1. Introduction
The coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly infectious virus that has a significant effect on public health [
1,
2]. The World Health Organization (WHO) reported that at least 17,000 healthcare workers lost their lives due to COVID-19, primarily as a consequence of cross-infection [
3]. As infectious disease hospitals have the largest number of confirmed patients, they confront more difficult challenges than other places. Therefore, the air quality in the hospital deserves attention to minimize the risk of cross infection.
Research indicates that the proper use of ventilation systems has been a crucial factor in the spread of COVID-19 [
4,
5,
6]. The rate of transmission is higher in buildings with lower fresh-air rates [
7,
8]. Inappropriate air circulation has been the cause of multiple viral transmission cases in indoor environments [
9]. However, general hospitals and infectious disease hospitals serve different functions. When facing sudden epidemics, general hospitals cannot meet standards for ventilation systems in infectious disease hospitals, leading to a risk of cross-infection when treating infectious patients. Meanwhile, infectious disease hospitals are easily exposed to resource shortages, and the rapid construction of emergency hospitals on a large scale, such as the Thunder Mountain God Hospital [
10], comes at a high cost [
11].
Therefore, an effective way to address these issues is to adopt dual-design operation ventilation systems (DOV). For example, in patient wards, it means to operate under two sets of ventilation conditions: 1) during normal times, fresh air rate is three air changes per hour (ACH) [
12], emphasizing increased cleanliness to create a slightly positive pressure environment; 2) during epidemic times, however, fresh air rate is 6 ACH, and the exhaust air rate needs to be at least 150 m
3/h more than the fresh air rate [
13], emphasizing the prevention of viral spread by creating a negative pressure environment.
For DOV, one of the challenges is to ensure the required airflow rate during normal and epidemic times while achieving hydraulic balance. In the design of ventilation systems, selecting more appropriate duct diameters can enhance the system's inherent hydraulic balance rate without air valves and reduce the usage of air valves, resulting in efficient hydraulic balancing commissioning during the transition from normal to epidemic times. This leads to faster response during the transition as well as easier operation and maintenance. However, the data of duct diameter combinations in ventilation systems is discrete and extensive, making it difficult to adjust them only based on design experience. This real-world pipe network problem is a type of discrete combination problem [
14,
15], which can be solved by heuristic algorithms [
16,
17,
18].
Previous studies have used genetic algorithms to optimize duct diameter combinations [
19,
20,
21]. There are various improved genetic algorithms, such as adaptive penalty functions [
22], improved crossover [
23] and mutation operators [
24,
25], and combinations with hydraulic simulation software [
26]. However, the optimization objects of previous studies are typically urban water supply networks, while this study focuses on DOV networks. There are differences between water supply networks and DOV networks: 1) optimization goal: Urban water supply networks primarily aim to reduce network construction costs, which typically account for 50% to 70% of the total investment in water supply systems. However, the optimization goal for DOV networks is to increase hydraulic balance rate and reduce the usage of air valves; 2) constraint condition: the terminals of urban water supply networks are buildings with higher resistance and can easily use pumps for hydraulic balance. In contrast, the terminals of ventilation systems are air outlets with lower resistance and greater difficulty in achieving hydraulic balance.
Considering the above factors, it's significant to improve the hydraulic balance rate of DOV networks. To achieve this, we should design proper objective functions and improved genetic algorithms to optimize duct diameter combinations of DOV. This study selects a ventilation system of a real hospital in China as a case study. The aim was to accomplish effective transition of ventilation systems from normal to epidemic times for treating normal and epidemic patients.
2. Mathematical Model of Ventilation System Network Optimization
The optimization of ventilation system network in this study is to find a better air duct diameters combination to improve the hydraulic balance rate. The hydraulic balance rate is related to the position, direction, diameter and length of air ducts, as well as local resistance components [
27,
28].
2.1. Hydraulic Imbalance Rate and Imbalanced Air Ducts
To obtain the hydraulic balance rate, it is necessary to calculate the frictional resistance and local resistance of each air duct, expressed as follows:
where
is the total resistance (Pa);
is the frictional resistance (Pa);
is the local resistance (Pa);
is the frictional resistance coefficient;
is the equivalent diameter (m);
is the dynamic air pressure (Pa),
is the density of air (kg/m
3),
is the air velocity (m/s);
is the local resistance coefficient, it can be obtained by interpolating the experimental data of a design manual [
28].
For the frictional resistance coefficient (
), it can be calculated by Colebrook-White equation [
29,
30] expressed as follows:
where
is the absolute roughness of air duct(m);
is the Reynolds number,
is the Kinematic viscosity (m
2/s).
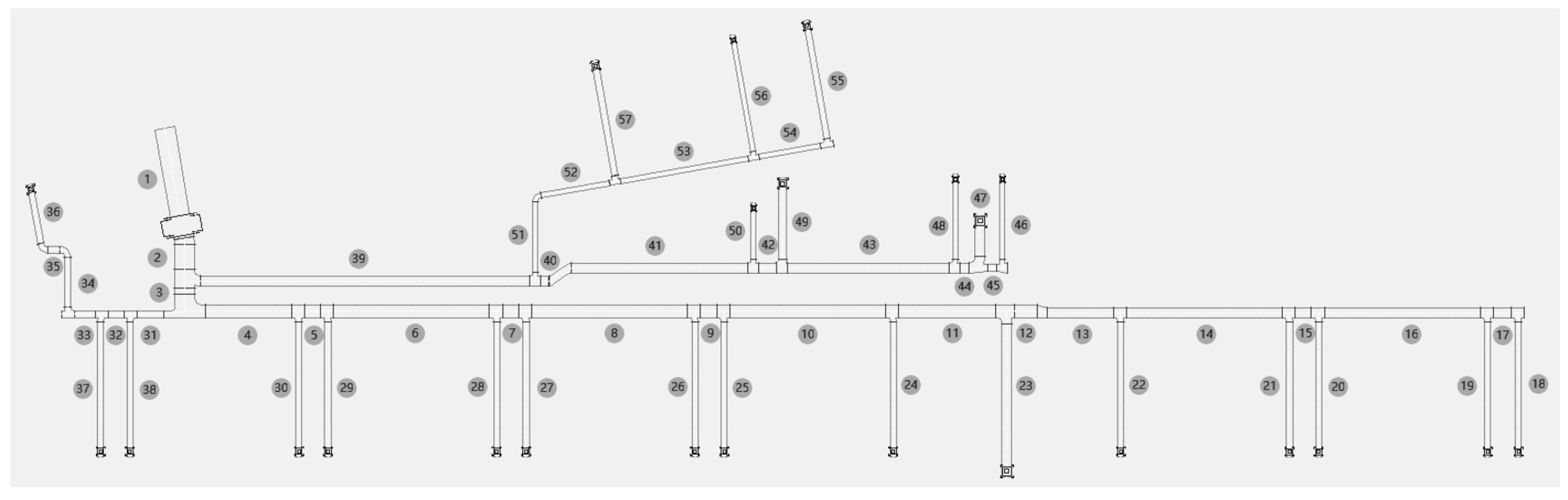
After calculating the total resistance of each air duct, the max downstream cumulative resistance (MR) of each air duct can be calculated, e.g., the case of ventilation system network in this study is shown in
Figure 1.
Then
is the greater of
and
. The hydraulic imbalance rate is the deviation of the MR between two parallel air ducts, e.g., air duct 53 and 57 are a pair of parallel air ducts. Hydraulic imbalance is defined as the hydraulic imbalance rate is greater than 15%. The number of imbalanced air ducts expressed as follows:
where n is the number of air ducts;
is the max MR of air duct i and its parallel ducts.
2.2. Velocity Constraint and Uneconomical Air Ducts
The economic velocity of the air duct in normal times is designed according to the recommended velocity with the requirements of noise reduction and vibration isolation [
31], and the range is 3m/s to 4m/s for main ducts and 2~3m/s for branch ducts and terminal ducts. In this way, when the ventilation system is transformed to epidemic times, the velocity increases to twice, the range is 6m/s to 8m/s for main ducts and 4~6m/s for branch ducts and terminal ducts, which is still within a reasonable range. The number of uneconomical air ducts expressed as follows:
where
and
is the minimum and maximum of economic velocity, which constitute the velocity constraint [
32].
2.3. Penalty Function
The air ducts velocity will be unstable if the traditional genetic algorithm is applied without the velocity constraint. The hydraulic performance of the entire ventilation system will be impacted by some velocity that greatly deviated from the economic velocity. Consequently, to lower the fitness of air duct diameters combinations whose velocity is deviated from the economic velocity, a penalty function limited by the velocity constraint should be constructed. The formula constructed by using (6), (8) and penalty function is as follows:
where k is the adaptive penalty factor [
33];
is the adjustable parameter,
; z is the proportion of feasible solutions in the current population, which is defined as the
is smaller than when using the original design air duct diameters combination.
There are few feasible solutions in the population at the beginning of evolution. At this point, k should take a larger value to make the search quickly enter the feasible region [
34]. When the proportion of feasible solutions is rising, a smaller k should be taken to make the feasible solutions that are being searched better and better. This is crucial for searching the global optimal solution. Consequently, the proportion of feasible solutions influences the penalty factor [
35,
36].
3. Improved Design of Genetic Algorithm
3.1. Coding Method
Ventilation system network optimization is a discrete combination problem for which integer coding can be used to increase efficiency. The air duct diameters and the corresponding integer encoding rule is shown in
Table 1.
There are 32 types of rectangular air duct sizes that may be used in this case are arranged according to the cross-sectional area from small to large, and are encoded as 1 to 32. After encoding, an air duct diameters combination will be converted into a chromosome, and its length is 57 (number of air ducts in this study), and each integer on it represents a type of air duct size.
3.2. Fitness Function and Selection Operator
The fitness function was constructed by using the reciprocal of (9). The formula is as follows:
where
is the reciprocal of penalty function of each individual,
is the fitness of each individual.
Obviously, the best air duct diameters combination, i.e., elite individual of the population, have a fitness of 1 and the rest of the individuals have fitness less than 1. The greater and , the greater penalty function and the smaller fitness of the individual, which more probably to be eliminated during the evolution.
The selection operator is based on fitness, it will select individuals with greater fitness and eliminate individuals with smaller fitness by proportional selection method, expressed as follows:
where
the probability that individual j in the population is selected;
is the number of individuals, i.e., the population size, in this study, N = 50.
Therefore, individuals with greater fitness are more likely to be selected and inherited into the next generation, while individuals with smaller fitness are more likely to be eliminated.
3.3. Crossover Probability and Mutation Probability
The crossover probability and mutation probability should be set to adjust automatically according to the fitness during the evolution, which will improve the global search ability. This study achieves adjustment based on the expectation of fitness, expressed as follows:
where
is the expectation of fitness, i.e., the mean fitness of all the individuals in the population;
is the crossover probability;
is the mutation probability;
and
are adjustable parameters,
.
As mentioned before, individuals with greater fitness are more likely to be selected and inherited into the next generation, causing to increase. Then the crossover probability will decrease and the mutation probability will increase, which is more similar to the actual biological evolution process, so that the improvement of the crossover probability and mutation probability can be achieved.
3.4. Crossover Operator and Mutation Operator
The crossover probability will determine the number of parent individuals in each generation. After each pair of parent individuals are selected by the selection operator, the crossover operator will perform one-point crossover, i.e., randomly selects the crossover position from which they exchange with each other.
For example, assuming that a pair of selected parent individuals are:
30 18 21 12 … 5 (length is 57)
25 15 18 11 … 2
Suppose that the crossover operator starts from the third position, then the child individuals will be:
30 18 18 11 … 2
25 15 21 12 … 5
The mutation probability will determine the number of integers which will mutate on all the chromosomes in each generation, the mutation operator randomly selects the mutation position and executes mutation. In addition, to prevent elite individuals from being destroyed, the elite individual in each generation do not participate in mutation.
Considering the characteristics of the ventilation system network, this study restricts the interval of mutation operator to be ±1 around the original integer.
For example, assuming that a parent individual is:
30 18 21 12 … 5
Suppose that the mutation operator occurs at the third and last position, then the child individual will be:
30 18 20~22 12 … 4~6
Since the air duct diameters are arranged according to the cross-sectional area from small to large during the encoding, this kind of mutation operator can prevent the air velocity from excessive change, which would result in exceeding the economic velocity range. The improved mutation operator can not only ensure the diversity of the population, but also prevent individuals with high fitness being destroyed.
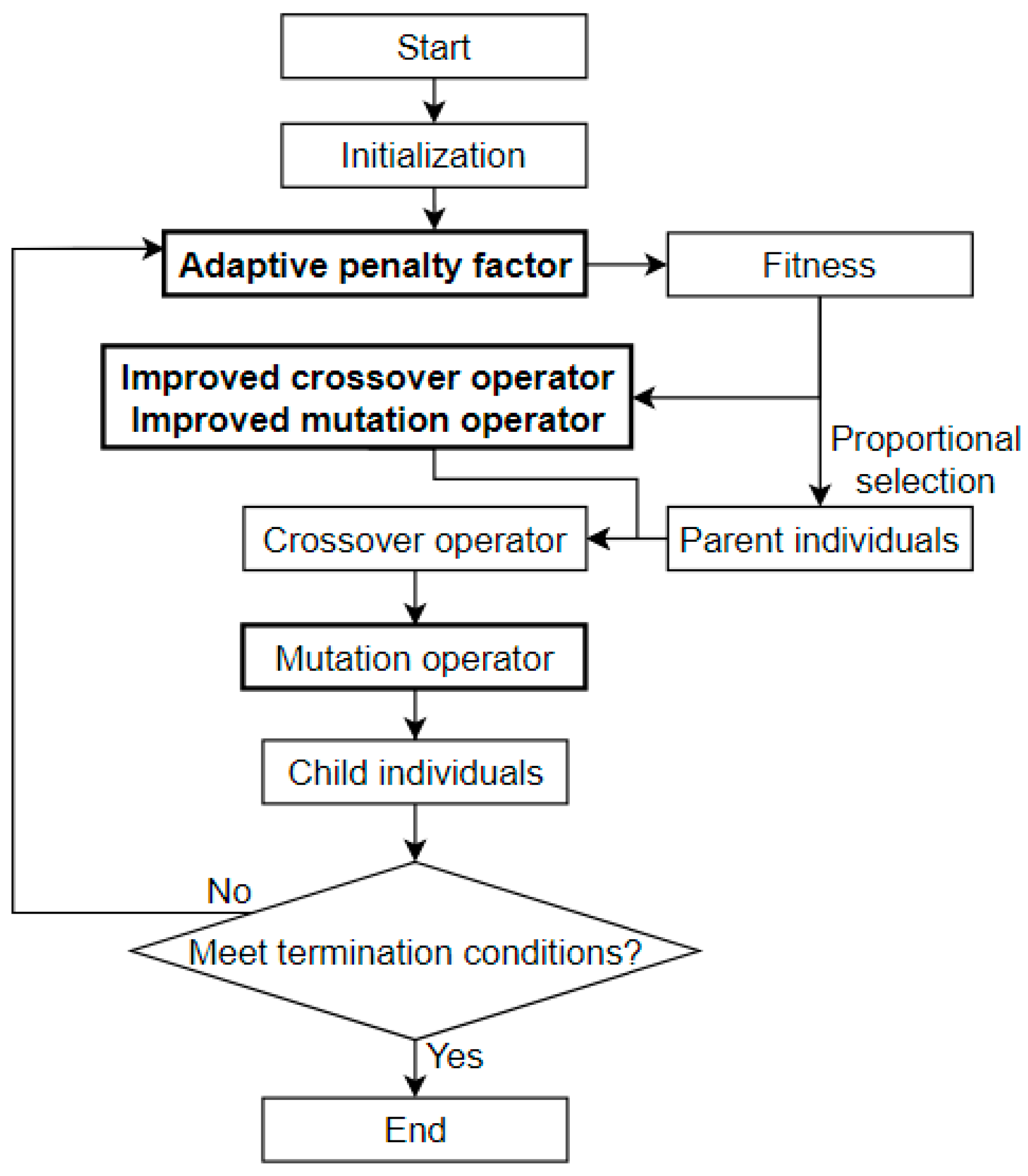
3.5. Ventilation System Network Optimization Process
The flow chart of ventilation system network optimization process is shown in
Figure 2.
The optimization process is: 1) Started: Read the original design air duct diameters combination of the ventilation system to obtain the initial individual; 2) Initialization: To initialize the population, new individuals are generated randomly along with the initial individual; 3) Calculate fitness: The fitness of each individual is calculated by penalty function; 4) Selection: According to fitness of each individual in each generation, parent individuals were selected by proportional selection method; 5) Crossover and mutation: According to the improved crossover and mutation probability, crossover and mutation operator are performed to obtain child individuals. 6) Iteration: Iterate to the max generation or the number of imbalanced air ducts () has reduced to the optimization goal; 7) End: Output optimization results.
The bold part in
Figure 2 illustrates the advantages of the improved genetic algorithm compared with the traditional genetic algorithm: 1) Adaptive penalty parameters are adjusted according to the proportion of feasible solutions during the evolution, which can improve the global search ability; 2) The improved crossover probability gradually decreases and the improved mutation probability gradually increases with the increase of the expectation of fitness, which is more similar to the actual biological evolution process; 3) The improved mutation operator can ensure the diversity of the population and prevent individuals with high fitness being destroyed.
4. Case Application
In this study, an air supply system of an actual hospital in China was selected as a case study, as shown in
Figure 1. The ventilation system network is a branching network with 23 nodes and 57 air ducts. The total supply airflow is 5150 m
3/h in normal times and 10300 m
3/h in epidemic times. The supply airflow and the length of each air duct are known.
4.1. Comparison of Improved Genetic Algorithms
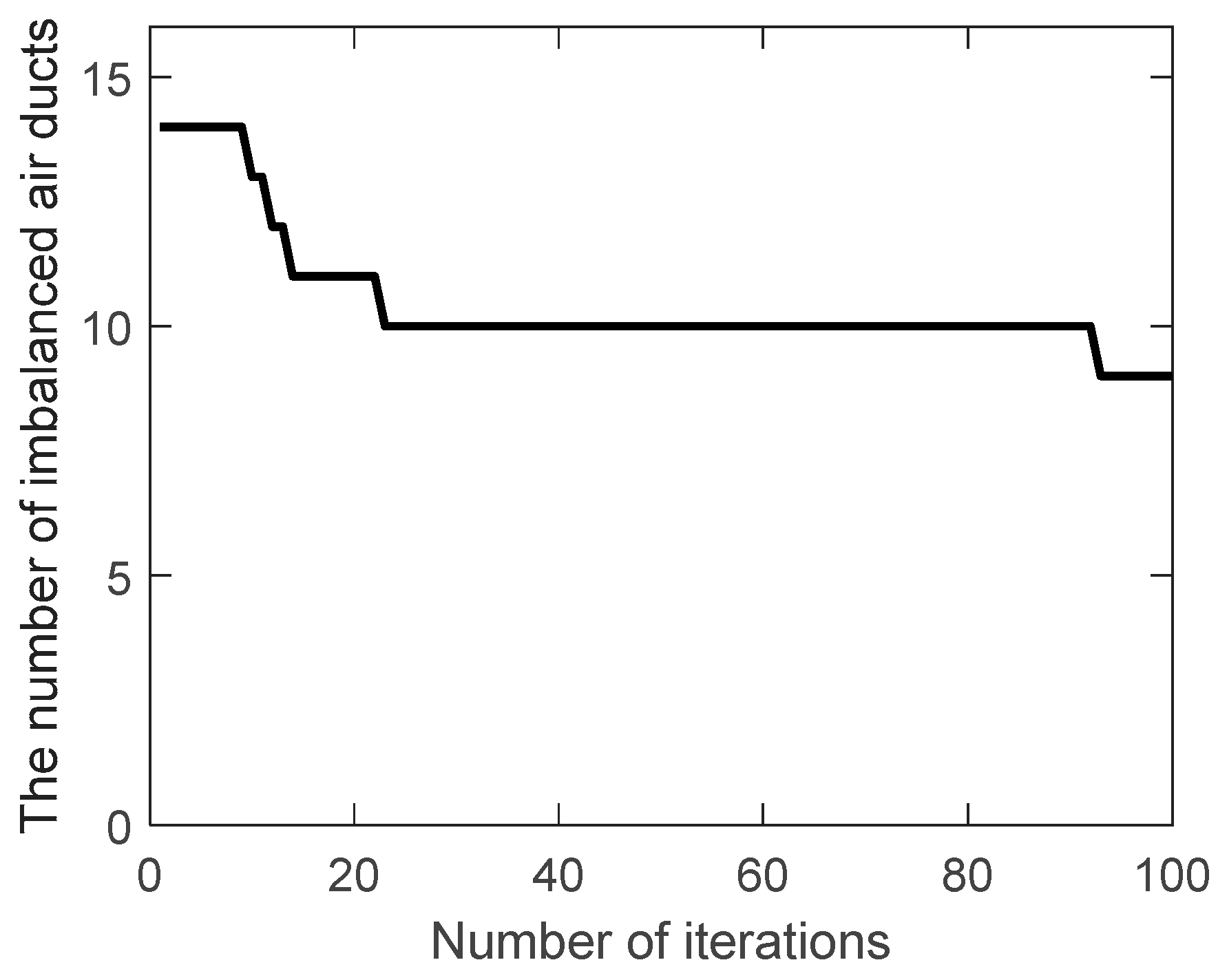
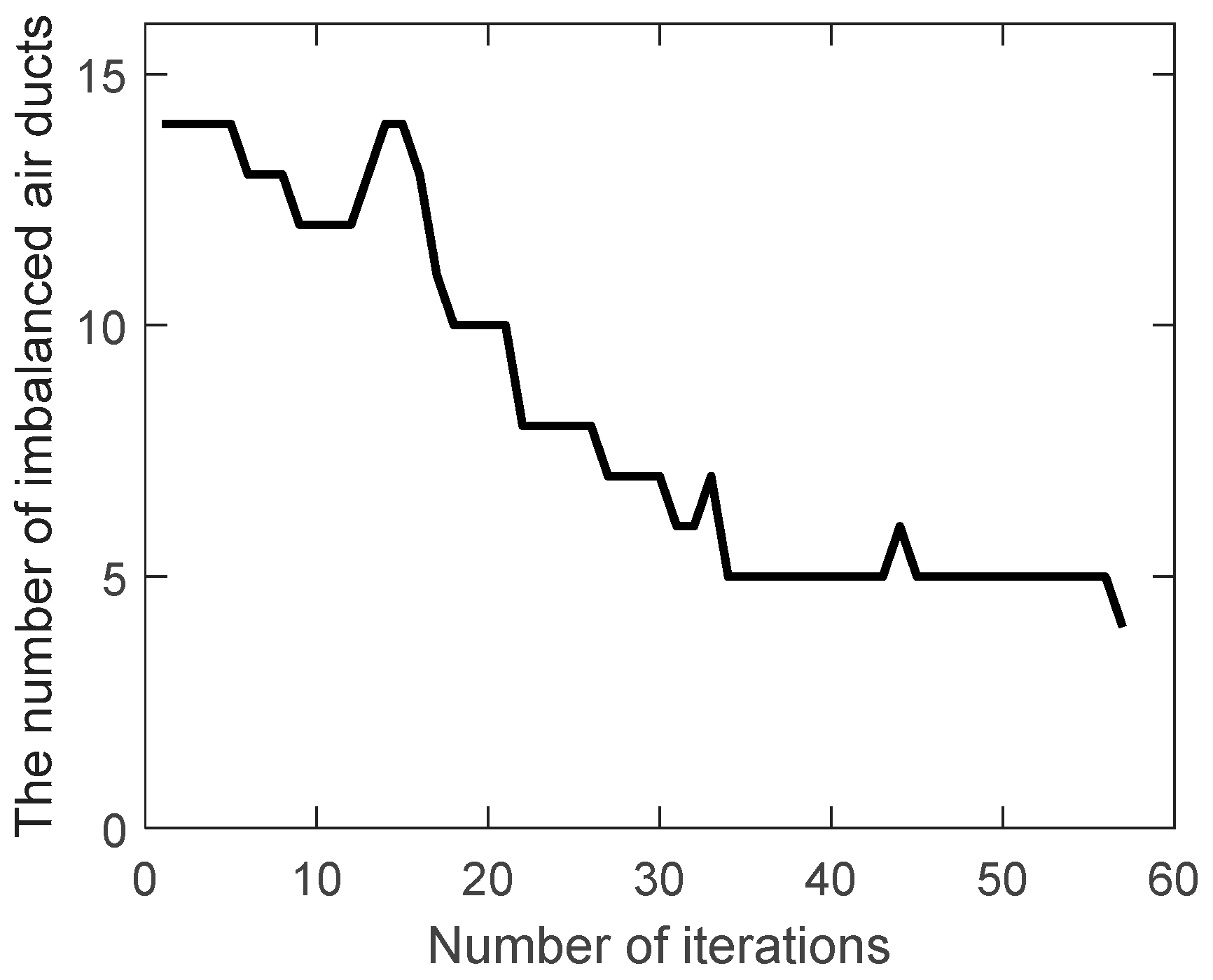
Traditional genetic algorithm and improved genetic algorithm are used to optimize the ventilation system network. The number of imbalanced air ducts (
) during the evolution are shown in
Figure 3 and
Figure 4.
It can be seen that decreases from 14 to 9 when the traditional genetic algorithm is iterated to the max generation (100), while decreases to 4 when the improved genetic algorithm is iterated to the 57th generation, reaching the optimization goal (below 5) and quitting the iteration. It shows that the improved genetic algorithm has a faster search speed and a better global search ability.
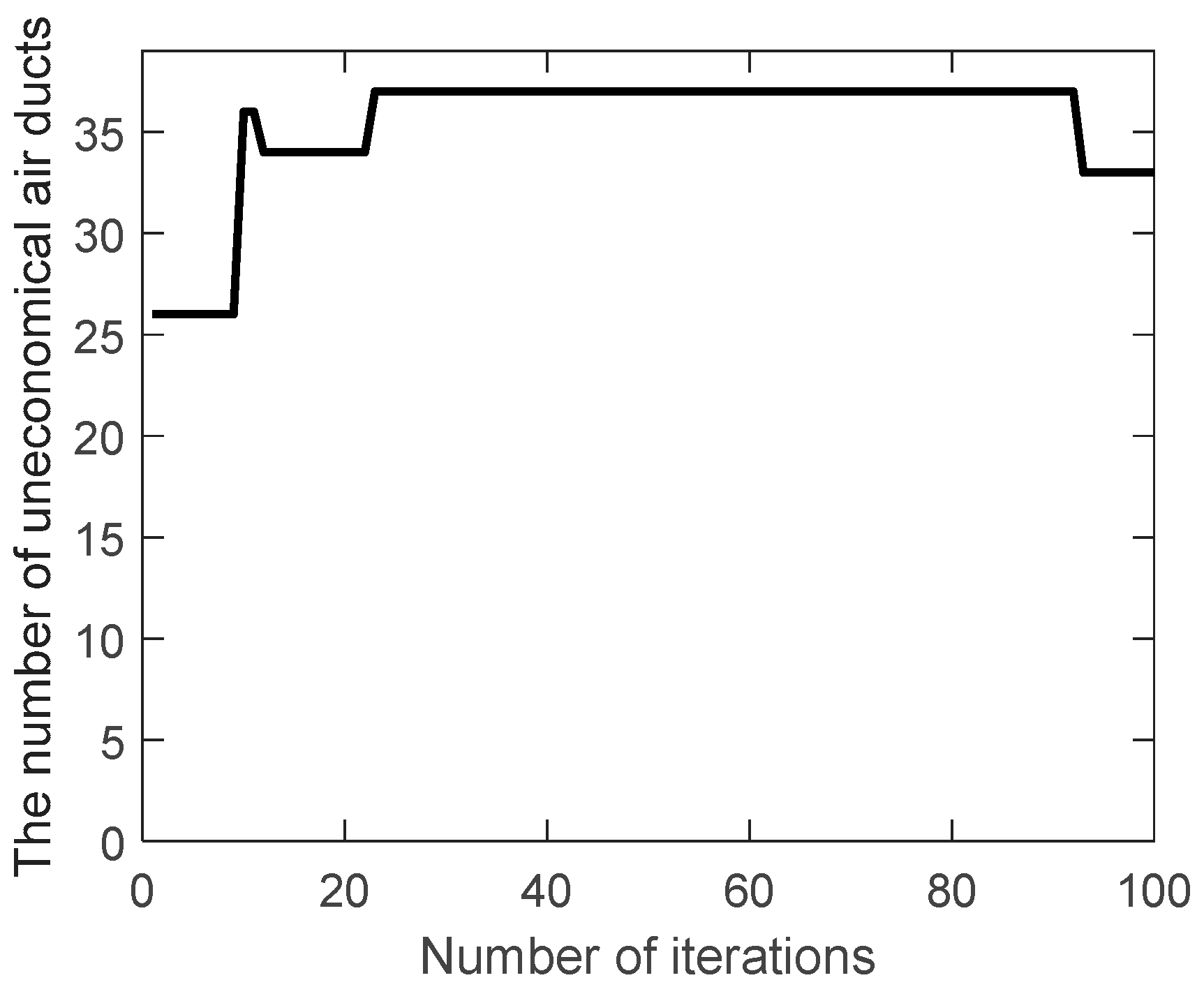
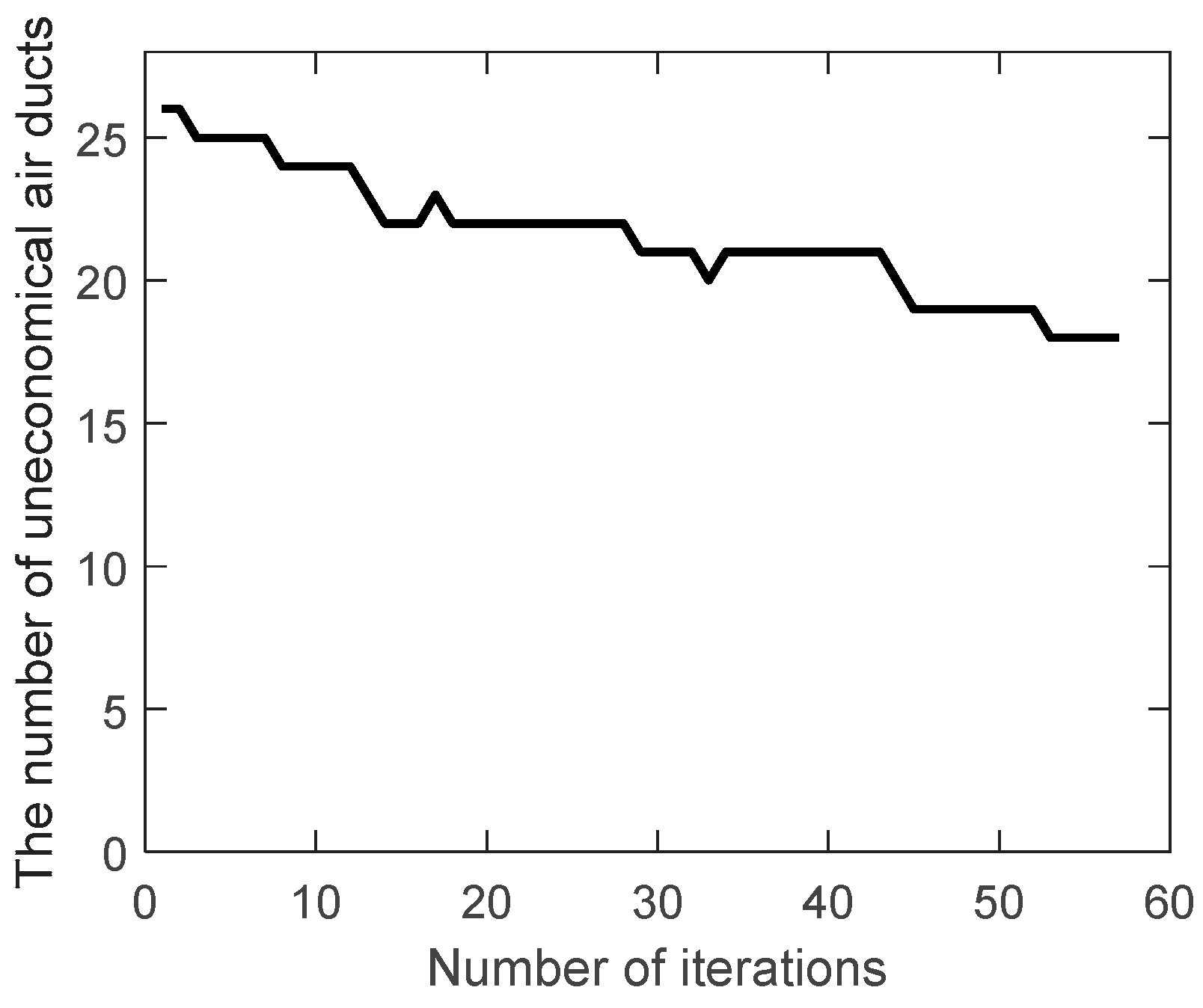
The number of uneconomical air ducts (
) during the evolution are shown in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6.
Obviously,
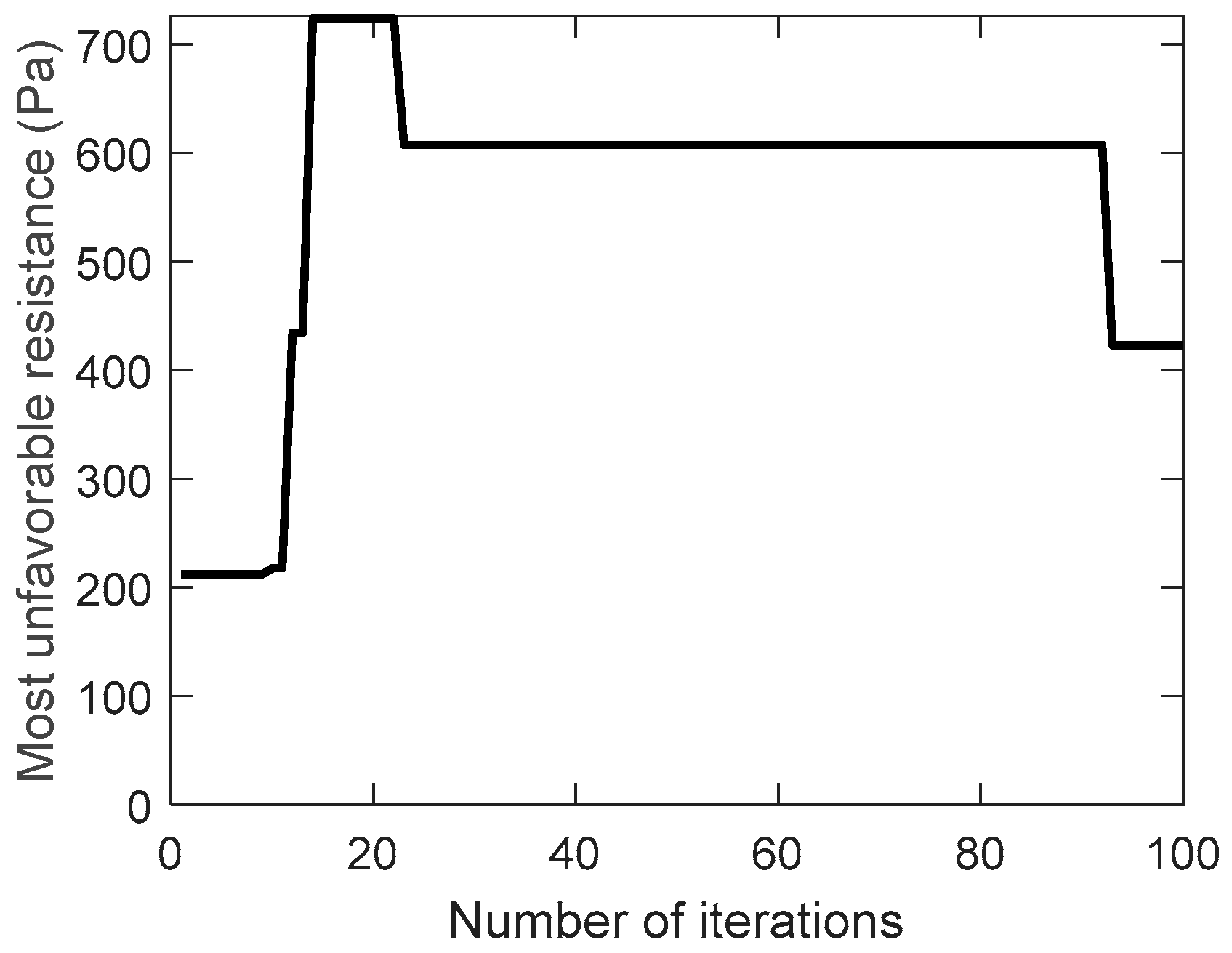
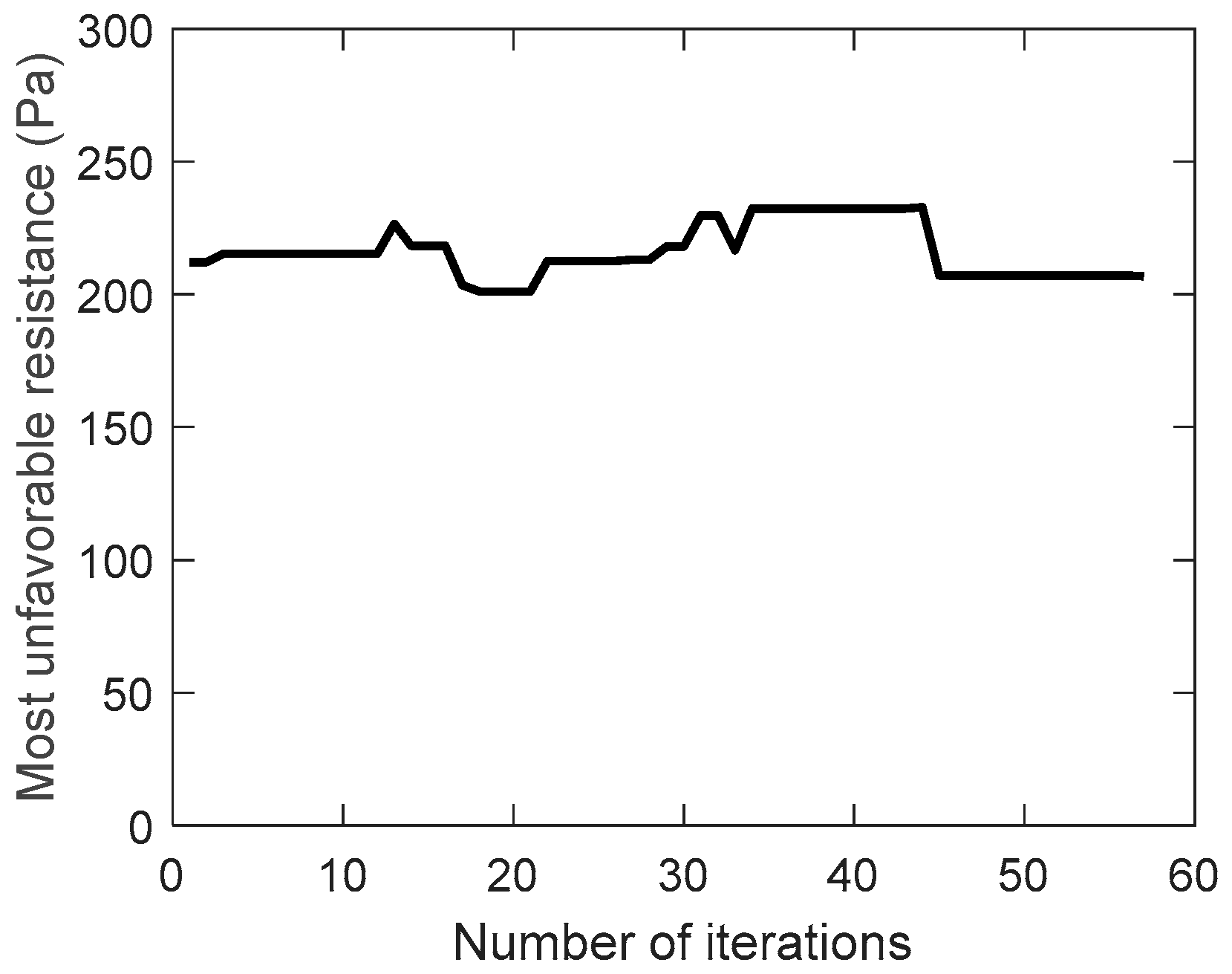
increases instead of decreasing during the evolution of the traditional genetic algorithm, while the improved genetic algorithm adopts the velocity constraint, so it decreases from 26 to 18 during the evolution. As a result, the most unfavorable resistance during the evolution are shown in
Figure 7 and
Figure 8.
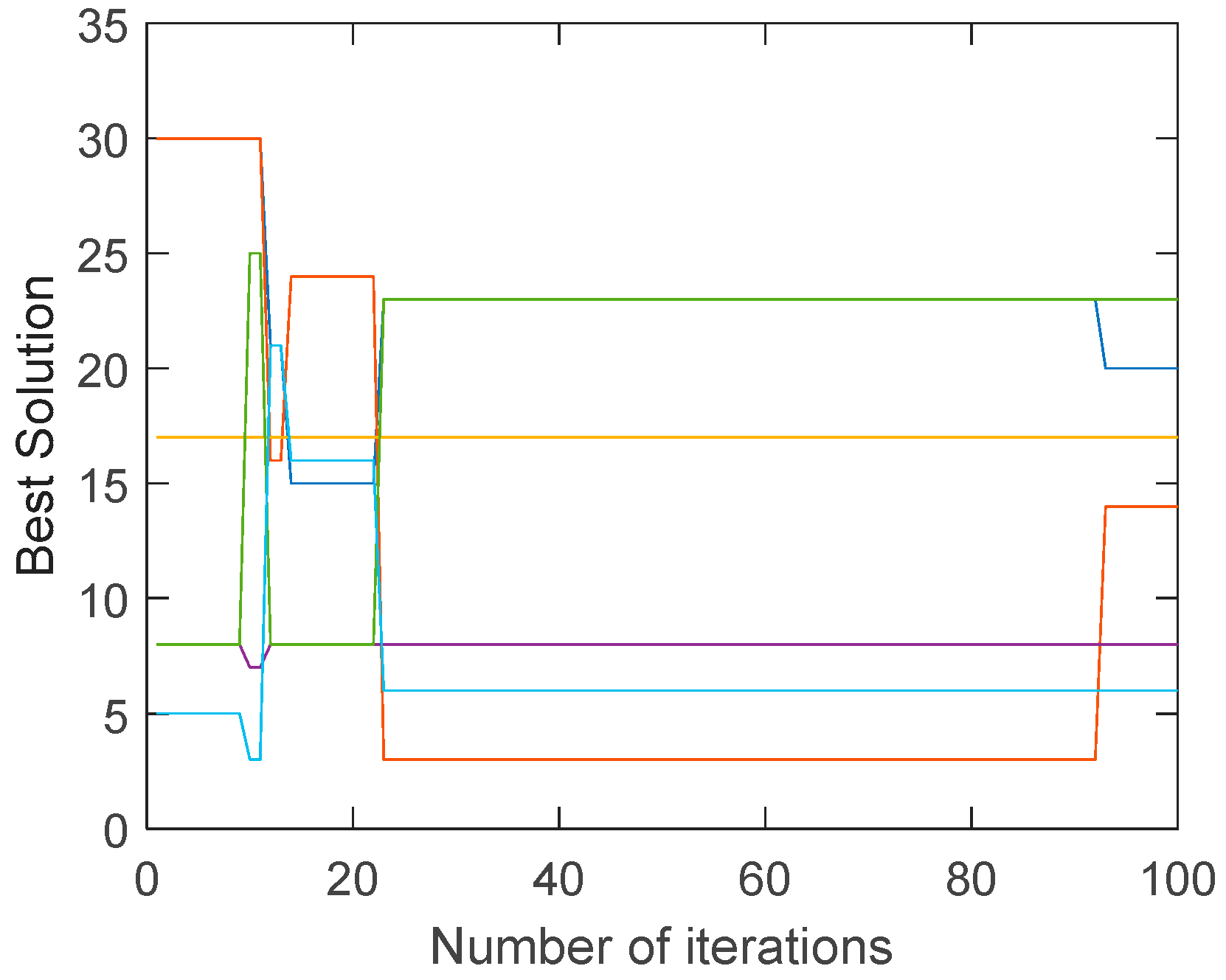
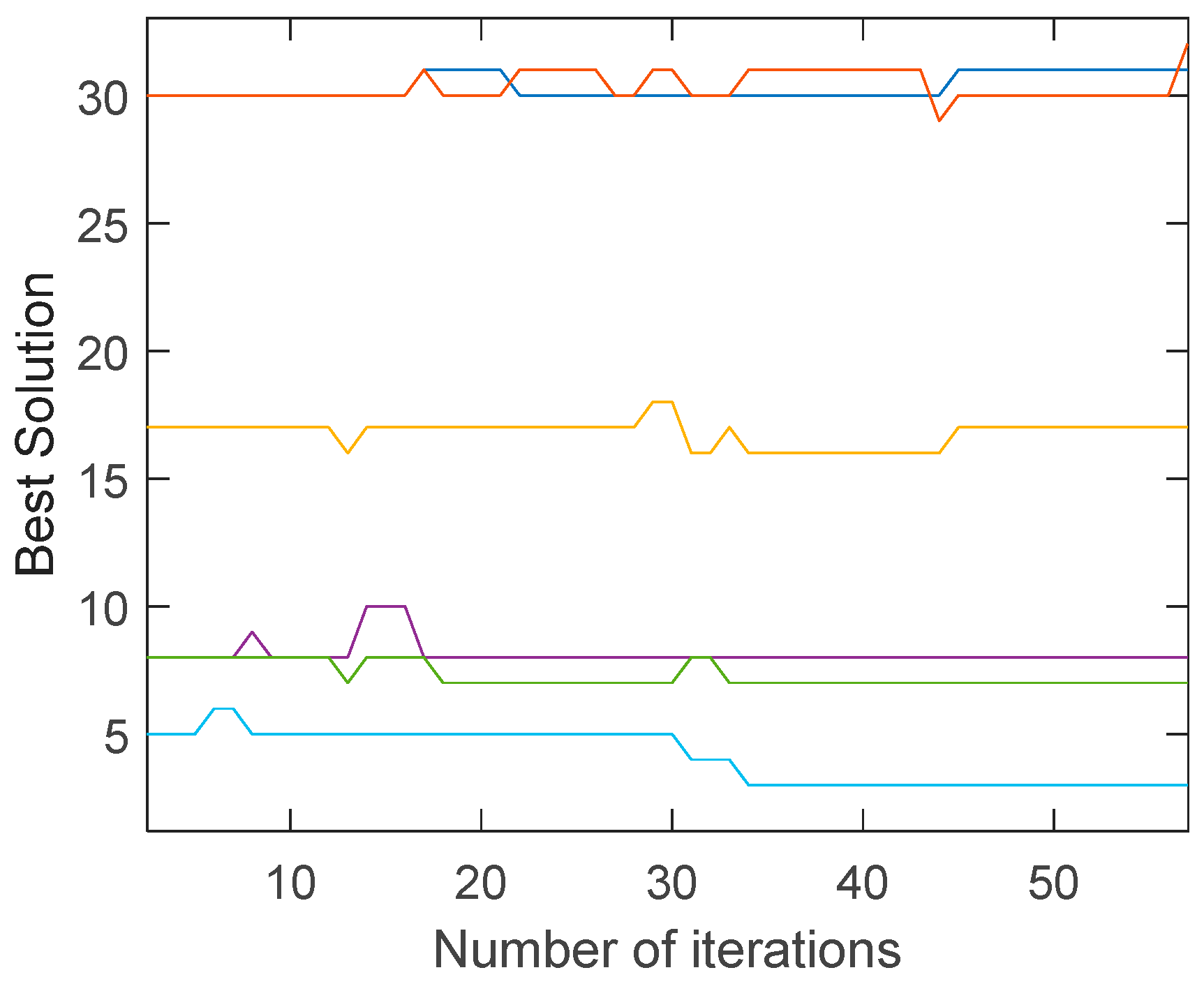
Because the uneconomical air ducts often have greater resistance, the most unfavorable resistance increases during the evolution of the traditional genetic algorithm. On the contrary, the most unfavorable resistance is slightly reduced during the evolution of the improved genetic algorithm. This can also be seen from the best solution of the air duct diameters combination (integer code of air duct diameters) on the most unfavorable path during the evolution, in
Figure 9 and
Figure 10.
As mentioned before, the improved mutation operator can prevent the air velocity from excessive change. While the mutation operator of traditional genetic algorithm performs random mutation, which would result in exceeding the economic velocity range.
4.2. Validation of the Improved Genetic Algorithm
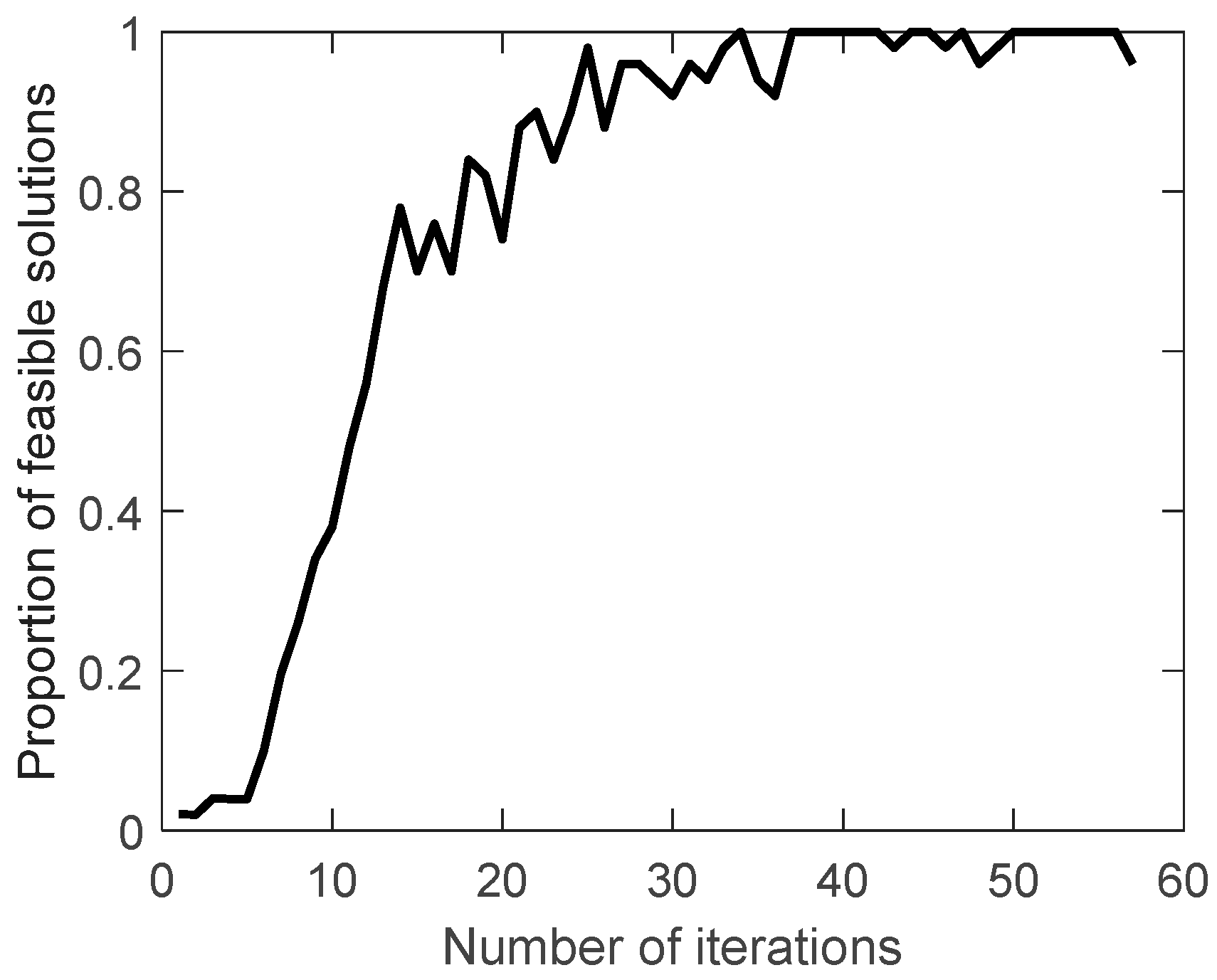
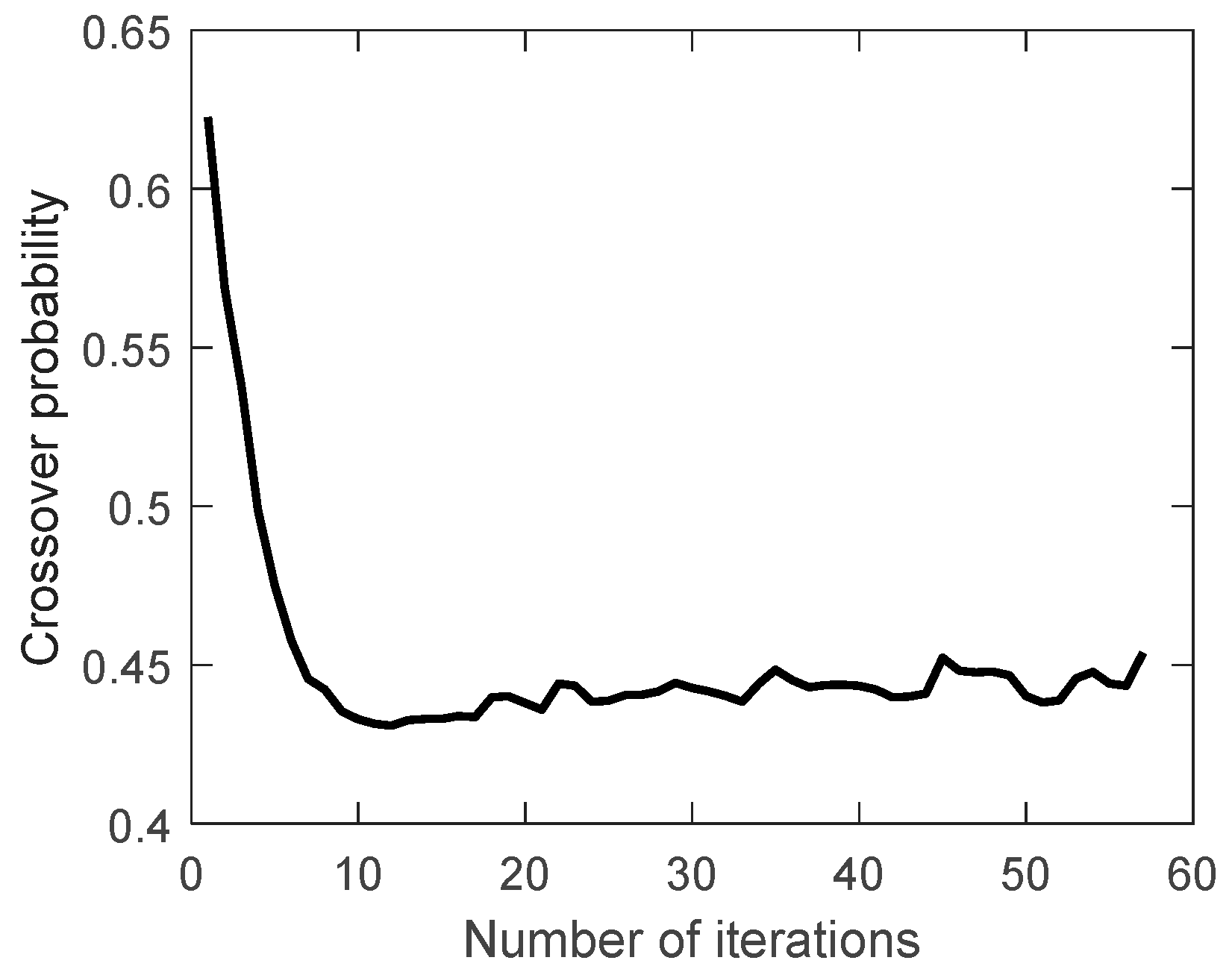
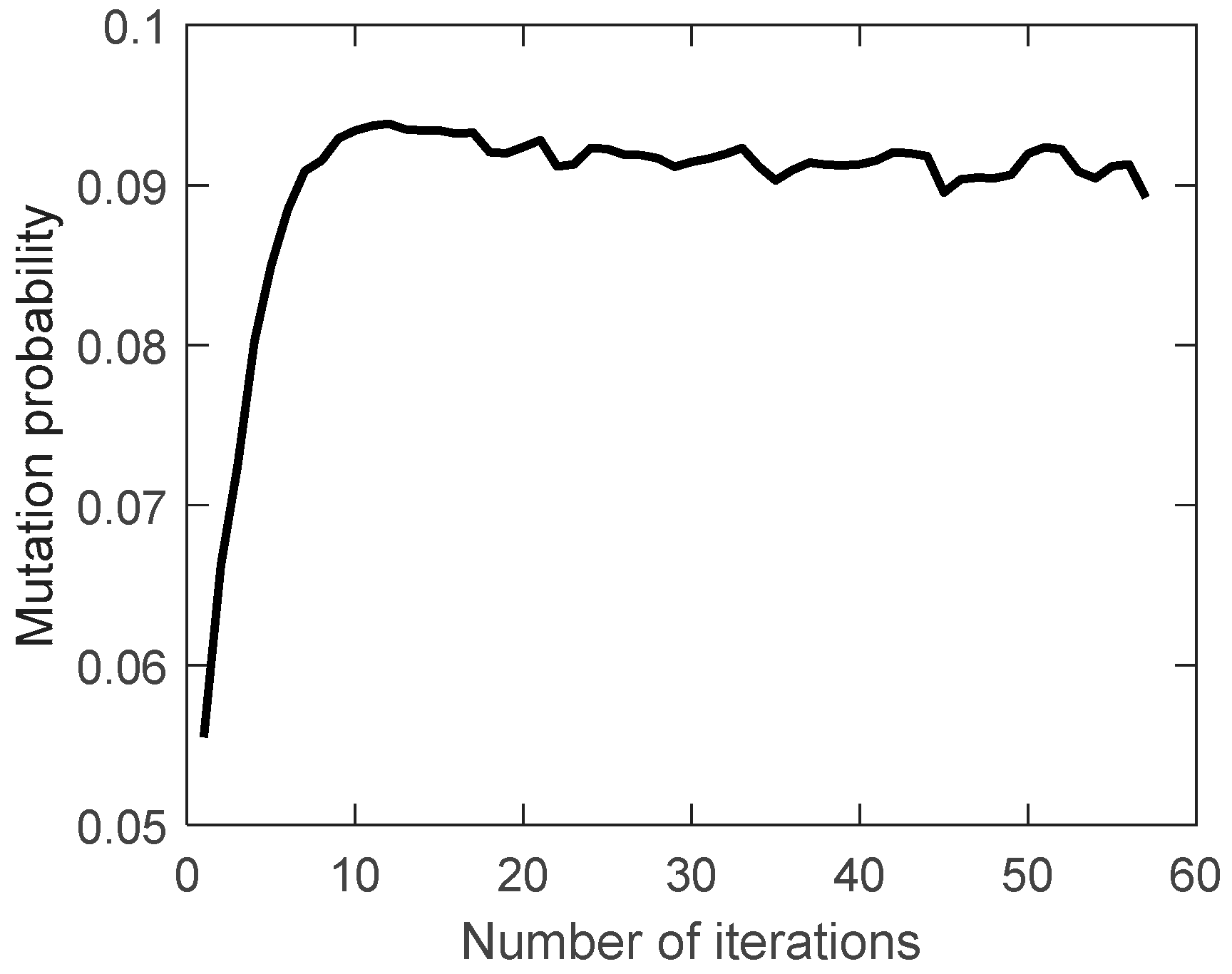
The proportion of feasible solutions, the crossover probability and the mutation probability during the evolution are shown in
Figure 11,
Figure 12 and
Figure 13.
The proportion of feasible solutions gradually increases during the evolution, indicating that the searched solutions obtained are getting better and better. The crossover probability and mutation probability gradually decrease and increase during the evolution. As mentioned before, this indicates that the expectation of fitness is increasing, which is consistent with the expected effect of the improved crossover probability and mutation probability.
5. Conclusions
The improved genetic algorithm introduced in this study can be applied to the design and optimiation of the ventilation system, and a better air duct diameters combination can be found during the iteration. It can improve the hydraulic balance rate of the ventilation system network and reduce the usage of air valves, which will help achieving efficient hydraulic balancing commissioning, especially for a dual-design operation ventilation system during the transition from normal to epidemic times. This leads to faster response during the transition as well as easier operation and maintenance.
Meanwhile, the number of uneconomical pipe sections can be reduced after the velocity constraint is adopted in the penalty function, and the most unfavorable resistance after optimization is slightly reduced. This indicate that the reduction of imbalanced and uneconomical air ducts is not at the cost of increasing energy consumption.
The genetic algorithm is improved by the adaptive penalty factor and the velocity constraint. The improved crossover and mutation probability will adjust automatically according to the fitness during the evolution. Compared with the traditional genetic algorithm, it has a faster search speed and a better global search ability. In conclusion, this method has good application value in the optimal design of the ventilation system network.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. The air duct diameters and the corresponding integer encoding rule is in Encoding rule.docx. The algorithm code and results are in the GA_AGA.zip.
References
- Zhang N, Chen X, Jia W, Jin T, Xiao S, Chen W, et al. Evidence for lack of transmission by close contact and surface touch in a restaurant outbreak of COVID-19. Journal of Infection 2021;83:207–16. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang L, Li M, Zhou X. Evaluating Transmission Heterogeneity and Super-Spreading Event of COVID-19 in a Metropolis of China. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH AND PUBLIC HEALTH 2020;17. [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas M, Chebbi A, Dybul M, Kazatchkine M, Liu J, Matsoso P, et al. COVID-19: Make it the last pandemic. Genf: WHO: The Indipendent Panel for Pandemic; 2021.
- Qian H, Li Y, Seto WH, Ching P, Ching WH, Sun HQ. Natural ventilation for reducing airborne infection in hospitals. Build Environ 2010;45:559–65. [CrossRef]
- Correia G, Rodrigues L, Gameiro da Silva M, Gonçalves T. Airborne route and bad use of ventilation systems as non-negligible factors in SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Medical Hypotheses 2020;141:109781. [CrossRef]
- Guo M, Xu P, Xiao T, He R, Dai M, Miller SL. Review and comparison of HVAC operation guidelines in different countries during the COVID-19 pandemic. Building and Environment 2021;187:107368. [CrossRef]
- Lewis D. Is the coronavirus airborne? Experts can’t agree. Nature 2020:0. [CrossRef]
- Morawska L, Cao J. Airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2: The world should face the reality. Environment International 2020;139:105730. [CrossRef]
- Chen C, Zhao B. Makeshift hospitals for COVID-19 patients: where health-care workers and patients need sufficient ventilation for more protection. Journal of Hospital Infection 2020;105:98–9. [CrossRef]
- Eng TLC, Eng LYS, Eng GHS, Eng YW. Rapid Design and Construction Management of Emergency Hospital During the COVID-19 Epidemic. Structural Engineering International 2022;32:142–6. [CrossRef]
- Zhou J, Yang L. Network-Based Research on Organizational Resilience in Wuhan Thunder God Mountain Hospital Project during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 2022;14. [CrossRef]
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. GB51039-2014. Code for design of general hospital. 2014.
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. GB50849–2014. Code for Design of Infectious Diseases Hospital. 2014.
- Gong D, Sun J, Miao Z. A Set-Based Genetic Algorithm for Interval Many-Objective Optimization Problems. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATION 2018;22:47–60. [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Tian G, Li Z. An adaptive Lagrangian relaxation-based algorithm for a coordinated water supply and wastewater collection network design problem. INFORMATION SCIENCES 2020;512:1335–59. [CrossRef]
- Sarbu I, Popa-Albu S. Optimization of urban water distribution networks using heuristic methods: an overview. Water International 2023;48:120–48. [CrossRef]
- Chugh T, Jin Y, Miettinen K, Hakanen J, Sindhya K. A Surrogate-Assisted Reference Vector Guided Evolutionary Algorithm for Computationally Expensive Many-Objective Optimization. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATION 2018;22:129–42. [CrossRef]
- Tian Y, Cheng R, Zhang X, Cheng F, Jin Y. An Indicator-Based Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm With Reference Point Adaptation for Better Versatility. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATION 2018;22:609–22. [CrossRef]
- Momeni A, Chauhan V, Bin Mahmoud A, Piratla KR, Safro I. Generation of Synthetic Water Distribution Data Using a Multiscale Generator-Optimizer. JOURNAL OF PIPELINE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND PRACTICE 2023;14. [CrossRef]
- Sangroula U, Han K-H, Koo K-M, Gnawali K, Yum K-T. Optimization of Water Distribution Networks Using Genetic Algorithm Based SOP-WDN Program. WATER 2022;14. [CrossRef]
- Johns MB, Keedwell E, Savic D. Knowledge-based multi-objective genetic algorithms for the design of water distribution networks. JOURNAL OF HYDROINFORMATICS 2020;22:402–22. [CrossRef]
- Ding K, Ni Y, Fan L, Sun T-L. Optimal Design of Water Supply Network Based on Adaptive Penalty Function and Improved Genetic Algorithm. MATHEMATICAL PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING 2022;2022. [CrossRef]
- Hassan WH, Jassem MH, Mohammed SS. A GA-HP Model for the Optimal Design of Sewer Networks. WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT 2018;32:865–79. [CrossRef]
- Cetin T, Yurdusev MA. Genetic algorithm for networks with dynamic mutation rate. GRADEVINAR 2017;69:1101–9. [CrossRef]
- Tan Z, Li K, Wang Y. Differential evolution with adaptive mutation strategy based on fitness landscape analysis. INFORMATION SCIENCES 2021;549:142–63. [CrossRef]
- Tao Y, Yan D, Yang H, Ma L, Kou C. Multi-objective optimization of water distribution networks based on non-dominated sequencing genetic algorithm. PLOS ONE 2022;17. [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE. 2021 ASHRAE Handbook—HVAC Applications, Chapter 21, Duct Design 2021.
- Lu Y. Practical Heating and Air Conditioning Design Manual 2nd Edition. China Architecture & Building Press; 2008.
- Hafsi Z. Accurate explicit analytical solution for Colebrook-White equation. Mechanics Research Communications 2021;111:103646. [CrossRef]
- Praks P, Brkic D. One-Log Call Iterative Solution of the Colebrook Equation for Flow Friction Based on Pade Polynomials. ENERGIES 2018;11. [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. GB50736-2012. Design code for heating ventilation and air conditioning of civil buildings. 2012.
- Deb K, Jain H. An Evolutionary Many-Objective Optimization Algorithm Using Reference-Point-Based Nondominated Sorting Approach, Part I: Solving Problems With Box Constraints. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATION 2014;18:577–601. [CrossRef]
- de Melo VV, Iacca G. A modified Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy with adaptive penalty function and restart for constrained optimization. EXPERT SYSTEMS WITH APPLICATIONS 2014;41:7077–94. [CrossRef]
- Liu J-B, Wang S, Wang C, Hayat S. Further results on computation of topological indices of certain networks. IET Control Theory & Applications 2017;11:2065–71. [CrossRef]
- Hong C, Estefen SF, Wang Y, Lourenço MI. An integrated optimization model for the layout design of a subsea production system. Applied Ocean Research 2018;77:1–13. [CrossRef]
- Mu T, Li Y, Li Z, Wang L, Tan H, Zheng C. Improved Network Reliability Optimization Model with Head Loss for Water Distribution System. Water Resour Manage 2021;35:2101–14. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).