Submitted:
07 November 2023
Posted:
07 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. OsNRAMP5 transported both Mn and Cd
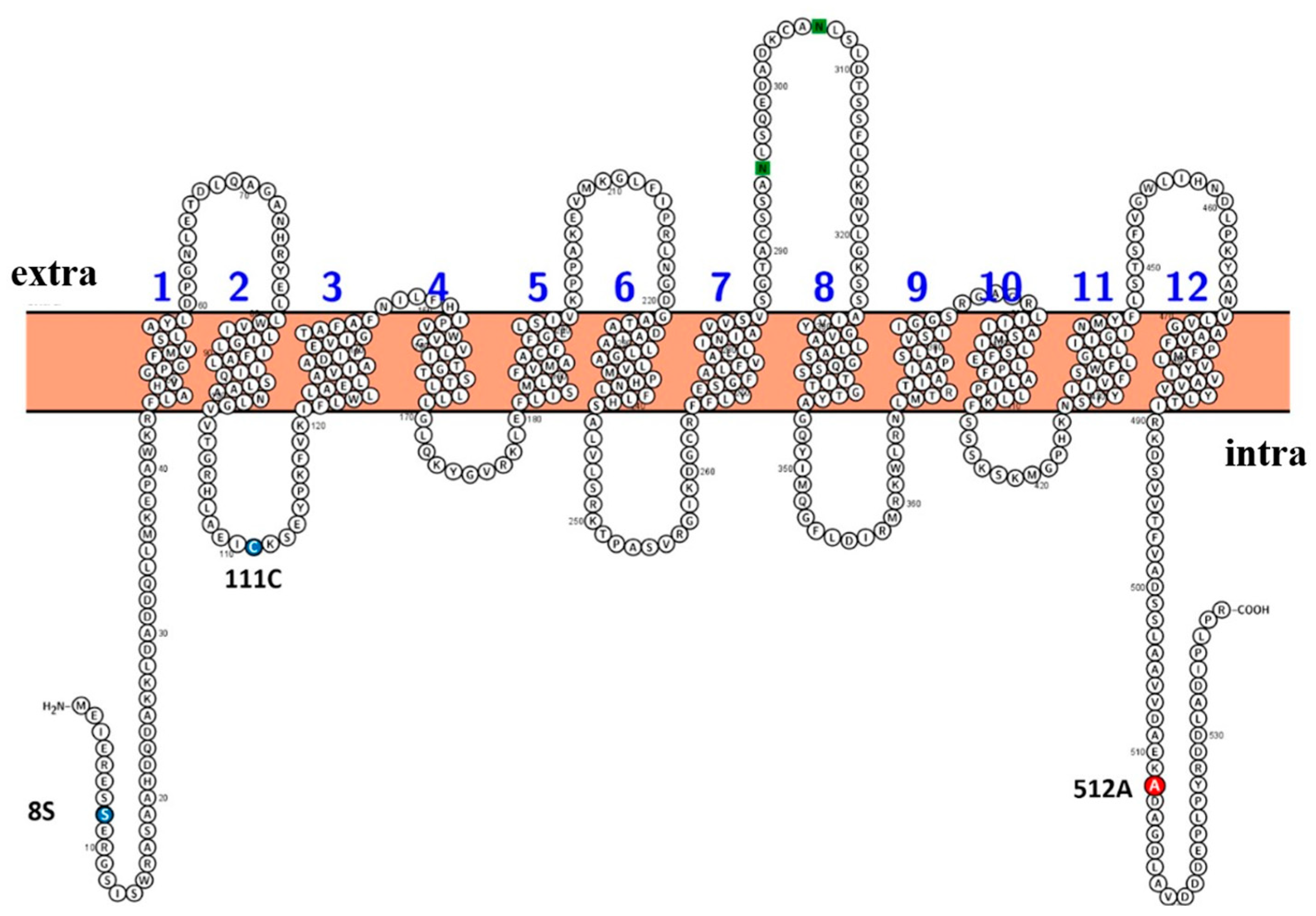
2.2. Patterns of OsNRAMP5 mutations
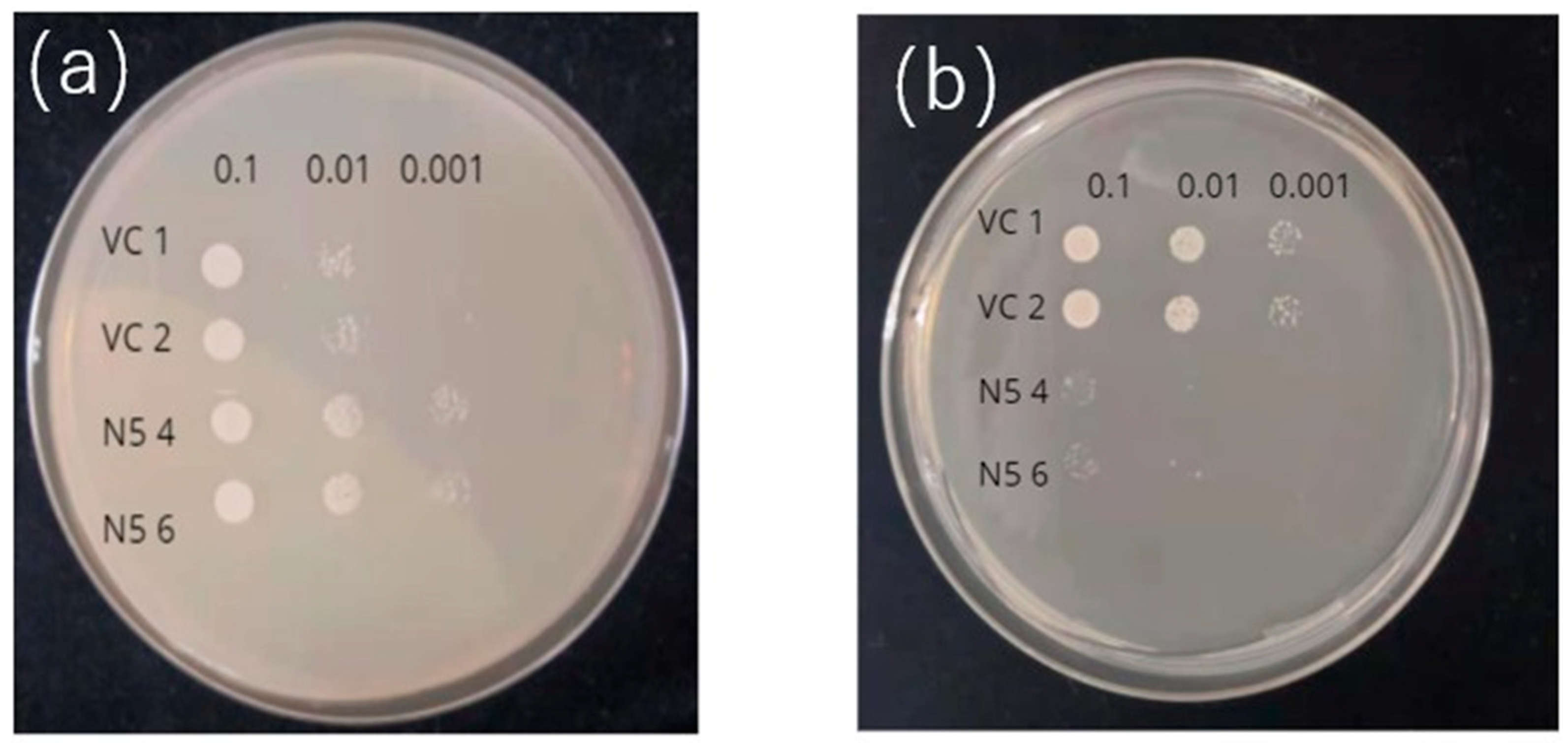
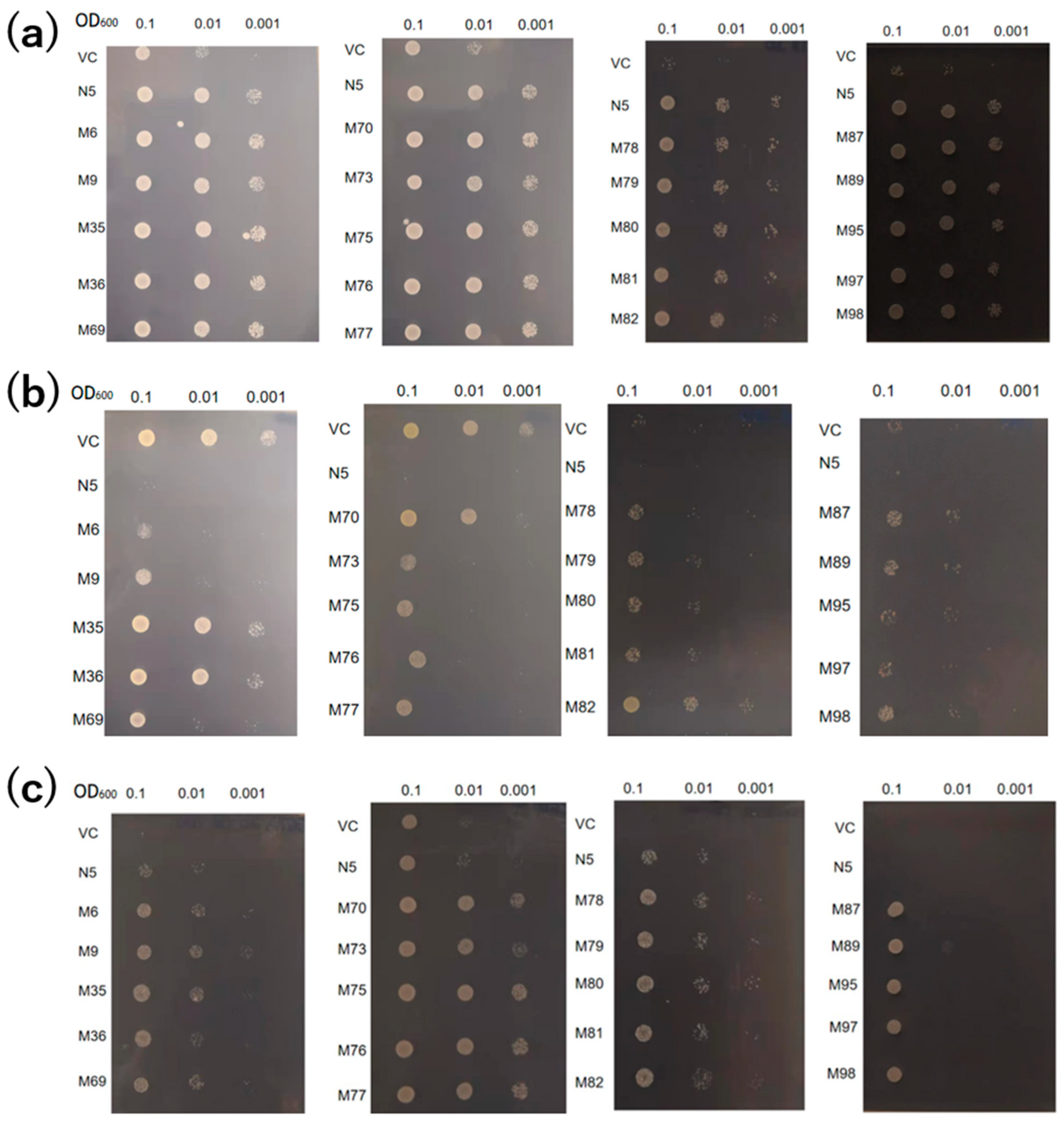
2.3. Mutants absorb Mn but not Cd
2.4. Mutants show reduced absorption of Cd, but similar absorption of Mn compared to N5
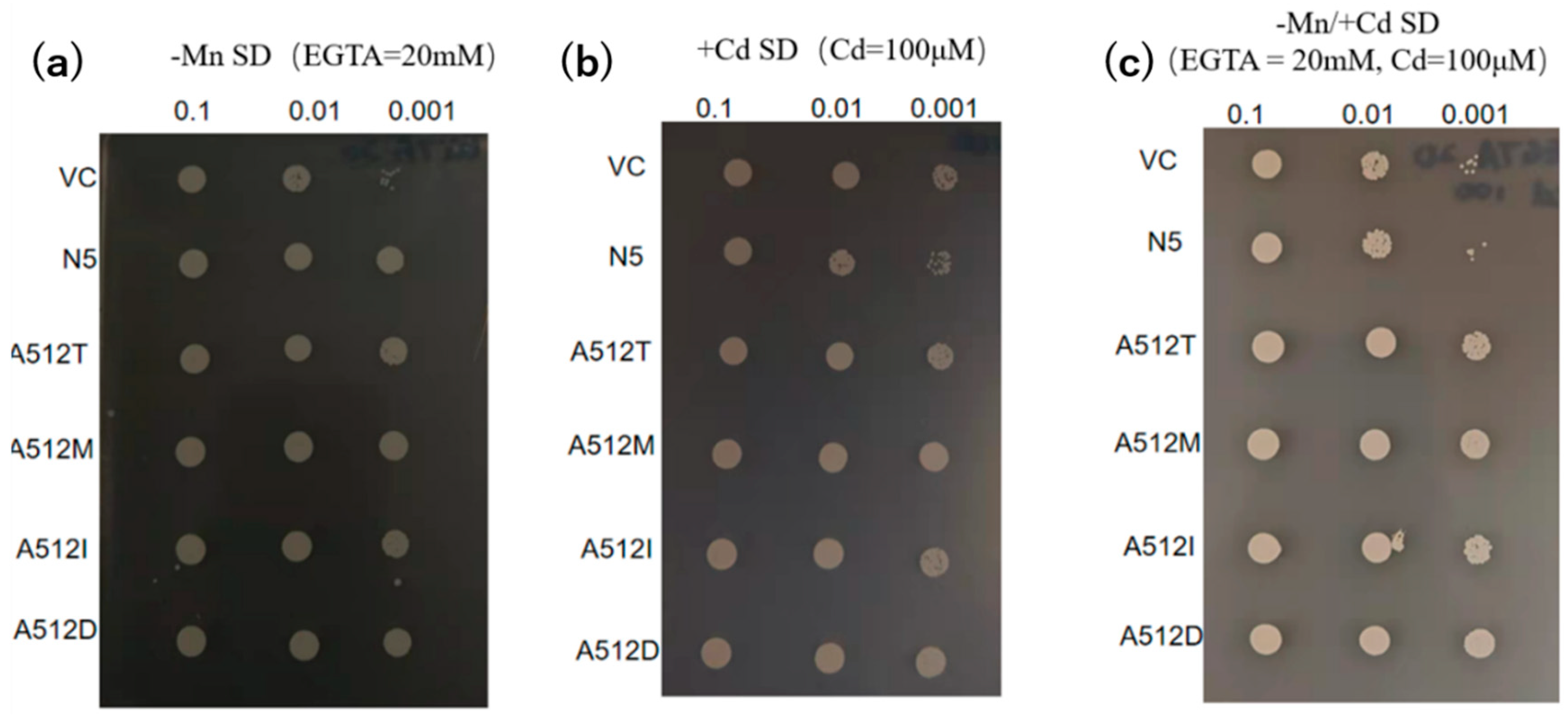
2.5. Alanine 512 is essential for Cd absorption
3. Discussion
4. Materials and methods
4.1. Mn and Cd absorption assays
4.2. Error-prone PCR
4.3. Screening
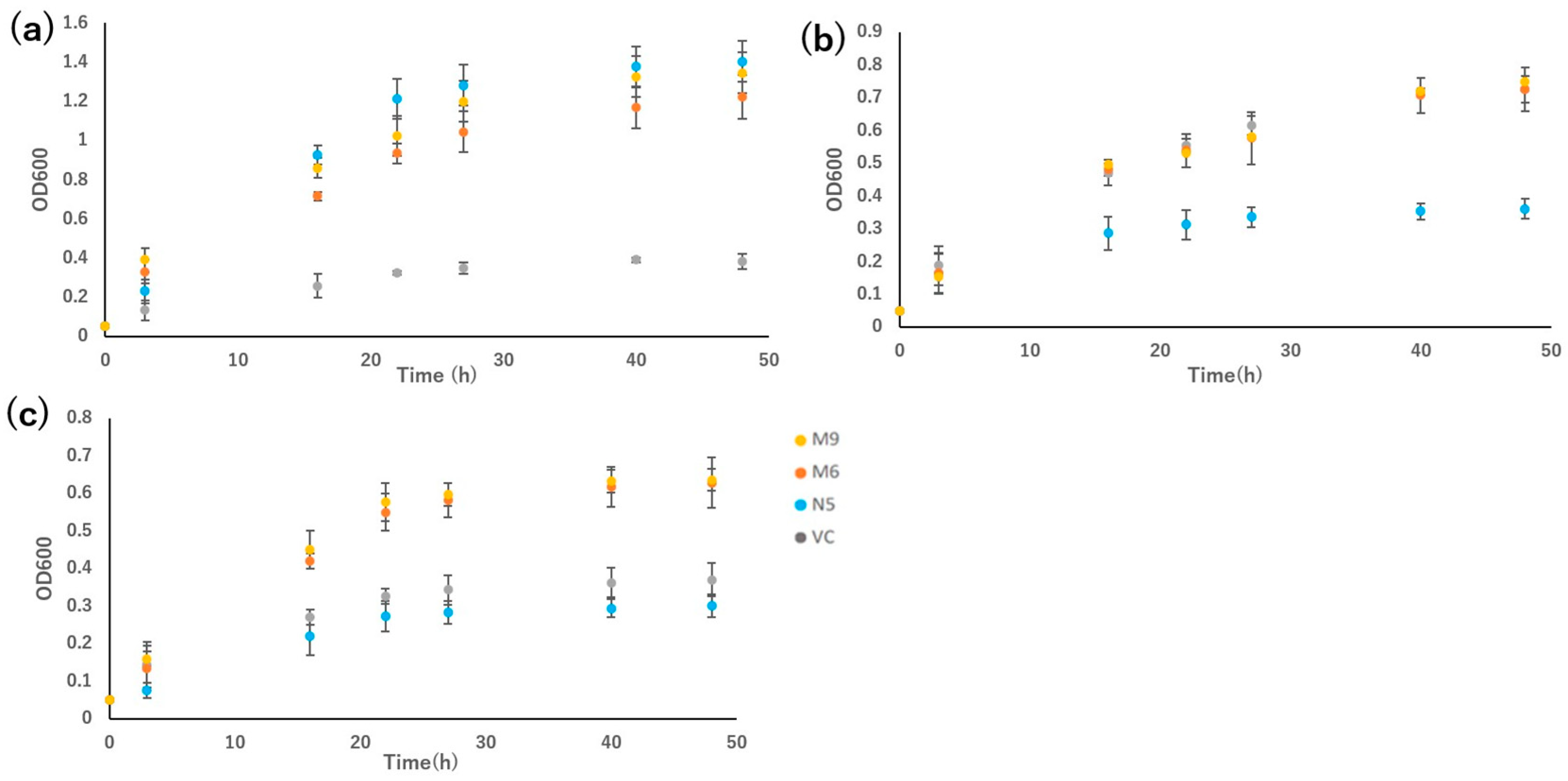
4.4. Growth assay
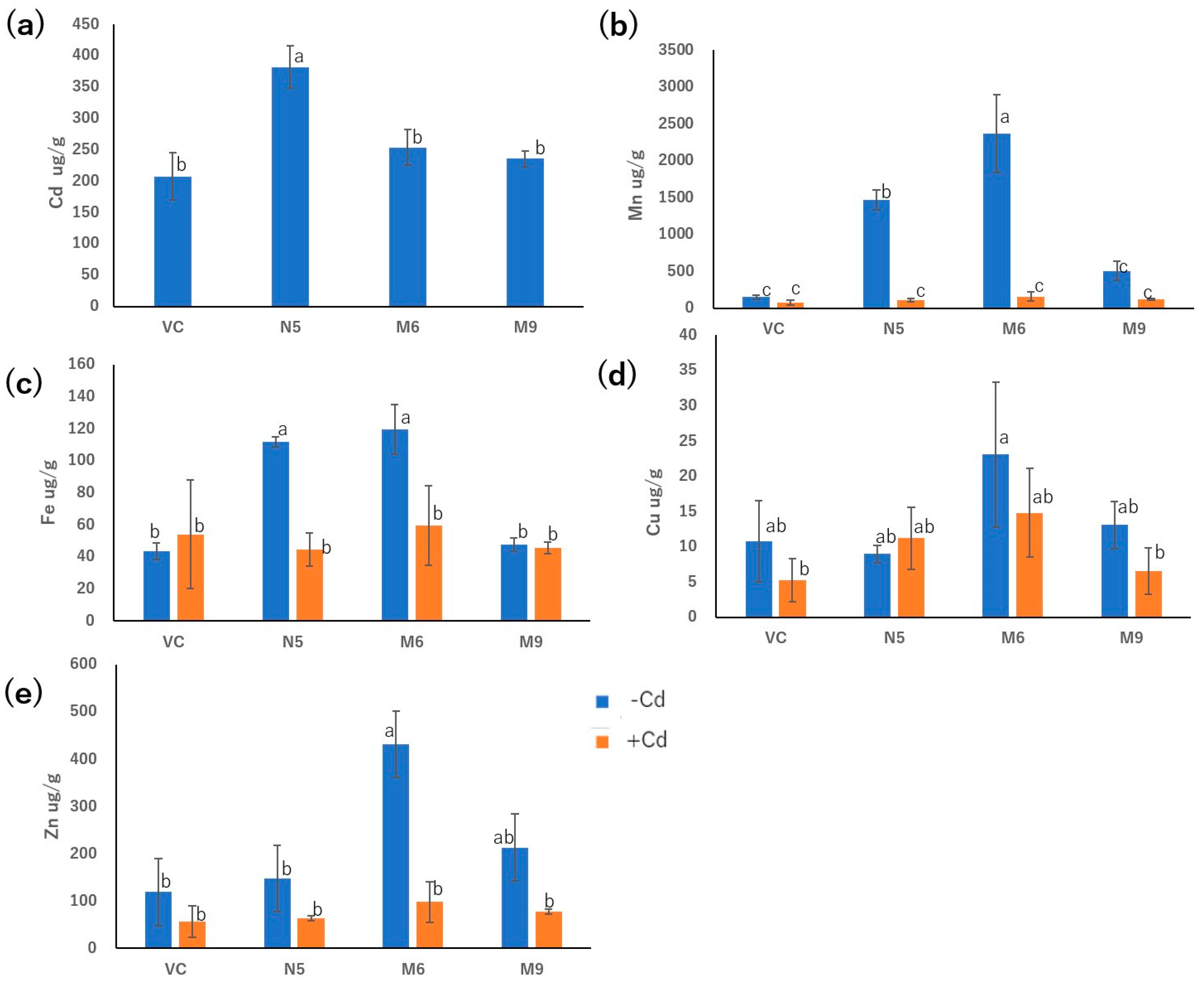
4.5. Uptake of metals
4.6. Amino acid substitution
4.7. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division. World Population Prospects; Key findings & advance tables 2015 REVISION.; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World; THE STATE OF FOOD SECURITY AND NUTRITION IN THE WORLD, TRANSFORMING FOOD SYSTEMS FOR AFFORDABLE HEALTHY DIETS.; Rome, Italy, 2020.
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. OurWorldInData; Land Use; Oxford, England, 2013.
- Haider, F.U.; Cai, L.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheema, SA.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Ma, W.; Muhammad, F. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021, Mar 15, 211:111887.
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.; Alam M. Soil contamination with cadmium, consequences and remediation using organic amendments. Sci Total Environ. 2017, Dec 1;601-602:1591-1605.
- Rafati Rahimzadeh, M.; Rafati Rahimzadeh M.; Kazemi, S.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Rafati Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update. Caspian J Intern Med. 2017, Summer;8(3):135-145.
- Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T. Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation. Rice (N Y). 2012 Feb 27;5(1):5.
- Department of Public Health, Environmental and Social Determinants of Health World Health Organization. EXPOSURE TO CADMIUM: A MAJOR PUBLIC HEALTH CONCERN.; Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Bellinger, D.; Bolger, M.; Goyer, R.; Barraj, L.; Baines, J. WHO food additives series: 46, cadmium. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland. 2001.
- China Food and Drug Administration. National food safety standard Contamination Limit in Food. Beijing, China. 2017. 9.
- Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Cadmium in food. The EFSA Journal 2009, 980, 1–139. [Google Scholar]
- Skorbiansky, S.R.; Childs, N.; Hansen, J. Rice in Asia’s Feed Markets. RCS-18L-01. USDA-ER: Washington DC, SW, USA 2018.
- Liu, B.; Li, T.; Cai, Y. Brief introduction to status quo, hazards and repair methods of cadmium rice. Modern Food. 2018. 21:86-89.
- Li, Q.; Shi, L.; Chen, J.; Tan, H.; Zhou, H.; Yao, L.; Xu, M.; Shang-guan, J.; Lu, K. Investigation on cadmium pollution in foods in country of Jiangxi Province. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene. 2008, 20(4):330-331.
- Lei, M.; Zeng, M.; Wang, L.; Williams Paul, N.; Sun, G. Arsenic, lead and cadmium pollution in rice from Hunan markets and contaminated areas and their health risk assessment. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae. 2010, 30(11):2314-2320.
- Wu, D.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Qin, F. Contrentations and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and rice and zinc-lead mining area in Guizhou province, China. Journal of Agro-Enviroment Science. 2013,32(10): 1992-1998.
- Cai, W.; Su, Z.; Hu, S.; Huang, W.; Xu, X.; Huang. X. Assessment of the content and exposure of lead and cadmium in the major food of Guangdong residents. Chin J Health Lab Tec. 2015, 25(14):2388-2392.
- Ren, R.; Gong, L.; Wang, S.; Jin, Q. Survey of heavy metal contamination and risk assessment of exposure in Hangzhou indigenous rice. Chin J Health Lab Tec. 2020, 30(12):1516-1520.
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, N.; Meng, H.; Shi, M.; Zhao, P. Risk assessment on the dietary exposure of cadmium in Guangxi residents. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene. 2021, 30(12):191-195.
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Feng, H.; Mahajan, MD.; Han, X. Influence and interaction of iron and cadmium on photosynthesis and antioxidative enzymes in two rice cultivars. Chemosphere. 2017, Mar; 171:240-247. 20.
- Gao, L.; Chang, J.; Chen, R.; Li, H.; Lu, H.; Tao, L.; Xiong, J. Comparison on cellular mechanisms of iron and cadmium accumulation in rice: prospects for cultivating Fe-rich but Cd-free rice. Rice (N Y). 2016, Dec;9(1):39.
- Sharma, S.S.; Kaul, S.; Metwally, A.; Goyal, K.C.; Finkemeier, I.; Dietz, K.J. Cadmium toxicity to barley (Hordeum vulgare) as affected by varying Fe nutritional status. Plant Science. 2004, 166(5): 1287-1295.
- Xu, S.S.; Lin, S.; Lai, Z. Cadmium impairs iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana by increasing the polysaccharide contents and the iron-binding capacity of root cell walls. Plant and Soil. 2015, 392, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Feng, H.; Mahajan, MD.; Han, X. Influence and interaction of iron and cadmium on photosynthesis and antioxidative enzymes in two rice cultivars. Chemosphere. 2017,171: 240–247.
- Liu, HJ.; Zhang, JL.; Zhang, FS. Role of iron plaque in Cd uptake by and translocation within rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings grown in solution culture. Environmental and Experimental Botany. 2007, 59: 314–320.
- Sasaki, A.; Yamaji, N.; Yokosho, K.; Ma, JF. Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice. Plant Cell. 2012; 24: 2155–2167.
- Wang, M.; Ma, W.; Chaney, RL.; Green, CE.; Chen W. Effects of Mn2+ on Cd accumulation and ionome in rice and spinach. J Environ Qual. 2022 Sep;51(5):890-898.
- Liu, WJ.; Zhu, YG.; Smith, FA. Effects of iron and manganese plaques on arsenic uptake by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture supplied with arsenate and arsenite. Plant and Soil. 2005, 277: 127–138.
- Sebastian, A.; Prasad, M. Iron-and manganese-assisted cadmium tolerance in Oryza sativa L.: lowering of rhizotoxicity next to functional photosynthesis. Planta. 2015, 241: 1519–1528.
- Hussain, B.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Tahir, N.; Ullah, A. Effects of Fe and Mn cations on Cd uptake by rice plant in hydroponic culture experiment. PLoS ONE. 2020, 15(12): e0243174.
- Uraguchi, S.; Fujiwara, T. Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation. Rice (N Y). 2012, Feb 27;5(1):5.
- Takahashi, R.; Ishimaru, Y.; Shimo, H.; Ogo, Y.; Senoura, T.; Nishizawa, NK.; Nakanishi H. The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2012 Nov;35(11):1948-57. Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T. Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation. Rice (N Y). 2012, Feb 27;5(1):5.
- Miyadate, H.; Adachi, S.; Hiraizumi, A.; Tezuka, K.; Nakazawa, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Katou, K.; Kodama, I.; Sakurai, K.; Takahashi, H.; Satoh-Nagasawa, N.; Watanabe, A.; Fujimura, T.; Akagi, H. OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles. New Phytol. 2011,5:190–199.
- Ueno, D.; Yamaji, N.; Kono, I.; Huang, CF.; Ando, T.; Yano, M.; Ma, JF. Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. PNAS. 2010, 5:16500–16505.
- Cui, J.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Li, F. Selenium reduces cadmium uptake into rice suspension cells by regulating the expression of lignin synthesis and cadmium-related genes. Science of the Total Environment. 2018, 644: 602–610.
- Chen, Z.; Tang, YT.; Yao, AJ.; Cao, J.; Wu, ZH.; Peng, ZR.; Wang, SZ.; Xiao, S.; Baker, A.J.M.; Qiu, RL. Mitigation of Cd accumulation in paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) by Fe fertilization. Environmental Pollution. 2017, 231: 549–559.
- Uraguchi, S.; Kamiya, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Kasai, K.; Sato, Y.; Nagamura, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Kyozuka, J.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, T. Low-affinity cation transporter (OsLCT1) regulates cadmium transport into rice grains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011, 108: 20959–20964.
- Zhong, S.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T.; Yin, H.; Qiao, J.; Chen, G.; Huang, F. Cadmium uptake and transport processes in rice revealed by stable isotope fractionation and Cd-related gene expression. Science of The Total Environment. 2021, 806(2):150633.
- Nevo, Y.; Nelson, N. The NRAMP family of metal-ion transporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006, Jul;1763(7):609-20.
- Takahashi, R.; Ishimaru, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, NK. Role of the iron transporter OsNRAMP1 in cadmium uptake and accumulation in rice. Plant Signal Behav. 2011 Nov;6(11):1813-6.
- Takahashi, R.; Ishimaru, Y.; Senoura, T.; Shimo, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Arao, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K. The OsNRAMP1 iron transporter is involved in Cd accumulation in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany. 2011, 62, 4843–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Tsukamoto, T.; Suzuki, K.; Nakazono, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Wada, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Matsuhashi, S.; Takahashi, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, NK. Rice plants take up iron as an Fe3+-phytosiderophore and as Fe2+ Plant J. 2006, 5:335–346.
- Nakanishi, H.; Ogawa, I.; Ishimaru, Y.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, NK. Iron deficiency enhances cadmium uptake and translocation mediated by the Fe2+ transporters OsIRT1 and OsIRT2 in rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2006. 5:464–469.
- Chang, JD.; Huang, S.; Yamaji, N.; Zhang, W.; Ma, JF.; Zhao FJ. OsNRAMP1 transporter contributes to cadmium and manganese uptake in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, Oct;43(10):2476-2491.
- Wang, J.; Wang, PM.; Gu, Y.; Kopittke, PM.; Zhao, FJ.; Wang, P. Iron-manganese (oxyhydro) oxides, rather than oxidation of sulfides, determine mobilization of Cd during soil drainage in paddy soil systems. Environmental Science & Technology. 2019, 53: 2500–2508. 45.
- Ishimaru, Y.; Bashir, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K. OsNRAMP5, a major player for constitutive iron and manganese uptake in rice. Plant Signal Behav. 2012, Jul;7(7):763-6.
- Ishimaru, Y.; Takahashi, R.; Bashir, K.; Shimo, H.; Senoura, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Ono, K.; Yano, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Arao, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K. Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in Manganese, Iron and Cadmium Transport. Sci Rep. 2012, 2:286.
- Rogers, E.E.; Eide, D.J.; Guerinot, M.L. Altered selectivity in an Arabidopsis metal transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000, 97(22):12356–12360.
- Jalali, M.; Moradi, F. Competitive sorption of Cd, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn in polluted and unpolluted calcareous soils. Environ Monit Assess. 2013, Nov;185(11):8831-46. Epub 2013 May 17. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; An, G. Over-expression of OsIRT1 leads to increased iron and zinc accumulations in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 5:408–416.
- Chamary, JV.; Hurst, LD.The PRICE of SILENT MUTATIONS. Scientific American. 2009, 300(6): 46–53.
- Kuramata, M.; Abe, T.; Tanikawa, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Ishikawa, S. A weak allele of OsNRAMP5 confers moderate cadmium uptake while avoiding manganese deficiency in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany. 2022, 73(18):6475–6489.
- Oki, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Nakanishi, H.; Mori, S. (1999) Introduction of the reconstructed yeast ferric reductase gene, refre1, into tobacco. Plant and Soil. 1999, 215: 211–220.
| Pattern | Plasmid No. | Mutation Location | Change in base | Chang in a.a. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6, 69, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 87, 95, 97, 98 | #21 #1534 |
C->T G->A |
− A->T |
| 2 | 9, 73 | #22 #291 #332 #1534 |
A->C T->C G->A G->A |
S->R − C->Y A->T |
| 3 | 35, 36, 70, 82 | #507 #1534 |
T->C G->A |
− A->T |
| 4 | 89 | #22 #332 #1534 |
A->C G->A G->A |
S->R C->Y A->T |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





