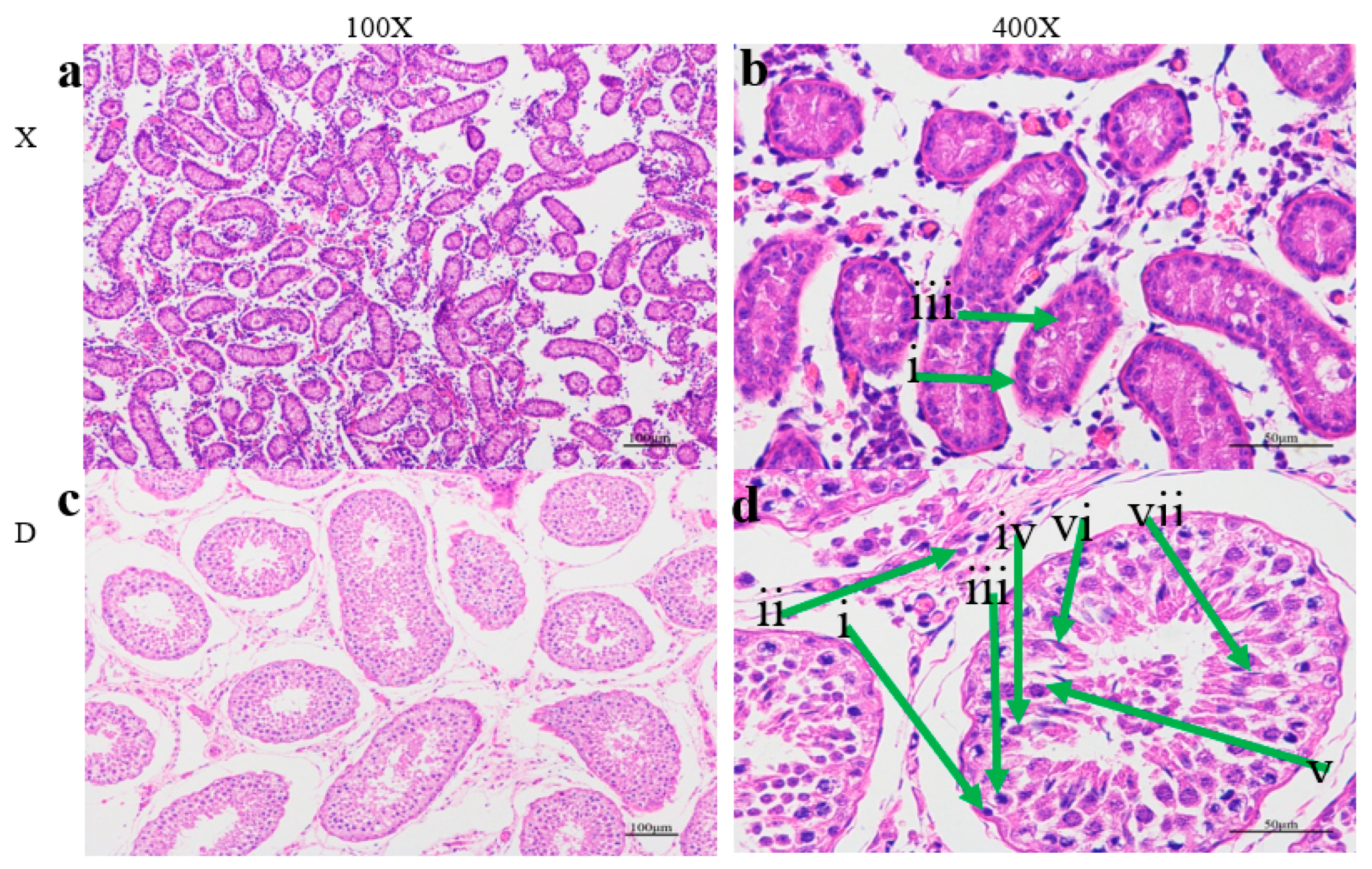
The testicular tissue sections of adult Holstein bull were found to possess seminiferous tubules that were highly vacuolated, with thinner walls as compared to young Holstein bull. The morphological structure of the testes indicated significant difference between the growing young and mature bulls with considerably larger diameter of the seminiferous tubules in sexually matured bulls when observed in 10X and 40 X microscopic magnifications. The interstitial connective tissues of the two groups had remarkably very comparable condition. It can be observed from
Figure 1 that the area of the longitudinal section of the testis was expanded in the case of adult Holstein bull. At 40X magnification, more clear structures and more developed stages of spermatogenesis were observed than the young Holstein bulls. It can be seen that there are very few germ cells or spermatocytes present in the seminiferous tubules of young Holstein bull, which is in contrast to Adult Holstein bulls. Moreover, significantly well developed and larger numbers of Sertoli cells were notably seen close to the seminiferous tubules basement (
Figure 1).
3.3. Quality Control
After high-throughput sequencing filtering the base quality values with FastQC software to remove the 3’ adaptors, the clean reads were then changed to FASTA format indicating the sequencing accuracy. A large number of clean reads, ranging from 83,607,760 to 88,281,454 were expertly generated through the meticulous process of filtering low-quality and covering repeated reads. These reads exhibited a remarkable clean reads rate percentage ranging from 98.17% to 98.33%, and all boasted Q20 and Q30 values that exceeded an impressive 97.98% and 93.77%, respectively (
Table 4). After filtering the low quality reads with fastx-toolkit-0.0.14 and with Cutadapt-1.7.1 to remove the 3’ adaptors, the clean reads were displayed with quality control statistics (
Table 5).
3.4. Reads Mapping and Filtration
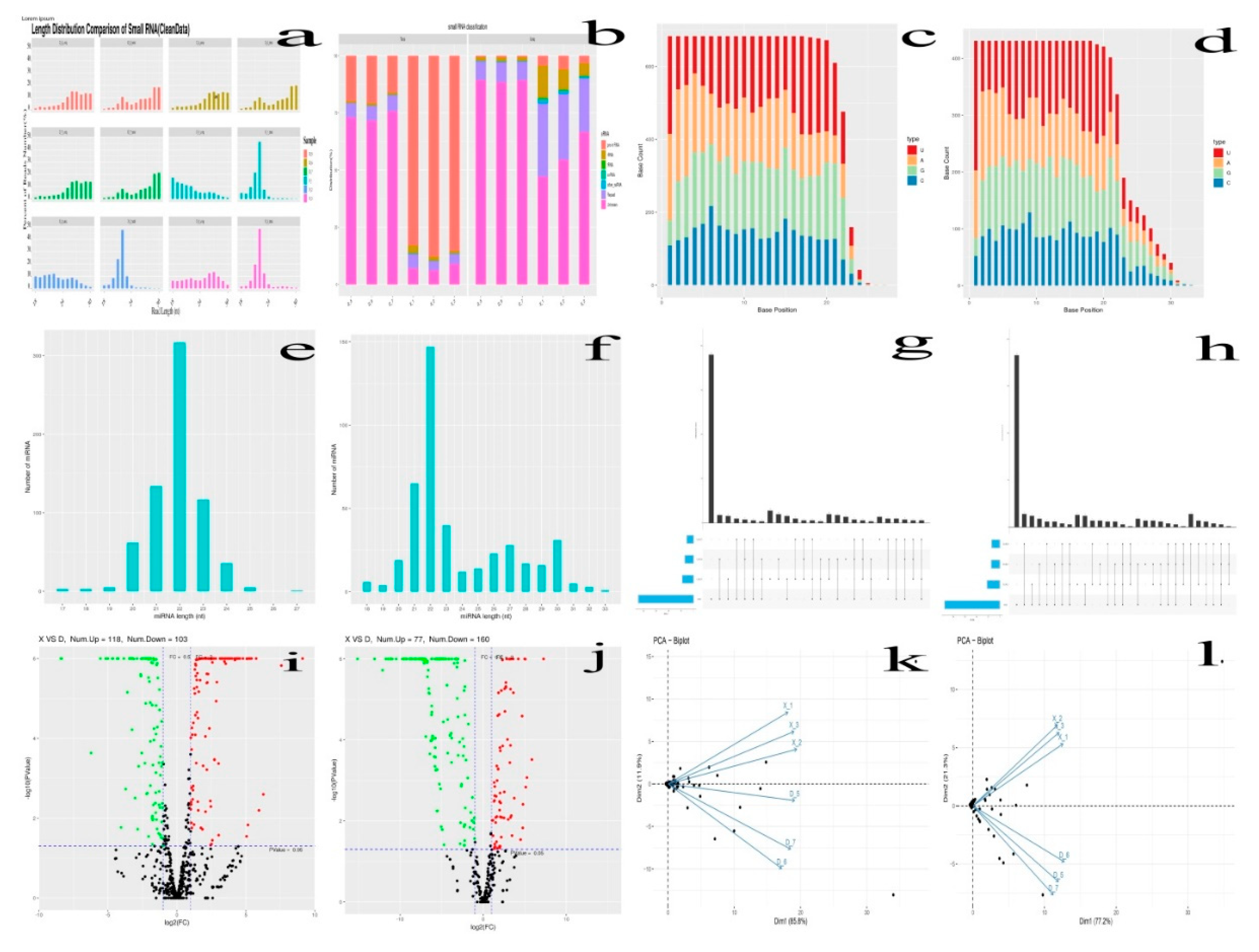
Blastn was utilized to precisely align the reads to the Rfam database, which includes Hairpin, repeats, rRNA, snRNA, snoRNA, tRNA and other ncRNAs (
Figure 2b). The mapped reads were then filtered using stringent criteria such as gapopen =0, value <0.01, and mismatch ≤1. Subsequently, Bowtie was used to map the exon and intron sequences, where they filtered the reads that could be mapped to the exon sequence but not to the intron sequence, keeping those with mismatch ≤1. Finally, the clean reads were mapped to the bovine reference genome (ARS-UCD1.3) with rigorous mismatch ≤1 criteria (
Table 6). The BeoCrystal Program; R language was also employed for the statistical analysis of the clean reads length sequence distribution of each sample, small RNA (sRNA) classification and length distribution (
Figure 2a). The clean reads obtained within certain length range from the two groups (X and D group) were further screened for sRNA and analyzed. The range length of the clean reads of sRNA in animals was from 18 to 35, and similarly, in this study also falls between 18 and 30nt. Thus, difference in peaks length distribution helps to the identification of different classes of sRNAs mainly the miRNA, which have predominantly concentrated within the range of 21~22 (
Figure 2e-f). A total of 1114 miRNAs were identified from the 8 week and 80 week old Holstein bull testes. The known and novel miRNAs base distribution map with the horizontal and vertical coordinate indicating the number of base and base positions, respectively, for the nucleotides was indicated (
Figure 2c-d). In addition, the principal component of these six samples was done (
Figure 2k-l), and determined that they could be separated into two distinct groups: X, and D.
3.5. The miRNAs Family and Expression Level Analysis
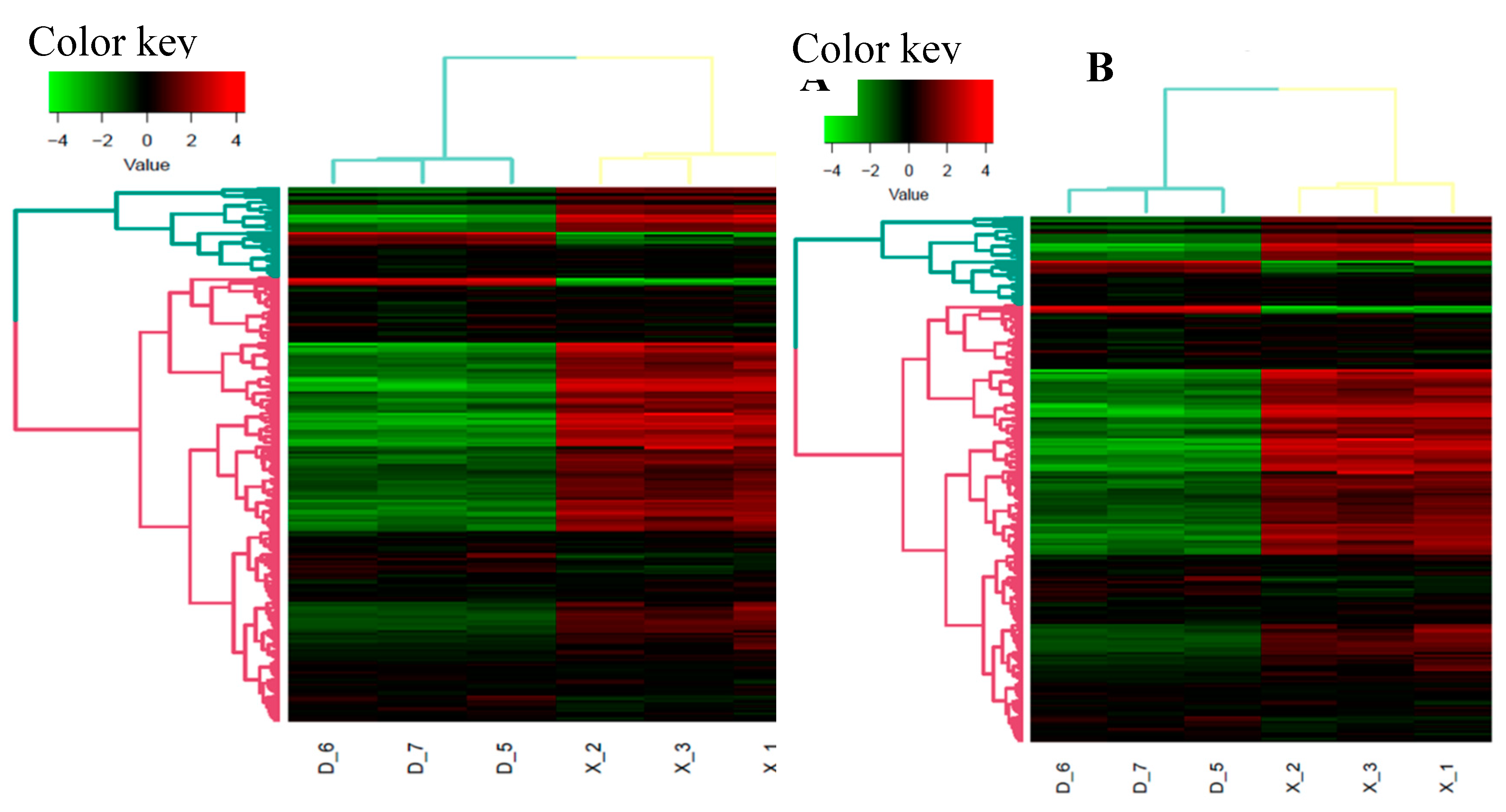
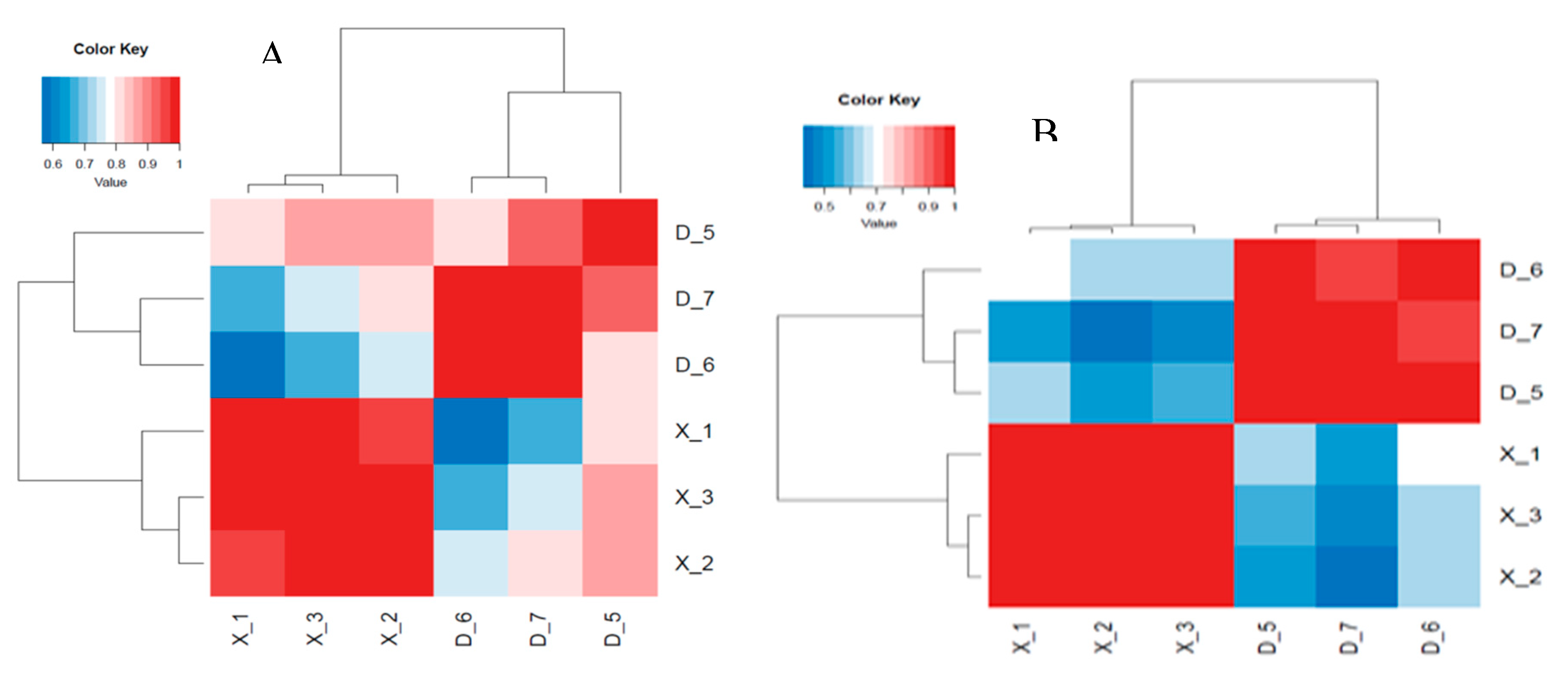
After removing the reads that were not miRNAs, mirDeep2 was utilized to make predictions about novel miRNAs and the secondary structure of miRNAs. Furthermore, quantification of miRNAs and an analysis of miRNA families were conducted in order to gain a deeper understanding of their function in relation to target genes. The counts obtained were then normalized using RPM, which can be visualized through the RPM Volcano plot of the six samples. Using the miRNA expression levels of each sample, the correlation between samples within each group (
Figure 4), as well as the distance between the two groups was analyzed and expressed in differential expression cluster heat map (
Figure 3) and volcano plot for the up and down regulated known miRNAs (
Figure 2i-j). The samples within each group were highly relevant, and that the distance between the two groups was quite noticeable.
3.6. Differential Expression Analysis of miRNAs and Target Genes
Through the process of analyzing differential expression, the miRNAs between six samples were examined, revealing unique and distinct patterns of genetic expression. The differential expression of miRNAs among nine samples with CPM >1, p-value < 0.05, |log2FoldChange| >1 was analyzed using the R package edgeR. Subsequently, a heat map was employed to graphically represent the clustering analysis and differentially expressed miRNAs of X vs D. A total of 1114 miRNAs were identified in two age groups (X vs D) with 683 known miRNAs and 431 novel miRNAs. Specifically, 221 known miRNAs were differentially expressed in X vs D, of which 118 were up regulated and 103 were down-regulated. Whereas 237 novel miRNAs were also found differentially expressed in X vs D, of which 77 were up regulated and 160 were down-regulated. The differentially expressed miRNAs were shown in volcano plot (
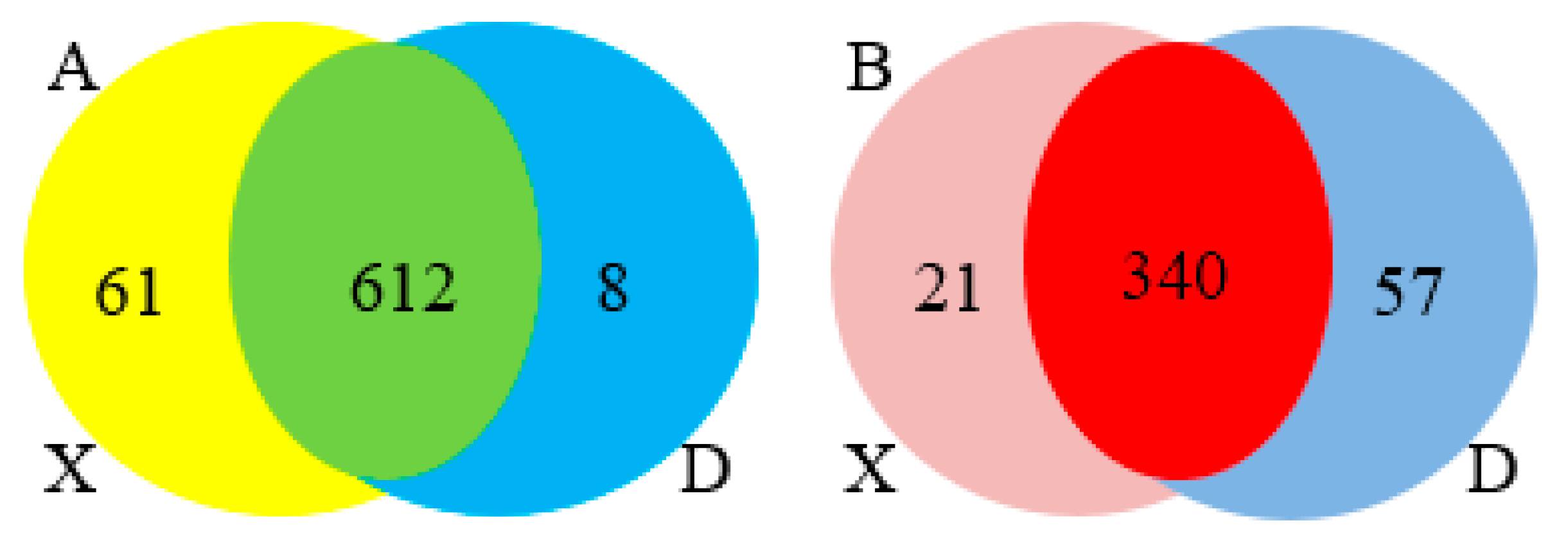
Figure 2i-j). A total of 1641 up and 1506 down regulated target genes with known miRNAs and 1100 up and 2254 down regulated target genes with novel miRNAs were identified based on the complementarity of miRNA sequences and candidate 3’UTR or mRNA sequences as well as the thermal stability of miRNA and mRNA duplexes. From the sequence analysis, 61 known miRNAs were expressed in the young Holstein bulls with 6 known miRNAs significantly different (p<0.05) and 8 known miRNAs expressed in the mature Holstein bull with one known miRNA significantly (p<0.05) expressed. Furthermore, 21 miRNA were expressed in the young Holstein bulls with 6 novel miRNAs significantly different (p<0.05) and 57 novel miRNAs expressed in the mature Holstein bulls, of which 55 novel miRNAs significantly different (p<0.05). Finally, a merged analysis of X vs D was conducted, where in the common up-regulated and down-regulated miRNAs of Holstein bulls were consolidated (
Figure 5).
3.7. Target Prediction, Functional Enrichment, and Network Analysis
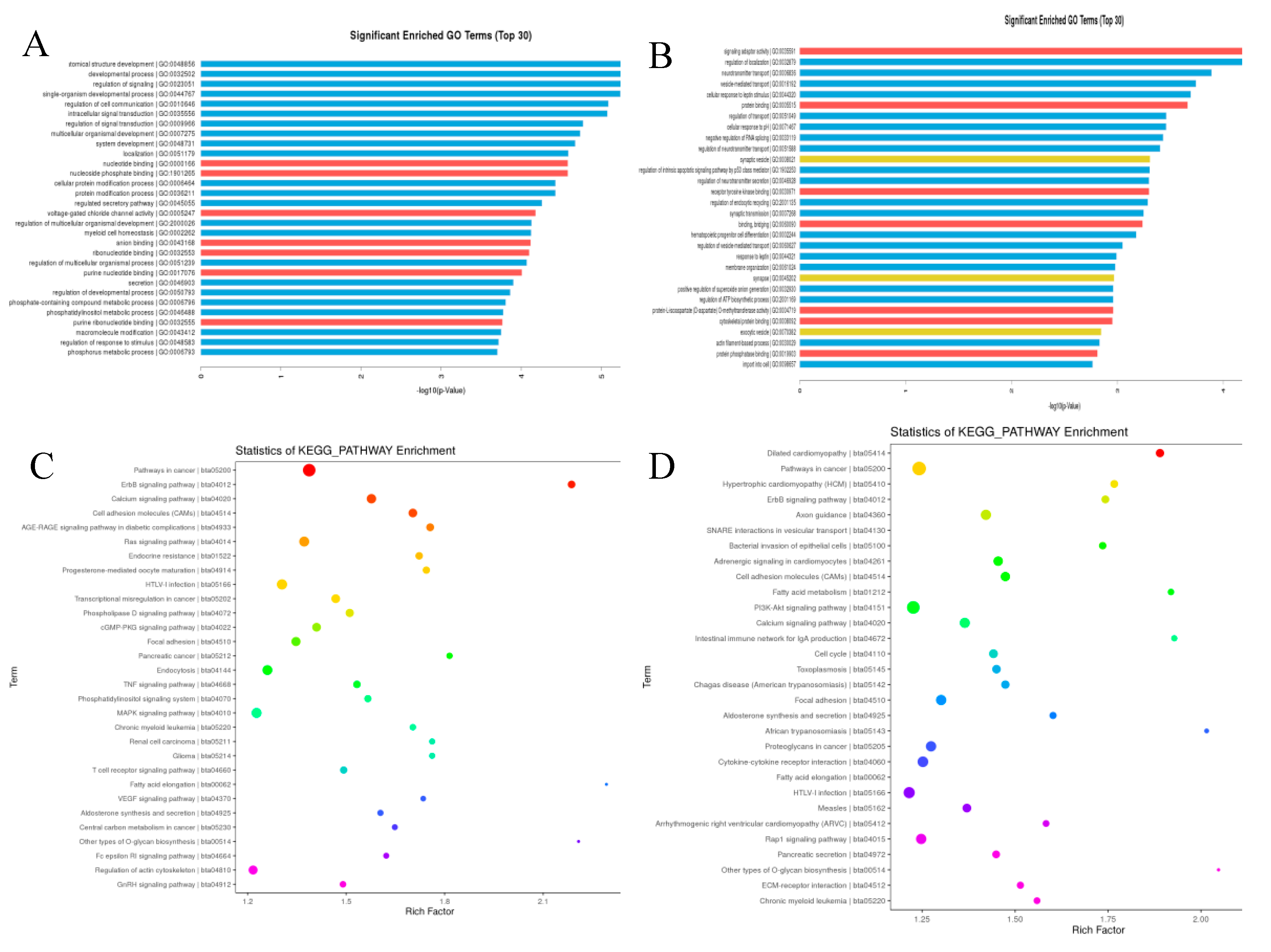
The target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs in X vs D. were predicted with the help of Miranda software. From the 1114 total known and novel miRNAs, 6501 up and down regulated target genes were predicted with miRanda target gene prediction software. The predicted target genes were significantly (p<0.05) participated in in a broad range of biological processes, molecular function and cellular component (
Figure 6 and
Figure 7). The regulation of mRNA expression by miRNAs was accomplished through patterns of down regulated mRNAs and up regulated miRNAs. The two age groups were examined individually for up-regulated mRNAs and down-regulated miRNAs for further investigation of the phenomena. Gene ontology analysis was conducted on the miRNA targets, and the results were further revealed in GO terms. Additionally, using GO and KEGG pathway analysis, the potential functions of differentially expressed genes in testicular development was investigated (
Table 7,
Figure 7 and
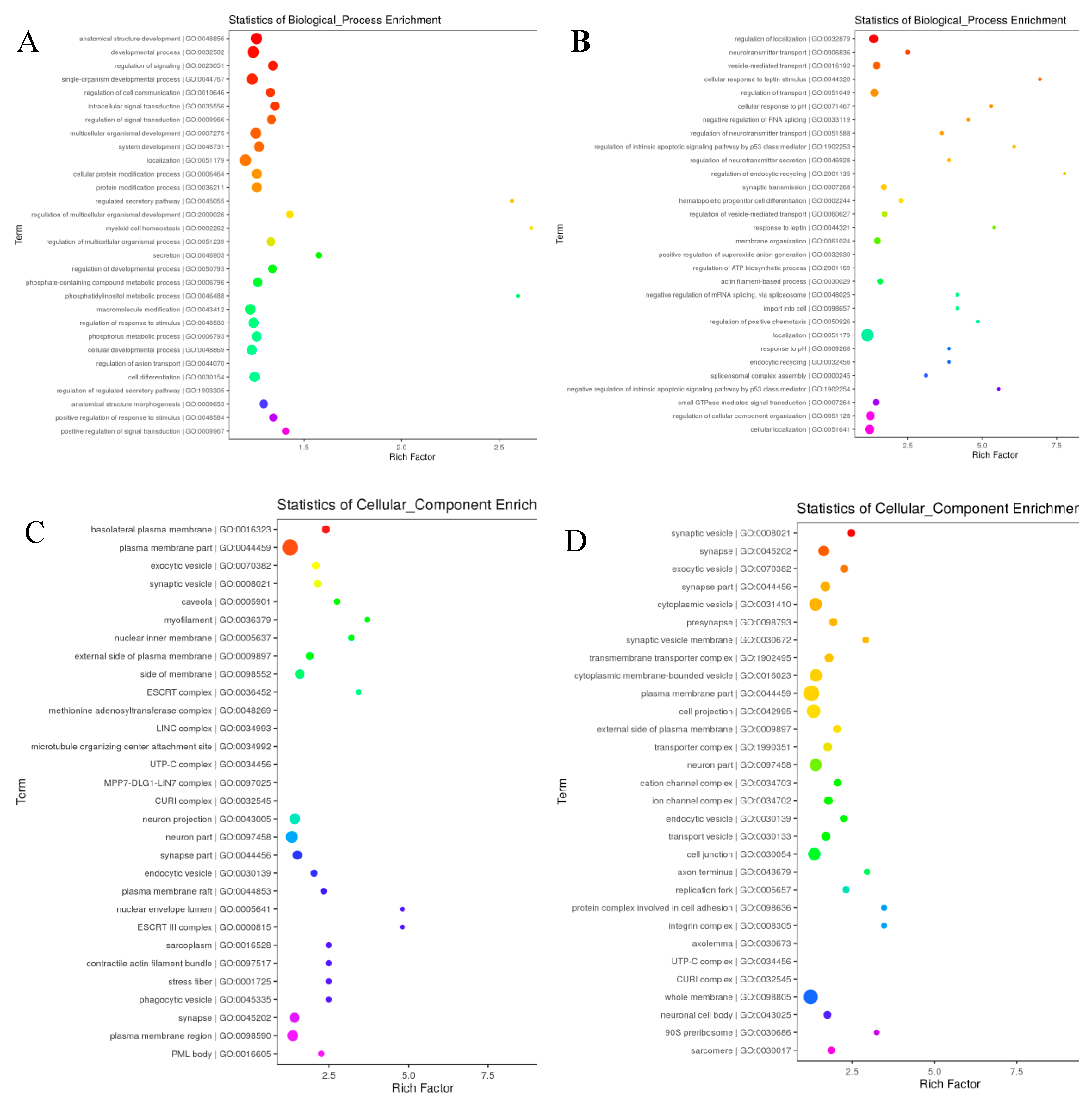
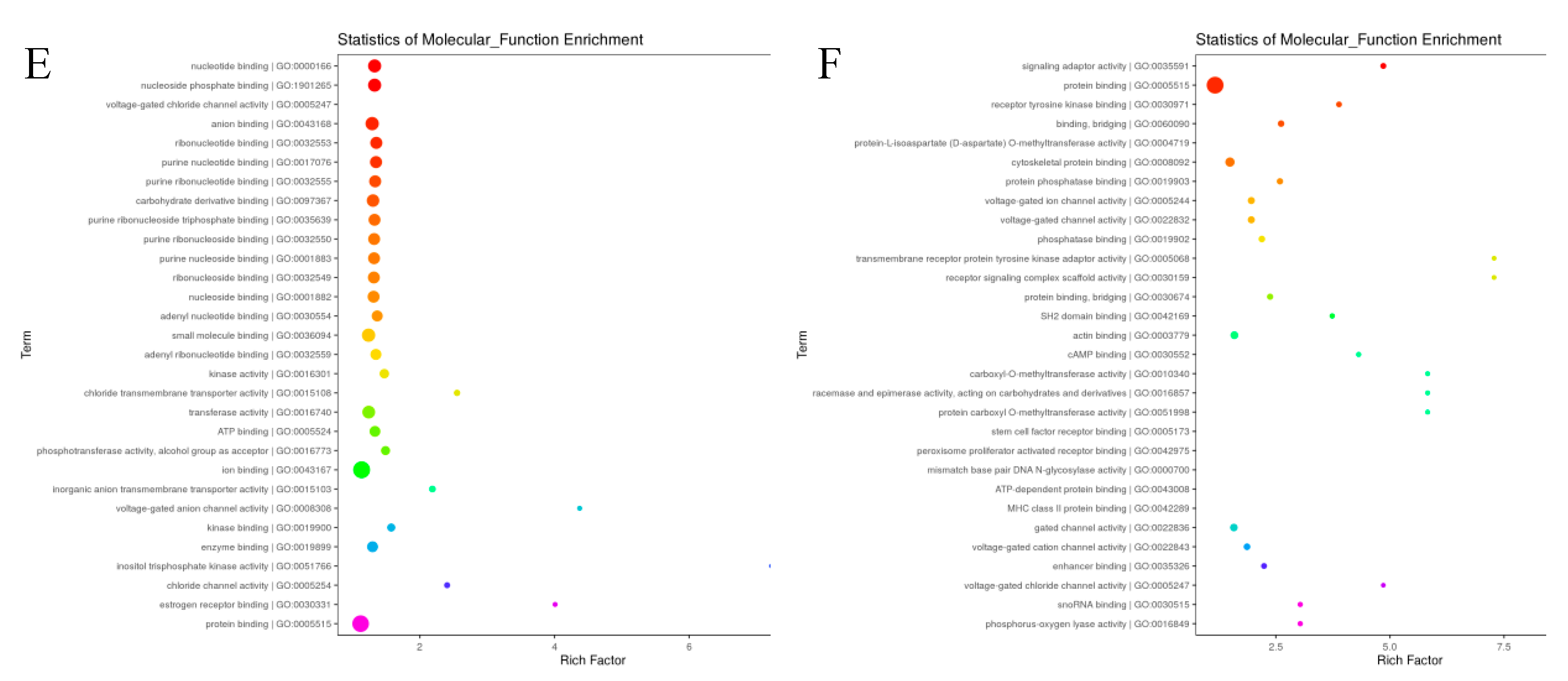
Figure 8). GO enrichment and KEGG functional enrichment analysis was done to provide insight into the DE target gene function in the miRNA-mRNA relationship pairs. From the Known miRNAs, a total of 8131 GO terms were determined from the GO analysis. From the total GO terms analyzed, 6090 terms involved in biological processes, 729 participated in cellular components and 1312 terms belonged to enriched molecular functions. These are significantly (corrected p-value<0.05) enriched processes. While a total of 7951 GO terms were found involved from the novel miRNAs GO term analysis mainly, 5873 GO terms participated in biological processes, 769 in cellular component and 1309 in molecular functions. The significantly differentially expressed miRNAs also enriched in related GO terms for bovine reproduction such as plasma membrane part, plasma membrane region, cell junction, anatomical structure development, cellular developmental process, system development, cell differentiation, and cellular localization (
Figure 8 and
Figure 9). A total of 458 DE genes, of which 195 up regulated genes and 263 down regulated genes are controlled by miRNAs, were enriched with Go terms associated with the descriptions of the development of the testes and spermatogenic processes.
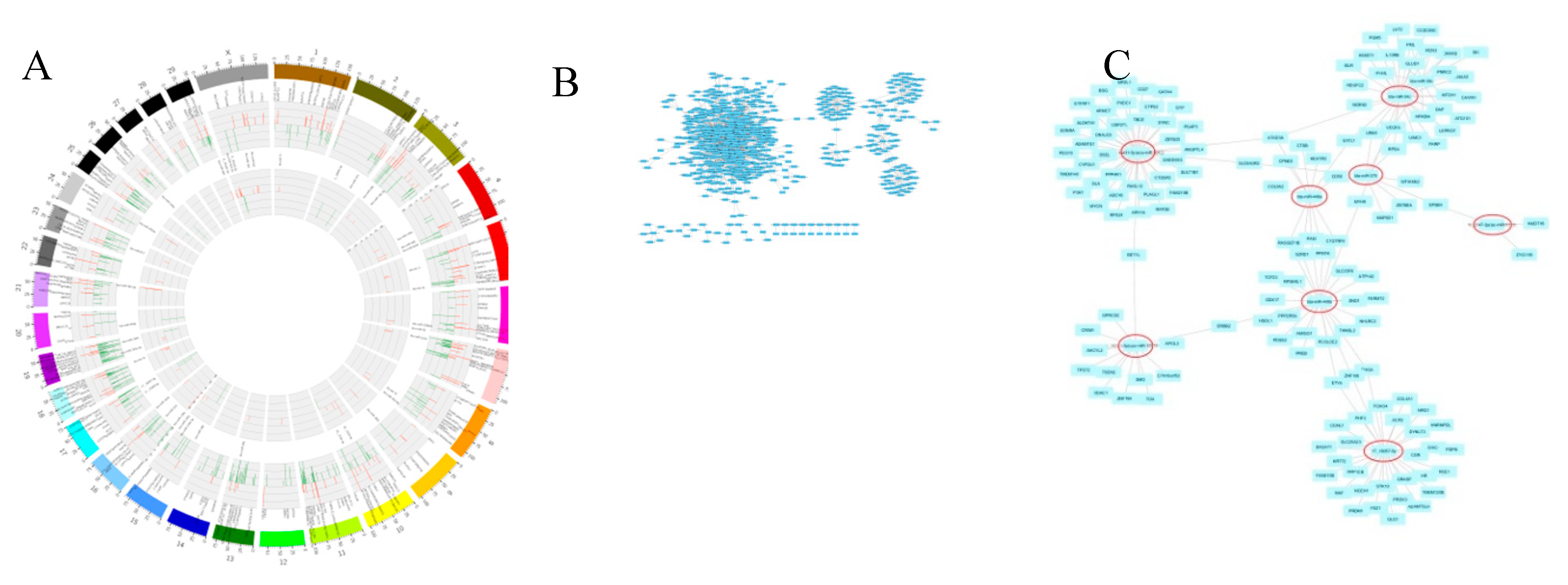
The miRNA-mRNA correlation network was extensive; therefore hub analysis was performed in order to extract miRNA datasets capable of controlling more than 152 differential genes from the 1295 miRNA-mRNA interaction pairings based on the findings of co-expression research. The differentially expressed genes that are closely associated with the spermatogenic processes are ANKRD49, PAIP2, ALKBH5, STRBP, LGR4, BCL2L11, TYRO3, TBPL1, RGS2, ACVR2A, AGFG1, HMGA2 and DDX25. The STRB with bta-miR-134 and BCL2L11 with bta-let-7e, bta-miR-181b and bta-miR-214 gene were found significantly correlated in the miRNA target gene correlation and network analysis results showing their significant correlation with the spermatogenesis process. The some of the candidate genes which are closely related to reproductive system development includes NOS3, KITLG, MDFI, LRRC6, BAK1, DHCR24, KRT19, BCL2L11, UBE3A, NKX3-1, TYRO3, UBE2Q1, ACVR2A, HMGA2, ADAMTS1, STAT5A, MED1, MAPK14, PRDM1, TTPA, WNT2, FEM1B, MAP2K1, STAT5B, ASCL2, CYP27B1and PDGFRA. The BCL2L11 with bta-let-7e, bta-miR-181b and bta-miR-214, ADAMTSI1 with 17_15431-5p (eca-miR-8912), MED1 with bta-miR-490, bta-miR-433, and 24_29969-5p (has-miR-7155-5p) and PRDM1 with 17_16057-5p were also found strongly linked in the network hub analysis as well as miRNA target gene correlation analysis indicating their involvement in the reproductive system development. More than eight network module results were identified by the hub analysis using Cytoscape, including 17_16057-5p, X_45311-3p (cpo-miR-12072-3p), bta-miR-34c, bta-miR-375, 17_15431-5p (eca-miR-8912), 10_2547-3p (isc-miR-5313), and bta-miR-449b (
Figure 6). The DE miRNAs were significantly (p<0.05) enriched in the top-30 KEGG pathways rich-factors including TNF signaling pathways, cell adhesion molecules(CAM), calcium signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Ras signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, cGMP-PKG signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, GnRH signaling pathway, VEGF signaling pathway and Rap 1 signaling pathway.
3.8. Functional Genes of Differentially Expressed (DE) in the GO Terms
The GO and KEGG-enriched pathways were implemented for the computation of DEGs within the networks. It's interesting to observe that the DEGs from the young and mature Holstein bull groups shared likely richer GO terms. The GO terms chosen to be most relevant to bovine reproduction were those that dealt with sexual reproduction, sperm part, lateral plasma membrane, androgen secretion, male genitalia development, male gonad development, Sertoli cell development, germ cell development, fusion of sperm and egg, germ cell migration, spermatid development, reproductive process, and the sperm component. It is notable that a considerable number of DE genes significantly enriched in signaling pathways coincide with to the listed GO terms (Table 9).
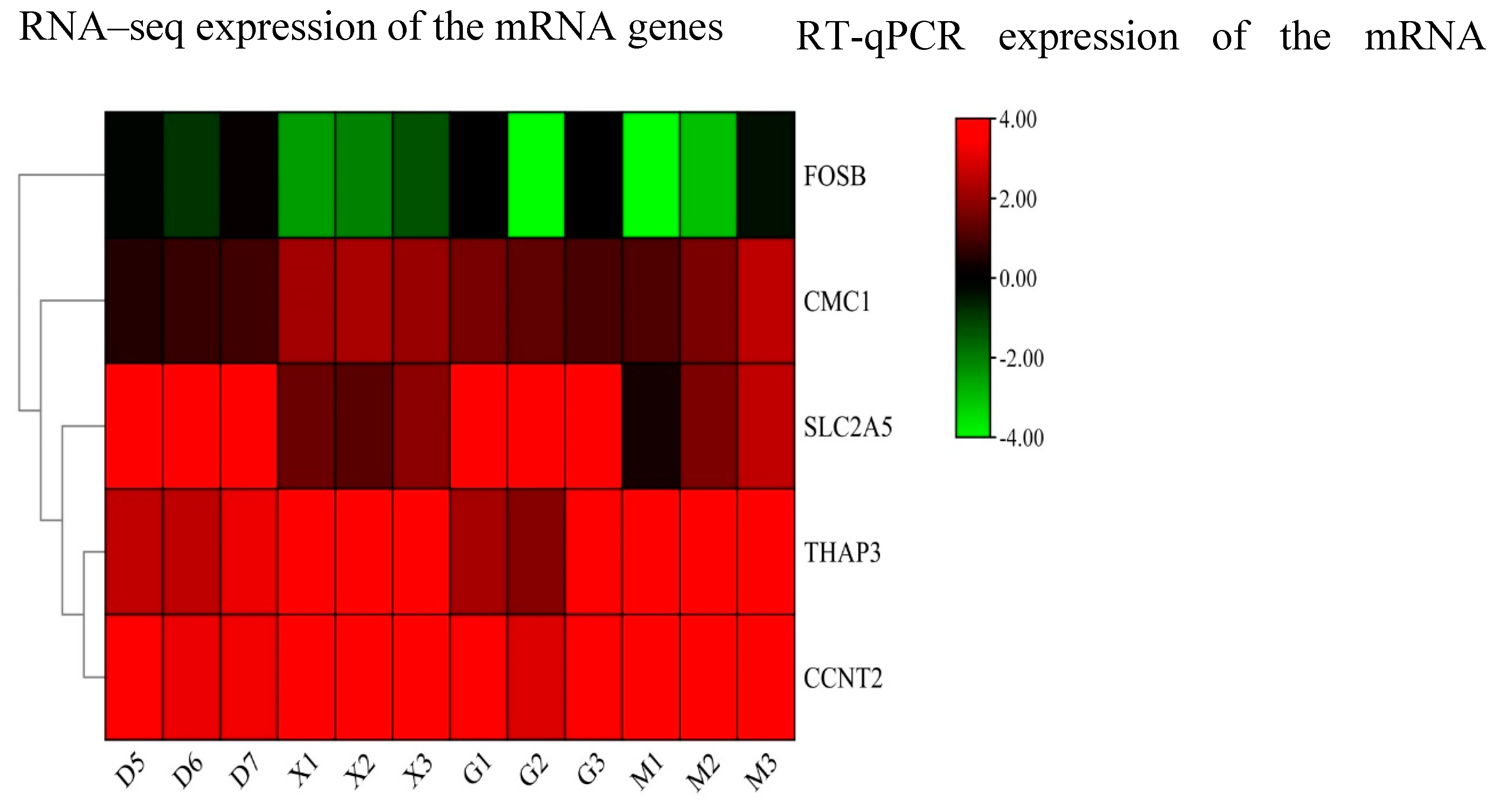
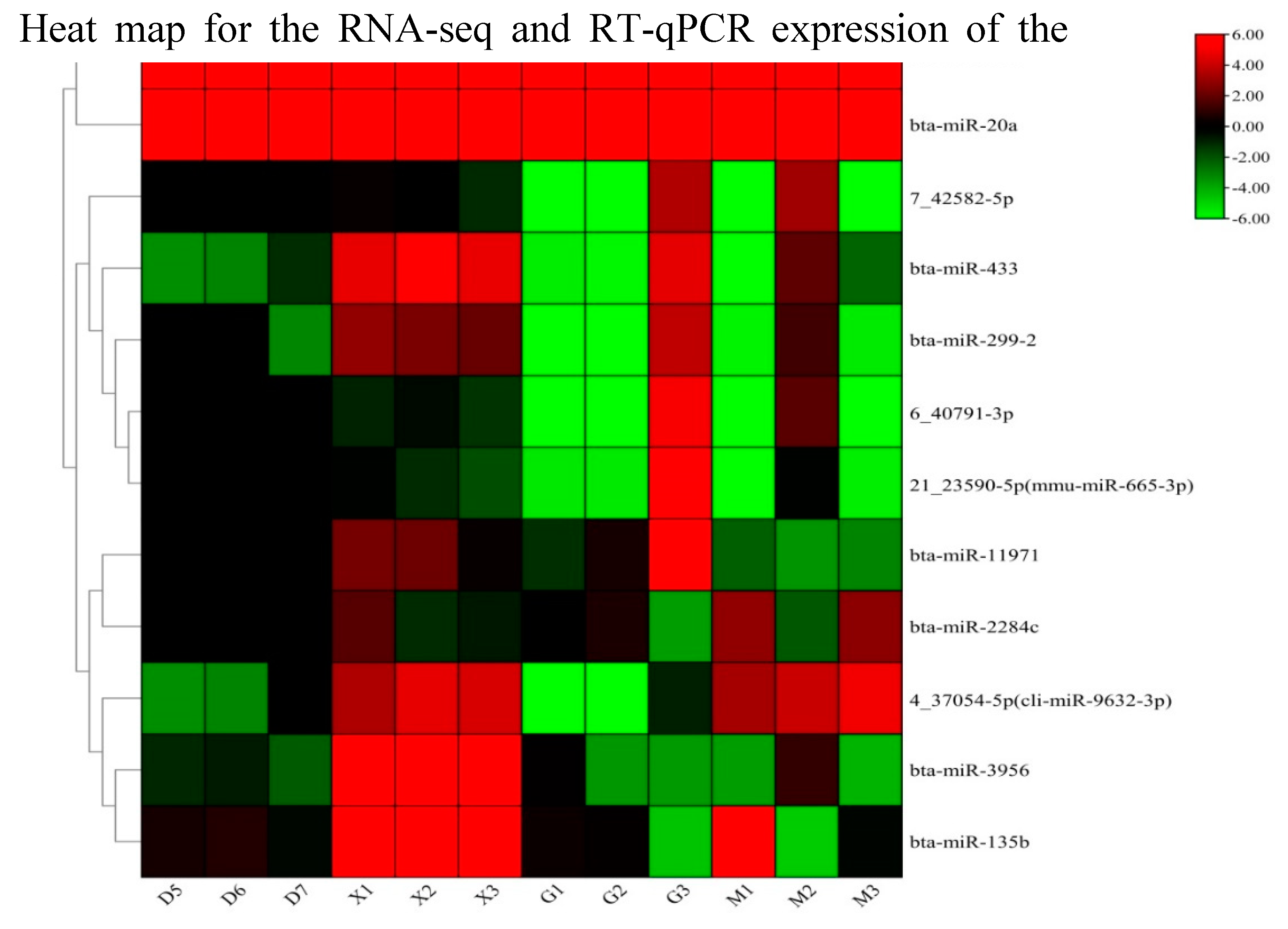
3.9. RT-qPCR Validation
To ensure the consistency of the expression levels of DE miRNAs and their target genes (FOSB, CMC1, SLC2A5, THAP3, and CCNT2), a qPCR validation on 12 miRNAs(bta-miR-11971,bta-miR-2284c, bta-miR-3956, bta-miR-135b, bta-miR-299-2, bta-miR-433, bta-miR-191, bta-miR-20a,4_37054-5p(cli-miR-9632-3p), 7_42582-5p, 6_40791-3p, 21_23590-5p(mmu-miR-665-3p) and its target genes were conducted. Our findings indicate the significance of relative expression of miRNAs compared to the young and adult Holstein bulls. Furthermore, the expression levels of the target genes and miRNAs were found to be consistent with the RNA sequence results (
Figure 9 and
Figure 10). The
Table S2 and
Table S4 contain further information on the expression levels of miRNA target genes in the RNA-sequence and RT-qPCR data from this investigation. Supplementary information on the expression levels of miRNAs in the RNA-sequence and RT-qPCR data in this investigation is provided in
Table S1 and
Table S3.
4. Discussion
The development of the reproductive system in male mammals is established primarily during the early stages of testicular development. During this time, the differentiation of somatic cells to Sertoli cells in the early gonad initiates male-specific development and guides germ cells to the spermatogenic lineage (Mäkelä et al., 2019). Thus, testicular development and spermatogenesis are critical processes that impact the reproductive efficiency of male Holstein bulls. Researchers have identified several functional genes that regulate testicular development and spermatogenesis in cattle breeds and yaks ( La et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2018). Moreover, recent studies have implicated miRNAs in gene regulation by repressing the translation or degradation of target mRNAs (Fabian et al., 2010). Many scholars found that miRNAs are involved in multiple processes of testicular development and spermatogenesis, such as testosterone hormone synthesis, cell proliferation, spermatocyte meiosis, and spermiogenesis of haploid spermatids (Yao et al., 2015). However, no research has been done to identify the miRNAs associated with the early puberty of Holstein bulls' testicles.
The study selected two age groups with 8 week and 80 week old Holstein bull testes to investigate the expression profiling of miRNAs and mRNA and their contribution to testes development and spermatogenesis. This study is conducted to discover the molecular pathways and mechanisms that control testis development. According to the most recent findings, miRNAs play an important role in early male germ cell development for spermatogenesis, beginning with spermatogonia and progressing to spermatocytes and spermatids, during postnatal male reproduction, mRNA degradation in germ cell proliferation and development via post-transcriptional processes, and expressing meiotic sex chromosome inactivation resistance (Buchold et al., 2010; Gong et al., 2013). A number of studies have found miRNAs to be significant biomarkers in spermatogenesis, testis development, and primordial germ cell proliferation (Gao et al., 2020; Hayashi et al., 2008). Testis development and spermatogenesis, which are governed by numerous functional genes and miRNAs that mainly participated in the spermatogenesis process and testis development, have an important influence on bull reproductive success, sexual maturity and sexual function development (Ding et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2022).
The cDNA libraries of young and mature Holstein bull testes tissues were constructed with clean reads ranging from 98.17% to 98.33%,Q20 exceeding 97.98% and Q30 exceeding 93.77%. The miRNA reads mapping, filtration, differential expression; target prediction and functional enrichment were performed. Furthermore, the expression level of both novel and known miRNAs of the Holstein bull testes tissues was determined through the utilization of the TPM value. Similar methodologies were employed in previous studies for the miRNAs characterization and DE genes identification, such as in the immature and mature testes of indigenous Wandong cattle (Liu et al., 2022), in three ruminant species testes ( Wang et al., 2018), in the cattle-yak male infertility (Zhao, Sun, et al., 2022), in the cattle yak and yak testis (Xu et al., 2018), in the Duroc and Meishan boars (Ding et al., 2016), in the 2-, 6- and 12-month-old small-tail Han-sheep testes (Bai et al., 2019) and in the Saanen Dairy Goat Testis (Wu et al., 2014).
The comparison analysis of miRNA profiles of young (8weeks) and mature (80weeks) of Holstein bull testes were performed to ascertain the potential role of specific miRNAs in the regulation of testicular development and spermatogenesis. A total of 458 miRNAs of which 195 genes significantly up regulated and 263 were observed to be down regulated miRNAs were found differentially expressed in the comparison of X (young) versus D (mature) Holstein bulls. A similar comparison of different pig breed age groups of DE 16 miRNAs with 28 targeted link genes related to spermatogenesis and 14 miRNAs with 18 targeted genes that have a connection to testes development associated with cell adhesion were identified (Li, Yao, et al., 2016). Furthermore, a total of 246 known miRNAs were co-expressed in testicular and ovarian tissues, of which 21 were testis-specific and 9 were ovary-specific, as described by (Huang et al., 2011). Zhao et al. (2022) also investigated the miRNA expression profiles of three ruminant species testis tissues to determine the regulation of spermatogenesis and their regulatory mechanisms involving in male sterility, which suggests our understanding of the physiology of sexual maturity in the testis tissue (Zhao, et al., 2022).
In this study, the Illumina high throughput sequencing technology was used to sequence small RNAs in testicular tissues of 8 weeks and 80 weeks of Holstein bulls. The analyzed DE miRNAs, predicted novel miRNAs, and performed GO enrichment and KEGG pathway analysis of miRNAs and target genes. The DE genes that are enriched in the GO terms in the study for spermatogenesis includes ANKRD49, PAIP2, ALKBH5, STRBP, LGR4, BCL2L11, TYRO3, TBPL1, RGS2, ACVR2A, AGFG1, HMGA2 and DDX25. During the post natal development, the TYRO3 gene is well expressed in Sertoli cells and lack of this gene in male mice results with no production of mature spermatozoa. The mammalian spermatogenesis is also essentially regulated by the Tyro-3 family receptors (Lu et al., 1999). Known and novel miRNAs the Holstein bull’s testes tissues were predicted from cattle (Bos taurus) miRBase data; therefore, more novel miRNAs were determined compared to known DE miRNAs. These newly identified novel miRNAs can serve to enhance our understanding of the crucial miRNAs involved in Holstein bull testis development, and can also provide new information for the cattle (Bos taurus) miRBase.The known DE Holstein bull miRNAs, such as bta-miR-122, bta-miR-146a, bta-miR-184, bta-miR-34c, bta-miR-93, bta-miR-455-3p, bta-miR-369-5p, miR-34a, miR-34b, miR-34c, bta-miR-382 and bta-miR-411c-5p were previously reported in several studies, and have been found to play vital roles in processes such as plasma membrane part, cell cycle, cellular protein modification process, reproductive processes and target protein coding genes regulating associated signaling pathways (Fang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2018; Zhao, et al., 2022). The expression of many miRNAs such as miR-34 family (miR-34a, miR-34b, and miR-34c) was also reported in other cattle breeds, yak and their interspecies called the dzo (H. Wang et al., 2018). Many authors reported that the miR-34 family involves in an increase of p53 activation in many cells (Cheng et al., 2014; Navarro & Lieberman, 2015) playing vital role in the downstream effector of p53 (Salzman et al., 2016) . The miR-34c inhibition also causes apoptosis of male germ cells in murine targeting activation transcription factor 1(atf1) (X. Liang et al., 2012) that involved in cell transformation and survival mediating various extracellular transcriptional signals and responses (Liang et al., 2012). The Ras signaling pathway, HTLV-I infection, cGMP-PKG signaling pathway, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, apoptosis - multiple species and oxytocin signaling pathways was assessed in relation to DE source genes associated with spermatogenesis such as BCL2L11, TBPL1, RGS2, ACVR2A, HMGA2 and determined to be linked to bovine male reproduction.
The results of this study may shed light on the molecular mechanisms that regulate testicular development and spermatogenesis in male Holstein bulls. Furthermore, this research could help to identify potential therapeutic targets for improving reproductive efficiency in male Holstein bulls. Ultimately, this study could have significant implications for the Holstein bulls breeding industry.
5. Conclusions
This study represents the first comprehensive analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression patterns in the developmental process of Holstein bull testes. Through this investigation, key miRNAs and miRNA-targets in three 8 weeks young Holstein bull testes (X) vs three 80 weeks old mature Holstein bull testes (D) were successfully explored. The insights gained from this study will serve as a solid foundation for elucidating the molecular regulatory mechanisms underlying Holstein bull testes development, as well as identifying biomarkers that can significantly affect the reproductive efficiency of Holstein bull testes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information is attached; Table S1: Expression levels of miRNAs in the RNA-seq data; Table S2. Expression levels of the miRNAs using RT-qPCR; Table S3. Expression levels of the miRNA target genes in RNA-seq data; Table S4. Expression levels of the miRNA target genes in RT-qPCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.W.S.; methodology and validation B.W.S.; data collection and writing original draft preparation, B.W.S. and S.Z.; Writing review & editing, B.W.S., S.Z., J.G. and Z.H.; Funding acquisition, Z.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (2023-YWF-ZX-07); The China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-36); The Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP-IAS06); The National Natural Science Foundation of China (32102549); The National Key R&D Program of Ningxia (2021BEF02023); Key technological innovations in advanced dairy breeding and efficient breeding (2022JBGS0021).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
B.W.S. and Z.H had full access to all the data in this study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ala, U. (2020). Competing Endogenous RNAs, Non-Coding RNAs and Diseases: An Intertwined Story. In Cells (Vol. 9, Issue 7). [CrossRef]
- Ansari-Lari, M., Kafi, M., Sokhtanlo, M., & Ahmadi, H. N. (2010). Reproductive performance of Holstein dairy cows in Iran. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 42(6), 1277–1283. [CrossRef]
- Bai, M., Sun, L., Jia, C., Li, J., Han, Y., Liu, H., Chen, Y., & Jiang, H. (2019). Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles reveals functional miRNA-targets in development testes of small tail han sheep. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 9(2), 523–533. [CrossRef]
- Baker, P. J., Pakarinen, P., Huhtaniemi, I. T., Abel, M. H., Charlton, H. M., Kumar, T. R., & O’Shaughnessy, P. J. (2003). Failure of normal Leydig cell development in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) receptor-deficient mice, but not FSHbeta-deficient mice: role for constitutive FSH receptor activity. Endocrinology, 144(1), 138–145. [CrossRef]
- Baohong, Qinglian, Wang, A., & Pan, X. (2007). MicroRNAs and Their Regulatory Roles in Animals and Plants. Journal Cellular Physiology, 210(May), 279–289. [CrossRef]
- Buchold, G. M., Coarfa, C., Kim, J., Milosavljevic, A., Gunaratne, P. H., & Matzuk, M. M. (2010). Analysis of microRNA expression in the prepubertal testis. PloS One, 5(12), e15317. [CrossRef]
- Carreau, S., Bouraima-Lelong, H., & Delalande, C. (2012). Role of estrogens in spermatogenesis. Frontiers in Bioscience (Elite Edition), 4(1), 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-Y., Hwang, C.-I., Corney, D. C., Flesken-Nikitin, A., Jiang, L., Öner, G. M., Munroe, R. J., Schimenti, J. C., Hermeking, H., & Nikitin, A. Y. (2014). miR-34 cooperates with p53 in suppression of prostate cancer by joint regulation of stem cell compartment. Cell Reports, 6(6), 1000–1007. [CrossRef]
- Ding, H., Luo, Y., Liu, M., Huang, J., & Xu, D. (2016). Histological and transcriptome analyses of testes from Duroc and Meishan boars. Scientific Reports, 6(January), 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M. R., Sonenberg, N., & Filipowicz, W. (2010). Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 79, 351–379. [CrossRef]
- Fang, X., Qin, L., Yu, H., Jiang, P., Xia, L., Gao, Z., Yang, R., Zhao, Y., Yu, X., & Zhao, Z. (2021). Comprehensive analysis of miRNAs and target mRNAS between immature and mature testis tissue in Chinese red steppes cattle. Animals, 11(11). [CrossRef]
- Friedländer, M. R., Mackowiak, S. D., Li, N., Chen, W., & Rajewsky, N. (2012). miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Research, 40(1), 37–52. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y., Wu, F., Ren, Y., Zhou, Z., Chen, N., Huang, Y., Lei, C., Chen, H., & Dang, R. (2020). MiRNAs Expression Profiling of Bovine (Bos taurus) Testes and Effect of bta-miR-146b on Proliferation and Apoptosis in Bovine Male Germline Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11). [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.-S., Li, X., & Wang, Y. (2021). Leydig Cell and Spermatogenesis. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1288, 111–129. [CrossRef]
- Gong, W., Pan, L., Lin, Q., Zhou, Y., Xin, C., Yu, X., Cui, P., Hu, S., & Yu, J. (2013). Transcriptome profiling of the developing postnatal mouse testis using next-generation sequencing. Science China. Life Sciences, 56(1), 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Grande, G., Barrachina, F., Soler-Ventura, A., Jodar, M., Mancini, F., Marana, R., Chiloiro, S., Pontecorvi, A., Oliva, R., & Milardi, D. (2022). The Role of Testosterone in Spermatogenesis: Lessons From Proteome Profiling of Human Spermatozoa in Testosterone Deficiency. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 13, 852661. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y., & Peñagaricano, F. (2016). Unravelling the genomic architecture of bull fertility in Holstein cattle. BMC Genetics, 17(1), 143. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K., Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S. M., Kaneda, M., Tang, F., Hajkova, P., Lao, K., O’Carroll, D., Das, P. P., Tarakhovsky, A., Miska, E. A., & Surani, M. A. (2008). MicroRNA biogenesis is required for mouse primordial germ cell development and spermatogenesis. PLoS ONE, 3(3), 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Huang, J., Ju, Z., Li, Q., Hou, Q., Wang, C., Li, J., Li, R., Wang, L., Sun, T., Hang, S., Gao, Y., Hou, M., & Zhong, J. (2011). Solexa sequencing of novel and differentially expressed microRNAs in testicular and ovarian tissues in Holstein cattle. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 7(7), 1016–1026. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, H., Baker, P. J., Abel, M., Charlton, H. M., Jackson, G., Fleming, L., Kumar, T. R., & O’Shaughnessy, P. J. (2004). Regulation of Sertoli cell number and activity by follicle-stimulating hormone and androgen during postnatal development in the mouse. Endocrinology, 145(1), 318–329. [CrossRef]
- Kastelic, J. P., & Thundathil, J. C. (2008). Breeding Soundness Evaluation and Semen Analysis for Predicting Bull Fertility. Reproduction in Domestic Animals, 43(SUPPL.2), 368–373. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D., Langmead, B., & Salzberg, S. L. (2015). HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nature Methods, 12(4), 357–360. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D., Yeong, Sung, & Jong-Hyuk. (2017). Regulatory role of microRNAs in the proliferation and differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Histology and Histopathology, 32(1), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- La, Y., Ma, F., Ma, X., Bao, P., Chu, M., Liang, C., Guo, X., Yin, M., Li, J., & Yan, P. (2022). Different expression of LHR, PRLR, GH and IGF1 during testicular development of yak. Reproduction in Domestic Animals = Zuchthygiene, 57(2), 221–227. [CrossRef]
- La, Y., Ma, X., Bao, P., Chu, M., Guo, X., Liang, C., & Yan, P. (2023). Identification and profiling of microRNAs during yak’s testicular development. BMC Veterinary Research, 19(1), 53. [CrossRef]
- Li, Yao, Li, J., Fang, C., Shi, L., Tan, J., Xiong, Y., Fan, B., & Li, C. (2016). Genome-wide differential expression of genes and small RNAs in testis of two different porcine breeds and at two different ages. Scientific Reports, 6, 26852. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z., Lan, X., Guo, W., Sun, J., Huang, Y., Wang, J., Huang, T., Lei, C., Fang, X., & Chen, H. (2012). Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of Dairy Goat MicroRNAs from Dry Period and Peak Lactation Mammary Gland Tissues. PLoS ONE, 7(12). [CrossRef]
- Liang, X., Zhou, D., Wei, C., Luo, H., Liu, J., Fu, R., & Cui, S. (2012). MicroRNA-34c enhances murine male germ cell apoptosis through targeting ATF1. PloS One, 7(3), e33861. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H., Khan, I. M., Liu, Y., Khan, N. M., Ji, K., Yin, H., Wang, W., Zhou, X., & Zhang, Y. (2022). A Comprehensive Sequencing Analysis of Testis-Born miRNAs in Immature and Mature Indigenous Wandong Cattle (Bos taurus). Genes, 13(12). [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q., Gore, M., Zhang, Q., Camenisch, T., Boast, S., Casagranda, F., Lai, C., Skinner, M. K., Klein, R., Matsushima, G. K., Earp, H. S., Goff, S. P., & Lemke, G. (1999). Tyro-3 family receptors are essential regulators of mammalian spermatogenesis. Nature, 398(6729), 723–728. [CrossRef]
- Luo, G., Hu, S., Lai, T., Wang, J., Wang, L., & Lai, S. (2020). MiR-9-5p promotes rabbit preadipocyte differentiation by suppressing leptin gene expression. Lipids in Health and Disease, 19(1), 126. [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, J.-A., Koskenniemi, J. J., Virtanen, H. E., & Toppari, J. (2019). Testis Development. Endocrine Reviews, 40(4), 857–905. [CrossRef]
- Navarro, F., & Lieberman, J. (2015). miR-34 and p53: New Insights into a Complex Functional Relationship. PloS One, 10(7), e0132767. [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z., Goodyear, S. M., Rao, S., Wu, X., Tobias, J. W., Avarbock, M. R., & Brinster, R. L. (2011). MicroRNA-21 regulates the self-renewal of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(31), 12740–12745. [CrossRef]
- Sahlu, B. W., Zhao, S., Wang, X., Umer, S., Zou, H., & Huang, J. (2020). Long noncoding RNAs : new insights in modulating mammalian spermatogenesis. 8, 1–12.
- Salzman, D. W., Nakamura, K., Nallur, S., Dookwah, M. T., Metheetrairut, C., Slack, F. J., & Weidhaas, J. B. (2016). miR-34 activity is modulated through 5’-end phosphorylation in response to DNA damage. Nature Communications, 7, 10954. [CrossRef]
- Schulster, M., Bernie, A. M., & Ramasamy, R. (2016). The role of estradiol in male reproductive function. Asian Journal of Andrology, 18(3), 435–440. [CrossRef]
- Smith, L. B., & Walker, W. H. (2014). The regulation of spermatogenesis by androgens. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 30, 2–13. [CrossRef]
- Staub, C., & Johnson, L. (2018). Review : Spermatogenesis in the bull. 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H. Z., Chen, Y., & Guan, L. L. (2019). MicroRNA expression profiles across blood and different tissues in cattle. Scientific Data, 6(1), 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Vigneault, F., Ter-Ovanesyan, D., Alon, S., Eminaga, S., Christodoulou, D. C., Seidman, J. G., Eisenberg, E., & Church, G. M. (2012). High-throughput multiplex sequencing of miRNA. Current Protocols in Human Genetics, SUPPL.73. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., Zhong, J., Chai, Z., Zhu, J., & Xin, J. (2018). Comparative expression profile of microRNAs and piRNAs in three ruminant species testes using next-generation sequencing. Reproduction in Domestic Animals, 53(4), 963–970. [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M. S., Ciccarelli, M., Oatley, M. J., Kaucher, A. V., Tibary, A., & Oatley, J. M. (2019). Enhanced sperm production in bulls following transient induction of hypothyroidism during prepubertal development. Journal of Animal Science, 97(4), 1468–1477. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J., Zhu, H., Song, W., Li, M., Liu, C., Li, N., Tang, F., Mu, H., Liao, M., Li, X., Guan, W., Li, X., & Hua, J. (2014). Identification of conservative MicroRNAs in saanen dairy goat testis through deep sequencing. Reproduction in Domestic Animals, 49(1), 32–40. [CrossRef]
- Xu, C., Wu, S., Zhao, W., Mipam, T., Liu, J., Liu, W., Yi, C., Shah, M. A., Yu, S., & Cai, X. (2018). Differentially expressed microRNAs between cattleyak and yak testis. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Yao, C., Liu, Y., Sun, M., Niu, M., Yuan, Q., Hai, Y., Guo, Y., Chen, Z., Hou, J., Liu, Y., & He, Z. (2015). MicroRNAs and DNA methylation as epigenetic regulators of mitosis, meiosis and spermiogenesis. Reproduction (Cambridge, England), 150(1), R25-34. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Qian, Chen, Y., & Zhou, X. (2019). The roles of microRNAs in epigenetic regulation. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 51, 11–17. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z., Xu, X., Tan, Y., Cao, H., Zhou, W., Dong, X., & Mao, H. (2021). Expression analysis of microRNAs and their target mRNAs of testes with high and low sperm motility in domestic pigeons (Columba livia). Genomics, 113(1), 257–264. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B., Yan, Z., Gao, Y., Li, J., Wang, Z., Wang, P., Yang, Q., Huang, X., & Gun, S. (2022). Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in testes of Landrace and Hezuo boars. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 9. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S., Heng, N., Sahlu, B. W., Wang, H., & Zhu, H. (2021). Long noncoding rnas: Recent insights into their role in male infertility and their potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(24). [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S., Sun, W., Chen, S.-Y., Li, Y., Wang, J., Lai, S., & Jia, X. (2022). The exploration of miRNAs and mRNA profiles revealed the molecular mechanisms of cattle-yak male infertility. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 9(5). [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S., Wang, H., Hu, Z., Sahlu, B. W., Heng, N., Gong, J., Wang, H., & Zhu, H. (2022). Identification of spermatogenesis-related lncRNA in Holstein bull testis after sexual maturity based on transcriptome analysis. Animal Reproduction Science, 247(October), 107146. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
The morphology of 80 weeks old mature Holstein bull (designated as D) and 8 weeks old young Holstein bulls (designated as X) testes tissues were studied under 100X and 400X microscopic magnifications. The sections (a,b) and (c,d) indicates the histologic morphology of the 8 week and 80 week old Holstein bulls respectively. The green arrows indicate the spermatogenic biogenesis of germ cells. i: Sertoli cells, ii :leydig cells, iii: spermatogonia, iv: spermatocytes, V: round spermatids, vi: elongated spermatids, vii: mature spermatozoa.
Figure 1.
The morphology of 80 weeks old mature Holstein bull (designated as D) and 8 weeks old young Holstein bulls (designated as X) testes tissues were studied under 100X and 400X microscopic magnifications. The sections (a,b) and (c,d) indicates the histologic morphology of the 8 week and 80 week old Holstein bulls respectively. The green arrows indicate the spermatogenic biogenesis of germ cells. i: Sertoli cells, ii :leydig cells, iii: spermatogonia, iv: spermatocytes, V: round spermatids, vi: elongated spermatids, vii: mature spermatozoa.
Figure 2.
The clean data length distribution comparison of sRNAs (a), sRNA classifications (b), known miRNA (c) and novel miRNA (d) base distribution map position and base count, nucleotide length of differentially expressed known (e) and novel miRNAs(f), up and down regulated known(g) and novel miRNAs (h) in venn with Y-axis indicating the intersection line showing the relationship between the X and D groups, expression of up and down regulated known(i) and novel miRNAs (j) in volcano plot indicating the Log2(FC) values of relative expression of the known and novel miRNAs versus −Log10(pvalue) of false discovery rate (FDR) with horizontal line at p=0.05 and the vertical lines in fold change (FC)between -2 and +2 where the not significant points, significant up regulated points and significant down regulated points are denoted by black, red and green respectively, principal component analysis (PCA) of known (k) and novel miRNAs (l). .
Figure 2.
The clean data length distribution comparison of sRNAs (a), sRNA classifications (b), known miRNA (c) and novel miRNA (d) base distribution map position and base count, nucleotide length of differentially expressed known (e) and novel miRNAs(f), up and down regulated known(g) and novel miRNAs (h) in venn with Y-axis indicating the intersection line showing the relationship between the X and D groups, expression of up and down regulated known(i) and novel miRNAs (j) in volcano plot indicating the Log2(FC) values of relative expression of the known and novel miRNAs versus −Log10(pvalue) of false discovery rate (FDR) with horizontal line at p=0.05 and the vertical lines in fold change (FC)between -2 and +2 where the not significant points, significant up regulated points and significant down regulated points are denoted by black, red and green respectively, principal component analysis (PCA) of known (k) and novel miRNAs (l). .
Figure 3.
Differential expression cluster of up and down regulated known (A) and novel miRNAs (B).
Figure 3.
Differential expression cluster of up and down regulated known (A) and novel miRNAs (B).
Figure 4.
Correlation heat map of the known (A) and novel miRNA (B) in the six samples.
Figure 4.
Correlation heat map of the known (A) and novel miRNA (B) in the six samples.
Figure 5.
Expression of up and down regulated known miRNAs (A) and novel miRNAs (B) in the two groups (X vs D) using Venn diagram.
Figure 5.
Expression of up and down regulated known miRNAs (A) and novel miRNAs (B) in the two groups (X vs D) using Venn diagram.
Figure 6.
Circos plot (A) and network annotated hubs (B,C) of different miRNA and mRNA genes.
Figure 6.
Circos plot (A) and network annotated hubs (B,C) of different miRNA and mRNA genes.
Figure 7.
Significant enriched biological process of GO terms (Top 30 ) of the Known (A) and novel (B) miRNAs linked, cellular component of GO terms(Top 30 ) of the Known (C) and novel (D) miRNAs linked genes, molecular process of GO terms(Top 30 ) of the Known (E) and novel (F) miRNAs linked genes in testicular samples.
Figure 7.
Significant enriched biological process of GO terms (Top 30 ) of the Known (A) and novel (B) miRNAs linked, cellular component of GO terms(Top 30 ) of the Known (C) and novel (D) miRNAs linked genes, molecular process of GO terms(Top 30 ) of the Known (E) and novel (F) miRNAs linked genes in testicular samples.
Figure 8.
Summary of GO enrichment (Top 30) analysis of differentially expressed known miRNAs and novel miRNAs, Significant KEGG PATHWAY enrichment (Top 30) of the known (C) and novel (D) miRNAs linked genes.
Figure 8.
Summary of GO enrichment (Top 30) analysis of differentially expressed known miRNAs and novel miRNAs, Significant KEGG PATHWAY enrichment (Top 30) of the known (C) and novel (D) miRNAs linked genes.
Figure 9.
Heat map RT-qPCR and RNA seq analysis for 5 the differentially expessed genes (D&G group represents the adult Holstein bull and M &X group represents the young Holstein bull) using GAPDH as housekeeping gene.
Figure 9.
Heat map RT-qPCR and RNA seq analysis for 5 the differentially expessed genes (D&G group represents the adult Holstein bull and M &X group represents the young Holstein bull) using GAPDH as housekeeping gene.
Figure 10.
Heat map RT-qPCR and RNA seq analysis for the differentially expessed 12 miRNA genes( D&G group represents the adult Holstein bull and M &X group represents the young Holstein bull) using U6 as internal housekeeping gene.
Figure 10.
Heat map RT-qPCR and RNA seq analysis for the differentially expessed 12 miRNA genes( D&G group represents the adult Holstein bull and M &X group represents the young Holstein bull) using U6 as internal housekeeping gene.
Table 3.
Hormonal profiles.
Table 3.
Hormonal profiles.
| Sample |
T (Testosterone) (ng/mL) |
Average |
Standard Deviation |
Estrogen(ng/mL) |
Average |
Standard Deviation |
Progesterone
(ng/mL) |
Average |
Standard Deviation |
| X1 |
0.002 |
0.003 |
0.001 |
65.05 |
62.12 |
7.07 |
0.12 |
0.12 |
0.01 |
| X2 |
0.004 |
|
|
54.05 |
|
|
0.11 |
|
|
| X3 |
0.004 |
|
|
67.25 |
|
|
0.13 |
|
|
| D5 |
0.199 |
0.166 |
0.078 |
73.03 |
57.22 |
21.41 |
0.14 |
0.16 |
0.04 |
| D6 |
0.222 |
|
|
32.85 |
|
|
0.14 |
|
|
| D7 |
0.076 |
|
|
65.78 |
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
Table 4.
Raw reads sequence data statistics.
Table 4.
Raw reads sequence data statistics.
| Sample |
Raw reads number |
Raw bases |
Clean reads number |
Clean bases |
Clean rate (%) |
Q20 (%) |
Q30 (%) |
| D_5 |
86639342 |
12995901300 |
85382674 |
12773620656 |
98.29 |
98.72 |
95.89 |
| X_1 |
84967166 |
12745074900 |
83607760 |
12511803713 |
98.17 |
98.6 |
95.59 |
| D_6 |
89752696 |
13462904400 |
88281454 |
13216123838 |
98.17 |
97.98 |
93.77 |
| X_3 |
88444394 |
13266659100 |
87142022 |
13044924344 |
98.33 |
98.58 |
95.55 |
| X_2 |
88046786 |
13207017900 |
86695100 |
12978591207 |
98.27 |
98.56 |
95.42 |
| D_7 |
88614166 |
13292124900 |
87268088 |
13060990754 |
98.26 |
98.71 |
95.86 |
Table 5.
QC summary statistic.
Table 5.
QC summary statistic.
| Sample |
Num. of Raw Reads |
Clean Reads% |
Remove Adapter% |
Insert Null% |
N% |
too_short% |
Poly-A% |
too_long% |
low_quality% |
| D_5 |
15259349 |
89.05% |
0.02% |
0.00% |
0.10% |
1.54% |
0.17% |
9.05% |
0.08% |
| D_6 |
13463407 |
87.95% |
0.03% |
0.01% |
0.10% |
2.72% |
0.13% |
8.97% |
0.09% |
| D_7 |
14244562 |
85.08% |
0.02% |
0.01% |
0.16% |
2.48% |
0.17% |
11.98% |
0.10% |
| X_1 |
13956441 |
70.09% |
0.02% |
0.04% |
0.11% |
28.52% |
0.05% |
1.06% |
0.11% |
| X_2 |
15869310 |
85.48% |
0.01% |
0.01% |
0.09% |
13.35% |
0.04% |
0.94% |
0.08% |
| X_3 |
19881140 |
91.83% |
0.01% |
0.01% |
0.10% |
6.72% |
0.05% |
1.18% |
0.10% |
Table 6.
The result of reads mapped to the reference genome.
Table 6.
The result of reads mapped to the reference genome.
| ID |
Type of reads |
Sum |
Hairpin |
rRNA |
tRNA |
snRNA |
other_ncRNA |
Repeat |
Unknown |
| D_5 |
Uniq |
2493381(100%) |
16835(0.68%) |
36744(1.47%) |
444(0.02%) |
3092(0.12%) |
3524(0.14%) |
202394(8.12%) |
2230348(89.45%) |
| Total |
13588224(100%) |
2690486(19.8%) |
115201(0.85%) |
802(0.01%) |
6017(0.04) |
7400(0.05%) |
847312(6.24%) |
9921006(73.01%) |
| D_6 |
Uniq |
2129032(100%) |
15962(0.75%) |
36429(1.71%) |
493(0.02%) |
3261(0.15%) |
3686(0.17%) |
186561(8.76%) |
1882640(88.43%) |
| Total |
11841624(100%) |
2457259(20.75%) |
128723(1.09%) |
946(0.01) |
6199(0.05%) |
8011(0.07%) |
756444(6.39%) |
8484042(71.65%) |
| D_7 |
Uniq |
2197903(100%) |
14767(0.67%) |
35337(1.61%) |
445(0.02%) |
3103(0.14%) |
3418(0.16%) |
179476(8.17%) |
1961357(89.24%) |
| Total |
12119198(100%) |
1939019(16%) |
130467(1.08) |
875(0.01%) |
5963(0.05%) |
8218(0.07%) |
856157(7.06%) |
9178499(75.14%) |
| X_1 |
Uniq |
588558(100%) |
25673(4.36%) |
82808(14.07%) |
1274(0.22%) |
6312(1.07%) |
6934(1.18%) |
188052(31.95%) |
277505(47.15%) |
| Total |
9781701(100%) |
8104780(82.86%) |
345098(3.53%) |
2382(0.02%) |
10984(0.11%) |
17844(0.18%) |
617283(6.31%) |
683330(6.99%) |
| X_2 |
Uniq |
487860(100%) |
29003(5.94%) |
43555(8.93%) |
795(0.16%) |
3818(0.78%) |
4272(0.88%) |
140384(28.78%) |
266033(54.53%) |
| Total |
13564919(100%) |
11914763(87.84%) |
242554(1.79%) |
1652(0.01%) |
6957(0.05%) |
11732(0.09%) |
548659(4.04%) |
838602(6.18%) |
| X_3 |
Uniq |
949314(100%) |
31531(3.32%) |
52596(5.54%) |
781(0.08%) |
4423(0.47%) |
5030(0.53%) |
222152(23.4%) |
632801(66.66%) |
| Total |
18256548(100%) |
15570998(85.29%) |
214214(1.17%) |
1541(0.01%) |
7468(0.04%) |
11602(0.06%) |
810797(4.44%) |
1639928(8.98%) |
Table 7.
The list of differentially expressed miRNAs with their target genes, FC and p-values.
Table 7.
The list of differentially expressed miRNAs with their target genes, FC and p-values.
| Known miRNA |
P value |
FC |
Target genes |
Up/Down |
| bta-miR-11971 |
0.00 |
190.67 |
SUPT6H, PCSK7, ALKBH5, CRELD1, CMC1, DAPK3, UNC5B, FAM78A |
Up |
| bta-miR-2284c |
0.00 |
77.16 |
SUPT7L, CXCL12 |
Up |
| bta-miR-3956 |
0.00 |
53.70 |
TM9SF4, TNK2, TRIM2, AFAP1, ABL1, TRIOBP, RNF122, GLRB |
Up |
| bta-miR-135b |
0.00 |
42.48 |
KCTD10, GPATCH11, NCKIPSD, ALDH2, TTC14, DUSP27, UBOX5, HMG20A, BCL2L14 |
Up |
| bta-miR-299-2 |
0.00 |
39.50 |
BET1, NRN1, RAB11FIP2, CD1E, GLCE, ADARB2, ATM, SYAP1, TTC9C |
Up |
| bta-miR-433 |
0.00 |
37.56 |
LRRTM3, MAPRE2, PAK4, SLC35D1, KCNJ14, MXI1 |
Up |
| bta-miR-191 |
0.0000 |
0.4188 |
AJAP1, SLC39A13, KCTD17, PRICKLE1, USP22, IER2, DSG1 |
Down |
| bta-miR-20a |
0.0000 |
0.4153 |
PLEKHM1, SAAL1, CFL2, ZNFX1, APP, RAB29, CAMK1G, METAP1, KCTD7 |
Down |
| Novel miRNAs |
|
| 4_37054-5p(cli-miR-9632-3p) |
0.00000 |
153.87736 |
GATAD2B, CD47, HEATR5A, USP43, NANOG, CHSY1, SLC38A3, ALX3, EFR3B |
Up |
| 7_42582-5p |
0.00030 |
58.00028 |
FCRL5, EMP1, TTPAL, CAMK2A, ESD, NMNAT2, CYP4V2, AKAP6 |
Up |
| 6_40791-3p |
0.00085 |
38.35687 |
BTBD7, FBXW11, KCNJ2, C18H19orf12, CMC1, PLD3, RACK1, SLC39A14 |
Up |
| 21_23590-5p(mmu-miR-665-3p) |
0.00146 |
34.79795 |
RHBDD1, FGF2,C1QTNF5,PLA2G3,BCO2,HDAC5,PRELP,TRMT12 |
Up |
Table 8.
The identified enriched GO terms and differentially expressed genes correlated with bull reproduction.
Table 8.
The identified enriched GO terms and differentially expressed genes correlated with bull reproduction.
| Groups |
Terms |
DEGs |
GO_Accession |
Some of the Genes ID associated with the GO terms |
| |
|
|
|
|
| X vs D |
Sexual reproduction |
279 |
GO:0019953 |
NOS3, CLIC4, BCL2L11, UBE3A, PLCD4,APP, TYRO3, UBE2Q1, TBPL1, ACVR2A, AGFG1, TEKT3, CD46, HMGA2, HSPA1L, ADAMTS1, DDX25, PRSS37, ALKBH5, PAIP2, PRDM1, B4GALT1, STRBP, LGR4, MCM8, PDE5A, TRIM36, RGS2,BCL6, FOSL1, STAT3, LEP, SPIN1, NPPC, PLA2G3, CIB1, NR2F2, FKBP6, OVOL1, RAD23B, DAZL, ALKBH5, CDC25B, FNDC3A, VIPAS39, RNF2 |
| Male gonad development |
39 |
GO:0008584 |
NKX3-1, KITLG, LRRC6, ACVR2A, PDGFRA, HMGA2, BCL2L11,FNDC3A |
| Germ cell development |
103 |
GO:0007281 |
PDE5A, TBPL1, AGFG1, PRDM1, STRBP, DDX25, DAZL, PLA2G3, CIB1, RNF2, CDC25B, FNDC3A, NPPC |
| Germ cell migration |
2 |
GO:0008354 |
TGFBR1,CXADR |
| Spermatid development |
58 |
GO:0007286 |
TBPL1, AGFG1, STRBP, DDX25, PLA2G3, CIB1, FNDC3A |
| Fusion of sperm to egg |
3 |
GO:0007342 |
CD9,SPESP1,SPAM1 |
| Sperm part |
62 |
GO:0097223 |
TRIM36, CABYR, CAV1, TEKT3, CD46, POMT1, AK1, FNDC3A, CD46 |
| Lateral plasma membrane |
24 |
GO:0016328 |
NSG1, AXIN1, BVES, CLDN12, ARL2 |
| Negative regulation of androgen secretion |
1 |
GO:2000835 |
GH1 |
| Androgen secretion |
3 |
GO:0035935 |
NKX3-1,CSN1S1, GH1 |
| Sertoli cell development |
3 |
GO:0060009 |
FNDC3A,FNDC3A,ARID4A |
| |
Male genitalia development |
9 |
GO:0030539 |
BMP5 , CTNNB1, DHCR24 , ASB1, FGF8, SRD5A2, AR, PDGFRA, HSD17B3 |
| |
Reproductive process |
498 |
GO:0022414 |
STAT5A, PAIP2, FZR1, PRDM1, B4GALT1, STRBP, LGR4, FEM1B, MAP2K1, ESPL1, STAT5B, RGS2, ASCL2, PDGFRA, KITLG, DHCR24, KRT19, BCL2L11, DRD2, UBE2A, TYRO3, APP, TBPL1, ACVR2A, TEKT3, CD46, ALKBH5, ERCC4, MED1, MAPK14, MCM8, TTPA, PDE5A, WNT2, CASP4, IL1A, TRIM36, CRHBP, CYP27B1 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).