Submitted:
31 October 2023
Posted:
31 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
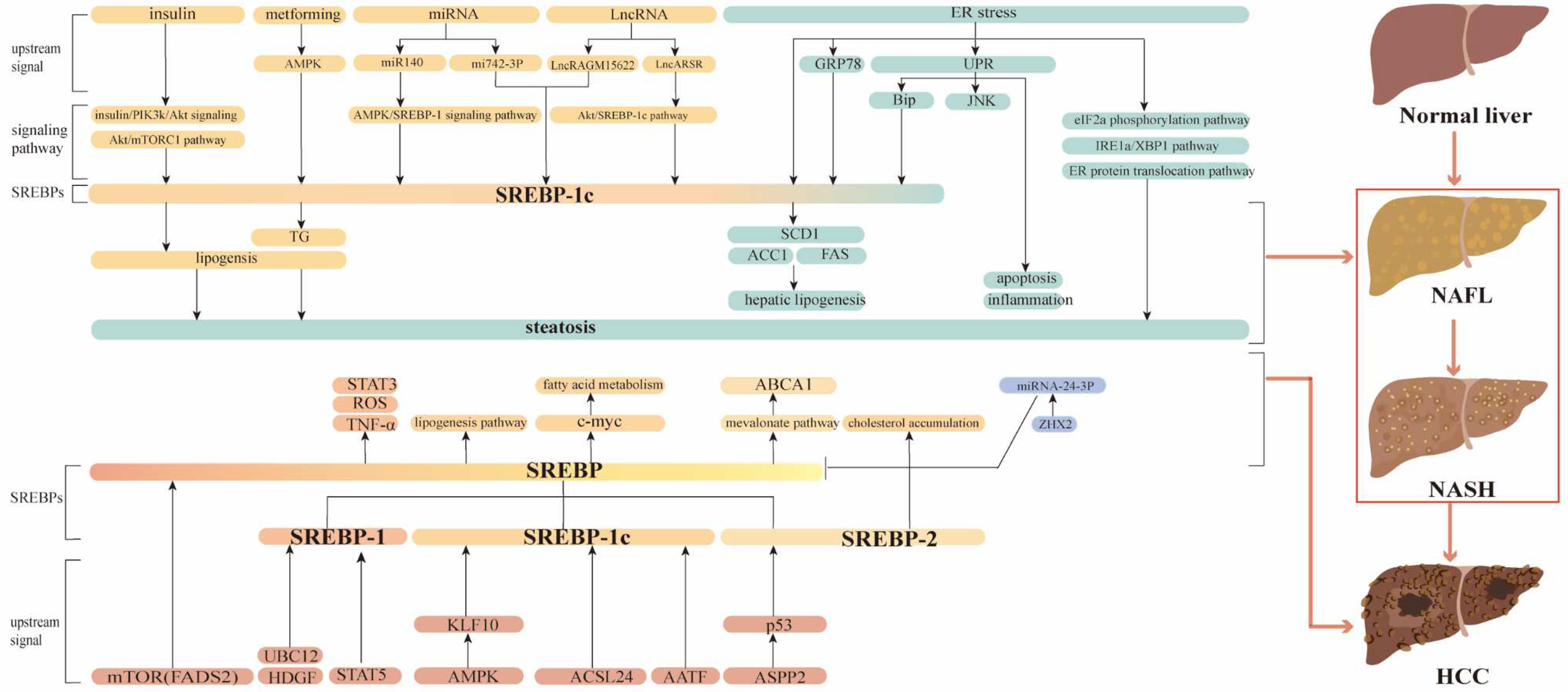
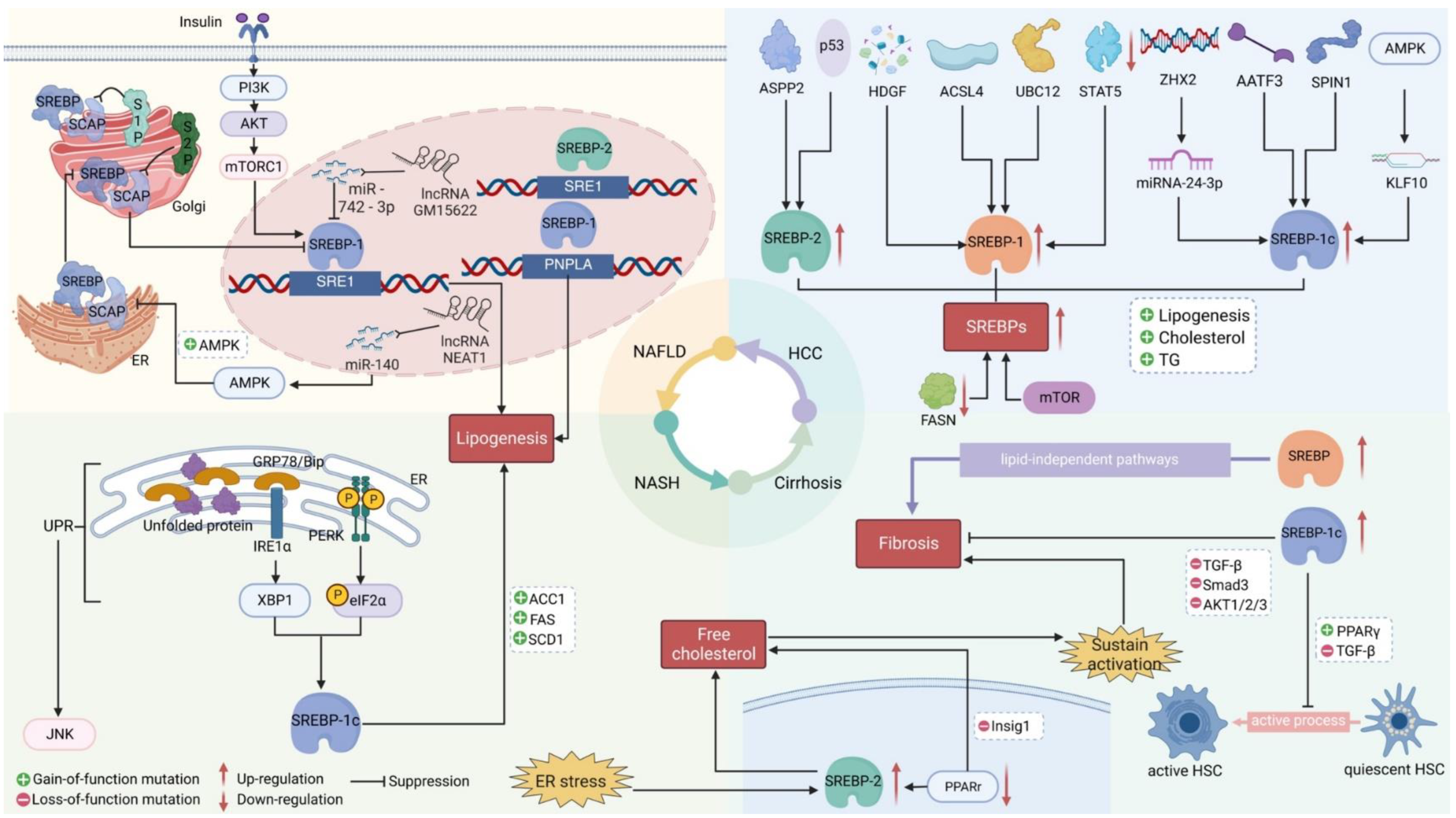
Multifunctional role of SREBPs in NAFLD and NASH
SREBPs may mediate Liver Fibrosis via TGF-β Signaling during Chronic liver disease progressing to HCC
Role of SREBPs in HCC
Targeting SREBPs for treating HCC and chronic liver disease
Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Quek, J.; Chan, K. E.; Wong, Z. Y.; Tan, C.; Tan, B.; Lim, W. H.; Tan, D. J. H.; Tang, A. S. P.; Tay, P.; Xiao, J.; Yong, J. N.; Zeng, R. W.; Chew, N. W. S.; Nah, B.; Kulkarni, A.; Siddiqui, M. S.; Dan, Y. Y.; Wong, V. W.; Sanyal, A. J.; Noureddin, M.; Muthiah, M.; Ng, C. H. Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Wong, R. J.; Harrison, S. A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Review: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Outcomes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015, 13, 2062–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, G.; Baranova, A.; Younossi, Z. M. Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011, 34, 274–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinjuvadia, R.; Patel, S.; Liangpunsakul, S. The association between metabolic syndrome and hepatocellular carcinoma: systemic review and meta-analysis. Journal of clinical gastroenterology 2014, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, F.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J Hepatol 2018, 68, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enooku, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Fujiwara, N.; Kondo, M.; Minami, T.; Hoshida, Y.; Shibahara, J.; Tateishi, R.; Koike, K. Altered serum acylcarnitine profile is associated with the status of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and NAFLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Umemura, A.; Taniguchi, K.; Font-Burgada, J.; Dhar, D.; Ogata, H.; Zhong, Z.; Valasek, M. A.; Seki, E.; Hidalgo, J.; Koike, K.; Kaufman, R. J.; Karin, M. ER stress cooperates with hypernutrition to trigger TNF-dependent spontaneous HCC development. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, K. L.; Smith, C. I.; Schwarzenberg, S. J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M. D.; Parks, E. J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest 2005, 115, 1343–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y. A. The SCAP/SREBP Pathway: A Mediator of Hepatic Steatosis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2017, 32, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimano, H.; Sato, R. SREBP-regulated lipid metabolism: convergent physiology - divergent pathophysiology. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2017, 13, 710–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R. Sterol metabolism and SREBP activation. Arch Biochem Biophys 2010, 501, 177–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, T. I.; Osborne, T. F. SREBPs: metabolic integrators in physiology and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2012, 23, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, S.; Cortes, V. A.; Rashid, S.; Anderson, N. N.; McDonald, J. G.; Liang, G.; Moon, Y. A.; Hammer, R. E.; Horton, J. D. Expression of SREBP-1c Requires SREBP-2-mediated Generation of a Sterol Ligand for LXR in Livers of Mice. Elife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Lee, J. N.; Lee, P. C.; Goldstein, J. L.; Brown, M. S.; Ye, J. Sterol-regulated ubiquitination and degradation of Insig-1 creates a convergent mechanism for feedback control of cholesterol synthesis and uptake. Cell Metab 2006, 3, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Reinitz, F.; Youssef, M.; Hong, C.; Nathanson, D.; Akhavan, D.; Kuga, D.; Amzajerdi, A. N.; Soto, H.; Zhu, S.; Babic, I.; Tanaka, K.; Dang, J.; Iwanami, A.; Gini, B.; Dejesus, J.; Lisiero, D. D.; Huang, T. T.; Prins, R. M.; Wen, P. Y.; Robins, H. I.; Prados, M. D.; Deangelis, L. M.; Mellinghoff, I. K.; Mehta, M. P.; James, C. D.; Chakravarti, A.; Cloughesy, T. F.; Tontonoz, P.; Mischel, P. S. An LXR agonist promotes glioblastoma cell death through inhibition of an EGFR/AKT/SREBP-1/LDLR-dependent pathway. Cancer Discov 2011, 1, 442–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porstmann, T.; Griffiths, B.; Chung, Y. L.; Delpuech, O.; Griffiths, J. R.; Downward, J.; Schulze, A. PKB/Akt induces transcription of enzymes involved in cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthesis via activation of SREBP. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6465–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Mihaylova, M. M.; Zheng, B.; Hou, X.; Jiang, B.; Park, O.; Luo, Z.; Lefai, E.; Shyy, J. Y.; Gao, B.; Wierzbicki, M.; Verbeuren, T. J.; Shaw, R. J.; Cohen, R. A.; Zang, M. AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab 2011, 13, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, D.; Clement, K.; Meyre, D.; Sahbatou, M.; Vaxillaire, M.; Le Gall, A.; Ferre, P.; Basdevant, A.; Froguel, P.; Foufelle, F. SREBF-1 gene polymorphisms are associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes in French obese and diabetic cohorts. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2153–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponugoti, B.; Fang, S.; Kemper, J. K. Functional interaction of hepatic nuclear factor-4 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1alpha in CYP7A1 regulation is inhibited by a key lipogenic activator, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c. Mol Endocrinol 2007, 21, 2698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimano, H.; Horton, J. D.; Shimomura, I.; Hammer, R. E.; Brown, M. S.; Goldstein, J. L. Isoform 1c of sterol regulatory element binding protein is less active than isoform 1a in livers of transgenic mice and in cultured cells. J Clin Invest 1997, 99, 846–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.-A.; Liang, G.; Xie, X.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Fitzgerald, K.; Koteliansky, V.; Brown, M. S.; Goldstein, J. L.; Horton, J. D. The Scap/SREBP pathway is essential for developing diabetic fatty liver and carbohydrate-induced hypertriglyceridemia in animals. Cell metabolism 2012, 15, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitto, M.; Luz, G.; Luciano, T.; Marques, S.; Souza, D.; Pinho, R.; Lira, F.; Cintra, D.; De Souza, C. Reversion of steatosis by SREBP-1c antisense oligonucleotide did not improve hepatic insulin action in diet-induced obesity mice. Hormone and Metabolic Research 2012, 44, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoine, M.; Barbu, V.; Girard, P. M.; Kim, M.; Bastard, J.-P.; Wendum, D.; Paye, F.; Housset, C.; Capeau, J.; Serfaty, L. Altered hepatic expression of SREBP-1 and PPARγ is associated with liver injury in insulin-resistant lipodystrophic HIV-infected patients. Aids 2006, 20, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. C.; Horton, J. D.; Hobbs, H. H. Human fatty liver disease: old questions and new insights. Science 2011, 332, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Donati, B.; Fares, R.; Lombardi, R.; Mancina, R. M.; Romeo, S.; Valenti, L. PNPLA3 I148M polymorphism and progressive liver disease. World journal of gastroenterology 2013, 19, 6969–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C. J. Meta-analysis of the influence of I148M variant of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene (PNPLA3) on the susceptibility and histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, A.; Liang, J.; Ke, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, H.; Cui, A.; Liu, X.; Liu, C. Mouse patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3 influences systemic lipid and glucose homeostasis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Hu, Z.; Cui, A.; Liu, Z.; Ma, F.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Y. Post-translational regulation of lipogenesis via AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of insulin-induced gene. Nature communications 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyau, C.-C.; Wang, H.-F.; Zhang, W.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; Huang, S.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Peng, R. Y. Antrodan alleviates high-fat and high-fructose diet-induced fatty liver disease in C57BL/6 mice model via AMPK/Sirt1/SREBP-1c/PPARγ pathway. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S.; Inoue, J.; Shimizu, M.; Sato, R. Xanthohumol improves diet-induced obesity and fatty liver by suppressing sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2015, 290, 20565–20579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K. F.; Oral, E. A.; Dufour, S.; Befroy, D.; Ariyan, C.; Yu, C.; Cline, G. W.; DePaoli, A. M.; Taylor, S. I.; Gorden, P. Leptin reverses insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in patients with severe lipodystrophy. The Journal of clinical investigation 2002, 109, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K. J.; Rayner, K. J.; Suárez, Y.; Fernández-Hernando, C., microRNAs and cholesterol metabolism. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism 2010, 21, 699-706. [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Hernando, C.; Suárez, Y.; Rayner, K. J.; Moore, K. J. MicroRNAs in lipid metabolism. Current opinion in lipidology 2011, 22, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chi, X.; Qu, N.; Wang, C. Long noncoding RNA lncARSR promotes hepatic lipogenesis via Akt/SREBP-1c pathway and contributes to the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2018, 499, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, C.; Geng, J. LncRNA NEAT1-MicroRNA-140 axis exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver through interrupting AMPK/SREBP-1 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2019, 516, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Duan, R.; Shen, L.; Liu, M.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Liang, T.; Li, X.; Guo, L. The lncRNA Gm15622 stimulates SREBP-1c expression and hepatic lipid accumulation by sponging the miR-742-3p in mice [S]. Journal of lipid research 2020, 61, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moslehi, A.; Nabavizadeh, F.; Zekri, A.; Amiri, F. Naltrexone changes the expression of lipid metabolism-related proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum stress induced hepatic steatosis in mice. Clinical and experimental pharmacology and physiology 2017, 44, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moslehi, A.; Farahabadi, M.; Chavoshzadeh, S. A.; Barati, A.; Ababzadeh, S.; Mohammadbeigi, A., The effect of amygdalin on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress induced hepatic steatosis in mice. The Malaysian journal of medical sciences: MJMS 2018, 25, 16. [CrossRef]
- Kammoun, H. L.; Chabanon, H.; Hainault, I.; Luquet, S.; Magnan, C.; Koike, T.; Ferré, P.; Foufelle, F. GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress–induced SREBP-1c activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. The Journal of clinical investigation 2009, 119, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, D. T.; Wu, J.; Back, S.-H.; Callaghan, M. U.; Ferris, S. P.; Iqbal, J.; Clark, R.; Miao, H.; Hassler, J. R.; Fornek, J. UPR pathways combine to prevent hepatic steatosis caused by ER stress-mediated suppression of transcriptional master regulators. Developmental cell 2008, 15, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyadomari, S.; Harding, H. P.; Zhang, Y.; Oyadomari, M.; Ron, D. Dephosphorylation of translation initiation factor 2α enhances glucose tolerance and attenuates hepatosteatosis in mice. Cell metabolism 2008, 7, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, P.; Baillie, R. A.; Wiest, M. M.; Mirshahi, F.; Choudhury, J.; Cheung, O.; Sargeant, C.; Contos, M. J.; Sanyal, A. J. A lipidomic analysis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Shin, H.-S.; Choi, H. S.; Park, J.-W.; Jo, I.; Oh, E.-S.; Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, B.-H.; Johnson, R. J.; Kang, D.-H. Uric acid induces fat accumulation via generation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and SREBP-1c activation in hepatocytes. Laboratory investigation 2014, 94, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Y.; Garcia-Carbonell, R.; Yamachika, S.; Zhao, P.; Dhar, D.; Loomba, R.; Kaufman, R. J.; Saltiel, A. R.; Karin, M., ER stress drives lipogenesis and steatohepatitis via caspase-2 activation of S1P. Cell 2018, 175, 133-145. e15. [CrossRef]
- Basseri, S.; Austin, R. C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipid metabolism: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochemistry research international 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, E.-J.; Shin, K.-O.; Kim, M. H.; Pewzner-Jung, Y.; Lee, Y.-M.; Park, J.-W.; Futerman, A. H.; Park, W.-J., Hepatic triglyceride accumulation via endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced SREBP-1 activation is regulated by ceramide synthases. Experimental & molecular medicine 2019, 51, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Dewidar, B.; Meyer, C.; Dooley, S.; Meindl-Beinker, A. N. TGF-beta in Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrogenesis-Updated 2019. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. Novel Therapeutic Targets in Liver Fibrosis. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 766855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Liu, C.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L. TGF-beta/SMAD Pathway and Its Regulation in Hepatic Fibrosis. J Histochem Cytochem 2016, 64, 157–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Yan, K.; Fan, J.; Niu, M.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y. The beta-catenin pathway contributes to the effects of leptin on SREBP-1c expression in rat hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol 2013, 169, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Tian, H.; Jia, X.; Zhu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y. Mechanistic insights into the effects of SREBP1c on hepatic stellate cell and liver fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 10063–10074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, K.; Teratani, T.; Suzuki, T.; Shimizu, M.; Sato, H.; Narimatsu, K.; Okada, Y.; Kurihara, C.; Irie, R.; Yokoyama, H.; Shimamura, K.; Usui, S.; Ebinuma, H.; Saito, H.; Watanabe, C.; Komoto, S.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nagao, S.; Sugiyama, K.; Hokari, R.; Kanai, T.; Miura, S.; Hibi, T. Free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate cells: mechanism of liver fibrosis aggravation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 154–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorotea, D.; Koya, D.; Ha, H. Recent Insights Into SREBP as a Direct Mediator of Kidney Fibrosis via Lipid-Independent Pathways. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; Yao, Y.; Tu, K.; Liu, Q. SREBP-1 has a prognostic role and contributes to invasion and metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. International journal of molecular sciences 2014, 15, 7124–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Bu, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, L. SPIN1 triggers abnormal lipid metabolism and enhances tumor growth in liver cancer. Cancer Letters 2020, 470, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Wen, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, K.; Li, Q.; Huang, G.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X. Role of hepatoma-derived growth factor in promoting de novo lipogenesis and tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Molecular oncology 2018, 12, 1480–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D. P.; Santhekadur, P. K.; Seneshaw, M.; Mirshahi, F.; Uram-Tuculescu, C.; Sanyal, A. J. A regulatory role of apoptosis antagonizing transcription factor in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Lin, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhao, S.; Song, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L. ZHX2 inhibits SREBP1c-mediated de novo lipogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma via miR-24-3p. The Journal of Pathology 2020, 252, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ding, C.; Chen, Y.; Hu, W.; Yu, C.; Peng, C.; Feng, X.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y. ACSL4 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myc/SREBP1 pathway. Cancer letters 2021, 502, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wong, V.; Wong, G.; Yang, W.; Sun, H.; Shen, J.; Tong, J.; Go, M.; Cheung, Y. S.; Lai, P., Histone deacetylase HDAC8 promotes insulin resistance and-catenin activation in NAFLD-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res,(Received on July 24, 2015). [CrossRef]
- Mueller, K. M.; Kornfeld, J. W.; Friedbichler, K.; Blaas, L.; Egger, G.; Esterbauer, H.; Hasselblatt, P.; Schlederer, M.; Haindl, S.; Wagner, K. U. Impairment of hepatic growth hormone and glucocorticoid receptor signaling causes steatosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, M. J.; Kang, S. H.; Kim, Y. S.; Lee, J. M.; Yu, J.; Kim, H. R.; Lim, H.; Kim, K. M.; Jung, J.; Jeong, L. S. UBC12-mediated SREBP-1 neddylation worsens metastatic tumor prognosis. International Journal of Cancer 2020, 147, 2550–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triki, M.; Rinaldi, G.; Planque, M.; Broekaert, D.; Winkelkotte, A. M.; Maier, C. R.; Raman, S. J.; Vandekeere, A.; Van Elsen, J.; Orth, M. F. mTOR signaling and SREBP activity increase FADS2 expression and can activate sapienate biosynthesis. Cell reports 2020, 31, 107806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, R.-J.; Peng, S.-Y.; Yu, W. C.; Chang, V. H.-S. Therapeutic Targeting of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Downregulating SREBP-1C Expression via AMPK-KLF10 Axis. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 2021, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhou, Z. S.; Shen, Y.; Xu, J.; Miao, H. H.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, F.; Li, B. L.; Luo, J.; Song, B. L. Inhibition of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein pathway suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing inflammation in mice. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H. Y.; Yamamoto, G.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Karin, D.; Kim, J. Y.; Alexandrov, L. B.; Koyama, Y.; Nishio, T.; Benner, C.; Heinz, S.; Rosenthal, S. B.; Liang, S.; Sun, M.; Karin, G.; Zhao, P.; Brodt, P.; McKillop, I. H.; Quehenberger, O.; Dennis, E.; Saltiel, A.; Tsukamoto, H.; Gao, B.; Karin, M.; Brenner, D. A.; Kisseleva, T. IL-17 signaling in steatotic hepatocytes and macrophages promotes hepatocellular carcinoma in alcohol-related liver disease. J Hepatol 2020, 72, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Chen, R.; Song, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, G.; Yang, H.; Jing, W.; Zhou, X.; Fu, Z.; Huang, G.; Zhao, J. ASPP2 inhibits tumor growth by repressing the mevalonate pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 2019, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Imaz, H.; Chico, Y.; Rueda, Y.; Fresnedo, O. Channeling of newly synthesized fatty acids to cholesterol esterification limits triglyceride synthesis in SND1-overexpressing hepatoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 2019, 1864, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, L.; Chi, W.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Jia, J.; Pilo, M. G.; Wang, J. Cholesterol biosynthesis supports the growth of hepatocarcinoma lesions depleted of fatty acid synthase in mice and humans. Gut 2020, 69, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvisi, D. F.; Wang, C.; Ho, C.; Ladu, S.; Lee, S. A.; Mattu, S.; Destefanis, G.; Delogu, S.; Zimmermann, A.; Ericsson, J., Increased lipogenesis, induced by AKT-mTORC1-RPS6 signaling, promotes development of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1071-1083. e5. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Kuang, S.; Cao, R.; Wang, J.; Peng, Q.; Sun, C. Sorafenib kills liver cancer cells by disrupting SCD1-mediated synthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids via the ATP-AMPK-mTOR-SREBP1 signaling pathway. The FASEB Journal 2019, 33, 10089–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Feng, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y., SREBP-1 inhibitor Betulin enhances the antitumor effect of Sorafenib on hepatocellular carcinoma via restricting cellular glycolytic activity. Cell death & disease 2019, 10, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.-z.; Hao, J.-f.; Zhou, X.-h. Inhibition of SREBP-1 Activation by a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor Enhances the Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissue to Radiofrequency Ablation. Frontiers in Oncology 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Shen, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Huang, G.; Liu, J. Novel SREBP1 inhibitor cinobufotalin suppresses proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting lipogenesis. European Journal of Pharmacology 2021, 906, 174280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Cai, X.; Cao, F.; Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Emodin induced SREBP1-dependent and SREBP1-independent apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2019, 10, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, Y.-M.; Oh, T.-I.; Shin, D. H.; Kim, G.-H.; Kan, S.-Y.; Kang, H.; Kim, J. H.; Kim, B. M.; Yim, W. J. Emodin sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to the anti-cancer effect of sorafenib through suppression of cholesterol metabolism. International journal of molecular sciences 2018, 19, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-H.; Kan, S.-Y.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.; Ko, H. M.; Kim, J. H.; Lim, J.-H. Ursolic acid suppresses cholesterol biosynthesis and exerts anti-cancer effects in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20, 4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S.; Matsushita, Y.; Kurosaki, S.; Tange, M.; Fujiwara, N.; Hayata, Y.; Hayakawa, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Hata, M.; Tsuboi, M. Inhibiting SCAP/SREBP exacerbates liver injury and carcinogenesis in murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Drug | Disease | Mechanism | Targets | Cell Lines Tested | Mouse Models Tested (Dose) | Reference |
| Xanthohumol | Fatty liver | Impairs ER–Golgi translocation of the SCAP-SREBP complex by binding to SEC23 and SEC24 and blocking SCAP–SREBP incorporation into common coated protein II vesicles | SREBP1 | Huh-7 | HFD-induced fatty liver in male C57BL/6J mice (0.2% or 0.4%) | [30] |
| Antrodan | NAFLD | Reduces HFD-induced NAFLD via the AMPK–SREBP1c–PPARγ pathway | SREBP1 | none | (20-40 mg/kg) | [29] |
| Betulin | HCC | Inhibits cell glucose metabolism to prevent metastatic potential and facilitate inhibitory effect of sorafenib | SREBP1 | MHCC97-H | MHCC97-H xenograft tumors (2 mg/kg) | [72] |
| HCC | Inhibits ER–Golgi translocation of SREBPs | SREBP1 | none | Diethylnitrosamine-induced HCC in mice (50 mg/kg) | [65] | |
| Emodin | HCC | Induces apoptosis and reduces mitochondrial membrane potential; anticancer effects |
SREBP1 and its downstream targets, ACLY, ACCa, FASN, and SCD1 | Bel-7402 | none | [75-76] |
| Sorafenib | HCC | Reduces cell viability | SREBP1 and its target SCD1 | human Huh7.5 liver cancer cells | Huh7.5 xenograft tumors (20 mg/kg/d) | [71] |
| Cinobufotalin | HCC | Induces cell cycle G2–M arrest and apoptosis; inhibits cell proliferation by inhibiting d novo lipid synthesis |
SREBP1 | HepG2, SMMC-7721 | SMMC-7721 xenograft tumors (2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg) | [74] |
| Ursolic acid | HCC | Activates SREBP2 and cholesterol biosynthesis-related genes and enzymes to lower cholesterol in cells | SREBP2 | SK-HEP-1, Hep3B | none | [77] |
| HFD, high-fat diet | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





