Submitted:
06 November 2023
Posted:
07 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
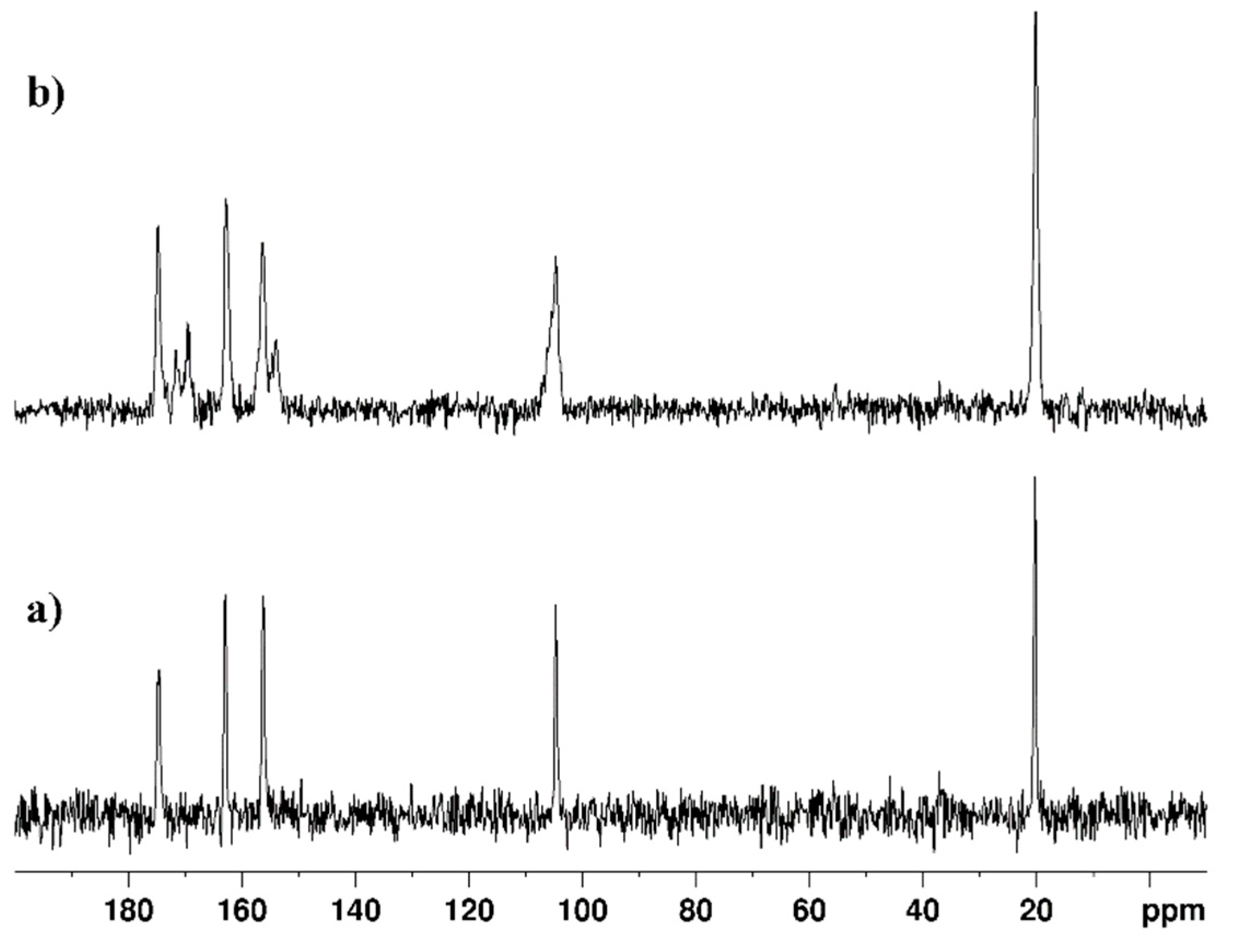
2.1. Spectra measurements
2.2. Microwave Plasma – Atomic emission spectrometry (MP-AES) determination of Cu and Pd in the complexes
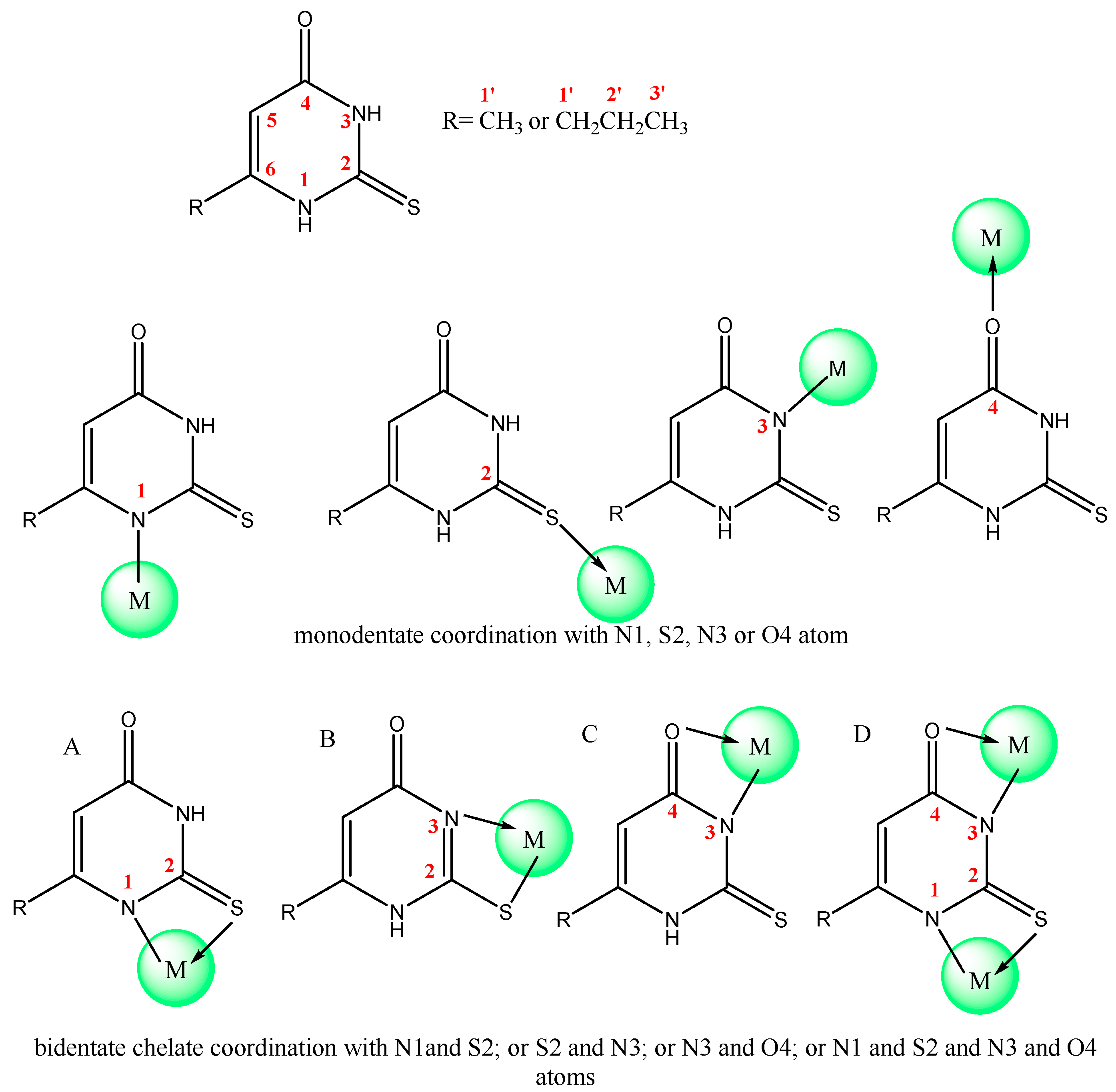
2.3. Synthesis of Cu(II) and Pd(II) complexes of 6-methyl-2-thiouracil (L1) and 6-propyl-2-thiouracil (L2)
2.3.1. Synthesis of Cu(II)L1
2.3.2. Synthesis of Pd(II)L1
2.3.3. Synthesis of Cu(II)L2
2.3.4. Synthesis of Pd(II)L2
2.4. Spectral data of the free ligands and their metal complexes
2.5. Antimicrobial assay
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Synthesis of the metal complexes
| complexes | Colour | Yield (%) | Melting point (°C) | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | colorless | 330 | soluble in DMSO | |
| Cu(II)L1 | yellow-green | 61 | >350 ᵒC | soluble in DMSO, DMF, C2H5OH, H2O and insoluble in THF, EtOAc and C6H12. |
| Pd(II)L1 | brown | 72 | >350 ᵒC | soluble in DMSO, DMF and insoluble in H2O, THF, C2H5OH, EtOAc and C6H12. |
| L2 | colorless | 218-220 | soluble in DMSO | |
| Cu(II)L2 | yellow-green | 43 | 260-263 ᵒC | soluble in DMSO and insoluble in H2O, THF, C2H5OH, EtOAc and C6H12. |
| Pd(II)L2 | brown | 70 | 255-257 ᵒC | soluble in DMSO, DMF and insoluble in H2O, THF, C2H5OH, EtOAc and C6H12. |
| assignment | L1 | Cu(II)L1 | Pd(II)L1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ν(OH) | - | - | 3442 |
| ν(NH) | 3115 sh | 3115 | 3111 |
| ν(NH) | 3080 | 3080 | 3071 |
| ν(=CH) | 3014 | 3003 | 3052 |
| ν(C=O) | 1676 m | 1637 | 1678 |
| 1560 w | 1559 | 1559 | |
| ν(C=S) | 1242 | 1242 | 1244 |
| 1167 s | 1167 | 1168 |
| assignment | L2 | Cu(II)L2 | Pd(II)L2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ν(OH) | - | 3451 | 3437 |
| ν(NH) | 3112 | - | 3117 |
| ν(NH) | 3093 | 3093 | 3080 |
| ν(=CH) | 3042 | 3042 | |
| ν(C=O) | 1656 | 1651 | 1657 |
| 1557 | 1553 | 1545 | |
| ν(C=S) | 1243 | 1232 | 1261 |
| 1165 | 1166 | 1175 |
| Atom | δ (13C) ppm | DEPT-135 | δ (1H) ppm | Multiplicity (J, Hz) | 1H-1H COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (NH) | 12.29 | s | ||||
| 2 (C=S) | 175.87 | C | ||||
| 3 (NH) | 12.29 | s | ||||
| 4 (C=O) | 161.06 | C | ||||
| 5 | 103.72 | CH | 5.68 | d (0.9) | 7 | 4b, 6, 7 |
| 6 | 153.20 | C | ||||
| 1’ | 18.11 | CH3 | 2.06 | d (0.7) | 5 | 5, 6 |
| Atom | δ (13C) ppm | DEPT -135 | δ (1H) ppm | Multiplicity (J, Hz) | 1H-1H COSY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (NH) | - | - | 12.20 | s | |
| 2 (C=S) | 176.08 | C | - | ||
| 3 (NH) | - | - | 12.31 | s | |
| 4 (C=O) | 161.22 | C | - | ||
| 5 | 103.06 | CH | 5.67 | s | |
| 6 | 156.74 | C | |||
| 1’ | 33.21 | CH2 | 2.32 | t(7.5) | 2’ |
| 2’ | 20.58 | CH2 | 1.54 | sx(7.4) | 1’, 3’ |
| 3‘ | 13.26 | CH3 | 0.87 | t(7.4) | 2’ |
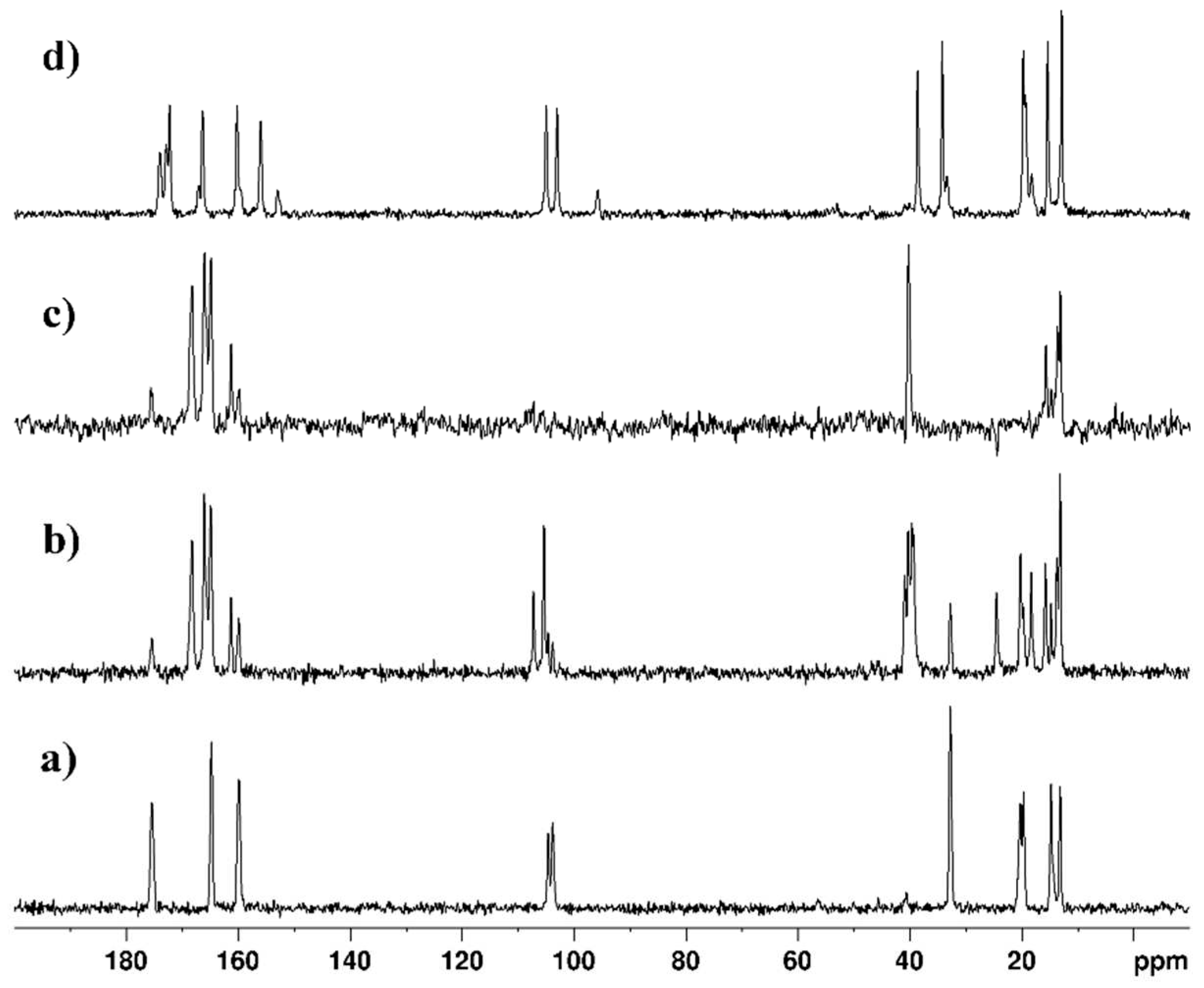
| Atom | L1 | L2 | Cu(II)L1 | Cu(II)L2 | Pd(II)L2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (NH) | |||||
| 2 (C=S) | 174.6 | 175.5 | 171.7/174.8 | 168.3/175.4 | 172.3/172.9/174.0 |
| 3 (NH) | |||||
| 4 (C=O) | 163.0 | 164.8 | 162.9/169.5 | 164.9/166.1 | 160.3/166.4/167.0 |
| 5 (CH) | 104.7 | 103.8/104.6 | 104.7/105.4 | 103.8/104.6/105.4/107.2 | 95.8/103.1/105.0 |
| 6 (C) | 156.2 | 159.9 | 154.0/156.4 | 159.9/161.3 | 153.0/156.0/159.7 |
| 1´ | 20.2 | 32.7 | 20.1 | 32.7/39.3/39.6/40.9 | 33.4/34.2/38.6 |
| 2´ | 19.6/20.2 | 18.2/19.7/20.2/24.4 | 18.2/19.3/19.7 | ||
| 3´ | 13.1/14.7 | 13.1/13.6/14.7/15.7 | 12.9/15.4 | ||
| DMSO | 40.3 |
3.2. Antimicrobial activity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abou El E. D., A.; Ghorab, M.M.; Noaman, E.; Heiba, H.I.; Khalil, A.I. Molecular modeling study and synthesis of novel pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines and pyrrolotriazolopyrimidines of expected antitumor and radioprotective activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renau, T.E.; Wotring, L.L.; Drach, J.C.; Townsend, L.B. Synthesis of Non-nucleoside Analogs of Toyocamycin, Sangivamycin, and Thiosangivamycin: Influence of Various 7-Substituents on Antiviral Activity. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuyper, L.F.; Garvey, J.M.; Baccanari, D.P.; Champness, J.N.; Stammers, D.K.; Beddell, C.R. Pyrrolo [2,3-d] pyrimidines and Pyrido [2,3-d] pyrimidines as Conformationally Restricted Analogues of the Antibacterial Agent Trimethoprim. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrus, P.K.; Fleck, T.J.; Oostveen, J.A.; Hall, E.D. Neuroprotective Effects of the Novel Brain-Penetrating Pyrrolopyrimidine Antioxidants U-101033E and U-104067F Against Post-Ischemic Degeneration of Nigrostriatal Neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 47, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain S., D.; Redman A., M.; Wilson J., W.; Deanda, F.; Shotwell J., B.; Gerding, R.; Lei, H.; Yang, B.; Stevens K., L.; Hassell A., M.; Shewchuk L., M.; Leesnitzer M., A.; Smith J., L.; Sabbatini, P.; Atkins, C.; Groy, A.; Rowand J., L.; Kumar, R.; Mook Jr R., A.; Moorthy, G.; Patnaik, S. ; Optimization of 4,6-bis-anilino-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine IGF-1R tyrosine kinase inhibitors towards JNK selectivity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, K.M.; Hanna, M.M.; Abo-Youssef, H.E.; George, R.F. Synthesis, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities evaluation of some bi-, tri- and tetracyclic condensed pyrimidines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44(11), 4572–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meade, E.A.; Sznaidman, M.; Pollard, G.T.; Beauchamp, L.M.; Howard, J.L. Anxiolytic activity of analogues of 4-benzylamino-2-methyl-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 33, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper D., S. ; Antithyroid Drugs. The New England Journal of Medicine 2005, 352, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpé, R. ; The Immunomodulatory Effects of Anti-thyroid Drugs are Mediated via Actions on Thyroid Cells, Affecting Thyrocyte-immunocyte Signalling: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2001, 7, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch H., B.; Cooper, D.S. Antithyroid drug therapy: 70 years later. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 179, R261–R274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.-M.; Li, H.-Q.; Li, Q.; Li, D.-M.; Xie, X.-J.; Yin, G.-P.; Zhang, P.; Xu, X.-H.; Wu, J.-D.; Chen, S.-W.; Wang, S.-K. Prevention of Relapse of Graves’ Disease by Treatment with an Intrathyroid Injection of Dexamethasone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009, 94, 4984–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, H.; Ornoy, A.; Shechtman, S.; Diav-Citrin, O. Pregnancy outcome, thyroid dysfunction and fetal goitre after in utero exposure to propylthiouracil: a controlled cohort study. B. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 68, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.G. Hyperthyroidism and pregnancy. Endocrinol Nutr. 2013, 60, 535–543. [Google Scholar]
- Shaban N., Z.; Masoud M., S.; Awad, D.; Mawlawia M., A.; Sadek O., M. Effect of Cd, Zn and Hg complexes of barbituric acid and thiouracil on rat brain monoamine oxidase-B (in vitro) Chem. -Biol. Interact. 2014, 208, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülcan, M.; Sönmez, M.; Berber, İ. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of a new pyrimidine Schiff base and its Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II), Pt(II), and Pd(II) complexes. Turk. J. Chem. 2012, 36, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleb S., M.; Askar M., E.; El-Kalyoubi S., A.; Gaballa, A.S. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of some 5-bromouracil−metal ion complexes. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2019, 33, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubyatnikova L., G.; Khisamutdinov R., А.; Grabovskii S., А.; Kabal’nova N., N.; Murinov Yu., I. Complexes of Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) with 6-tert-Butyl-2-thiouracil. Russ. J. Gen.Chem. 2017, 87, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, M. A.; Isola, K. T. , Coordination Possibility of Uracil and Applications of Some of Its Complexes: A Review — Res. J. Pharm., Biol.Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusty J., R.; Peeling, J.; Abdel-Aal M., A. Complexes of 6-Methyl-2-thiouracil with Rhodium, Iridium, Platinum and Palladium Inorg. Chim. Acta, 1981, 56, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paizanos, K.; Charalampou, D.; Kourkoumelis, N.; Kalpogiannaki, D.; Hadjiarapoglou, L.; Spanopoulou, A.; Lazarou, K.; Manos M., J.; Tasiopoulos A., J.; Kubicki, M.; Hadjikakou S., K. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of New Cu(I) Complexes with the Antithyroid Drug 6-n-Propyl-thiouracil. Study of the Cu(I)-Catalyzed Intermolecular Cycloaddition of Iodonium Ylides toward Benzo[b]furans with Pharmaceutical Implementations. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 12248–12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar A., R.; Sarkar, M. ; Cadmium(II) Complexes of 1, 3-Propanediamine with 2- Thiouracil and its 6-Methyl Derivative. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Chem. 1998, 28, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar A., R.; Mandal, S. Mixed-Ligand Peroxo Complexes of Vanadium Containing 2-Thiouracil and its 6-methyl Derivative. Syntli. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Chem, 2000; 30, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomfim, L.M.; de Araujo F., A.; Dias R., B.; Sales C. B., S.; Gurgel Rocha, C.A.; Correa R., S.; Soares M. B., P.; Batista A., A.; Bezerra D., P. Ruthenium(II) complexes with 6-methyl-2-thiouracil selectively reduce cell proliferation, cause DNA double-strand break and trigger caspase-mediated apoptosis through JNK/p38 pathways in human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Melha K., S. Elaborated studies for the ligitional behavior of thiouracil derivative towards Ni(II), Pd(II), Pt(IV), Cu(II) and UO22 2 ions. Spectrochim. Acta Part (A): Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2012, 97, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoud, M.S.; Amira, M.F.; Ramadan, A.M.; El- Ashry, G.M. Synthesis and characterization of some pyrimidine, purine, amino acid and mixed ligand complexes. Spectrochim. Acta Part(A) 2008, 69, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh U., P.; Ghose, R.; Ghose A., K.; Sodhi, A.; Singh S., M.; Singh R., K. J Inorg Biochem, 1989; 37, 325–329.
- El-Morsy, F.A.; Jean-Claude, B.J.; Butler, I.S.; El- Sayed, S.A.; Mostafa, S.I. Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity of new zinc(II), molybdate(II), palladium(II), silver(I), rhodium(III), ruthenium(II) and platinum(II) complexes of 5,6-diamino-4-hydroxy2-mercaptopyrimidine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2014, 423, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abás, E.; Pena-Martínez, R.; Aguirre-Ramírez, D.; Rodríguez-Diéguez, A.; Laguna, M.; Grasa, L. New selective thiolate gold(I) complexes inhibit proliferation of different human cancer cells and induce apoptosis in primary cultures of mouse colon tumors. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Shrivastva, S.; Rani, P. Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of mixed ligand complexes of transition and inner transition metals with a substituted benzimidazole derivative and RNA bases. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2012, 4, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Shobana, S.; Dharmaraja, J.; Kamatchi, P.; Selvaraj, S. Mixed ligand complexes of Cu (II) / Ni (II) / Zn (II) ions with 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) in the presence of some amino acid moieties: Structural and antimicrobial studies. J Chem Pharm Res 2012, 4, 4995–5004, https://www.jocpr.com/articles/mixed-ligand-complexes-of-cu-ii--ni-ii--zn-ii-ions-with-5fluorouracil-5fuin-the-presence-of-some-amino-acid-moieties-str.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalakannan P.; Venkappayya D.; Balasubramanian T. A new antimetabolite, 5-morpholinomethyl-2-thiouracil—spectral properties, thermal profiles, antibacterial, antifungal and antitumour studies of some of its metal chelates. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans, 2002; 3381–3391. [CrossRef]
- Abou-Melha K., S. A series of Nano-sized metal ion–thiouracil complexes, tem, spectral, γ-irradiation, molecular modeling and biological studies. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 31, 1897–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh U., P.; Singh, S.; Singh S., M. Synthesis, characterization and antitumour activity of metal complexes of 5-carboxy-2-thiouraci. Metal-Based Drugs, 1998; 5, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, I.; Cox, P.J.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Kokotidou, C.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Aslanidis, P. Copper(I) halide complexes of 5-carbethoxy-2-thiouracil: Synthesis, structure and in vitro cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 78, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeschele J. D.; Piscataway, N.J. Ethylenediamineplatinum(II) 2,4-dioxopyrimidine complexes, US Patent 4 207 416, 1980.
- Supaluk, P.; Apilak, W.; Ratchanok, P.; Thummaruk, S.; Chartchalerm, I.; Somsak, R.; Virapong, P. Metal Complexes of Uracil Derivatives with Cytotoxicity and Superoxide Scavenging Activity. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2012, 9, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illán-Cabeza N., A.; García-García A., R.; Moreno-Carretero M., N.; Martínez-Martos J., M.; Ramírez-Expósito M., J. Synthesis, characterization and antiproliferative behavior of tricarbonyl complexes of rhenium(I) with some 6-amino-5-nitrosouracil derivatives: Crystal structure of fac-[ReCl(CO)3(DANU-N5,O4 )] (DANU = 6-amino-1,3-dimethyl-5-nitrosouracil). J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, S.; Nozaka, Y.; Munakata, M.; Kawata, S. Synthesis and crystal structures of tetra- and hexanuclear copper(I) complexes of pyrimidine derivatives, [Cu4(C4H8N2S4)](ClO4)4 and [Cu6(C5H5N2S)6]. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 1992, 197, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, F.; Badashah, A.; Gielen, M.; Marchio, L.; Vos D., de; Khosa M, K. ., Synthesis, characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity of homobimetallic complexes of palladium(II) with 2-thiouracil ligands. Crystal structure of [Pd2(TU)(PPh3)3Cl2]. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 21, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sce, F.; Beobide, G.; Castillo, O.; Pedro I., de; Pérez-Yáñez, S.; Reyes, E. Supramolecular architectures based on p-cymene/ruthenium complexes functionalized with nucleobases. Cryst.Eng.Comm. 2017, 19, 6039–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, V.I.; Verginadis, I.I.; Geromichalos, G.D.; Kourkoumelis, N.; Male, L.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Repana, K.H.; Yiannaki, E.; Charalabopoulos, K.; Bakas, T.; Hadjikakou, S.K. Synthesis, structural characterization and biological studies of the triphenyltin(IV) complex with 2-thiobarbituric acid. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N.N. Golovnev, M.S. 42. N.N. Golovnev, M.S. Molokeev, S.N. Vereshchagin, V.V. Atuchin, M.Y. Sidorenko, M.S. Dmitrushkov, Crystal structure and properties of the precursor [Ni(H2O)6](HTBA)2.2H2O and the complexes M(HTBA)2(H2O)2 (M = Ni, Co, Fe). Polyhedron, 2014; 70, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.R.; Zhang, Y.C.; Song, Y.L.; Zhuo, X.; Li, Y.Z.; Zheng, H.G. Synthesis, structure and nonlinear optical properties of three dimensional compounds. J. Coord. Chem. 2008, 61, 3189–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, M.; Weis, K.; Vahrenkamp, H. ; Pyrazolylborate-Zinc Complexes of RNA Precursors and Analogues Thereof. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanari, K.; Kida, M.; Fuyuhiro, A.; Kita, M.; Kaizaki, S. Cobalt(III) promoted ligand fusion reactions of thiobarbituric acid and 4,6-diamino-2-thiouracil (or 4-amino-2-thiouracil). Inorganica Chim. Acta. 2002, 332, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteruelas, M.A.; García-Raboso, J.; Oliván, M. ; Reactions of an Osmium-Hexahydride Complex with Cytosine, Deoxycytidine, and Cytidine: The Importance of the Minor Tautomers. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 9522–9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Laye, R.H.; Munshi, P.; Paul, R.L.; Ward, M.D.; Kumar Lahiri, G. Dinuclear bis(bipyridine)ruthenium(II) complexes [(bpy)2RuII{L}2-RuII(bpy)2]2+ incorporating thiouracil-based dianionic asymmetric bridging ligands: synthesis, structure, redox and spectroelectrochemical properties. J. Chem. Soc. Dalt. Trans. 2002, 2348–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Tian, G.; Zhang, R. New triorganotin(IV) complexes of polyfunctional S,N,O-ligands: Supramolecular structures based on π-π and/or C–H-π interactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2006, 691, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| metal complex | composition* | formula | Moleculаr weight | W(M)% calc./exp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu(II)L1 | [3LCu.(DMSO)] | C17H24N6O4S4Cu | M=568.22 g/mol | 11.2 / 11.6±0.6 |
| Pd(II)L1 | [5LPd.(DMSO)].H2O | C27H38N10O7S6Pd | M=913.46 g/mol | 11.6 / 11.1±0.6 |
| Cu(II)L2 | [LCu.H2O.(OH-)2.(DMSO)2] | C11H26N2O6S3Cu | M=442.07 g/mol | 14.4 / 14.3±0.7 |
| Pd(II)L2 | [4LPd.(DMSO)2].H2O | C32H54N8O7S6Pd | M=961.63 g/mol | 11.1 / 11.5±0.5 |
| Atom | L1 (6-methyl-2-thiouracil) |
Cu(II)L1 Multiplicity (J, Hz) |
Pd(II)L1 Multiplicity (J, Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (NH) | 12.29 s | 12.24 s | 12.24 s and 10.80 |
| 2 (C=S) | – | – | – |
| 3 (NH) | 12.29 s | 12.29 s | 12.30 s and 10.86 |
| 4 (C=O) | – | – | – |
| 5 | 5.68 | 5.68 s | 5.68 s and 5.31 |
| 6 | - | - | - |
| 1’ | 2.06 | 2.07 | 2.07 and 2.01 |
| Atom | δ (13C) ppm, L1 | Cu(II)L1 | Pd(II)L1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (NH) | – | – | – |
| 2 (C=S) | 175.87 | 175.86 | 175.86 / ? |
| 3 (NH) | – | – | – |
| 4 (C=O) | 161.06 | 161.01 | 161.01 / ? |
| 5 | 103.72 | 103.69 | 103.69 and 98.71 |
| 6 | 153.20 | 153.12 | 153.12 / ? |
| 1’ | 18.11 | 18.06 | 18.06 and 18.20 |
| Atom | L2 (6-propyl-2-thiouracil) |
Cu(II)L2 Multiplicity (J, Hz) |
Pd(II)L2 Multiplicity (J, Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (NH) | 12.20 s | 12.20 s | 12.20 and 10.77 s |
| 2 (C=S) | - | - | - |
| 3 (NH) | 12.31 s | 12.31 s | 12.32 and 10.87 s |
| 4 (C=O) | - | - | - |
| 5 | 5.67 s | 5.67 s | 5.68 and 5.31 s and t(1.8) |
| 6 | - | - | - |
| 1’ | 2.32 t(7.5) | 2.32 t(7.4) | 2.32 and 2.25 t(7.3) and t(7.3) |
| 2’ | 1.54 sx(7.4) | 1.54 sx(7.5) | 1.54 and 1.48 sx(7.6) and m |
| 3’ | 0.87 t(7.4) | 0.88 t(7.3) | 0.87 and 0.82 t(7.3) and m |
| DMSO | - | 2.54 s | 2.54 s |
| Atom | δ (13C) ppm, L2 | Cu(II)L2 | Pd(II)L2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (NH) | - | - | - |
| 2 (C=S) | 176.08 | 176.02 | |
| 3 (NH) | - | - | - |
| 4 (C=O) | 161.22 | 164.19 and 161.09 | |
| 5 | 103.06 | 98.03 | |
| 6 | 156.74 | 156.61 and 156.33 and 151.71 | |
| 1’ | 33.21 | 33.24 | 33.56 and 33.14 |
| 2’ | 20.58 | 20.55 | 20.50 and 20.24 |
| 3’ | 13.26 | 13.25 | 13.20 |
| Test microorganisms | Complexes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 6-methyl-2- thiouracil |
Cu(II)L1 | Pd(II)L1 | |
| Inhibition zone, mm | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | - | 8 | - |
| Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 | - | 11* | 10* |
| Eterococcus faecalis ATCC 19433 | 11 | 13 | - |
| Salmonella enterica ssp. enterica ser. Enetritidis ATCC 13076 | - | 13 | 8 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 | 9 | 12 | 9 |
| Proteus vulgaris G | 9* | 11* | 9* |
| Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 | 9* | 9 | 10* |
| Bacillus cereus ATCC 11778 | 9* | 8 | 9* |
| Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 8787 | 9* | 11 | 8 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883 | 9* | 13* | 11* |
| Candida albicans ATCC 10231 | 11 | 11 | 9/10* |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | - | 9 | - |
| Test microorganisms | Complexes | ||
| 6-propyl-2-thiouracil | Cu(II)L2 | Pd(II)L2 | |
| Inhibition zone, mm | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | - | 8 | 11/16* |
| Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 | - | 10* | - |
| Eterococcus faecalis ATCC 19433 | - | 12 | 15 |
| Salmonella enterica ssp. enterica ser. Enetritidis ATCC 13076 | 8 | 12 | 15 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 | 8 | 12 | 14 |
| Proteus vulgaris G | 10 | 9* | - |
| Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 | 8 | 12* | 12 |
| Bacillus cereus ATCC 11778 | 10* | 8 | 11/15* |
| Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 8787 | 8 | 9 | 14 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883 | 11* | 12* | 12* |
| Candida albicans ATCC 10231 | 12 | 11 | 11 |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 11* | 9 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





