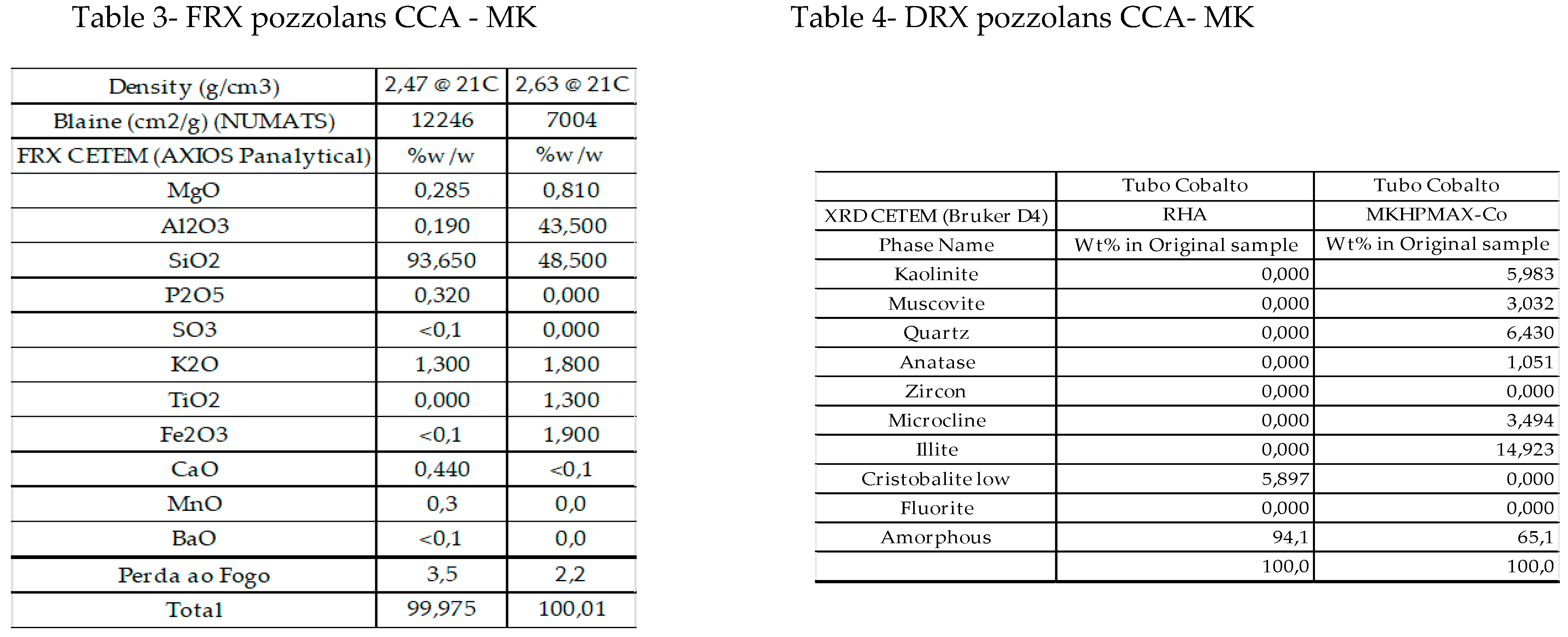
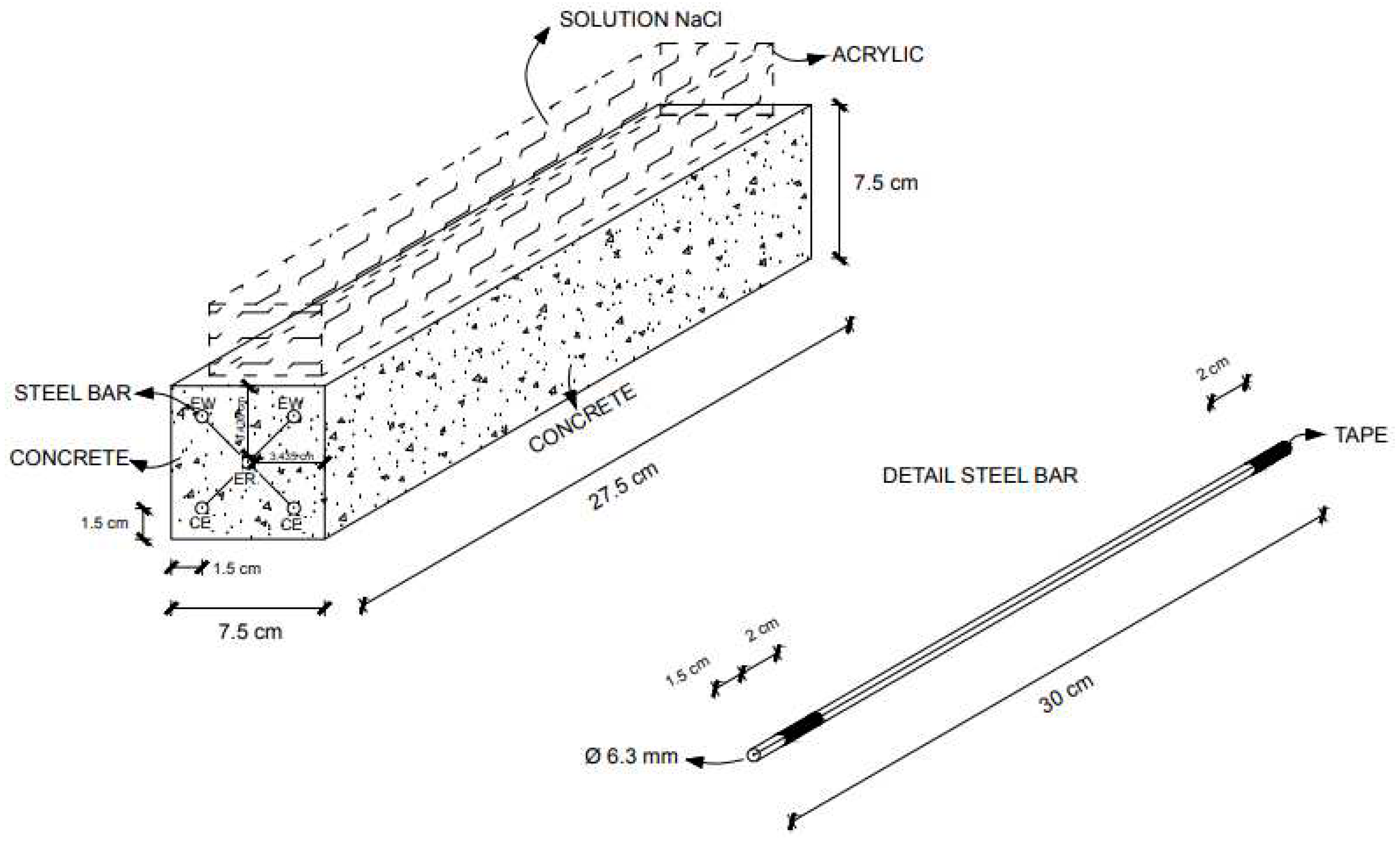
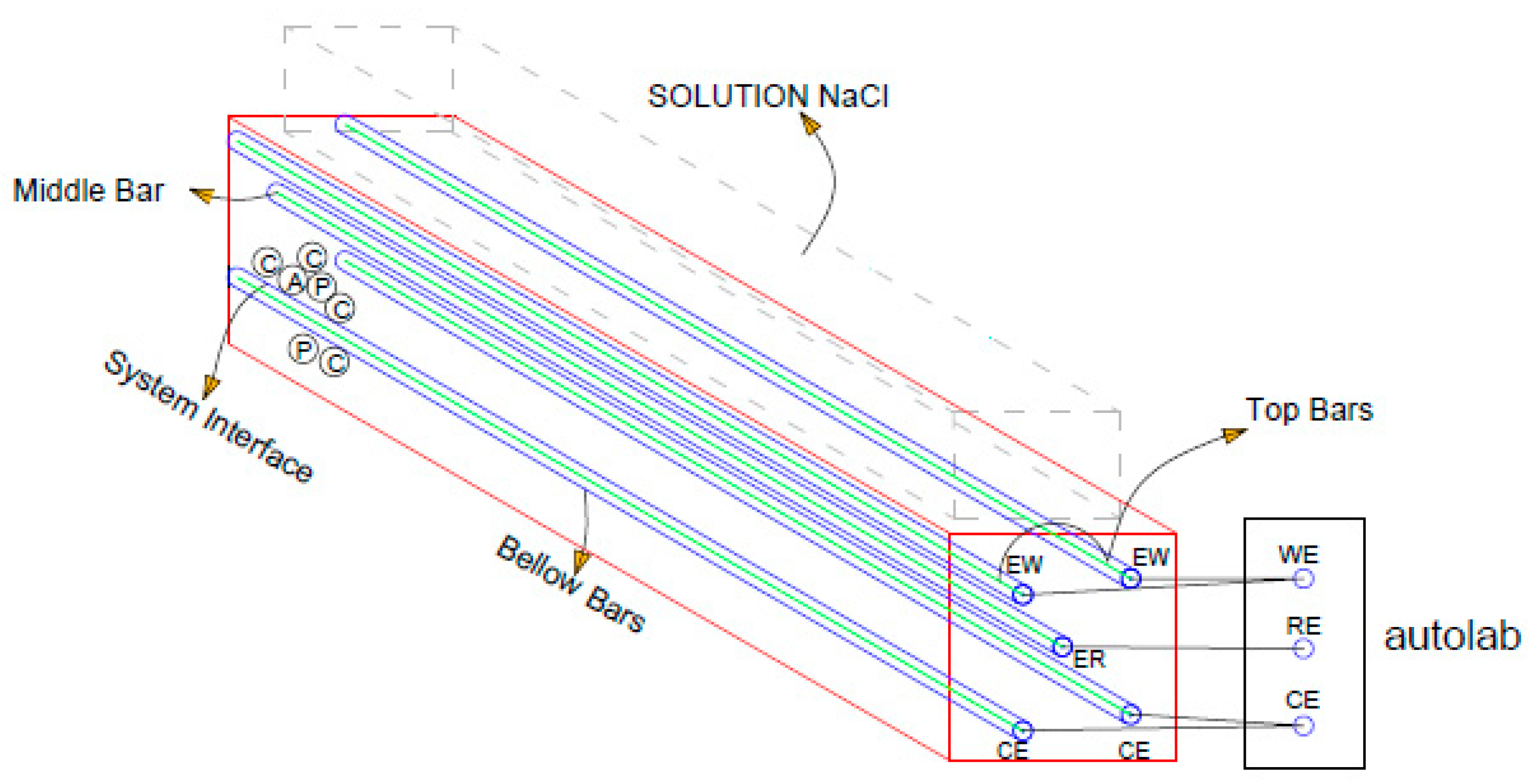
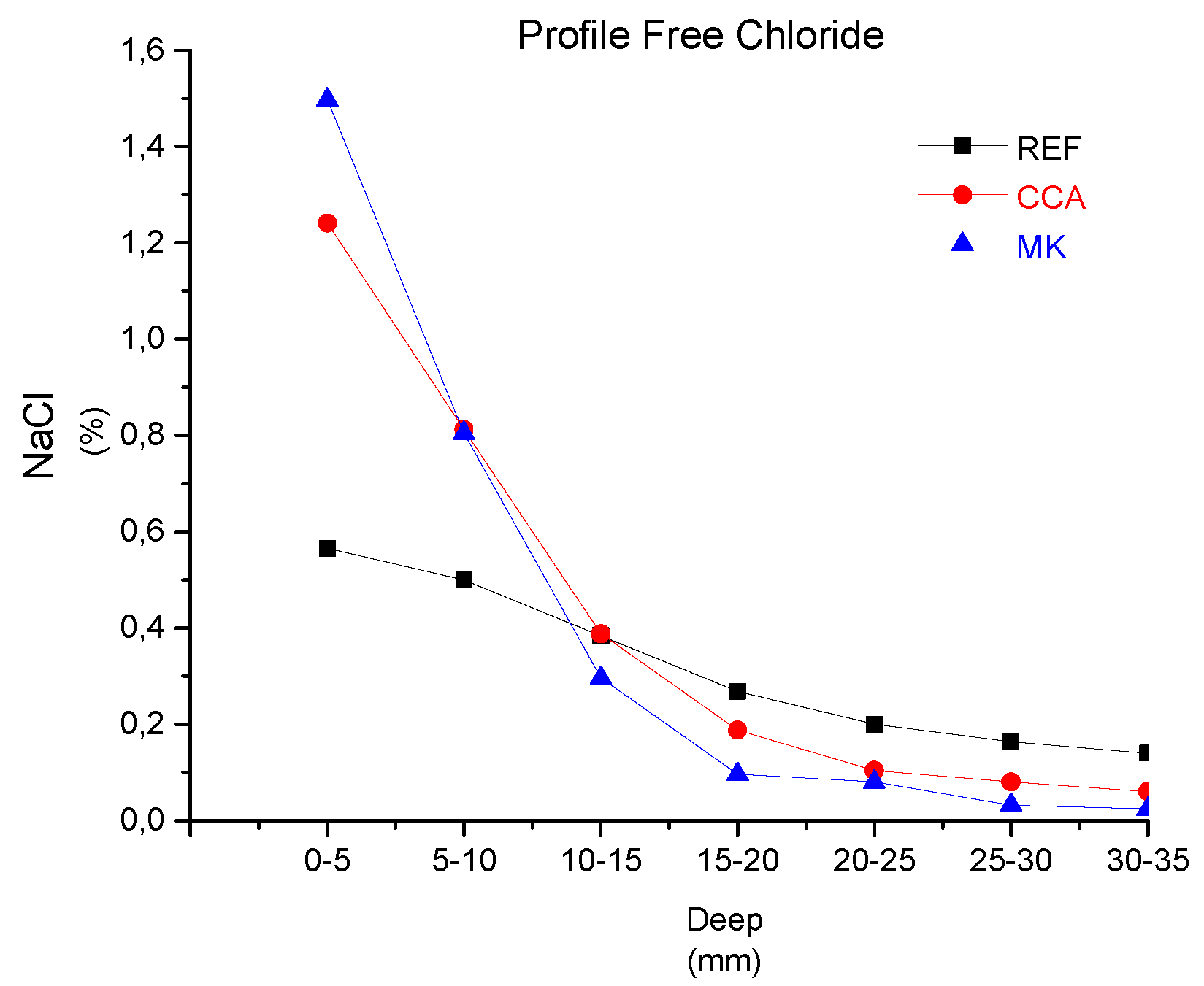
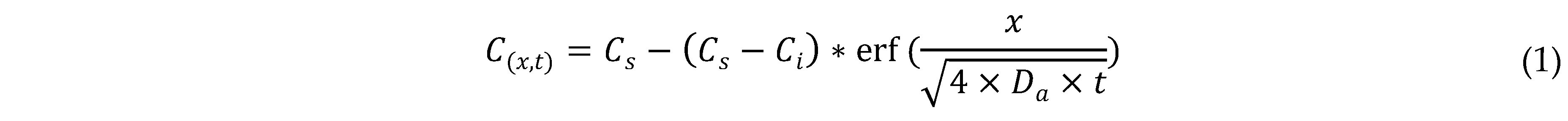4.2. Tomography
With the objective of searching for more elements of information to better understand the physical state in the microstructure of the analyzed concrete, it was decided to use a non-destructive imaging technique (NDT), using a tomograph [
14]. With this analysis technique, the internal structural conditions of the materials remain unchanged. As the durability test carried out according to ASTM 1556 involves immersion of concrete in sodium chloride, the mercury porosimetry technique was discarded. According to [
15], in cement-based systems, the technique overestimates the volume of fine capillary pores and underestimates the volume of coarse capillary pores, although it remains a valuable technique to compare pore refinement in a given system [
16]. The technique based on measuring the pore volume, defined according to the ASTM C642-13 standard, was discarded in the present work, as it requires the use of water, which would make it difficult to clearly perceive the physical changes caused by the absorption of NaCl in the pores.
Initially, a scan was performed on the cylindrical concrete samples, visualizing the pore system in 3D, which allowed viewing only the largest pores. As we were interested in visualizing the entire pore system, including the smallest ones, in approximately one scale (100µm), the highest resolution was used [
10]. The results are presented below, in
Table 7,
Table 8 and
Table 9, for reference concrete (REF), concrete with addition of rice husk ash (RCA) and concrete with addition of metakaolin (MK). Likewise, it will be possible to compare the concrete itself, without exposure to NaCl and with exposure to it [
17].
The tables show the distribution of the amount of pores as a function of the pore area measured before and after NaCl absorption, for a scan with a resolution of 100 µm. A greater number of pores was detected as being, in the central value of the range, 8.38 mm2 and the smallest number of 0.004 mm2. In both cases, the number of pores in each interval and the total that they represent in the sample were quantified, with numerical data detailed in
Table 7. The data show that for the concrete REF- without NaCl absorption, the total porosity was 2 .48%, increasing after chloride absorption to 2.80%, representing an increase of 11%.
A similar analysis was carried out on the CCA concrete samples, with results shown in
Table 8, representing the CCA sample without chloride absorption, and CCA concrete after NaCl absorption. The distribution of pore dimensions, for a scan with a resolution of 100 µm, showed the largest pore being 16.75 mm
2 for the CCA-without chloride concrete and 33.5 mm
2 for the concrete after chloride absorption. The smallest void size detected was 0.004 mm
2 for both conditions. It is observed that for the CCA-concrete without chloride the total porosity was 1.06%, increasing after the absorption of chloride to 1.32%, representing an increase of 26%.
The results corresponding to the MK concrete are shown in
Table 9, representing the MK sample without chloride and Fig. 9, after the absorption of chloride. The total distribution of pore sizes is also plotted, for a scan with a resolution of 100 µm. The largest pore size detected was 16.76 mm
2 for MK concrete without chloride absorption and 8.38 mm
2 after absorption. Similarly, the smallest pore size detected was 0.004 mm
2 in both conditions. For concrete MK- without chloride absorption, the total porosity was 2.43%, increasing when it was analyzed after chloride absorption, passing to 2.60%, representing an increase of 17%.
The reduction of porosity in concrete with pozzolanic additions, in relation to common concrete, could be explained by the specificity of the physico-chemical reactions that occur between the different components of the same mixture. These reactions directly influence the content of amorphous, glassy or crystalline fraction, its silicic or calcareous nature, its acidic or basic chemical character and particle size, among other parameters. When analyzing the behavior of common portland cement concrete (REF), one must consider that hydration stimulation occurs directly, according to a purely physical mechanism, in which once the cement particles are hydrated, the fraction water runs out. By adding a pozzolanic component to this cement, there will be an effect of a physical-chemical nature, in addition to the first stimulation mentioned, introducing a second variant of stimulation of hydration of the CP indirectly. [
8,
18,
19].
As a result, in concrete with mineral additions, a denser matrix is obtained, as is the case with CCA and MK concrete when compared to REF. Having the physical protective effect against the entry of chloride ion, more accentuated. Specifically with silicic-based additions, as observed in the CCA concrete proving to be the least porous when compared to the aluminum-silicic-based MK, therefore, it will create a matrix of low porosity[
20]
4.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
Next, the results are presented and discussed through Nyquist graphs, for the 3 materials (REF, CCA, MK). Using the EIE technique as a basis for obtaining them, with the application specifications described above in epigraph 3.4.
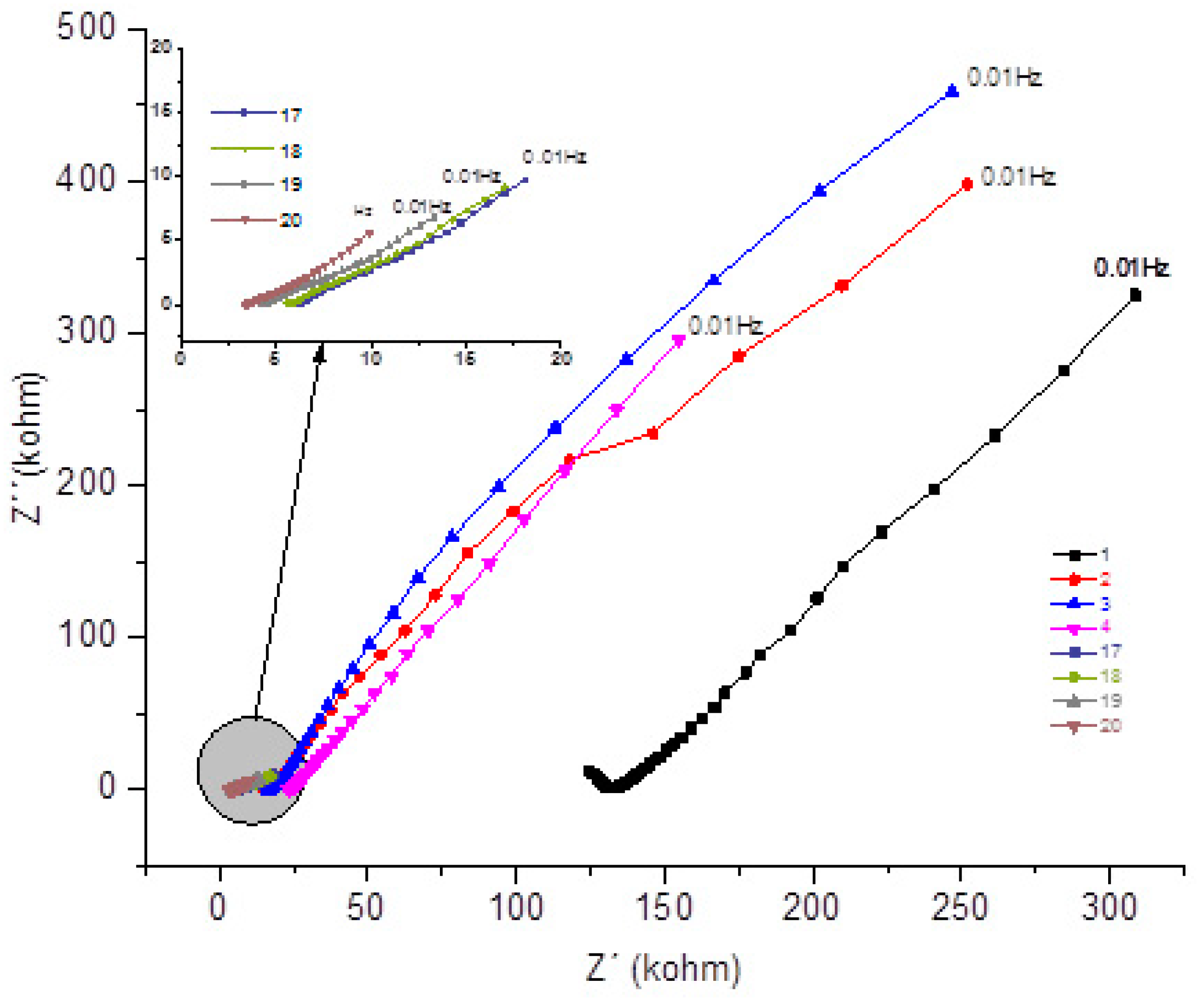
Figure 5 presents the Nyquits graph for the REF concrete, which was monitored over a period of 1 year, exposed to NaCl. The spectra of the first 4 measurements and the last 4 are shown, for the lowest frequency in 10 mHz.
Figure 5.
- Nyquist plot for the concrete system REF for 1 year with NaCl.
Figure 5.
- Nyquist plot for the concrete system REF for 1 year with NaCl.
Comparing the evolution over time of the real component attributed to the system's resistance to the corrosive process, this decreases with the time of exposure to NaCl. Comparing the impedances at 10mHz, for example, the decreasing value of the real component can be observed as a function of the exposure time (308 kΩ); (154 KΩ); (26 kΩ); (19 kΩ); (9 kΩ). Showing a significant decrease with the passage of it, of the resistance of the system, from the second month of exposure. This decreasing phenomenon of the real component as a function of time is also repeated for high frequencies, as shown in
Table 10. Being at low frequencies, associated with resistance (R4), which would be the resistance to the polarization of the electrical charges that the electrodes accumulate, i.e. from the reinforcing bars.
Analyzing the behavior of the material at medium frequencies of the real component, for example 39Hz, the decrease in system resistance is repeated over time, ranging from (134 kΩ); (24 KΩ); (11 kΩ); (7 kΩ); (3 kΩ). This fact may be associated with the resistance of the system bar (electrode) / concrete (electrolyte) R2, behaving in the analysis of the spectra as a critical point.
Observing the imaginary component, comparing the values, also at 10mHz, it is observed the decrease of the imaginary component with the passage of time (325 kΩ); (295KΩ); (13 kΩ); (10 kΩ); (5 kΩ). Component associated with the system reactance, which shows the opposition to the flow of current, decreasing at all frequencies, as shown in
Table 11.
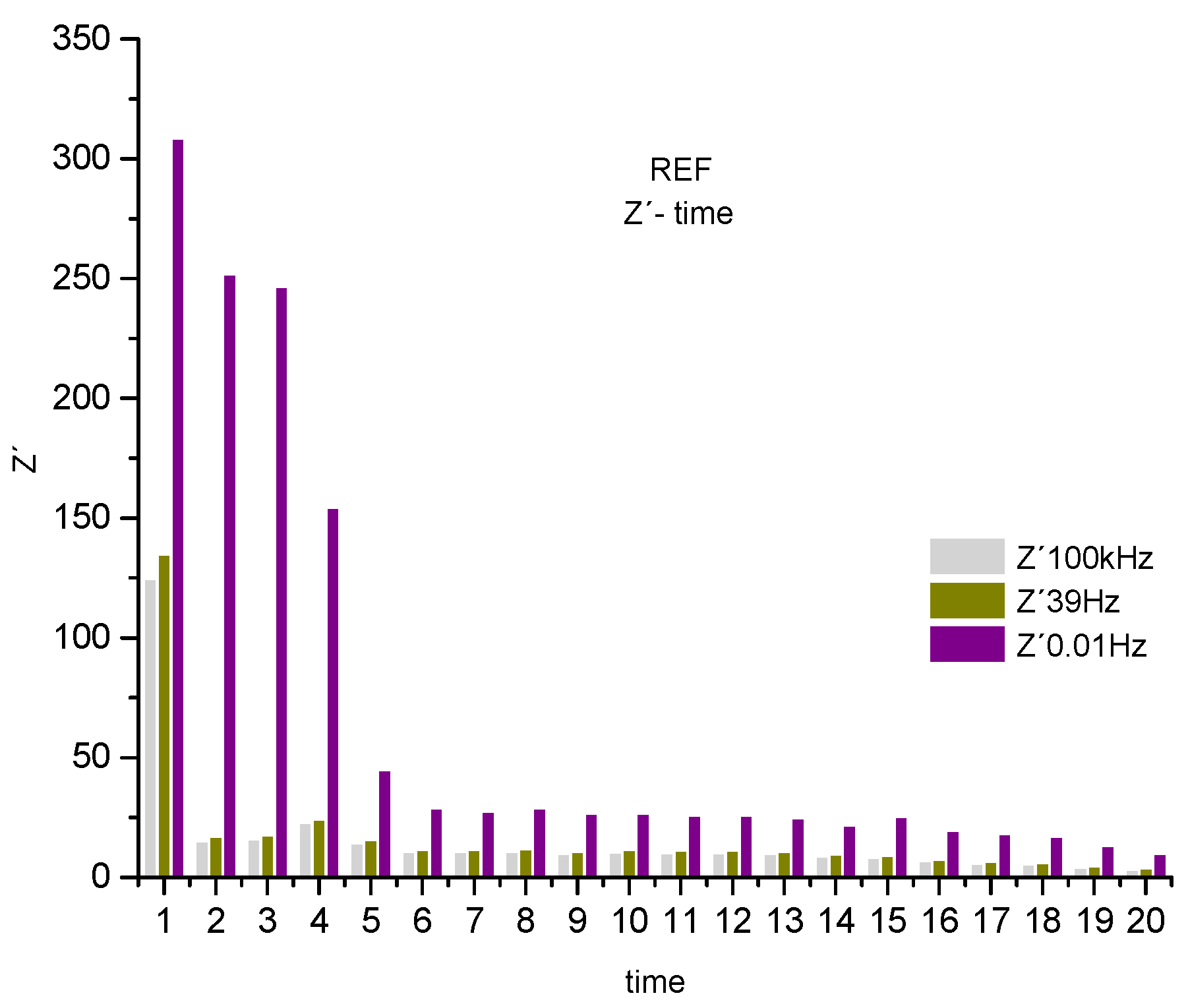
Figure 6, shown below, serves to visualize the decreasing behavior described above for the real component, associated with the system resistance. Where 3 frequency ranges were selected, observing a decreasing trend over time
Figure 6.
Real component of the histogram (Z') for REF associated with the system resistance at 3 frequencies, 100kHz, 39Hz 0.01Hz.
Figure 6.
Real component of the histogram (Z') for REF associated with the system resistance at 3 frequencies, 100kHz, 39Hz 0.01Hz.
An abrupt drop in the real component is observed, associated with the system's resistance to the corrosive process, represented by the frequencies 0.01Hz, 39Hz and 100KHz. De-scribing a drop in resistance of the sweep frequency system, from 0.01 Hz to the highest 100 kHz of 68%. Showing a system, where none of the parameters that compose it, such as the electrolyte and the steel-concrete bar system, presents resistance to the polarization of the electric charges accumulated in the R4 electrodes. Affecting the protection of the steel armor and, consequently, allowing the attack of chloride ions to the reinforced, endangering its integrity. [
21]
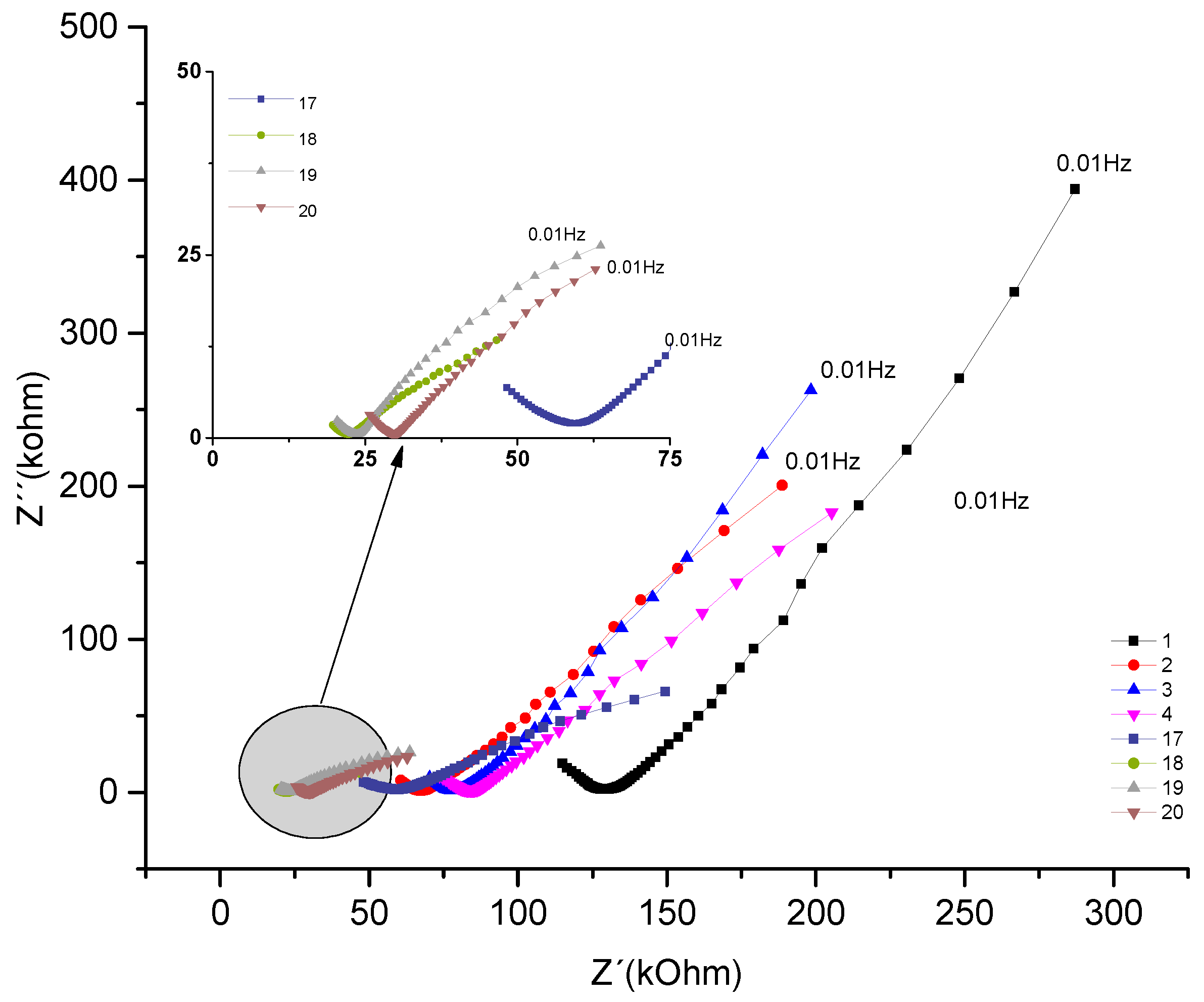
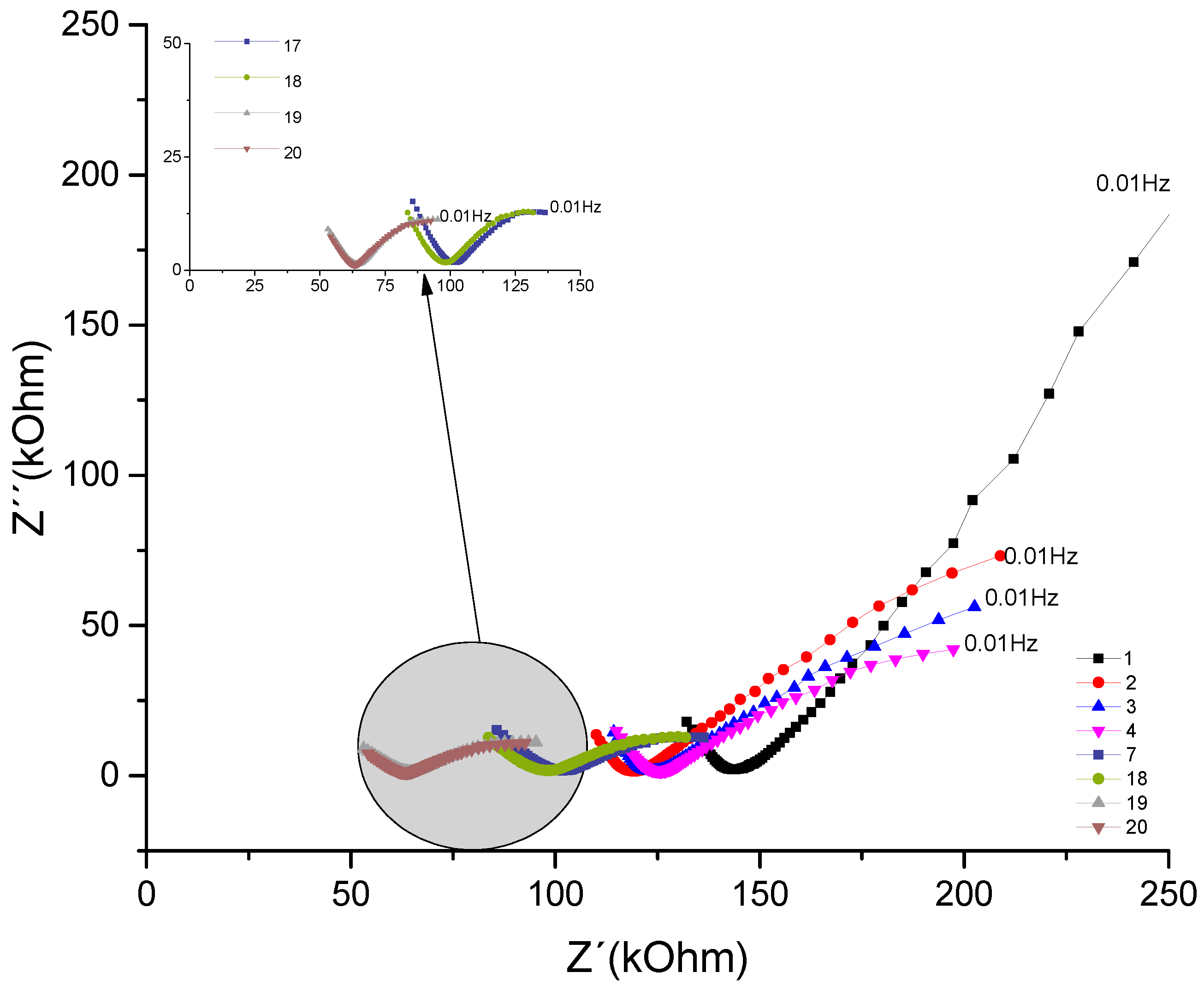
The Nyquist plot below represents the concrete sample named CCA, which contains rice husk ash addition, for the same w/c ratio of 0.7.
Figure 7.
- Nyquist plot for the concrete system CCA for 1year with NaCl.
Figure 7.
- Nyquist plot for the concrete system CCA for 1year with NaCl.
Analyzing the evolution over time of the real component attributed to the system's resistance to the corrosive process and comparing the impedances at low frequencies of 10mHz. The behavior that initially decreases as a function of exposure time from 287 kΩ to 198 kΩ. The behavior increased from the fourth test from (205 KΩ) to (244kΩ), later the values decreased in the 13th measurement from (149kΩ); a (34 kΩ). This range of frequencies is associated with resistance (R4), which would be the resistance to the polarization of electrical charges that accumulate in this region, of the armatures (electrode) / electrolyte (concrete).
Analyzing the behavior of the material's real component at medium frequencies, for example 39Hz. It is observed how this is decreasing, initially from 131 kΩ to 72kΩ. Then, from the sixth test, from 92kΩ it increases to 15 measurements with 112kΩ. From the 16th measurement, it gradually decreases by 47 kΩ until it reaches 15kΩ. This fact is associated with the resistance of the R2 bar//concrete system, and when compared to the REF material, the addition of pozzolans gains importance. Showing, as described in section 4.1, the protective effect of adding pozzolans against chloride attack.
By observing the imaginary component and comparing the values at 10mHz, a behavior that initially decreases as a function of exposure time is shown, which ranges from 394 kΩ to 145kΩ. From the sixth test, it increases from 167 KΩ to 183kΩ; being again decreasing from the 10th measurement with (117kΩ) until reaching (10 kΩ). Component associated with the system reactance, which shows the opposition to the flow of current, as can be seen in
Table 13.
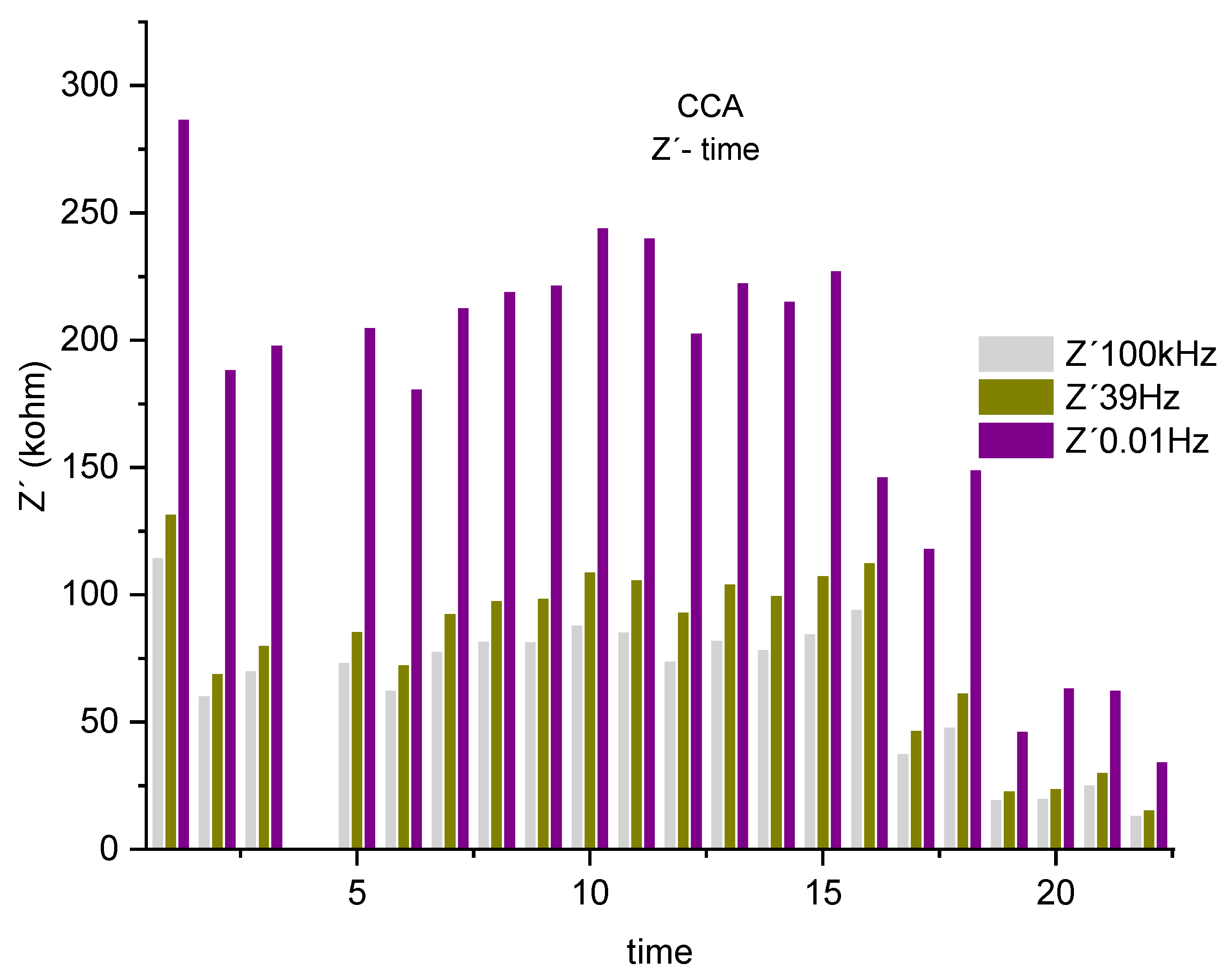
Figure 8, shown next, serves to visualize the previously described alterations of the real component, associated with the resistance of the system. Where 3 frequency bands 0.01 Hz, 39 Hz and 100 KHz were selected.
Figure 8.
Real component histogram (Z´) for CCA associated with the system resistance at 3 frequencies, 100kHz, 39Hz 0.01Hz.
Figure 8.
Real component histogram (Z´) for CCA associated with the system resistance at 3 frequencies, 100kHz, 39Hz 0.01Hz.
A drop in the real component is observed, associated with the system's resistance to the corrosive process, represented by the frequencies 0.01Hz, 39 Hz and 100KHz. Describing a decreasing trend up to the sixth test, it increases as described in the impedance spectrum up to the 14th measurement. This phenomenon is repeated from the lowest frequency of 0.01 Hz to the highest 100 kHz, varying around 62%. Showing a system, where all the parameters that compose it, such as electrolyte, steel-concrete bar system, present at certain times, an increase in the resistance offered by the system. An effect that may be associated with decreased mobility of chloride ions [
8]. As a result of the higher density of the matrix due to the hydration reaction, caused by the addition of the active mineral, based on silicon, where the physical effect is predominant.
Next, the spectra are presented through the Nyquist graph resulting from the concrete sample called MK, which contains an addition of 10% metakaolin replacing the cement
Figure 9.
- Nyquist plot for the concrete system MK for 1 year with NaCl.
Figure 9.
- Nyquist plot for the concrete system MK for 1 year with NaCl.
By observing the evolution over time of the real component attributed to the system's resistance to the corrosive process and comparing the impedances at low frequencies 10mHz. A decreasing behavior is noticed, depending on the exposure time, which initially goes from 337 kΩ until the sixth measurement of 170kΩ. As this range of frequencies is associated with resistance (R4), which would be the resistance to the polarization of the electrical charges that accumulate in this region, that is, resistance (bar electrode) // electrolyte (concrete). After the seventh measurement it shows relative stability, going from 181 kΩ to 168 kΩ. After the 15th measurement, it starts to decrease from 168 kΩ to 92 kΩ.[
1].
When analyzing the behavior of the material at average frequencies of the real component, for example 39Hz, a decreasing behavior is repeated initially from 147kΩ to 107kΩ in the fifth measurement. From the sixth test with 118kΩ it maintains stability until the 15th measurement 131kΩ. After the 16th measurement, it gradually decreases from 102kΩ to 66kΩ. This fact may be associated with the resistance of the bar / concrete R2 system, and when compared with the REF material, the addition of pozzolan to concrete gains importance, especially when these are based on aluminum-silicon [
8], as described. in section 4.1 shows the chemical-physical protective effect of this pozzolan against chloride attack.[
13] .
The component would imagine that when comparing the resulting values, at 10mHz, it is possible to initially observe a decrease as a function of the exposure time from 337 kΩ to 170 kΩ. In the seventh test it increased to 181 KΩ, until the eighth measurement the values again decreased from 180kΩ to 92 kΩ. Remember that the component associated with the reactance of the system, which shows the opposition to the passage of current that varies with frequency, as shown in
Table 15.
The following figure is used to visualize the changes previously described in the real component, associated with the resistance of the system. Where 3 frequency bands 0.01Hz, 39Hz and 100KHz were selected for the concrete MK.
Figure 10.
Real component of the histogram (Z') associated with the resistance of the MK system at 3 frequencies, 100kHz, 39Hz 0.01Hz.
Figure 10.
Real component of the histogram (Z') associated with the resistance of the MK system at 3 frequencies, 100kHz, 39Hz 0.01Hz.
When checking the real component, associated with the system's resistance to the corrosive process, there is a decreasing trend up to the sixth test, showing some stability, as described in the impedance spectrum up to the 15th measurement. This phenomenon is repeated from the lowest frequency of 0.01 Hz to the highest of 100 kHz, varying around 39%. This shows a system where all the parameters that compose it are present, such as the electrolyte, steel-concrete bar system, where the first mentioned resists the passage of chloride ions, which will provide the integrity or not of the reinforcement.
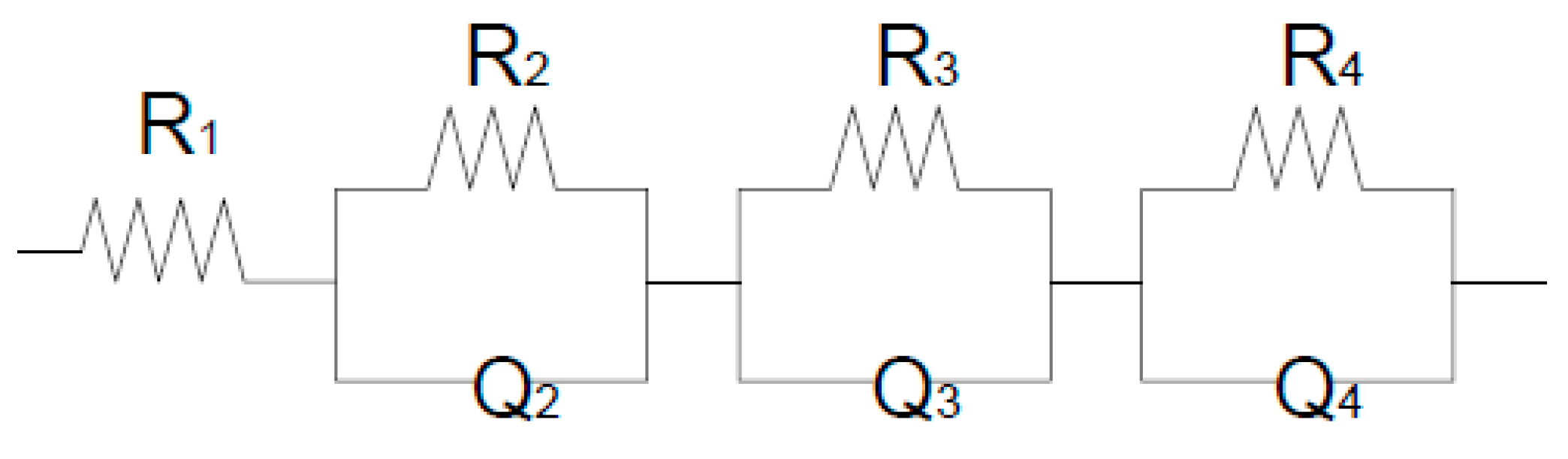
Through an analysis of all Nyquist spectra over 1 year for all 3 materials (REF, CCA, MK). It was possible to observe an equivalent circuit, in principle, it can be represented by Resistance R in parallel with a pseudo-capacitor represented by Q, the total circuit would be four sub-circuits in series as shown in Figure 11 below represents.
Figure 11.
Equivalent circuit of the studied system. José Jurado Egea (JURADO, J. R) Complutense de Madrid.
Figure 11.
Equivalent circuit of the studied system. José Jurado Egea (JURADO, J. R) Complutense de Madrid.
The equivalent circuit would be R1 (R2Q2) (R3Q3) (R4Q4) that is, 4 sub-circuits. The first corresponds to the resistance of the electrolyte (R1), the second would be the semicircle associated with the concrete system plus the steel bar (R2), a fact that coincides with [
22]. The third arc would also be associated with the anterior interface plus the diffusion process (R3) and the fourth arc is the effect of resistance to the polarization of electrical charges, which accumulate in the electrodes (R4). From obtaining the equivalent circuit of the system under study, each of the parameters obtained in the 3 materials can be evaluated as a function of time. (Ref Jose Jurado Egea).
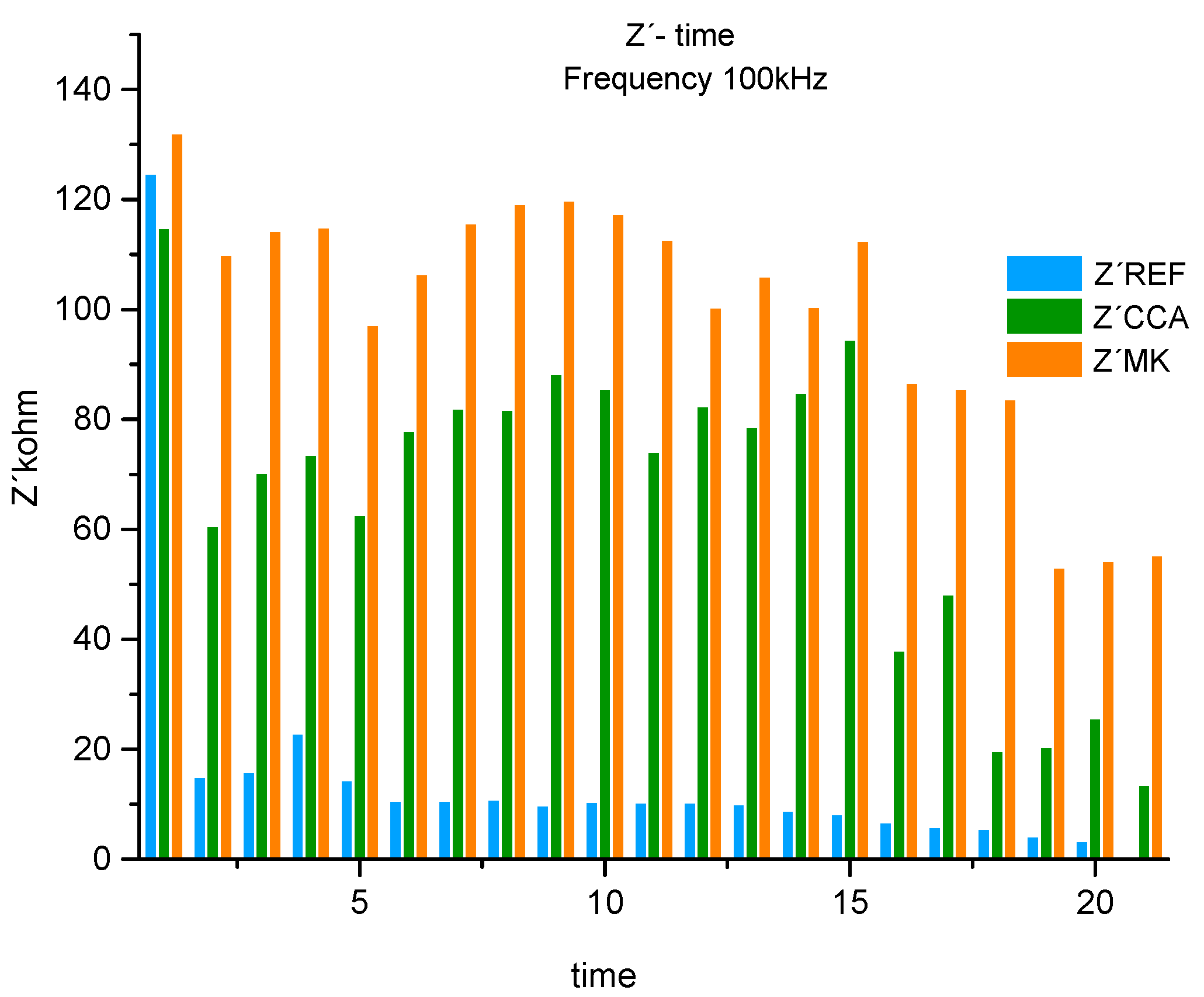
Figure 12.
Real component of the histogram (Z´) associated with the system resistance at 1 frequency 100kHz for REF, CCA and MK.
Figure 12.
Real component of the histogram (Z´) associated with the system resistance at 1 frequency 100kHz for REF, CCA and MK.
After having all the impedance spectra some analyzes were carried out. The first one makes an ANOVA comparison in
Table 16, which is based on an assessment of the variance between groups (REF, CCA, MK) for the frequencies 100kHz, 39Hz and 0.01Hz of the real component over time. Subsequently overlapping them with the previously analyzed frequencies 100kHz, 39Hz and 0.01Hz through a histogram for each of these. The methodology used in the second analysis was based on the calculation of the maximum value among the three materials, for each of the chosen frequencies. Subsequently, the percentage in which the resulting maximum impedance varies in relation to other impedance values, which are lower[
23].
At high frequencies 100kHz for the 3 materials (REF, CCA, MK) there is a significant difference when comparing the means. Since comparing MK - REF this difference was greater than when comparing CCA-REF. This difference is smaller when compared to CCA-MK.
In average frequencies for the 3 materials (REF, CCA, MK) there is a significant difference when comparing the averages. Since comparing MK - REF this difference was greater than when comparing CCA-REF. This difference is smaller when compared to CCA-MK.
At low frequencies for the 3 materials (REF, CCA, MK) there is a significant difference in terms of comparing the averages. Since comparing CCA - REF this difference was greater than when comparing MK-REF. Since there is no significant difference between the CCA-MK groups.
A seguir, os 3 materiais que fazem parte deste trabalho, REF, CCA e MK, são analisados na Figura 11.
Figure 10.
Real Component of the Histogram (Z´) associated with the system resistance at 1 frequency 0.01 Hz for REF, CCA and MK.
Figure 10.
Real Component of the Histogram (Z´) associated with the system resistance at 1 frequency 0.01 Hz for REF, CCA and MK.
Analyzing the current histogram in Figure 10 it is possible to observe, at low frequencies, referring to the System Resistance to the polarization of electric charges, in the electrodes (bars / concrete) and resistance to the transfer of charges. Where before the first measurement corresponding to the first month of exposure to NaCl, the maximum corresponds to the MK resistance, with a difference in% in relation to the CCA of 14% and with REF of 8%. From the second measurement to the third, the maximum corresponds to the REF, with a difference in relation to the CCA 22% and the MK 17%. This may be related to the delay in the hydration process of the cement grains provided by the active additions when we compare a common concrete with some concrete with pozzolanic addition [
10]. There is the possibility of being described in these first measurements, that I could be mastering the cement hydration process, in each of the materials [
21].
From the fourth measurement to the thirteenth, the maximum corresponds to the CCA Resistance, with a difference in relation to the REF in the fourth measurement of 24%, then varying to 86% until measurement 13. The difference of the CCA material in relation to the MK was 4 % in the fourth and fifth measure. From the fifth to the eighth measurement, it was 19% and then it increases to 27% until the 13th measurement. Showing an increase in MK and CCA resistance when compared to REF, which may be showing the efficiency of the existing pozzolanic additions and how you are doing opposing chloride ion entry, possibly overcoming opposition to chloride ions by physical over chemical process[
20,
24,
25].
Observing from the measure number 14 to the last one in 20, the maximum refers to the Resistance of the MK, when compared to the rest of the materials. The difference between MK and REF is 88%, remaining constant until the last measurement. When we compare MK with CCA, this difference, in addition to oscillating, starts at 5%, 29%, 59%, 34%, 63% and 34%. Showing that a chemical phenomenon may be dominating the System's Resistance over physics, as described in the title of the tomography. Based on two performed techniques, one showing that the CCA material has lower porosity than the MK material. This fact would gain importance if the dominant process was physical over the chemical, but as shown by the chloride diffusion test and in the EIE results, a chemical process is dominating the physical before the entry of chloride ions.[
13,
26]
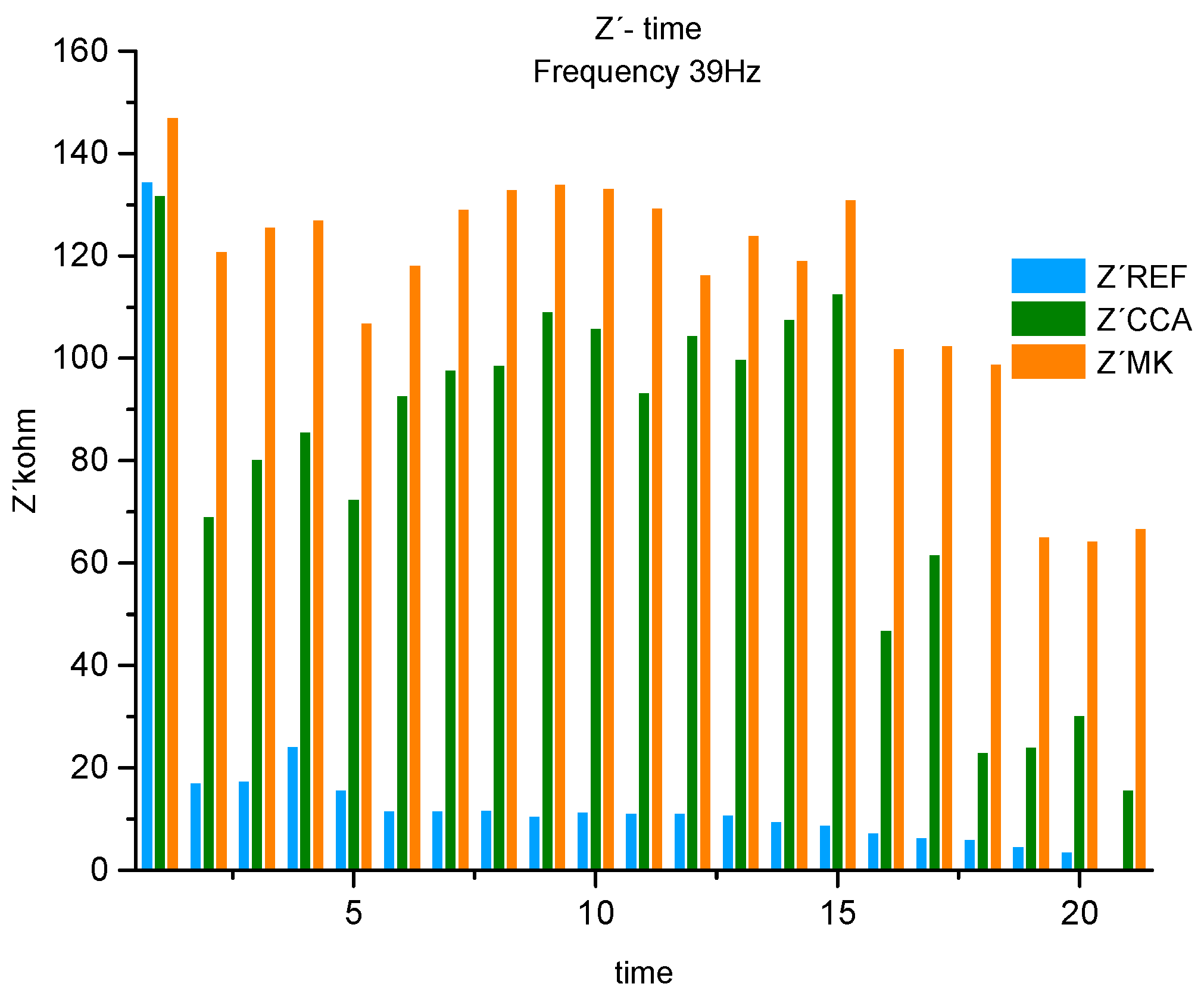
Figure 11.
Real component of the histogram (Z´) associated with the system resistance at 1 frequency 39Hz for REF, CCA and MK.
Figure 11.
Real component of the histogram (Z´) associated with the system resistance at 1 frequency 39Hz for REF, CCA and MK.
Analyzing the histogram of fig. 11 for the 3 materials, at a frequency of 39Hz, corresponding to the medium frequency range, referring to the Concrete Bar System (bars / concrete). The maximum value of the first measurement, from the first month of exposure to NaCl, until the last measurement 20, corresponds to the strength of the system formed by the MK concrete. When we compare the MK with the results in the REF concrete, we obtain a difference in% in relation to this one, in the first measurement of 8%, from measurement 2, a constant difference was maintained, around 90% on average that oscillates from 85%, gradually increasing until it reaches 94%. Describe the REF concrete system as a material that offers no protection (no resistance) against the passage of chloride ions.
Comparing the MK concrete with the CCA concrete, it is possible to observe in the first measurement a difference between the two resistances of the System of 10%, from the second measurement it starts to oscillate. Showing values between the second and fifth measurements with an average difference of 42%, then from the sixth to the eleventh measurement it decreases to 21%. When you reach measures 12 to 15, it decreases to 10%. Describe from measures 16 and 17 an increase to 53% and finally from 18 to measure 20 it increases again to 76%. Which represents a decrease in the resistance of the CCA material to the entry of the aggressive agent. Specifying that this behavior may be associated with a dominant chemical-physical domain at the steel//concrete interface, being even more visible after measurement 15, located in the eighth month of exposure[
8]
Finally, when analyzing the histogram for the 3 materials in fig. 12, at a frequency of 100kHz, corresponding to the high frequency range, referring to the resistance of the electrolyte (concrete + water + NaCl). Since the first measurement corresponding to the first month of exposure to NaCl until the last measurement 20, the maximum corresponds to the MK resistance. Showing a difference in% in relation to the REF in the first measurement of 6%, from measurement 2 onwards a constant difference remained, around 90% of the average that varied from 86%, increasing until it reached 94%. Describing a material that offers no protection (no resistance) against the passage of chloride ions.
Comparing the MK concrete, in relation to the CCA concrete, it is possible to observe in a first measurement a difference between the two resistances of the System was 13%, from the second measurement it starts to oscillate. Showing the values from the second measurement to the fifth with an average difference of 38%, from the sixth measurement to the 13th it decreases to 27%, also decreasing in the measurement from 14 to 6%. Describing from measure 15 to 16% an increase to 44% and finally from measure 17 to measure 20 it again increases to 67%. Quantitatively justified, there is a Resistance System related to a predominantly chemical-physical process, which increased from measurement 15 onwards.