Submitted:
31 October 2023
Posted:
01 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The DNA and RNA Sequencing
2.2. Genome Assembling and Gene Prediction
2.3. Identification of Antithrombotic Genes
2.4. Variation Analysis of Antithrombotic Proteins
2.5. Anticoagulation Analyses of Hirudins
3. Results
3.1. This Genome Sequencing and Assembling
3.2. Gene prediction and Annotation
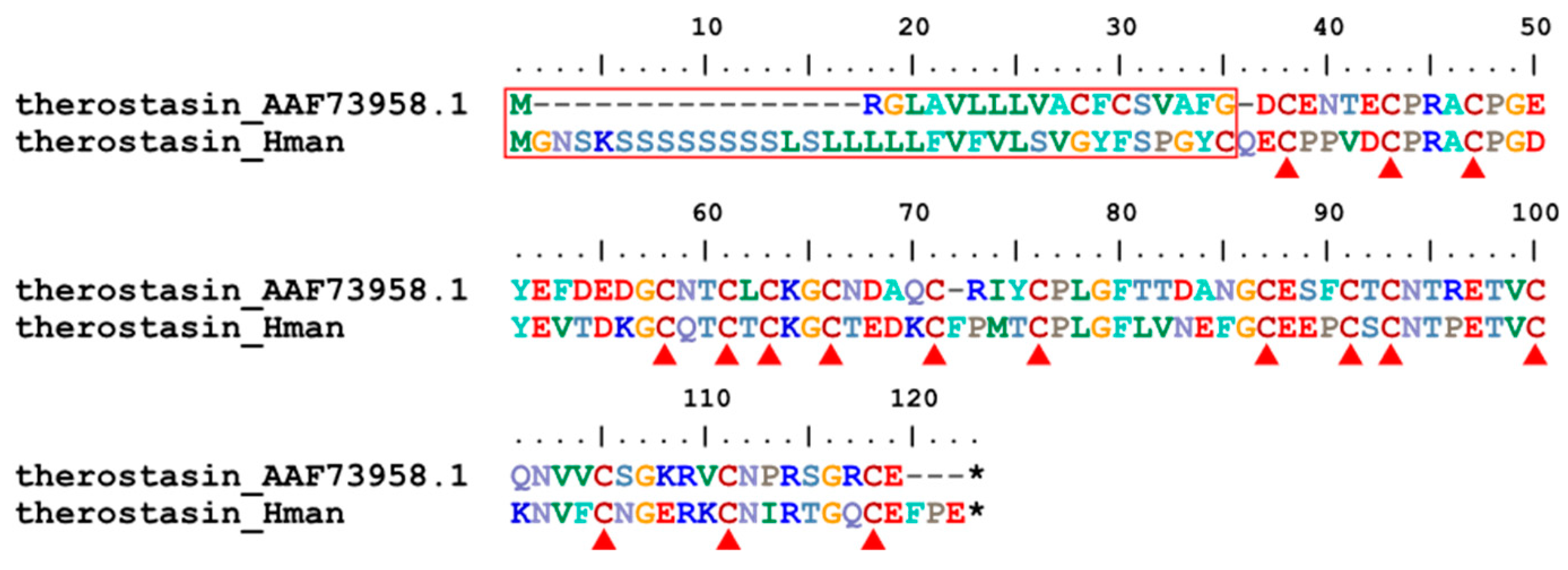
3.3. Identification of Antithrombotic Genes
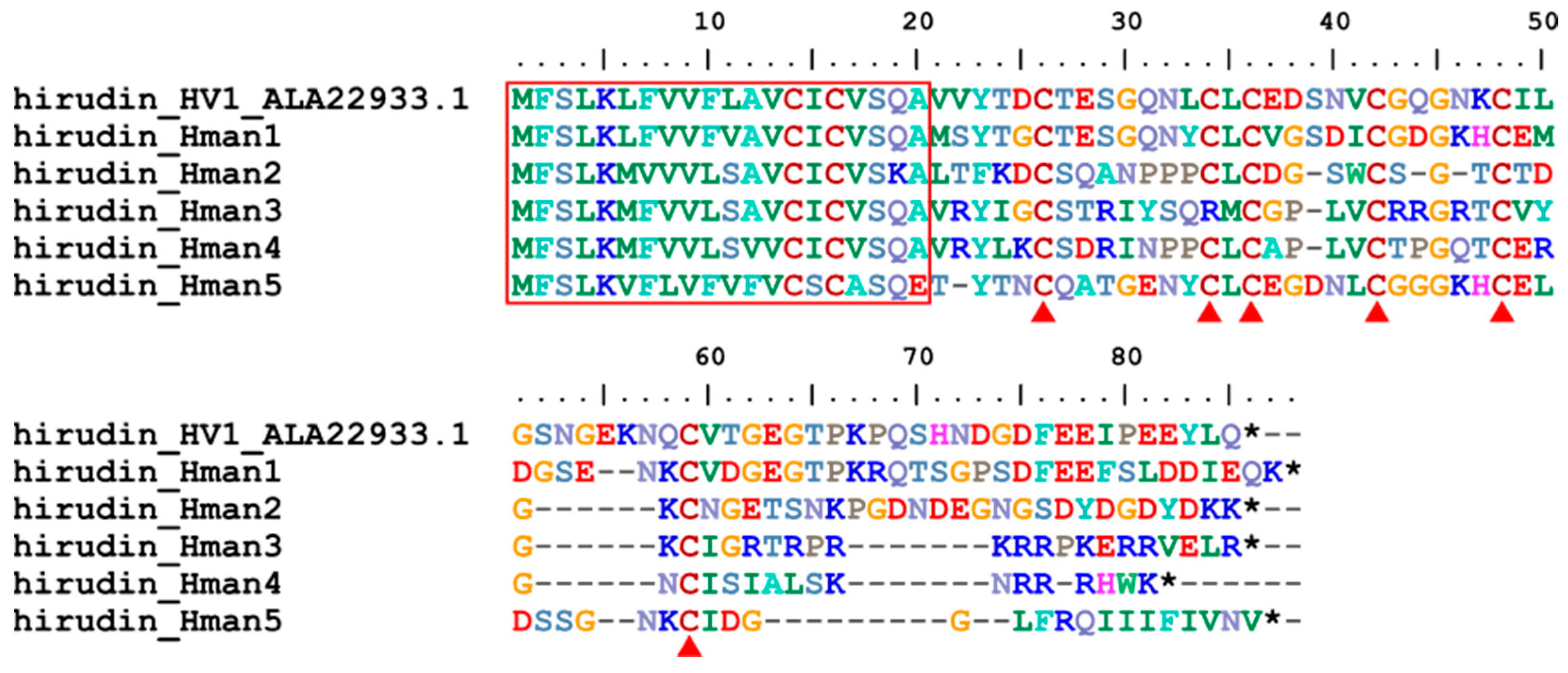
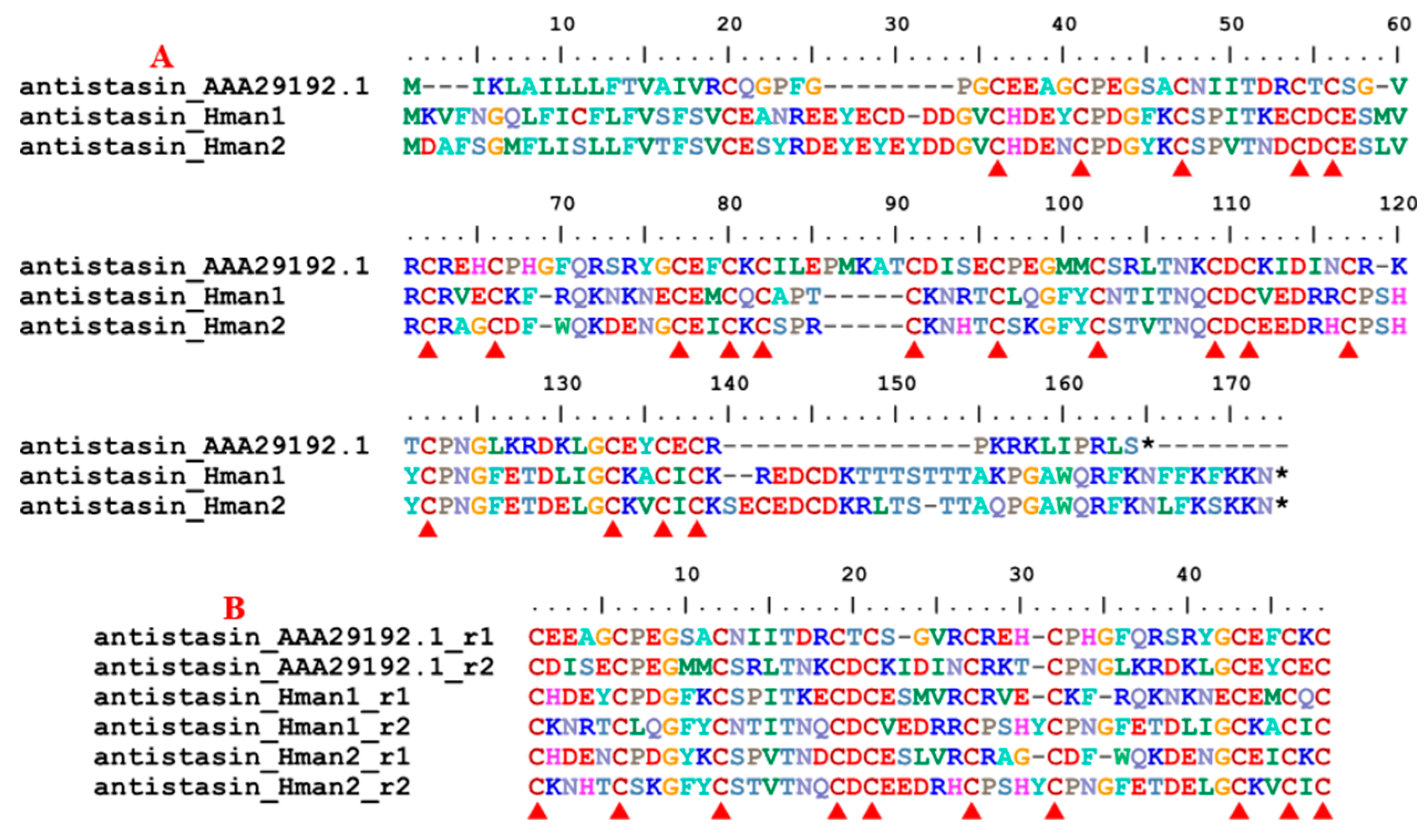
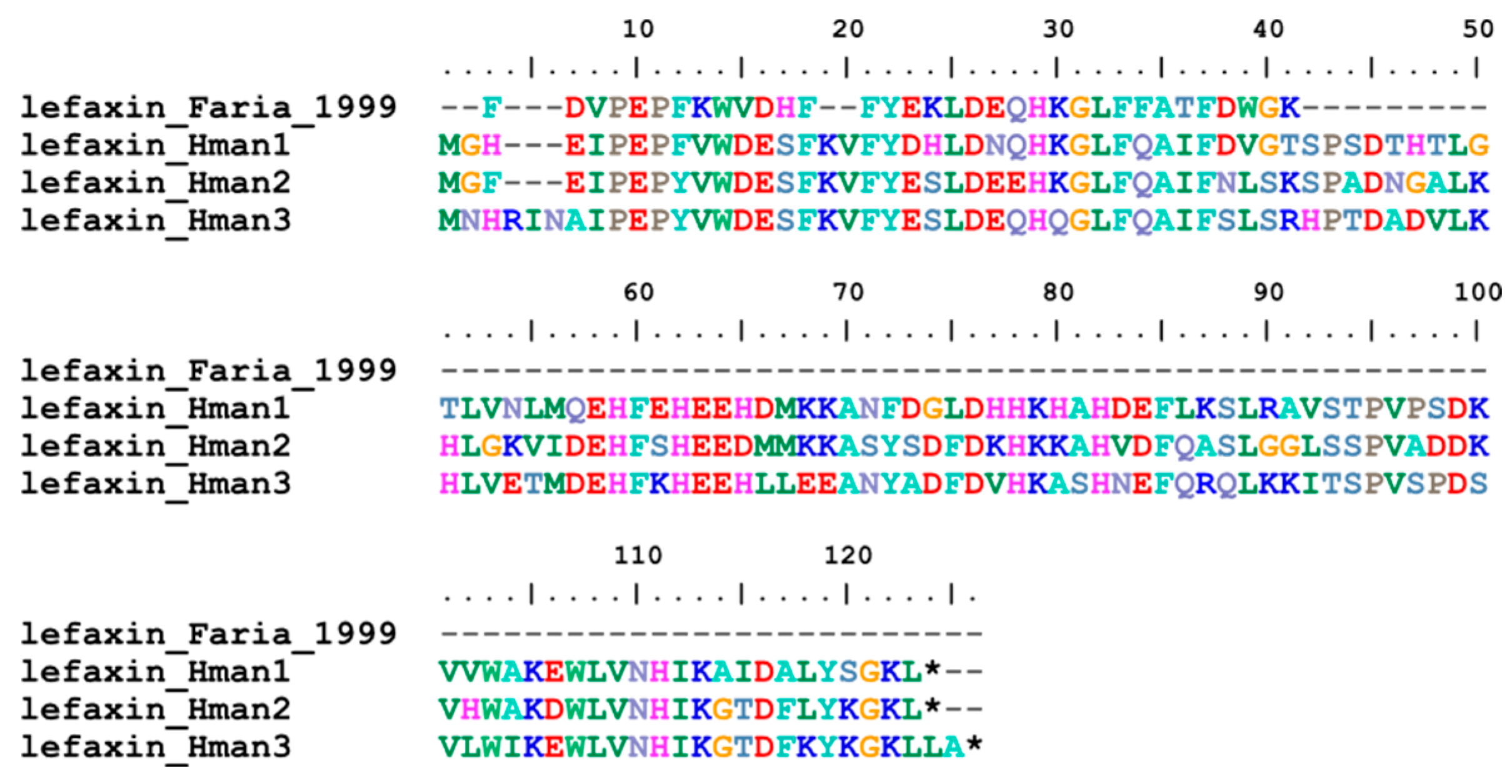
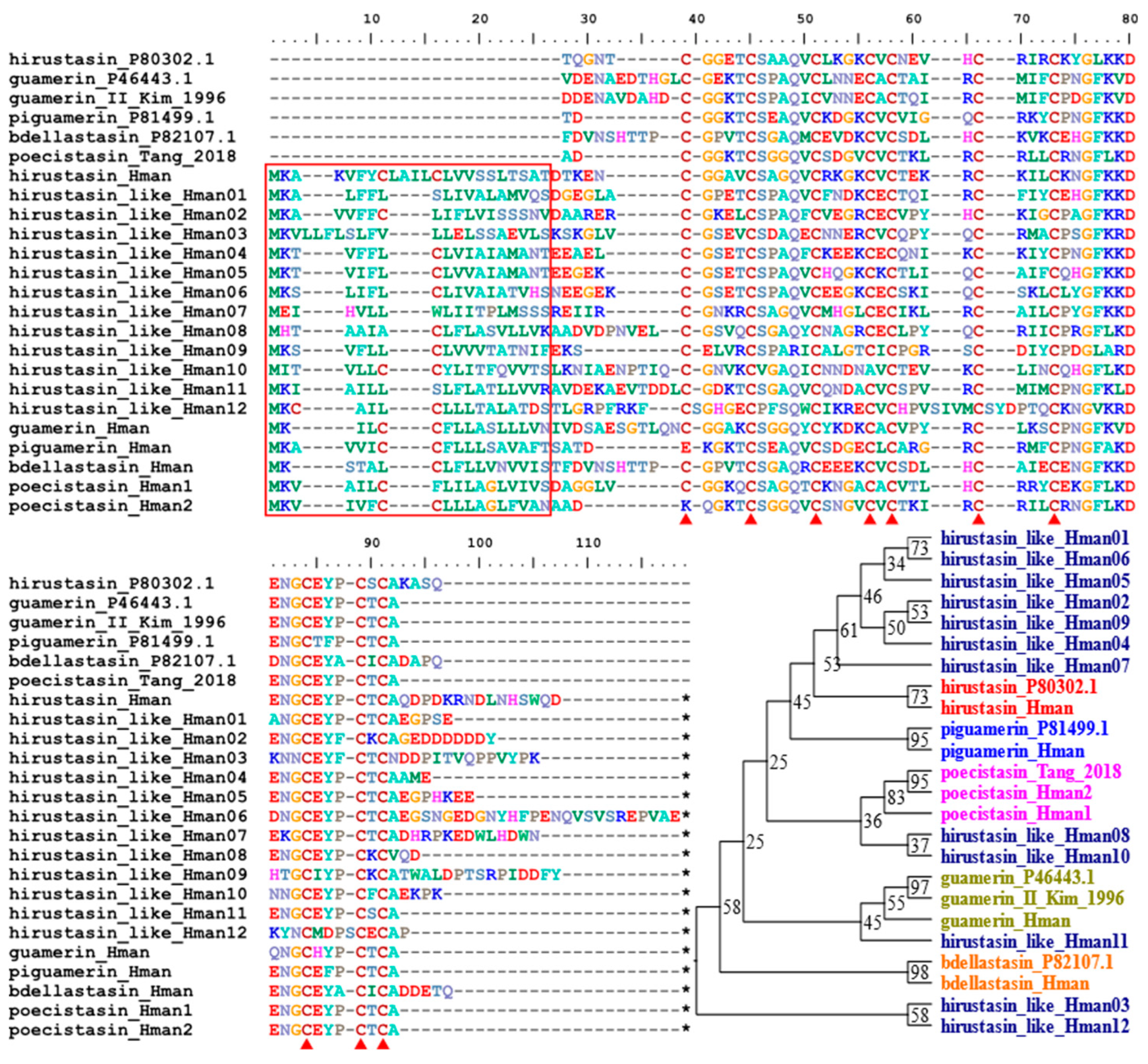
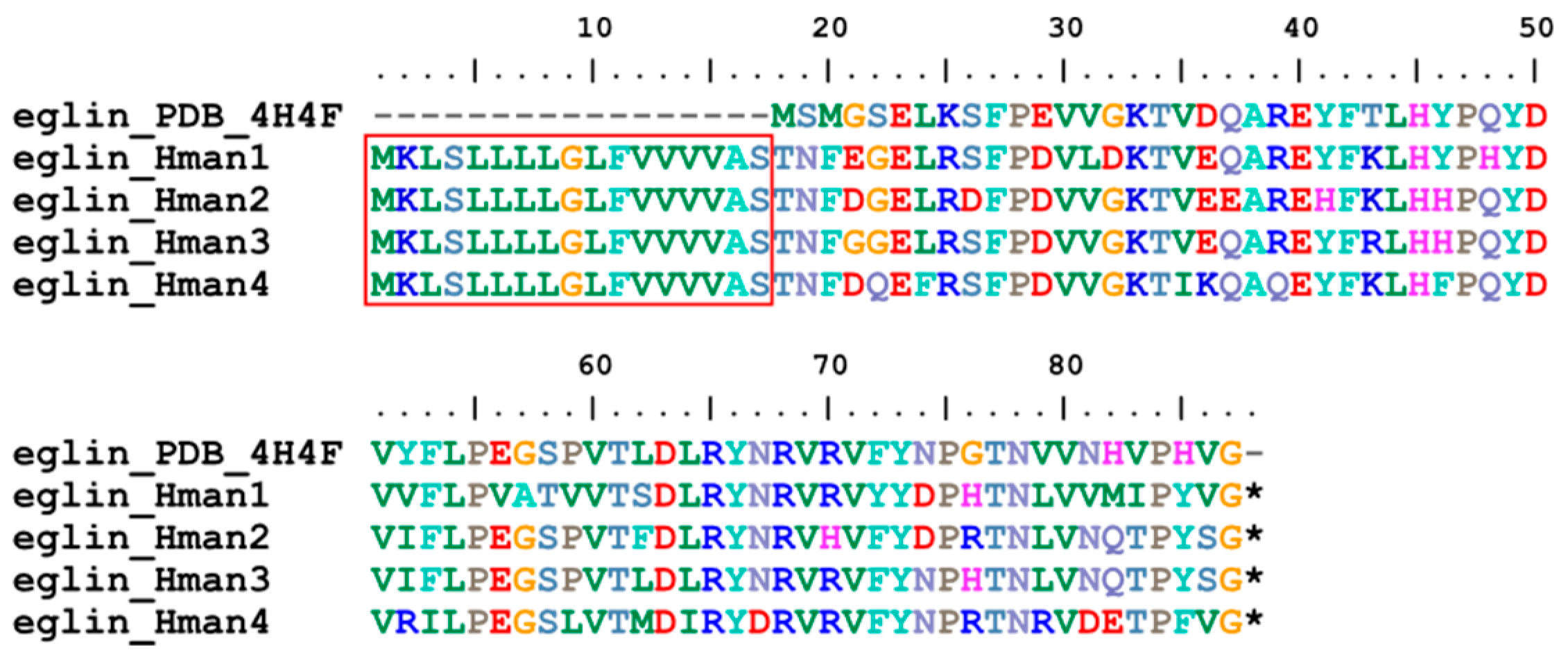
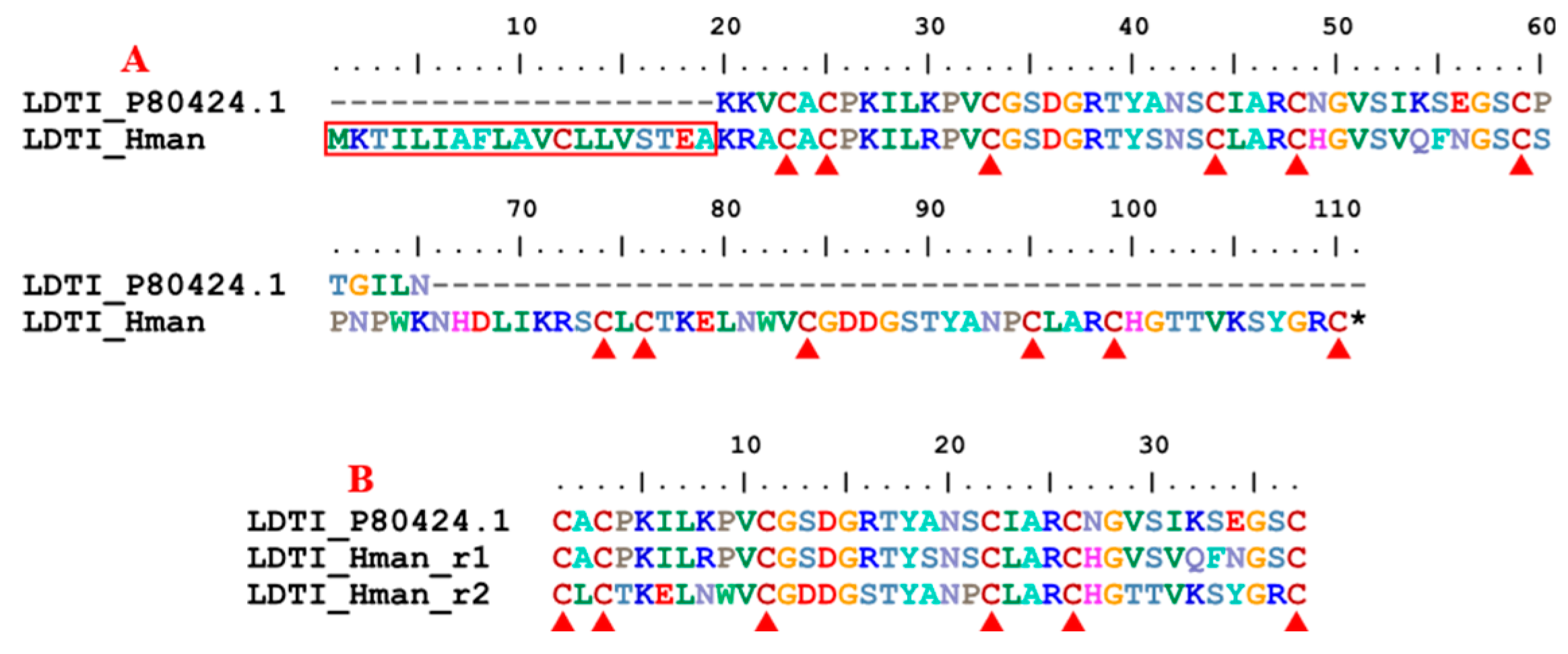
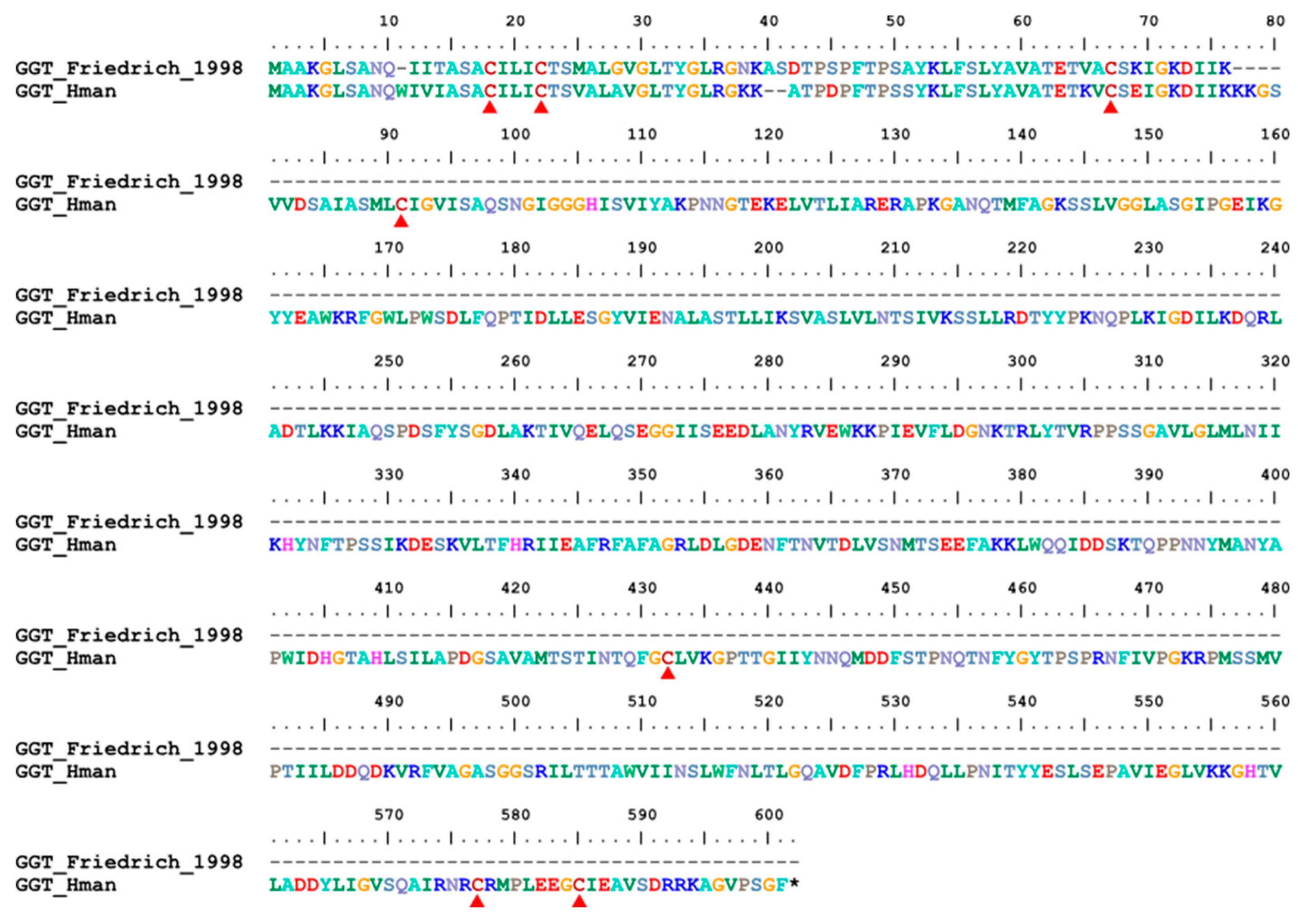
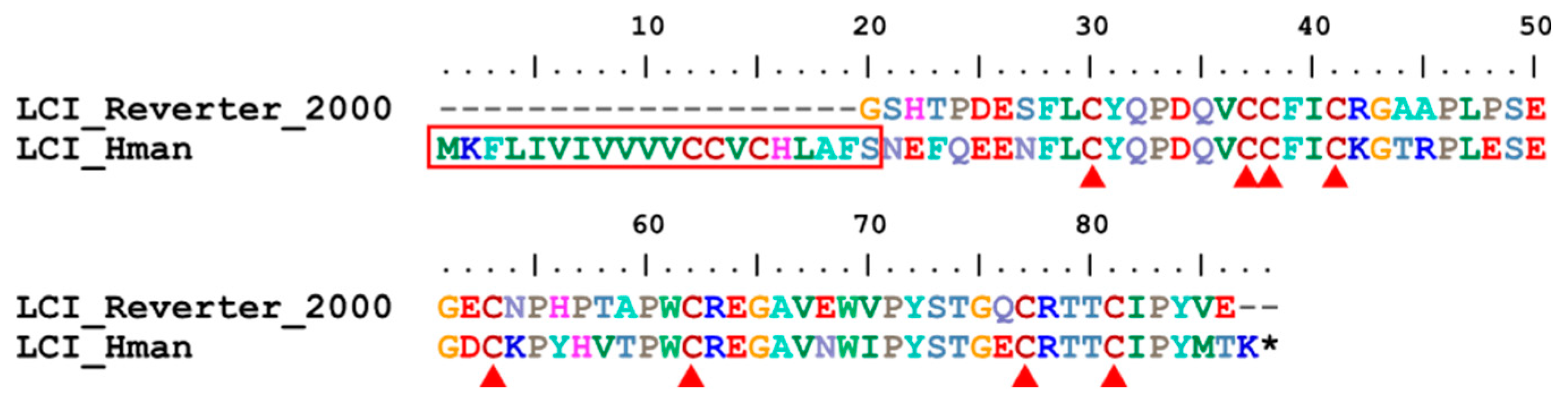
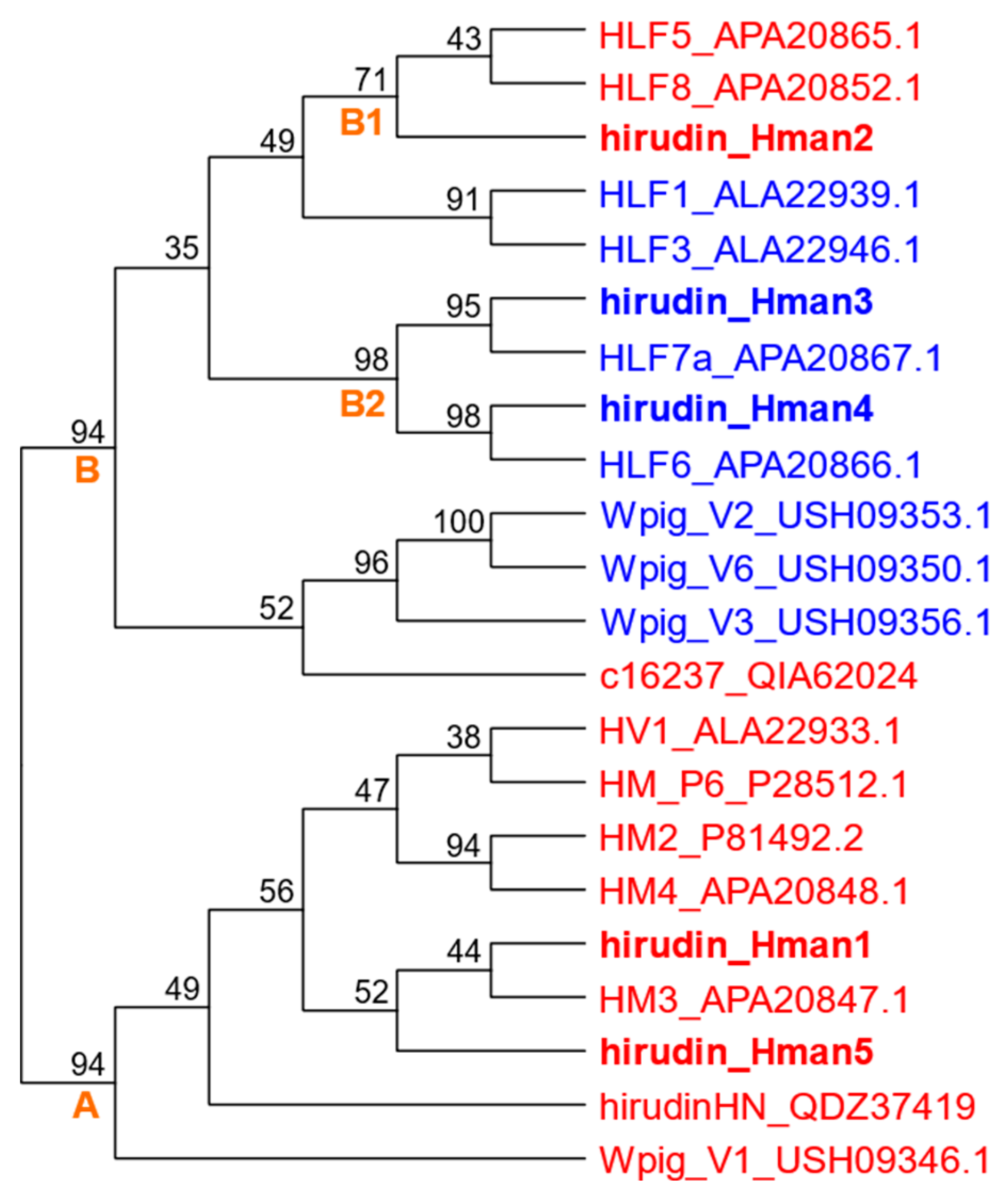
3.4. Genetic Variation of Antithrombotic Proteins
3.5. Anticoagulation of Recombinant Hirudins
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeLoughery, T.G. Hemostasis and thrombosis. Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Switzerland, 2019.
- WHO. The top 10 causes of death. 2020.
- Mackman, N.; Bergmeier, W.; Stouffer, G.A.; Weitz, J.I. Therapeutic strategies for thrombosis: new targets and approaches. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 333–352. [CrossRef]
- Elantably, D.; Mourad, A.; Elantably, A.; Effat, M. Warfarin induced leukocytoclastic vasculitis: an extraordinary side effect. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 49, 149–152. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, Q.; Qiu, K.; Liu, M. Use of anticoagulant therapy and cerebral microbleeds: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 1666–1679. [CrossRef]
- Al-Husein, B.A.; Al-Azzam, S.I.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Khabour, O.F.; Nusair, M.B.; Alzayadeen, S. Investigating the Effect of Demographics, Clinical Characteristics, and Polymorphism of MDR-1, CYP1A2, CYP3A4, and CYP3A5 on Clopidogrel Resistance. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 72, 296–302. [CrossRef]
- Giahchi, F.; Mohammadi, M. Reteplase versus Streptokinase in Management of ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction; a Letter to the Editor. Adv J Emerg Med 2019, 3, e34. [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.T. Leech biology and behaviour. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1986.
- Kvist, S.; Manzano-Marín, A.; de Carle, D.; Trontelj, P.; Siddall, M.E. Draft genome of the European medicinal leech Hirudo medicinalis (Annelida, Clitellata, Hirudiniformes) with emphasis on anticoagulants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9885. [CrossRef]
- Sket, B.; Trontelj, P. Global diversity of leeches (Hirudinea) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 129–137. [CrossRef]
- Sig, A.K.; Guney, M.; Guclu, A.U.; Ozmen, E. Medicinal leech therapy—an overall perspective. Integr. Med. Res. 2017, 6, 337–343. [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, X.; Chen, H. Research progress in the use of leeches for medical purposes. Tradit. Med. Res. 2021, 6, 56-69. [CrossRef]
- Shakouri, A.; Adljouy, N.; Balkani, S.; Mohamadi, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Abdolalizadeh, J.; Shakouri, S.K. Effectiveness of topical gel of medical leech (Hirudo medicinalis) saliva extract on patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized clinical trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pr. 2018, 31, 352–359. [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, C.-D.; Stange, R.; Steckhan, N.; Robens, S.; Ostermann, T.; Paetow, A.; Michalsen, A. The Effectiveness of Leech Therapy in Chronic Low Back Pain. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Online 2018, 115, 785–792. [CrossRef]
- Hamidizadeh, N.; Azizi, A.; Zarshenas, M.M.; Ranjbar, S. Leech therapy in treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis: a case report. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 15, 407–410. [CrossRef]
- Michalsen, A.; Roth, M.; Dobos, G.; Aurich, M.; Blessmann, M.; Flecken, P.; Graf, J.; Gross, U.; Schmelzle, R.; Storck, U.; et al. Medicinal Leech Therapy; Georg Thieme Verlag KG: Stuttgart, Germany, 2007; ISBN: 9781588905635.
- Elyassi, A.R.; Terres, J.; Rowshan, H.H. Medicinal leech therapy on head and neck patients: a review of literature and proposed protocol. Oral Surgery, Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 116, e167–e172. [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Ren, J.-X.; Wang, J.-J.; Ding, L.-S.; Zhao, J.-J.; Liu, S.-Y.; Gao, H.-M. Chinese Medicinal Leech: Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Activities. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 7895935. [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lyu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, L.; Tong, X. Treatment of Human Urinary Kallidinogenase Combined with Maixuekang Capsule Promotes Good Functional Outcome in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 84. [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.M.A.; Jameel, S.S.; Zaman, F.; Jilani, S.; Sultana, A.; A Khan, S. A systematic overview of the medicinal importance of sanguivorous leeches. Altern Med Rev. 2011, 16, 59–65.
- Fritsma, G.A. Monitoring the Direct Thrombin Inhibitors. Am. Soc. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2013, 26, 54–57. [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Lukas, P.; Böhmert, M.; Hildebrandt, J. Hirudin or hirudin-like factor - that is the question: insights from the analyses of natural and synthetic HLF variants. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 841–850. [CrossRef]
- Mousa, R.; Hidmi, T.; Pomyalov, S.; Lansky, S.; Khouri, L.; Shalev, D.E.; Shoham, G.; Metanis, N. Diselenide crosslinks for enhanced and simplified oxidative protein folding. Commun. Chem. 2021, 4, 30. [CrossRef]
- Montinari, M.R.; Minelli, S. From ancient leech to direct thrombin inhibitors and beyond: New from old. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112878. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.R.; Xie, X.F.; Zhang, H.Q.; Li, G.M.; Yin, Y.P.; Cao, X.Y.; Gao, Y.Q.; Li, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, F.; et al. Pharmacological activities and mechanisms of hirudin and its derivatives—a review. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 660757. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.-M.; Tang, X.-P.; Long, A.-L.; Mwangi, J.; Lai, R.; Sun, R.-P.; Long, C.-B.; Zhang, Z.-Q. Purification and characterization of a novel anti-coagulant from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Zool. Res. 2019, 40, 205–210. [CrossRef]
- Zavalova, L.; Lukyanov, S.; Baskova, I.; Snezhkov, E.; Akopov, S.; Berezhnoy, S.; Bogdanova, E.; Barsova, E.; Sverdlov, E.D. Genes from the medicinal leech (Hirudo medicinalis) coding for unusual enzymes that specifically cleave endo-epsilon (gamma-Glu)-Lys isopeptide bonds and help to dissolve blood clots. Mol Gen Genet 1996, 253, 20-25. [CrossRef]
- Holak, T.A.; Avilés, F.X.; Reverter, D.; Fernández-Catalán, C.; Baumgartner, R.; Pfänder, R.; Huber, R.; Bode, W.; Vendrell, J. Structure of a novel leech carboxypeptidase inhibitor determined free in solution and in complex with human carboxypeptidase A2. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 322–328. [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Du, G.; Chen, J. High-yield novel leech hyaluronidase to expedite the preparation of specific hyaluronan oligomers. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4471. [CrossRef]
- Gronwald, W.; Bomke, J.; Maurer, T.; Domogalla, B.; Huber, F.; Schumann, F.; Kremer, W.; Fink, F.; Rysiok, T.; Frech, M.; et al. Structure of the Leech Protein Saratin and Characterization of Its Binding to Collagen. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 381, 913–927. [CrossRef]
- Kvist, S.; Min, G.; E Siddall, M. Diversity and selective pressures of anticoagulants in three medicinal leeches (Hirudinida: Hirudinidae, Macrobdellidae). Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 918–933. [CrossRef]
- Iwama, R.E.; Tessler, M.; Kvist, S. Leech anticoagulants are ancestral and likely to be multifunctional. Zoöl. J. Linn. Soc. 2022, 196, 137–148. [CrossRef]
- Babenko, V.V.; Podgorny, O.V.; Manuvera, V.A.; Kasianov, A.S.; Manolov, A.I.; Grafskaia, E.N.; Shirokov, D.A.; Kurdyumov, A.S.; Vinogradov, D.V.; Nikitina, A.S.; et al. Draft genome sequences of Hirudo medicinalis and salivary transcriptome of three closely related medicinal leeches. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 331. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Wu, F.; Wang, G.; Feng, X.; Ombati, R.; Zuo, R.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; et al. Prostaglandin E1 Is an Efficient Molecular Tool for Forest Leech Blood Sucking. Front. Veter- Sci. 2021, 7, 615915. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Yan, X.; Shan, H.; Ma, X.; Zhou, W.; Xu, W.; Lu, L.; et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying hematophagia revealed by comparative analyses of leech genomes. GigaScience 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Haase, M.; Lemke, S.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. Hirudins and hirudin-like factors in Hirudinidae: implications for function and phylogenetic relationships. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 313–325. [CrossRef]
- Panha, S.; Tubtimon, J.; Jeratthitikul, E.; Sutcharit, C.; Kongim, B. Systematics of the freshwater leech genus Hirudinaria Whitman, 1886 (Arhynchobdellida, Hirudinidae) from northeastern Thailand. ZooKeys 2014, 452, 15–33. [CrossRef]
- Jeratthitikul, E.; Jiranuntskul, P.; Nakano, T.; Sutcharit, C.; Panha, S. A new species of buffalo leech in the genus Hirudinaria Whitman, 1886 (Arhynchobdellida, Hirudinidae) from Thailand. ZooKeys 2020, 933, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Electricwala, A.; Hartwell, R.; Scawen, M.D.; Atkinson, T. The complete amino acid sequence of a hirudin variant from the leechHirudinaria manillensis. J Protein Chem 1993, 12, 365–370. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Guo, Q.-S.; Shi, H.-Z.; Cheng, B.-X.; Lu, Y.-X.; Gou, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, W.-B.; Yan, S.-M.; Wu, M.-J. Genetic variation in Whitmania pigra, Hirudo nipponica and Poecilobdella manillensis, three endemic and endangered species in China using SSR and TRAP markers. Gene 2016, 579, 172–182. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Gong, Y.; Yu, X.; Lv, J.Y. Anticoagulant active substances extraction and anti-thrombin activity analysis of several species of leeches. Acta Sci Nat Univ Sun 2012, 51, 92-96. [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.-L.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.-K.; Li, Y.; Mi, D.; Ma, L.-B.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Xu, S.-Q.; Qiu, Q. Draft Genome of the Asian Buffalo Leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1321. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Fan, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, S. NextPolish: a fast and efficient genome polishing tool for long-read assembly. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2253–2255. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078-2079. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Wang, C.; Meyer, C.A.; Liu, T.; Tang, M.; Aluru, S.; Yue, F.; et al. Fast alignment and preprocessing of chromatin profiles with Chromap. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6566. [CrossRef]
- Durand, N.C.; Shamim, M.S.; Machol, I.; Rao, S.S.P.; Huntley, M.H.; Lander, E.S.; Aiden, E.L. Juicer Provides a One-Click System for Analyzing Loop-Resolution Hi-C Experiments. Cell Syst. 2016, 3, 95–98. [CrossRef]
- Durand, N.C.; Robinson, J.T.; Shamim, M.S.; Machol, I.; Mesirov, J.P.; Lander, E.S.; Aiden, E.L. Juicebox Provides a Visualization System for Hi-C Contact Maps with Unlimited Zoom. Cell Syst. 2016, 3, 99–101. [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: a fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [CrossRef]
- Seppey, M.; Manni, M.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing Genome Assembly and Annotation Completeness. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1962, 227–245. [CrossRef]
- Rhie, A.; Walenz, B.P.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. Merqury: reference-free quality, completeness, and phasing assessment for genome assemblies. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 245. [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.M.; Hubley, R.; Goubert, C.; Rosen, J.; Clark, A.G.; Feschotte, C.; Smit, A.F. RepeatModeler2 for automated genomic discovery of transposable element families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9451–9457. [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Kojima, K.K.; Kohany, O. Repbase Update, a database of repetitive elements in eukaryotic genomes. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 11. [CrossRef]
- Majoros, W.H.; Pertea, M.; Salzberg, S.L. TigrScan and GlimmerHMM: two open source ab initio eukaryotic gene-finders. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2878–2879. [CrossRef]
- Korf, I. Gene finding in novel genomes. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 59. [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.D.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Delcher, A.L.; Mount, S.M.; Wortman, J.R.; Smith, R.K.J.; Hannick, L.I.; Maiti, R.; Ronning, C.M.; Rusch, D.B.; Town, C.D.; et al. Improving the Arabidopsis genome annotation using maximal transcript alignment assemblies. Nucleic Acids Res 2003, 31, 5654-5666. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [CrossRef]
- Hoff, K.J.; Lange, S.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M.; Stanke, M. BRAKER1: Unsupervised RNA-seq-based genome annotation with GeneMark-ET and AUGUSTUS. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 767-769. [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Zhu, W.; Pertea, M.; Allen, J.E.; Orvis, J.; White, O.; Buell, C.R.; Wortman, J.R. Automated eukaryotic gene structure annotation using EVidenceModeler and the Program to Assemble Spliced Alignments. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R7. [CrossRef]
- Pertea, G.; Pertea, M. GFF utilities: GffRead and GffCompare. F1000Res 2020, 9, ISCB Comm J-304.
- Sharma, K.; Singh, A.K.; Maddipatla, D.K.; Deshwal, G.K.; Rao, P.S.; Sharma, H. Eggnog: process optimization and characterization of a dairy-based beverage. J. Dairy Res. 2023, 90, 205–212. [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419.
- Tang, S.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Identification of protein coding regions in RNA transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e78. [CrossRef]
- Slater, G.S.C.; Birney, E. Automated generation of heuristics for biological sequence comparison. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 31. [CrossRef]
- Dainat, J. AGAT: Another gff analysis toolkit to handle annotations in any GTF/GFF format. (v0.7.0). Zenodo 2021. [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Le, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, F. SeqKit: A Cross-Platform and Ultrafast Toolkit for FASTA/Q File Manipulation. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0163962. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, L.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.L.; Zhang, N.; Gu, F.; Li, Y.; Deng, X.J.; Chen, G.P. Expression, purification and characterization of recombinant targeting bifunctional hirudin in Pichia pastoris. Afr J Biotechnol 2009, 8, 5582-5588.
- Commission, C.P. Pharmacopoeia of the people’s republic of China. Medicine Science and Technology Press, Beijing, China, 2020.
- Markwardt, F. Untersuchungen über hirudin. Naturwissenschaften 1955, 42, 537-538.
- Vitali, J.; Martin, P.; Malkowski, M.; Robertson, W.; Lazar, J.; Winant, R.; Johnson, P.; Edwards, B. The structure of a complex of bovine alpha-thrombin and recombinant hirudin at 2.8-A resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 17670–17678. [CrossRef]
- Dodt, J.; Müller, H.P.; Seemüller, U.; Chang, J.Y. The complete amino acid sequence of hirudin, a thrombin specific inhibitor: application of colour carboxymethylation. FEBS Lett 1984, 165, 180-184. [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.P.; Degryse, E.; Stefani, L.; Schamber, F.; Cazenave, J.P.; Courtney, M.; Tolstoshev, P.; Lecocq, J.P. Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for the anticoagulant hirudin from the bloodsucking leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 1084–1088. [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Mescke, K.; Liebig, S.; Mahfoud, H.; Lemke, S.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. More than just one: multiplicity of Hirudins and Hirudin-like Factors in the Medicinal Leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 227–240. [CrossRef]
- Scacheri, E.; Nitti, G.; Valsasina, B.; Orsini, G.; Visco, C.; Ferrera, M.; Sawyer, R.T.; Sarmientos, P. Novel hirudin variants from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Amino acid sequence, cDNA cloning and genomic organization. Eur J Biochem 1993, 214, 295–304. [CrossRef]
- Strube, K.; Kröger, B.; Bialojan, S.; Otte, M.; Dodt, J. Isolation, sequence analysis, and cloning of haemadin. An anticoagulant peptide from the Indian leech. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8590–8595. [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Dai, S.-X.; Kong, D.-J.; Yang, P.-P.; Tong, X.; Tong, X.-R.; Bi, X.-X.; Su, Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Liu, Z.-C. The genome of medicinal leech (Whitmania pigra) and comparative genomic study for exploration of bioactive ingredients. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 76. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Suzuki, G.; Matsuwaki, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Serrano, G.; Beach, T.G.; Yamanouchi, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Nishihara, M. Progranulin regulates lysosomal function and biogenesis through acidification of lysosomes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 969–988. [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Kang, K.W. Purification of Granulin-like Polypeptide from the Blood-Sucking Leech, Hirudo nipponia. Protein Expr. Purif. 1999, 16, 340–346. [CrossRef]
- Mittl, P.R.; Di Marco, S.; Fendrich, G.; Pohlig, G.; Heim, J.; Sommerhoff, C.; Fritz, H.; Priestle, J.P.; Grütter, M.G. A new structural class of serine protease inhibitors revealed by the structure of the hirustasin–kallikrein complex. Structure 1997, 5, 253–264. [CrossRef]
- Dunwiddie, C.; A Thornberry, N.; Bull, H.G.; Sardana, M.; A Friedman, P.; Jacobs, J.W.; Simpson, E. Antistasin, a leech-derived inhibitor of factor Xa. Kinetic analysis of enzyme inhibition and identification of the reactive site. J Biol Chem. 1989, 264, 16694–9. [CrossRef]
- Nutt, E.; Gasic, T.; Rodkey, J.; Gasic, G.J.; Jacobs, J.W.; A Friedman, P.; Simpson, E. The amino acid sequence of antistasin. A potent inhibitor of factor Xa reveals a repeated internal structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 10162–10167. [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, D.T.; Brankamp, R.G.; Manley, G.D.; Cardin, A.D. Amino acid sequence of ghilanten: Anticoagulant-antimetastatic principle of the south American leech, Haementeria ghilianii. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 166, 1384–1389. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Law, S.W.; Keller, P.M.; Kniskern, P.J.; Silberklang, M.; Tung, J.-S.; Gasic, T.B.; Gasic, G.J.; Friedman, P.A.; Ellis, R.W. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding antistasin, a leech-derived protein having anti-coagulant and anti-metastatic properties. Gene 1989, 75, 47–57. [CrossRef]
- Faria, F.; Kelen, E.M.A.; Sampaio, C.A.M.; Bon, C.; Duval, N.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M. A New Factor Xa Inhibitor (Lefaxin) from the Haementeria depressa Leech. Arthritis Res. Ther. 1999, 82, 1469–1473. [CrossRef]
- Chopin, V.; Salzet, M.; Baert, J.-L.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Sautière, P.-E.; Kerckaert, J.-P.; Malecha, J. Therostasin, a Novel Clotting Factor Xa Inhibitor from the Rhynchobdellid Leech, Theromyzon tessulatum. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32701–32707. [CrossRef]
- Söllner, C.; Mentele, R.; Eckerskorn, C.; Fritz, H.; Sommerhoff, C.P. Isolation and characterisation of hirustasin, an antistasin-type serine-proteinase inhibitor from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis. Eur J Biochem 1994, 219, 937-943. [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.I.; Kim, S.I.; Ha, K.-S.; O Joe, C.; Kang, K.W. Isolation and Characterization of Guamerin, a New Human Leukocyte Elastase Inhibitor from Hirudo nipponia. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 13879–13884. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.R.; Kang, K.W. Amino acid sequence of piguamerin, an antistasin-type protease inhibitor from the blood sucking leech Hirudo nipponia. Eur J Biochem 1998, 254, 692-697. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.R.; Hong, S.J.; Ha, K.-S.; O Joe, C.; Kang, K.W. A Cysteine-Rich Serine Protease Inhibitor (Guamerin II) from the Non-Blood Sucking Leech Whitmania edentula: Biochemical Characterization and Amino Acid Sequence Analysis. J. Enzym. Inhib. 1996, 10, 81–91. [CrossRef]
- Moser, M.; Auerswald, E.; Mentele, R.; Eckerskorn, C.; Fritz, H.; Fink, E. Bdellastasin, a serine protease inhibitor of the antistasin family from the medical leech (Hirudo medicinalis)—Primary structure, expression in yeast, and characterisation of native and recombinant inhibitor. Eur J Biochem 1998, 253, 212-220. [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.P.; Chen, M.R.; Duan, Z.L.; Mwangi, J.; Li, P.P.; Lai, R. Isolation and characterization of poecistasin, an anti-thrombotic antistasin-type serine protease inhibitor from leech Poecilobdella manillensis. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 429. [CrossRef]
- Seemüller, U.; Eulitz, M.; Fritz, H.; Strobl, A. Structure of the elastase-cathepsin G inhibitor of the leech Hirudo medicinalis. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980, 361, 1841–6. [CrossRef]
- Renesto, P.; Ferrer-Lopez, P.; Chignard, M. Eglin C and Heparin Inhibition of Platelet Activation Induced by Cathepsin G or Human Neutrophils. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1991, 624, 321–324. [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Knecht, R.; Maschler, R.; Seemüller, U. Elastase-cathepsin G inhibitors eglin b and eglin c differ by a single Tyr----His substitution. A micro-method for the identification of amino-acid substitution. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 1985, 366, 281-286. [CrossRef]
- Fritz, H.; Oppitz, K.H.; Gebhardt, M.; Oppitz, I.; Werle, E.; Marx, R. On the presence of a trypsin-plasmin inhibitor in hirudin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969, 350, 91–2.
- Fink, E.; Rehm, H.; Gippner, C.; Bode, W.; Eulitz, M.; Machleidt, W.; Fritz, H. The primary structure of bdellin B-3 from the leech Hirudo medicinalis. Bdellin B-3 is a compact proteinase inhibitor of a “non-classical” Kazal type. It is present in the leech in a high molecular mass form. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 1986, 367, 1235-1242. [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, M., Jr.; Kato, I. Protein Inhibitors of Proteinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1980, 49, 593–626. [CrossRef]
- Campos, I.T.; Silva, M.M.; Azzolini, S.S.; Souza, A.F.; Sampaio, C.A.; Fritz, H.; Tanaka, A.S. Evaluation of phage display system and leech-derived tryptase inhibitor as a tool for understanding the serine proteinase specificities. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 425, 87–94. [CrossRef]
- Sommerhoff, C.P.; Söllner, C.; Mentele, R.; Piechottka, G.P.; Auerswald, E.A.; Fritz, H. A Kazal-type inhibitor of human mast cell tryptase: isolation from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis, characterization, and sequence analysis. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 1994, 375, 685-694. [CrossRef]
- Pohlig, G.; Fendrich, G.; Knecht, R.; Eder, B.; Piechottka, G.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Heim, J. Purification, Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Recombinant Leech-Derived Tryptase Inhibitor (rLDTI) Expressed at High Level in the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 241, 619–626. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.S.; Silva, M.M.; Torquato, R.J.; Noguti, M.A.; Sampaio, C.A.; Fritz, H.; Auerswald, E.A. Functional phage display of leech-derived tryptase inhibitor (LDTI): construction of a library and selection of thrombin inhibitors. FEBS Lett. 1999, 458, 11–16. [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.-H.; Zhou, M.; Wu, F.-L.; Tang, X.-P.; Lu, Q.-M.; Lai, R.; Long, C.-B. Identification and characterization of a novel elastase inhibitor from Hirudinaria manillensis. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 540–544. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z. Impact of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps on Thrombosis Formation: New Findings and Future Perspective. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 910908. [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.P.; Alshafie, T.A.; Cruz, C.P.; Fan, C.-Y.; Brown, A.T.; Wang, Y.; Eidt, J.F.; Moursi, M.M. Saratin, an Inhibitor of Collagen-Platelet Interaction, Decreases Venous Anastomotic Intimal Hyperplasia in a Canine Dialysis Access Model. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2003, 37, 259–269. [CrossRef]
- White, T.C.; Bernyl, M.A.; Robinson, D.K.; Yin, H.; DeGrado, W.F.; Hanson, S.R.; McCarthy, O.J.T. The leech product saratin is a potent inhibitor of platelet integrin α2β1 and von Willebrand factor binding to collagen. FEBS J 2007, 274, 1481-1491. [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.P.; Eidt, J.; Drouilhet, J.; Brown, A.T.; Wang, Y.; Barnes, C.S.; Moursi, M.M. Saratin, an inhibitor of von Willebrand factor–dependent platelet adhesion, decreases platelet aggregation and intimal hyperplasia in a rat carotid endarterectomy model. J. Vasc. Surg. 2001, 34, 724–729. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Kuang, S.; Shao, G.; Tian, Q.; Gao, T.; Che, X.; Ao, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, F. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of HnSaratin from Hirudo nipponia. Gene 2023, 869, 147401. [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.S.; Krafft, B.; Frech, M.; Hofmann, U.R.; Papendieck, A.; Dahlems, U.; Gellissen, G.; Hoylaerts, M.F. Production and Characterization of Saratin, an Inhibitor of von Willebrand Factor-Dependent Platelet Adhesion to Collagen. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2001, 27, 337–348. [CrossRef]
- Huizinga, E.G.; Schouten, A.; Connolly, T.M.; Kroon, J.; Sixma, J.J.; Gros, P. The structure of leech anti-platelet protein, an inhibitor of haemostasis. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Struct. Biol. 2001, 57, 1071–1078. [CrossRef]
- Pérez, L.A.A.; Tabachnick, W.J. Apyrase activity and adenosine diphosphate induced platelet aggregation inhibition by the salivary gland proteins of Culicoides variipennis, the North American vector of bluetongue viruses. Vet Parasitol 1996, 61, 327-338. [CrossRef]
- Rigbi, M.; Orevi, M.; Eldor, A. Platelet Aggregation and Coagulation Inhibitors in Leech Saliva and Their Roles in Leech Therapy. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1996, 22, 273–278. [CrossRef]
- Agoncillo, A. Meta-analysis on the safety and efficacy of Lumbrokinase in peripheral arterial disease. Eur. Hear. Journal. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Mihara, H.; Sumi, H.; Yoneta, T.; Mizumoto, H.; Ikeda, R.; Seiki, M.; Maruyama, M. A Novel Fibrinolytic Enzyme Extracted from the Earthworm, Lumbricus rubellus. Jpn. J. Physiol. 1991, 41, 461–472. [CrossRef]
- Iannucci, N.; Camperi, S.; Cascone, O. Purification of lumbrokinase from Eisenia fetida using aqueous two-phase systems and anion-exchange chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 64, 131–134. [CrossRef]
- Bobrovsky, P.; Manuvera, V.; Baskova, I.; Nemirova, S.; Medvedev, A.; Lazarev, V. Recombinant Destabilase from Hirudo medicinalis Is Able to Dissolve Human Blood Clots In Vitro. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 2068–2081. [CrossRef]
- Baskova, I.P.; I Nikonov, G. [Destabilase: an enzyme of medicinal leech salivary gland secretion hydrolyzes the isopeptide bonds in stabilized fibrin]. Biokhimiia 1985, 50, 424–31.
- Kurdyumov, A.S.; Manuvera, V.A.; Baskova, I.P.; Lazarev, V.N. A comparison of the enzymatic properties of three recombinant isoforms of thrombolytic and antibacterial protein—Destabilase-Lysozyme from medicinal leech. BMC Biochem. 2015, 16, 27. [CrossRef]
- Castellano, I.; Merlino, A. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidases: Structure and function. In: Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidases, Springer, Basel, 2013.
- Friedrich, T.; Kröger, B.; Koerwer, W.; Strube, K.H.; Meyer, T.; Bialojan, S. An isopeptide bond splitting enzyme from Hirudo medicinalis similar to gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Eur J Biochem 1998, 256, 297-302. [CrossRef]
- Reverter, D.; Vendrell, J.; Canals, F.; Horstmann, J.; Avilés, F.X.; Fritz, H.; Sommerhoff, C.P. A Carboxypeptidase Inhibitor from the Medical Leech Hirudo medicinalis. Isolation, sequence analysis, cDNA cloning, recombinant expression, and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32927–32933. [CrossRef]
- Arolas, J.L.; Castillo, V.; Bronsoms, S.; Aviles, F.X.; Ventura, S. Designing Out Disulfide Bonds of Leech Carboxypeptidase Inhibitor: Implications for Its Folding, Stability and Function. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 392, 529–546. [CrossRef]
- Jung, H. Hyaluronidase: An overview of its properties, applications, and side effects. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2020, 47, 297–300. [CrossRef]
- Linker, A.; Hoffman, P.; Meyer, K. The Hyaluronidase of the Leech: an Endoglucuronidase. Nature 1957, 180, 810–811. [CrossRef]
- Das, B.K. An overview on hirudotherapy/leech therapy. Ind ResJ Pharm Sci 2014, 1, 33-45.
- Hovingh, P.; Linker, A. Hyaluronidase activity in leeches (Hirudinea). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 124, 319–326. [CrossRef]
- Feyertag, F.; Alvarez-Ponce, D. Disulfide Bonds Enable Accelerated Protein Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 1833–1837. [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.A.; Perez-Iratxeta, C.; Ponting, C.P. Protein Repeats: Structures, Functions, and Evolution. J. Struct. Biol. 2001, 134, 117–131. [CrossRef]
- Salzet, M. Anticoagulants and inhibitors of platelet aggregation derived from leeches. FEBS Lett. 2001, 492, 187–192. [CrossRef]
- Electricwala, A.; Sawyer, R.T.; Jones, C.P.; Atkinson, T. Isolation of thrombin inhibitor from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1991, 2, 83–90. [CrossRef]
- Markwardt, F. Hirudin As Alternative Anticoagulant- A Historical Review. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2002, 28, 405–414. [CrossRef]
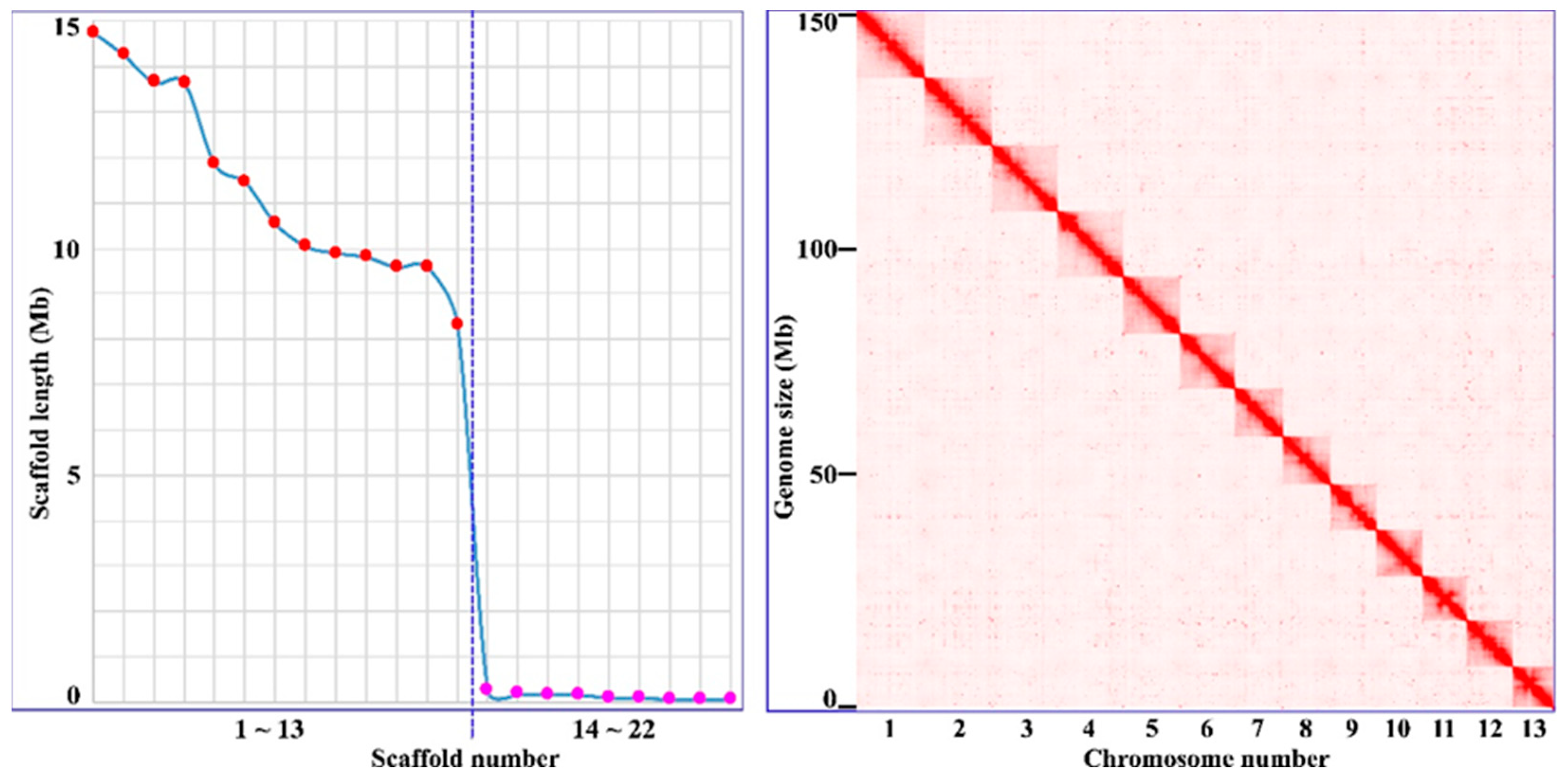




| Annotation approach | Gene number | Total CDS length (Mb) |
N50 of CDS (bp) |
No. of hirudins |
| GlimmerHMM | 56,061 | 31,047,090 | 873 | 2 |
| SNAP | 45,826 | 26,341,403 | 762 | 2 |
| PASA | 37,111 | 33,145,509 | 1,122 | 0 |
| Stringtie | 32,919 | 40,238,799 | 1,554 | 0 |
| BRAKER | 25,331 | 36,676,815 | 2,151 | 3 |
| EVidenceModeler | 21,828 | 26,863,541 | 1,731 | 0 |
| Annotation approach | Gene number | Percentage |
| NR | 17,411 | 68.73% |
| TrEmbl | 17,421 | 68.77% |
| EggNOG | 15,952 | 62.97% |
| Pfam | 15,675 | 61.88% |
| integration | 18,373 | 72.53% |
| No. | Protein | Leech species | Accession/reference | Function |
| 1 | hirudin | H. medicinalis | ALA22933.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
| 2 | granulin | H. nipponia | [83] | coagulation inhibitor |
| 3 | antistasin | Haementeria officinalis | AAA29192.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
| 4 | lefaxin | Haementeria depressa | P86681.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
| 5 | therostasin | Theromyzon tessulatum | AAF73958.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
| 6 | hirustasin | H. medicinalis | P80302.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
| 7 | guamerin | H. nipponia | P46443.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
| 8 | piguamerin | H. nipponia | P81499.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
| 9 | bdellastasin | H. medicinalis | P82107.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
| 10 | poecistasin | H. manillensis | [96] | coagulation inhibitor |
| 11 | eglin | H. medicinails | PDB: 4H4F | coagulation inhibitor |
| 12 | bdellin | H. nipponia | AAK58688.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
| 13 | LDTI | H. medicinails | P80424.1 | coagulation inhibitor |
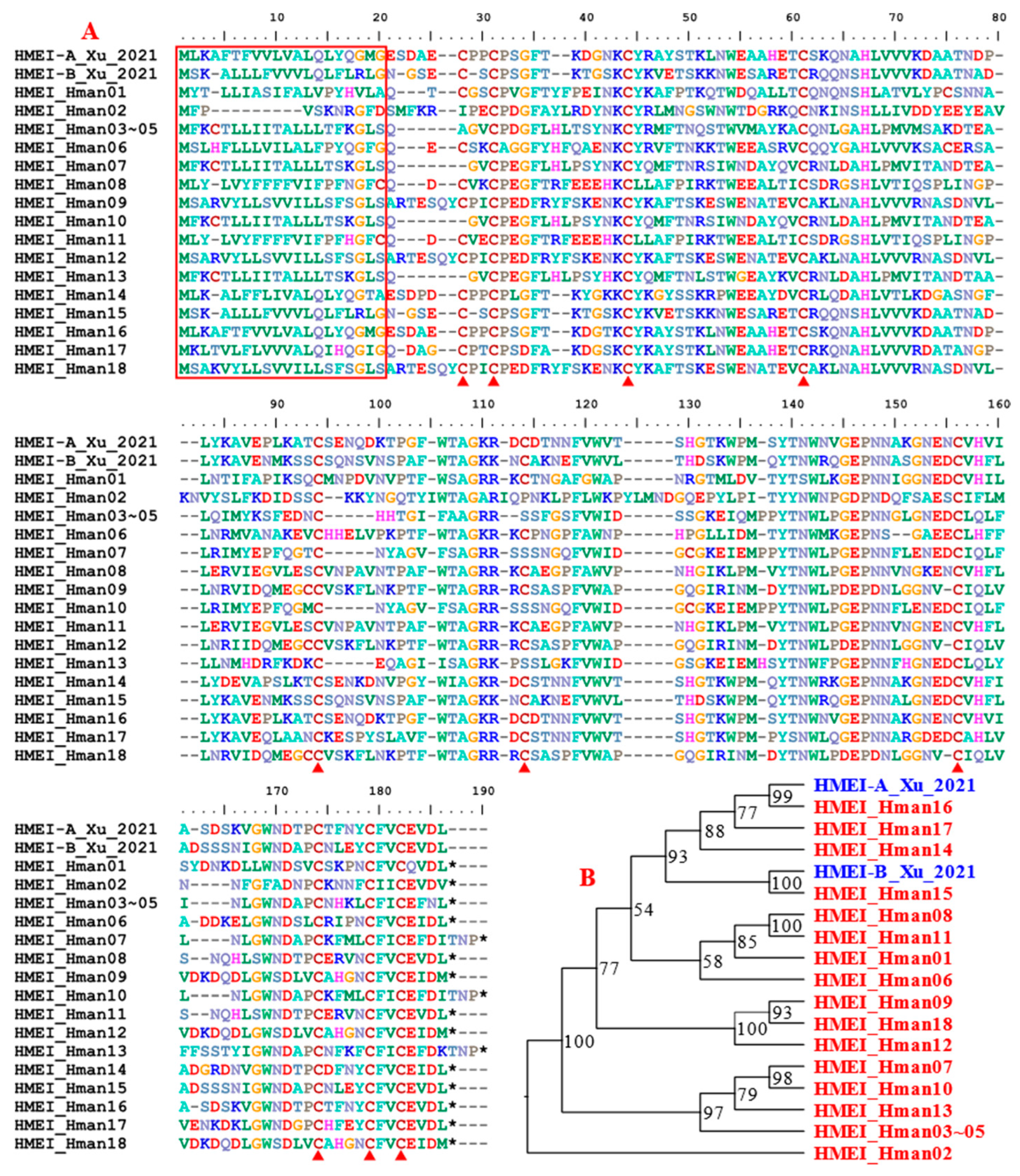
| 14 | HMEI | H. manillensis | [107] | coagulation inhibitor |
| 15 | saratin | H. officinalis | PDB: 2K13 | platelet aggregation inhibitor |
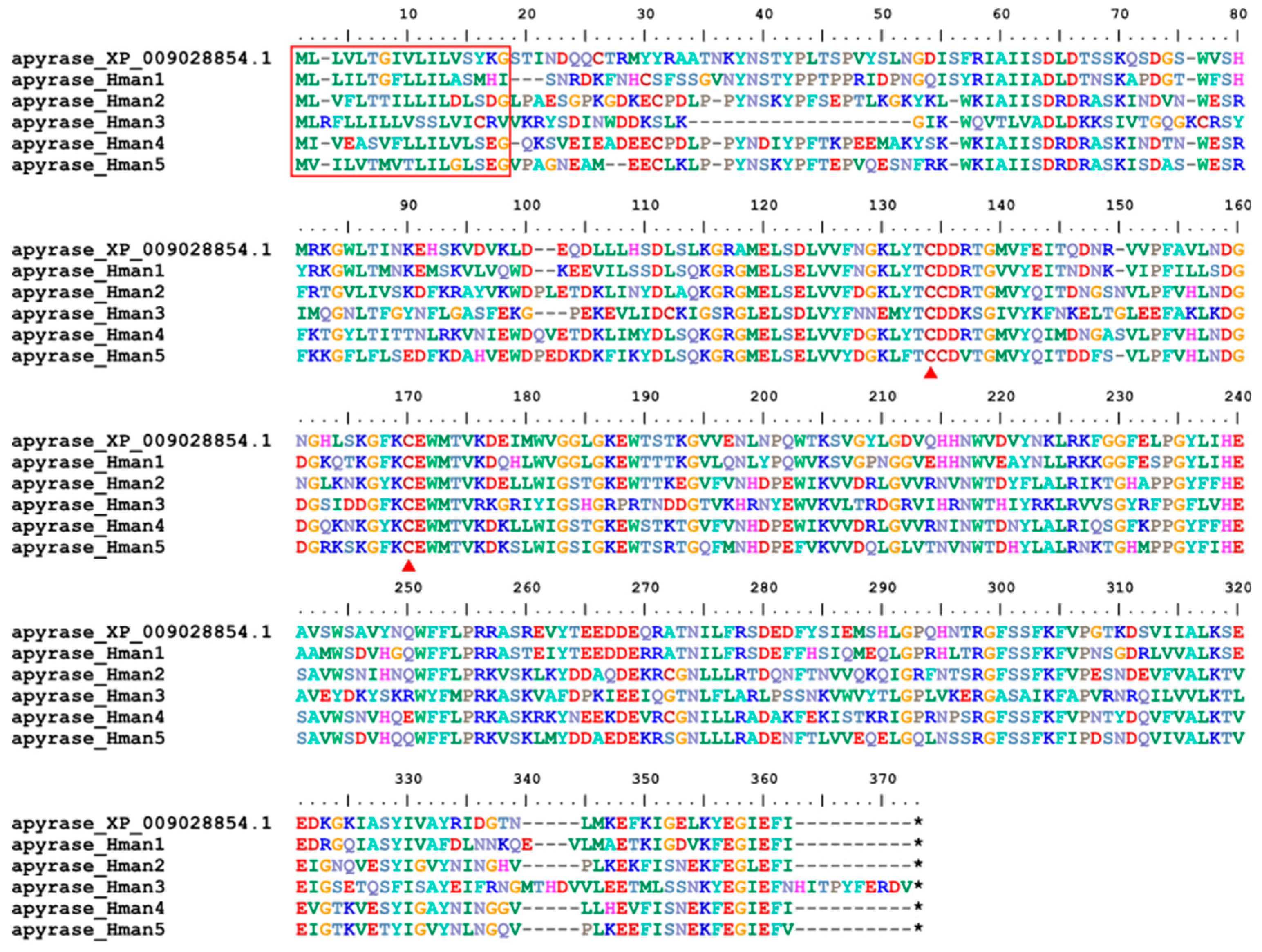
| 16 | apyrase | Helobdella robusta | XP_009028854.1 | platelet aggregation inhibitor |
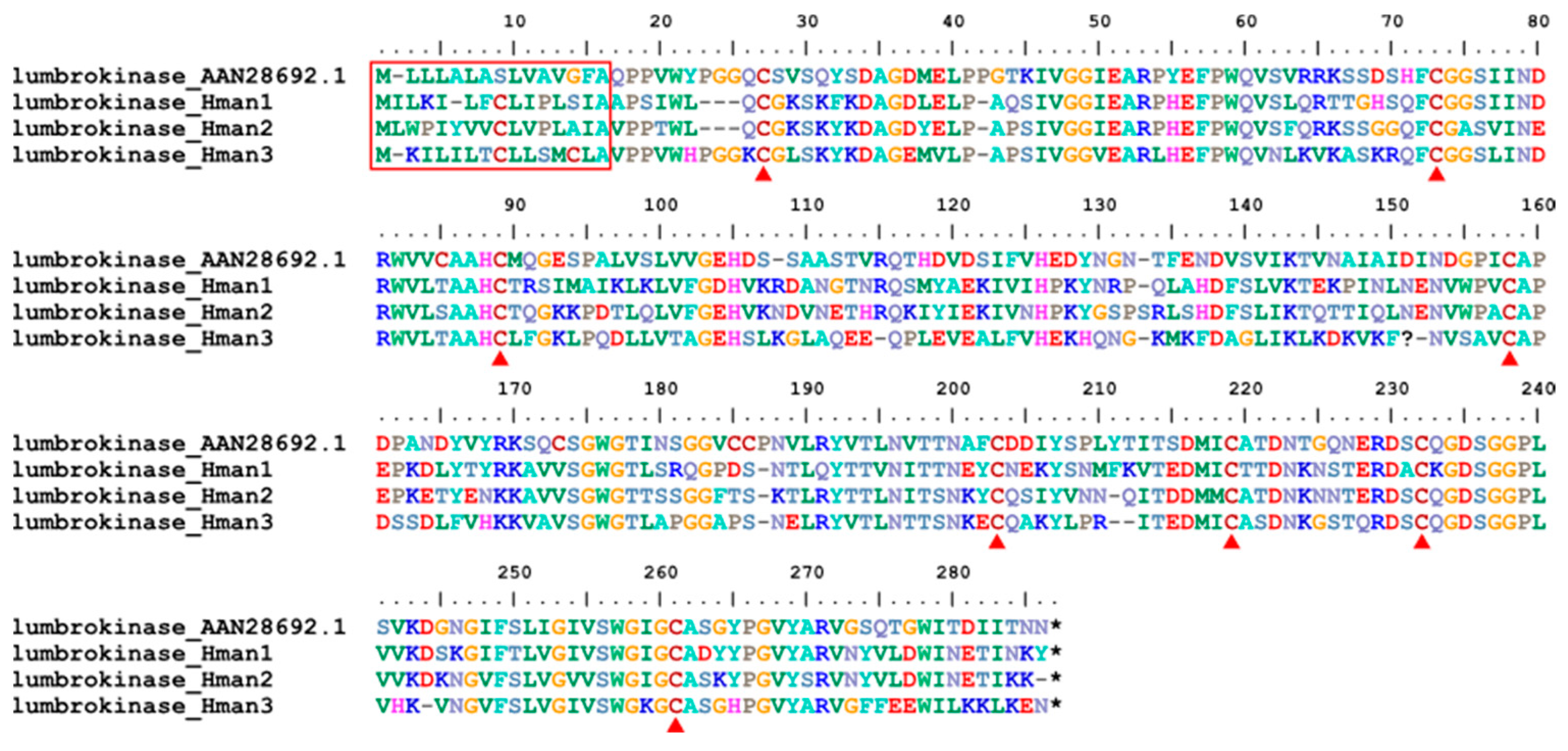
| 17 | lumbrokinase | L. rubellus | AAN28692.1 | platelet aggregation inhibitor |
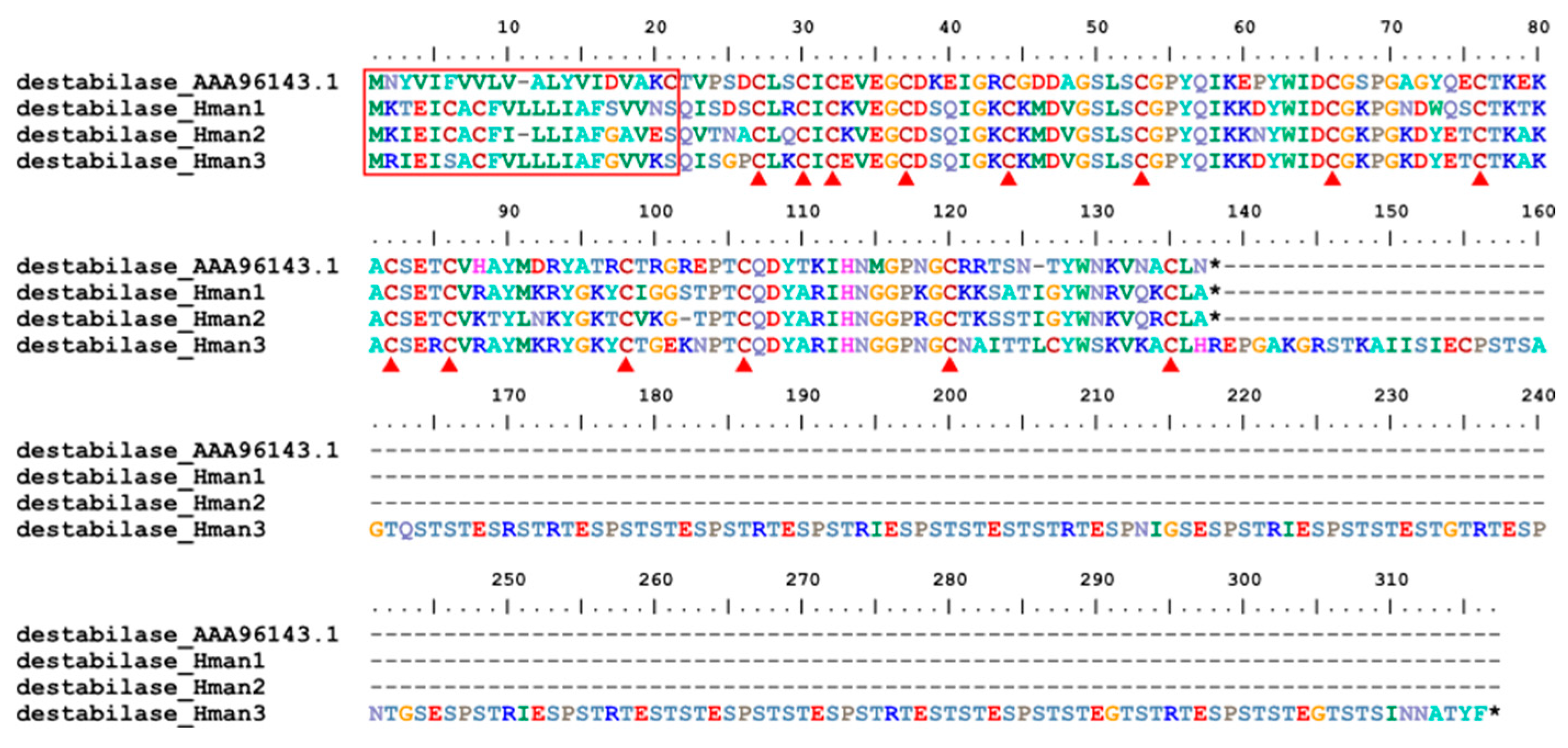
| 18 | destabilase | H. medicinails | AAA96143.1 | fibrinolysis enhancer |
| 19 | GGT | H. medicinails | [124] | fibrinolysis enhancer |
| 20 | LCI | H. medicinails | [28] | fibrinolysis enhancer |
| 21 | hyaluronidase | H. nipponia | AHV78514.1 | tissue penetration enhancer |
| No. | Gene family | Guan et al. [42] | Zheng et al. [35] | BRAKER prediction | BRAKER-plus prediction |
| 1 | hirudin | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| 2 | progranulin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | antistasin | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | lefaxin | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | therostasin | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | hirustasin / hirustasin-like | 1 / 3 | 1 / 5 | 1/11 | 1 / 12 |
| 7 | guamerin | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | piguamerin | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | bdellastasin | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 10 | poecistasin | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 11 | eglin | 0 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| 12 | bdellin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 13 | LDTI | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 14 | HMEI | 4 | 9 | 15 | 18 |
| 15 | saratin | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 16 | apyrase | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 17 | lumbrokinase | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 18 | destabilase | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 19 | GGT | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 20 | LCI | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 21 | hyaluronidase | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| — | total | 28 | 46 | 61 | 72 |
| hirudin | Target species | Protein | Accession | Identity |
| hirudin_Hman1 | H. manillensis | HM1 | Q07558.1 | 76.83% |
| hirudin_Hman2 | H. manillensis | HLF8 | APA20852.1 | 57.63% |
| hirudin_Hman3 | H. manillensis | HLF7 | APA20868.1 | 62.96% |
| hirudin_Hman4 | H. manillensis | HLF6 | APA20866.1 | 73.68% |
| hirudin_Hman5 | H. manillensis | HM1 | Q07558.1 | 68.33% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





