Submitted:
02 November 2023
Posted:
02 November 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- To explore the method of establishing the index system of measuring the spatial damage degree of historic sites;
- To classify the degree of damage of historic sites units of the three research areas based on K-means clustering analysis;
- Training and testing the clustering results based on the K-nearest neighbor (KNN) classifier;
- Using multiple linear regression equations to analyze the damage factors of historic sites.
2. Materials and Methods
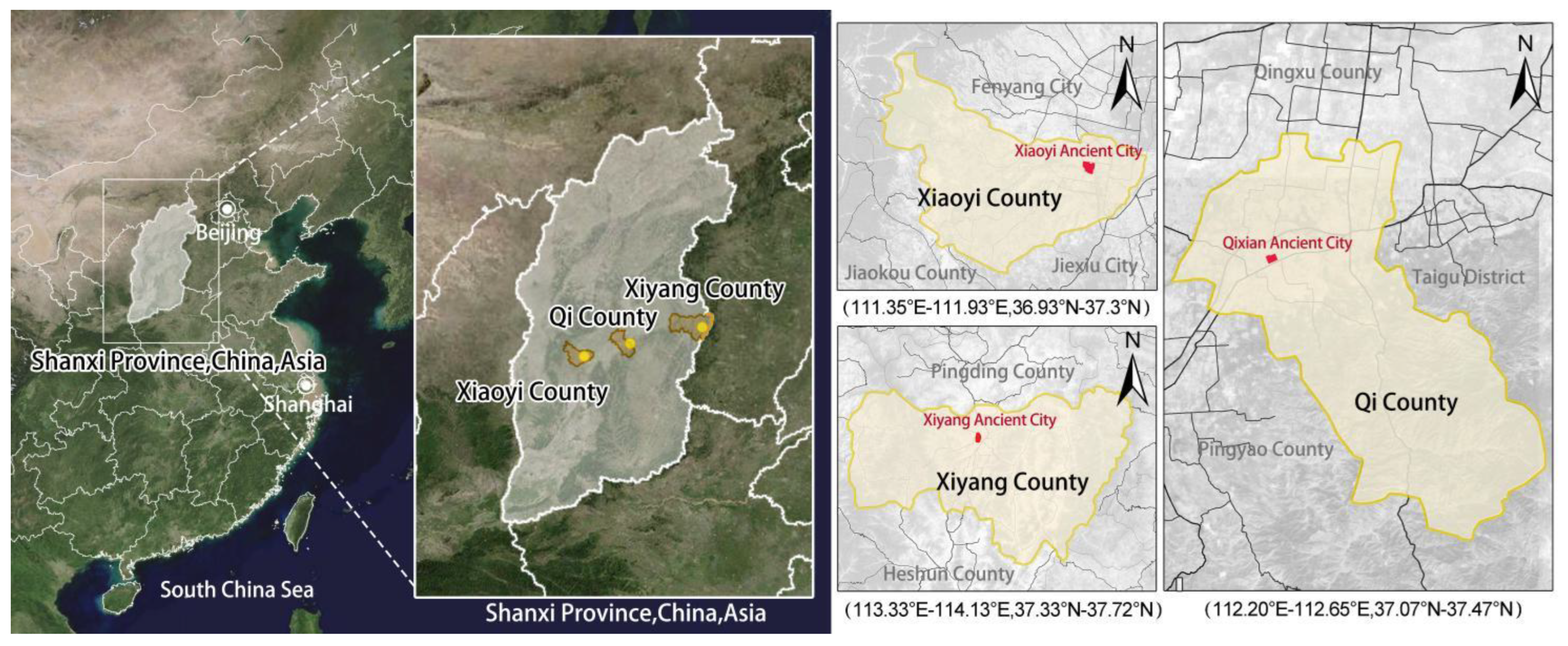
2.1. Data Sources and Study Area
2.1.1. Data Sources
2.1.2. Study Area
2.2. Research Methods
- Constructing an indicator system for measuring spatial damage degree;
- Determining the indicator weights;
- Calculating the comprehensive evaluation value;
- Classifying the damage degree of samples in the research areas through K-means clustering analysis;
- Verifying clustering results using the K-nearest neighbor classifier;
- Using multiple linear regression equations to analyze the damage factors of historic sites.
2.2.1. Step 1: Construction of spatial damage index system
2.2.2. Step 2: Determine the weight of indicators
- 1.
- Delphi Method
- 2.
- CRITIC weight method
- 3.
- Multiplicative synthesis
2.2.3. Step 3: Calculating comprehensive evaluation value
2.2.4. Step 4: Classifying the damage degree of samples in the research areas through K-means clustering analysis
2.2.5. Step 5: Verifying clustering results using K-nearest neighbor (KNN) classifier
2.2.6. Step 6: Researching method of damage factors of historic sites: multiple linear regression analysis
3. Results
3.1. Index System and Weight
3.1.1. Index system
3.1.2. Weight Determination
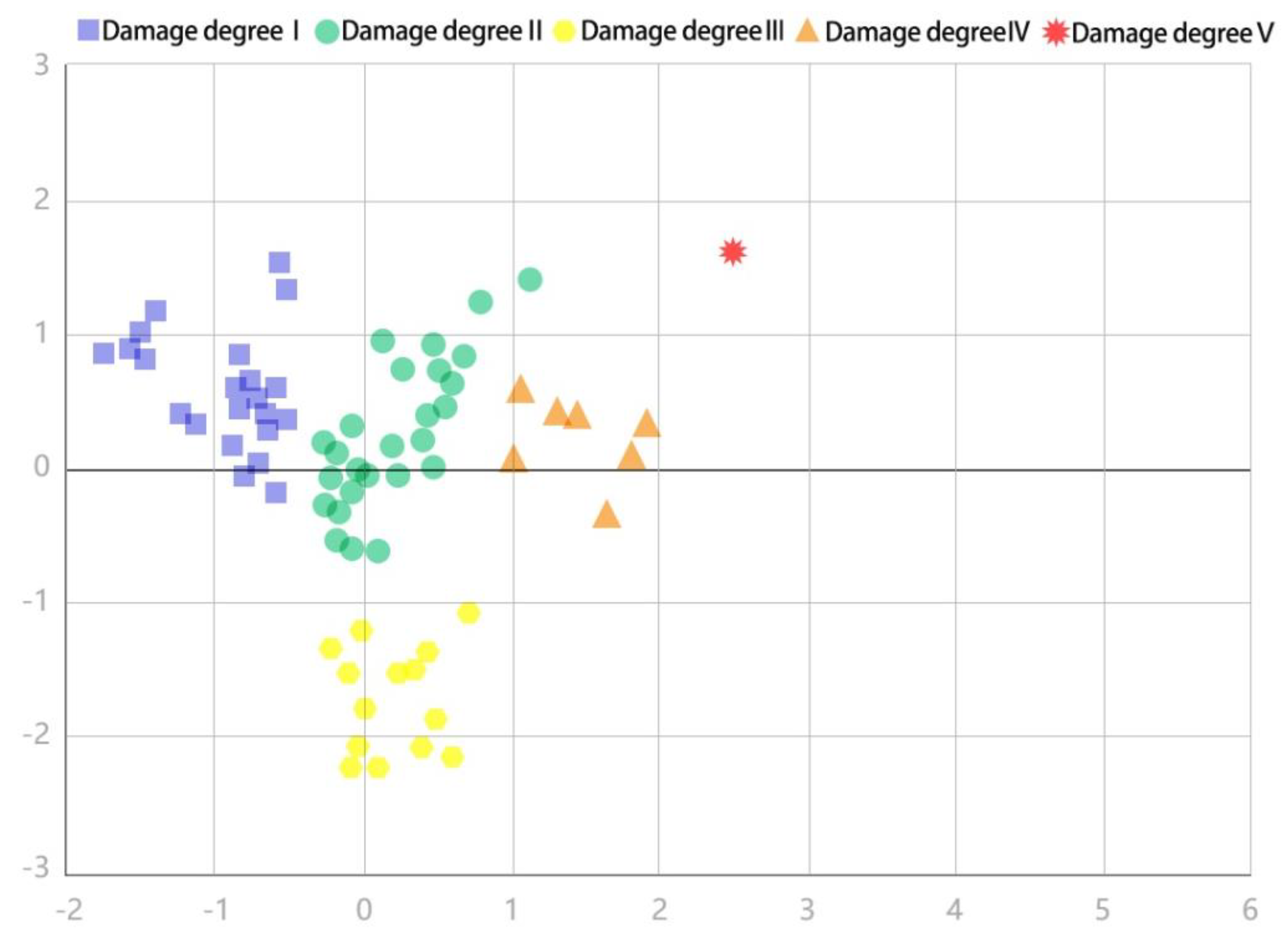
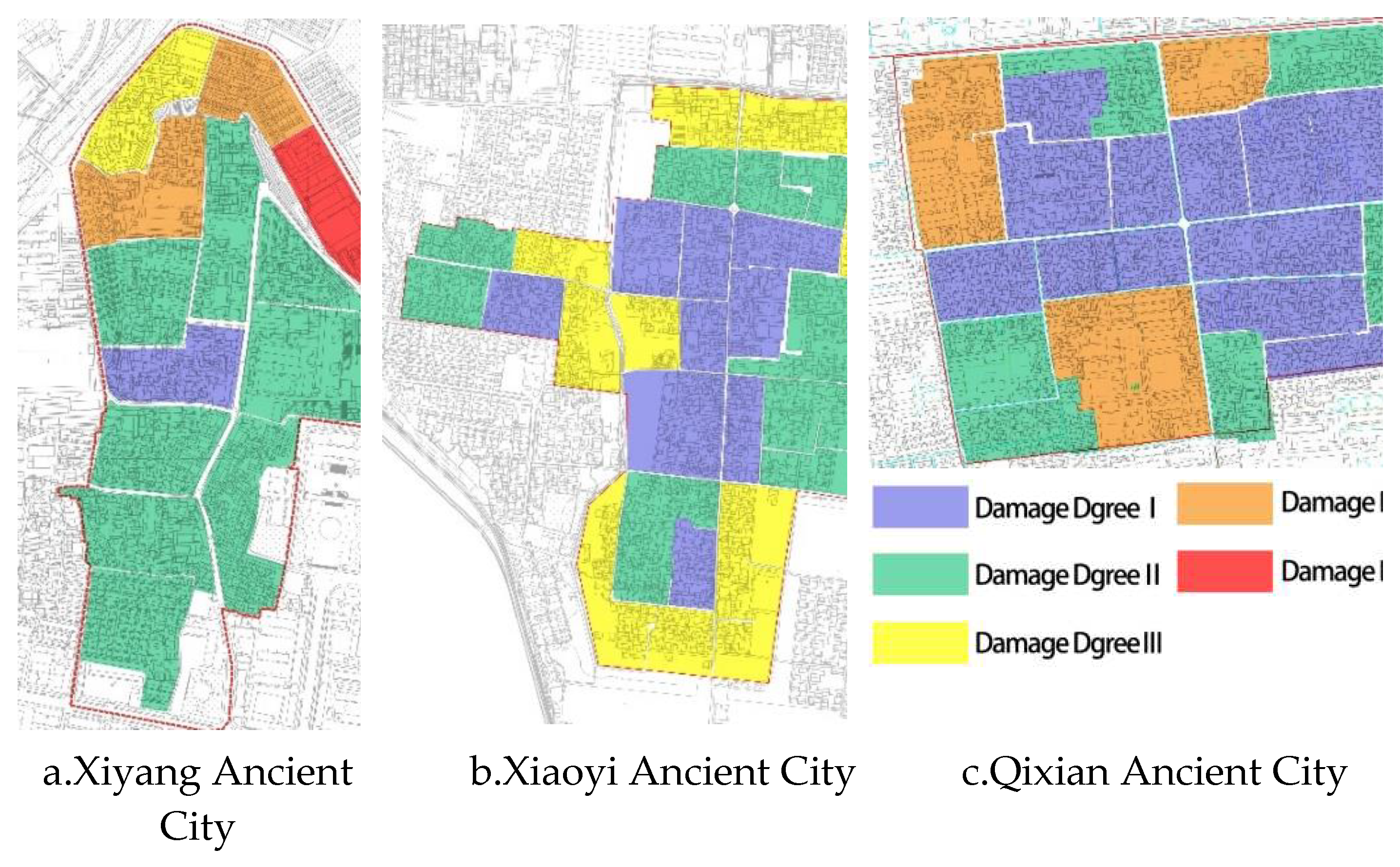
3.2. Results of Cluster Analysis
3.3. KNN Verification Analysis Results
3.4. Linear Regression Analysis Results
| Variable class | Independent variable | Standardization coefficient | significance | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building component | Building roof X1 | 0.114 | 0.296 | 3.595 |
| Building structure X2 | 0.222 | 0.331 | 15.696 | |
| Feature and form | Building feature X3 | -0.334 | 0.048 | 8.399 |
| Courtyard form X4 | -0.076 | 0.543 | 4.750 | |
| Street coordination X5 | -0.378 | 0.001 | 3.782 | |
| Building land use | Building dimension X6 | -0.028 | 0.903 | 16.624 |
| Building functions X7 | -0.097 | 0.286 | 2.492 | |
| Enclosing boundary survivability X8 | 0.728 | 0.000 | 1.443 | |
| Building fabric | Fabric evolution X9 | -0.093 | 0.278 | 2.235 |
| Street scale X10 | 0.028 | 0.684 | 1.443 | |
| Street continuity X11 | 0.144 | 0.181 | 3.469 |
4. Discussion
4.1. Application and Deficiency of SDDM
4.1.1. Application of SDDM
- Conservation Planning: SDDM can more comprehensively assess the extent of spatial damage in historic sites. The introduction of this comprehensive protection concept will help the protectors grasp the characteristics and problems of the historic sites more comprehensively. By analyzing the degree of damage to different historic sites, we can understand the impact of different decisions on historical heritage and choose the most appropriate scheme.
- Repair Guidance: SDDM can be used to prioritize and scope repair works. By assessing the extent of spatial damage in historic sites, it is possible to determine which parts need to be prioritized for repairs, as well as the extent and method of restoration. This helps ensure the effectiveness and sustainability of the restoration work.
4.1.2. Shortcomings and Improvement Direction of SDDM
- The objectivity of data collection needs to be strengthened.
- 2.
- Maintenance and repair should be taken into account.
- 3.
- The information and database of the system need to be sorted out.
4.2. Study on the Influencing Factors of Spatial Damage in Historic Sites
4.2.1. Natural erosion
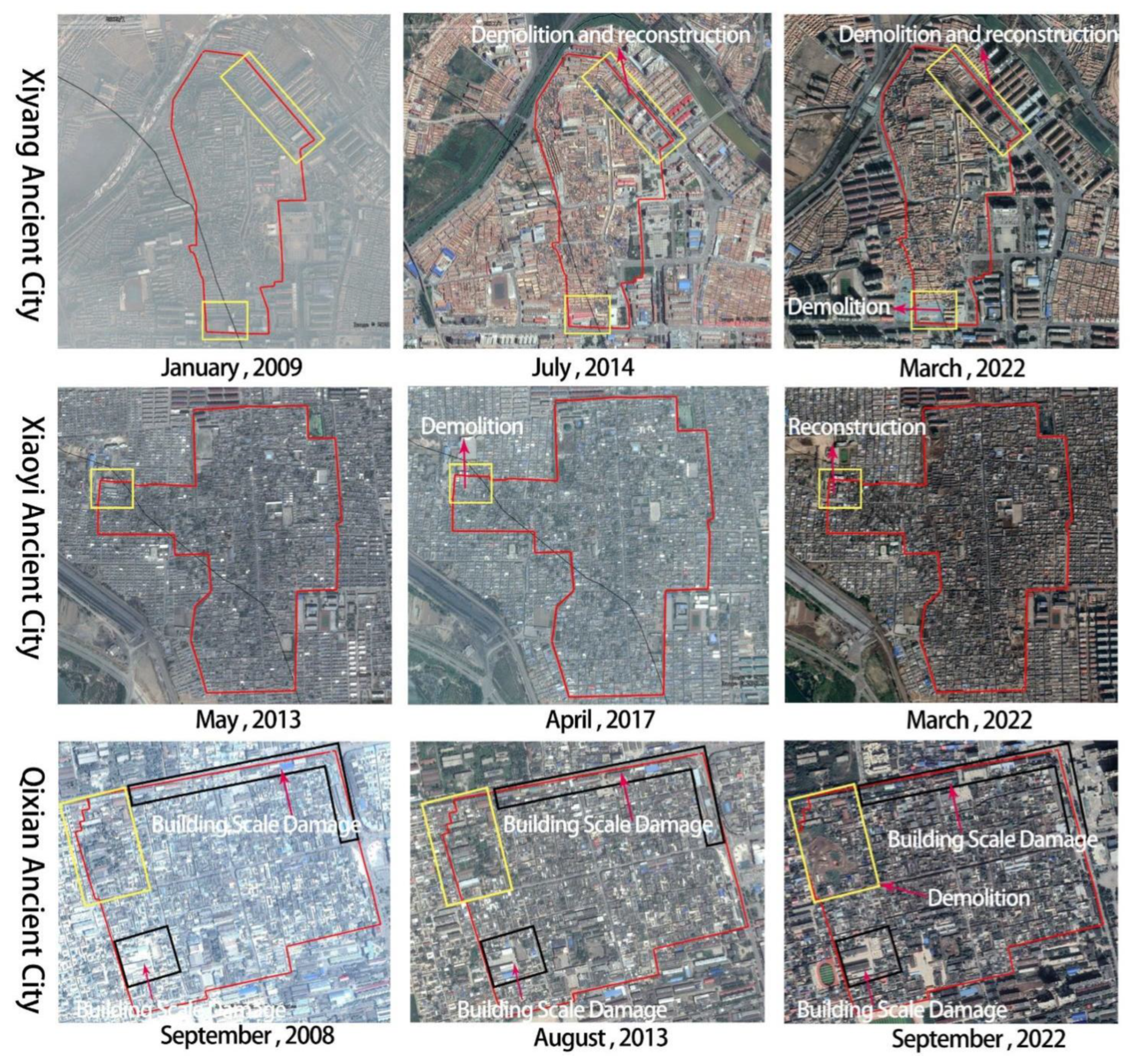
4.2.2. Construction damage
4.2.3. Planning and Policy
5. Conclusions
- The establishment of a spatial damage degree model (SDDM) of historic sites is an innovation to the traditional conservation work. The model can not only accurately assess the spatial damage degree of historic sites and formulate accurate protection strategies, but also fill the blank in the field of quantifying the spatial damage degree of historic sites.
- In the study area, the spatial damage degree tended to be higher around and lower in the middle. The core areas of the three research regions are mostly first-degree damaged plots, and a few are second-degree damaged plots. Most of the four and five-degree damaged plots are around the boundaries. The third-degree damaged plots are located outside the first and second-degree damaged plots. In terms of the number of plots in damage degrees, degree level five (5) is the least, followed by degree level four (4). Degree levels three (3) and two (2) followed in that order with degree level one (1) being the most.
- The coupling interaction of multiple factors such as natural erosion, construction damage, planning and policy affects the spatial damage degree of historic sites. Natural erosion mainly includes natural disasters, environmental pollution, and time erosion, and its damage to historic sites is objective. The damage of construction is mainly caused by the residents' lack of consciousness and improper urban renewal, which is subjective. Improper planning and lack of policies have a great impact on the spatial damage of historic sites, which determines the compliance and legitimacy of historic site protection, and is the main direction to be improved in the future.
- In the future, the spatial damage degree model (SDDM) of historic sites can be introduced into urban physical examination assessment and urban renewal. It can be used to formulate rational conservation strategies, prioritize urban renewal, and monitor restoration effects.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Index Classification | Pattern attribute | Index Name | Index Definition | Symbolic representation and calculation method | Index annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static index | Buildings (Node) | Building roof damage degree | The degree of damage to the roof of a building | is the weight of roofs with different degrees of damage | |
| Building structural damage degree | The proportion of the number of buildings with structural damage to the total number of buildings | is the total number of roofs within the plot | |||
| Building feature damage degree | Weighted summation of the proportion of the land area of buildings with different styles and features to the total building area of the entire plot | is the weight of buildings with different styles and features | |||
| Building function change rate | The proportion of buildings with changed functions to the total number of buildings | is the total number of buildings within the plot | |||
| Building dimenssion contradictionrate | The proportion of uncoordinated building area in total building area | is the total base area of buildings within the plot | |||
| Courtyard(Node) | Damage degree of courtyard form | The proportion of different degrees of collapsed courtyards to the total number of courtyards | is the weight of courtyards with different degrees of damage | ||
| Street system(Path) | Street scale damage degree | Absolute value of the difference between the width to height ratio of main streets and historical street standard values | is the standard aspect ratio of historical streets and alleys | ||
| Street coordination | The coordination degree of the main street and alley facades in terms of style and appearance | is the coordination degree of the facade style of the main streets and alleys in the i-th plot | |||
| Street continuity | Main Street thread adhesion rate | is the length of the centerline of the street and alley | |||
| Boundary (Edge) | Enclosing boundary survivability | Comparing historical data, the remains of authentic city walls, green belts, rivers and other surrounding boundaries in the block | is the remaining situation of the i-th plot's enclosing boundary | ||
| Dynamic index | Evolution(Domain) | Architectural evolution degree | Compare the historical buildings of the plot in historical data, overlap them with the current historical buildings, and determine the degree of preservation of the historical buildings | is the base area of historical buildings within the plot | |
| Evolution degree of streets | Compare the road network system of the plot in historical data, overlap it with the current road network, and determine the degree of preservation of the historical road network | is the area of past streets and alleys within the plot | |||
| Fabric evolution degree | The sum of architectural evolution and street evolution | TE=|AE-1|+|SE-1| | AE is the degree of architectural evolution; SE is the degree of evolution of streets |
Appendix C

References
- Resolution, G. A. J. U. D. A. R. , Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015.
- Glendinning, M. , The conservation movement: a history of architectural preservation: antiquity to modernity. Routledge: 2013.
- Charter, V. In International charter for the conservation and restoration of monuments and sites,(ICOMOS), Proceedings of the 2nd international congress of architects and technicians oh historical monuments. Venice, Italy, 1964; 1964.
- Charter, W. J. A. b. I. G. A. , Charter for the conservation of historic towns and urban areas. 1987.
- Bonazza, A.; Sardella, A. Climate Change and Cultural Heritage: Methods and Approaches for Damage and Risk Assessment Addressed to a Practical Application. Heritage 2023, 6, 3578–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.; Hess, M.; Lo, E.; Wittich, C.E.; Hutchinson, T.C.; Kuester, F. In UAV-based post disaster assessment of cultural heritage sites following the 2014 South Napa Earthquake, 2015 Digital heritage, 2015; IEEE: 2015; pp 421-424.
- Salazar, L.G.F.; Romao, X.; Pauperio, E. Review of vulnerability indicators for fire risk assessment in cultural heritage. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 60, 102286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, G.J. The War-Ravaged Cultural Heritage of Afghanistan: An Overview of Projects of Assessment, Mitigation, and Preservation. Near East. Archaeol. 2015, 78, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakhan, B. Creating the Iraq cultural property destruction database: calculating a heritage destruction index. Int. J. Heritage Stud. 2015, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecvagars, K. , Valuing damage and losses in cultural assets after a disaster: concept paper and research options. ECLAC: 2006.
- Vafadari, A.; Philip, G.; Jennings, R. J. T. I. A. o. t. P., Remote Sensing; Sciences, S. I., Damage assessment and monitoring of cultural heritage places in a disaster and post-disaster event–a case study of Syria 2017, 42, 695-701. [CrossRef]
- Karataş, L.; Ateş, T.; Alptekin, A.; Dal, M.; Yakar, M. J. A. E. S. , A systematic method for post-earthquake damage assessment: Case study of the Antep Castle, Türkiye. 2023, 3, 62-71.
- Tapete, D.; Cigna, F. Trends and perspectives of space-borne SAR remote sensing for archaeological landscape and cultural heritage applications. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 14, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Lasaponara, R.; Shi, P.; Bachagha, N.; Li, L.; Yao, Y.; Masini, N.; Chen, F.; et al. Google Earth as a Powerful Tool for Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Applications: A Review. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, E.; Seth, P.; Pande, H.; Raghavendra, S.; Kushwaha, S. In Application of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for damage assessment of a cultural heritage monument, Proceedings of UASG 2019: Unmanned Aerial System in Geomatics 1, 2020; Springer: 2020; pp 123-131.
- Cerra, D.; Plank, S.; Lysandrou, V.; Tian, J. Cultural Heritage Sites in Danger—Towards Automatic Damage Detection from Space. Remote. Sens. 2016, 8, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, L.; Collina, M.; Ricca, M.; Barbieri, L.; Bruno, F.; Arcudi, A.; La Russa, M.F. Damage Indices and Photogrammetry for Decay Assessment of Stone-Built Cultural Heritage: The Case Study of the San Domenico Church Main Entrance Portal (South Calabria, Italy). Sustainability 2020, 12, 5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romão, X.; Paupério, E. An Indicator for Post-disaster Economic Loss Valuation of Impacts on Cultural Heritage. Int. J. Arch. Heritage 2019, 15, 678–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zong, R.; Kou, Z.; Shang, L.; Wang, D. CollabLearn: An Uncertainty-Aware Crowd-AI Collaboration System for Cultural Heritage Damage Assessment. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2021, 9, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz-Mellado, E.; Mascort-Albea, E.J.; Romero-Hernández, R.; Galán-Marín, C.; Rivera-Gómez, C.; Ruiz-Jaramillo, J.; Jaramillo-Morilla, A. Non-destructive testing and Finite Element Method integrated procedure for heritage diagnosis: The Seville Cathedral case study. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 37, 102134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor, B.; Lucchi, E.; Bienvenido-Huertas, D.; Nardi, I. Non-destructive techniques (NDT) for the diagnosis of heritage buildings: Traditional procedures and futures perspectives. Energy Build. 2022, 263, 112029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.; Mas. ; Lerma, C.; Torner, M.E.; Vercher, J. Non-destructive Techniques Methodologies for the Detection of Ancient Structures under Heritage Buildings. Int. J. Arch. Heritage 2021, 15, 1457–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, G. F. J. A.; Planning, U. , Analysis of Cultural Heritage by Non-Destructive Methods: The Case of Sivas Congress Museum. 2023, 19, (1), 1-16.
- Isik, N.; Halifeoglu, F.M.; Ipek, S. Nondestructive testing techniques to evaluate the structural damage of historical city walls. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, G.; Giani, E.; Giovagnoli, A. The Risk Map of Italian Cultural Heritage. J. Arch. Conserv. 2003, 9, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, M.; Song, J.; Du, Y.; Gao, F. The Risk Map of Cross-Regional Cultural Heritage: From a Perspective of Slow Degradation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A.; Lysandrou, V.; Themistocleous, K.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Risk assessment of cultural heritage sites clusters using satellite imagery and GIS: the case study of Paphos District, Cyprus. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K. A. J. M. P. , The Image of the City. 1962.
- ižović, M.; Miljković, B.; Marinkovic, D. , Objective methods for determining criteria weight coefficients: a modificationof the critic method. 2020. [CrossRef]
- McPherson, S.; Reese, C.; Wendler, M. C. , Methodology Update: Delphi Studies. 2018, 67, (5), 404-410. [CrossRef]
- Zou, H. Clustering Algorithm and Its Application in Data Mining. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 110, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhao, T.; Biljecki, F. Revealing spatio-temporal evolution of urban visual environments with street view imagery. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzcategui-Salazar, M.; Lillo, J. A new approach to pollution vulnerability assessment in aquifers using K-means analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L. J. S. , K-nearest neighbor. 2009, 4, 1883.
- Danielsson, P.-E. J. C. G.; processing, i. , Euclidean distance mapping. 1980, 14, 227-248. [CrossRef]
- Sinwar, D.; Kaushik, R. J. I. J. R. A. S. E. T. , Study of Euclidean and Manhattan distance metrics using simple k-means clustering. 2014, 2, 270-274.
- Groenen, P.J.; Jajuga, K. Fuzzy clustering with squared Minkowski distances. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2001, 120, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, N. R.; Smith, H. , Applied regression analysis. John Wiley & Sons: 1998; Vol. 326.
- Seyedashrafi, B.; Ravankhah, M.; Weidner, S.; Schmidt, M. Applying Heritage Impact Assessment to urban development: World Heritage property of Masjed-e Jame of Isfahan in Iran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 31, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weththimuni, M.L.; Licchelli, M. Heritage Conservation and Restoration: Surface Characterization, Cleaning and Treatments. Coatings 2023, 13, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, A.; Chambre, D.; Copolovici, D.M.; Bungau, T.; Bungau, C.C.; Copolovici, L. Heritage Building Preservation in the Process of Sustainable Urban Development: The Case of Brasov Medieval City, Romania. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Houdalieh, S.H.; Sauders, R.R. Building Destruction: The Consequences of Rising Urbanization on Cultural Heritage in the Ramallah Province. Int. J. Cult. Prop. 2009, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Name | Data type | Data sources |
|---|---|---|
| Google Satellite Maps | Tif | Google Earth |
| Osm Building Outline Data | Osm | https://www.openstreetmap.org/ |
| Osm Road Data | Osm | https://www.openstreetmap.org/ |
| Baidu Streetscape Map | Map | https://map.baidu.com/ |
| CAD topographic map | Dwg | Local Housing and Urban-Rural Development Bureau |
| Third National Land Survey Data | shapefile | Local Housing and Urban-Rural Development Bureau |
| Aerial view of the site | Jpg | On-site research (UAV) |
| Index name | Delphi method | CRITIC | Multiplication synthesis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Building roof damage degree | 0.064 | 0.089 | 0.050 |
| Building feature damage degree | 0.205 | 0.170 | 0.308 |
| Building function change rate | 0.048 | 0.021 | 0.009 |
| Building dimension contradiction rate | 0.072 | 0.029 | 0.018 |
| Building structural damage degree | 0.062 | 0.028 | 0.016 |
| Damage degree of courtyard form | 0.119 | 0.211 | 0.222 |
| Street scale damage degree | 0.050 | 0.055 | 0.024 |
| Street coordination | 0.108 | 0.194 | 0.186 |
| Street continuity | 0.073 | 0.022 | 0.014 |
| Enclosing boundary survivability | 0.091 | 0.137 | 0.111 |
| Fabric evolution degree | 0.108 | 0.044 | 0.042 |
| Accuracy rate | Recall rate | Precision rate | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | 0.939 | 0.939 | 0.925 | 0.93 |
| Testing set | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.695 | 0.738 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




