Submitted:
03 November 2023
Posted:
06 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
3. Critical Analysis
3.1. Product Development Process and Lean Product Development Process description
3.2. Critical analysis and problems identification through VSDiA
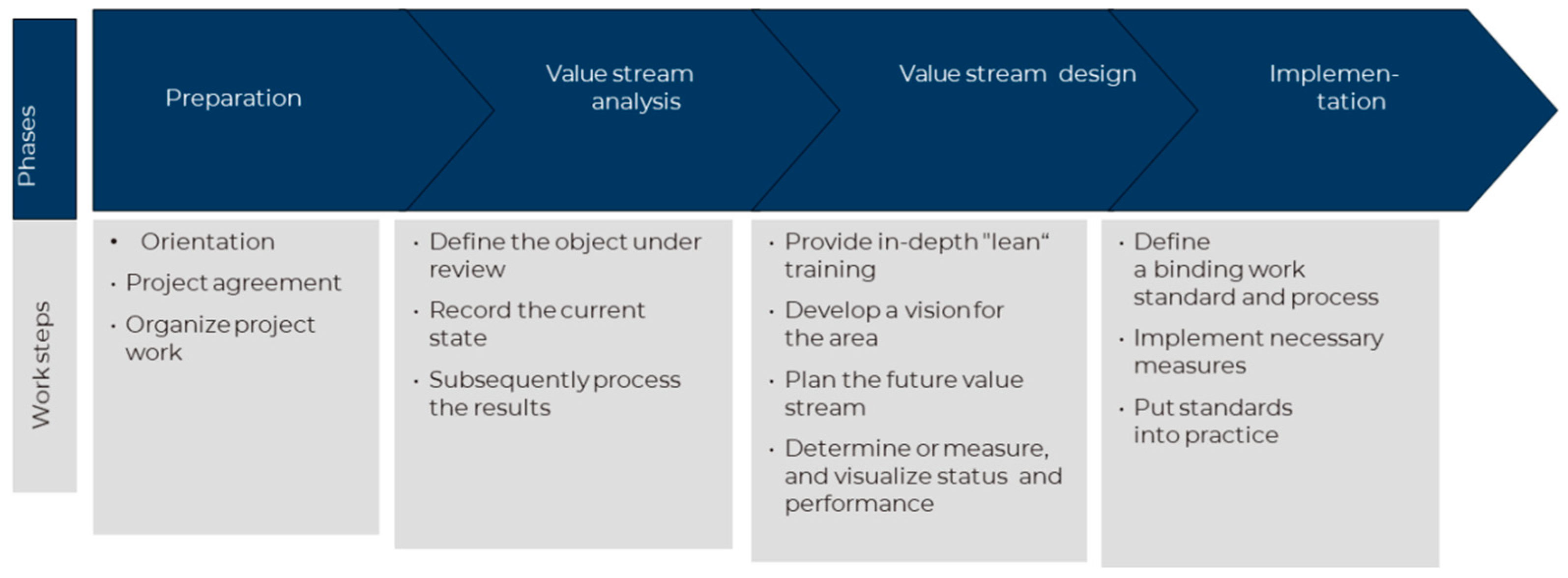
3.3. Preparation
3.4. Data Collection
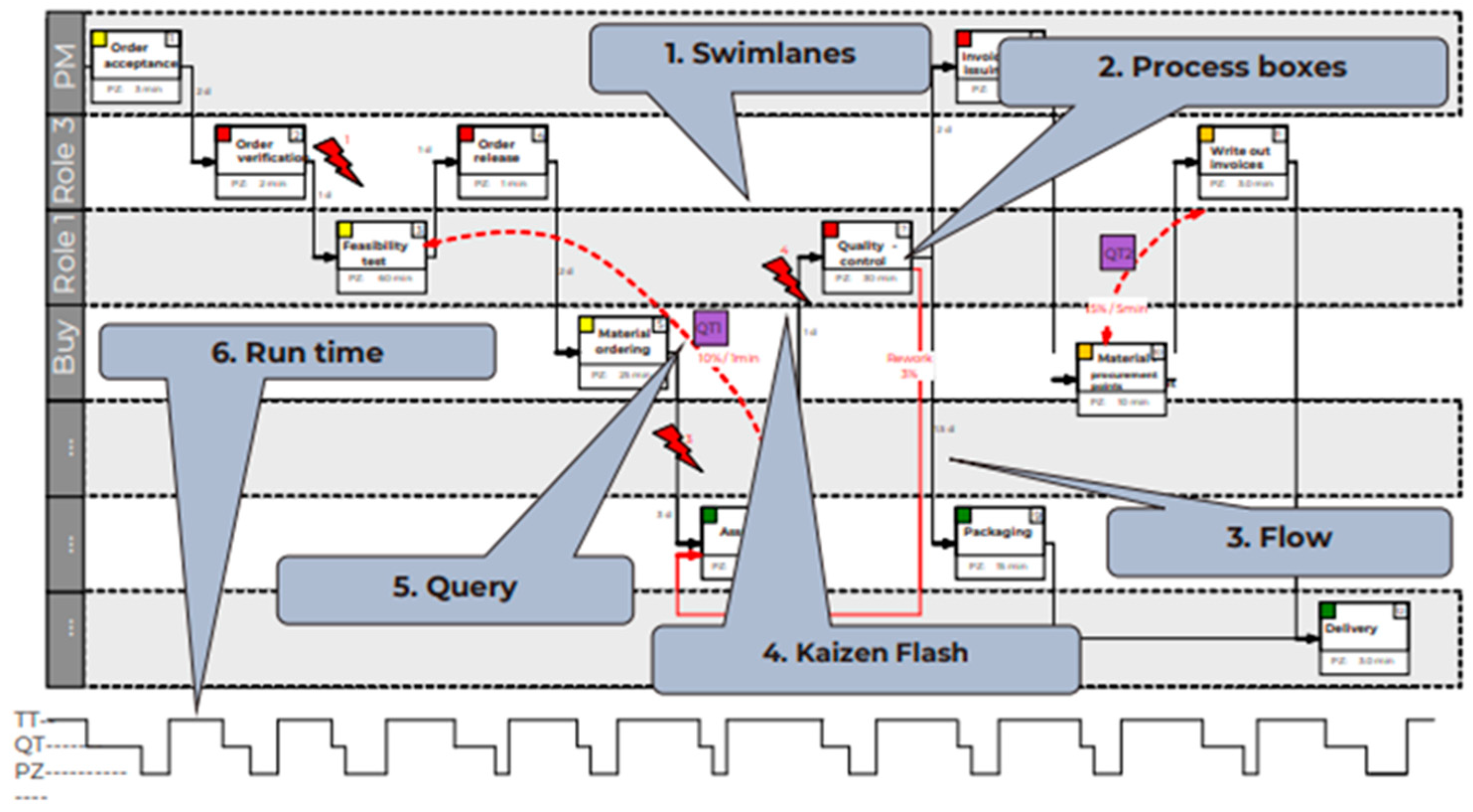
3.5. Value Stream Mapping Analysis
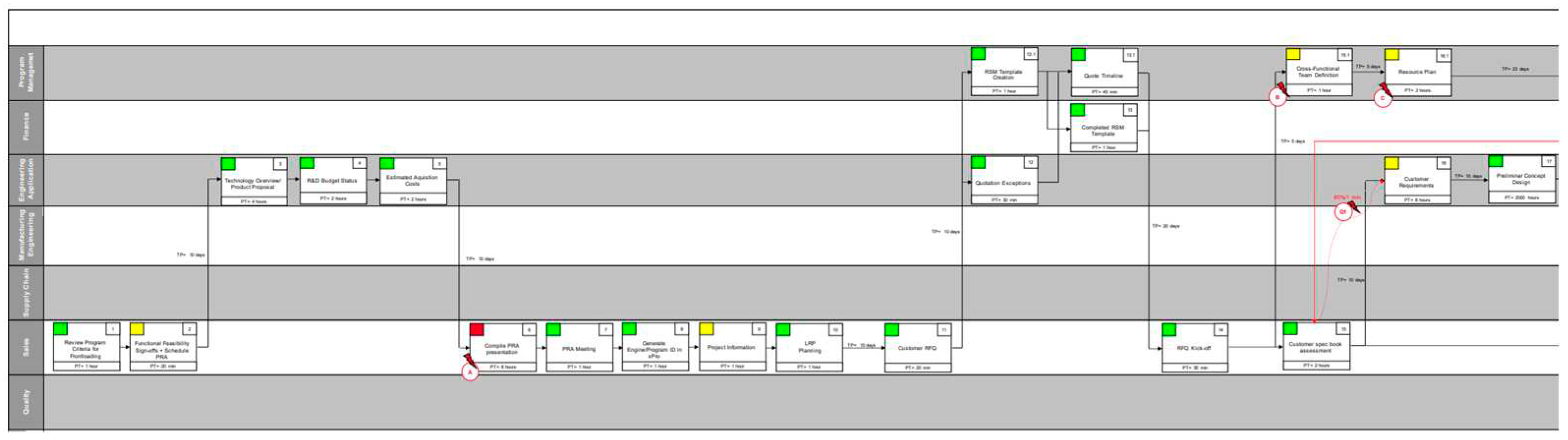
3.5.1. Current State
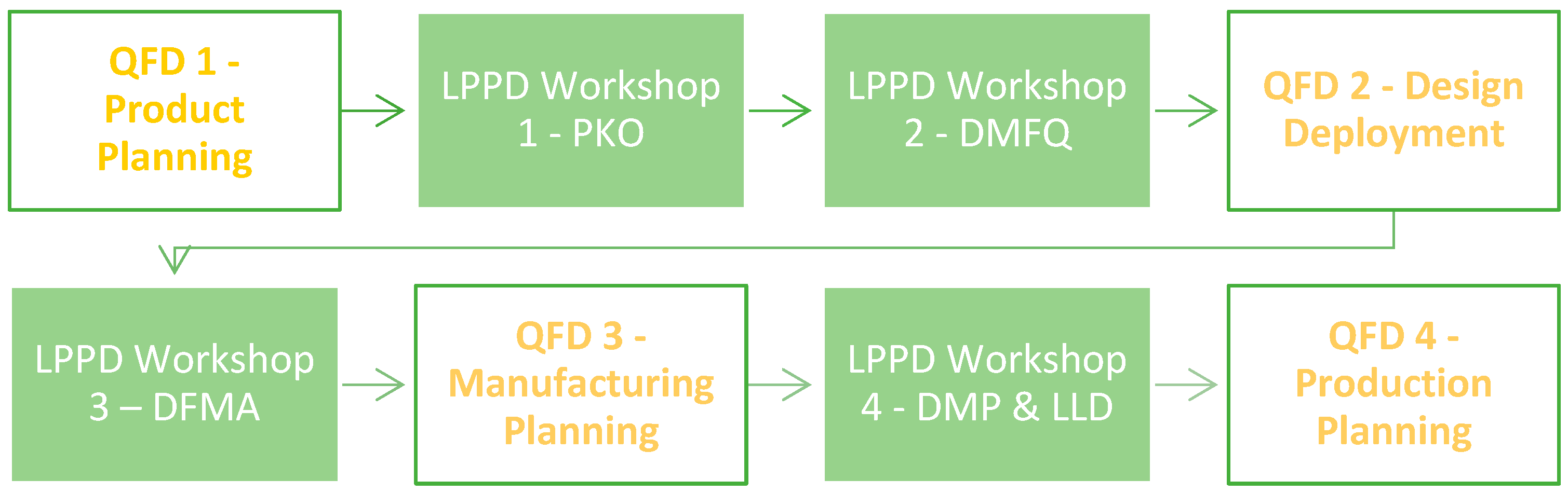
3.5.2. LPPD Workshops
- LPPD Workshop Design Manufacturing for Quotation (DMFQ)
- LPPD Workshop Program Kick-Off (PKO)
- LPPD Workshop Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)
- LPPD Workshop Detailed Manufacturing Process & Lean Line Design (DMP & LLD)
3.5.3. Identification of Problems
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Value Stream Design
- Customer Requirements: Customer needs should be well understood;
- Simplicity and transparency: the process should be as simple as possible for employees in order to provide the desired output to the customer (internal / external);
- Elimination of all mental barriers: all suggestions should be respected even less hypothetical since they can be beneficial for combination with others.
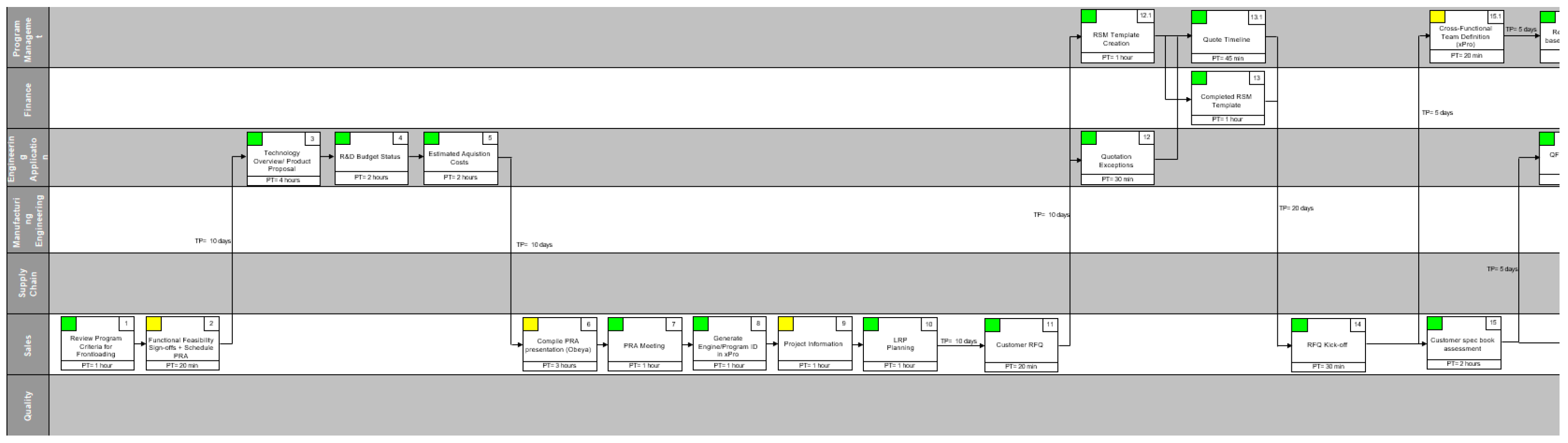
4.1.1. Future State
4.1.2. Key performance indicators
4.2. Implementation
4.2.1. Obeya room
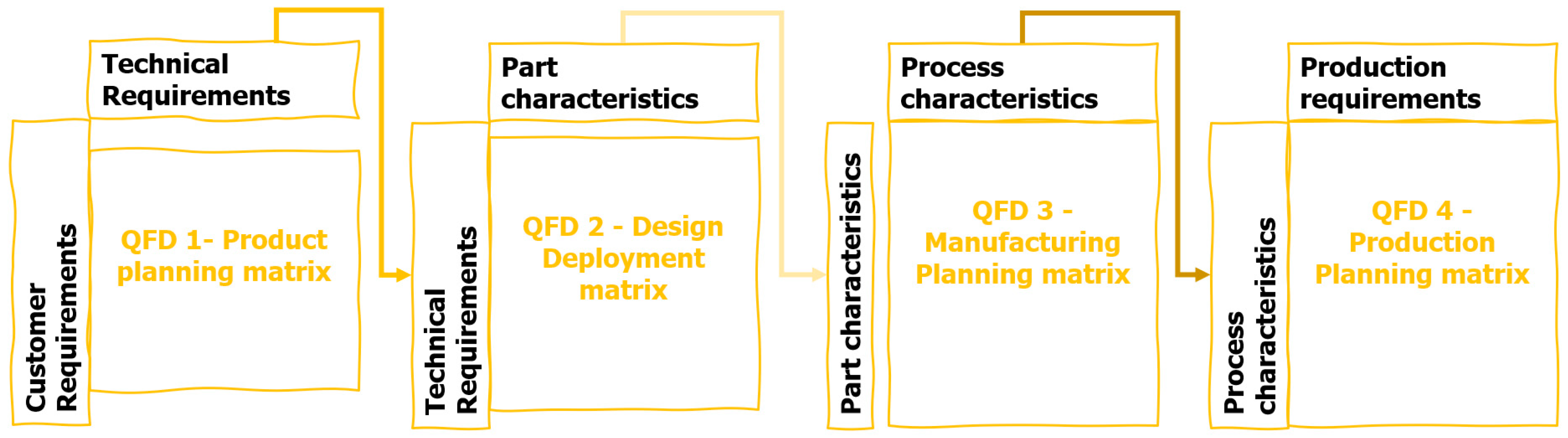
4.2.2. Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
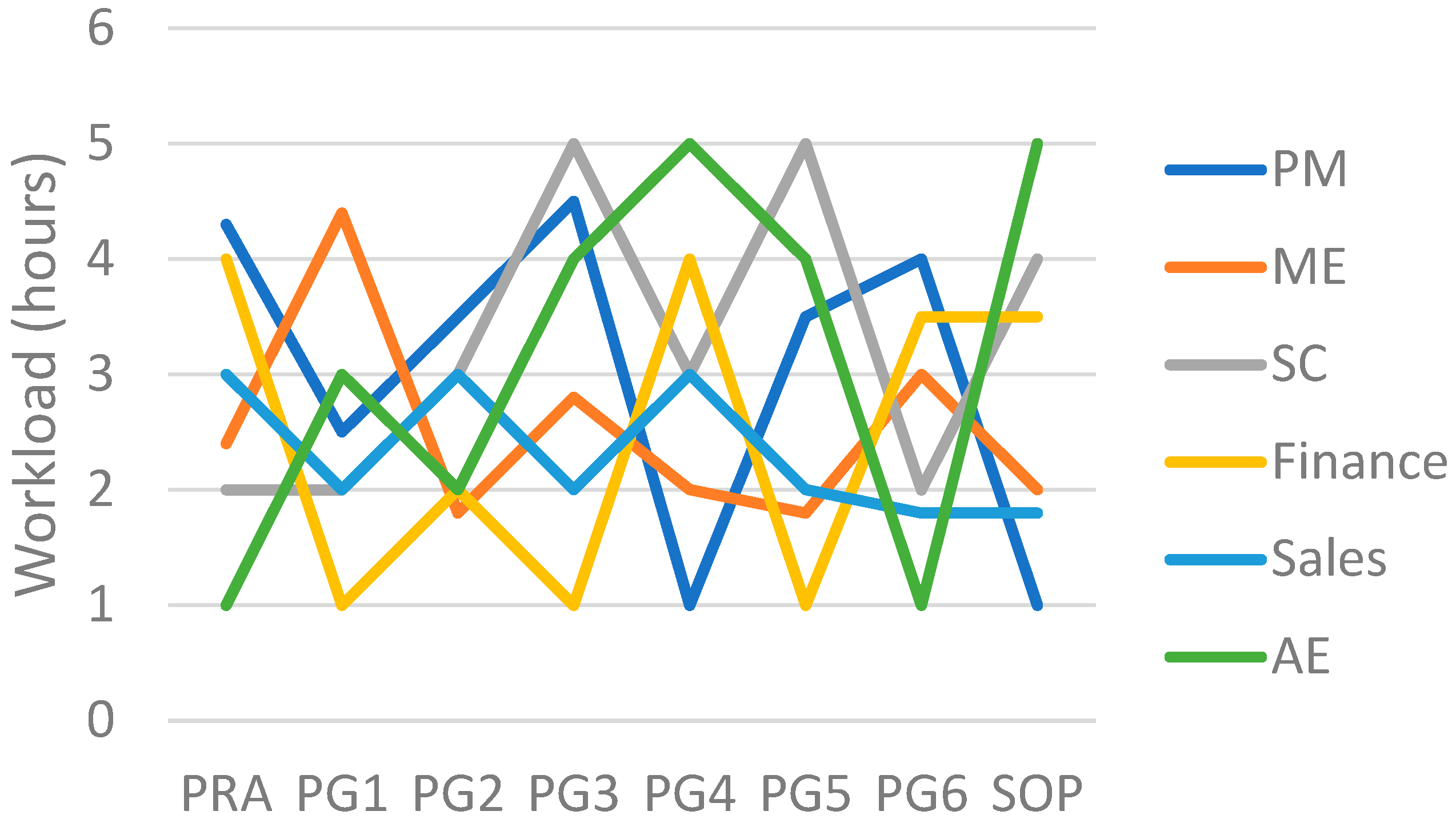
4.2.3. Workload Graphic
4.2.4. LPPD Workshops improvement proposals
- LPPD Workshop – PKO
- QFD 1 – Product Planning
- 2.
- LPPD Workshop – DMFQ
- Preliminary Process Assembly
- Lessons Learned
- 3.
- LPPD Workshop – DFMA
- QFD 2 – Production Planning
- 4.
- LPPD Workshop – DMP & LLD
- QFD 3 - Manufacturing Planning
- Data Base for Capital expenditures (Capex) and Tools
- Definition of standard shapes for layouts
- Integration of Value Stream Mapping tool
- o Cycle time or processing time
- o Changeover time
- o Reliability of equipment
- o First pass yield
- o Quantities
- o Number of operators and shifts
- o Hard copy information
- o Electronic information
- o Inventory levels
- o Queue or waiting times
- Simulation Tool for Lean Line Design
- QFD 4 - Production Planning
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Papilloma, Z., Gažová, A. & Šufliarský, L. Implementation of Automation Technologies of Industry 4.0 in Automotive Manufacturing Companies. Procedia Comput Sci 200, 1488–1497 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Liker, J. K. & Morgan, J. Lean Product Development as a System: A Case Study of Body and Stamping Development at Ford. Engineering Management Journal 23, 16–28 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J. M. & Liker, J. K. The Toyota product development system : integrating people, process, and technology. (Productivity Press, 2006).
- Parsons, M. J. & Josefik, N. M. Accelerating Production Readiness Using Lean Product Development. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Fuel Cell Science, Engineering, and Technology 2009 813–817 (2010) . [CrossRef]
- Wangwacharakul, P., Berglund, M., Harlin, U. & Gullander, P. Cultural aspects when implementing lean production and lean product development -experiences from a Swedish perspective. Quality Innovation Prosperity 18, 125–140 (2014). [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, R. An Overview of the Methodological Approach of Action Research. (2008).
- Susman, G. I. & Evered, R. D. An Assessment of the Scientific Merits of Action Research. Adm Sci Q 23, 582 (1978). [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A. M., Siddhalingeshwar, I. G. & Ekabote, N. Implementation of Advanced Product Quality Planning in Engineering Project. Journal of Engineering Education Transformations 0, (2016). [CrossRef]
- Rother, M., Shook, J., Womack, J. & Jones, D. Learning to See: Value Stream Mapping to Add Value and Eliminate MUDA. (Lean Enterprise Institute, 1999).
- Tapping, D. & Shuker, T. Value Stream Management for the Lean Office. (Productivity Press, 2003).
- Etzel, M. & Kutz, R. Process optimization Value Stream Design in indirect Areas (VSDiA) Basic information for managers. (2010).
- Cooper, R. & John, S. Ideation for Product Innovation: What are the Best Methods? www.stage-gate.com (2008).
- Yang, N., Kornas, T. & Daub, R. A KPI System for small sample sizes based on the Bayesian estimation of Cpk in the production of Lithium-ion batteries. Procedia CIRP 99, 526–530 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M., Morgan, J. & Shook, J. Lean Product and Process Development. (2016) . [CrossRef]
- Chan, C. Y. P. et al. The US Automotive Industry and Major Developments of QFD. (2019).
- Chan, L.-K. & Wu, M.-L. Quality Function Deployment: A Comprehensive Review of Its Concepts and Methods. Qual Eng 15, 23–35 (2002). [CrossRef]
- Batwara, A., Sharma, V., Makkar, M. & Giallanza, A. Towards smart sustainable development through value stream mapping – a systematic literature review. Heliyon 9, e15852 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Stechert, C. & Balzerkiewitz, H. P. Digitalization of a Lean Product Development Organization. in Procedia CIRP vol. 91 764–769 (Elsevier B.V., 2020). [CrossRef]

| Types of Waste | Lean Production | Lean PD |
|---|---|---|
| Overproduction | Wasteful input of raw materials in an early stage | Information and analysis not required |
| Transportation | Various types of transports (trucks, conveyers) | Flow of communication not effective |
| Waiting | Operator not working | Delay for approval a prototype |
| Inventory | Excess of stock not needed | Redundant information |
| Motion | Persons not working as they should (not-adding-value) | Wrong flow of information to people |
| Over Processing | Improper technology that leads to design gaps and deburring | Information not well stored and unnecessary analysis |
| Defects | Damage of machines and rework | Testes failed and inaccurate data |
| Problems | Consequences | Type of Wastes |
|---|---|---|
| Spec-book is not well organized | Delay for organize the spec book and write down the specifications | Waiting |
| Customer requirements change | Late design changes | Rework; Waiting. |
| Departments do not communicate between each other | Flow of communication not effective | Transportation |
| LPPD 2 - DMFQ was developed on a late stage | Information and analysis not required: 8 loops of Quotations | Overproduction |
| CFT Resources are not well nominated | High workload of resources, overlaps with other programs | Waiting |
| Production Concept is not considering Logistics | High storage costs, low rate of turnover, low flexibility and low | Transportation; Inventory. |
| Tear-Down Analysis is not reviewed by Quality | Testes failed and inaccurate data | Defects |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





