1. Introduction
Paragonimiasis, caused by trematode of the genus
Paragonimus, is a zoonotic disease posing a significant health threat, primarily affecting economically disadvantaged communities in Asia, Africa, and Latin America where freshwater crab consumption is common [
1,
2,
3]. Considered as a Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD) by the World Health Organization (WHO), paragonimiasis is alarmingly prevalent, with estimated 20 million infections globally [
4,
5]. The South Asian region, including countries like China, the Philippines, and Vietnam reports the highest incidence, although this likely represents only a fraction of the actual cases [
6,
7,
8]. Therefore, understanding the disease’s epidemiology, transmission pathways, diagnostics, and treatment efficacy is crucial.
There are over 40 species of
Paragonimus worldwide, and 16 of these are pathogenic to humans [
1]. Noteworthy among them are
P. westermani in Southeast Asia,
P. africanus in West Africa,
P. mexicanus in South America, and
P. kellicotti in North America [
9]. The disease cycle begins with the consumption of inadequately cooked freshwater crabs, which harbor the larval form of the parasite known as metacercariae [
10]. The clinical symptoms can be misleading, often resembling tuberculosis or lung cancer, such as chronic cough, hemoptysis, and respiratory or gastrointestinal issues, making diagnosis complex [
5,
11,
12,
13].
In the Indian subcontinent, the first case of paragonimiasis was identified in Manipur in 1981 [
14]. Subsequent investigations have pinpointed other states in North Eastern (NE) regions of India as a hotspot for this disease, with
P. westermani and
P. heterotremus as the predominant lung fluke species [
8,
11,
15,
16,
17,
18]. Molecular diversity suggests genetic diversity within the
P. westermani species, potentially indicating a species complex. Notably, a study by Devi et al. [
19] identified two distinct genotypes of
P. westermani from NE Indian freshwater crab, with one genotype (Type 1) differing from its East Asian counterparts. This diversity can impact the disease’s behavior, underscoring the need for a nuanced understanding of host-parasite interactions, especially in terms of antibody response [
20]. Given the prevalence of pulmonary pragonimiais in India’s NE regions, particularly in Manipur, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, and Assam our study focuses on investigating the antibody response to different antigenic extracts of adult lung flukes. In this study, we conducted immunoblot analyses using the sera from confirmed paragonimiasis patients to identify antigenic extracts with diagnostic value.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological samples
Metacercariae of
P. westermani type 1 were harvested from fresh water crabs (
Maydelliathelphusa lugubris) collected from Arunachal Pradesh, NE India, as detailed in previous work [
21]. Female wistar rats (approximately 2 months old, n=50) were fed with 20 metacercariae, obtained from infected crabs [
22]. Rats were dissected weekly (upto 15
th week post-infection) and blood was collected through cardiac puncture. After clotting at room temperature for 1 h, the blood was centrifuged at 1000-2000 g for 10 minutes at 4°C to obtain serum. Serum was stored at -20°C for subsequent use. Adult
P. westermani type 1 flukes were harvested by sacrificing infected rats after 45 days of infection. The flukes were carefully extracted from the lungs and cleaned. Use of Wistar rats for pulmonary paragonimiasis was approved by Institutional Animal Ethics Committee, ICMR-RMRC, Dibrugarh, India.
This study included human serum samples from selected fresh-water crab-eating communities of Arunachal Pradesh, NE India that were collected and tested in the previous study by the authors [
23]. All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study. Serum samples from 22 parasitologically confirmed patients and pooled serum of 10 healthy subjects were analyzed for immunoblotting. Confirmed patients exhibited symptoms such as chronic cough with haemoptysis, with negative sputum samples for acid-fast bacilli (AFB, Mycobacterium tuberculosis) but positive sputum samples for lung fluke eggs. The anti-Paragonimus IgG antibodies as confirmed by in-house ELISA kit (the first indigenously developed test from India) [
23].
2.2. Preparation of adult worm somatic antigens and immunoblotting
Live adult
Paragonimus worms were homogenized to obtain soluble somatic antigens [
23]. Protein concentration of the adult worm (AW) extract was estimated by the Bradford method [
24] and the homogeneity of extract was determined by running the samples in Tris-Glycine SDS-PAGE gels [
25]. The protein bands in gels were observed by coomassie and silver staining procedures [
26]. Immunoblotting was performed using sera from infected rats collected over time. At first, the AW protein sample was resolved in 15% Tris-Glycine SDS-PAGE gels procured from BioRad (Hercules, California, USA). The electrotransfer of proteins from gel to polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (PVDF) was performed in a Bio-Rad Trans-Blot transfer Cell (Hercules, California, USA) for 90 min at 100V. Next, the blotted membrane was incubated with blocking buffer containing 5% BSA in wash buffer (0.1% Tween20 in Tris-NaCl; TBST) for 1 h. The blotted PVDF were cut into vertical strips and stored overnight with sera collected weekly from infected rats. The rat sera were diluted in the ratio 1:100 with blocking buffer. An uninfected rat serum was taken as negative control group. Next, the membrane strips was washed in TBST and incubated in solution containing secondary antibody HRP conjugated anti-rat IgG (Promega Corporation, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). The membrane strips were then washed with TBST and antibody-antigen reaction was observed using chromogenic substrate.
2.3. Preparation of excretory-secretory antigenic proteins
Live adult worms collected from experimental rats were used for the preparation of excretory-secretory (ES) antigenic proteins [
23]. The adult worms were first washed at least 10 times in 1X PBS (pH 7.4) and then soaked in 1 ml of 1X PBS (pH 7.4) for 3 h under shaking conditions. The adult lung flukes were removed and the spent culture was centrifuged at 15,000 g to eliminate eggs and debris. The supernatant was treated with complete Roche Protease Inhibitor Cocktail solution and filtered through 0.2 µm membrane to obtain ES proteins. The protein concentration of ES antigens was determined by Bradford assay. Subsequently, ReadyPrep™ 2-D clean-up kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA) was used for quantitatively precipitate sample proteins and removal of contaminants [
27]. The dried pellet obtained after cleanup was suspended by adding 125 µl of rehydration buffer and stored at -80°C. To check the quality of antigenic extract, two replicates of ES proteins (5 µg each) were resolved in Tris-glycine SDS-PAGE and stained by coomassie Brilliant Blue-R250. Bio-Rad precision plus (Catalog No. 161-0377) protein marker was used for determining the molecular weights of the protein bands.
2.4. Immunoblot analysis using human serum
Immunoblotting was performed using AW and ES protein antigens and the pooled sera of confirmed pulmonary paragonimiasis patients. The protein antigens were loaded on SDS-PAGE gels to perform SDS-PAGE in Bio-Rad Mini PROTEAN cell (Hercules, California, USA). After completion of electrophoresis, a portion of the gel was cut and subjected to silver staining. The remaining part of gel was used for immunoblotting procedure as described above. The blotted membrane was incubated overnight at 4°C with the sera of confirmed pulmonary paragonimiasis patients (diluted 1:100 ratio). For negative control, pooled sera of 10 uninfected individuals were used. The strips were incubated with secondary antibody (dilution ratio 1:1000). Immunoreactive proteins were visualized using a chromogenic substrate.
ES protein samples were also separated in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2D-PAGE). At first, isoelectric focusing was carried out in 7 cm (pH 3-10) IPG strips (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA) in Bio-Rad PROTEAN IEF Cell under standardized running conditions [
28]. After focussing, the strips were equilibrated in two equilibration steps – 10 min in Equilibration I containing DTT, followed by 10 min incubation in Equilibration Buffer II containing iodoacetamide. The equilibrated strips were applied to 12% SDS-PAGE gels and electrophoresis carried out. The gel was coomassie brilliant blue stained to visualize protein spots and peptide mass fingerprinting of protein spots were performed by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Remaining gels were used for immunoblot analysis as described above. To study interactions of protein spots with serum antibody, the blotted PVDF membrane was incubated with pooled sera of confirmed patients (diluted 1:100).
3. Results
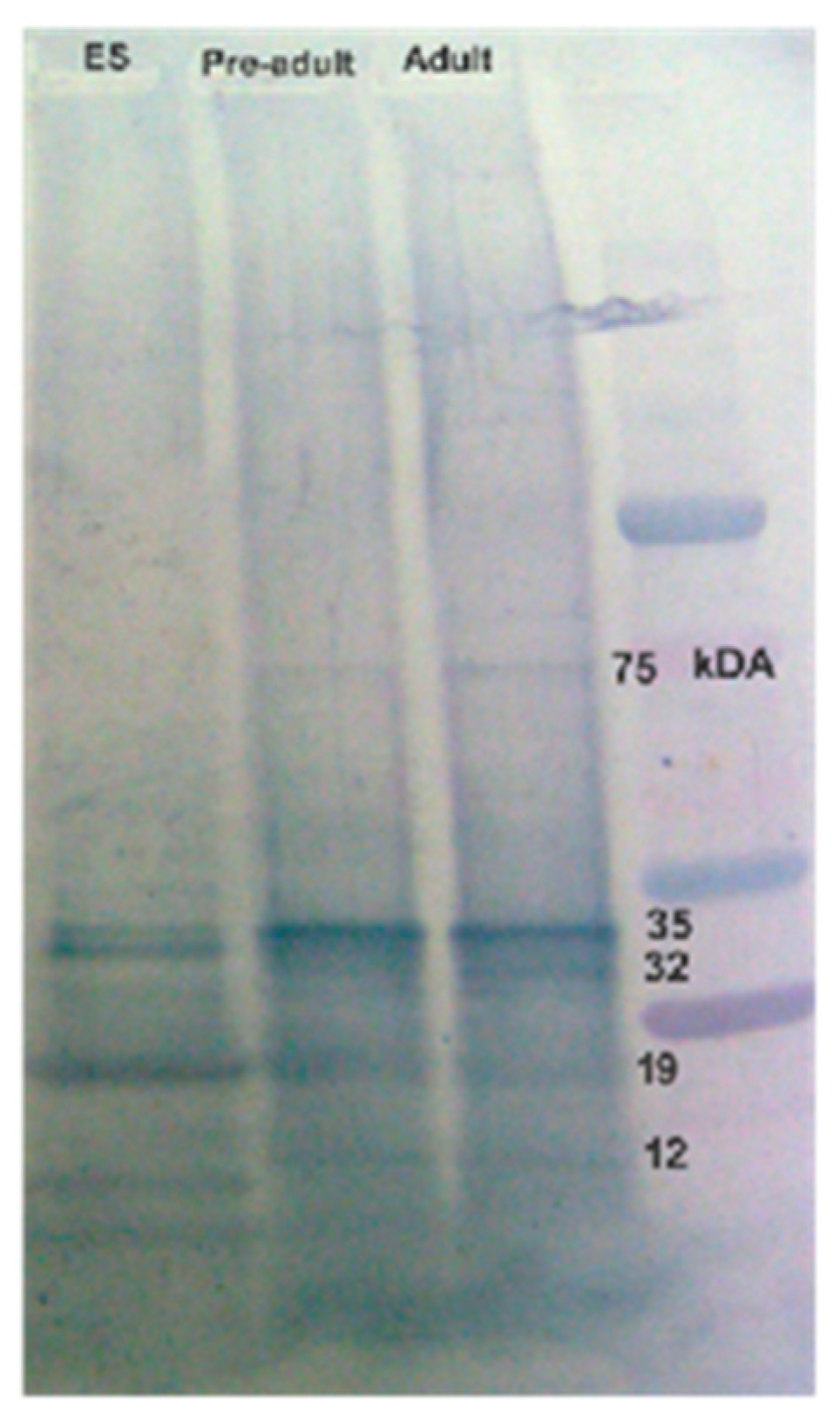
3.1. Protein profiling of different antigenic extracts
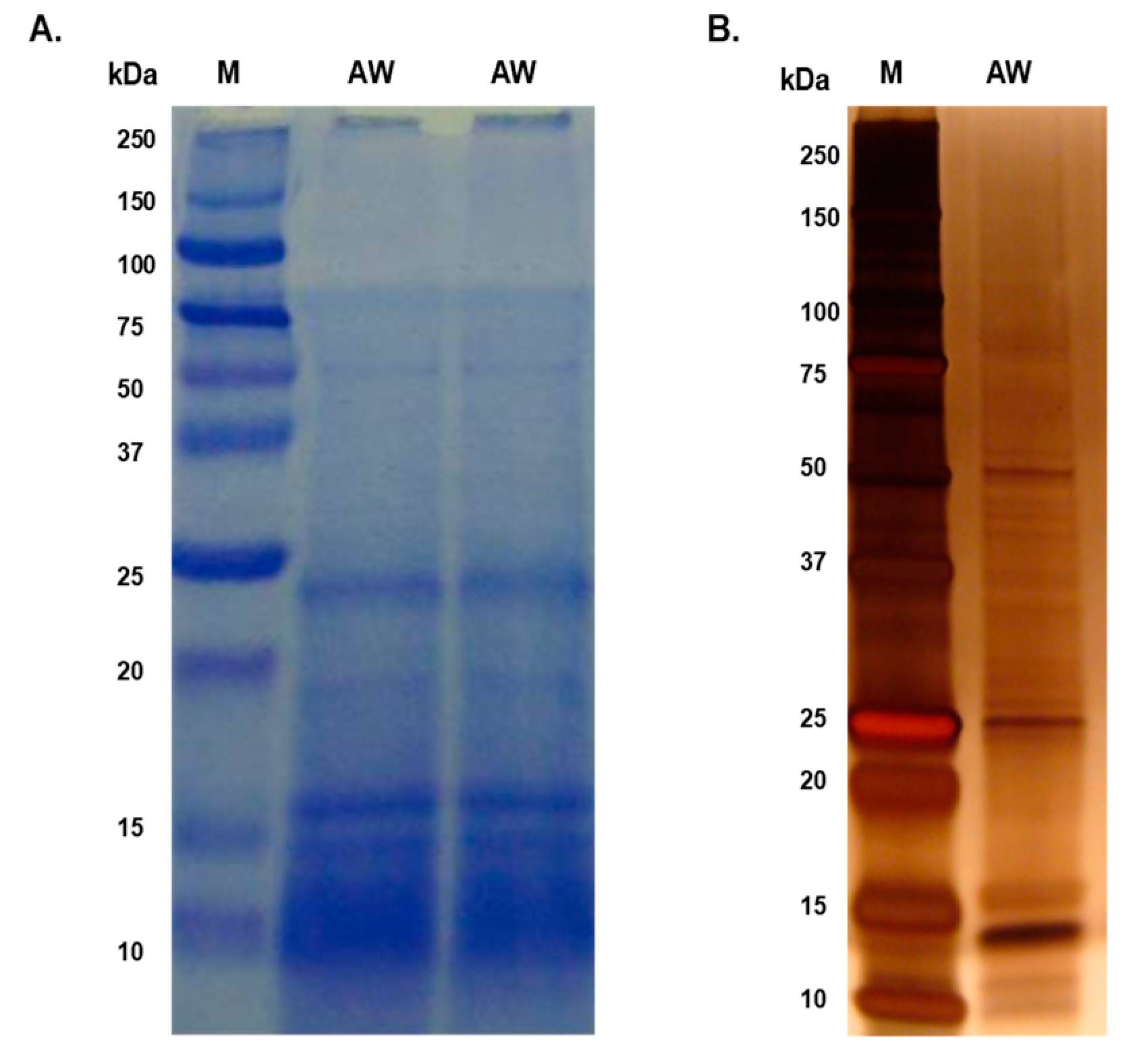
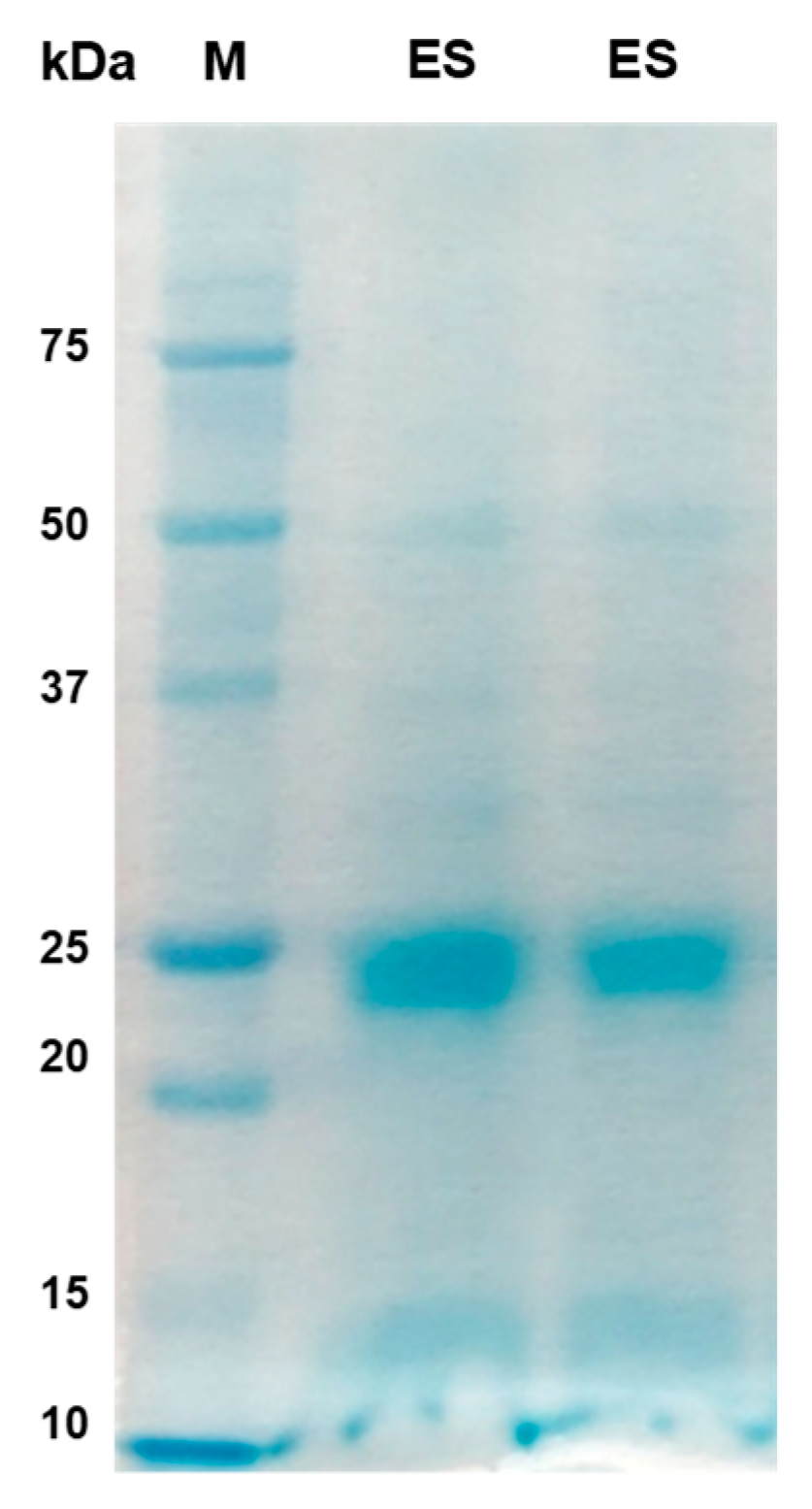
The majority of proteins in both AW and ES extracts fell within the molecular mass range of 10 kDa to 50 kDa, with faint bands above 50 kDa in the AW extract (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). Prominent protein bands were observed in both extracts, with cluster around 20-25 kDa and faints bands near 37 kDa were observed in SDS-PAGE gels.
3.2. Serum antibody responses in experimental rats
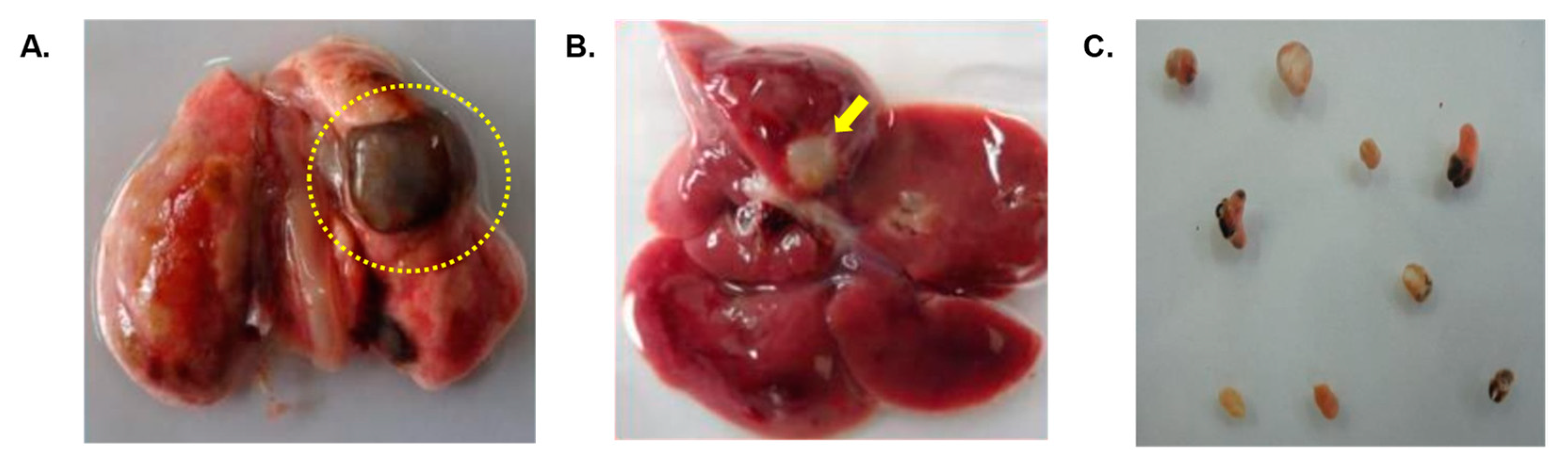
Rats infected with metacercariae developed lung cysts, juvenile worms in the peritoneal cavity, and later, adult worms in lung cysts, with parasitic cysts also found in liver (
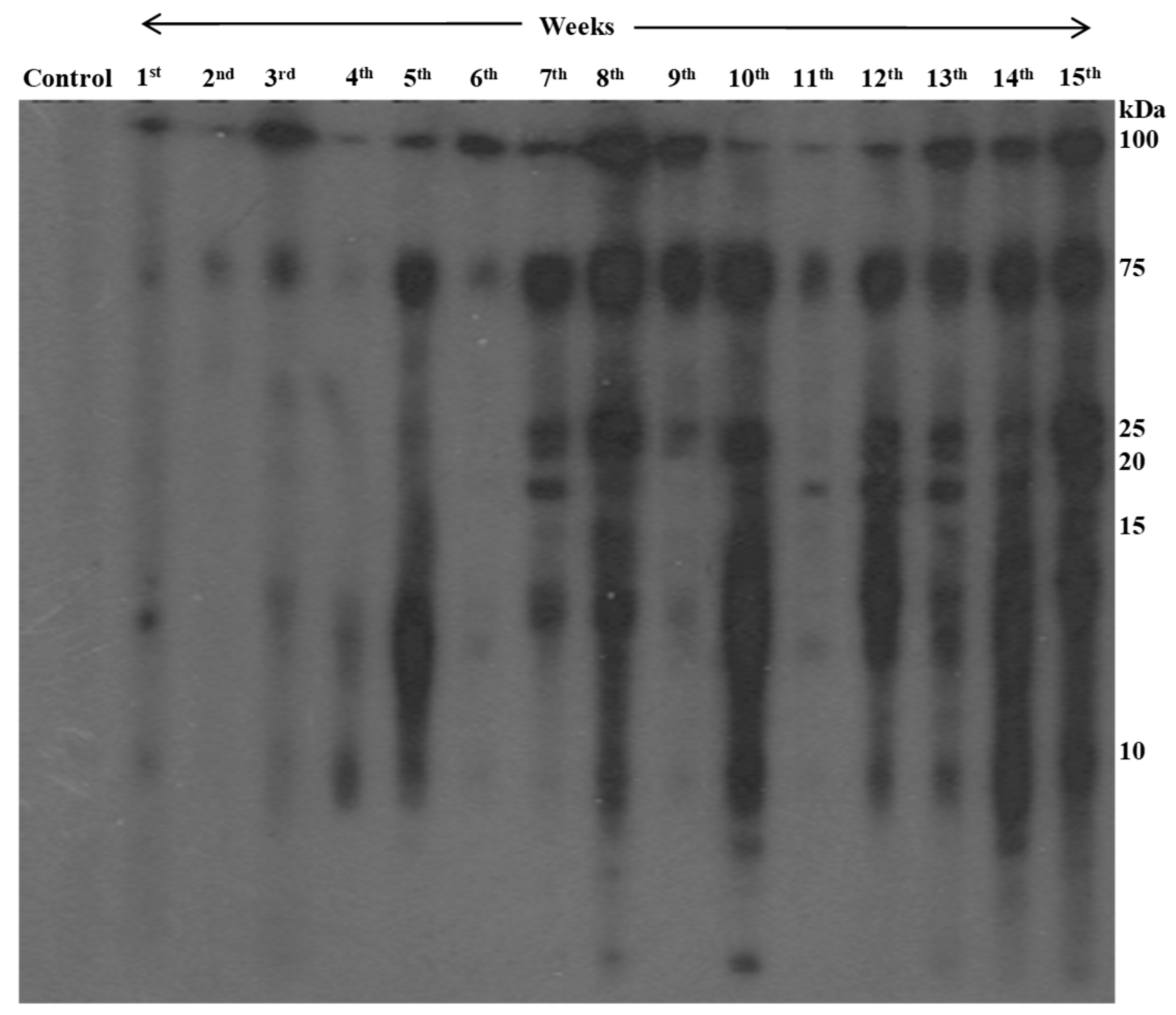
Figure 3). Using immunoblotting, we monitored IgG antibody development against AW antigens (
Figure 4 &
Table 1). Reactive fractions emerged from 1st week, expanding upto 15 weeks. Additional fractions displayed immune reactivity from the 7th week post-infection. Pre-infection sera from experimental rats were non-reactive to AW antigens.
3.3. Immunoreactivity of human sera with antigenic extracts
Serum antibodies from confirmed paragonimiasis patients reacted with specific protein bands, including ~34, ~32 and ~25 kDa of adult worm antigens and ~34 kDa and ~25 kDa in ES sample (
Figure 5).
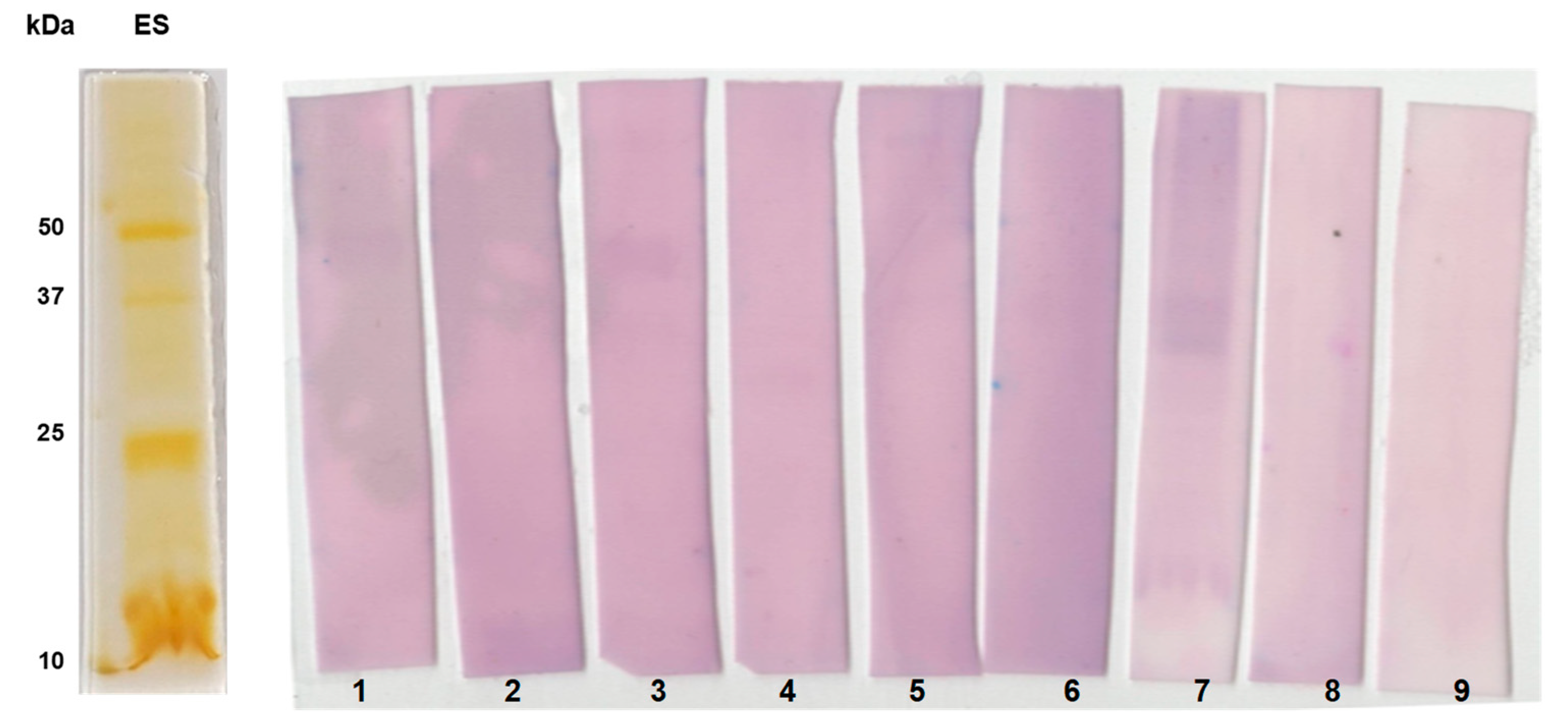
Further, we studied immunoreactive pattern of individual sera of confirmed paragonimiasis patients (n=7) with ES proteins by immunoblotting (
Figure 6). Particularly, the protein bands of size 25 and 35 kDa were found to be highly immunoreactive.
3.4.2. DE immunoblot analysis of ES antigens
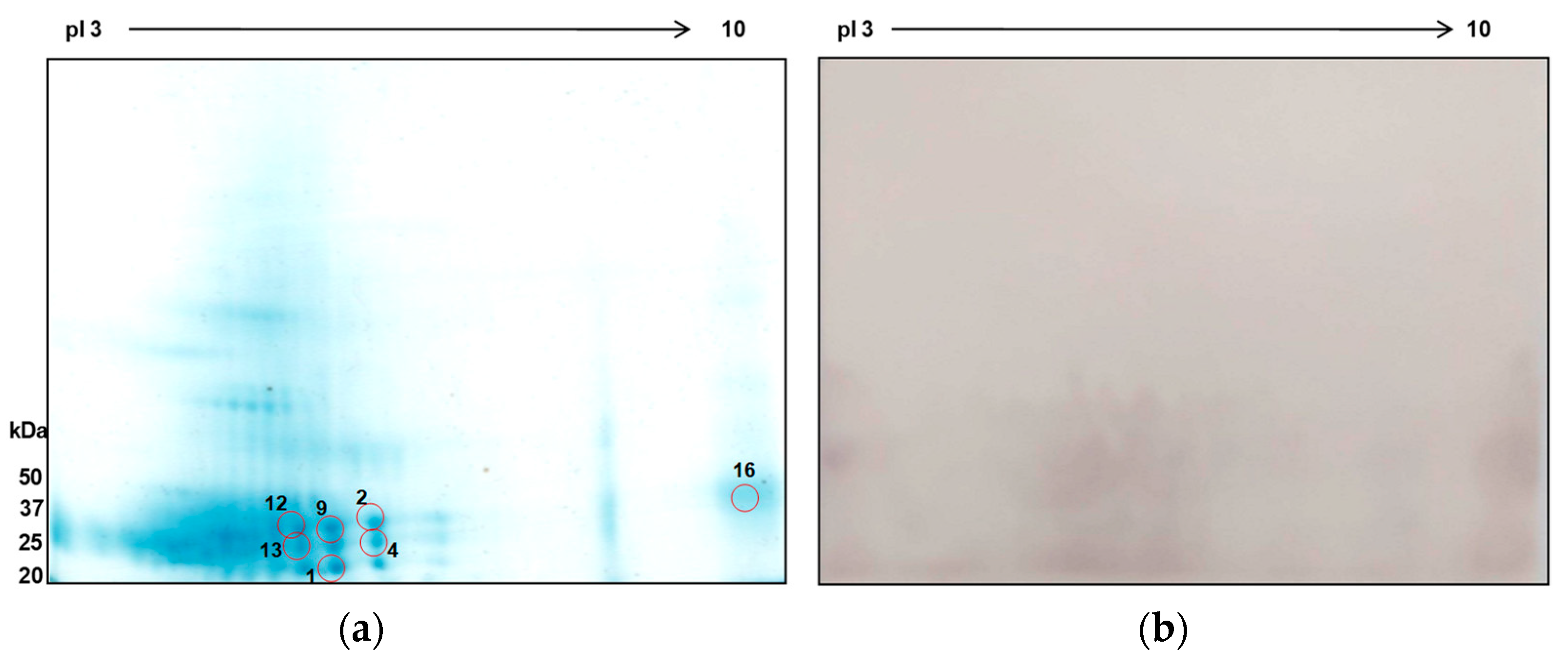
Numerous protein spots were identified within molecular weight and pI ranges of 25 to 50 kDa and pI 3-6, respectively (Figure 7A). Seven protein spots were positively identified using mass spectrometry, with matches predominantly from P. westermani and some from other related species (
Table 2). Seven peptides of protein spot 1 was found to match with globin family profile domain-containing protein of P. westermani upon MASCOT search. Cathepsin F, a cysteine protease, was identified in spot 9. The other proteins identified in this study were carboxylesterase B, nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 1, 5'-Nucleotidase C-terminal domain protein, Ras and EF-hand domain-containing protein, SET domain-containing protein. These proteins were previously not reported from ES extract of P. westermani. Furthermore, ES antigenic extract were tested against sera of confirmed paragonimiasis patients, revealing strong reactivity in 25-50 kDa (pI 4-8). The MS identified proteins were effectively recognized by host humoral immune response and therefore, determined to be antigenic with serodiagnostic potential.
4. Discussion
Human pulmonary paragonimiasis disease is a pressing public health concern in the northeastern (NE) staes of India, primarily caused by
Paragonimus species such as
P. westermani and
P. heterotremus. Notably, the NE Indian form of
P. westermani type 1 has distinct characteristics from its East Asian counterparts [
21]. While prior studies have reported on the immunodominant antigens of different antigenic extracts of lung flukes [
29,
30,
31], the protein profile and immunoreactivity patterns of
P. westermani type 1 of NE Indian origin remains elusive. Understanding the protein composition of antigenic extracts is crucial, as it offers insights into the biologically active molecules involved in the infection’s pathophysiology. In this context, we investigated the protein profiles of adult worm (AW) somatic and excretory-secretory (ES) protein extracts of
P. westermani type 1 by 1D SDS-PAGE. The presence of doublet protein band at 21/23 kDa and a diffuse band at 35 kDa supports exposure to
Paragonimus species. These bands are known to contain highly immunogenic antigens [
31,
32]. Notably, a ~15 kDa in the ES sample aligns with the previous identification of host tissue-derived hemoglobin [
29]. The presence of host proteins in ES extracts could indicate symbiotic interactions aiding the parasite’s survival and infection process [
33].
Further, we aimed to unveil the pathology and dynamics of antibody response following infection with
P. westermani type 1. The appearance of parasitic cysts in the experimental animals correlated with detectable antigen-specific antibodies. The antibody response varied based on the maturation stage of the lung flukes, suggesting dynamic interaction. Similar observations were also reported previously
[22].
Laboratory diagnosis of human pulmonary paragonimiasis typically relies on detecting parasite eggs in clinical samples [
23,
34]. However, this method is not always feasible, especially in early stages or extra-pulmonary infections [
35,
36,
37]. In these cases, serological assays are valuable, particularly in regions where paragonimiasis coexists with other infections like tuberculosis. ELISA and immunoblot assay are common approaches for detecting of parasite-specific antibodies [
38,
39,
40,
41]. Several studies have evaluated serodiagnostic potential of adult worm somatic extracts, excretory-secretory antigens and recombinant proteins of
Paragonimus species using ELISA and western blot for screening of human paragonimiasis [
23,
30,
32,
42,
43]. Taking into consideration the genetically and geographically diverse complex of
P. westermani populations found in Asia [
44,
45,
46], it is crucial to identify and characterize repertoire of antigenic proteins present in different samples. The present study evaluated different antigenic extracts of
P. westermani type 1 (pre-adult/juvenile, adult worms and excretory-secretory) for their potential as serodiagnostic antigens using sera of parasitologically confirmed pulmonary paragonimiasis human patients. The results obtained in this study are in line with previous studies [
29,
30]. The immunoreactive antigens of adult
P. westermani was identified to be cysteine proteases of molecular weights between 27-35 kDa that largely reacted with the sera of paragonimiasis patients [
29]. The results are in line with previous studies [
29,
30]. The immunoreactive antigens of adult
P. westermani was identified to be cysteine proteases of molecular weights between 27-35 kDa that largely reacted with the sera of paragonimiasis patients.
Although the banding pattern varied among the samples, it could recognize the different proteins of molecular size 10-75 kDa. The developmental stage of parasite responsible for infection in patients could be one of the explanations for reactivity pattern variation. The antigenic determinants of proteins are usually lost during denaturation process in immunoblot assay, while the same protein in native form may expose relevant epitopes in ELISA test. Studies on parasitic diseases have suggested use of western blotting and ELISA as confirmatory tests for positive cases in order to distinguish false positive sera from true positive sera [47,48,49]. In summary, combining ELISA and immunoblotting could enhance the serodiagnosis of human pulmonary paragonimiasis in endemic areas.
Excretory-secretory proteins of helminth parasitic worms are known to be ideal candidates for serodiagnostic protein antigens due to host-parasite interactions [
50]. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE) based immunoblotting approach combined with mass spectrometry is the most popular research technique to get an overview on the specific protein antigens recognized by human patients sera [
51,
52]. Hence, to gain insight into the proteins present, we analyzed ES extracts of
P. westermani type 1 worm by 2D-PAGE followed by protein identification. Cathepsin F and globins were identified in this study. High content of globins in adult lung flukes have been reported previously making it another diagnostic candidate but it requires further exploration [
31,
50]. Cysteine proteases which has implications in pathogenesis and immune modulation [
31,
44], are known to share high sequence similarity among many
Paragonimus species. Selecting unique regions of these cysteine proteases and use of recombinant technology might prove useful for designing species-specific diagnostic kit. Lately, the cathepsin F gene expression has been detected in different developmental stages of
P. westermani worms and the recombinant protein expressed was found to be highly immunoreactive with patient sera of paragonimiasis [56]. This study supports cysteine proteases as promising diagnostic targets. Carboxylesterase B domain-containing protein identified in this study may have role in metabolism of parasitic helminths and might be associated with resistance against anthelmintics [
54]. Overall, the findings in this study provide a foundation for identifying potential diagnostic antigens. Additionally, comprehensive proteomics studies using for high-throughput technologies are warranted to fully characterize the host-parasite interaction and the proteins involved.
5. Conclusions
Our study has successfully identified specific antigenic fractions with immunodiagnostic potential for paragonimiasis. By using an experimental infection model involving laboratory rats and sera from confirmed human paragonimiasis cases, we have pinpointed antigenic markers that hold promise for accurate diagnosis. Moreover, we have unraveled the temporal evolution of immunoreactivity in response to the duration of infection in rodent models of paragonimiasis. These findings are anticipated to significantly contribute to the diagnosis of both early and chronic stages of paragonimiasis. Importantly, this investigation marks the first of its kind in India, shedding light on the reactivity patterns between P. westermani protein antigens and sera from ELISA-positive patients by immunoblotting. Our results underscore the value of combining ELISA and immunoblot assays to effectively screen for paragonimisis in endemic regions. Of particular significance is the identification of cathepsin F through MALDI-TOF MS analysis, representing a highly promising serodiagnostic antigen. The potential of cathepsin F along with other antigenic candidates merits further exploration for the development of diagnostic kits that offer enhanced sensitivity and specificity for paragonimiasis. Overall, this study contributes valuable insights into the realm of paragonimiasis diagnostics and sets for continued advancements in the field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.N. and K.R.D.; methodology, A.D., K.R.D., K.N.; validation, K.N., K.R.D. and A.D.; formal analysis, A.D., D.M., K.N., H.M., K.R.D.; investigation, K.N and K.R.D.; resources, K.N and K.R.D.; data curation, K.N and K.R.D.; writing—original draft preparation, A.D., D.M.; writing—review and editing, A.D., D.M., K.N., K.R.D.; visualization, K.N., K.R.D.; supervision, K.N., H.M., K.R.D.; project administration, K.N., H.M., K.R.D.; funding acquisition, K.N., K.R.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Indian Council of Medical Research, Govt. of India: grant number Y110118/1/2020-21-(199).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of ICMR-Regional Medical Research Centre, Dibrugarh, India (RMRC/Dib/IEC (Human)/2017-18/3483; date of approval 07/03/2018). The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee, ICMR-RMRC, Dibrugarh, India.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by The Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India. The authors thank all the project staffs for their help in the field and laboratory work. AD acknowledges Indian Council of Medical Research, Govt. of India for ICMR-Research Associate Fellowship (Sanction No. 2021-8051/PROTEOMICS-BMS).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yoshida, A., Doanh, P.N., & Maruyama, H. Paragonimus and paragonimiasis in Asia: An update. Acta Trop. 2019, 199, 105074. [CrossRef]
- Rabone, M., Wiethase, J., Clark, P.F., Rollinson, D., Cumberlidge, N., & Emery, A.M. Endemicity of Paragonimus and paragonimiasis in Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and mapping reveals stability of transmission in endemic foci for a multi-host parasite system. PLoS.Negl.Trop.Dis. 2021, 15, e0009120. [CrossRef]
- Cumberlidge, N., Rollinson, D., Vercruysse, J., Tchuem Tchuente, L.A., Webster, B., & Clark, P.F. Paragonimus and paragonimiasis in West and Central Africa: unresolved questions. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1748-1757,.
- Furst, T., Keiser, J., & Utzinger, J. Global burden of human food-borne trematodiasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect.Dis. 2012, 12, 210-221. [CrossRef]
- Control of foodborne trematode infections. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech. Rep.Ser. 1995, 849, 1-157.
- Betson, M., Alonte, A.J., Ancog, R.C., Aquino, A.M., Belizario, V.Y., Bordado, A.M., Clark, J., Corales, M., Dacuma, M.G., Divina, B.P., Dixon, M.A., Gourley, S.A., Jimenez, J.R., Jones, B.P., Manalo, S.M., Prada, J.M., van Vliet, A.H.M., Whatley, K.C.L., and Paller, V.G., Chapter Two - Zoonotic transmission of intestinal helminths in southeast Asia: Implications for control and elimination. In "Advances in Parasitology" (D.Rollinson and R.Stothard, Eds.), pp. 47-131, Academic Press, 2020.
- Zhou, X.J., Yang, Q., Tan, Q.H., Zhang, L.Y., Shi, L.B., & Zou, J.X. Paragonimus and its hosts in China: An update. Acta Trop. 2021, 106094. [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.S., Sugiyama, H., & Rangsiruji, A. Paragonimus & paragonimiasis in India. Indian J.Med.Res. 2012, 136, 192-204.
- Castilla, E.A., Jessen, R., Sheck, D.N., and Procop, G.W., Cavitary mass lesion and recurrent pneumothoraces due to Paragonimus kellicotti infection: North American paragonimiasis. Am.J.Surg.Pathol. 2003, 27, 1157-1160.
- Blair,D. Paragonimiasis. Adv.Exp.Med.Biol. 2019, 1154, 105-138.
- Devi, K.R., Narain, K., Bhattacharya, S., Negmu, K., Agatsuma, T., Blair, D., Wickramashinghe, S., & Mahanta, J. Pleuropulmonary paragonimiasis due to Paragonimus heterotremus: molecular diagnosis, prevalence of infection and clinicoradiological features in an endemic area of northeastern India. Trans.R.Soc.Trop.Med.Hyg. 2007,101, 786-792. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.C. Paragonimiasis causing diagnostic confusion with tuberculosis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2005,5, 538, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, K., Koh, W.J., Kim, H., Kwon,O.J., Kim,T.S., Lee,K.S., & Han,J., Clinical features of recently diagnosed pulmonary paragonimiasis in Korea. Chest 2005, 128, 1423-1430. [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.I., Singh, N.B., Devi, S.S., Singh, Y.M., & Razaque, M., Pulmonary paragonimiasis in Manipur. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 1982, 24, 304-306, 1982.
- Das, M., Doleckova, K., Shenoy, R., Mahanta, J., Narain, K., Devi, K.R., Konyak, T., Mansoor, H., & Isaakidis, P. Paragonimiasis in tuberculosis patients in Nagaland, India. Glob.Health Action. 2016, 9, 32387. [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.S., Sugiyama, H., Umehara, A., Hiese, S., and Khalo, K., Paragonimus heterotremus infection in Nagaland: A new focus of Paragonimiasis in India. Indian J Med.Microbiol. 2009, 27, 123-127. [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.S., Das, P.P., Borah, A.K., & Das, J.K., Paragonimiasis in a Child from Assam, India. J.Clin.Diagn.Res. 2016, 10, DD06-DD07.
- Singh, T.S., Hiromu, S., Devi, K.R., & Singh, W.A., First case of Paragonimus westermani infection in a female patient in India. Indian J.Med.Microbiol. 2015, 33, 156-159. [CrossRef]
- Rekha, D.K., Narain, K., Mahanta, J., Nirmolia, T., Blair, D., Saikia, S.P., & Agatsuma, T., Presence of three distinct genotypes within the Paragonimus westermani complex in northeastern India. Parasitology 2013, 140, 76-86. [CrossRef]
- Dreyfuss,G. and Rondelaud,D. Biodiversity of flukes. Parasite 2008, 15, 282-285. [CrossRef]
- Devi, K. R., Narain, K., Agatsuma, T., Blair, D., Nagataki, M., Wickramasinghe, S., & Mahanta, J. Morphological and molecular characterization of Paragonimus westermani in northeastern India. Acta Tropica 2010, 116(1), 31-38. [CrossRef]
- Narain, K., Rekha, D.K., & Mahanta, J. A rodent model for pulmonary paragonimiasis. Parasitol.Res. 2003, 91, 517-519. [CrossRef]
- Narain, K., Devi, K. R., & Mahanta, J. Development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serodiagnosis of human paragonimiasis. Indian Journal of Medical Research 2005, 121(6), 739.
- Bradford, M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical biochemistry 1976, 72(1-2), 248-254.
- Laemmli, U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227(5259), 680-685.
- De Kostha, Y. S., Pathirana, S. L., Handunnetti, S. M., & Gunawardena, S. (2022). Characterization of antigens of Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) eggs. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 14414.
- Morassutti, A. L., Levert, K., Pinto, P. M., da Silva, A. J., Wilkins, P., & Graeff-Teixeira, C. Characterization of Angiostrongylus cantonensis excretory–secretory proteins as potential diagnostic targets. Experimental parasitology 2012, 130(1), 26-31.
- Deka, A., Reza, M. A., Hoque, K. M. F., Deka, K., Saha, S., & Doley, R. (2019). Comparative analysis of Naja kaouthia venom from North-East India and Bangladesh and its cross reactivity with Indian polyvalent antivenoms. Toxicon 2019, 164, 31-43.
- Lee, E. G., Na, B. K., Bae, Y. A., Kim, S. H., Je, E. Y., Ju, J. W., & Kong, Y. Identification of immunodominant excretory–secretory cysteine proteases of adult Paragonimus westermani by proteome analysis. Proteomics 2006, 6(4), 1290-1300.
- Fischer, P. U., Curtis, K. C., Folk, S. M., Wilkins, P. P., Marcos, L. A., & Weil, G. J. Serological diagnosis of North American Paragonimiasis by Western blot using Paragonimus kellicotti adult worm antigen. The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene 2013, 88(6), 1035.
- McNulty, S. N., Fischer, P. U., Townsend, R. R., Curtis, K. C., Weil, G. J., & Mitreva, M. Systems biology studies of adult paragonimus lung flukes facilitate the identification of immunodominant parasite antigens. PLoS neglected tropical diseases 2014, 8(10), e3242.
- Kang, S. Y., Cho, S. Y., Kong, Y., Gan, X. X., & Hong, S. J. Recombinant Paragonimus westermani yolk ferritin is a useful serodiagnostic antigen. The Journal of infectious diseases 2012, 185(9), 1373-1375.
- Dagenais, M., & Tritten, L. Hidden in plain sight: How helminths manage to thrive in host blood. Frontiers in Parasitology 2023, 2, 1128299.
- Odermatt, P., Veasna, D., Zhang, W., Vannavong, N., Phrommala, S., Habe, S., & Strobel, M. Rapid identification of paragonimiasis foci by lay informants in Lao People's Democratic Republic. PLoS neglected tropical diseases 2009, 3(9), e521.
- Kim, K. E., Jung, S. S., Park, H. S., Lee, J. E., Chung, C., Lee, S. I., & Park, D. The first case report of Paragonimus westermani infection diagnosed by transbronchial lung cryobiopsy. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2023, 128, 184-186.
- Poudyal, B. S., Paudel, B., Bista, B., Shrestha, G. S., & Pudasaini, P. Clinical, Laboratory and Radiological Features of Paragonimiasis Misdiagnosed as Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Iranian Journal of Parasitology 2022, 17(3), 410.
- Hwang, K. E., Song, H. Y., Jung, J. W., Oh, S. J., Yoon, K. H., Park, D. S., & Kim, H. R. Pleural fluid characteristics of pleuropulmonary paragonimiasis masquerading as pleural tuberculosis. The Korean journal of internal medicine 2015, 30(1), 56.
- Sharifi, Y., Sadjjadi, S. M., Jafari, S. H., Nikoupour Deilami, H., Mardani, P., & Solgi, R. Application and evaluation of native antigen B from Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto and E. canadensis alone or mixture for serodiagnosis of human G1-G3 and G6/G7 genotypes cystic echinococcosis sera, using ELISA and Western blotting. Parasitology Research 2023, 1-10.
- del Carmen Medina-Rojas, R., Zuñiga-Sanchez, H. A., Castillo-Coaquira, I. E., Sucari-Turpo, W. G., Hoces-La-Rosa, Z. P., & Sarayasi-Alencastre, Y. Western Blot for the diagnosis of the acute and chronic phase of animal and human fasciolosis, using different antigens of Fasciola hepatica. Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences 2023, 10(3S), 1362-1373.
- Suescún-Carrero, S. H., Tadger, P., Sandoval Cuellar, C., Armadans-Gil, L., & Ramirez Lopez, L. X. Rapid diagnostic tests and ELISA for diagnosing chronic Chagas disease: Systematic revision and meta-analysis. PLoS neglected tropical diseases 2022, 16(10), e0010860.
- Meftahi, G. H., Bahari, Z., Zarei Mahmoudabadi, A., Iman, M., & Jangravi, Z. Applications of western blot technique: From bench to bedside. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education 2021, 49(4), 509-517.
- Qiu, X. G., Nakamura-Uchiyama, F., Nawa, Y., & Itoh, M. A tool for mass-screening of paragonimiasis: an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with urine samples. Tropical Medicine and Health 2016, 44(1), 1-4.
- Kim, J. G., Ahn, C. S., Kang, I., Shin, J. W., Jeong, H. B., Nawa, Y., & Kong, Y. Cerebral paragonimiasis: Clinicoradiological features and serodiagnosis using recombinant yolk ferritin. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2022, 16(3), e0010240.
- Rosa, B. A., Choi, Y. J., McNulty, S. N., Jung, H., Martin, J., Agatsuma, T., & Mitreva, M. Comparative genomics and transcriptomics of 4 Paragonimus species provide insights into lung fluke parasitism and pathogenesis. GigaScience 2020, 9(7), giaa073.
- Oey, H., Zakrzewski, M., Narain, K., Devi, K. R., Agatsuma, T., Nawaratna, S., & Krause, L. Whole-genome sequence of the oriental lung fluke Paragonimus westermani. Gigascience 2019, 8(1), giy146.
- Doanh, N. P., Tu, A. L., Bui, T. D., Loan, T. H., Nonaka, N., Horii, Y., & Nawa, Y. Molecular and morphological variation of Paragonimus westermani in Vietnam with records of new second intermediate crab hosts and a new locality in a northern province. Parasitology 2016, 143(12), 1639-1646.
- Persichetti, M. F., Solano-Gallego, L., Vullo, A., Masucci, M., Marty, P., Delaunay, P., & Pennisi, M. G. Diagnostic performance of ELISA, IFAT and Western blot for the detection of anti-Leishmania infantum antibodies in cats using a Bayesian analysis without a gold standard. Parasites & vectors 2017, 10, 1-8.
- Gómez-Morales, M. A., Ludovisi, A., Amati, M., Blaga, R., Zivojinovic, M., Ribicich, M., & Pozio, E. A distinctive Western blot pattern to recognize Trichinella infections in humans and pigs. International Journal for Parasitology 2012, 42(11), 1017-1023.
- Shiguekawa, K. Y. M., Mineo, J. R., de Moura, L. P., & Costa-Cruz, J. M. ELISA and western blotting tests in the detection of IgG antibodies to Taenia solium metacestodes in serum samples in human neurocysticercosis. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2000, 5(6), 443-449.
- Yeshi, K., Ruscher, R., Loukas, A., & Wangchuk, P. Immunomodulatory and biological properties of helminth-derived small molecules: Potential applications in diagnostics and therapeutics. Frontiers in Parasitology 2022, 1, 984152.
- Becerro-Recio, D., González-Miguel, J., Ucero, A., Sotillo, J., Martínez-Moreno, Á., Pérez-Arévalo, J., & Siles-Lucas, M. Recognition pattern of the Fasciola hepatica excretome/secretome during the course of an experimental infection in sheep by 2D Immunoproteomics. Pathogens 2021, 10(6), 725.
- Grzelak, S., Stachyra, A., Stefaniak, J., Mrówka, K., Moskwa, B., & Bień-Kalinowska, J. Immunoproteomic analysis of Trichinella spiralis and Trichinella britovi excretory-secretory muscle larvae proteins recognized by sera from humans infected with Trichinella. PLoS One 2020, 15(11), e0241918.
- Pedroza-Gómez, Y. J., Cossio-Bayugar, R., Aguilar-Díaz, H., Scarcella, S., Reynaud, E., Sanchez-Carbente, M. D. R., & Miranda-Miranda, E. Transcriptome-Based Identification of a Functional Fasciola Hepatica Carboxylesterase B. Pathogens 2021, 10(11), 1454.
- Ahn, C. S., Na, B. K., Chung, D. L., Kim, J. G., Kim, J. T., & Kong, Y. Expression characteristics and specific antibody reactivity of diverse cathepsin F members of Paragonimus westermani. Parasitology international 2015, 64(1), 37-42.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).