1. Introduction
Intrauterine adhesions (IUA) is a common gynecological disease caused by endometrial injury and abnormal proliferation of fibrous tissue, which has become one of the main causes of female infertility [
1,
2,
3]. At present, the main treatment for IUA is transcervical resection of adhesions (TCRA), which uses miniature scissors to separate the adhesion part [
4]. However, since TCRA is still hysteroscopic surgery in nature, mechanical damage will be caused again during the separation process, beyond that, the incidence of postoperative re-adhesion can reach up to 62.5% [
5]. Therefore, how to safely and effectively prevent re-adhesion after TCRA has become a key issue in clinical treatment.
At present, physical barriers such as intrauterine device and films are mainly used in clinical practice to prevent re-adhesion [
6,
7,
8]. However, due to various reasons such as poor biocompatibility and mismatch of mechanical properties, the treatment effect is limited, which can only alleviate or reduce adhesion to a certain extent [
9,
10,
11,
12]. Hydrogel is an extremely hydrophilic three-dimensional network gel that can rapidly swell in water and retain a large amount of water without dissolving [
13,
14,
15], and its physical and chemical properties can be adjusted to have a good ability to match biological tissues [
16,
17]. Nowadays, some kinds of hydrogels have been used in clinical cases to prevent re-adhesion after TCRA surgery [
18]. As a commonly used intraluminal anti-adhesion hydrogel, alginate has good biocompatibility and antibacterial properties, but its poor mechanical properties cannot achieve complete wound separation, which may lead to re-adhesion [
19,
20]. And because of this, further clinical application is limited[
21]. To meet the demand for stronger mechanical properties, Suo et al. [
22] designed a double-network hydrogel that combines two single-network gels, calcium ion cross-linked alginate and polyacrylamide, to break through the disadvantage of poor mechanical properties of hydrogels. However, the hydrogel was not adhesive and difficult to be in the same position for a long time.
In order to stabilize the anti-adhesion hydrogel on the uterine cavity wound, with excellent mechanical properties, good tissue adhesion is also required. For purpose of this, researchers have begun to focus on mussel biomimetic materials in recent years [
23,
24]. The strong adhesion ability of mussels is due to their unique adhesion proteins, in which a large number of catechol groups can allow mussels to adsorb to objects through hydrogen bonds [
25]. PDA is obtained by oxidation and self-polymerization of DA in a weak alkaline environment and the structure of PDA contains a large number of catechol groups, which is relatively similar to that of adhesion proteins and can achieve the purpose of strong adhesion [
26]. At the same time, the surface modification of materials with dopamine can also bring good biocompatibility, degradation, hemostasis and other comprehensive properties [
27,
28]. It seems that the introduction of PDA into dual-network hydrogels can combine excellent mechanical properties with adhesion ability.
Based on this, this study aims to synthesize a PDA dopation-modified calcium alginate/polyacrylamide double-network hydrogel, and optimize its mechanical properties and tissue adhesion ability by adjusting the immersion concentration and doping amount of PDA. At the same time, the swelling, degradation, hemostatic ability and biocompatibility of the hydrogel were also tested, and the application prospect of the hydrogel as an anti-adhesion hydrogel in preventing re-adhesion after TCRA was systematically studied and evaluated. The potential of the hydrogel using as an anti-adhesion hydrogel for clinical application is expected.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Acrylamide (AM), sodium alginate (SA), dopamine hydrochloride (DA), N,N′-bis(acrylyl)cystamine (BAC), ammonium persulfate (APS), N,N,N-,N-tetramethylenediamine (TEMED), trimethylol aminomethane (Tris) were purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co. Ltd and anhydrous calcium chloride(CaCl2) was purchased from Tianjin Kemiou Chemical Reagent Co. Deionized (DI) water was homemade by the laboratory.
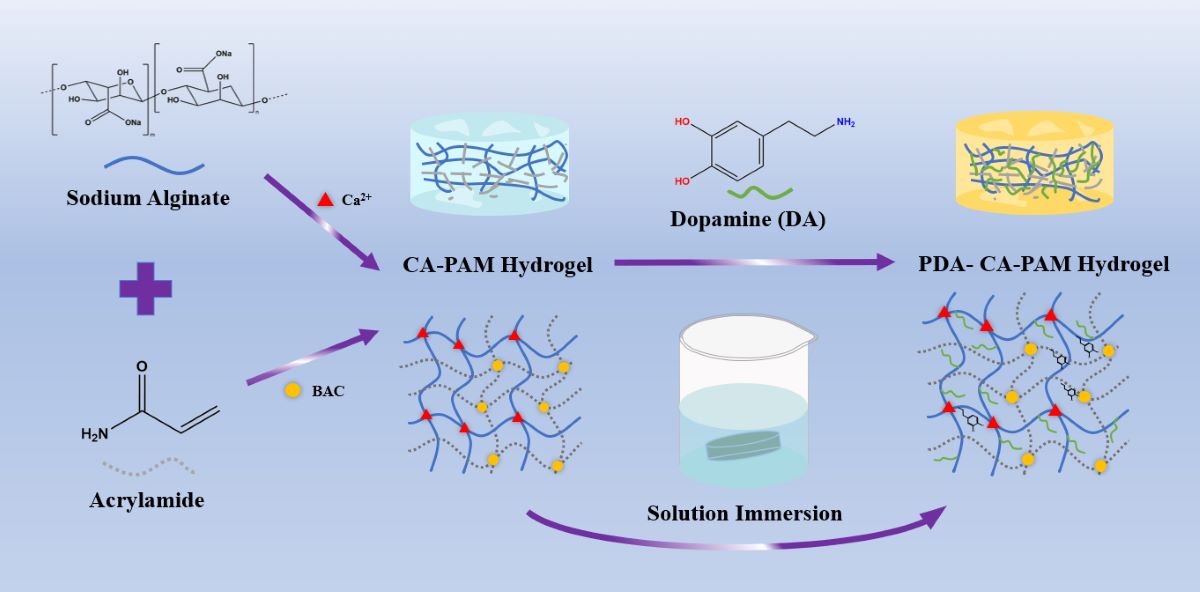
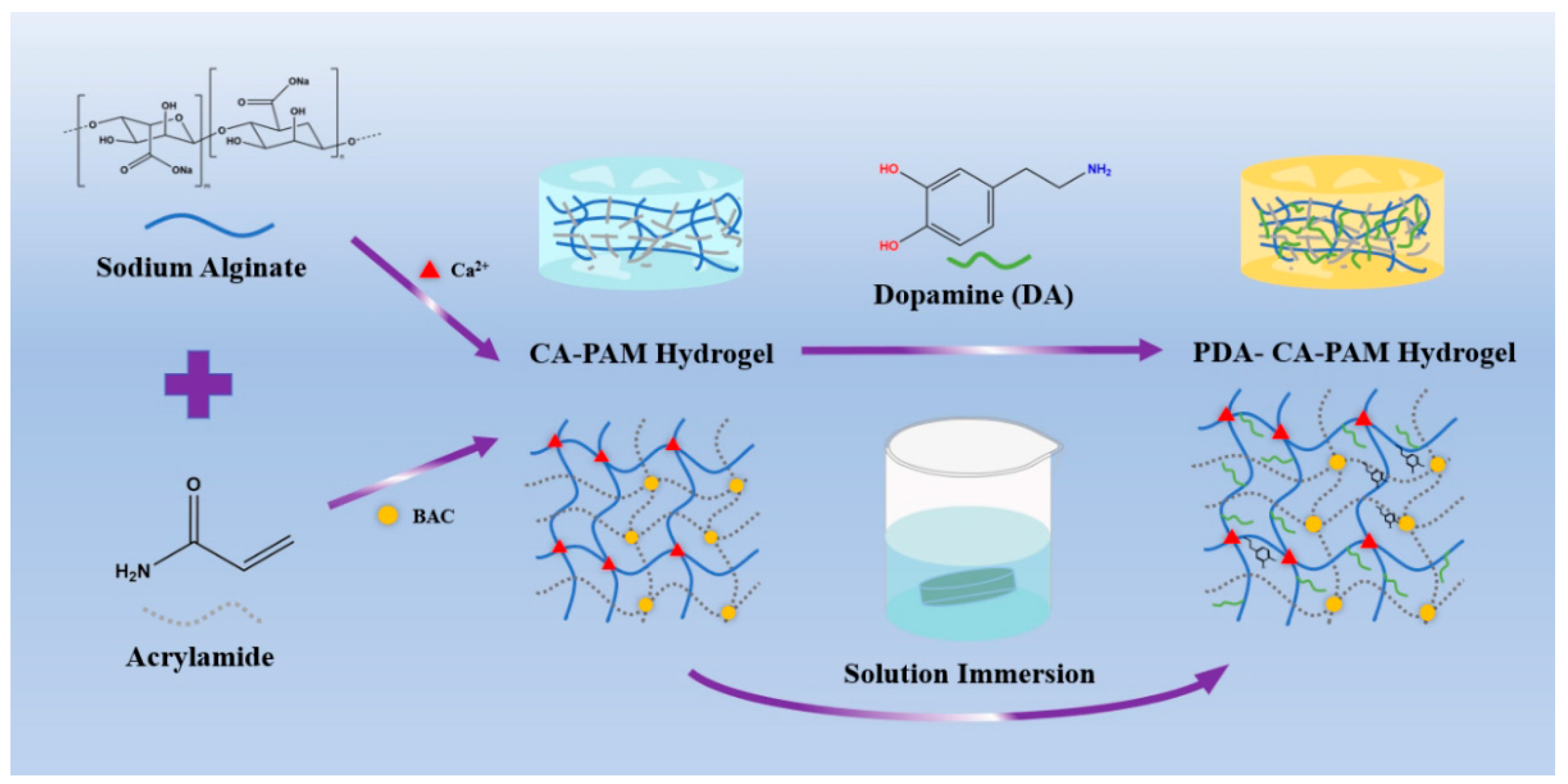
2.2. Preparation of PDA-CA-PAM Hydrogels
As shown in
Scheme 1, the hydrogels were prepared by following two steps. First, AM (3.6 g), BAC (0.0132 g), SA (0.6 g) were dissolved in 30 mL DI water under ice bath. Then, APS and TEMED were added into the mixture and stirred for another 15 min. The hydrogel was left for 24 h and then immersed in 0.01 M CaCl
2 solution for another 6 h to obtain CA-PAM hydrogel. Then, 5 mg/mL DA were dissolved in 0.01 M Tris solution with pH = 8.5 to form the dopamine solution. The CA-PAM hydrogel was immersed into the solution and stirred for 24 h to obtain 5 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel. Using the same method, 10 and 20 mg/mL DA solutions were prepared to obtain 10 PDA-CA-PAM and 20 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogels.
2.3. Characterization
The chemical structure of the hydrogels was verified via Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy Nicolet iS20 (FTIR, Thermo Scientific, USA) in the range of 4000-500 cm-1. The morphologies were observed via field emission scanning electron microscope IT800-SHL (FESEM, JEOL, Japan) at a voltage of 10 kV. The mechanical properties were tested by universal testing machine (HY-0580) with the speed of 30 mm/min. The compression tests were carried out using the cylindrical hydrogels, which were compressed to 75% strain at a speed of 50 mm/min. Rheology analysis were performed using the MCR301 rheometer at 37℃ with a plate with a diameter of 13 mm with thickness of 2 mm.
2.4. Adhesion Measurements
The adhesive strength of the PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel was investigated via a lap shear method following a previously reported study with some modifications[
29]. Fresh hydrogel was cut into 22 × 22 × 2 mm and adhered to the middle of two pieces of pig skin, which were attached to two identical slides. And then, the slide was stretched to failure at a speed of 5 mm/min by HY-0580 electronic universal testing machine. The adhesive strength was calculated from dividing the maximum force over the area of the adhesive overlap. All samples were tested three times.
2.5. Swelling Behavior
Before the test, the initial weight W
0 was weighed, and then the PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel was soaked in PBS at 37°C, and removed at regular intervals. Before every weighing, filter paper will be used to remove the water on the surface, and the weight of the hydrogel after the swelling time t, W
t will be obtained. Swelling ratio was calculated by formula (1):
2.6. Biodegradation Behavior
The initial weight W
0 of the PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel was weighed, and then the hydrogel was soaked in PBS and 20 μM cysteine, and placed in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C. The samples were periodically removed and washed with water, then freeze-dried for 48 h and weighed again, recorded as W
d. The biodegradation was measured as the percent mass loss of the hydrogel samples, calculated by formula (2):
2.7. Hydrophilicity Assay
The surface hydrophilicity of the hydrogel was tested using a contact Angle meter (DSA100, KRUSS, Germany). 2μL DI water was dropped on the surface of the sample, the image after the droplet touched the surface was recorded, and the water contact angle was calculated.
2.8. Hemolysis Assay
Fresh goat blood was diluted with saline. The PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel was rinsed and immersed in centrifuge tube containing 10 mL saline. The centrifuge tube was incubated at 37℃ for 30 min, and then 0.2 mL diluted blood was added and incubated at 37℃ for 60 min. Saline was used as negative control group while DI water as positive control group. All tubes were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 min, collecting the supernatant, and the optical density value (OD) was recorded at 540 nm microplate reader. The hemolysis rate was calculated by formula (3):
2.9. Hemostasis Assay
Goat blood was diluted with CaCl
2 solution at a ratio of 1:9 and then dropped on the surface of the PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel. The dishes were transferred to an incubator for 5 min at 37℃. After the reaction, DI water was added to dissolve the uncoagulated blood cells. The 100 μL supernatant was added to the 96-well plate, and the OD value at 540 nm was read with an enzyme marker. The blank dish served as the control group. The final coagulation index (BCI) value was calculated by quantifying the percentage of blood cells that had not coagulated into blood clots, referring to formula (4):
2.10. Cytocompatibility
NIH/3T3 cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/mL penicillin G and 100 mg/mL streptomyces at 37℃ and 5% CO2. The 2×104 cells/mL NIH/3T3 were inoculated into 24-well plate containing PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel, cultured for 1 d, 2 d, and 3 d. For the corresponding points, the cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min, and then rinsed again for 3 times. Finally, 0.1% TritonX-100 was used to permeate the cells. The cytoskeleton was stained with AcN-Trackergreen-488 and observed by fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Japan).
The proliferation of the NIH/3T3 cells in hydrogel was accessed by CCK-8 assay. In short, 1 × 10
4 cells/mL of the cells were seeded and cultured overnight. The cell proliferation capacity was detected after 1, 2, and 3 days of incubation by using cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8, Solarbio, China). 100 μL of fresh medium and 10 μL of CCK-8 solution were added to each well, and incubated at 37℃ for 4 h. Thereafter, the OD value at 450 nm was measured and the cell viability was calculated by formula (5).
2.11. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were repeated three times and data were analyzed using SPSS13.0 software. All data were given as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) and p<0.05 showed that the results were statistically significant. (p < 0.05 was marked as “*”, p < 0.01 was marked as “**”, and p < 0.001 was marked as “***”).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of PDA-CA-PAM Hydrogel
This work presented a novel hydrogel that combined excellent mechanical properties, adhesion, stable degradation, and hemostasis, and the synthesis process was shown in scheme 1. Based on the synthesis of the CA-PAM, the double-network hydrogel was immersed in DA solution. PDA chains would be formed by self-polymerization in a weakly alkaline environment and then introduced into the gel network. Chemical cross-linking between molecular chains provided a rigid network, and the abundant phenolic hydroxyl groups of PDA could form a large number of intermolecular hydrogen bonds with the surface of biological tissues, which provided good adhesion ability. For easily describing, the PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel obtained by immersion in 5 mg/mL DA solution will be referred to as 5 PDA-CA-PAM for short. Similarly, 10 mg/mL and 20 mg/mL were named 10 PDA-CA-PAM and 20 PDA-CA-PAM, respectively.
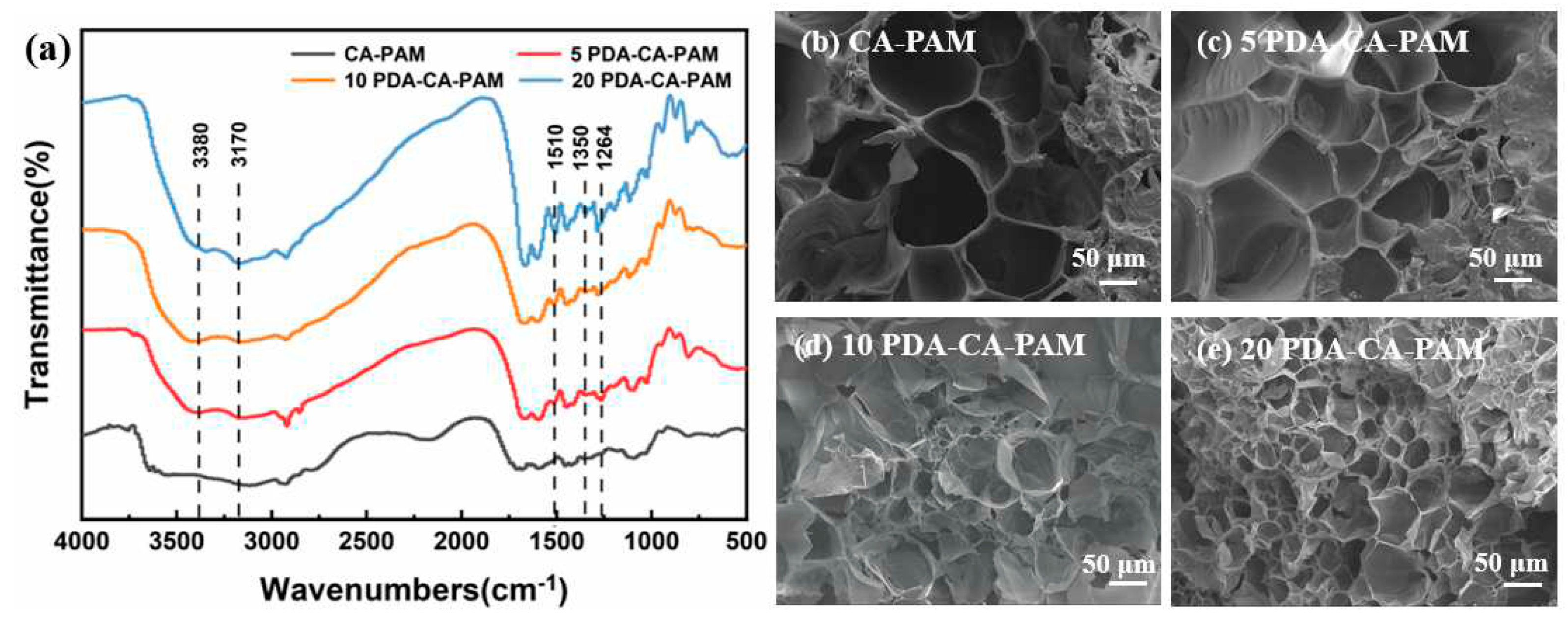
To demonstrate that PDA was successfully doped, the chemical structure inside the hydrogel was characterized using FTIR. The results showed that PDA was successfully doped into the hydrogel by soaking in solution, as shown in
Figure 1 (a). Compared with the CA-PAM hydrogel, the PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel showed a peak at 1264 cm
-1, which corresponded to the stretching vibration of C-N in PDA aniline, and this band’s appearance implied the interaction between the NH
2 group of PAM and the catechol groups of PDA. Meanwhile, the characteristic peaks of the aromatic ring belonging to PDA also appeared at 1510 cm
-1 and 1350 cm
-1. The absorption peaks located at 3380 cm
-1 and 3170 cm
-1 were characteristic tensile vibration peaks of O-H and N-H, indicating the successful introduction of PDA [
30,
31].
In order to study the effect of DA concentration in solution on the structure of hydrogel, SEM was used to investigate the internal structural changes of the PDA-CA-PAM hydrogels after immersion in the solution with different DA concentrations.
Figure 1 (b-e) showed SEM images of the cross sections of CA-PAM and PDA-CA-PAM hydrogels. By comparing the SEM images of the hydrogels, it could be seen intuitively that the CA-PAM and PDA-CA-PAM hydrogels all had a good three-dimensional porous network structure. With the increase of DA concentration, the pore density in the gel increased, and also the pore size gradually decreased. Presumably, it is because PDA entered the interior of the gel network during the immersion, and formed a new internal structure through non-covalent bonding, further dividing the original internal pores. This structural change ensured a higher elastic modulus and more desired mechanical properties.
3.2. Mechanical Properties and Rheological Analysis
Excellent mechanical properties are important for anti-adhesion hydrogels, which enable them to act as support and barrier in the uterine cavity. Tensile and compression tests and rheological analysis were carried out on the hydrogels as shown in
Figure 2.
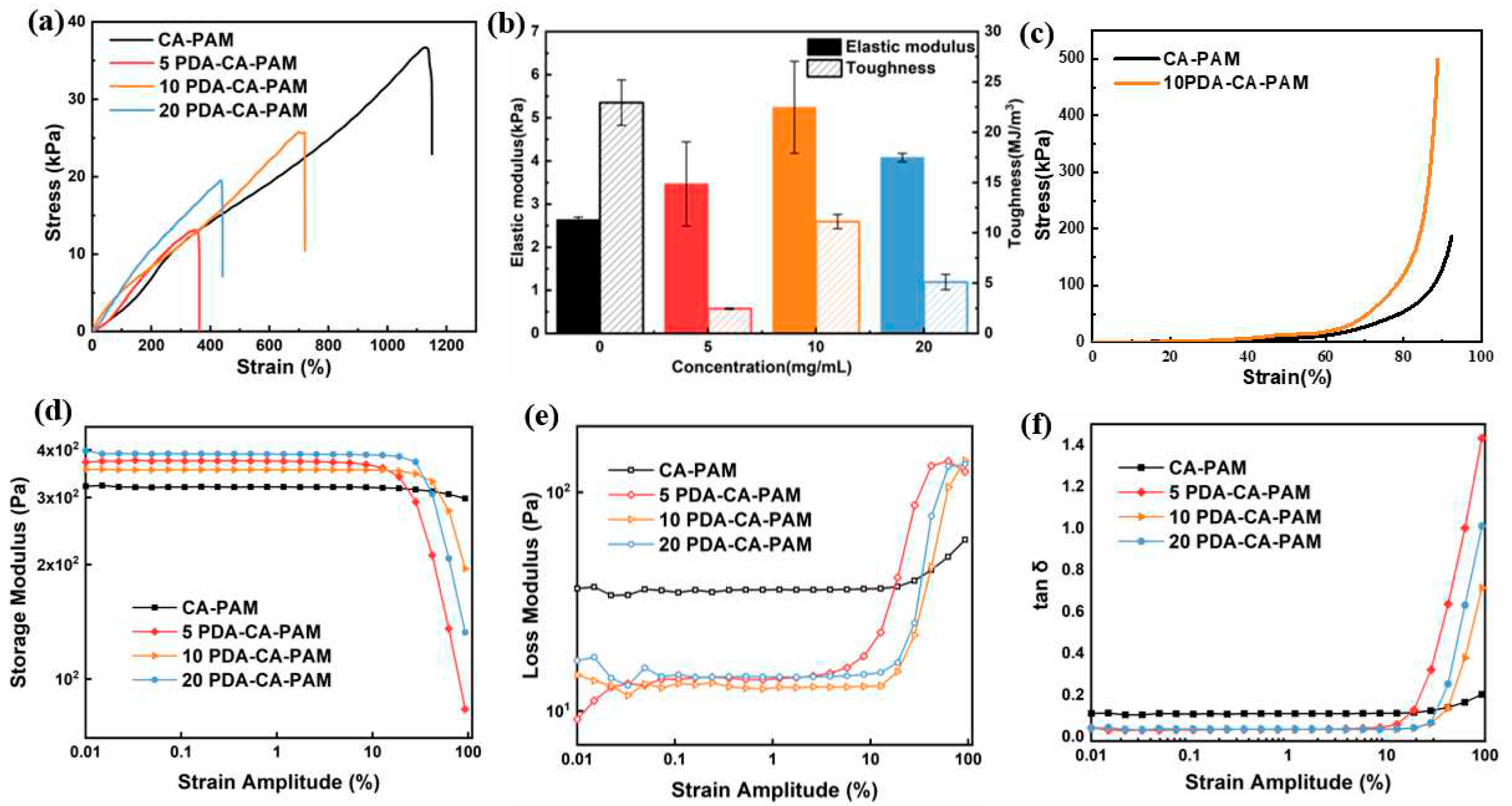
Figure 2 (a) shows that compared with CA-PAM, the elongation rate and tensile strength of PDA-CA-PAM decreased, which was because the doped PDA limited the movement and extension of the polymer chain during stretching. The elongation at break of PDA-CA-PAM increased with DA concentration increasing. The reason was that during the PDA coating process, the polymerized PDA chain infiltrated into the hydrogel network, increasing the number of non-covalent bonding sites within the gel, and when the molecular chain slipped during stretching, new non-covalent bonds were formed. Consequently, this resulted an increase in elongation at break. However, when the concentration of DA was over 10 mg/mL, the elongation rate began to decrease, which was caused by the uneven coating of PDA.
Figure 2 (b) showed the corresponding elastic modulus and toughness calculated from the tensile stress-strain curve. It could be seen that the elastic modulus of the original CA-PAM hydrogel was slightly increased after coating with PDA, which was because the internal structure of the PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel became closer due to the PDA coating. When the concentration of DA was 10 mg/mL, the elongation at break of 10 PDA-CA-PAM was 720%, which indicated excellent flexibility. The elastic modulus (5.24 ± 1.06 kPa) of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel was close to that of natural rat uterine tissue, proving the potential to be used in uterine cavity anti-adhesion.
The compressive stress-strain curve of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel was shown in
Figure 2 (c). It could be found that the compression strain of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel was 89% when the compression stress was as high as 0.5 MPa. After PDA doping, the hydrogel had better compression performance because of the denser internal network structure, indicating that it could smoothly play a supporting role on the uterine cavity wound.
To further investigate the effect of PDA doping on the internal structure of the hydrogels, the shear viscoelasticity was analyzed at 37℃.
Figure 2 (d, e) showed the storage modulus G′ and loss modulus G" of the hydrogels as a function of the shear strain amplitude. Within the strain amplitude range of 0.01% ~ 10%, because of the denser structure due to PDA doping, PDA-CA-PAM hydrogels had higher G′ and lower G″ compared to CA-PAM, showing better elasticity. When the strain amplitude was greater than 10%, the internal network structure of the hydrogels had lost stability. Among these, the intersection points of G′ and G″ of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogels was more posterior, indicating that it had the highest stability. Overall comparison, it could also be found that 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel had lower G″ with more stable internal structure, which could be confirmed by the results of tensile test.
Figure 2 (f) showed the loss factor of hydrogels as a function of the shear strain amplitude. When the strain amplitude was less than 10%, the tan δ of the PDA-CA-PAM hydrogels was lower than that of CA-PAM, indicating better elasticity. When the strain amplitude was greater than 10%, the tan δ rised rapidly. Among them, 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel had the lowest tan δ, and its rapidly rising initial strain was more posterior, proving that it had relatively stronger elasticity. Based on the above analysis, 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel had the most ideal viscoelastic properties.
3.3. Adhesive Performance
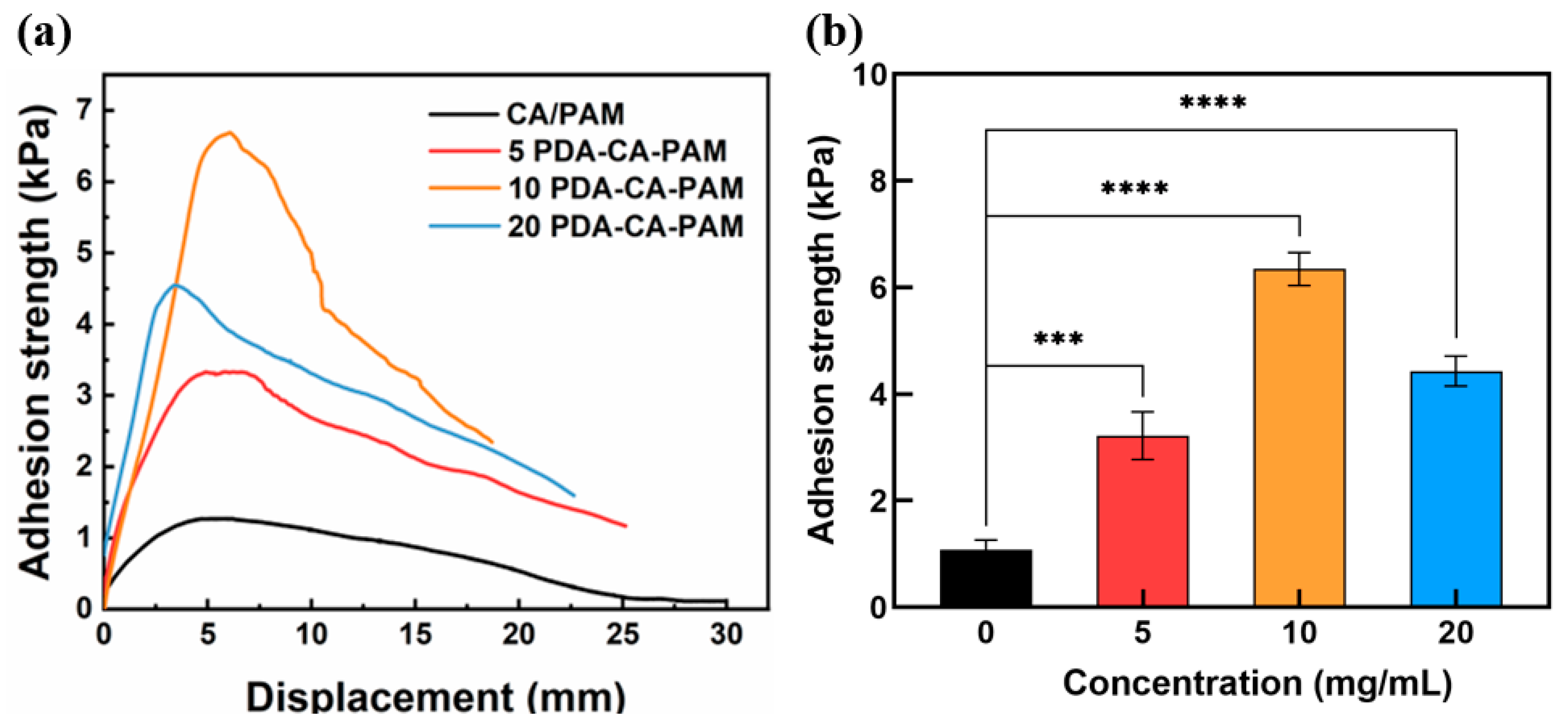
In order to obtain the adhesive properties of the hydrogel, the lap shear test was performed. The PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel also exhibited excellent adhesion to biological tissues, which ensured its stable fixation on the uterine cavity wound. The adhesion stress-displacement curves were shown in
Figure 3 (a) and the maximum value on the adhesion curve was extracted to obtain
Figure 3 (b). It could be seen that the adhesion strength increased with the increase of DA concentration. When the concentration of DA reached 10 mg/mL, the adhesion strength between PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel and pig skin reached 6.35 ± 0.31 kPa, which was higher than the adhesion strength of commercial tissue adhesive fibrin glue (about 5 kPa)[
32]. The 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel also showed good adhesion to other materials (
Figure S1).
The good adhesion performance of PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel was mainly attributed to the catechol, amino and carboxyl groups of PDA, which could generate hydrogen bonds with biological tissue interfaces and mimicked the adhesion function of mussel. The 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel had the best adhesion properties. However, when the concentration of DA exceeded 10 mg/mL, the PDA surface of the hydrogel had reached saturation, and further increasing the concentration surface of PDA would cause agglomeration, resulting in fewer adhesion sites and reduced adhesion performance. Due to 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel had the highest elastic modulus (5.24 ± 1.06 kPa) as well as the best adhesion ability (6.35 ± 0.31 kPa), it was selected for further investigation.
3.4. Swelling and Biodegradation
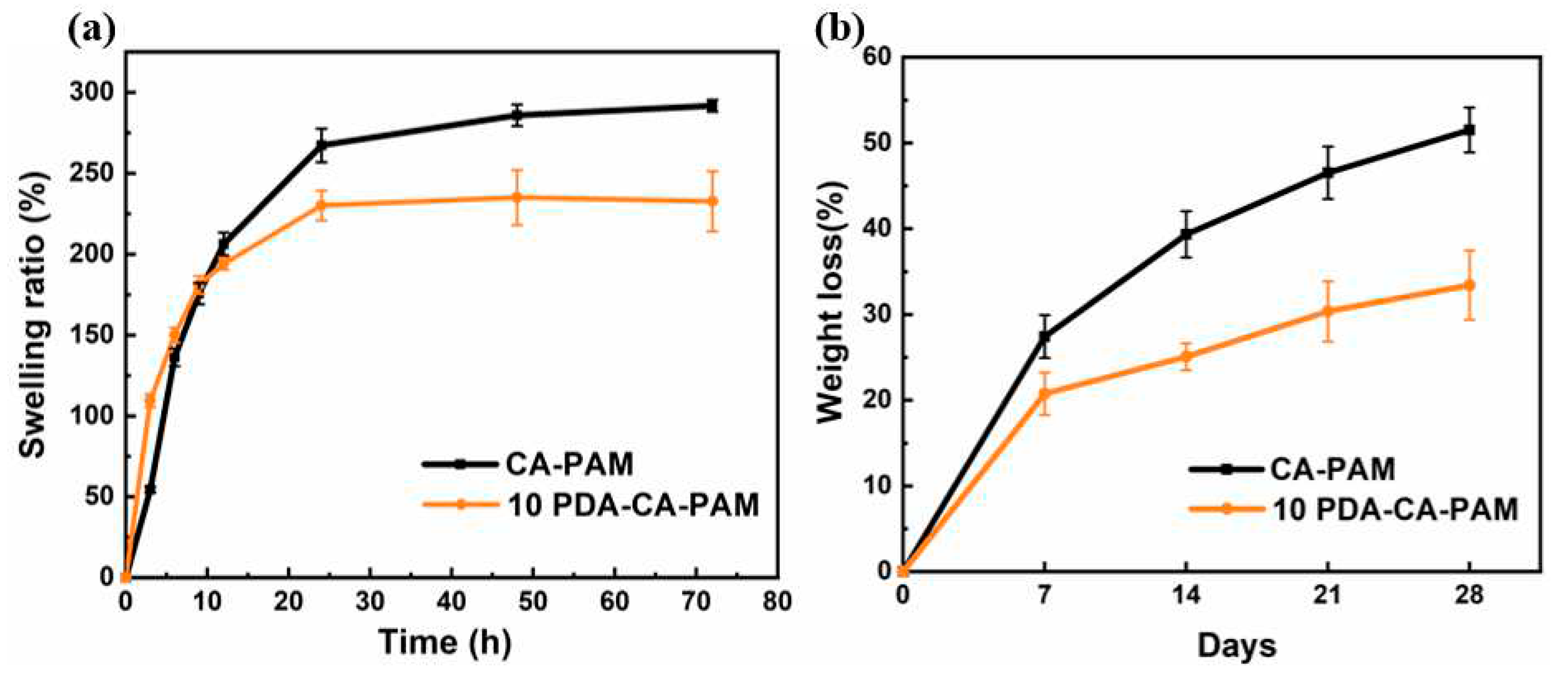
As a hydrogel applied to uterine cavity wounds, its good swelling property can effectively absorb wound exudate. The swelling properties of both hydrogels were tested using PBS as the simulated body fluid. 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel also showed good swelling ability, providing a guarantee for the absorption of secretions around the uterine cavity wound. As shown in
Figure 4 (a), after 72 h of swelling in PBS solution, the maximum swelling rate of 10 PDA-CA-PAM reached 235% and kept the shape intact (
Figure S2). Compared to that of CA-PAM (292%), the swelling ability of 10 PDA-CA-PAM decreased because PDA doping resulted in more entanglement of molecular chains, lower extension ability of molecular chain segments, and less space for storing water molecules. Even so, the swelling rate could still reach more than 200%, and it had the ability to absorb wound exudate.
As a kind of body implant material, the degradation rate of anti-adhesion hydrogels ideally should match the tissue regeneration rate. Since alginate was degraded by Na
+ and Ca
2+ ion exchange, and PAM was degraded by the reaction between disulfide bond and cysteine[
33,
34], cysteine was added into PBS at 37℃ to further simulate body fluid for a more realistic degradation rate.
Figure 4 (b) showed that 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel had a more stable degradation rate, with a loss of about 33.5% after 4 weeks. The incorporation of PDA could increase the cross-linking density of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel network, reduce the inside reactant content, and form a coating to reduce the contact area between the gel matrix and the simulated body fluid, so as to achieve more stable degradation.
3.5. Hydrophilicity and Hemostasis Performance
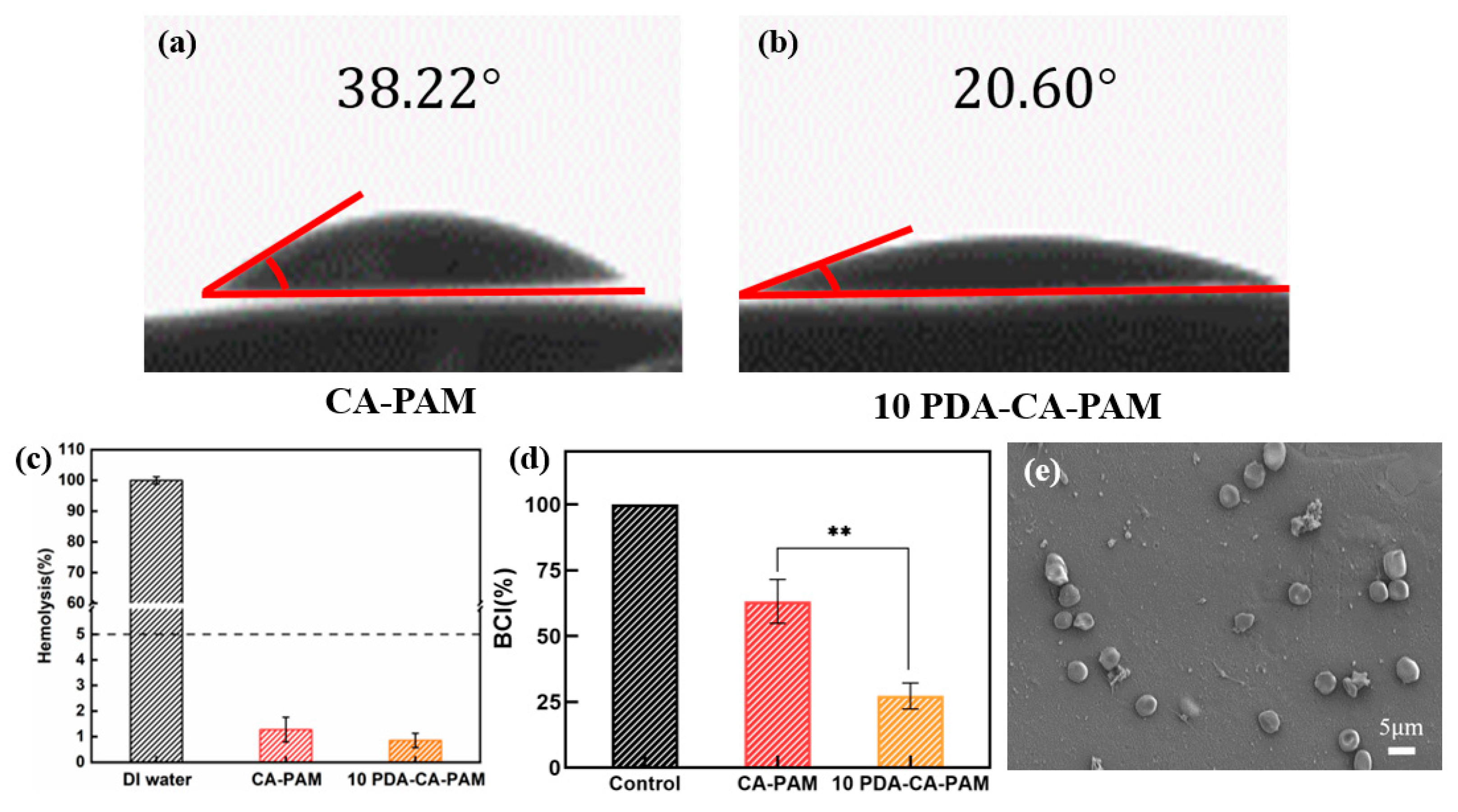
Anti-adhesion hydrogels require good hydrophilicity in order to adhere to cells, and it is necessary to test the water contact angle. As shown in
Figure 5 (a-b), 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel had a water contact angle of 20.60°, while CA-PAM hydrogel had a water contact angle of 38.22°. Due to the large number of hydrophilic groups present in the PDA chain segment, its presence reduced the water contact angle and enhanced hydrophilicity.
According to the international standard (ISO/TR 7405), the hemolysis rate of anti-adhesion hydrogel in contact with blood should be less than 5.0% before it can be used normally. It was necessary to perform in vitro hemolysis assays to assess the hemolytic effect of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel. As shown in
Figure 5 (c), the hemolysis rates of CA-PAM and 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogels were both lower than the red line of 5%, and the latter was lower, indicating that the doping PDA could make the hydrogel have better blood compatibility. The results showed that 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel had good blood compatibility.
Hemostasis is the first step in the healing process of the uterine cavity wound to prevent excessive blood loss before regrowth of the cell and tissue[
35], and an ideal anti-adhesion hydrogel requires good hemostasis ability. The hemostatic ability of 10 PDA-CA-PAM was evaluated by blood clotting index (BCI).
Figure 5 (d) showed that besides excellent mechanical and adhesion properties, 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel also had hemostatic ability. Compared with the control group, the coagulation index of 10 PDA-CA-PAM was 27.27 ± 4.91 and that of CA-PAM was 63.02 ± 8.36. The results also showed that the 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel had a lower BCI index than the commercial available gauze (minimum 40) [
36]. The PDA coating on the surface of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel could improve the hydrogel’s hydrophilicity, promoted more blood cells to adhere to the surface, and had better hemostatic ability.
10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel may have a potential effect on the morphological changes of blood cells, which was investigated by SEM.
Figure 5 (e) showed that blood cells have a certain degree of aggregation and adhesion on the surface of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel, but no abnormal deformation or aggregation, which further proved that the hydrogel had good blood compatibility and hemostatic ability.
3.6. Cell Proliferation, Viability, and Attachment
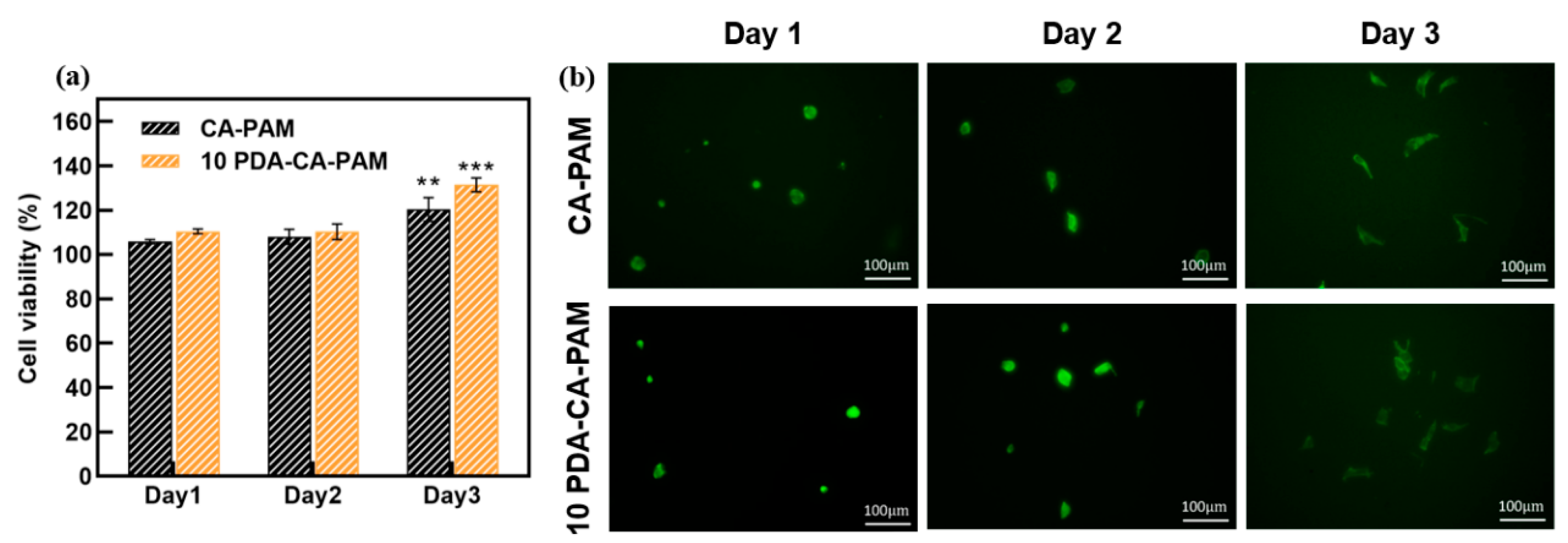
Good biocompatibility is the basic characteristic of anti-adhesion hydrogels. The cytotoxicity of the extract of CA-PAM and 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel was evaluated by CCK-8 assay using NIH-3T3 cells.
Figure 6 (a) showed that NIH-3T3 cells were cultured on the surface of the two hydrogels for 1 d, 2 d and 3 d, and the cell viability was always greater than 100%, indicating that the cells could grow and proliferate normally on the surface, and the hydrogels had good cytocompatibility. Compared with CA-PAM, the cell viability of 10 PDA-CA-PAM surface was higher, because the PDA coating made the surface have better hydrophilicity, and promoted cell adhesion and proliferation. This demonstrated that 10 PDA-CA-PAM was not only safe but also had the potential to accelerate wound healing.
Fibroblasts play a very important role in the formation of postoperative adhesion, and it is necessary to observe the cells adhesion on the surface of hydrogel by fluorescence staining. As shown in
Figure 6 (b), NIH-3T3 cells could gradually spread on the surface of CA-PAM hydrogel and 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel, without abnormal proliferation or agglomeration. Due to the better surface hydrophilicity caused by the PDA coating, more NIH-3T3 cells were attached to the surface of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel, but gradually dispersed over culture time without excessive attachment. The good biocompatibility further indicated that 10 PDA-CA-PAM would be a kind of anti-adhesion material with application potential.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a multifunctional hydrogel with good mechanical properties, adhesion, and hemostasis has been prepared. The hydrogel was prepared on the basis of the dual-network CA-PAM hydrogel by DA solution immersion. It has been shown that PDA can regulate the hydrogel structure through non-covalent hydrogen bonding, thereby modulating the mechanical properties. Hydrogels with desirable mechanical properties can be obtained at specific DA solution concentrations. The presence of PDA coating optimizes the degradation rate, blood compatibility, and cytocompatibility of the hydrogel to meet the requirements of implantation. In addition, the excellent adhesion and hemostatic ability help to seal the uterine cavity wound quickly and maintain stably on the wound for a period of time. Overall, this hydrogel contains almost all the desired beneficial properties, and has great clinical application potential in the prevention of postoperative re-adhesion.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: Adhesion of 10 PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel to other materials; Figure S2: Comparison between CA-PAM and PDA-CA-PAM hydrogel before and after swelling.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.S.; methodology, Z.S. and B.X.; investigation, C.X. and B.X.; data curation, Z.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.S.; writing—review and editing, Z.S., B.X., C.X. and X.D.; supervision, C.X.; funding acquisition, X.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China under the grant numbers of No. DUT22QN203 and DUT22YG201.
Data Availability Statement
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Yue Kang at Department of Breast Surgery, Liaoning Cancer Hospital & Institute, for her writing and editing contributions. This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China under the grant numbers of No. DUT22QN203 and DUT22YG201.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Yu, D.; Wong, Y.M.; Cheong, Y.; Xia, E.L.; Li, T.C. Asherman syndrome-one century later. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 89, 759–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardo, A.D.; Calagna, G.; Scognamiglio, M.; O’Donovan, P.; Campo, R.; De Wilde, R.L. Prevention of intrauterine post-surgical adhesions in hysteroscopy. A systematic review. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. R. B 2016, 203, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, L.; Shi, L.; Yang, W.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, S. Overactivated sonic hedgehog signaling aggravates intrauterine adhesion via inhibiting autophagy in endometrial stromal cells (vol 11, 755, 2020). Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Deans, R.; Abbott, J. Review of Intrauterine Adhesions. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2010, 17, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wong, Y.; Cheong, Y.; Xia, E.; Li, T. Asherman syndrome-one century later. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 89, 759–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, U.; Xue, M.; Sayed, A.S.M.; Xu, D.B. Efficacy of Intrauterine Device in the Treatment of Intrauterine Adhesions. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhou, F.; Wei, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, S. Randomized, controlled trial comparing the efficacy of intrauterine balloon and intrauterine contraceptive device in the prevention of adhesion reformation after hysteroscopic adhesiolysis. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.S.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, K.; Song, B.Y.; Zhu, H.; Han, X.F.; Shi, Y.J.; Yang, C.B.; Zeng, Z.P.; Cao, Z.Q. Biodegradable Zwitterionic Cream Gel for Effective Prevention of Postoperative Adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonguc, E.A.; Var, T.; Yilmaz, N.; Batioglu, S. Intrauterine device or estrogen treatment after hysteroscopic uterine septum resection. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2010, 109, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdi, M.; Saruwatari, M.S.; Rozyyev, S.; Acha, C.; Ayyub, O.B.; Sandler, A.D.; Kofinas, P. Controlled Release of a Therapeutic Peptide in Sprayable Surgical Sealant for Prevention of Postoperative Abdominal Adhesions. Acs Appl. Mater. Inter. 2023, 15, 14089–14098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.K.; Yue, P.P.; Cao, H.K.; Wu, L.Q.; Xu, L.; Liu, Z.Z.; Wu, S.Q.; Ye, Q.F. Biocompatible and biodegradable chitin-based hydrogels crosslinked by BDDE with excellent mechanical properties for effective prevention of postoperative peritoneal adhesion. Carbohyd Polym. 2023, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhue, A.A.E.; Aziken, M.E.; Igbefoh, J.O. A comparison of two adjunctive treatments for intrauterine adhesions following lysis. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2003, 82, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, D.M.R.; Black, C.R.M.; Dawson, J.I.; Oreffo, R.O.C. A review of hydrogel use in fracture healing and bone regeneration. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khademhosseini, A. Advances in engineering hydrogels. Science 2017, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naahidi, S.; Jafari, M.; Logan, M.; Wang, Y.J.; Yuan, Y.F.; Bae, H.; Dixon, B.; Chen, P. Biocompatibility of hydrogel-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdick, J.A.; Murphy, W.L. Moving from static to dynamic complexity in hydrogel design. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliktar, D. Designing Cell-Compatible Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Science 2012, 336, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z.; Xin, X.; Fei, H.; Cui, Y. Meta-analysis of the use of hyaluronic acid gel to prevent intrauterine adhesions after miscarriage. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. R. B 2020, 244, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Ahn, K.H.; Choi, D.S.; Hwang, K.J.; Lee, B.I.; Jung, M.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Cha, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, K.S.; Oh, S.T.; Cho, C.H.; Rhee, J.H. A Randomized, Multi-Center, Clinical Trial to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of Alginate Carboxymethylcellulose Hyaluronic Acid Compared to Carboxymethylcellulose Hyaluronic Acid to Prevent Postoperative Intrauterine Adhesion. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2012, 19, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.Y.; Chung, H.J.; Sim, N.S.; Jo, K.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, C.H.; Yoon, J.H. Comparison of calcium alginate and carboxymethyl cellulose for nasal packing after endoscopic sinus surgery: a prospective, randomised, controlled single-blinded trial. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2016, 41, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, A.; Carruthers, J. Non-animal-based hyaluronic acid fillers: Scientific and technical considerations. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 120, 33s–40s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W.R.K.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature 2012, 489, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Y.; Mao, C.; Yang, M. Polydopamine-Coated Antheraea pernyi (A. pernyi) Silk Fibroin Films Promote Cell Adhesion and Wound Healing in Skin Tissue Repair. Acs Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 34736–34743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Mi, H.; Lin, Y.; Enriquez, E.; Peng, X.; Turng, L.S. Highly Stretchable and Biocompatible Strain Sensors Based on Mussel-Inspired Super-Adhesive Self-Healing Hydrogels for Human Motion Monitoring. Acs Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 20897–20909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Peng, Y.; Tu, X.; Du, P.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X. Facile Preparation of Mussel-Inspired Polyurethane Hydrogel and Its Rapid Curing Behavior. Acs Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 12495–12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sileika, T.S.; Kim, H.D.; Maniak, P.; Messersmith, P.B. Antibacterial Performance of Polydopamine-Modified Polymer Surfaces Containing Passive and Active Components. Acs Appl. Mater. Inter. 2011, 3, 4602–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Floren, M.; Tan, W. Mussel-inspired polydopamine for bio-surface functionalization. Biosurf. Biotribol. 2016, 2, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suneetha, M.; Rao, K.; Han, S. Mussel-Inspired Cell/Tissue-Adhesive, Hemostatic Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Acs Omega 2019, 4, 12647–12656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Li, H.; Mi, H.; Feng, P.; Liu, Y.; Jing, X. Freezing-tolerant, widely detectable and ultra-sensitive composite organohydrogel for multiple sensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2021, 9, 10127–10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneetha, M.; Rao, K.M.; Han, S.S. Mussel-Inspired Cell/Tissue-Adhesive, Hemostatic Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Acs Omega 2019, 4, 12647–12656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lih, E.; Lee, J.S.; Park, K.M.; Park, K.D. Rapidly curable chitosan-PEG hydrogels as tissue adhesives for hemostasis and wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3261–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cleveland, C.; Yin, X.; Booth, L.; Lin, J.; Lee, Y.A.L.; Mazdiyasni, H.; Saxton, S.; Kirtane, A.R.; von Erlach, T.; Rogner, J.; Langer, R.; Traverso, G. Triggerable tough hydrogels for gastric resident dosage forms. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Suo, Z.; Vlassak, J.J. Stiff, strong, and tough hydrogels with good chemical stability. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6708–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ma, P.; Guo, B. Antibacterial adhesive injectable hydrogels with rapid self-healing, extensibility and compressibility as wound dressing for joints skin wound healing. Biomaterials 2018, 183, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, Z.; Correia, A.; Hasany, M.; Figueiredo, P.; Dobakhti, F.; Eskandari, M.R.; Hosseini, S.H.; Abiri, R.; Khorshid, S.; Hirvonen, J.; Santos, H.A.; Shahbazi, M.A. A Hydrogen-Bonded Extracellular Matrix-Mimicking Bactericidal Hydrogel with Radical Scavenging and Hemostatic Function for pH-Responsive Wound Healing Acceleration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).